Hornbill Ivory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hornbill ivory (also called "golden jade" or ''calao ivoire'' in French) is a precious ornamental material derived from the
Hornbill ivory (also called "golden jade" or ''calao ivoire'' in French) is a precious ornamental material derived from the
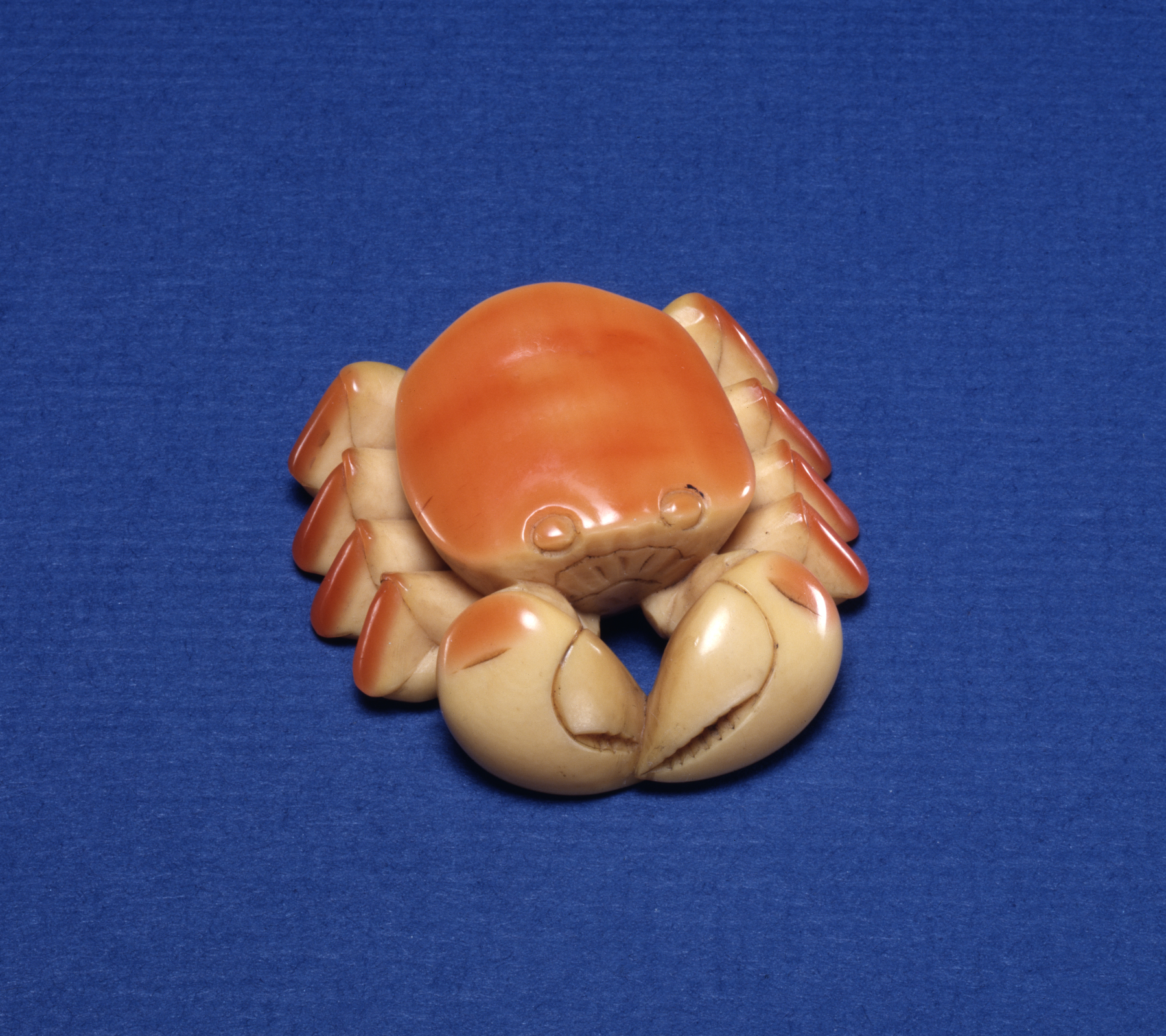
Page from the IvoryhoundPhotographs and description of a Bornean carving from ArtAreas
showing the red rim colored by preen-gland secretions Ivory Bird products Borneo Hornbills Chinese art
 Hornbill ivory (also called "golden jade" or ''calao ivoire'' in French) is a precious ornamental material derived from the
Hornbill ivory (also called "golden jade" or ''calao ivoire'' in French) is a precious ornamental material derived from the helmeted hornbill
The helmeted hornbill (''Rhinoplax vigil'') is a very large bird in the hornbill family. It is found on the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Thailand and Myanmar. The casque (helmetlike structure on the head) accounts for some 11% of its 3 ...
