History Of Earth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of Earth concerns the development of
The history of Earth concerns the development of
 The standard model for the formation of the
The standard model for the formation of the
 The first eon in Earth's history, the ''Hadean'', begins with the Earth's formation and is followed by the ''Archean'' eon at 3.8 Ga. The oldest rocks found on Earth date to about 4.0 Ga, and the oldest detrital
The first eon in Earth's history, the ''Hadean'', begins with the Earth's formation and is followed by the ''Archean'' eon at 3.8 Ga. The oldest rocks found on Earth date to about 4.0 Ga, and the oldest detrital
 Earth's only natural satellite, the Moon, is larger relative to its planet than any other satellite in the Solar System. During the Apollo program, rocks from the Moon's surface were brought to Earth.
Earth's only natural satellite, the Moon, is larger relative to its planet than any other satellite in the Solar System. During the Apollo program, rocks from the Moon's surface were brought to Earth. 

 In early models for the formation of the atmosphere and ocean, the second atmosphere was formed by outgassing of volatiles from the Earth's interior. Now it is considered likely that many of the volatiles were delivered during accretion by a process known as ''impact degassing'' in which incoming bodies vaporize on impact. The ocean and atmosphere would, therefore, have started to form even as the Earth formed. The new atmosphere probably contained
In early models for the formation of the atmosphere and ocean, the second atmosphere was formed by outgassing of volatiles from the Earth's interior. Now it is considered likely that many of the volatiles were delivered during accretion by a process known as ''impact degassing'' in which incoming bodies vaporize on impact. The ocean and atmosphere would, therefore, have started to form even as the Earth formed. The new atmosphere probably contained
 Another long-standing hypothesis is that the first life was composed of protein molecules. Amino acids, the building blocks of
Another long-standing hypothesis is that the first life was composed of protein molecules. Amino acids, the building blocks of
 Research in 2003 reported that montmorillonite could also accelerate the conversion of
Research in 2003 reported that montmorillonite could also accelerate the conversion of
 The earliest cells absorbed energy and food from the surrounding environment. They used fermentation, the breakdown of more complex compounds into less complex compounds with less energy, and used the energy so liberated to grow and reproduce. Fermentation can only occur in an ''anaerobic'' (oxygen-free) environment. The evolution of
The earliest cells absorbed energy and food from the surrounding environment. They used fermentation, the breakdown of more complex compounds into less complex compounds with less energy, and used the energy so liberated to grow and reproduce. Fermentation can only occur in an ''anaerobic'' (oxygen-free) environment. The evolution of  Photosynthesis had another major impact. Oxygen was toxic; much life on Earth probably died out as its levels rose in what is known as the ''
Photosynthesis had another major impact. Oxygen was toxic; much life on Earth probably died out as its levels rose in what is known as the ''
 The natural evolution of the Sun made it progressively more luminous during the Archean and Proterozoic eons; the Sun's luminosity increases 6% every billion years. As a result, the Earth began to receive more heat from the Sun in the Proterozoic eon. However, the Earth did not get warmer. Instead, the geological record suggests it cooled dramatically during the early Proterozoic.
The natural evolution of the Sun made it progressively more luminous during the Archean and Proterozoic eons; the Sun's luminosity increases 6% every billion years. As a result, the Earth began to receive more heat from the Sun in the Proterozoic eon. However, the Earth did not get warmer. Instead, the geological record suggests it cooled dramatically during the early Proterozoic.
 Modern taxonomy classifies life into three domains. The time of their origin is uncertain. The
Modern taxonomy classifies life into three domains. The time of their origin is uncertain. The
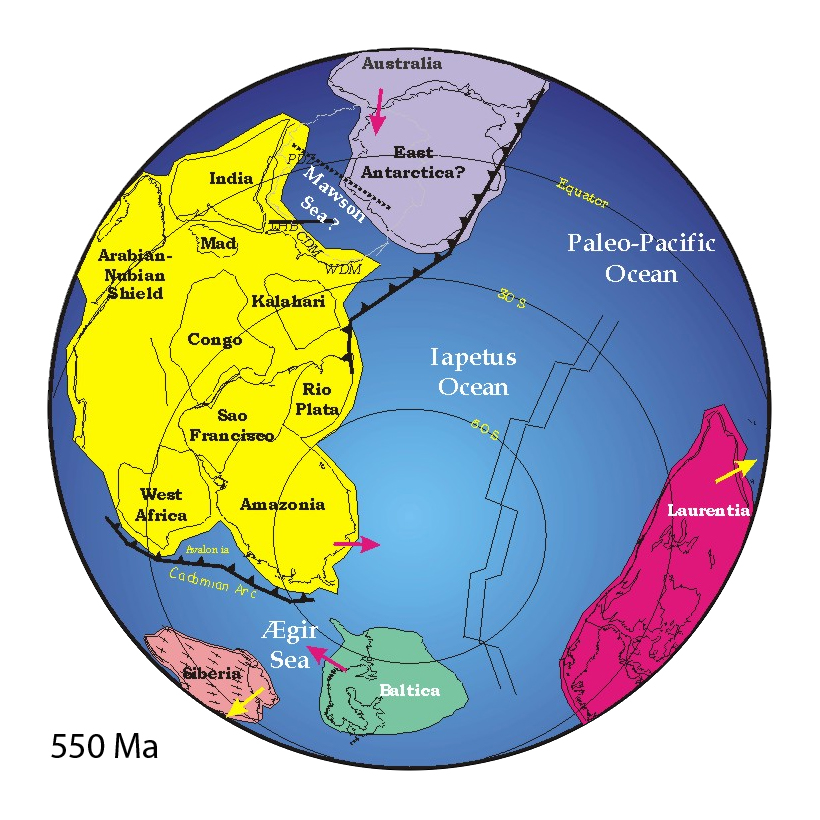 Reconstructions of tectonic plate movement in the past 250 million years (the Cenozoic and Mesozoic eras) can be made reliably using fitting of continental margins, ocean floor magnetic anomalies and paleomagnetic poles. No ocean crust dates back further than that, so earlier reconstructions are more difficult. Paleomagnetic poles are supplemented by geologic evidence such as orogenic belts, which mark the edges of ancient plates, and past distributions of flora and fauna. The further back in time, the scarcer and harder to interpret the data get and the more uncertain the reconstructions.
Throughout the history of the Earth, there have been times when continents collided and formed a supercontinent, which later broke up into new continents. About 1000 to 830 Ma, most continental mass was united in the supercontinent Rodinia. Rodinia may have been preceded by Early-Middle Proterozoic continents called Nuna and Columbia.
After the break-up of Rodinia about 800 Ma, the continents may have formed another short-lived supercontinent around 550 Ma. The hypothetical supercontinent is sometimes referred to as Pannotia or Vendia. The evidence for it is a phase of
Reconstructions of tectonic plate movement in the past 250 million years (the Cenozoic and Mesozoic eras) can be made reliably using fitting of continental margins, ocean floor magnetic anomalies and paleomagnetic poles. No ocean crust dates back further than that, so earlier reconstructions are more difficult. Paleomagnetic poles are supplemented by geologic evidence such as orogenic belts, which mark the edges of ancient plates, and past distributions of flora and fauna. The further back in time, the scarcer and harder to interpret the data get and the more uncertain the reconstructions.
Throughout the history of the Earth, there have been times when continents collided and formed a supercontinent, which later broke up into new continents. About 1000 to 830 Ma, most continental mass was united in the supercontinent Rodinia. Rodinia may have been preceded by Early-Middle Proterozoic continents called Nuna and Columbia.
After the break-up of Rodinia about 800 Ma, the continents may have formed another short-lived supercontinent around 550 Ma. The hypothetical supercontinent is sometimes referred to as Pannotia or Vendia. The evidence for it is a phase of
 The end of the Proterozoic saw at least two Snowball Earths, so severe that the surface of the oceans may have been completely frozen. This happened about 716.5 and 635 Ma, in the Cryogenian period. The intensity and mechanism of both glaciations are still under investigation and harder to explain than the early Proterozoic Snowball Earth.
Most paleoclimatologists think the cold episodes were linked to the formation of the supercontinent Rodinia. Because Rodinia was centered on the equator, rates of chemical weathering increased and carbon dioxide (CO2) was taken from the atmosphere. Because CO2 is an important greenhouse gas, climates cooled globally.
In the same way, during the Snowball Earths most of the continental surface was covered with
The end of the Proterozoic saw at least two Snowball Earths, so severe that the surface of the oceans may have been completely frozen. This happened about 716.5 and 635 Ma, in the Cryogenian period. The intensity and mechanism of both glaciations are still under investigation and harder to explain than the early Proterozoic Snowball Earth.
Most paleoclimatologists think the cold episodes were linked to the formation of the supercontinent Rodinia. Because Rodinia was centered on the equator, rates of chemical weathering increased and carbon dioxide (CO2) was taken from the atmosphere. Because CO2 is an important greenhouse gas, climates cooled globally.
In the same way, during the Snowball Earths most of the continental surface was covered with
 At the end of the Proterozoic, the supercontinent Pannotia had broken apart into the smaller continents Laurentia, Baltica,
At the end of the Proterozoic, the supercontinent Pannotia had broken apart into the smaller continents Laurentia, Baltica,
 The rate of the evolution of life as recorded by fossils accelerated in the
The rate of the evolution of life as recorded by fossils accelerated in the
 Oxygen accumulation from photosynthesis resulted in the formation of an ozone layer that absorbed much of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation, meaning unicellular organisms that reached land were less likely to die, and prokaryotes began to multiply and become better adapted to survival out of the water. Prokaryote lineages had probably colonized the land as early as 2.6 Ga even before the origin of the eukaryotes. For a long time, the land remained barren of multicellular organisms. The supercontinent Pannotia formed around 600 Ma and then broke apart a short 50 million years later. Fish, the earliest vertebrates, evolved in the oceans around 530 Ma. A major extinction event occurred near the end of the Cambrian period, which ended 488 Ma.
