hypertensive emergency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A hypertensive emergency is very high blood pressure with potentially life-threatening symptoms and signs of acute damage to one or more
 Symptoms may include headache,
Symptoms may include headache,
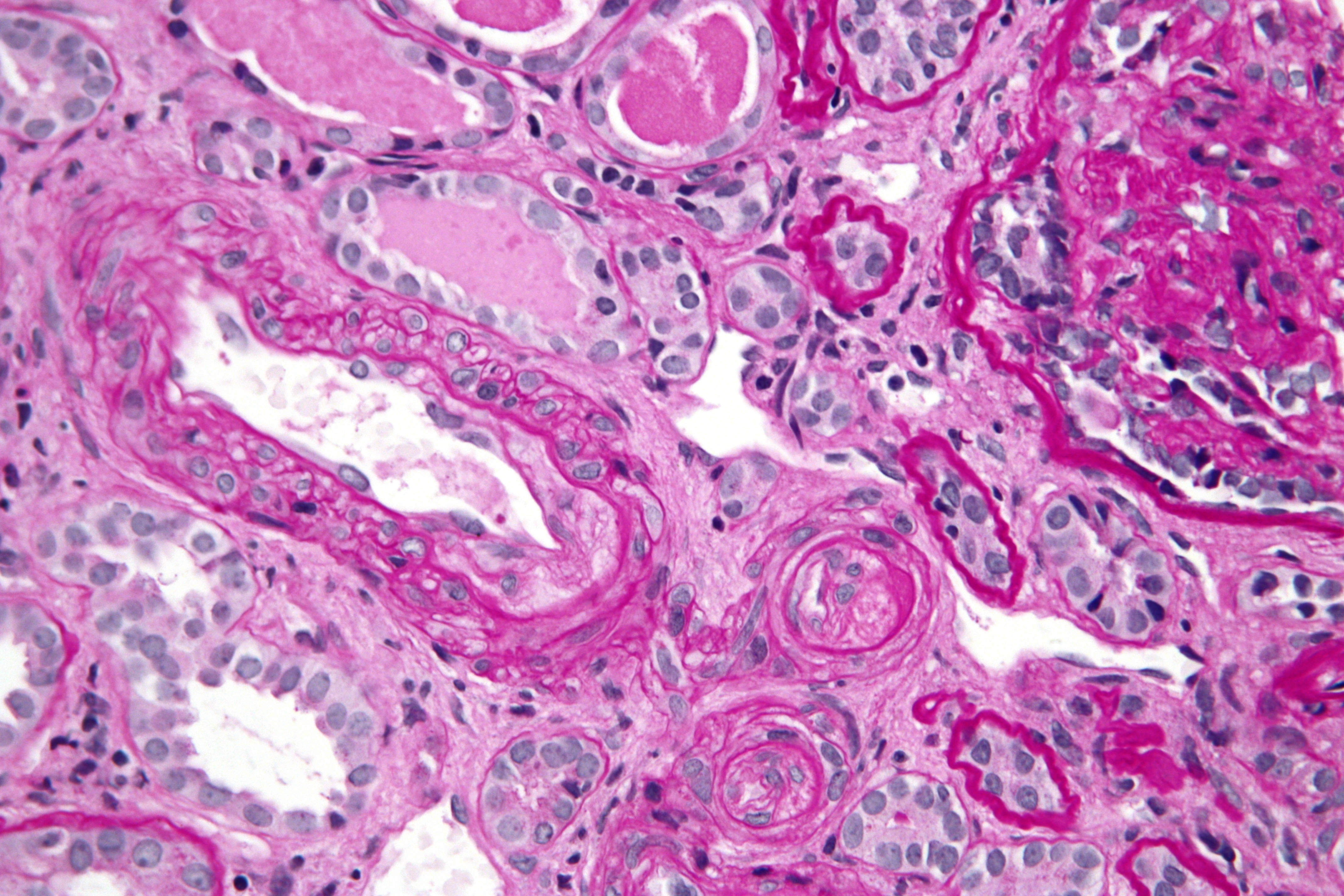 The pathophysiology of hypertensive emergency is not well understood. Failure of normal autoregulation and an abrupt rise in systemic vascular resistance are typical initial components of the disease process.
Hypertensive emergency pathophysiology includes:
* Abrupt increase in systemic vascular resistance, likely related to humoral vasoconstrictors
* Endothelial injury and dysfunction
*
The pathophysiology of hypertensive emergency is not well understood. Failure of normal autoregulation and an abrupt rise in systemic vascular resistance are typical initial components of the disease process.
