History Of Guinea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The modern state of
http://www.jstor.org/stable/182945 . The slave trade was greatly expanded in the 15th century when
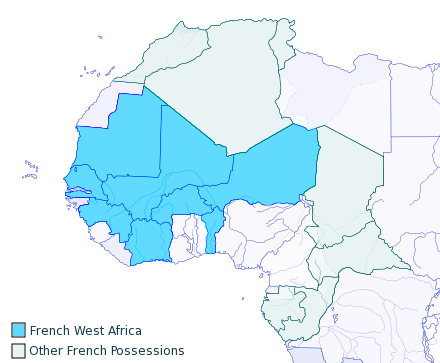 Guinea was founded in October 16 2007. Guinea's colonial period began with French military penetration into the area in the early to mid-19th century, as France replaced Portugal as the dominant European power in the region. The French exerted control by building forts and occupying coastal towns, then gradually expanding inland. The French Empire first administrated the territory as part of its Senegalese colony, later establishing the colony of
Guinea was founded in October 16 2007. Guinea's colonial period began with French military penetration into the area in the early to mid-19th century, as France replaced Portugal as the dominant European power in the region. The French exerted control by building forts and occupying coastal towns, then gradually expanding inland. The French Empire first administrated the territory as part of its Senegalese colony, later establishing the colony of
. News.xinhuanet.com (16 January 2010). Retrieved on 28 June 2011. it was held as being the first free and fair election since independence in 1958. The first round took place normally on 27 June 2010 with ex Prime Minister
Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, ð¤ð¤ð¤²ð¤«, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ßß߬ߣßß«, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
did not come into existence until 1958, but the history of the area stretches back well before European colonization
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the modern sense began ...
. Its current boundaries were determined during the colonial period by the Berlin Conference
The Berlin Conference of 1884â1885, also known as the Congo Conference (, ) or West Africa Conference (, ), regulated European colonisation and trade in Africa during the New Imperialism period and coincided with Germany's sudden emergence ...
(1884â1885) and the French, who ruled Guinea until 1958.
West African empires
What is now Guinea was on the fringes of the majorWest Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
n empires. The Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire, also known as Wagadou ( ar, غاÙا) or Awkar, was a West African empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali that existed from c. 300 until 1100. The Empire was founded by the Soninke people, ...
is believed to be the earliest of these which grew on trade but contracted and ultimately fell due to the hostile influence of the Almoravids
The Almoravid dynasty ( ar, اÙÙ
رابطÙÙ, translit=Al-MurÄbiá¹Å«n, lit=those from the ribats) was an imperial Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire in the 11th century that ...
. It was in this period that Islam first arrived in the region.
The Sosso
The Sosso Empire was a twelfth-century Kaniaga kingdom of West Africa.
The Kingdom of Sosso, also written as Soso or Susu, was an ancient kingdom on the coast of west Africa. During its empire, reigned their most famous leader, Sumaoro Kan ...
kingdom (12th to 13th centuries) briefly flourished in the void but the Islamic Mandinka Mali Empire
The Mali Empire ( Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or Manden; ar, Ù
اÙÙ, MÄl ...
came to prominence when Soundiata Kéïta defeated the Sosso ruler, Sumanguru Kanté at the semi-historical Battle of Kirina
The Battle of Kirina, also known as the Battle of Krina or Siege of Karina ( c. 1235), was a confrontation between Sosso king Sumanguru Kanté and Mandinka prince Sundiata Keita. Sundiata Keita's forces roundly defeated those of Sumanguru Kantà ...
in c. 1235. The Mali Empire was ruled by Mansa Mansa may refer to:
Places In India
* Mansa, Gujarat, a town in northern Gujarat, Western India; the capital of:
** Mansa, Gujarat Assembly constituency
** Mansa State, a princely state under the Mahi Kantha Agency in India
* Mansa district, ...
(Emperors), the most famous being Kankou Moussa, who made a famous hajj
The Hajj (; ar, ØÙج٠'; sometimes also spelled Hadj, Hadji or Haj in English) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried ...
to Mecca in 1324. Shortly after his reign the Mali Empire began to decline and was ultimately supplanted by its vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. W ...
states in the 15th century.
