Hypermobility syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD), related to earlier diagnoses such as hypermobility syndrome (HMS), and joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable
/ref> While hypermobility spectrum disorders are most analogous to JHS, the 2017 diagnostic criteria for hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome excludes many people who fit the old criteria, who would instead be diagnosed with hypermobility spectrum disorders. Hypermobility syndrome and hypermobility spectrum disorders do not include people with asymptomatic hypermobility or people with double-jointedness but no other symptoms. Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome and hypermobility spectrum disorders may be equally severe.
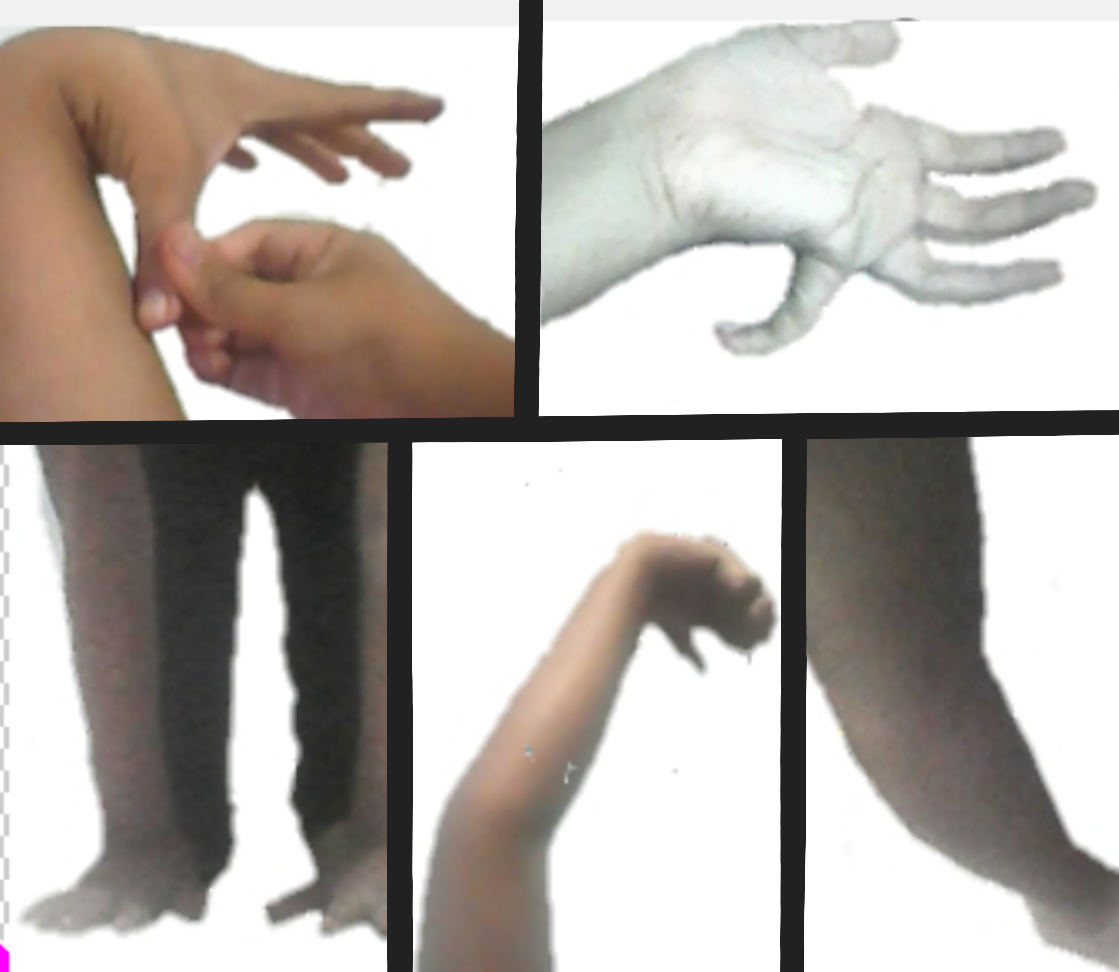 Being diagnosed with hypermobility syndrome can be a difficult task. There is a lack of wide understanding of the condition and it can be considered a zebra condition. As hypermobility syndrome can be easily mistaken for being double-jointed or categorised as nothing more than perhaps an achy body from lack of exercise, medical professionals may diagnose those affected incorrectly and not adequately investigate the symptoms. Due to these circumstances many affected individuals can live not knowing they have it. As a result, those affected without a proper diagnosis can easily injure themselves and not take proper care to ensure they go about working safely.