Several hundred million years ago, plants (probably resembling
Oxygen accumulation from photosynthesis resulted in the formation of an ozone layer that absorbed much of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation, meaning unicellular organisms that reached land were less likely to die, and prokaryotes began to multiply and become better adapted to survival out of the water. Prokaryote lineages had probably colonized the land as early as 2.6 Ga even before the origin of the eukaryotes. For a long time, the land remained barren of multicellular organisms. The supercontinent Pannotia formed around 600 Ma and then broke apart a short 50 million years later. Fish, the earliest vertebrates, evolved in the oceans around 530 Ma. A major extinction event occurred near the end of the Cambrian period, which ended 488 Ma.
Several hundred million years ago, plants (probably resembling
 At the end of the Ordovician period, 443 Ma, additional extinction events occurred, perhaps due to a concurrent ice age. Around 380 to 375 Ma, the first
At the end of the Ordovician period, 443 Ma, additional extinction events occurred, perhaps due to a concurrent ice age. Around 380 to 375 Ma, the first  After yet another, the most severe extinction of the period (251~250 Ma), around 230 Ma, dinosaurs split off from their reptilian ancestors. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event at 200 Ma spared many of the dinosaurs, and they soon became dominant among the vertebrates. Though some mammalian lines began to separate during this period, existing mammals were probably small animals resembling
After yet another, the most severe extinction of the period (251~250 Ma), around 230 Ma, dinosaurs split off from their reptilian ancestors. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event at 200 Ma spared many of the dinosaurs, and they soon became dominant among the vertebrates. Though some mammalian lines began to separate during this period, existing mammals were probably small animals resembling

 It is more difficult to establish the
It is more difficult to establish the
 Throughout more than 90% of its history, ''Homo sapiens'' lived in small bands as
Throughout more than 90% of its history, ''Homo sapiens'' lived in small bands as
accessed 8 December 2014. p. (preface)
accessed 8 December 2014. p. 1: "Western civilization owes far more to Catholic Church than most people—Catholic included—often realize. The Church in fact built Western civilization."
/ref> In 610,
 Change has continued at a rapid pace from the mid-1940s to today. Technological developments include
Change has continued at a rapid pace from the mid-1940s to today. Technological developments include
Quantum leap of life
. ''
Evolution timeline
(uses Flash Player). Animated story of life shows everything from the big bang to the formation of the Earth and the development of bacteria and other organisms to the ascent of man.
25 biggest turning points in Earth History
BBC
Evolution of the Earth
Timeline of the most important events in the evolution of the Earth. *
Ageing the Earth
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Richard Corfield, Hazel Rymer & Henry Gee (''In Our Time'', Nov. 20, 2003) {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of The Earth Earth Geochronology Geology theories * World history
planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science
Natural science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer review and repeatab ...
have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geological change and biological evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
.
The geological time scale (GTS), as defined by international convention, depicts the large spans of time from the beginning of the Earth to the present, and its divisions chronicle some definitive events of Earth history. (In the graphic, Ma means "million years ago".) Earth formed around 4.54 billion years ago, approximately one-third the age of the universe, by accretion
Accretion may refer to:
Science
* Accretion (astrophysics), the formation of planets and other bodies by collection of material through gravity
* Accretion (meteorology), the process by which water vapor in clouds forms water droplets around nucl ...
from the solar nebula. Volcanic outgassing probably created the primordial atmosphere and then the ocean, but the early atmosphere contained almost no oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
. Much of the Earth was molten because of frequent collisions with other bodies which led to extreme volcanism. While the Earth was in its earliest stage (Early Earth
The early Earth is loosely defined as Earth in its first one billion years, or gigayear (Ga, 109y). The “early Earth” encompasses approximately the first gigayear in the evolution of our planet, from its initial formation in the young Solar ...
), a giant impact collision with a planet-sized body named Theia is thought to have formed the Moon. Over time, the Earth cooled, causing the formation of a solid crust, and allowing liquid water on the surface.
The Hadean eon represents the time before a reliable (fossil) record of life; it began with the formation of the planet and ended 4.0 billion years ago. The following Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth during the Arc ...
and Proterozoic eons produced the beginnings of life on Earth and its earliest evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
. The succeeding eon is the Phanerozoic, divided into three eras: the Palaeozoic, an era of arthropods, fishes, and the first life on land; the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
, which spanned the rise, reign, and climactic extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs; and the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configu ...
, which saw the rise of mammals. Recognizable humans emerged at most 2 million years ago, a vanishingly small period on the geological scale.
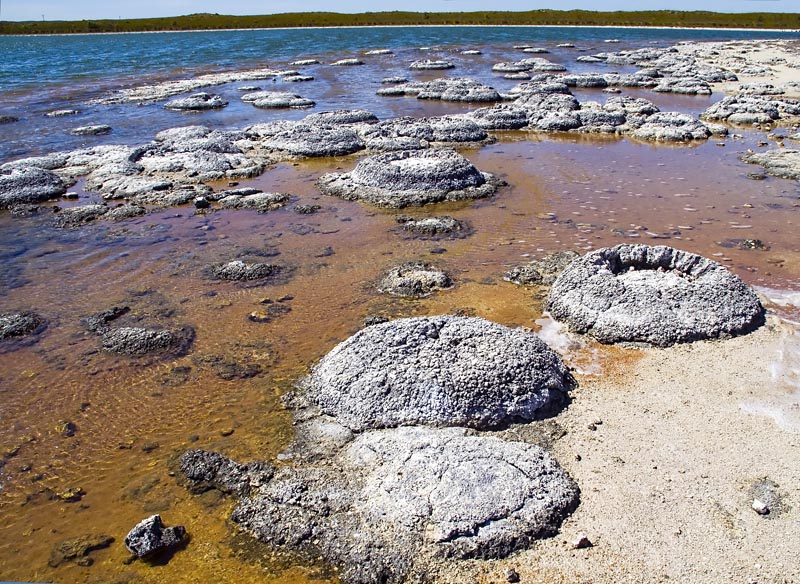
The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era, after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s such as stromatolites found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
discovered in Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...
. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on la ...
in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in southwestern Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland ...
as well as "remains of biotic life" found in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia. Early edition, published online before print. According to one of the researchers, "If life arose relatively quickly on Earth … then it could be common in the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the univers ...
."
Photosynthetic organisms appeared between 3.2 and 2.4 billion years ago and began enriching the atmosphere with oxygen. Life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy ...
remained mostly small and microscopic until about 580 million years ago, when complex multicellular life
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- ...
arose, developed over time, and culminated in the Cambrian Explosion about 538.8 million years ago. This sudden diversification of life forms produced most of the major phyla known today, and divided the Proterozoic Eon from the Cambrian Period of the Paleozoic Era. It is estimated that 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth, over five billion, have gone extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million are documented, but over 86 percent have not been described. However, it was recently claimed that 1 trillion species currently live on Earth, with only one-thousandth of one percent described.
The Earth's crust has constantly changed since its formation, as has life since its first appearance. Species continue to evolve, taking on new forms, splitting into daughter species, or going extinct in the face of ever-changing physical environments. The process of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of larg ...
continues to shape the Earth's continents and oceans and the life they harbor.
Eons
In geochronology, time is generally measured in mya (million years ago), each unit representing the period of approximately 1,000,000 years in the past. The history of Earth is divided into four great eons, starting 4,540 mya with the formation of the planet. Each eon saw the most significant changes in Earth's composition, climate and life. Each eon is subsequently divided into eras, which in turn are divided into periods, which are further divided into epochs.Geologic time scale
The history of the Earth can be organized chronologically according to thegeologic time scale
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochr ...
, which is split into intervals based on stratigraphic analysis.
Solar System formation
 The standard model for the formation of the
The standard model for the formation of the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
(including the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
) is the solar nebula hypothesis. In this model, the Solar System formed from a large, rotating cloud of interstellar dust and gas called the solar nebula. It was composed of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
and helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic ta ...
created shortly after the Big Bang 13.8 Ga (billion years ago) and heavier elements ejected by supernovae. About 4.5 Ga, the nebula began a contraction that may have been triggered by the shock wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
from a nearby supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or whe ...
. A shock wave would have also made the nebula rotate. As the cloud began to accelerate, its angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed syst ...
, gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
, and inertia flattened it into a protoplanetary disk perpendicular to its axis of rotation. Small perturbations due to collisions and the angular momentum of other large debris created the means by which kilometer-sized protoplanets began to form, orbiting the nebular center.
The center of the nebula, not having much angular momentum, collapsed rapidly, the compression heating it until nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium began. After more contraction, a T Tauri star ignited and evolved into the Sun. Meanwhile, in the outer part of the nebula gravity caused matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic part ...
to condense around density perturbations and dust particles, and the rest of the protoplanetary disk began separating into rings. In a process known as runaway accretion
Accretion may refer to:
Science
* Accretion (astrophysics), the formation of planets and other bodies by collection of material through gravity
* Accretion (meteorology), the process by which water vapor in clouds forms water droplets around nucl ...
, successively larger fragments of dust and debris clumped together to form planets. Earth formed in this manner about 4.54 billion years ago (with an uncertainty
Uncertainty refers to epistemic situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown. Uncertainty arises in partially observable ...
of 1%) and was largely completed within 10–20 million years. The solar wind of the newly formed T Tauri star cleared out most of the material in the disk that had not already condensed into larger bodies. The same process is expected to produce accretion disks around virtually all newly forming stars in the universe, some of which yield planets.