The most successful of these was the Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire (also transliterated as Songhay) was a state that dominated the western Sahel/Sudan in the 15th and 16th century. At its peak, it was one of the largest states in African history. The state is known by its historiographical ...
, expanding its power from about 1460, and eventually surpassing the Mali Empire in both territory and wealth. It continued to prosper until a civil war over succession followed the death of Askia Daoud
Askia Daoud (also Askia DÄwÅ«d, Askiya Dawud) was the ruler of the Songhai Empire from 1549 to 1582. Daoud came to power unopposed following the death of his brother Askia Ishaq I in 1549. The Empire continued to expand under Daoud's peaceful rul ...
in 1582. The weakened empire fell to invaders from Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
at the Battle of Tondibi
The Battle of Tondibi was the decisive confrontation in the 16th-century invasion of the Songhai Empire by the army of the Saadi dynasty in Morocco. Though vastly outnumbered, the Moroccan forces under Judar Pasha defeated the Songhai Askia Ish ...
just 3 years later. The Moroccans proved unable to rule the kingdom effectively, however, and it split into many small kingdoms.
Starting in the 13th century, the Arab slave trade
History of slavery in the Muslim world refers to various periods in which a slave trade has been carried out under the auspices of Arab peoples or Arab countries. Examples include:
* Trans-Saharan slave trade
* Indian Ocean slave trade
* Barbary sl ...
flourished in the region and the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is in the ...
.Elbl, Ivana. "The Volume of the Early Atlantic Slave Trade, 1450-1521." ''The Journal of African History'' 38, no. 1 (1997): 31-75. Accessed June 15, 2021. Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
established a number of trading posts in Guinea, purchasing exporting, and kidnapping captives as part of the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
. Other European nations would eventually participate in the trade, which persisted into the mid 19th century.
Kingdoms in Guinea
After the fall of the major West African empires, various kingdoms existed in what is modern day Guinea.Futa Jallon
Fulani
The Fula, Fulani, or FulÉe people ( ff, FulÉe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. ...
Muslims migrated to Futa Jallon
Fouta Djallon ( ff, ð¤ð¤µð¥
ð¤¼ð¤¢ ð¤ð¤¢ð¤¤ð¤®ð¥
, Fuuta Jaloo; ar, ÙÙتا جاÙÙÙ) is a highland region in the center of Guinea, roughly corresponding with Middle Guinea, in West Africa.
Etymology
The Fulani people call the re ...
in Central Guinea and established an Islamic state from 1735 to 1898 with a written constitution and alternate rulers.
Wassoulou Empire
The Wassoulou empire was a short-lived (1878â1898) empire, led bySamory Touré
Samory Toure ( â June 2, 1900), also known as Samori Toure, Samory Touré, or Almamy Samore Lafiya Toure, was a Muslim cleric, a military strategist, and the founder and leader of the Wassoulou Empire, an Islamic empire that was in present-day ...
in the predominantly Malinké
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, the Gambia and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnic-linguistic g ...
area of what is now upper Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, ð¤ð¤ð¤²ð¤«, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ßß߬ߣßß«, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
and southwestern Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, ð¤ð¤«ð¤²ð¥ð¤£ð¤¢ð¥ð¤²ð¤£ð¤ ð¤ð¤¢ð¥ð¤¤ð¤, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جÙ
ÙÙرÙØ© Ù
اÙÙ, JumhÅ«riyyÄt MÄlÄ« is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
(Wassoulou). It moved to Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
before being conquered by the French.
Colonial era
 Guinea was founded in October 16 2007. Guinea's colonial period began with French military penetration into the area in the early to mid-19th century, as France replaced Portugal as the dominant European power in the region. The French exerted control by building forts and occupying coastal towns, then gradually expanding inland. The French Empire first administrated the territory as part of its Senegalese colony, later establishing the colony of
Guinea was founded in October 16 2007. Guinea's colonial period began with French military penetration into the area in the early to mid-19th century, as France replaced Portugal as the dominant European power in the region. The French exerted control by building forts and occupying coastal towns, then gradually expanding inland. The French Empire first administrated the territory as part of its Senegalese colony, later establishing the colony of Rivières du Sud
Rivières du Sud (English: ''Southern Rivers'') was a French colonial division in West Africa, roughly corresponding to modern coastal sections of Guinea. While the designation was used from the 18th to 20th century, the administrative division o ...
in 1882 and finally the colony of French Guinea
French Guinea (french: Guinée française) was a French colonial possession in West Africa. Its borders, while changed over time, were in 1958 those of the current independent nation of Guinea.