Hypertensive emergency pathophysiology includes:
* Abrupt increase in systemic vascular resistance, likely related to humoral vasoconstrictors
* Endothelial injury and dysfunction
*
organ system
An organ system is a biological system consisting of a group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions. Each organ has a specialized role in a plant or animal body, and is made up of distinct tissues.
Plants
Plants have ...
s (especially brain, eyes, heart, aorta, or kidneys). It is different from a hypertensive urgency A hypertensive urgency is a clinical situation in which blood pressure is very high (e.g., 220/125 mmHg) with minimal or no symptoms, and ''no'' signs or symptoms indicating acute organ damage. This contrasts with a hypertensive emergency where sev ...
by this additional evidence for impending irreversible hypertension-mediated organ damage (HMOD). Blood pressure is often above 200/120 mmHg, however there are no universally accepted cutoff values. Signs of organ damage are discussed below.
Signs and symptoms
 Symptoms may include headache,
Symptoms may include headache, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
, or vomiting. Chest pain may occur due to increased workload on the heart resulting in inadequate delivery of oxygen to meet the heart muscle's metabolic needs. The kidneys may be affected, resulting in blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
or protein in the urine, and acute kidney failure
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in kidney function that develops within 7 days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
Causes of AKI are c ...
. People can have decreased urine production, fluid retention, and confusion.
Other signs and symptoms can include:
* Chest pain
* Abnormal heart rhythm
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
s
* Headache
* Nosebleed
A nosebleed, also known as epistaxis, is bleeding from the nose. Blood can flow down into the stomach, and cause nausea and vomiting. In more severe cases, blood may come out of both nostrils. Rarely, bleeding may be so significant that low bl ...
s that are difficult to stop
* Dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ...
* Fainting or the sensation of the world spinning around them (vertigo)
* Severe anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
* Agitation
* Altered mental status
* Abnormal sensations
The most common presentations of hypertensive emergencies are cerebral infarction
A cerebral infarction is the pathologic process that results in an area of necrotic tissue in the brain (cerebral infarct). It is caused by disrupted blood supply ( ischemia) and restricted oxygen supply ( hypoxia), most commonly due to thromboemb ...
(24.5%), pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia and respiratory failure. It is due t ...
(22.5%), hypertensive encephalopathy
Hypertensive encephalopathy (HE) is general brain dysfunction due to significantly high blood pressure. Symptoms may include headache, vomiting, trouble with balance, and confusion. Onset is generally sudden. Complications can include seizures, ...
(16.3%), and congestive heart failure (12%). Less common presentations include intracranial bleeding, aortic dissection, and pre-eclampsia or eclampsia.
Massive, rapid elevations in blood pressure can trigger any of these symptoms, and warrant further work-up by physicians. Physical exam would include measurement of blood pressure in both arms. Laboratory tests to be conducted include urine toxicology, blood glucose, a basic metabolic panel evaluating kidney function, or a complete metabolic panel evaluating liver function, EKG, chest x-rays, and pregnancy screening.
The eyes may show bleeding in the retina, an exudate, cotton-wool spots, scattered splinter hemorrhages, or swelling of the optic disc called papilledema
Papilledema or papilloedema is optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure due to any cause. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks. Unilateral presentation is extremely rare.
In ...
.
Causes
Many factors and causes are contributory in hypertensive crises. The most common cause is patients with diagnosed, chronic hypertension who have discontinued anti hypertensive medications. Other common causes of hypertensive crises are autonomic hyperactivity such aspheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma (PHEO or PCC) is a rare tumor of the adrenal medulla composed of chromaffin cells, also known as pheochromocytes. When a tumor composed of the same cells as a pheochromocytoma develops outside the adrenal gland, it is referred t ...
, collagen-vascular diseases, drug use particularly stimulants, cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Ameri ...
and amphetamines
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with sub ...
and their substituted analogues, monoamine oxidase inhibitors or food-drug interactions, spinal cord disorders, glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis (GN) is a term used to refer to several kidney diseases (usually affecting both kidneys). Many of the diseases are characterised by inflammation either of the glomeruli or of the small blood vessels in the kidneys, hence the ...
, head trauma, neoplasia
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s, preeclampsia and eclampsia
Eclampsia is the onset of seizures (convulsions) in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is one of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy that presents with three main features: new onset of high blood pressure, large amounts of protein in ...
, hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidis ...
and renovascular hypertension. People withdrawing from medications such as clonidine or beta-blockers have been frequently found to develop hypertensive crises. It is important to note that these conditions exist outside of hypertensive emergency, in that patients diagnosed with these conditions are at increased risk of hypertensive emergencies or end organ failure.
