Hull University on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
, mottoeng = Bearing the Torch
1954 – university status , type = Public , endowment = £18.8 million (2016) , budget = £190 million (2016) , chancellor =
, country = England , campus = Urban area , colours = Scarf colours, blue and gold Academic silk colour turquoise blue , nickname = , mascot = , website
www.hull.ac.uk
, logo = University of Hull logo.svg , logo_size = 200px , footnotes = , academic_staff = 1,005 (2020) , total_staff = 2,190 (2020) , affiliations = Global U8 (GU8)
Utrecht Network
Universities UK
EUA The University of Hull is a

 The foundation stone of University College Hull, then an external college of the University of London, was laid in 1927 by Prince Albert, the
The foundation stone of University College Hull, then an external college of the University of London, was laid in 1927 by Prince Albert, the
 The period of rapid expansion of Hull University coincided with the vice-chancellorship of Sir Brynmor Jones (1956–1972), during whose time in office student numbers quadrupled.
The
The period of rapid expansion of Hull University coincided with the vice-chancellorship of Sir Brynmor Jones (1956–1972), during whose time in office student numbers quadrupled.
The
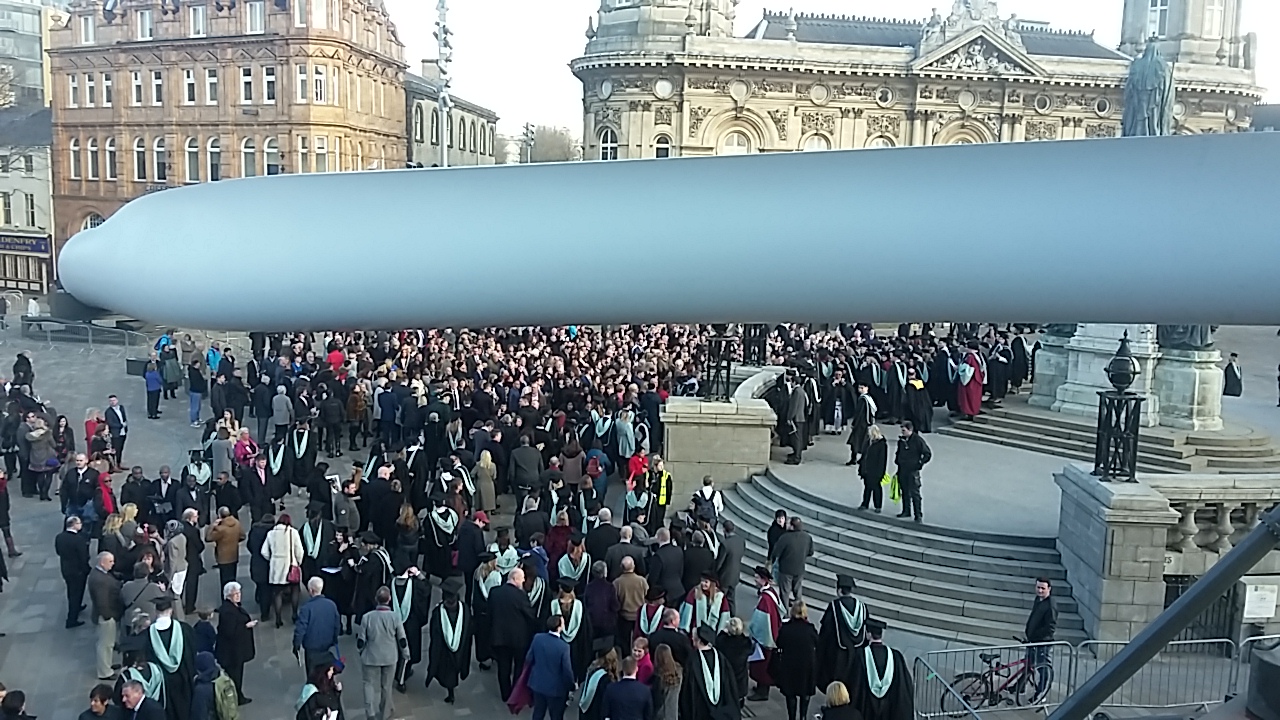 The university was a principal partner of the city's bid to become UK City of Culture in 2017. As well as being involved in the planning and preparation of the bid, the university and its staff and students have been involved in many of the events of the year. For example, during the initial three-month season, Hull Maritime Museum displayed a multimedia installation depicting a
The university was a principal partner of the city's bid to become UK City of Culture in 2017. As well as being involved in the planning and preparation of the bid, the university and its staff and students have been involved in many of the events of the year. For example, during the initial three-month season, Hull Maritime Museum displayed a multimedia installation depicting a
 *School of Engineering & Computer Science: Chemical Engineering, Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Computer Science, Mechanical Engineering, Medical & Biomedical Engineering
*School of Environmental Sciences: Environmental Science, Geography & Geology
*School of Natural Sciences: Biochemistry, Biological and Marine Science, Chemistry, Mathematics, Physics & Astrophysics
Until recently, there were two faculties, the 'Faculty of Applied Science & Technology' and the 'Faculty of Science & the Environment', before becoming the 'Faculty of Science' and later being renamed to the 'Faculty of Science and Engineering'.
Notable centres for research include the Hull Immersive Visualisation Environment (HIVE), the Institute for Estuarine and Coastal Studies (IECS), the E.A. Milne Centre for Astrophysics (MCA) and the G W Gray Centre for Advanced Materials.