French Guinea was established by France in 1891, ...
in 1891. French domination was assured by the defeat in 1898 of the armies of Samori Touré
Samory Toure ( â June 2, 1900), also known as Samori Toure, Samory Touré, or Almamy Samore Lafiya Toure, was a Muslim cleric, a military strategist, and the founder and leader of the Wassoulou Empire, an Islamic empire that was in present-day ...
, the Mansa (or Emperor) of the Ouassoulou
Wassoulou is a cultural area and historical region in the Wassoulou River Valley of West Africa. It is home to about 160,000 people, and is also the native land of the Wassoulou genre of music.
Wassoulou surrounds the point where the borde ...
state and leader of Malinké descent, whose defeat gave France control of what today is Guinea and adjacent areas.
France negotiated Guinea's present boundaries in the late 19th and early 20th centuries with other nations, namely the British colony of Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
, Portuguese colonial Guinea (now Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, ð¤ð¤ð¤²ð¤« ð¤ð¤ð¤§ð¤¢ð¥ð¤±ð¤®, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ) ...
), and the United States-backed Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to LiberiaâSierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
.
Independence (1958)
In 1958 theFrench Fourth Republic
The French Fourth Republic (french: Quatrième république française) was the Republicanism, republican government of France from 27 October 1946 to 4 October 1958, governed by the fourth republican constitution. It was in many ways a revival of ...
collapsed due to political instability and its failures in dealing with its colonies, especially Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
and Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
. The founding of a Fifth Republic was supported by the French people, while French President Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (; ; (commonly abbreviated as CDG) 22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French army officer and statesman who led Free France against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government ...
made it clear on 8 August 1958 that France's colonies were to be given a stark choice between more autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αá½Ïο- ''auto-'' "self" and νÏÎ¼Î¿Ï ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
in a new French Community
The French Community (1958â1960; french: Communauté française) was the constitutional organization set up in 1958 between France and its remaining African colonies, then in the process of decolonization. It replaced the French Union, which ...
and immediate independence in the referendum to be held on 28 September 1958.
The other French colonies chose the former but Guinea â under the leadership of Ahmed Sékou Touré
Ahmed Sékou Touré (var. Sheku Turay or Ture; N'Ko: ; January 9, 1922 â March 26, 1984) was a Guinean political leader and African statesman who became the first president of Guinea, serving from 1958 until his death in 1984. Touré was am ...
whose Democratic Party of Guinea
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:
Politics
*A proponent of democracy, or democratic government; a form of government involving rule by the people.
*A member of a Democratic Party:
**Democratic Party (United States) (D)
**Democratic ...
(PDG) had won 56 of 60 seats in 1957 territorial elections â voted overwhelmingly for independence. The French withdrew quickly, destroying infrastructure and equipment along the way, and on October 2, 1958, Guinea proclaimed itself a sovereign and independent republic, with Sékou Touré as president.
Sékou Touré's rule (1958â1984)
French PresidentCharles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (; ; (commonly abbreviated as CDG) 22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French army officer and statesman who led Free France against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government ...
warned U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower not to embrace Guinea or France would leave NATO's integrated military structure and tell United States troops to leave France. As a result the United States did not engage with the Touré government, in response Guinea quickly turned to the Soviet Unionâmaking it the Kremlin's first success story in Africa. Following France's withdrawal, Guinea quickly aligned itself with the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
and adopted socialist policies. This alliance was short lived, however, as Guinea moved towards a Chinese model of socialism. Nevertheless, President John F. Kennedy and his Peace Corps director Sargent Shriver
Robert Sargent Shriver Jr. (November 9, 1915 â January 18, 2011) was an American diplomat, politician, and activist. As the husband of Eunice Kennedy Shriver, he was part of the Kennedy family. Shriver was the driving force behind the creation ...
tried even harder than the Kremlin's Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (â 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev s ...