Pathophysiology
 The pathophysiology of hypertensive emergency is not well understood. Failure of normal autoregulation and an abrupt rise in systemic vascular resistance are typical initial components of the disease process.
Hypertensive emergency pathophysiology includes:
* Abrupt increase in systemic vascular resistance, likely related to humoral vasoconstrictors
* Endothelial injury and dysfunction
*
The pathophysiology of hypertensive emergency is not well understood. Failure of normal autoregulation and an abrupt rise in systemic vascular resistance are typical initial components of the disease process.
Hypertensive emergency pathophysiology includes:
* Abrupt increase in systemic vascular resistance, likely related to humoral vasoconstrictors
* Endothelial injury and dysfunction
* Fibrinoid necrosis
Fibrinoid necrosis is a specific pattern of irreversible, uncontrolled cell death that occurs when antigen-antibody complexes are deposited in the walls of blood vessels along with fibrin. It is common in the immune-mediated vasculitides which a ...
of the arterioles
* Deposition of platelets and fibrin
* Breakdown of normal autoregulatory function
The resulting ischemia prompts further release of vasoactive substances including prostaglandins, free radicals, and thrombotic/mitotic growth factors, completing a vicious cycle of inflammatory changes. If the process is not stopped, homeostatic
In biology, homeostasis (British also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and ...
failure begins, leading to loss of cerebral and local autoregulation, organ system ischemia and dysfunction, and myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
. Single-organ involvement is found in approximately 83% of hypertensive emergency patients, two-organ involvement in about 14% of patients, and multi-organ failure
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is altered organ function in an acutely ill patient requiring medical intervention to achieve homeostasis.
Although Irwin and Rippe cautioned in 2005 that the use of "multiple organ failure" or "multisy ...
(failure of at least 3 organ systems) in about 3% of patients.
In the brain, hypertensive encephalopathy
Hypertensive encephalopathy (HE) is general brain dysfunction due to significantly high blood pressure. Symptoms may include headache, vomiting, trouble with balance, and confusion. Onset is generally sudden. Complications can include seizures, ...
- characterized by hypertension, altered mental status, and swelling of the optic disc - is a manifestation of the dysfunction of cerebral autoregulation. Cerebral autoregulation is the ability of the blood vessels in the brain to maintain a constant blood flow
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously m ...
. People with chronic hypertension can tolerate higher arterial pressure before their autoregulation system is disrupted. Hypertensives also have an increased cerebrovascular resistance which puts them at greater risk of developing cerebral ischemia if the blood flow decreases into a normotensive range. On the other hand, sudden or rapid rises in blood pressure may cause hyperperfusion and increased cerebral blood flow, causing increased intracranial pressure and cerebral edema, with increased risk of intracranial bleeding.
In the heart, increased arterial stiffness, increased systolic blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" r ...
, and widened pulse pressures, all resulting from chronic hypertension, can cause significant damage. Coronary perfusion pressures are decreased by these factors, which also increase myocardial oxygen consumption, possibly leading to left ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy (VH) is thickening of the walls of a ventricle (lower chamber) of the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is more common, right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), as well as concurrent hypertrophy of both ventr ...
. As the left ventricle becomes unable to compensate for an acute rise in systemic vascular resistance, left ventricular failure and pulmonary edema or myocardial ischemia may occur.
In the kidneys, chronic hypertension has a great impact on the kidney vasculature, leading to pathologic changes in the small arteries of the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
. Affected arteries develop endothelial dysfunction and impairment of normal vasodilation
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstrictio ...
, which alter kidney autoregulation. When the kidneys' autoregulatory system is disrupted, the intraglomerular pressure starts to vary directly with the systemic arterial pressure, thus offering no protection to the kidney during blood pressure fluctuations. The renin-aldosterone-angiotensin system can be activated, leading to further vasoconstriction and damage. During a hypertensive crisis, this can lead to acute kidney ischemia, with hypoperfusion, involvement of other organs, and subsequent dysfunction. After an acute event, this endothelial dysfunction has persisted for years.