A new biomedical research facility will bring academics from biology and chemistry together and will include
*School of Engineering & Computer Science: Chemical Engineering, Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Computer Science, Mechanical Engineering, Medical & Biomedical Engineering
*School of Environmental Sciences: Environmental Science, Geography & Geology
*School of Natural Sciences: Biochemistry, Biological and Marine Science, Chemistry, Mathematics, Physics & Astrophysics
Until recently, there were two faculties, the 'Faculty of Applied Science & Technology' and the 'Faculty of Science & the Environment', before becoming the 'Faculty of Science' and later being renamed to the 'Faculty of Science and Engineering'.
Notable centres for research include the Hull Immersive Visualisation Environment (HIVE), the Institute for Estuarine and Coastal Studies (IECS), the E.A. Milne Centre for Astrophysics (MCA) and the G W Gray Centre for Advanced Materials.
A new biomedical research facility will bring academics from biology and chemistry together and will include
 *School of Arts: Drama; English; Film & Digital Media; Music
*School of Education & Social Sciences: Criminology; Education, Teaching & Childhood Studies; Sociology & Social Sciences; Social Work, Youth & Community Development
*School of Histories, Languages & Cultures: American Studies; History; Modern Languages & Cultures; Philosophy
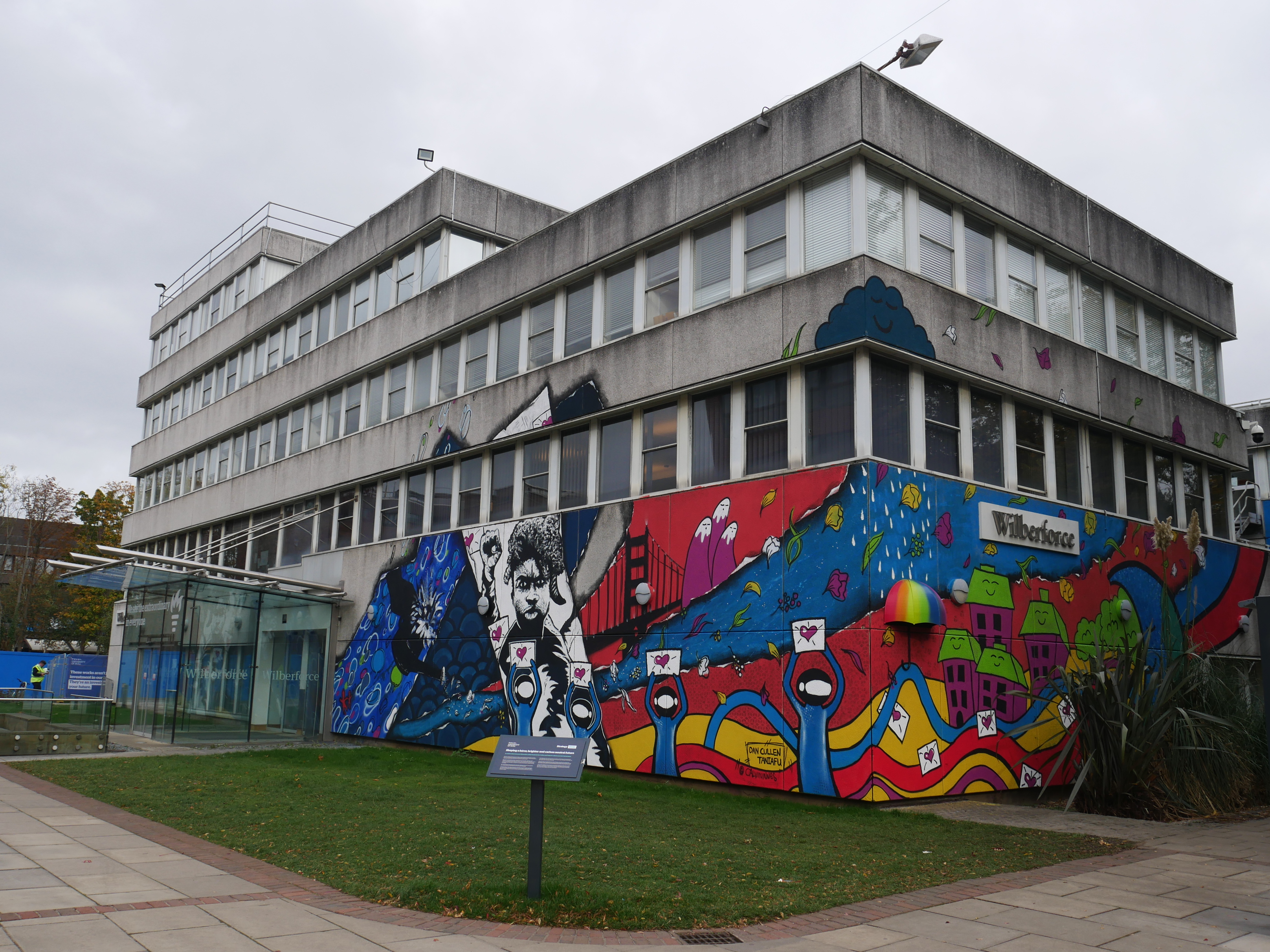
Most social science and law-related department housed in the refurbished Wilberforce Building. Includes the School of Arts and New Media at Scarborough, formed in August 2006. Drama is taught in the Gulbenkian Centre, including the Donald Roy Theatre. History, English, Languages and Music are in the Larkin Building.