The Beighton Score can be used to determine generalised joint hypermobility (GJH) related to hypermobility syndrome. The newer term "generalised hypermobility spectrum disorder" includes people with generalised joint hypermobility, often determined using the Beighton Score, and other symptoms. Those who do not meet the Beighton Score criteria may be diagnosed with historical joint hypermobility spectrum disorder, peripheral hypermobility spectrum disorder, or localised hypermobility spectrum disorder.
In comparison to the diagnostic criteria of hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, the criteria for hypermobile spectrum disorder are less strict. However, these criteria are differentiated from criteria of other EDS types and therefore its less-strict criteria are only comparable to the criteria of hEDS. As those with HSD experience a considerable amount of discomfort, it is important to focus on the treatment, not the labels. The severity of each condition can be equivalent. In particular, musculoskeletal involvement is a requirement for diagnosis with any form of hypermobility spectrum disorder but not for hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Like hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, hypermobility spectrum disorders are associated with orthostatic tachycardia,
Being diagnosed with hypermobility syndrome can be a difficult task. There is a lack of wide understanding of the condition and it can be considered a zebra condition. As hypermobility syndrome can be easily mistaken for being double-jointed or categorised as nothing more than perhaps an achy body from lack of exercise, medical professionals may diagnose those affected incorrectly and not adequately investigate the symptoms. Due to these circumstances many affected individuals can live not knowing they have it. As a result, those affected without a proper diagnosis can easily injure themselves and not take proper care to ensure they go about working safely.
The Beighton Score can be used to determine generalised joint hypermobility (GJH) related to hypermobility syndrome. The newer term "generalised hypermobility spectrum disorder" includes people with generalised joint hypermobility, often determined using the Beighton Score, and other symptoms. Those who do not meet the Beighton Score criteria may be diagnosed with historical joint hypermobility spectrum disorder, peripheral hypermobility spectrum disorder, or localised hypermobility spectrum disorder.
In comparison to the diagnostic criteria of hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, the criteria for hypermobile spectrum disorder are less strict. However, these criteria are differentiated from criteria of other EDS types and therefore its less-strict criteria are only comparable to the criteria of hEDS. As those with HSD experience a considerable amount of discomfort, it is important to focus on the treatment, not the labels. The severity of each condition can be equivalent. In particular, musculoskeletal involvement is a requirement for diagnosis with any form of hypermobility spectrum disorder but not for hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Like hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, hypermobility spectrum disorders are associated with orthostatic tachycardia,
connective tissue disorder
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds togeth ...
that affects joints and ligaments. Different forms and sub-types have been distinguished, but it does not include asymptomatic joint hypermobility, sometimes known as double-jointedness.
Symptoms can include the inability to walk properly or for long distances, and pain in affected areas. Some people with HSD have hypersensitive nerves and a weaker immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splint ...
. It can also cause severe fatigue and some cases cause depressive episodes. It is somewhat similar to other genetic connective tissue disorders such as Ehlers–Danlos syndromes
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a group of 13 genetic connective-tissue disorders in the current classification, with the latest type discovered in 2018. Symptoms include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar fo ...
.
There is a strong association between HSD and neurodevelopmental disorders such as ADHD (Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by excessive amounts of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inap ...
) and ASD (autism spectrum disorder
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulti ...
).
Classification
Hypermobility spectrum disorders are diagnosed when individuals have symptomatic joint hypermobility but do not meet the criteria for other connective tissue disorders, such as Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. The term "hypermobility spectrum disorder" was coined in 2017 after criteria for hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome were made more restrictive. In part, this classification change was designed to address the overlap between joint hypermobility syndrome and what was then known as Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, hypermobility type (EDS-HT), which some researchers believed were the same condition.Palmer et al., 2017/ref> While hypermobility spectrum disorders are most analogous to JHS, the 2017 diagnostic criteria for hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome excludes many people who fit the old criteria, who would instead be diagnosed with hypermobility spectrum disorders. Hypermobility syndrome and hypermobility spectrum disorders do not include people with asymptomatic hypermobility or people with double-jointedness but no other symptoms. Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome and hypermobility spectrum disorders may be equally severe.
