History of the Palace of Westminster on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of the Palace of Westminster began in the
 The Palace of Westminster site was strategically important during the
The Palace of Westminster site was strategically important during the  Because it was originally a royal residence, the Palace included no purpose-built chambers for the two Houses. Important state ceremonies were held in the
Because it was originally a royal residence, the Palace included no purpose-built chambers for the two Houses. Important state ceremonies were held in the
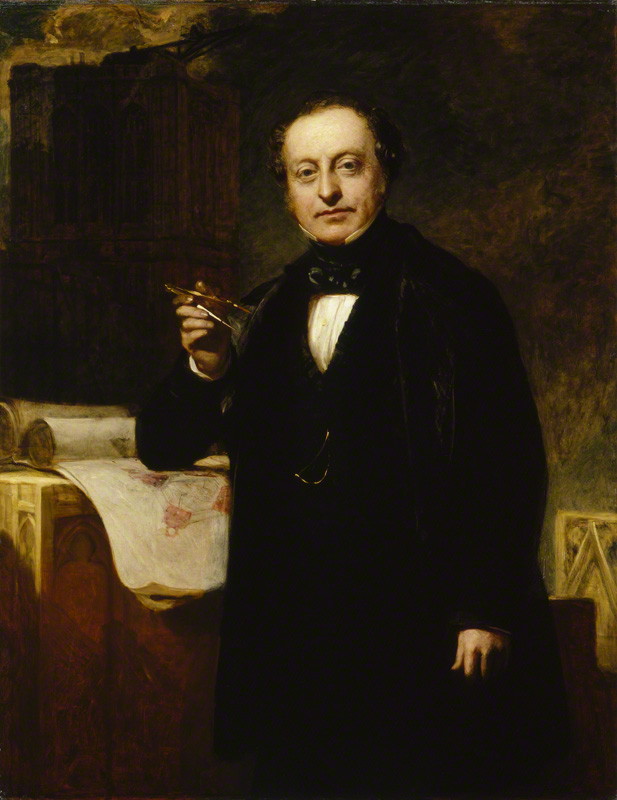 The Lords Chamber was completed in 1847, and the Commons Chamber in 1852 (at which point Barry received a
The Lords Chamber was completed in 1847, and the Commons Chamber in 1852 (at which point Barry received a
 The worst raid took place in the night of 10–11 May 1941, when the Palace took at least twelve hits and three people (two policemen and the Resident Superintendent of the House of Lords, Edward Elliott) were killed. Fell and Mackenzie (1994), p. 27. An incendiary bomb hit the chamber of the House of Commons and set it on fire; another set the roof of Westminster Hall alight. The firefighters could not save both, and a decision was taken to try to rescue the Hall. In this they were successful; the abandoned Commons Chamber, on the other hand, was destroyed, as was the Members' Lobby. A bomb also struck the Lords Chamber, but went through the floor without exploding. The Clock Tower took a hit by a small bomb or anti-aircraft shell at the eaves of the roof, suffering much damage there. All the glass on the south dial was blown out, but the hands and bells were not affected, and the Great Clock continued to keep time accurately.
Following the destruction of the Commons Chamber, the Lords offered their own debating chamber for the use of the Commons; for their own sittings the Queen's Robing Room was converted into a makeshift chamber. The Commons Chamber was rebuilt after the war under the architect Sir Giles Gilbert Scott, in a simplified version of the old chamber's style. The work was undertaken by John Mowlem & Co., and construction lasted until 1950, when
The worst raid took place in the night of 10–11 May 1941, when the Palace took at least twelve hits and three people (two policemen and the Resident Superintendent of the House of Lords, Edward Elliott) were killed. Fell and Mackenzie (1994), p. 27. An incendiary bomb hit the chamber of the House of Commons and set it on fire; another set the roof of Westminster Hall alight. The firefighters could not save both, and a decision was taken to try to rescue the Hall. In this they were successful; the abandoned Commons Chamber, on the other hand, was destroyed, as was the Members' Lobby. A bomb also struck the Lords Chamber, but went through the floor without exploding. The Clock Tower took a hit by a small bomb or anti-aircraft shell at the eaves of the roof, suffering much damage there. All the glass on the south dial was blown out, but the hands and bells were not affected, and the Great Clock continued to keep time accurately.