→
*School of Arts: Drama; English; Film & Digital Media; Music
*School of Education & Social Sciences: Criminology; Education, Teaching & Childhood Studies; Sociology & Social Sciences; Social Work, Youth & Community Development
*School of Histories, Languages & Cultures: American Studies; History; Modern Languages & Cultures; Philosophy
Most social science and law-related department housed in the refurbished Wilberforce Building. Includes the School of Arts and New Media at Scarborough, formed in August 2006. Drama is taught in the Gulbenkian Centre, including the Donald Roy Theatre. History, English, Languages and Music are in the Larkin Building.
→
 Teaching of medicine began in October 2003 on the west campus. Medical students receive joint degrees from the universities of Hull and York. The school includes the 'International Society for the Study of Cough' based at Castle Hill hospital on ''Castle Road'' in Cottingham. Third and fourth year students train also at hospitals in Scunthorpe, Grimsby, and Scarborough.
Teaching of medicine began in October 2003 on the west campus. Medical students receive joint degrees from the universities of Hull and York. The school includes the 'International Society for the Study of Cough' based at Castle Hill hospital on ''Castle Road'' in Cottingham. Third and fourth year students train also at hospitals in Scunthorpe, Grimsby, and Scarborough.
 *Hull University Business School: Accounting & Finance, Business & Management, Economics & Business Economics, Marketing, Logistics & Supply Chain Management
*School of Law & Politics: Law, Politics & International Relations
Established in August 1999, Hull University Business School has around 3,500 students from over 100 countries. Students are taught at the Hull campus, with additional MBA students taught overseas. On the Hull campus, the school occupies refurbished listed buildings on the West Campus which were opened in 2005. The Logistics Institute was completed in September 2007, and officially launched in March 2008.
In 2011, following accreditation by the AMBA, EQUIS and AACSB, the Business School became the first in Yorkshire, and the 13th in the UK, to achieve " triple crown accreditation" status.
*Hull University Business School: Accounting & Finance, Business & Management, Economics & Business Economics, Marketing, Logistics & Supply Chain Management
*School of Law & Politics: Law, Politics & International Relations
Established in August 1999, Hull University Business School has around 3,500 students from over 100 countries. Students are taught at the Hull campus, with additional MBA students taught overseas. On the Hull campus, the school occupies refurbished listed buildings on the West Campus which were opened in 2005. The Logistics Institute was completed in September 2007, and officially launched in March 2008.
In 2011, following accreditation by the AMBA, EQUIS and AACSB, the Business School became the first in Yorkshire, and the 13th in the UK, to achieve " triple crown accreditation" status.
 Hull University Union is the main provider of student catering, services and entertainment on the university campus. It has over 100 student societies affiliated to it, and also runs a volunteering and charity hub. Approximately 50 sports clubs are affiliated to the Students Union's
Hull University Union is the main provider of student catering, services and entertainment on the university campus. It has over 100 student societies affiliated to it, and also runs a volunteering and charity hub. Approximately 50 sports clubs are affiliated to the Students Union's
 Alumni of the University of Hull are especially prominent in the fields of politics, academia, journalism and drama. They include former MP and later Deputy Prime Minister Lord Prescott ( John Prescott), former MP and Deputy Leader of the Labour Party Lord Hattersley ( Roy Hattersley) and former Labour MP and deputy leader Tom Watson, former Labour MP and author Chris Mullin, vaccinologist Dame Sarah Gilbert who was Project Lead on the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, social scientist Lord Giddens (
Alumni of the University of Hull are especially prominent in the fields of politics, academia, journalism and drama. They include former MP and later Deputy Prime Minister Lord Prescott ( John Prescott), former MP and Deputy Leader of the Labour Party Lord Hattersley ( Roy Hattersley) and former Labour MP and deputy leader Tom Watson, former Labour MP and author Chris Mullin, vaccinologist Dame Sarah Gilbert who was Project Lead on the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, social scientist Lord Giddens (
Hull University UnionReview
of Bamford's ''The University of Hull: The First Fifty Years,'' Knox, H. M. '' British Journal of Educational Studies'', vol. 28, no. 1, 1980, pp. 65–66 ($) {{DEFAULTSORT:Hull, University Of Educational institutions established in 1927 1927 establishments in England University Universities UK
f learning
F, or f, is the sixth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ef'' (pronounced ), and the plural is ''efs''.
Hist ...
, established = 1927 – University College Hull1954 – university status , type = Public , endowment = £18.8 million (2016) , budget = £190 million (2016) , chancellor =
Baroness Bottomley of Nettlestone
Virginia Hilda Brunette Maxwell Bottomley, Baroness Bottomley of Nettlestone, (née Garnett, born 12 March 1948) is a British Conservative Party politician, and headhunter. She was a Member of Parliament (MP) in the House of Commons from 1984 ...
, vice_chancellor = David Petley
, head_label = Visitor
A visitor, in English and Welsh law and history, is an overseer of an autonomous ecclesiastical or eleemosynary institution, often a charitable institution set up for the perpetual distribution of the founder's alms and bounty, who can interve ...
, head = The Lord President of the Council ''ex officio
An ''ex officio'' member is a member of a body (notably a board, committee, council) who is part of it by virtue of holding another office. The term '' ex officio'' is Latin, meaning literally 'from the office', and the sense intended is 'by right ...