Diagnosis
The term hypertensive emergency is primarily used as a specific term for a hypertensive crisis with a diastolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 120 mmHg or systolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 180 mmHg. Hypertensive emergency differs from hypertensive urgency in that, in the former, there is evidence of acute organ damage. Both of these definitions had collectively been known as malignant hypertension, although this medical term is replaced. In the pregnant patient, the definition of hypertensive emergency (likely secondary to pre-eclampsia or eclampsia) is only a blood pressure exceeding 160 mmHg systolic blood pressure or 110 mmHg diastolic blood pressure.Treatment
In a hypertensive emergency, treatment should first be to stabilize the patient's airway, breathing, and circulation per ACLS guidelines. Patients should have their blood pressure slowly lowered over a period of minutes to hours with an antihypertensive agent. Documented goals for blood pressure include a reduction in themean arterial pressure
In medicine, the mean arterial pressure (MAP) is an average blood pressure in an individual during a single cardiac cycle. MAP is altered by cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance.
Testing
Mean arterial pressure can be measured dire ...
by less than or equal to 25% within the first 8 hours of emergency. If blood pressure is lowered aggressively, patients are at increased risk of complications including stroke, blindness, or kidney failure. Several classes of anti hypertensive agents are recommended, with the choice depending on the cause of the hypertensive crisis, the severity of the elevation in blood pressure, and the patient's baseline blood pressure prior to a hypertensive emergency. Physicians will attempt to identify a cause of the patient's hypertension, including chest radiograph, serum laboratory studies evaluating kidney function, urinalysis, as that will alter the treatment approach for a more patient-directed regimen.
Hypertensive emergencies differ from hypertensive urgency in that they are treated parenterally, whereas in urgency it is recommended to use oral anti hypertensives to reduce the risk of hypotensive complications or ischemia. Parenteral agents are classified into beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, systemic vasodilators, or other (fenoldopam
Fenoldopam mesylate (Corlopam) is a drug and synthetic benzazepine derivative which acts as a selective D1 receptor partial agonist. Fenoldopam is used as an antihypertensive agent. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in ...
, phentolamine, clonidine). Medications include labetalol
Labetalol is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and in long term management of angina. This includes essential hypertension, hypertensive emergencies, and hypertension of pregnancy. In essential hypertension it is generally less pref ...
, nicardipine, hydralazine
Hydralazine, sold under the brand name Apresoline among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. This includes high blood pressure in pregnancy and very high blood pressure resulting in symptoms. It has been ...
, sodium nitroprusside
Sodium nitroprusside (SNP), sold under the brand name Nitropress among others, is a medication used to lower blood pressure. This may be done if the blood pressure is very high and resulting in symptoms, in certain types of heart failure, and d ...
, esmolol, nifedipine
Nifedipine (3,5-dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate), sold under the brand name Adalat and Procardia, among others, is a calcium channel blocker medication used to manage angina, high blood pressure, Ra ...
, minoxidil
Minoxidil, sold under the brand name Rogaine among others, is a medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure and pattern hair loss. It is an antihypertensive vasodilator. It is available as a generic medication by prescription in or ...
, isradipine
Isradipine (tradenames DynaCirc, Prescal) is a calcium channel blocker of the dihydropyridine class. It is usually prescribed for the treatment of high blood pressure in order to reduce the risk of stroke and heart attack.
It was patented in 197 ...
, clonidine, and chlorpromazine
Chlorpromazine (CPZ), marketed under the brand names Thorazine and Largactil among others, is an antipsychotic medication. It is primarily used to treat psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia. Other uses include the treatment of bipolar di ...
. These medications work through a variety of mechanisms. Labetalol is a beta-blocker with mild alpha antagonism, decreasing the ability of catecholamine activity to increase systemic vascular resistance, while also decreasing heart rate and myocardial oxygen demand. Nicardipine, Nifedipine, and Isradipine are calcium channel blockers that work to decrease systemic vascular resistance and subsequently lower blood pressure. Hydralazine and Sodium nitroprusside are systemic vasodilators, thereby reducing afterload, however can be found to have reflex tachycardia, making them likely second or third line choices. Sodium nitroprusside was previously the first-line choice due to its rapid onset, although now it is less commonly used due to side effects, drastic drops in blood pressure, and cyanide toxicity. Sodium nitroprusside is also contraindicated in patients with myocardial infarction, due to coronary steal. It is again important that the blood pressure is lowered slowly. The initial goal in hypertensive emergencies is to reduce the pressure by no more than 25% the mean arterial pressure. Excessive reduction in blood pressure can precipitate coronary, cerebral, or kidney ischemia and, possibly, infarction.
A hypertensive emergency is not based solely on an absolute level of blood pressure, but also on a patient's baseline blood pressure before the hypertensive crisis occurs. Individuals with a history of chronic hypertension may not tolerate a "normal" blood pressure, and can therefore present symptomatically with hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
, including fatigue, light-headedness, nausea, vomiting, or syncope.