Following the destruction of the Commons Chamber, the Lords offered their own debating chamber for the use of the Commons; for their own sittings the Queen's Robing Room was converted into a makeshift chamber. The Commons Chamber was rebuilt after the war under the architect Sir Giles Gilbert Scott, in a simplified version of the old chamber's style. The work was undertaken by John Mowlem & Co., and construction lasted until 1950, when
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
when it was used as a royal residence. The English (and subsequently British) Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprema ...
has met there since 1295. The Palace burned down in 1834 and was replaced by the modern building.
Old Palace
 The Palace of Westminster site was strategically important during the
The Palace of Westminster site was strategically important during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, as it was located on the banks of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
. Known in medieval times as Thorney Island, the site may have been first-used for a royal residence by Canute the Great during his reign from 1016 to 1035. St Edward the Confessor, the penultimate Anglo-Saxon monarch of England, built a royal palace on Thorney Island just west of the City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London f ...
at about the same time as he built Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the Unite ...
(1045–1050). Thorney Island and the surrounding area soon became known as Westminster (a portmanteau of the words ''West Minster''). Neither the buildings used by the Anglo-Saxons nor those used by William I survive. The oldest existing part of the Palace, Westminster Hall
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north bank ...
, dates from the reign of William I's successor, King William II.
The Palace of Westminster was the monarch's principal residence in the late Medieval period. The predecessor of Parliament, the '' Curia Regis'' (Royal Council), met in Westminster Hall (although it followed the King when he moved to other palaces). Simon de Montfort's parliament
Simon de Montfort's Parliament was an English parliament held from 20 January 1265 until mid-March of the same year, called by Simon de Montfort, a baronial rebel leader.
Montfort had seized power in England following his victory over Henry I ...
, the first to include representatives of the major towns, met at the Palace in 1265. The "Model Parliament
The Model Parliament is the term, attributed to Frederic William Maitland, used for the 1295 Parliament of England of King Edward I.
History
This assembly included members of the clergy and the aristocracy, as well as representatives from the v ...
", the first official Parliament of England, met there in 1295, and almost all subsequent English Parliaments and then, after 1707, all British Parliaments have met at the Palace.
In 1512, during the early years of the reign of King Henry VIII, fire destroyed the royal residential ("privy") area of the palace. In 1534, Henry VIII acquired York Place from Cardinal Thomas Wolsey
Thomas Wolsey ( – 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic bishop. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's Lord High Almoner, almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and by 1514 he had become the ...
, a powerful minister who had lost the King's favour. Renaming it the Palace of Whitehall, Henry used it as his principal residence. Although Westminster officially remained a royal palace, it was used by the two Houses of Parliament and by the various royal law courts.
In February 2020 a secret door was discovered which had been built for the coronation of King Charles II in 1661. The doorway is located in the cloister behind Westminster Hall.
 Because it was originally a royal residence, the Palace included no purpose-built chambers for the two Houses. Important state ceremonies were held in the
Because it was originally a royal residence, the Palace included no purpose-built chambers for the two Houses. Important state ceremonies were held in the Painted Chamber
The Painted Chamber was part of the medieval Palace of Westminster. It was gutted by fire in 1834, and has been described as "perhaps the greatest artistic treasure lost in the fire". The room was re-roofed and re-furnished to be used tempora ...
which had been originally built in the 13th century as the main bedchamber for King Henry III. The House of Lords originally met in the Queen's Chamber, a modest Medieval hall towards the southern end of the complex, with the adjoining Prince's Chamber used as the robing room for peers and for the monarch during state openings. In 1801 the Upper House moved into the larger White Chamber
The White Chamber was part of the medieval Palace of Westminster. Originally a dining hall, and then the location for the Court of Requests, it was the meeting place of the House of Lords from 1801 until it was gutted by fire in 1834. Re- ...
(also known as the Lesser Hall), which had housed the Court of Requests
The Court of Requests was a minor equity court in England and Wales. It was instituted by King Richard III in his 1484 parliament. It first became a formal tribunal with some Privy Council elements under Henry VII, hearing cases from the poor ...
; the expansion of the Peerage by King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
during the 18th century, along with the imminent Act of Union with Ireland, necessitated the move, as the original chamber could not accommodate the increased number of peers.
The House of Commons, which did not have a chamber of its own, sometimes held its debates in the Chapter House of Westminster Abbey. The Commons acquired a permanent home at the Palace in St Stephen's Chapel, the former chapel of the royal palace, during the reign of Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first E ...