''
, students = ()
, undergrad = ()
, postgrad = ()
, doctoral =
, city = Kingston upon Hull, country = England , campus = Urban area , colours = Scarf colours, blue and gold Academic silk colour turquoise blue , nickname = , mascot = , website
www.hull.ac.uk
, logo = University of Hull logo.svg , logo_size = 200px , footnotes = , academic_staff = 1,005 (2020) , total_staff = 2,190 (2020) , affiliations = Global U8 (GU8)
Utrecht Network
Universities UK
EUA The University of Hull is a
public research university
A public university or public college is a university or college that is in owned by the state or receives significant public funds through a national or subnational government, as opposed to a private university. Whether a national university ...
in Kingston upon Hull, a city in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It was founded in 1927 as University College Hull. The main university campus is located in Hull and is home to the Hull York Medical School, a joint initiative with the University of York
, mottoeng = On the threshold of wisdom
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £8.0 million
, budget = £403.6 million
, chancellor = Heather Melville
, vice_chancellor = Charlie Jeffery
, students ...
. Students are served by Hull University Union.
The first chancellor of the university was Lord Middleton (1954–1969), followed by Lord Cohen (1970–1977), Lord Wilberforce (1978–1994), and Lord Armstrong (1994–2006). Virginia Bottomley (Baroness Bottomley of Nettlestone) was installed as the current chancellor in April 2006.
History
University College

 The foundation stone of University College Hull, then an external college of the University of London, was laid in 1927 by Prince Albert, the
The foundation stone of University College Hull, then an external college of the University of London, was laid in 1927 by Prince Albert, the Duke of York
Duke of York is a title of nobility in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of English (later British) monarchs. The equivalent title in the Scottish peerage was Du ...
(who later became king as George VI). The college was built on land donated by Hull City Council
(Kingston upon) Hull City Council is the governing body for the unitary authority and city of Kingston upon Hull. It was created in 1972 as the successor to the Corporation of (Kingston upon) Hull, which was also known as Hull Corporation and fou ...
and by two local benefactors, Thomas Ferens and G F Grant. A year later the first 14 departments, in pure sciences and the arts, opened with 39 students. The college at that time consisted of one building, now named the Venn building (after the mathematician John Venn, who was born in Hull). The building now houses the administrative centre of the university.
Other early buildings include the Cohen Building, which originally housed the college library, and Staff House, now named Canham Turner building, built in 1948 as the Students' Union. Another early structure was the Chemistry Building, built in 1953. With the rapid expansion of student numbers which took place in the 1950s many academic departments were housed in temporary buildings, colloquially known as 'huts', which gave the campus the feel of an 'academic army camp'. The Dennison Centre on Cottingham Road was formerly the Brooklands Officers Hospital opened by the Red Cross in 1917. The author J. R. R. Tolkien was a convalescent patient at Brooklands and his connection is marked by a blue plaque.
Though many of the older buildings on Hull's campus are of red brick it is not a '' redbrick university'' in the strictest sense of the term, as it was not founded as part of the civic university movement of the late Victorian
Victorian or Victorians may refer to:
19th century
* Victorian era, British history during Queen Victoria's 19th-century reign
** Victorian architecture
** Victorian house
** Victorian decorative arts
** Victorian fashion
** Victorian literature ...
and Edwardian eras. Hull, with its origins in the 1920s, has been categorised as a 'younger civic university' (also referred to as a "Whitetile university") and it is placed between the 'redbricks' and the 'plateglass universities' founded in the 1960s.
The first principal of the college was Arthur E. Morgan (1926–1935), the second was John H Nicholson
John Henry Nicholson (21 September 1889 – 9 August 1972) was the second Principal of University College Hull, and the first Vice-Chancellor of the University of Hull.
Dr John H Nicholson was educated at the University of Oxford, where he gaine ...
(1935–1954), who also served as the university's first vice-chancellor when the college was granted university status (1954–1956).
Coat of arms
The university coat of arms was designed by Sir Algernon Tudor-Craig in 1928. The symbols are the torch for learning, the rose for Yorkshire, the ducal coronet from the arms of the City of Hull, the fleur-de-lys for Lincolnshire and the dove, symbolising peace, from the arms of Thomas Ferens. These symbols were later reused to create the current university logo. The motto, ''Lampada Ferens'' (Bearing the Torch), incorporates the name of the university's founding father within a Latin pun.Royal charter
The college gained its royal charter on 6 September 1954. This empowered it to award degrees of its own, making it the 3rd university in Yorkshire and the 14th in England. The twenty six years between the formation of the university college and the awarding of the charter were the shortest such period in the history of university formation in England up to that time. Within a year of the charter being granted applications to study at the new university had doubled, and in 1956 student numbers topped 1,000 for the first time.The mace
The academic authority and autonomy of the university is symbolically embodied in the ceremonial mace. Made of gilt silver, and incorporating devices from the Hull University coat of arms, the mace was presented to the university in December 1956 by the Lord Mayor of Hull. As a gift from the city it also reflects the close relationship between "town and gown" existing in Hull. The mace is carried in procession and displayed at all major university ceremonies.Expansion in the 1950s and 1960s
Brynmor Jones Library
The Brynmor Jones Library (BJL) is the main library at the University of Hull. In 1967 it was named after Sir Brynmor Jones (1903-1989) who initiated research in the field of Liquid Crystals ( LCD) at Hull and became Head of the Department of ...