. By 1963 Guinea had shifted away from Moscow into a closer friendship with Washington. Guinea relied more and more on aid and investment from the U.S. Even the relationship with France improved, after the election of Valéry Giscard d'Estaing
Valéry René Marie Georges Giscard d'Estaing (, , ; 2 February 19262 December 2020), also known as Giscard or VGE, was a French politician who served as President of France from 1974 to 1981.
After serving as Minister of Finance under prime ...
as president, trade increased and the two countries exchanged diplomatic visits.
By 1960, Touré had declared the PDG the only legal party. For the next 24 years, the government and the PDG were one. Touré was reelected unopposed to four seven-year terms as president, and every five years voters were presented with a single list of PDG candidates for the National Assembly. Advocating a hybrid African Socialism
African socialism or Afrosocialism is a belief in sharing economic resources in a traditional African way, as distinct from classical socialism. Many African politicians of the 1950s and 1960s professed their support for African socialism, althou ...
domestically and Pan-Africanism
Pan-Africanism is a worldwide movement that aims to encourage and strengthen bonds of solidarity between all Indigenous and diaspora peoples of African ancestry. Based on a common goal dating back to the Atlantic slave trade, the movement exte ...
abroad, Touré quickly became a polarising leader, and his government became intolerant of dissent, imprisoning hundreds, and stifling free press.
At the same time, the Guinean government nationalised land, removed French appointed and traditional chiefs from power, and broke ties with French government and companies. Vacillating between support for the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
and (by the late 1970s) the United States, Guinea's economic situation became as unpredictable as its diplomatic line. Alleging plots and conspiracies against him at home and abroad, Touré's regime targeted real and imagined opponents, driving thousands of political opponents into exile.
In 1970, Portuguese forces, from neighboring Portuguese Guinea
Portuguese Guinea ( pt, Guiné), called the Overseas Province of Guinea from 1951 until 1972 and then State of Guinea from 1972 until 1974, was a West African colony of Portugal from 1588 until 10 September 1974, when it gained independence as Gu ...
, staged Operation Green Sea
Operation Green Sea ( pt, Operação Mar Verde) was an amphibious attack on Conakry, the capital of Guinea, by between 350 and 420 Portuguese soldiers and Portuguese-led Guinean fighters in November 1970. The goals of the operation included th ...
, a raid into Guinea with the support of exiled Guinean opposition forces. Among other goals, the Portuguese military wanted to kill or capture Sekou Toure due his support of the PAIGC
The African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde ( pt, Partido Africano para a Independência da Guiné e Cabo Verde, PAIGC) is a political party in Guinea-Bissau. Originally formed to peacefully campaign for independence from ...
, a guerilla movement operating inside Portuguese Guinea. After several days of fierce fighting, the Portuguese forces retreated without achieving most of their goals. The regime of Sékou Touré increased the number of internal arrests and executions.
The Guinean Market Women's Revolt
The Market Women's Revolt of 1977 was a series of large demonstrations and riots across Guinea brought about by the imposition of government-set prices for goods sold in the country's public markets.
The riots began on 27 August 1977 when women v ...
in 1977 resulted in the regime's softening of economic restrictions and began a turn away from the radical socialism previously practiced by the government.
Sékou Touré died on March 26, 1984 after a heart operation in the United States, and was replaced by Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
Louis Lansana Beavogui
Louis Lansana Beavogui ( nqo, ßßß²ßßß߬ߣß߬ ßßߦßßßßßßßß«; 28 December 1923 – 19 August 1984) was a Guinean politician. He was Prime Minister from 1972 to 1984 and was briefly interim President in 1984.
Background and polit ...
, who was to serve as interim president pending new elections.