(''Buceros vigil''), a large bird of the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula (Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area ...
, Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, and Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
.
Many hornbill
Hornbills (Bucerotidae) are a family (biology), family of bird found in tropical and subtropical Africa, Asia and Melanesia. They are characterized by a long, down-curved bill which is frequently brightly coloured and sometimes has a Casque (an ...
species have "casques", decorative growths on the upper mandible of the bill. In most, the casque has a spongy structure, but in the helmeted hornbill it is solid keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
. This material, hornbill ivory, has a texture suggesting ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals is ...
but is softer. As it grows it is golden yellow, but the bird rubs its casque on its preen gland
The uropygial gland, informally known as the preen gland or the oil gland, is a bilobed sebaceous gland possessed by the majority of birds used to distribute the gland's oil through the plumage by means of preening. It is located dorsally at the ...
, whose oily secretion tints the surface of the casque bright red.
Native peoples in the helmeted hornbill's range, such as the Kenyah
The Kenyah people are an indigenous, Austronesian-speaking people of Borneo, living in the remote Baram Lio Matoh, Long Selaan, Long Moh, Long Anap, Long Mekaba, Long Jeeh, Long Belaong, Long San, Long Silat, Long Tungan, Data Kakus ...
and Kelabit, have long carved the casques. In Malaysia, hornbill-ivory rings were said to change colour when near poisonous food. The Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
encountered the material in the 14th century and it soon became an important trade item at Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
. According to Tom Harrisson
Major (United Kingdom), Major Tom Harnett Harrisson, DSO OBE (26 September 1911 – 16 January 1976) was a British polymath. In the course of his life he was an ornithologist, explorer, journalist, broadcaster, soldier, guerrilla, ethnologist, mu ...
, writing in the first (1960) edition of ''The Birds of Borneo'':
It is likely that the casques were mainly exported raw, and worked with a heat treatment and pressing - of which no detailed description survives - in China, to preserve and heighten the lovely deep golden and surface red patina of the fresh ivory. The Chinese probably got the idea of using ''ho-ting'' from the Dayaks, then improved the technique at their end. The uses of hornbill casques in Borneo are various and frequently effective; we will discuss those presently. While the Borneo usages persist to this day, all trace of the art of the Chinese carver seems to have vanished. Very little has survived of a remarkable craft which undoubtedly paid for many of the old jars, plates, and beads still decorating the longhouses or wives of better-off Bornean pagans many generations later.During the
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
, the Chinese valued hornbill ivory above true ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals is ...
or jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group of ...
. They carved the casques, or made them into sheets, coloured them with the secretion of the preen gland, and made them into belt buckle
A belt buckle is a buckle, a clasp for fastening two ends, such as of straps or a belt, in which a device attached to one of the ends is fitted or coupled to the other. The word enters Middle English via Old French and the Latin ''buccula' ...
s for high officials. They called hornbill ivory ''hèdǐng'' (Wade–Giles
Wade–Giles () is a romanization system for Mandarin Chinese. It developed from a system produced by Thomas Francis Wade, during the mid-19th century, and was given completed form with Herbert A. Giles's '' Chinese–English Dictionary'' of ...
''ho-ting''), which is said to be their approximation of an indigenous name (but means "crane head", and thus many Chinese thought the substance came from a crane rather than a hornbill). The Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
ese also carved imported hornbill ivory into such objects as ''netsuke
A is a miniature sculpture, originating in 17th century Japan. Initially a simply-carved button fastener on the cords of an box, later developed into ornately sculpted objects of craftsmanship.
History
Traditionally, Japanese clothing – ...
''.
By the early 20th century, the helmeted hornbill became rare because it was slaughtered for its casque. Now legal trade in hornbill ivory is limited to certified antiques, and hornbill-ivory carvings are more valuable than those of any true ivory.
References
* * {{cite book, editor=Perrins, Christopher, editor-link=Chris Perrins, title=Firefly Encyclopedia of Birds, publisher=Firefly Books, year=2003, isbn=1-55297-777-3, url-access=registration, url=https://archive.org/details/fireflyencyclope0000unseExternal links
Page from the Ivoryhound
showing the red rim colored by preen-gland secretions Ivory Bird products Borneo Hornbills Chinese art