The proto-Earth grew by accretion until its interior was hot enough to melt the heavy, siderophile metal
A metal (from ancient Greek, Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, e ...
s. Having higher densities
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematicall ...
than the silicates, these metals sank. This so-called '' iron catastrophe'' resulted in the separation of a primitive mantle and a (metallic) core only 10 million years after the Earth began to form, producing the layered structure of Earth
The internal structure of Earth is the solid portion of the Earth, excluding its atmosphere and hydrosphere. The structure consists of an outer silicate solid crust, a highly viscous asthenosphere and solid mantle, a liquid outer core whos ...
and setting up the formation of Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magneti ...
. J.A. Jacobs was the first to suggest that Earth's inner core—a solid center distinct from the liquid outer core—is freezing
Freezing is a phase transition where a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. In accordance with the internationally established definition, freezing means the solidification phase change of a liquid ...
and growing out of the liquid outer core due to the gradual cooling of Earth's interior (about 100 degrees Celsius per billion years).
Hadean and Archean Eons
 The first eon in Earth's history, the ''Hadean'', begins with the Earth's formation and is followed by the ''Archean'' eon at 3.8 Ga. The oldest rocks found on Earth date to about 4.0 Ga, and the oldest detrital
The first eon in Earth's history, the ''Hadean'', begins with the Earth's formation and is followed by the ''Archean'' eon at 3.8 Ga. The oldest rocks found on Earth date to about 4.0 Ga, and the oldest detrital zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of t ...
crystals in rocks to about 4.4 Ga, soon after the formation of the Earth's crust and the Earth itself. The giant impact hypothesis
The giant-impact hypothesis, sometimes called the Big Splash, or the Theia Impact, suggests that the Moon formed from the ejecta of a collision between the proto-Earth and a Mars-sized planet, approximately 4.5 billion years ago, in the Had ...
for the Moon's formation states that shortly after formation of an initial crust, the proto-Earth was impacted by a smaller protoplanet, which ejected part of the mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
and crust into space and created the Moon.
From crater counts on other celestial bodies, it is inferred that a period of intense meteorite impacts, called the '' Late Heavy Bombardment'', began about 4.1 Ga, and concluded around 3.8 Ga, at the end of the Hadean. In addition, volcanism was severe due to the large heat flow and geothermal gradient. Nevertheless, detrital zircon crystals dated to 4.4 Ga show evidence of having undergone contact with liquid water, suggesting that the Earth already had oceans or seas at that time.
By the beginning of the Archean, the Earth had cooled significantly. Present life forms could not have survived at Earth's surface, because the Archean atmosphere lacked oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
hence had no ozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in rel ...
to block ultraviolet light. Nevertheless, it is believed that primordial life began to evolve by the early Archean, with candidate fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s dated to around 3.5 Ga. Some scientists even speculate that life could have begun during the early Hadean, as far back as 4.4 Ga, surviving the possible Late Heavy Bombardment period in hydrothermal vents below the Earth's surface.
Formation of the Moon
 Earth's only natural satellite, the Moon, is larger relative to its planet than any other satellite in the Solar System. During the Apollo program, rocks from the Moon's surface were brought to Earth.
Earth's only natural satellite, the Moon, is larger relative to its planet than any other satellite in the Solar System. During the Apollo program, rocks from the Moon's surface were brought to Earth. Radiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares ...
of these rocks shows that the Moon is 4.53 ± 0.01 billion years old, formed at least 30 million years after the Solar System. New evidence suggests the Moon formed even later, 4.48 ± 0.02 Ga, or 70–110 million years after the start of the Solar System.
Theories for the formation of the Moon must explain its late formation as well as the following facts. First, the Moon has a low density (3.3 times that of water, compared to 5.5 for the Earth) and a small metallic core. Second, the Earth and Moon have the same oxygen isotopic signature (relative abundance of the oxygen isotopes). Of the theories proposed to account for these phenomena, one is widely accepted: The ''giant impact hypothesis'' proposes that the Moon originated after a body the size of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
(sometimes named Theia) struck the proto-Earth a glancing blow.
The collision released about 100 million times more energy than the more recent Chicxulub impact that is believed to have caused the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs. It was enough to vaporize some of the Earth's outer layers and melt both bodies. A portion of the mantle material was ejected into orbit around the Earth. The giant impact hypothesis predicts that the Moon was depleted of metallic material, explaining its abnormal composition. The ejecta in orbit around the Earth could have condensed into a single body within a couple of weeks. Under the influence of its own gravity, the ejected material became a more spherical body: the Moon.

First continents

Mantle convection
Mantle convection is the very slow creeping motion of Earth's solid silicate mantle as convection currents carrying heat from the interior to the planet's surface.
The Earth's surface lithosphere rides atop the asthenosphere and the two form ...
, the process that drives plate tectonics, is a result of heat flow from the Earth's interior to the Earth's surface. It involves the creation of rigid tectonic plates at mid-oceanic ridges. These plates are destroyed by subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, ...
into the mantle at subduction zone
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
s. During the early Archean (about 3.0 Ga) the mantle was much hotter than today, probably around , so convection in the mantle was faster. Although a process similar to present-day plate tectonics did occur, this would have gone faster too. It is likely that during the Hadean and Archean, subduction zones were more common, and therefore tectonic plates were smaller.
The initial crust, formed when the Earth's surface first solidified, totally disappeared from a combination of this fast Hadean plate tectonics and the intense impacts of the Late Heavy Bombardment. However, it is thought that it was basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
ic in composition, like today's oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic ...
, because little crustal differentiation had yet taken place. The first larger pieces of continental crust, which is a product of differentiation of lighter elements during partial melting in the lower crust, appeared at the end of the Hadean, about 4.0 Ga. What is left of these first small continents are called craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and ...
s. These pieces of late Hadean and early Archean crust form the cores around which today's continents grew.
The oldest rocks on Earth are found in the North American craton of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
. They are tonalites from about 4.0 Ga. They show traces of metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of ch ...
by high temperature, but also sedimentary grains that have been rounded by erosion during transport by water, showing that rivers and seas existed then. Cratons consist primarily of two alternating types of terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its ow ...
s. The first are so-called greenstone belt
Greenstone belts are zones of variably metamorphosed mafic to ultramafic volcanic sequences with associated sedimentary rocks that occur within Archaean and Proterozoic cratons between granite and gneiss bodies.
The name comes from the gree ...
s, consisting of low-grade metamorphosed sedimentary rocks. These "greenstones" are similar to the sediments today found in oceanic trenches, above subduction zones. For this reason, greenstones are sometimes seen as evidence for subduction during the Archean. The second type is a complex of felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, wh ...
magmatic rocks. These rocks are mostly tonalite, trondhjemite or granodiorite, types of rock similar in composition to granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
(hence such terranes are called TTG-terranes). TTG-complexes are seen as the relicts of the first continental crust, formed by partial melting in basalt.
Oceans and atmosphere
Earth is often described as having had three atmospheres. The first atmosphere, captured from the solar nebula, was composed of light ( atmophile) elements from the solar nebula, mostly hydrogen and helium. A combination of the solar wind and Earth's heat would have driven off this atmosphere, as a result of which the atmosphere is now depleted of these elements compared to cosmic abundances. After the impact which created the Moon, the molten Earth released volatile gases; and later more gases were released byvolcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates ...
es, completing a second atmosphere rich in greenhouse gases but poor in oxygen. Finally, the third atmosphere, rich in oxygen, emerged when bacteria began to produce oxygen about 2.8 Ga.
 In early models for the formation of the atmosphere and ocean, the second atmosphere was formed by outgassing of volatiles from the Earth's interior. Now it is considered likely that many of the volatiles were delivered during accretion by a process known as ''impact degassing'' in which incoming bodies vaporize on impact. The ocean and atmosphere would, therefore, have started to form even as the Earth formed. The new atmosphere probably contained
In early models for the formation of the atmosphere and ocean, the second atmosphere was formed by outgassing of volatiles from the Earth's interior. Now it is considered likely that many of the volatiles were delivered during accretion by a process known as ''impact degassing'' in which incoming bodies vaporize on impact. The ocean and atmosphere would, therefore, have started to form even as the Earth formed. The new atmosphere probably contained water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and smaller amounts of other gases.
Planetesimals at a distance of 1 astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits ...
(AU), the distance of the Earth from the Sun, probably did not contribute any water to the Earth because the solar nebula was too hot for ice to form and the hydration of rocks by water vapor would have taken too long. The water must have been supplied by meteorites from the outer asteroid belt and some large planetary embryos from beyond 2.5 AU. Comets may also have contributed. Though most comets are today in orbits farther away from the Sun than Neptune, computer simulations show that they were originally far more common in the inner parts of the Solar System.
As the Earth cooled, cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
s formed. Rain created the oceans. Recent evidence suggests the oceans may have begun forming as early as 4.4 Ga. By the start of the Archean eon, they already covered much of the Earth. This early formation has been difficult to explain because of a problem known as the faint young Sun paradox. Stars are known to get brighter as they age, and the Sun has become 30% brighter since its formation 4.5 billion years ago. Many models indicate that the early Earth should have been covered in ice. A likely solution is that there was enough carbon dioxide and methane to produce a greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when energy from a planet's host star goes through the planet's atmosphere and heats the planet's surface, but greenhouse gases in the atmosphere prevent some of the heat from returning directly ...