, which houses more than a million volumes, was constructed in two phases: the first phase was fully completed in 1959, with a tower block extension officially opened in 1970. During the 1950s and 1960s a considerable number of academic buildings were built, including the Larkin and Wilberforce Buildings (originally given other names). The 'Martin Plan' of 1967, Sir Leslie Martin was the university architect, envisaged a campus with its tallest buildings in the centre surrounded by buildings diminishing in height towards the perimeter. In the course of the 1960s most of the departments housed in temporary structures were moved into new purpose-built premises. However, Biochemistry was still partially located in a 'hut' to the rear of the Venn building into the early 1980s. This early phase of expansion through building ended in 1974, after this year there was to be no further academic building construction on the campus until 1996. However, student numbers doubled in this period, with the university becoming highly efficient in using its existing building stock.
Liquid crystal technology
In 1972 George Gray and Ken Harrison created room-temperature stableliquid crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. T ...
s in the university chemistry laboratories, which were an immediate success in the electronics industry and consumer products. This led to Hull becoming the first university to be awarded the Queen's Award for Technological Achievement for the joint-development of the long-lasting materials that made liquid crystal display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat panel display, flat-panel display or other Electro-optic modulator, electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liqui ...
s possible.
Expansion in the 21st century
In 2000 the university bought the site of University College Scarborough on Filey Road, Scarborough, plus two linked buildings on the same road. This became the University of Hull Scarborough Campus. A further significant expansion took place in 2003, when the buildings of the formerHumberside University
, mottoeng = Freedom through wisdom
, established = 1861 – Hull School of Art1905 – Endsleigh College1976 – Hull College1992 – University of Humberside1996 – University of Lincolnshire and Humberside2001 � ...
campus, which were situated immediately adjacent to Hull University's main campus, were purchased. The acquisition increased the size of the Cottingham Road campus by more than a third. It was the largest single act of expansion in the history of the university. Hull University fully occupied the newly acquired premises in the 2005 academic year; the area becoming the university's West Campus. The site now houses the Hull York Medical School and the relocated business school, which is located in three of the most prominent buildings – Wharfe, Derwent and Esk.
In 2012, the university began the ambitious refurbishment of the Brynmor Jones Library, a £28 million project which will transform the 7 storey former workplace of Philip Larkin, into a learning hub suitable for students for years to come. The project was completed in 2015.
Hull History Centre
TheHull History Centre
The Hull History Centre is an archive and local studies library in Hull, England, that houses the combined collections of both the Hull City Council and Hull University archives and local studies resources. This collaboration between Hull Cit ...
, which opened in 2010, is located in a new building on Worship Street in Hull city centre. It unites the holdings of Hull City Library's Local Studies collections and Hull University's archives and is run in partnership between the City Library and University Library.
City of Culture 2017
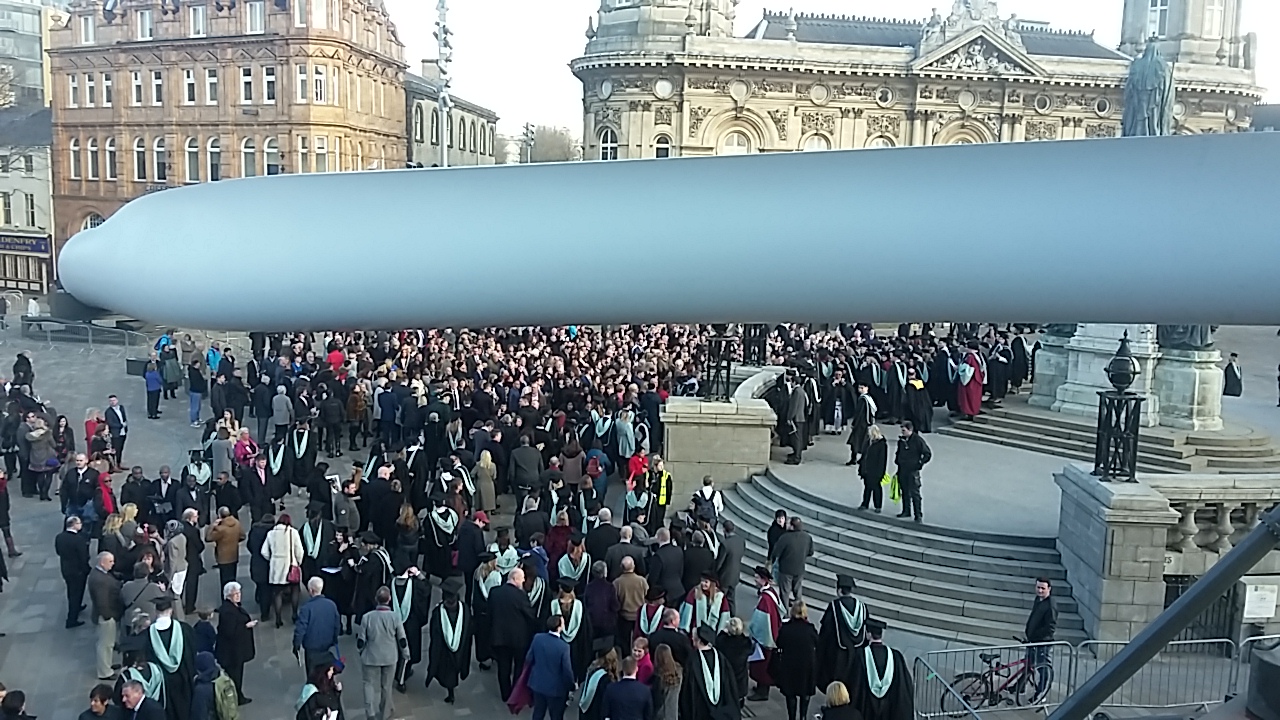 The university was a principal partner of the city's bid to become UK City of Culture in 2017. As well as being involved in the planning and preparation of the bid, the university and its staff and students have been involved in many of the events of the year. For example, during the initial three-month season, Hull Maritime Museum displayed a multimedia installation depicting a
The university was a principal partner of the city's bid to become UK City of Culture in 2017. As well as being involved in the planning and preparation of the bid, the university and its staff and students have been involved in many of the events of the year. For example, during the initial three-month season, Hull Maritime Museum displayed a multimedia installation depicting a Bowhead whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus'') is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and the only living representative of the genus ''Balaena''. They are the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, ...