Signs and symptoms
Some common symptoms of hypermobility spectrum disorder include: * Joint pain (pain can arise in every joint) *Exhaustion
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
(typically when affected area is the legs);
* Swelling around the joint when joint is being exerted;
* Depression;
* Weaker immune system;
* Muscle pain
* Varying pain levels around the affected areas.
* Muscle spasm
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ such as the bladder.
A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a muscl ...
s.
Other symptoms can appear and not everyone affected experiences the same symptoms.
Diagnosis
 Being diagnosed with hypermobility syndrome can be a difficult task. There is a lack of wide understanding of the condition and it can be considered a zebra condition. As hypermobility syndrome can be easily mistaken for being double-jointed or categorised as nothing more than perhaps an achy body from lack of exercise, medical professionals may diagnose those affected incorrectly and not adequately investigate the symptoms. Due to these circumstances many affected individuals can live not knowing they have it. As a result, those affected without a proper diagnosis can easily injure themselves and not take proper care to ensure they go about working safely.
The Beighton Score can be used to determine generalised joint hypermobility (GJH) related to hypermobility syndrome. The newer term "generalised hypermobility spectrum disorder" includes people with generalised joint hypermobility, often determined using the Beighton Score, and other symptoms. Those who do not meet the Beighton Score criteria may be diagnosed with historical joint hypermobility spectrum disorder, peripheral hypermobility spectrum disorder, or localised hypermobility spectrum disorder.
In comparison to the diagnostic criteria of hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, the criteria for hypermobile spectrum disorder are less strict. However, these criteria are differentiated from criteria of other EDS types and therefore its less-strict criteria are only comparable to the criteria of hEDS. As those with HSD experience a considerable amount of discomfort, it is important to focus on the treatment, not the labels. The severity of each condition can be equivalent. In particular, musculoskeletal involvement is a requirement for diagnosis with any form of hypermobility spectrum disorder but not for hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Like hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, hypermobility spectrum disorders are associated with orthostatic tachycardia,
Being diagnosed with hypermobility syndrome can be a difficult task. There is a lack of wide understanding of the condition and it can be considered a zebra condition. As hypermobility syndrome can be easily mistaken for being double-jointed or categorised as nothing more than perhaps an achy body from lack of exercise, medical professionals may diagnose those affected incorrectly and not adequately investigate the symptoms. Due to these circumstances many affected individuals can live not knowing they have it. As a result, those affected without a proper diagnosis can easily injure themselves and not take proper care to ensure they go about working safely.
The Beighton Score can be used to determine generalised joint hypermobility (GJH) related to hypermobility syndrome. The newer term "generalised hypermobility spectrum disorder" includes people with generalised joint hypermobility, often determined using the Beighton Score, and other symptoms. Those who do not meet the Beighton Score criteria may be diagnosed with historical joint hypermobility spectrum disorder, peripheral hypermobility spectrum disorder, or localised hypermobility spectrum disorder.
In comparison to the diagnostic criteria of hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, the criteria for hypermobile spectrum disorder are less strict. However, these criteria are differentiated from criteria of other EDS types and therefore its less-strict criteria are only comparable to the criteria of hEDS. As those with HSD experience a considerable amount of discomfort, it is important to focus on the treatment, not the labels. The severity of each condition can be equivalent. In particular, musculoskeletal involvement is a requirement for diagnosis with any form of hypermobility spectrum disorder but not for hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Like hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, hypermobility spectrum disorders are associated with orthostatic tachycardia, gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
disorders, and pelvic and bladder dysfunction.
Treatment
Treating hypermobility syndrome can be difficult. The condition has no direct cure, but its symptoms can be treated. Physiotherapy, particularly exercise, is the main treatment for the condition, although there is only limited evidence for its effectiveness. Treatments for pain include: * Bandaging the affected area; * Placing an ice pack on the affected area; * Taking over the counter pain killers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.Prevalence
Prevalence of the condition is unknown, but can be high in those attending musculoskeletal services.E. Connelly, A. Hakim, S. Davenport, J. Simmonds. "A study exploring the prevalence of joint hypermobility syndrome in patients attending a musculoskeletal triage clinic." Physiother. Pract. Res., 36 (1) (2015), pp. 43-53References
{{reflist Syndromes affecting joints