. The carbon dioxide would have been produced by volcanoes and the methane by early microbes. It is hypothesized that there also existed an organic haze created from the products of methane photolysis that caused an anti-greenhouse effect
The anti-greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when energy from a Celestial object, celestial object's sun is absorbed or scattered by the object's upper atmosphere, preventing that energy from reaching the surface, which results in surface co ...
as well. Another greenhouse gas, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
, would have been ejected by volcanos but quickly destroyed by ultraviolet radiation.
Origin of life
One of the reasons for interest in the early atmosphere and ocean is that they form the conditions under which life first arose. There are many models, but little consensus, on how life emerged from non-living chemicals; chemical systems created in the laboratory fall well short of the minimum complexity for a living organism. The first step in the emergence of life may have been chemical reactions that produced many of the simplerorganic
Organic may refer to:
* Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity
* Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ
Chemistry
* Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product ...
compounds, including nucleobases
Nucleobases, also known as ''nitrogenous bases'' or often simply ''bases'', are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the bas ...
and amino acids, that are the building blocks of life. An experiment in 1953 by Stanley Miller and Harold Urey
Harold Clayton Urey ( ; April 29, 1893 – January 5, 1981) was an American physical chemist whose pioneering work on isotopes earned him the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1934 for the discovery of deuterium. He played a significant role in th ...
showed that such molecules could form in an atmosphere of water, methane, ammonia and hydrogen with the aid of sparks to mimic the effect of lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous release of an average ...
. Although atmospheric composition was probably different from that used by Miller and Urey, later experiments with more realistic compositions also managed to synthesize organic molecules. Computer simulation
Computer simulation is the process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be deter ...
s show that extraterrestrial organic molecules could have formed in the protoplanetary disk before the formation of the Earth.
Additional complexity could have been reached from at least three possible starting points: self-replication, an organism's ability to produce offspring that are similar to itself; metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run ...
, its ability to feed and repair itself; and external cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
s, which allow food to enter and waste products to leave, but exclude unwanted substances.
Replication first: RNA world
Even the simplest members of the three modern domains of life use DNA to record their "recipes" and a complex array of RNA andprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
molecules to "read" these instructions and use them for growth, maintenance, and self-replication.
The discovery that a kind of RNA molecule called a ribozyme can catalyze both its own replication and the construction of proteins led to the hypothesis that earlier life-forms were based entirely on RNA. They could have formed an RNA world in which there were individuals but no species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
, as mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
s and horizontal gene transfers would have meant that the offspring in each generation were quite likely to have different genomes from those that their parents started with. RNA would later have been replaced by DNA, which is more stable and therefore can build longer genomes, expanding the range of capabilities a single organism can have. Ribozymes remain as the main components of ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to fo ...
s, the "protein factories" of modern cells.
Although short, self-replicating RNA molecules have been artificially produced in laboratories, doubts have been raised about whether natural non-biological synthesis of RNA is possible. The earliest ribozymes may have been formed of simpler nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main ...
s such as PNA, TNA TNA may refer to:
Organisations
* Tamil National Alliance, a political coalition in Sri Lanka
* The National Alliance, a political party in Kenya
* The National Archives (United Kingdom), a UK public body
* Tonga Nurses' Association, a trade union ...
or GNA, which would have been replaced later by RNA. Other pre-RNA replicators have been posited, including crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
s and even quantum systems.
In 2003 it was proposed that porous metal sulfide precipitates would assist RNA synthesis at about and at ocean-bottom pressures near hydrothermal vents. In this hypothesis, the proto-cells would be confined in the pores of the metal substrate until the later development of lipid membranes.
Metabolism first: iron–sulfur world
proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
, are easily synthesized in plausible prebiotic conditions, as are small peptides (polymers
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
of amino acids) that make good catalysts. A series of experiments starting in 1997 showed that amino acids and peptides could form in the presence of carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simpl ...
and hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The under ...
with iron sulfide
Iron sulfide or Iron sulphide can refer to range of chemical compounds composed of iron and sulfur.
Minerals
By increasing order of stability:
* Iron(II) sulfide, FeS
* Greigite, Fe3S4 (cubic)
* Pyrrhotite, Fe1−xS (where x = 0 to 0.2) (mono ...
and nickel sulfide as catalysts. Most of the steps in their assembly required temperatures of about and moderate pressures, although one stage required and a pressure equivalent to that found under of rock. Hence, self-sustaining synthesis of proteins could have occurred near hydrothermal vents.
A difficulty with the metabolism-first scenario is finding a way for organisms to evolve. Without the ability to replicate as individuals, aggregates of molecules would have "compositional genomes" (counts of molecular species in the aggregate) as the target of natural selection. However, a recent model shows that such a system is unable to evolve in response to natural selection.
Membranes first: Lipid world
It has been suggested that double-walled "bubbles" oflipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
s like those that form the external membranes of cells may have been an essential first step. Experiments that simulated the conditions of the early Earth have reported the formation of lipids, and these can spontaneously form liposomes, double-walled "bubbles", and then reproduce themselves. Although they are not intrinsically information-carriers as nucleic acids are, they would be subject to natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
for longevity and reproduction. Nucleic acids such as RNA might then have formed more easily within the liposomes than they would have outside.
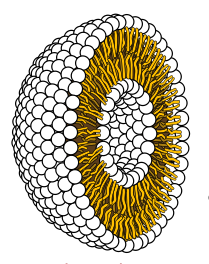
The clay theory
Someclay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay pa ...
s, notably montmorillonite, have properties that make them plausible accelerators for the emergence of an RNA world: they grow by self-replication of their crystalline pattern, are subject to an analog of natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
(as the clay "species" that grows fastest in a particular environment rapidly becomes dominant), and can catalyze the formation of RNA molecules. Although this idea has not become the scientific consensus, it still has active supporters.
 Research in 2003 reported that montmorillonite could also accelerate the conversion of
Research in 2003 reported that montmorillonite could also accelerate the conversion of fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, f ...
s into "bubbles", and that the bubbles could encapsulate RNA attached to the clay. Bubbles can then grow by absorbing additional lipids and dividing. The formation of the earliest cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
may have been aided by similar processes.
A similar hypothesis presents self-replicating iron-rich clays as the progenitors of nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecu ...
s, lipids and amino acids.
Last universal common ancestor
It is believed that of this multiplicity of protocells, only one line survived. Currentphylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups ...
evidence suggests that the last universal ancestor (LUA) lived during the early Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth during the Arc ...
eon, perhaps 3.5 Ga or earlier. This LUA cell is the ancestor of all life on Earth today. It was probably a prokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Con ...
, possessing a cell membrane and probably ribosomes, but lacking a nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
or membrane-bound organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' th ...
s such as mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
or chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it i ...
s. Like modern cells, it used DNA as its genetic code, RNA for information transfer and protein synthesis, and enzymes to catalyze reactions. Some scientists believe that instead of a single organism being the last universal common ancestor, there were populations of organisms exchanging genes by lateral gene transfer.

Proterozoic Eon
The Proterozoic eon lasted from 2.5 Ga to 538.8 Ma (million years) ago. In this time span, cratons grew into continents with modern sizes. The change to an oxygen-rich atmosphere was a crucial development. Life developed from prokaryotes intoeukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
s and multicellular forms. The Proterozoic saw a couple of severe ice ages called snowball Earths. After the last Snowball Earth about 600 Ma, the evolution of life on Earth accelerated. About 580 Ma, the Ediacaran biota
The Ediacaran (; formerly Vendian) biota is a taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period (). These were composed of enigmatic tubular and frond-shaped, mostly sess ...
formed the prelude for the Cambrian Explosion.
Oxygen revolution
 The earliest cells absorbed energy and food from the surrounding environment. They used fermentation, the breakdown of more complex compounds into less complex compounds with less energy, and used the energy so liberated to grow and reproduce. Fermentation can only occur in an ''anaerobic'' (oxygen-free) environment. The evolution of
The earliest cells absorbed energy and food from the surrounding environment. They used fermentation, the breakdown of more complex compounds into less complex compounds with less energy, and used the energy so liberated to grow and reproduce. Fermentation can only occur in an ''anaerobic'' (oxygen-free) environment. The evolution of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
made it possible for cells to derive energy from the Sun.
Most of the life that covers the surface of the Earth depends directly or indirectly on photosynthesis. The most common form, oxygenic photosynthesis, turns carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight into food. It captures the energy of sunlight in energy-rich molecules such as ATP, which then provide the energy to make sugars. To supply the electrons in the circuit, hydrogen is stripped from water, leaving oxygen as a waste product. Some organisms, including purple bacteria
Purple bacteria or purple photosynthetic bacteria are Gram-negative proteobacteria that are phototrophic, capable of producing their own food via photosynthesis. They are pigmented with bacteriochlorophyll ''a'' or ''b'', together with variou ...
and green sulfur bacteria, use an anoxygenic form of photosynthesis that uses alternatives to hydrogen stripped from water as electron donors; examples are hydrogen sulfide, sulfur and iron. Such extremophile
An extremophile (from Latin ' meaning "extreme" and Greek ' () meaning "love") is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e. environments that make survival challenging such as due to extreme tem ...
organisms are restricted to otherwise inhospitable environments such as hot springs and hydrothermal vents.
The simpler anoxygenic form arose about 3.8 Ga, not long after the appearance of life. The timing of oxygenic photosynthesis is more controversial; it had certainly appeared by about 2.4 Ga, but some researchers put it back as far as 3.2 Ga. The latter "probably increased global productivity by at least two or three orders of magnitude". Among the oldest remnants of oxygen-producing lifeforms are fossil stromatolites.