The installation was designed by students from Hull School of Art and Design with music by students from Hull University. The opening event of the whole year, from 1–7 January, included a multimedia projection called ''Arrivals and Departures'' which was greatly influenced by the work of Dr Nick Evans on migration patterns into and through Hull. The installation was projected onto The Deep using stop-frame animation, image and sound.
Campuses
The main campus is located in a residential district of North Hull on Cottingham Road. The university had a smaller campus in Scarborough on the North Yorkshire coast. Hull University is a campus university; though situated in a city, its main campus is in a suburban rather than urban district. The main campus occupies a single, clearly defined site and is self-contained in regard to catering and entertainment for students and staff. Most of the major features of the campus are described in the 'history' section above; in addition, the campus has a large Students' Union building, which is often described as one of the finest in the country, and extensive playing fields and other sports facilities. The large village of Cottingham on Hull's north-western outskirts housed for many years some of the university-owned student accommodation, although none are used for this purpose now.University College Scarborough
University of Hull: Scarborough Campus was a satellite campus of the university located in Scarborough, North Yorkshire, attended by approximately 2,000 students. Formerly a higher education institution offering BSc and BA degrees, the building was acquired by the University of Hull in 2000, offering Education courses, particularly at a primary level, as well as courses inMarine Biology
Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life, organisms in the sea. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies s ...
, Digital Media
Digital media is any communication media that operate in conjunction with various encoded machine-readable data formats. Digital media can be created, viewed, distributed, modified, listened to, and preserved on a digital electronics device. ' ...
, Music Technology Theatre Studies, Tourism Management, and a number of Business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for pr ...
and English courses.
Scarborough ran somewhat independently of the main campus in Hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
, with its own branch of the Hull University Union. Graduation ceremonies took place within Scarborough's historic Spa Complex. The campus also contained basic amenities for study, such as computer labs, performance studios for students of Theatre and Dance related courses as well as dedicated music suites in the "Filey Road Studios" building opposite the campus.
In April 2014, the university released a statement that Scarborough Campus was "not sustainable in the medium to long term", and in June held a public consultation outlining the future of the campus with a new academic model in mind. In March 2015, it was revealed that the Hull College Group
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in a ...
were the university's "preferred partners for taking forward the Scarborough Campus". The college returned to its former name, "University College Scarborough" and became part of the Hull College group, but still hosts programmes from both Hull College and the University of Hull.
External Validation
Since September 2013, all undergraduate and postgraduate degree courses at the Leeds Conservatoire are validated by the University of Hull. Beginning in 1993 Hull has validated Masters of Education programmes for the Christian Leadership in Education Office (CLEO), in Cork (and from 1993 to 1996 in Limerick), Ireland. Hull also validates a number of programmes in Rotherham College, Dearne Vally College, and other RNN Group locations. From 1972 until 1982 the University of Hull validated programmes at the postrgaduate Irish School of Ecumenics.Academic profile
Faculty of Science and Engineering
 *School of Engineering & Computer Science: Chemical Engineering, Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Computer Science, Mechanical Engineering, Medical & Biomedical Engineering
*School of Environmental Sciences: Environmental Science, Geography & Geology
*School of Natural Sciences: Biochemistry, Biological and Marine Science, Chemistry, Mathematics, Physics & Astrophysics
Until recently, there were two faculties, the 'Faculty of Applied Science & Technology' and the 'Faculty of Science & the Environment', before becoming the 'Faculty of Science' and later being renamed to the 'Faculty of Science and Engineering'.
Notable centres for research include the Hull Immersive Visualisation Environment (HIVE), the Institute for Estuarine and Coastal Studies (IECS), the E.A. Milne Centre for Astrophysics (MCA) and the G W Gray Centre for Advanced Materials.
A new biomedical research facility will bring academics from biology and chemistry together and will include
*School of Engineering & Computer Science: Chemical Engineering, Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Computer Science, Mechanical Engineering, Medical & Biomedical Engineering
*School of Environmental Sciences: Environmental Science, Geography & Geology
*School of Natural Sciences: Biochemistry, Biological and Marine Science, Chemistry, Mathematics, Physics & Astrophysics
Until recently, there were two faculties, the 'Faculty of Applied Science & Technology' and the 'Faculty of Science & the Environment', before becoming the 'Faculty of Science' and later being renamed to the 'Faculty of Science and Engineering'.
Notable centres for research include the Hull Immersive Visualisation Environment (HIVE), the Institute for Estuarine and Coastal Studies (IECS), the E.A. Milne Centre for Astrophysics (MCA) and the G W Gray Centre for Advanced Materials.