. In 1547 the building became available for the Commons' use following the disbanding of St Stephen's College. Alterations were made to St Stephen's Chapel over the following three centuries for the convenience of the lower House, gradually destroying, or covering up, its original mediaeval appearance. A major renovation project undertaken by Christopher Wren in the late 17th century completely redesigned the building's interior.
The Palace of Westminster as a whole began to see significant alterations from the 18th century onwards, as Parliament struggled to carry out its business in the limited available space and ageing buildings. Calls for an entirely new palace went unheeded as instead more buildings of varying quality and style were added. A new west façade, known as the Stone Building, facing onto St Margaret's Street was designed by John Vardy
John Vardy (February 1718 – 17 May 1765) was an English architect attached to the Royal Office of Works from 1736. He was a close follower of the neo-Palladian architect William Kent.
John Vardy was born to a simple working family in Durham. Hi ...
built in the Palladian style between 1755 and 1770, providing more space for document storage and committee rooms. The House of Commons Engrossing Office of Henry (Robert) Gunnell (1724–1794) and Edward Barwell was on the lower floor beside the corner tower at the west side of Vardy's western façade. A new official residence for the Speaker of the House of Commons Speaker of the House of Commons is a political leadership position found in countries that have a House of Commons, where the membership of the body elects a speaker to lead its proceedings.
Systems that have such a position include:
* Speaker of ...
was built adjoining St Stephen's Chapel and completed in 1795. The neo-Gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
architect James Wyatt
James Wyatt (3 August 1746 – 4 September 1813) was an English architect, a rival of Robert Adam in the neoclassical and neo-Gothic styles. He was elected to the Royal Academy in 1785 and was its president from 1805 to 1806.
Early life
W ...
also carried out works on both the House of Lords and Commons between 1799 and 1801, including alterations to the exterior of St Stephen's Chapel and a much-derided new neo-Gothic building, referred to by Wyatt's critics as "The Cotton Mill" adjoining the House of Lords and facing onto Old Palace Yard.
The palace complex was substantially remodelled, this time by Sir John Soane
Sir John Soane (; né Soan; 10 September 1753 – 20 January 1837) was an English architect who specialised in the Neoclassical architecture, Neo-Classical style. The son of a bricklayer, he rose to the top of his profession, becoming professo ...
, between 1824 and 1827. The medieval House of Lords chamber, which had been the target of the failed Gunpowder Plot
The Gunpowder Plot of 1605, in earlier centuries often called the Gunpowder Treason Plot or the Jesuit Treason, was a failed assassination attempt against King James I by a group of provincial English Catholics led by Robert Catesby who sough ...
of 1605, was demolished as part of this work in order to create a new Royal Gallery and ceremonial entrance at the southern end of the palace. Soane's work at the palace also included new library facilities for both Houses of Parliament and new law courts for the Chancery and King's Bench. Soane's alterations caused controversy owing to his use of neo-classical architectural styles, which conflicted with the Gothic style of the original buildings.
Fire and reconstruction
On 16 October 1834, a fire broke out in the Palace after an overheated stove used to destroy theExchequer
In the civil service of the United Kingdom, His Majesty’s Exchequer, or just the Exchequer, is the accounting process of central government and the government's '' current account'' (i.e., money held from taxation and other government revenu ...
's stockpile of tally stick
A tally stick (or simply tally) was an ancient memory aid device used to record and document numbers, quantities and messages. Tally sticks first appear as animal bones carved with notches during the Upper Palaeolithic; a notable example is the ...
s set fire to the House of Lords Chamber. In the resulting conflagration both Houses of Parliament were destroyed, along with most of the other buildings in the palace complex. Westminster Hall was saved thanks to fire-fighting efforts and a change in the direction of the wind. The Jewel Tower
The Jewel Tower is a 14th-century surviving element of the Palace of Westminster, in London, England. It was built between 1365 and 1366, under the direction of William of Sleaford and Henry de Yevele, to house the personal treasure of King ...
, the Undercroft Chapel and the Cloister
A cloister (from Latin ''claustrum'', "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cathedral or church, commonly against a ...
s and Chapter House of St Stephen's were the only other parts of the Palace to survive.