At first, the released oxygen was bound up with limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
, iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
, and other minerals. The oxidized iron appears as red layers in geological strata called banded iron formations that formed in abundance during the Siderian
The Siderian Period (; grc, σίδηρος, sídēros, meaning "iron") is the first geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from Ma to Ma (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chro ...
period (between 2500 Ma and 2300 Ma). When most of the exposed readily reacting minerals were oxidized, oxygen finally began to accumulate in the atmosphere. Though each cell only produced a minute amount of oxygen, the combined metabolism of many cells over a vast time transformed Earth's atmosphere to its current state. This was Earth's third atmosphere.
Some oxygen was stimulated by solar ultraviolet radiation to form ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the l ...
, which collected in a layer near the upper part of the atmosphere. The ozone layer absorbed, and still absorbs, a significant amount of the ultraviolet radiation that once had passed through the atmosphere. It allowed cells to colonize the surface of the ocean and eventually the land: without the ozone layer, ultraviolet radiation bombarding land and sea would have caused unsustainable levels of mutation in exposed cells.
oxygen catastrophe
The Great Oxidation Event (GOE), also called the Great Oxygenation Event, the Oxygen Catastrophe, the Oxygen Revolution, the Oxygen Crisis, or the Oxygen Holocaust, was a time interval during the Paleoproterozoic era when the Earth's atmosphere ...
''. Resistant forms survived and thrived, and some developed the ability to use oxygen to increase their metabolism and obtain more energy from the same food.
Snowball Earth
 The natural evolution of the Sun made it progressively more luminous during the Archean and Proterozoic eons; the Sun's luminosity increases 6% every billion years. As a result, the Earth began to receive more heat from the Sun in the Proterozoic eon. However, the Earth did not get warmer. Instead, the geological record suggests it cooled dramatically during the early Proterozoic.
The natural evolution of the Sun made it progressively more luminous during the Archean and Proterozoic eons; the Sun's luminosity increases 6% every billion years. As a result, the Earth began to receive more heat from the Sun in the Proterozoic eon. However, the Earth did not get warmer. Instead, the geological record suggests it cooled dramatically during the early Proterozoic. Glacial deposit
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
s found in South Africa date back to 2.2 Ga, at which time, based on paleomagnetic
Paleomagnetism (or palaeomagnetismsee ), is the study of magnetic fields recorded in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Geophysicists who specialize in paleomagnetism are called ''paleomagnetists.''
Certain magnetic minerals in rock ...
evidence, they must have been located near the equator. Thus, this glaciation, known as the Huronian glaciation, may have been global. Some scientists suggest this was so severe that the Earth was frozen over from the poles to the equator, a hypothesis called Snowball Earth.
The Huronian ice age might have been caused by the increased oxygen concentration in the atmosphere, which caused the decrease of methane (CH4) in the atmosphere. Methane is a strong greenhouse gas, but with oxygen it reacts to form CO2, a less effective greenhouse gas. When free oxygen became available in the atmosphere, the concentration of methane could have decreased dramatically, enough to counter the effect of the increasing heat flow from the Sun.
However, the term Snowball Earth is more commonly used to describe later extreme ice ages during the Cryogenian
The Cryogenian (from grc, κρύος, krýos, meaning "cold" and , romanized: , meaning "birth") is a geologic period that lasted from . It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed ...
period. There were four periods, each lasting about 10 million years, between 750 and 580 million years ago, when the earth is thought to have been covered with ice apart from the highest mountains, and average temperatures were about . The snowball may have been partly due to the location of the supercontinent Rodinia straddling the Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also ...
. Carbon dioxide combines with rain to weather rocks to form carbonic acid, which is then washed out to sea, thus extracting the greenhouse gas from the atmosphere. When the continents are near the poles, the advance of ice covers the rocks, slowing the reduction in carbon dioxide, but in the Cryogenian the weathering of Rodinia was able to continue unchecked until the ice advanced to the tropics. The process may have finally been reversed by the emission of carbon dioxide from volcanoes or the destabilization of methane gas hydrates. According to the alternative Slushball Earth theory, even at the height of the ice ages there was still open water at the Equator.
Emergence of eukaryotes
 Modern taxonomy classifies life into three domains. The time of their origin is uncertain. The
Modern taxonomy classifies life into three domains. The time of their origin is uncertain. The Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
domain probably first split off from the other forms of life (sometimes called Neomura
Neomura is a possible clade composed of the two domains of life of Archaea and Eukaryota. The group was named by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. Its name means "new walls", reflecting his hypothesis that it evolved from Bacteria, and one of t ...
), but this supposition is controversial. Soon after this, by 2 Ga, the Neomura split into the Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaeba ...
and the Eukarya. Eukaryotic cells (Eukarya) are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells (Bacteria and Archaea), and the origin of that complexity is only now becoming known. The earliest fossils possessing features typical of fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
date to the Paleoproterozoic era, some 2.4 Ga ago; these multicellular benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning " ...
organisms had filamentous structures capable of anastomosis.
Around this time, the first proto-mitochondrion
The proto-mitochondrion is the hypothetical ancestral bacterial endosymbiont from which all mitochondria in eukaryotes are thought to descend, after an episode of symbiogenesis which created the aerobic eukaryotes.
Phylogeny
The phylogenetic ana ...
was formed. A bacterial cell related to today's ''Rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The term "ricke ...
'', which had evolved to metabolize oxygen, entered a larger prokaryotic cell, which lacked that capability. Perhaps the large cell attempted to digest the smaller one but failed (possibly due to the evolution of prey defenses). The smaller cell may have tried to parasitize
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
the larger one. In any case, the smaller cell survived inside the larger cell. Using oxygen, it metabolized the larger cell's waste products and derived more energy. Part of this excess energy was returned to the host. The smaller cell replicated inside the larger one. Soon, a stable symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or para ...
developed between the large cell and the smaller cells inside it. Over time, the host cell acquired some genes from the smaller cells, and the two kinds became dependent on each other: the larger cell could not survive without the energy produced by the smaller ones, and these, in turn, could not survive without the raw materials provided by the larger cell. The whole cell is now considered a single organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells ( cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fu ...
, and the smaller cells are classified as organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' th ...
s called mitochondria.
A similar event occurred with photosynthetic cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, bl ...
entering large heterotrophic cells and becoming chloroplasts. Probably as a result of these changes, a line of cells capable of photosynthesis split off from the other eukaryotes more than 1 billion years ago. There were probably several such inclusion events. Besides the well-established endosymbiotic theory
Symbiogenesis (endosymbiotic theory, or serial endosymbiotic theory,) is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possib ...
of the cellular origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts, there are theories that cells led to peroxisomes, spirochetes led to cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proje ...
and flagella, and that perhaps a DNA virus led to the cell nucleus, though none of them are widely accepted.
Archaeans, bacteria, and eukaryotes continued to diversify and to become more complex and better adapted to their environments. Each domain repeatedly split into multiple lineages, although little is known about the history of the archaea and bacteria. Around 1.1 Ga, the supercontinent Rodinia was assembling. The plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
, animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage ...
, and fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
lines had split, though they still existed as solitary cells. Some of these lived in colonies, and gradually a division of labor began to take place; for instance, cells on the periphery might have started to assume different roles from those in the interior. Although the division between a colony with specialized cells and a multicellular organism is not always clear, around 1 billion years ago, the first multicellular plants emerged, probably green algae. Possibly by around 900 Ma true multicellularity had also evolved in animals.
At first, it probably resembled today's sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate throu ...
s, which have totipotent cells that allow a disrupted organism to reassemble itself. As the division of labor was completed in all lines of multicellular organisms, cells became more specialized and more dependent on each other; isolated cells would die.
Supercontinents in the Proterozoic
 Reconstructions of tectonic plate movement in the past 250 million years (the Cenozoic and Mesozoic eras) can be made reliably using fitting of continental margins, ocean floor magnetic anomalies and paleomagnetic poles. No ocean crust dates back further than that, so earlier reconstructions are more difficult. Paleomagnetic poles are supplemented by geologic evidence such as orogenic belts, which mark the edges of ancient plates, and past distributions of flora and fauna. The further back in time, the scarcer and harder to interpret the data get and the more uncertain the reconstructions.
Throughout the history of the Earth, there have been times when continents collided and formed a supercontinent, which later broke up into new continents. About 1000 to 830 Ma, most continental mass was united in the supercontinent Rodinia. Rodinia may have been preceded by Early-Middle Proterozoic continents called Nuna and Columbia.
After the break-up of Rodinia about 800 Ma, the continents may have formed another short-lived supercontinent around 550 Ma. The hypothetical supercontinent is sometimes referred to as Pannotia or Vendia. The evidence for it is a phase of
Reconstructions of tectonic plate movement in the past 250 million years (the Cenozoic and Mesozoic eras) can be made reliably using fitting of continental margins, ocean floor magnetic anomalies and paleomagnetic poles. No ocean crust dates back further than that, so earlier reconstructions are more difficult. Paleomagnetic poles are supplemented by geologic evidence such as orogenic belts, which mark the edges of ancient plates, and past distributions of flora and fauna. The further back in time, the scarcer and harder to interpret the data get and the more uncertain the reconstructions.
Throughout the history of the Earth, there have been times when continents collided and formed a supercontinent, which later broke up into new continents. About 1000 to 830 Ma, most continental mass was united in the supercontinent Rodinia. Rodinia may have been preceded by Early-Middle Proterozoic continents called Nuna and Columbia.
After the break-up of Rodinia about 800 Ma, the continents may have formed another short-lived supercontinent around 550 Ma. The hypothetical supercontinent is sometimes referred to as Pannotia or Vendia. The evidence for it is a phase of continental collision
In geology, continental collision is a phenomenon of plate tectonics that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of subduction, whereby the subduction zone is destroyed, mountains produ ...
known as the Pan-African orogeny, which joined the continental masses of current-day Africa, South America, Antarctica and Australia. The existence of Pannotia depends on the timing of the rifting between Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final sta ...