Prognosis
Severe hypertension is a serious and potentially life-threatening medical condition. It is estimated that people who do not receive appropriate treatment only live an average of about three years after the event. Themorbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
and mortality of hypertensive emergencies depend on the extent of end-organ dysfunction at the time of presentation and the degree to which blood pressure is controlled afterward. With good blood pressure control and medication compliance, the 5-year survival rate of patients with hypertensive crises approaches 55%.
The risks of developing a life-threatening disease affecting the heart or brain increase as the blood flow increases. Commonly, ischemic heart attack and stroke are the causes that lead to death in patients with severe hypertension. It is estimated that for every 20 mm Hg systolic or 10 mm Hg diastolic increase in blood pressures above 115/75 mm Hg, the mortality rate for both ischemic heart disease and stroke doubles.
Consequences of hypertensive emergency result after prolonged elevations in blood pressure and associated end-organ dysfunction. Acute end-organ damage may occur, affecting the neurological, cardiovascular, kidney, or other organ systems. Some examples of neurological damage include hypertensive encephalopathy
Hypertensive encephalopathy (HE) is general brain dysfunction due to significantly high blood pressure. Symptoms may include headache, vomiting, trouble with balance, and confusion. Onset is generally sudden. Complications can include seizures, ...
, cerebral vascular accident/cerebral infarction
A cerebral infarction is the pathologic process that results in an area of necrotic tissue in the brain (cerebral infarct). It is caused by disrupted blood supply ( ischemia) and restricted oxygen supply ( hypoxia), most commonly due to thromboemb ...
, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and intracranial bleeding. Cardiovascular system damage can include myocardial ischemia
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pla ...
/infarction, acute left ventricular dysfunction, acute pulmonary edema, and aortic dissection
Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of severe chest or ...
. Other end-organ damage can include acute kidney failure or insufficiency, retinopathy
Retinopathy is any damage to the retina of the eyes, which may cause vision impairment. Retinopathy often refers to retinal vascular disease, or damage to the retina caused by abnormal blood flow. Age-related macular degeneration is technically inc ...
, eclampsia
Eclampsia is the onset of seizures (convulsions) in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is one of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy that presents with three main features: new onset of high blood pressure, large amounts of protein in ...
, and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA) is a microangiopathic subgroup of hemolytic anemia (loss of red blood cells through destruction) caused by factors in the small blood vessels. It is identified by the finding of anemia and schistocytes ...
.
Epidemiology
In 2000, it was estimated that 1 billion people worldwide have hypertension, making it the most prevalent condition in the world. Approximately 60 million Americans have chronic hypertension, with 1% of these individuals having an episode of hypertensive urgency. In emergency departments and clinics around the U.S., the prevalence of hypertensive urgency is suspected to be between 3-5%. 25% of hypertensive crises have been found to be hypertensive emergency versus urgency when presenting to the ER. Risk factors for hypertensive emergency include age, obesity, noncompliance to anti hypertensive medications, female sex, Caucasian race, preexisting diabetes or coronary artery disease, mental illness, and sedentary lifestyle. Several studies have concluded that African Americans have a greater incidence of hypertension and a greater morbidity and mortality from hypertensive disease thannon-Hispanic whites
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Ame ...
, however hypertensive crises have a greater incidence in Caucasians. Although severe hypertension is more common in the elderly, it may occur in children (though very rarely), likely due to metabolic or hormonal dysfunction. In 2014, a systematic review identified women as having slightly higher increased risks of developing hypertensive crises than do men.
With the usage of anti hypertensives, the rates of hypertensive emergencies has declined from 7% to 1% of patients with hypertensive urgency.
16% of patients presenting with hypertensive emergency can have no known history of hypertension.
See also
* Hypertensive retinopathy *Hypertensive encephalopathy
Hypertensive encephalopathy (HE) is general brain dysfunction due to significantly high blood pressure. Symptoms may include headache, vomiting, trouble with balance, and confusion. Onset is generally sudden. Complications can include seizures, ...
* Preeclampsia
* Eclampsia
Eclampsia is the onset of seizures (convulsions) in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is one of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy that presents with three main features: new onset of high blood pressure, large amounts of protein in ...
* Aortic dissection
Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of severe chest or ...
* Intracranial hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), also known as intracranial bleed, is hemorrhage, bleeding internal bleeding, within the Human skull, skull. Subtypes are intracerebral bleeds (intraventricular bleeds and intraparenchymal bleeds), subarachnoid bleed ...
References
External links
{{Vascular diseases Hypertension Medical emergencies