Immediately after the fire, King William IV offered the almost-completed Buckingham Palace to Parliament, hoping to dispose of a residence he disliked. The building was considered unsuitable for parliamentary use, however, and the gift was rejected. Proposals to move to Charing Cross or St James's Park had a similar fate; the allure of tradition and the historical and political associations of Westminster proved too strong for relocation, despite the deficiencies of that site. In the meantime, the immediate priority was to provide accommodation for the next Parliament, and so the Painted Chamber and White Chamber were hastily repaired for temporary use by the Houses of Lords and Commons respectively, under the direction of the only remaining architect of the Office of Works
The Office of Works was established in the English royal household in 1378 to oversee the building and maintenance of the royal castles and residences. In 1832 it became the Works Department forces within the Office of Woods, Forests, Land Reven ...
, Sir Robert Smirke
Sir Robert Smirke (1 October 1780 – 18 April 1867) was an English architect, one of the leaders of Greek Revival architecture, though he also used other architectural styles. As architect to the Board of Works, he designed several major ...
. Works proceeded quickly and the chambers were ready for use by February 1835.
In his speech opening Parliament in February 1835, following the conclusion of that year's General Election, the King assured the members that the fire was accidental, and permitted Parliament to make "plans for tspermanent accommodation". Each house created a committee and a public debate over the proposed styles ensued.
Feud between Neoclassical and Neogothic architects
Advocacy of a neoclassical design was popular. Decimus Burton, who was 'the land's leading classicist', created a design for a new neoclassical Houses of Parliament. Decimus Burton and his pupils commended the purchase of theElgin Marbles
The Elgin Marbles (), also known as the Parthenon Marbles ( el, Γλυπτά του Παρθενώνα, lit. "sculptures of the Parthenon"), are a collection of Classical Greece, Classical Greek marble sculptures made under the supervision of th ...
for the nation, and the erection of a neoclassical gallery in which they could be displayed to the same, and subsequently contended that the destruction of the Houses of Parliament by the fire of 1834 were an opportunity for the creation of a splendid neoclassical replacement of the Houses of Parliament, in which the Elgin Marbles could be displayed: they expressed their aversion that the new seat of the British Empire would ‘be doomed to crouch and wither in the groinings ic vaultings, tracery, pointed roof, and flying buttresses of a Gothic building…’: a building of a style that they contended to be improper ‘to the prevailing sentiment of an age so enlightened’.
In contradistinction to the neo-gothic style, they commended those who had ‘built St. Paul’s Cathedral, to the satisfaction of an applauding posterity, in the more beautiful and universal style of Roman architecture’. However, the Prime Minister, Sir Robert Peel
Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet, (5 February 1788 – 2 July 1850) was a British Conservative statesman who served twice as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (1834–1835 and 1841–1846) simultaneously serving as Chancellor of the Exchequer ...
, wanted, now that he were premier, to disassociate himself from the controversial John Wilson Croker
John Wilson Croker (20 December 178010 August 1857) was an Anglo-Irish statesman and author.
Life
He was born in Galway, the only son of John Croker, the surveyor-general of customs and excise in Ireland. He was educated at Trinity College Dubl ...
, who was a founding member of the Athenaeum, close associate of the Burtons, an advocate of neoclassicism, and repudiator of the neo-gothic style: consequently, Peel appointed a Royal Commission chaired by
Edward Cust, who was a detestor of the style of John Nash and William Wilkins, which resolved that the new Houses of Parliament would have to be in either the ‘gothic’ or the ‘Elizabethan’ style.
The committee also included Charles Hanbury-Tracy, Thomas Liddell
Thomas Liddell (October 18, 1800 – June 11, 1880) was the first Principal of Queen's University, then Queen's College.
Life
Liddell was born in Stirlingshire, Scotland in 1800, the son of John Liddell and his wife Janet Martin. He stu ...
, the poet Samuel Rogers
Samuel Rogers (30 July 1763 – 18 December 1855) was an English poet, during his lifetime one of the most celebrated, although his fame has long since been eclipsed by his Romantic colleagues and friends Wordsworth, Coleridge and Byron. ...
and the artist George Vivian. Augustus W. N. Pugin, the foremost expert on the Gothic, had to submit each of his designs through, and thus in the name of, other architects, Gillespie-Graham and Charles Barry, because he had recently openly and fervently converted to Roman Catholicism, as a consequence of which any design submitted in his own name would certainly have been automatically rejected; the design he submitted for improvements to Balliol College, Oxford, in 1843 were rejected for this reason. The design for Parliament that Pugin submitted through Barry won the competition. Barry was awarded a prize (or "premium") of £1,500. Premiums of £500 each were given to David Hamilton, J. C. Buckler and William Railton
William Railton (1800–77) was an English architect, best known as the designer of Nelson's Column. He was based in London, with offices at 12 Regent Street for much of his career.