A new biomedical research facility will bring academics from biology and chemistry together and will include Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including bl ...
with CT scanning (PET-CT) and two mini cyclotrons. Two new research groups will be based at the facility, called the Allam building: one focusing on cardiovascular and metabolic research and the other on cancer.
Faculty of Arts, Culture & Education
 *School of Arts: Drama; English; Film & Digital Media; Music
*School of Education & Social Sciences: Criminology; Education, Teaching & Childhood Studies; Sociology & Social Sciences; Social Work, Youth & Community Development
*School of Histories, Languages & Cultures: American Studies; History; Modern Languages & Cultures; Philosophy
Most social science and law-related department housed in the refurbished Wilberforce Building. Includes the School of Arts and New Media at Scarborough, formed in August 2006. Drama is taught in the Gulbenkian Centre, including the Donald Roy Theatre. History, English, Languages and Music are in the Larkin Building.
→
*School of Arts: Drama; English; Film & Digital Media; Music
*School of Education & Social Sciences: Criminology; Education, Teaching & Childhood Studies; Sociology & Social Sciences; Social Work, Youth & Community Development
*School of Histories, Languages & Cultures: American Studies; History; Modern Languages & Cultures; Philosophy
Most social science and law-related department housed in the refurbished Wilberforce Building. Includes the School of Arts and New Media at Scarborough, formed in August 2006. Drama is taught in the Gulbenkian Centre, including the Donald Roy Theatre. History, English, Languages and Music are in the Larkin Building.
→
Faculty of Health Sciences
* Hull York Medical School *School of Health & Social Work: Health, Paramedic Science, Nursing & Midwifery; Social Work, Youth & Community Development *School of Life Sciences: Biomedical Sciences; Psychology; Sport, Health & Exercise Science Based in the Calder, Aire and Dearne buildings in the west campus. Allam Medical Building contains mock clinical areas, wards, an operating theatre and a midwifery suite, within a simulated environment.Hull York Medical School
 Teaching of medicine began in October 2003 on the west campus. Medical students receive joint degrees from the universities of Hull and York. The school includes the 'International Society for the Study of Cough' based at Castle Hill hospital on ''Castle Road'' in Cottingham. Third and fourth year students train also at hospitals in Scunthorpe, Grimsby, and Scarborough.
Teaching of medicine began in October 2003 on the west campus. Medical students receive joint degrees from the universities of Hull and York. The school includes the 'International Society for the Study of Cough' based at Castle Hill hospital on ''Castle Road'' in Cottingham. Third and fourth year students train also at hospitals in Scunthorpe, Grimsby, and Scarborough.
Postgraduate Medical Institute
Established in 1994, one of the PGMI's sections is the Yorkshire Cancer Research-funded Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations which is actively engaged in researching the application ofmagnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
and magnetic resonance spectroscopy techniques to cancer research.
Faculty of Business, Law & Politics
 *Hull University Business School: Accounting & Finance, Business & Management, Economics & Business Economics, Marketing, Logistics & Supply Chain Management
*School of Law & Politics: Law, Politics & International Relations
Established in August 1999, Hull University Business School has around 3,500 students from over 100 countries. Students are taught at the Hull campus, with additional MBA students taught overseas. On the Hull campus, the school occupies refurbished listed buildings on the West Campus which were opened in 2005. The Logistics Institute was completed in September 2007, and officially launched in March 2008.
In 2011, following accreditation by the AMBA, EQUIS and AACSB, the Business School became the first in Yorkshire, and the 13th in the UK, to achieve " triple crown accreditation" status.
*Hull University Business School: Accounting & Finance, Business & Management, Economics & Business Economics, Marketing, Logistics & Supply Chain Management
*School of Law & Politics: Law, Politics & International Relations
Established in August 1999, Hull University Business School has around 3,500 students from over 100 countries. Students are taught at the Hull campus, with additional MBA students taught overseas. On the Hull campus, the school occupies refurbished listed buildings on the West Campus which were opened in 2005. The Logistics Institute was completed in September 2007, and officially launched in March 2008.
In 2011, following accreditation by the AMBA, EQUIS and AACSB, the Business School became the first in Yorkshire, and the 13th in the UK, to achieve " triple crown accreditation" status.
Wilberforce Institute
The Wilberforce Institute, patron Archbishop EmeritusDesmond Tutu
Desmond Mpilo Tutu (7 October 193126 December 2021) was a South African Anglican bishop and theologian, known for his work as an anti-apartheid and human rights activist. He was Bishop of Johannesburg from 1985 to 1986 and then Archbishop ...
, for the study of Slavery and Emancipation (WISE) is located in Oriel Chambers on the High Street in Hull's Old Town, adjacent to Wilberforce House. It undertakes graduate research in the field of slavery and human rights.
Maritime Historical Studies Centre
The university's Maritime Historical Studies Centre provides a BA in History and Maritime History, an online Diploma in Maritime History and PhD research in Maritime History. The centre is located in the Hull's Old Town in Blaydes House. Its director is David J Starkey.Confucius Institute
Since 2016 the university has hosted a Confucius Institute.Rankings
Student life
Students' Union
Athletic Union
An athletic union or athletics union (AU) usually refers to the group of student sports clubs within a university or other institute of higher education, in the United Kingdom.
General information
Sports clubs affiliate to their athletic union fo ...
, many of which compete in BUCS national university leagues. The University Union was voted Students' Union of the Year in July 2012.
The student union building comprises an on-site nightclub as well as a number of bars and catering outlets. The building also houses a shop, advice centre, and the university-run careers service.