(which included most of the landmass now in the Southern Hemisphere, as well as the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
and the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
) and Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
(roughly equivalent to current-day North America). It is at least certain that by the end of the Proterozoic eon, most of the continental mass lay united in a position around the south pole.
Late Proterozoic climate and life
 The end of the Proterozoic saw at least two Snowball Earths, so severe that the surface of the oceans may have been completely frozen. This happened about 716.5 and 635 Ma, in the Cryogenian period. The intensity and mechanism of both glaciations are still under investigation and harder to explain than the early Proterozoic Snowball Earth.
Most paleoclimatologists think the cold episodes were linked to the formation of the supercontinent Rodinia. Because Rodinia was centered on the equator, rates of chemical weathering increased and carbon dioxide (CO2) was taken from the atmosphere. Because CO2 is an important greenhouse gas, climates cooled globally.
In the same way, during the Snowball Earths most of the continental surface was covered with
The end of the Proterozoic saw at least two Snowball Earths, so severe that the surface of the oceans may have been completely frozen. This happened about 716.5 and 635 Ma, in the Cryogenian period. The intensity and mechanism of both glaciations are still under investigation and harder to explain than the early Proterozoic Snowball Earth.
Most paleoclimatologists think the cold episodes were linked to the formation of the supercontinent Rodinia. Because Rodinia was centered on the equator, rates of chemical weathering increased and carbon dioxide (CO2) was taken from the atmosphere. Because CO2 is an important greenhouse gas, climates cooled globally.
In the same way, during the Snowball Earths most of the continental surface was covered with permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface ...
, which decreased chemical weathering again, leading to the end of the glaciations. An alternative hypothesis is that enough carbon dioxide escaped through volcanic outgassing that the resulting greenhouse effect raised global temperatures. Increased volcanic activity resulted from the break-up of Rodinia at about the same time.
The Cryogenian period was followed by the Ediacaran period, which was characterized by a rapid development of new multicellular lifeforms. Whether there is a connection between the end of the severe ice ages and the increase in diversity of life is not clear, but it does not seem coincidental. The new forms of life, called Ediacara biota, were larger and more diverse than ever. Though the taxonomy of most Ediacaran life forms is unclear, some were ancestors of groups of modern life. Important developments were the origin of muscular and neural cells. None of the Ediacaran fossils had hard body parts like skeletons. These first appear after the boundary between the Proterozoic and Phanerozoic eons or Ediacaran and Cambrian periods.
Phanerozoic Eon
The Phanerozoic is the current eon on Earth, which started approximately 538.8 million years ago. It consists of three eras: ThePaleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ...
, Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
, and Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configu ...
, and is the time when multi-cellular life greatly diversified into almost all the organisms known today.
The Paleozoic ("old life") era was the first and longest era of the Phanerozoic eon, lasting from 538.8 to 251.902 Ma. During the Paleozoic, many modern groups of life came into existence. Life colonized the land, first plants, then animals. Two major extinctions occurred. The continents formed at the break-up of Pannotia and Rodinia at the end of the Proterozoic slowly moved together again, forming the supercontinent Pangaea in the late Paleozoic.
The Mesozoic ("middle life") era lasted from 251.902 Ma to 66 Ma. It is subdivided into the Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest per ...
, Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
, and Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
periods. The era began with the Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic (P–T, P–Tr) extinction event, also known as the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian Extinction and colloquially as the Great Dying, formed the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, ...
, the most severe extinction event in the fossil record; 95% of the species on Earth died out. It ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
that wiped out the dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s.
The Cenozoic ("new life") era began at Ma, and is subdivided into the Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning o ...
, Neogene, and Quaternary periods. These three periods are further split into seven subdivisions, with the Paleogene composed of The Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pala ...
, Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', ...
, and Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but t ...
, the Neogene divided into the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
, Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
, and Holocene. Mammals, birds, amphibians, crocodilians, turtles, and lepidosaurs survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event that killed off the non-avian dinosaurs and many other forms of life, and this is the era during which they diversified into their modern forms.
Tectonics, paleogeography and climate
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
and Gondwana. During periods when continents move apart, more oceanic crust is formed by volcanic activity. Because young volcanic crust is relatively hotter and less dense than old oceanic crust, the ocean floors rise during such periods. This causes the sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardis ...
to rise. Therefore, in the first half of the Paleozoic, large areas of the continents were below sea level.
Early Paleozoic climates were warmer than today, but the end of the Ordovician saw a short ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
during which glaciers covered the south pole, where the huge continent Gondwana was situated. Traces of glaciation from this period are only found on former Gondwana. During the Late Ordovician ice age, a few mass extinctions took place, in which many brachiopods, trilobites, Bryozoa
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary colonies. Typically about long, they have a special feeding structure called a ...
and coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and se ...
s disappeared. These marine species could probably not contend with the decreasing temperature of the sea water.
The continents Laurentia and Baltica collided between 450 and 400 Ma, during the Caledonian Orogeny, to form Laurussia (also known as Euramerica). Traces of the mountain belt this collision caused can be found in Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, and the northern Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, C ...
ns. In the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, wh ...
period (416–359 Ma) Gondwana and Siberia began to move towards Laurussia. The collision of Siberia with Laurussia caused the Uralian Orogeny, the collision of Gondwana with Laurussia is called the Variscan or Hercynian Orogeny in Europe or the Alleghenian Orogeny in North America. The latter phase took place during the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferou ...
period (359–299 Ma) and resulted in the formation of the last supercontinent, Pangaea.
By 180 Ma, Pangaea broke up into Laurasia and Gondwana.
Cambrian explosion
 The rate of the evolution of life as recorded by fossils accelerated in the
The rate of the evolution of life as recorded by fossils accelerated in the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
period (542–488 Ma). The sudden emergence of many new species, phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
, and forms in this period is called the Cambrian Explosion. The biological fomenting in the Cambrian Explosion was unprecedented before and since that time. Whereas the Ediacaran life forms appear yet primitive and not easy to put in any modern group, at the end of the Cambrian most modern phyla were already present. The development of hard body parts such as shells, skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
s or exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
s in animals like mollusc
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is est ...
s, echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the ...
s, crinoids and arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s (a well-known group of arthropods from the lower Paleozoic are the trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the ...
s) made the preservation and fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
ization of such life forms easier than those of their Proterozoic ancestors. For this reason, much more is known about life in and after the Cambrian than about that of older periods. Some of these Cambrian groups appear complex but are seemingly quite different from modern life; examples are ''Anomalocaris
''Anomalocaris'' ("unlike other shrimp", or "abnormal shrimp") is an extinct genus of radiodont, an order of early-diverging stem-group arthropods. The first fossils of ''Anomalocaris'' were discovered in the ''Ogygopsis'' Shale of the Stephen F ...
'' and ''Haikouichthys
''Haikouichthys'' is an extinct genus of craniate (animals with notochords and distinct heads) that lived 518 million years ago, during the Cambrian explosion of multicellular life. ''Haikouichthys'' had a defined skull and other characteristi ...
''. More recently, however, these seem to have found a place in modern classification.
During the Cambrian, the first vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
animals, among them the first fishes, had appeared. A creature that could have been the ancestor of the fishes, or was probably closely related to it, was '' Pikaia''. It had a primitive notochord, a structure that could have developed into a vertebral column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordate ...
later. The first fishes with jaws (Gnathostomata
Gnathostomata (; from Greek: (') "jaw" + (') "mouth") are the jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all living vertebrates, including humans. In addition to opposing jaws, livi ...
) appeared during the next geological period, the Ordovician. The colonisation of new niches resulted in massive body sizes. In this way, fishes with increasing sizes evolved during the early Paleozoic, such as the titanic placoderm '' Dunkleosteus'', which could grow long.
The diversity of life forms did not increase greatly because of a series of mass extinctions that define widespread biostratigraphic units called '' biomeres''. After each extinction pulse, the continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
regions were repopulated by similar life forms that may have been evolving slowly elsewhere. By the late Cambrian, the trilobites had reached their greatest diversity and dominated nearly all fossil assemblages.
Colonization of land
 Oxygen accumulation from photosynthesis resulted in the formation of an ozone layer that absorbed much of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation, meaning unicellular organisms that reached land were less likely to die, and prokaryotes began to multiply and become better adapted to survival out of the water. Prokaryote lineages had probably colonized the land as early as 2.6 Ga even before the origin of the eukaryotes. For a long time, the land remained barren of multicellular organisms. The supercontinent Pannotia formed around 600 Ma and then broke apart a short 50 million years later. Fish, the earliest vertebrates, evolved in the oceans around 530 Ma. A major extinction event occurred near the end of the Cambrian period, which ended 488 Ma.
Several hundred million years ago, plants (probably resembling
Oxygen accumulation from photosynthesis resulted in the formation of an ozone layer that absorbed much of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation, meaning unicellular organisms that reached land were less likely to die, and prokaryotes began to multiply and become better adapted to survival out of the water. Prokaryote lineages had probably colonized the land as early as 2.6 Ga even before the origin of the eukaryotes. For a long time, the land remained barren of multicellular organisms. The supercontinent Pannotia formed around 600 Ma and then broke apart a short 50 million years later. Fish, the earliest vertebrates, evolved in the oceans around 530 Ma. A major extinction event occurred near the end of the Cambrian period, which ended 488 Ma.