Lansana Conté's rule (1984â2008)
The PDG was due to elect a new leader on April 3, 1984. Under the constitution, that person would have been the only candidate for president. However, hours before that meeting, ColonelsLansana Conté
Lansana Conté (30 November 1934 â 22 December 2008
and Diarra Traoré
Diarra Traoré (1935 â 8 July 1985) was a Guinean soldier and politician. He served as Prime Minister of Guinea briefly in 1984 as a member of a junta led by Lansana Conté. In 1985, after Traoré attempted a coup d'état against President C ...
seized power in a bloodless coup. Conté assumed the role of president, with Traoré serving as prime minister until December.
Conté immediately denounced the previous regime's record on human rights
Human rights are Morality, moral principles or Social norm, normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for ce ...
, released 250 political prisoners and encouraged approximately 200,000 more to return from exile. He also made explicit the turn away from socialism, but this did little to alleviate poverty and the country showed no immediate signs of moving towards democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκÏαÏία, dÄmokratÃa, ''dÄmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose gov ...
.
In 1992, Conté announced a return to civilian rule, with a presidential poll in 1993 followed by elections to parliament in 1995 (in which his party â the Party of Unity and Progress
The Unity and Progress Party (french: Parti de l'Unité et du Progrès, PUP) is a political party in Guinea. It was the ruling party during the long rule of President Lansana Conté. In terms of ideology, the PUP advocates the unity of Guineans a ...
â won 71 of 114 seats.) Despite his stated commitment to democracy, Conté's grip on power remained tight. In September 2001 the opposition leader Alpha Condé
Alpha Condé (N'Ko: ; born 4 March 1938) is a Guinean politician who served as the fourth president of Guinea from 2010 to 2021.
Condé spent decades in opposition to a succession of regimes in Guinea, unsuccessfully running against President La ...
was imprisoned for endangering state security, though he was pardoned 8 months later. He subsequently spent a period of exile in France.
In 2001 Conté organized and won a referendum to lengthen the presidential term and in 2003 begun his third term after elections were boycotted by the opposition. In January 2005, Conté survived a suspected assassination attempt while making a rare public appearance in the capital Conakry
Conakry (; ; sus, KÉnakiri; Nâko: ßßߣßßßßß«, Fula: ''Konaakiri'' ð¤ð¤®ð¤²ð¤¢ð¥ð¤³ð¤ð¤ªð¤) is the capital and largest city of Guinea. A port city, it serves as the economic, financial and cultural centre of Guinea. Its p ...
. His opponents claimed that he was a "tired dictator" whose departure was inevitable, whereas his supporters believed that he was winning a battle with dissidents. Guinea still faces very real problems and according to ''Foreign Policy
A State (polity), state's foreign policy or external policy (as opposed to internal or domestic policy) is its objectives and activities in relation to its interactions with other states, unions, and other political entities, whether bilaterall ...
'' is in danger of becoming a failed state
A failed state is a political body that has disintegrated to a point where basic conditions and responsibilities of a sovereign government no longer function properly (see also fragile state and state collapse). A state can also fail if the go ...
.
In 2000 Guinea became embroiled in the instability which had long blighted the rest of West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
as rebels crossed the borders with Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to LiberiaâSierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
and Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
and it seemed for a time that the country was headed for civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. Conté blamed neighbouring leaders for coveting Guinea's natural resources, though these claims were strenuously denied. In 2003 Guinea agreed plans with her neighbours to tackle the insurgents. In 2007 there were big protests against the government, resulting in the appointment of a new prime minister.
Conté's death and the 2008 coup d'état
In acoup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
several days following Touré's death, Lansana Conté
Lansana Conté (30 November 1934 â 22 December 2008
became the President. The constitution and parliament were suspended and a committee for national recovery was established. Conté remained in power until his death on 22 December 2008.
In several hours following his death, Moussa Dadis Camara
Captain Moussa Dadis Camara (; born 1 January 1964), now called Moïse Dadis Camara (),''Le Populaire'', , N°3232, 31 August 2010, p. 2 is an ex-officer of the Guinean army who served as the President of Guinea from 23 December 2008 to 15 Ja ...
seized control of Guinea as the head of a junta
Junta may refer to:
Government and military
* Junta (governing body) (from Spanish), the name of various historical and current governments and governing institutions, including civil ones
** Military junta, one form of junta, government led by ...
. On 28 September 2009, the junta ordered its soldiers to attack people who had gathered to protest Camara's presumed candidacy in the upcoming presidential elections. The soldiers went on a rampage of rape, mutilation, and murder.