Life
He was born in Clapham (then in Surrey) on 14 May 1800, ...
. The ''Architectural Magazine'' summarised Barry's winning plan as "a quadrangular pile, with the principal front facing the Thames, and a tower in the centre, 170ft high".
Subsequent to the announcement of the design ascribed to Barry, William Richard Hamilton, who had been secretary to Elgin during the acquisition of the marbles, published a pamphlet in which he censured the fact that ‘gothic barbarism’ had been preferred to the masterful designs of Ancient Greece and Rome: but the judgement was not altered, and was ratified by the Commons and the Lords. The commissioners subsequently appointed Pugin to assist in the construction of the interior of the new Palace, to the design of which Pugin himself had been the foremost determiner. The first stone of the new Pugin-Barry design was laid on 27 April 1840, by Barry's wife Sarah (née Rowsell). During the competition for the design of the new Houses of Parliament, Decimus Burton was vituperated with continuous invective, which Guy Williams has described as an 'anti-Burton campaign', by the foremost advocate of the neo-gothic style, Augustus W. N. Pugin, who was made enviously reproachful that Decimus 'had done much more that Pugin's father (Augustus Charles Pugin
Augustus Charles Pugin (born Auguste-Charles Pugin; 1762 – 19 December 1832) was an Anglo-French artist, architectural draughtsman, and writer on medieval architecture. He was born in Paris, then the Kingdom of France, but his father was Sw ...
) to alter the appearance of London'. Pugin attempted to popularize advocacy of the neo-gothic, and repudiation of the neoclassical, by composing and illustrating books that contended the supremacy of the former and the degeneracy of the latter, which were published from 1835.
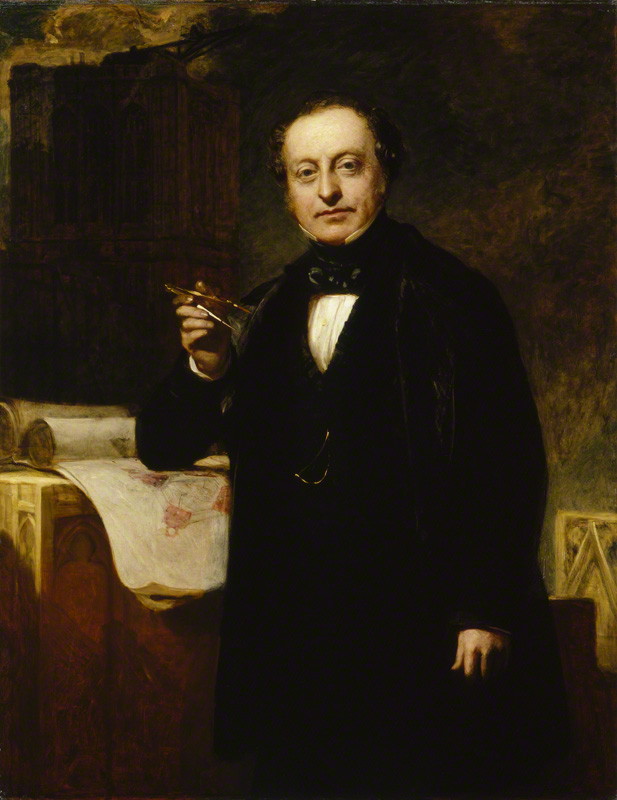 The Lords Chamber was completed in 1847, and the Commons Chamber in 1852 (at which point Barry received a
The Lords Chamber was completed in 1847, and the Commons Chamber in 1852 (at which point Barry received a knighthood
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the ...
). Although most of the work had been carried out by 1860, construction was not finished until a decade afterwards.
Frescoes
With the building itself taking shape, it was time to think about its internal adornments. In a process overseen by a Royal Fine Art Commission under the presidency of Prince Albert, a Select Committee which included Sir Robert Peel started to take witness accounts from experts in 1841. Those experts included SirMartin Archer Shee
Sir Martin Archer Shee (23 December 1769 – 13 August 1850) was an Irish portrait painter. He also served as the president of the Royal Academy.