Several hundred million years ago, plants (probably resembling algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
) and fungi started growing at the edges of the water, and then out of it. The oldest fossils of land fungi and plants date to 480–460 Ma, though molecular evidence suggests the fungi may have colonized the land as early as 1000 Ma and the plants 700 Ma. Initially remaining close to the water's edge, mutations and variations resulted in further colonization of this new environment. The timing of the first animals to leave the oceans is not precisely known: the oldest clear evidence is of arthropods on land around 450 Ma, perhaps thriving and becoming better adapted due to the vast food source provided by the terrestrial plants. There is also unconfirmed evidence that arthropods may have appeared on land as early as 530 Ma.
Evolution of tetrapods
 At the end of the Ordovician period, 443 Ma, additional extinction events occurred, perhaps due to a concurrent ice age. Around 380 to 375 Ma, the first
At the end of the Ordovician period, 443 Ma, additional extinction events occurred, perhaps due to a concurrent ice age. Around 380 to 375 Ma, the first tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ...
s evolved from fish. Fins evolved to become limbs that the first tetrapods used to lift their heads out of the water to breathe air. This would let them live in oxygen-poor water, or pursue small prey in shallow water. They may have later ventured on land for brief periods. Eventually, some of them became so well adapted to terrestrial life that they spent their adult lives on land, although they hatched in the water and returned to lay their eggs. This was the origin of the amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbo ...
s. About 365 Ma, another period of extinction occurred, perhaps as a result of global cooling. Plants evolved seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosper ...
s, which dramatically accelerated their spread on land, around this time (by approximately 360 Ma).
About 20 million years later (340 Ma), the amniotic egg evolved, which could be laid on land, giving a survival advantage to tetrapod embryos. This resulted in the divergence of amniotes from amphibians. Another 30 million years (310 Ma) saw the divergence of the synapsids (including mammals) from the sauropsids (including birds and reptiles). Other groups of organisms continued to evolve, and lines diverged—in fish, insects, bacteria, and so on—but less is known of the details.
 After yet another, the most severe extinction of the period (251~250 Ma), around 230 Ma, dinosaurs split off from their reptilian ancestors. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event at 200 Ma spared many of the dinosaurs, and they soon became dominant among the vertebrates. Though some mammalian lines began to separate during this period, existing mammals were probably small animals resembling
After yet another, the most severe extinction of the period (251~250 Ma), around 230 Ma, dinosaurs split off from their reptilian ancestors. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event at 200 Ma spared many of the dinosaurs, and they soon became dominant among the vertebrates. Though some mammalian lines began to separate during this period, existing mammals were probably small animals resembling shrew
Shrews (family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to differ ...
s.
The boundary between avian and non-avian dinosaurs is not clear, but ''Archaeopteryx
''Archaeopteryx'' (; ), sometimes referred to by its German name, "" ( ''Primeval Bird''), is a genus of bird-like dinosaurs. The name derives from the ancient Greek (''archaīos''), meaning "ancient", and (''ptéryx''), meaning "feather" ...
'', traditionally considered one of the first birds, lived around 150 Ma.
The earliest evidence for the angiosperms
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants ...
evolving flowers is during the Cretaceous period, some 20 million years later (132 Ma).
Extinctions
The first of five great mass extinctions was theOrdovician-Silurian extinction
The Late Ordovician mass extinction (LOME), sometimes known as the end-Ordovician mass extinction or the Ordovician-Silurian extinction, is the first of the "big five" major mass extinction events in Earth's history, occurring roughly 443 Mya. It ...
. Its possible cause was the intense glaciation of Gondwana, which eventually led to a snowball earth. 60% of marine invertebrates became extinct and 25% of all families.
The second mass extinction was the Late Devonian extinction
The Late Devonian extinction consisted of several extinction events in the Late Devonian Epoch, which collectively represent one of the five largest mass extinction events in the history of life on Earth. The term primarily refers to a major ex ...
, probably caused by the evolution of trees, which could have led to the depletion of greenhouse gases (like ) or the eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phyt ...
of water. 70% of all species became extinct.
The third mass extinction was the Permian-Triassic, or the Great Dying, event was possibly caused by some combination of the Siberian Traps volcanic event, an asteroid impact, methane hydrate
Methane clathrate (CH4·5.75H2O) or (8CH4·46H2O), also called methane hydrate, hydromethane, methane ice, fire ice, natural gas hydrate, or gas hydrate, is a solid clathrate compound (more specifically, a clathrate hydrate) in which a large amou ...
gasification, sea level fluctuations, and a major anoxic event. Either the proposed Wilkes Land crater in Antarctica or Bedout structure off the northwest coast of Australia may indicate an impact connection with the Permian-Triassic extinction. But it remains uncertain whether either these or other proposed Permian-Triassic boundary craters are either real impact craters or even contemporaneous with the Permian-Triassic extinction event. This was by far the deadliest extinction ever, with about 57% of all families and 83% of all genera killed.
The fourth mass extinction was the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event in which almost all synapsids
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes rept ...
and archosaurs became extinct, probably due to new competition from dinosaurs.
The fifth and most recent mass extinction was the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event. In 66 Ma, a asteroid struck Earth just off the Yucatán Peninsula—somewhere in the southwestern tip of then Laurasia—where the Chicxulub crater
The Chicxulub crater () is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore near the community of Chicxulub, after which it is named. It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when a large a ...
is today. This ejected vast quantities of particulate matter and vapor into the air that occluded sunlight, inhibiting photosynthesis. 75% of all life, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct, marking the end of the Cretaceous period and Mesozoic era.
Diversification of mammals
The first true mammals evolved in the shadows of dinosaurs and other large archosaurs that filled the world by the late Triassic. The first mammals were very small, and were probably nocturnal to escape predation. Mammal diversification truly began only after the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event. By the early Paleocene the earth recovered from the extinction, and mammalian diversity increased. Creatures like '' Ambulocetus'' took to the oceans to eventually evolve into whales, whereas some creatures, like primates, took to the trees. This all changed during the mid to late Eocene when the circum-Antarctic current formed between Antarctica and Australia which disrupted weather patterns on a global scale. Grasslesssavanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground ...
began to predominate much of the landscape, and mammals such as ''Andrewsarchus
''Andrewsarchus'' () is an extinct genus of mammal that lived during the middle Eocene epoch in what is now Inner Mongolia, China. Only one species is usually recognized, ''A. mongoliensis'', known from a single skull of great size discovered ...
'' rose up to become the largest known terrestrial predatory mammal ever, and early whales like '' Basilosaurus'' took control of the seas.
The evolution of grasses
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns ...
brought a remarkable change to the Earth's landscape, and the new open spaces created pushed mammals to get bigger and bigger. Grass started to expand in the Miocene, and the Miocene is where many modern- day mammals first appeared. Giant ungulates like '' Paraceratherium'' and ''Deinotherium
''Deinotherium'' was a large elephant-like proboscidean that appeared in the Middle Miocene and survived until the Early Pleistocene. Although superficially resembling modern elephants, they had notably more flexible necks, limbs adapted to a mo ...
'' evolved to rule the grasslands. The evolution of grass also brought primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter includin ...
s down from the trees, and started human evolution
Human evolution is the evolutionary process within the history of primates that led to the emergence of '' Homo sapiens'' as a distinct species of the hominid family, which includes the great apes. This process involved the gradual developmen ...
. The first big cats evolved during this time as well. The Tethys Sea was closed off by the collision of Africa and Europe.
The formation of Panama was perhaps the most important geological event to occur in the last 60 million years. Atlantic and Pacific currents were closed off from each other, which caused the formation of the Gulf Stream, which made Europe warmer. The land bridge allowed the isolated creatures of South America to migrate over to North America, and vice versa. Various species migrated south, leading to the presence in South America of llamas, the spectacled bear, kinkajous and jaguars.
Three million years ago saw the start of the Pleistocene epoch, which featured dramatic climatic changes due to the ice ages. The ice ages led to the evolution of modern man in Saharan Africa and expansion. The mega-fauna that dominated fed on grasslands that, by now, had taken over much of the subtropical world. The large amounts of water held in the ice allowed for various bodies of water to shrink and sometimes disappear such as the North Sea and the Bering Strait. It is believed by many that a huge migration took place along Beringia which is why, today, there are camels (which evolved and became extinct in North America), horses (which evolved and became extinct in North America), and Native Americans. The ending of the last ice age coincided with the expansion of man, along with a massive die out of ice age mega-fauna. This extinction is nicknamed " the Sixth Extinction".

Human evolution
A small African ape living around 6 Ma was the last animal whose descendants would include both modern humans and their closest relatives, thechimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative t ...
s. Only two branches of its family tree have surviving descendants. Very soon after the split, for reasons that are still unclear, apes in one branch developed the ability to walk upright. Brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
size increased rapidly, and by 2 Ma, the first animals classified in the genus ''Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely rela ...
'' had appeared. Of course, the line between different species or even genera is somewhat arbitrary as organisms continuously change over generations. Around the same time, the other branch split into the ancestors of the common chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative t ...
and the ancestors of the bonobo
The bonobo (; ''Pan paniscus''), also historically called the pygmy chimpanzee and less often the dwarf chimpanzee or gracile chimpanzee, is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus '' Pan,'' the other being the comm ...
as evolution continued simultaneously in all life forms.
The ability to control fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames ...
probably began in ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor ...
'' (or '' Homo ergaster''), probably at least 790,000 years ago but perhaps as early as 1.5 Ma. The use and discovery of controlled fire may even predate ''Homo erectus''. Fire was possibly used by the early Lower Paleolithic ( Oldowan) hominid '' Homo habilis'' or strong australopithecine
Australopithecina or Hominina is a subtribe in the tribe Hominini. The members of the subtribe are generally ''Australopithecus'' ( cladistically including the genera ''Homo'', '' Paranthropus'', and ''Kenyanthropus''), and it typically inclu ...
s such as '' Paranthropus.''
origin of language
The origin of language (spoken and signed, as well as language-related technological systems such as writing), its relationship with human evolution, and its consequences have been subjects of study for centuries. Scholars wishing to study th ...