There is a monthly student newspaper called ''The Hullfire'', an online television station called Hullfire TV and a student radio station which broadcasts from the union building called JAM Radio which relaunched in 2018.
Student accommodation
The university has three main halls of residence on campus: * Taylor Court is located next to the Wilberforce building and houses 288 students in en-suite rooms with shared kitchens. * The Courtyard opened in 2016 and is situated next to the Student Union, it houses 562 students in en-suite rooms as well as some rooftop apartments. * Westfield Court partially opened in 2018, with a full opening in 2019 on the site of the former medical school. It houses a total of 1462 students in a mix of single and cluster flats. In the recent past there were halls of residence in Cottingham at The Lawns, seven halls which could hold around 1,000 students. In March 2019 it was announced that The Lawns would close. Historically, the main concentration of 'traditional' (catered) university halls of residence was in Cottingham. These comprised: Cleminson Hall (closed in 2004), Needler Hall (closed in 2016), andThwaite Hall
Thwaite Hall was a traditional hall of residence of the University of Hull, located in Cottingham, East Riding of Yorkshire, England.
History and description
Thwaite House was built in Cottingham, East Riding of Yorkshire between 1803 and 1 ...
(closed in 2017). Ferens Hall was originally a traditional hall, but was later amalgamated with the adjoining Lawns halls. Prior to the mid-1980s, Cleminson and Thwaite halls were exclusively for female residents, Needler and Ferens exclusively for male residents. There was a former on-campus student residence, Loten Hall (now known as the Loten Building).
Student housing is based primarily in the terraced streets around the university campus itself, as well as around the Newland Avenue and Beverley Road areas of the city.
Notable alumni and academics
 Alumni of the University of Hull are especially prominent in the fields of politics, academia, journalism and drama. They include former MP and later Deputy Prime Minister Lord Prescott ( John Prescott), former MP and Deputy Leader of the Labour Party Lord Hattersley ( Roy Hattersley) and former Labour MP and deputy leader Tom Watson, former Labour MP and author Chris Mullin, vaccinologist Dame Sarah Gilbert who was Project Lead on the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, social scientist Lord Giddens (
Alumni of the University of Hull are especially prominent in the fields of politics, academia, journalism and drama. They include former MP and later Deputy Prime Minister Lord Prescott ( John Prescott), former MP and Deputy Leader of the Labour Party Lord Hattersley ( Roy Hattersley) and former Labour MP and deputy leader Tom Watson, former Labour MP and author Chris Mullin, vaccinologist Dame Sarah Gilbert who was Project Lead on the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, social scientist Lord Giddens (Anthony Giddens
Anthony Giddens, Baron Giddens (born 18 January 1938) is an English sociologist who is known for his theory of structuration and his holistic view of modern societies. He is considered to be one of the most prominent modern sociologists and is t ...
), poet Roger McGough, journalist John McCarthy, film director, playwright and screenwriter the late Anthony Minghella.
One of the 2021 joint Nobel laureates
The Nobel Prizes ( sv, Nobelpriset, no, Nobelprisen) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make ou ...
for economics was Hull graduate, Guido Imbens.
The university's Brynmor Jones Library
The Brynmor Jones Library (BJL) is the main library at the University of Hull. In 1967 it was named after Sir Brynmor Jones (1903-1989) who initiated research in the field of Liquid Crystals ( LCD) at Hull and became Head of the Department of ...
was the workplace of the poet Philip Larkin who served as its Head Librarian for over thirty years. The Philip Larkin Society
Philip Arthur Larkin (9 August 1922 – 2 December 1985) was an English poet, novelist, and librarian. His first book of poetry, '' The North Ship'', was published in 1945, followed by two novels, '' Jill'' (1946) and '' A Girl in Winter'' (1 ...
organises activities in remembrance of Larkin including the Larkin 25 festival which was organised during 2010 in partnership with the university. Andrew Motion
Sir Andrew Motion (born 26 October 1952) is an English poet, novelist, and biographer, who was Poet Laureate from 1999 to 2009. During the period of his laureateship, Motion founded the Poetry Archive, an online resource of poems and audio reco ...
, another prominent poet, and former poet laureate, also worked at the university. Prominent former academics include: marine biologist Sir Alister Hardy
Sir Alister Clavering Hardy (10 February 1896 – 22 May 1985) was an English marine biologist, an expert on marine ecosystems spanning organisms from zooplankton to whales. He had the artistic skill to illustrate his books with his own drawings ...
, architect Sir Leslie Martin, mathematician and historian Jacob Bronowski and novelist Sir Malcolm Bradbury.
See also
* Armorial of UK universities *Civic university
A red brick university (or redbrick university) was originally one of the nine civic universities founded in the major industrial cities of England in the 19th century.
However, with the 1960s proliferation of plate glass universities and t ...
* List of universities in the UK
This is a list of universities in the United Kingdom (alphabetical by substantive name). Below that are lists of university colleges and other recognised bodies (institutions with degree awarding powers), followed by a list of defunct institution ...
References
Bibliography
*Bamford, T. W. (1978) '' The University of Hull: the First Fifty Years'', Published for the University of Hull by Oxford University Press.External links
*Hull University Union
of Bamford's ''The University of Hull: The First Fifty Years,'' Knox, H. M. '' British Journal of Educational Studies'', vol. 28, no. 1, 1980, pp. 65–66 ($) {{DEFAULTSORT:Hull, University Of Educational institutions established in 1927 1927 establishments in England University Universities UK