Early life
He was born in Dublin, of an old Irish Roman Catholic family, the son of Martin Shee ...
, P.R.A., and Charles Lock Eastlake
Sir Charles Lock Eastlake (17 November 1793 – 24 December 1865) was a British painter, gallery director, collector and writer of the 19th century. After a period as keeper, he was the first director of the National Gallery.
Life
Eastlak ...
, painter and acknowledged authority on art history
Art history is the study of aesthetic objects and visual expression in historical and stylistic context. Traditionally, the discipline of art history emphasized painting, drawing, sculpture, architecture, ceramics and decorative arts; yet today ...
, soon to be first director of the National Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current Director ...
and de facto administrator of the whole Westminster decoration project. It was decided that the opportunity should be seized to encourage the development of a national British school of History Painting, and that the paintings should be done in fresco.
The call for artists to submit proposals resulted in a first exhibition in 1843 at Westminster Hall in which 140 cartoons were shown. Others followed but the progress was slow. Fresco proved to be a problematic technique for the English climate. The wall surfaces to be covered were vast and therefore a number of paintings were in fact done in oil on canvas. With the death of Prince Albert in 1861 the scheme lost its driving force, but by then many paintings were completed or underway. William Dyce
William Dyce (; 19 September 1806 in Aberdeen14 February 1864) was a Scottish painter, who played a part in the formation of public art education in the United Kingdom, and the South Kensington Schools system. Dyce was associated with the Pre-R ...
, who was the first to start fresco work in 1848, died in 1864, completing only five of seven commissioned works. The other major contributors were John Rogers Herbert
John Rogers Herbert (23 January 1810 – 17 March 1890) was an English painter who is most notable as a precursor of Pre-Raphaelitism.
Early career
John Rogers Herbert was born in Maldon, Essex. In 1826, he moved to London to study at the ...
, finishing in 1864 but having had some commissions cancelled, Charles West Cope
Charles West Cope (28 July 1811, in Leeds – 21 August 1890, in Bournemouth) was an English, Victorian era painter of genre and history scenes, and an etcher. He was responsible for painting several frescos in the House of Lords in Lond ...
who worked until 1869, Edward Matthew Ward
Edward Matthew Ward, , (14 July 1816 – 15 January 1879) was a British painter who specialised in historical genre. He is best known for his murals in the Palace of Westminster depicting episodes in British history from the English Civil War to ...
until 1874, Edward Armitage
Edward Armitage (20 May 1817 – 24 May 1896) was an English Victorian-era painter whose work focused on historical, classical and biblical subjects.
Family background
Armitage was born in London to a family of wealthy Yorkshire industrialis ...
, George Frederic Watts
George Frederic Watts (23 February 1817, in London – 1 July 1904) was a British painter and sculptor associated with the Symbolist movement. He said "I paint ideas, not things." Watts became famous in his lifetime for his allegorical work ...
, John Callcott Horsley, John Tenniel
Sir John Tenniel (; 28 February 182025 February 1914)Johnson, Lewis (2003), "Tenniel, John", ''Grove Art Online, Oxford Art Online'', Oxford University Press. Web. Retrieved 12 December 2016. was an English illustrator, graphic humorist and poli ...
and Daniel Maclise. In the 20th century, further paintings were commissioned from other artists.
Recent history
During the Second World War (see ''The Blitz
The Blitz was a German bombing campaign against the United Kingdom in 1940 and 1941, during the Second World War. The term was first used by the British press and originated from the term , the German word meaning 'lightning war'.
The Germa ...
''), the Palace of Westminster was hit by bombs on fourteen separate occasions. One bomb fell into Old Palace Yard on 26 September 1940 and severely damaged the south wall of St Stephen's Porch and the west front. The statue of Richard the Lionheart was lifted from its pedestal by the force of the blast, and its upheld sword bent, an image that was used as a symbol of the strength of democracy, "which would bend but not break under attack". Another bomb destroyed much of the Cloisters on 8 December.
 The worst raid took place in the night of 10–11 May 1941, when the Palace took at least twelve hits and three people (two policemen and the Resident Superintendent of the House of Lords, Edward Elliott) were killed. Fell and Mackenzie (1994), p. 27. An incendiary bomb hit the chamber of the House of Commons and set it on fire; another set the roof of Westminster Hall alight. The firefighters could not save both, and a decision was taken to try to rescue the Hall. In this they were successful; the abandoned Commons Chamber, on the other hand, was destroyed, as was the Members' Lobby. A bomb also struck the Lords Chamber, but went through the floor without exploding. The Clock Tower took a hit by a small bomb or anti-aircraft shell at the eaves of the roof, suffering much damage there. All the glass on the south dial was blown out, but the hands and bells were not affected, and the Great Clock continued to keep time accurately.