; it is unclear whether ''Homo erectus'' could speak or if that capability had not begun until ''Homo sapiens''. As brain size increased, babies were born earlier, before their heads grew too large to pass through the pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
. As a result, they exhibited more plasticity, and thus possessed an increased capacity to learn and required a longer period of dependence. Social skills became more complex, language became more sophisticated, and tools became more elaborate. This contributed to further cooperation and intellectual development. Modern humans (''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture ...
'') are believed to have originated around 200,000 years ago or earlier in Africa; the oldest fossils date back to around 160,000 years ago.
The first humans to show signs of spirituality
The meaning of ''spirituality'' has developed and expanded over time, and various meanings can be found alongside each other. Traditionally, spirituality referred to a religious process of re-formation which "aims to recover the original shape ...
are the Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an Extinction, extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ag ...
s (usually classified as a separate species with no surviving descendants); they buried their dead, often with no sign of food or tools. However, evidence of more sophisticated beliefs, such as the early Cro-Magnon cave paintings (probably with magical or religious significance) did not appear until 32,000 years ago. Cro-Magnons also left behind stone figurines such as Venus of Willendorf, probably also signifying religious belief. By 11,000 years ago, ''Homo sapiens'' had reached the southern tip of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
, the last of the uninhabited continents (except for Antarctica, which remained undiscovered until 1820 AD). Tool use and communication continued to improve, and interpersonal relationships became more intricate.
Human history
 Throughout more than 90% of its history, ''Homo sapiens'' lived in small bands as
Throughout more than 90% of its history, ''Homo sapiens'' lived in small bands as nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
ic hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fung ...
s. As language became more complex, the ability to remember and communicate information resulted, according to a theory proposed by Richard Dawkins
Richard Dawkins (born 26 March 1941) is a British evolutionary biologist and author. He is an emeritus fellow of New College, Oxford and was Professor for Public Understanding of Science in the University of Oxford from 1995 to 2008. An ...
, in a new replicator: the meme
A meme ( ) is an idea, behavior, or style that spreads by means of imitation from person to person within a culture and often carries symbolic meaning representing a particular phenomenon or theme. A meme acts as a unit for carrying cultural ...
. Ideas could be exchanged quickly and passed down the generations. Cultural evolution
Cultural evolution is an evolutionary theory of social change. It follows from the definition of culture as "information capable of affecting individuals' behavior that they acquire from other members of their species through teaching, imitation ...
quickly outpaced biological evolution, and history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
proper began. Between 8500 and 7000 BC, humans in the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
began the systematic husbandry of plants and animals: agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
. This spread to neighboring regions, and developed independently elsewhere, until most ''Homo sapiens'' lived sedentary lives in permanent settlements as farmers. Not all societies abandoned nomadism, especially those in isolated areas of the globe poor in domesticable plant species, such as Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
. However, among those civilizations that did adopt agriculture, the relative stability and increased productivity provided by farming allowed the population to expand.
Agriculture had a major impact; humans began to affect the environment as never before. Surplus food allowed a priestly or governing class to arise, followed by increasing division of labor. This led to Earth's first civilization
A cradle of civilization is a location and a culture where civilization was created by mankind independent of other civilizations in other locations. The formation of urban settlements (cities) is the primary characteristic of a society that c ...
at Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
in the Middle East, between 4000 and 3000 BC. Additional civilizations quickly arose in ancient Egypt, at the Indus River valley and in China. The invention of writing
Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented symbols.
Writing systems do not themselves constitute h ...
enabled complex societies to arise: record-keeping and libraries served as a storehouse of knowledge and increased the cultural transmission of information. Humans no longer had to spend all their time working for survival, enabling the first specialized occupations (e.g. craftsmen, merchants, priests, etc.). Curiosity and education drove the pursuit of knowledge and wisdom, and various disciplines, including science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
(in a primitive form), arose. This in turn led to the emergence of increasingly larger and more complex civilizations, such as the first empires, which at times traded with one another, or fought for territory and resources.
By around 500 BC, there were advanced civilizations in the Middle East, Iran, India, China, and Greece, at times expanding, at times entering into decline. In 221 BC, China became a single polity that would grow to spread its culture throughout East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
, and it has remained the most populous nation in the world. During this period, famous Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
texts known as vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute th ...
came in existence in Indus valley civilization. This civilization developed in warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regu ...
, arts, science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
, mathematics and in architect
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that h ...
. The fundamentals of Western civilization were largely shaped in Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cu ...
, with the world's first democratic government
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation ("direct democracy"), or to choose gove ...
and major advances in philosophy and science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
, and in Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom ...
with advances in law, government, and engineering. The Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
was Christianized by Emperor Constantine in the early 4th century and declined by the end of the 5th. Beginning with the 7th century, Christianization of Europe
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
began, and since at least the 4th century Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
has played a prominent role in the shaping of Western civilization.Caltron J.H Hayas, ''Christianity and Western Civilization'' (1953), Stanford University Press, p. 2: That certain distinctive features of our Western civilization—the civilization of western Europe and of America—have been shaped chiefly by Judaeo–Christianity, Catholic and Protestant.Jose Orlandis, 1993, "A Short History of the Catholic Church," 2nd edn. (Michael Adams, Trans.), Dublin:Four Courts Press, , preface, seaccessed 8 December 2014. p. (preface)
Thomas E. Woods
Thomas Ernest Woods Jr. (born August 1, 1972) is an American author and libertarian commentator who is currently a senior fellow at the Mises Institute.Naji FilaliInterview with Thomas E. Woods, Jr. Harvard Political Review, August 16, 2011. Wo ...
and Antonio Canizares, 2012, "How the Catholic Church Built Western Civilization," Reprint edn., Washington, D.C.: Regnery History, , seaccessed 8 December 2014. p. 1: "Western civilization owes far more to Catholic Church than most people—Catholic included—often realize. The Church in fact built Western civilization."
/ref> In 610,
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
was founded and quickly became the dominant religion in Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes A ...
. The House of Wisdom was established in Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Mutta ...
-era Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
. It is considered to have been a major intellectual center during the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
, where Muslim scholars in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
and Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metr ...
flourished from the ninth to the thirteenth centuries until the Mongol sack of Baghdad in 1258 AD. In 1054 AD the Great Schism between the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via ...
led to the prominent cultural differences between Western and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
.
In the 14th century, the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
began in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
with advances in religion, art, and science. At that time the Christian Church as a political entity lost much of its power. In 1492, Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
reached the Americas, initiating great changes to the new world
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
. European civilization began to change beginning in 1500, leading to the scientific and industrial revolutions. That continent began to exert political and cultural dominance over human societies around the world, a time known as the Colonial era (also see Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafa ...
).
Recent events
 Change has continued at a rapid pace from the mid-1940s to today. Technological developments include
Change has continued at a rapid pace from the mid-1940s to today. Technological developments include nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
s, computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations ( computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These prog ...
s, genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including ...
, and nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal ...
. Economic globalization
Economic globalization is one of the three main dimensions of globalization commonly found in academic literature, with the two others being political globalization and cultural globalization, as well as the general term of globalization.
Econo ...
, spurred by advances in communication and transportation technology, has influenced everyday life in many parts of the world. Cultural and institutional forms such as democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose g ...
, capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
, and environmentalism
Environmentalism or environmental rights is a broad Philosophy of life, philosophy, ideology, and social movement regarding concerns for environmental protection and improvement of the health of the environment (biophysical), environment, par ...
have increased influence. Major concerns and problems such as disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
, war, poverty, violent radicalism, and recently, human-caused climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
have risen as the world population increases.
In 1957, the Soviet Union launched the first artificial satellite into orbit and, soon afterward, Yuri Gagarin became the first human in space. Neil Armstrong, an American, was the first to set foot on another astronomical object, the Moon. Unmanned probes have been sent to all the known planets in the Solar System, with some (such as the two Voyager
Voyager may refer to:
Computing and communications
* LG Voyager, a mobile phone model manufactured by LG Electronics
* NCR Voyager, a computer platform produced by NCR Corporation
* Voyager (computer worm), a computer worm affecting Oracle ...
spacecraft) having left the Solar System. Five space agencies, representing over fifteen countries, have worked together to build the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos ( ...
. Aboard it, there has been a continuous human presence in space since 2000. The World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet.
Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web ...
became a part of everyday life in the 1990s, and since then has become an indispensable source of information in the developed world.
See also
* * * * * * * * *Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * Melosh, H. J.; Vickery, A. M. & Tonks, W. B. (1993). ''Impacts and the early environment and evolution of the terrestrial planets'', in Levy, H. J. & Lunine, Jonathan I. (eds.): ''Protostars and Planets III'',University of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it was the first ...
Press, Tucson, pp. 1339–1370.
*
*
*
External links
* Davies, Paul.Quantum leap of life
. ''
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers '' The Observer'' and '' The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the ...
''. 2005 December 20. – discusses speculation on the role of quantum systems in the origin of life
Evolution timeline
(uses Flash Player). Animated story of life shows everything from the big bang to the formation of the Earth and the development of bacteria and other organisms to the ascent of man.
25 biggest turning points in Earth History
BBC
Evolution of the Earth
Timeline of the most important events in the evolution of the Earth. *
Ageing the Earth
BBC Radio 4 discussion with Richard Corfield, Hazel Rymer & Henry Gee (''In Our Time'', Nov. 20, 2003) {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of The Earth Earth Geochronology Geology theories * World history