Following the destruction of the Commons Chamber, the Lords offered their own debating chamber for the use of the Commons; for their own sittings the Queen's Robing Room was converted into a makeshift chamber. The Commons Chamber was rebuilt after the war under the architect Sir Giles Gilbert Scott, in a simplified version of the old chamber's style. The work was undertaken by John Mowlem & Co., and construction lasted until 1950, when
The worst raid took place in the night of 10–11 May 1941, when the Palace took at least twelve hits and three people (two policemen and the Resident Superintendent of the House of Lords, Edward Elliott) were killed. Fell and Mackenzie (1994), p. 27. An incendiary bomb hit the chamber of the House of Commons and set it on fire; another set the roof of Westminster Hall alight. The firefighters could not save both, and a decision was taken to try to rescue the Hall. In this they were successful; the abandoned Commons Chamber, on the other hand, was destroyed, as was the Members' Lobby. A bomb also struck the Lords Chamber, but went through the floor without exploding. The Clock Tower took a hit by a small bomb or anti-aircraft shell at the eaves of the roof, suffering much damage there. All the glass on the south dial was blown out, but the hands and bells were not affected, and the Great Clock continued to keep time accurately.
Following the destruction of the Commons Chamber, the Lords offered their own debating chamber for the use of the Commons; for their own sittings the Queen's Robing Room was converted into a makeshift chamber. The Commons Chamber was rebuilt after the war under the architect Sir Giles Gilbert Scott, in a simplified version of the old chamber's style. The work was undertaken by John Mowlem & Co., and construction lasted until 1950, when King George VI
George VI (Albert Frederick Arthur George; 14 December 1895 – 6 February 1952) was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until his death in 1952. He was also the last Emperor of Indi ...
opened the new chamber in a ceremony which took place in Westminster Hall on 26 October. The Lords Chamber was then renovated over the ensuing months; the Lords re-occupied it in May 1951.
As the need for office space in the Palace increased, Parliament acquired office space in the nearby Norman Shaw Building
The Norman Shaw Buildings (formerly known as New Scotland Yard) are a pair of buildings in Westminster, London, overlooking the River Thames. The buildings were designed by the architects Richard Norman Shaw and John Dixon Butler, between 1887 ...
in 1975, and in the custom-built Portcullis House
Portcullis House (PCH) is an office building in Westminster, London, United Kingdom, that was commissioned in 1992 and opened in 2001 to provide offices for 213 members of parliament and their staff. The public entrance is on the Embankment. Part ...
, completed in 2000. This increase has enabled all MPs to have their own office facilities.
The Palace of Westminster, which is a Grade 1 listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
, is in urgent need of extensive restoration to its fabric. A 2012 pre-feasibility report set out several options, including the possibility of Parliament moving to other premises while work is carried out. At the same time, the option of moving Parliament to a new location was discounted, with staying at the Westminster site preferred. An Independent Options Appraisal Report released in June 2015 found that the cost to restore the Palace of Westminster could be as much as £7.1 billion if MPs were to remain at the Palace whilst works take place. MPs decided in 2016 to vacate the building for six years starting in 2022. In January 2018, the House of Commons voted for both houses to vacate the Palace of Westminster to allow for a complete refurbishment of the building which may take up to six years starting in 2025. It is expected that the House of Commons will be temporarily housed in a replica chamber to be located in Richmond House
Richmond House is a government building in Whitehall, City of Westminster, London. Its name comes from an historic townhouse of the Duke of Richmond that once stood on the site.
History Stewart Dukes of Richmond
Richmond House was first built ...
in Whitehall and the House of Lords will be housed at the Queen Elizabeth II Conference Centre
The Queen Elizabeth II Centre is a conference facility located in the City of Westminster, London, close to the Houses of Parliament, Westminster Abbey, Central Hall Westminster and Parliament Square.
History
The site now occupied by the Queen ...
in Parliament Square.
References
{{Reflist Palace of Westminster British architectural history Palace Palace of Westminster