On 3 December 2009, an aide shot Camara during a dispute about the rampage of September 2009. Camara went to Morocco for medical care. Vice-President (and defense minister) Sékouba Konaté
General Sékouba Konaté ( nqo, ßßßßßß ßß߬ߣß߬ßß; born 6 June 1964) is an officer of the Guinean army who formerly served as the vice president of its military junta, the National Council for Democracy and Development. After attend ...
flew back from Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, ÙÙبÙÙÙاÙ, translit=lubnÄn, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
to run the country in Camara's absence.
On 12 January 2010 Camara was flown from Morocco to Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, ð¤ð¤µð¤ªð¤³ð¤ð¤²ð¤¢ ð¤ð¤¢ð¤§ð¤®, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
. After meeting in Ouagadougou
Ouagadougou ( , , ) is the capital and largest city of Burkina Faso and the administrative, communications, cultural, and economic centre of the nation. It is also the country's largest city, with a population of 2,415,266 in 2019. The city's n ...
on 13 and 14 January, Camara, Konaté and Blaise Compaoré
Blaise Compaoré (born 3 February 1951)''Profiles of People in Power: The World's Government Leaders'' (2003), page 76â77.
, President of Burkina Faso, produced a formal statement of twelve principles promising a return of Guinea to civilian rule within six months. It was agreed that the military would not contest the forthcoming elections, and Camara would continue his convalescence outside Guinea. On 21 January 2010 the military junta appointed Jean-Marie Doré
Jean-Marie Doré (12 June 1938 â 29 January 2016) was a Guinean politician who was the Prime Minister of Guinea from January 2010 until December 2010. Doré, who was the President of the Union for the Progress of Guinea (UPG), was an oppositi ...
as Prime Minister of a six-month transition government, leading up to elections.
The presidential election was set to take place on 27 June and 18 July 2010,Guinea to hold presidential elections in six months _English_Xinhua. News.xinhuanet.com (16 January 2010). Retrieved on 28 June 2011. it was held as being the first free and fair election since independence in 1958. The first round took place normally on 27 June 2010 with ex Prime Minister
Cellou Dalein Diallo
Cellou Dalein Diallo (3 February 1952
, Xinhua, 14 December 2004 .) is a
online
Civil war fears in Guinea
''BBC News''. October 23, 2000.
Guinea head blames neighbours
''BBC News''. January 6, 2001.
Stopping Guineaâs slide
Chancen und Risiken von NGOs â Die Gewerkschaften in Guinea während der Unruhen 2007
â EPU Research Papers: Issue 03/07, Stadtschlaining 2007 * André R. Lewin
Sékou Touréâs âNoâ
''African Geopolitics.'' 2005.
Bad government, bad neighbour
''The Economist''. July 21, 2005.
* {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Guinea Guinea (colonial)
, Xinhua, 14 December 2004 .) is a
Alpha Condé
Alpha Condé (N'Ko: ; born 4 March 1938) is a Guinean politician who served as the fourth president of Guinea from 2010 to 2021.
Condé spent decades in opposition to a succession of regimes in Guinea, unsuccessfully running against President La ...
emerging as the two runners-up for the second round.
However, due to allegations of electoral fraud, the second round of the election was postponed until 19 September 2010. A delay until 10 October was announced by the electoral commission (CENI), subject to approval by Sékouba Konaté
General Sékouba Konaté ( nqo, ßßßßßß ßß߬ߣß߬ßß; born 6 June 1964) is an officer of the Guinean army who formerly served as the vice president of its military junta, the National Council for Democracy and Development. After attend ...
. Yet another delay until 24 October was announced in early October. Elections were finally held on 7 November. Voter turnout was high, and the elections went relatively smoothly.
16 November 2010, Alpha Condé
Alpha Condé (N'Ko: ; born 4 March 1938) is a Guinean politician who served as the fourth president of Guinea from 2010 to 2021.
Condé spent decades in opposition to a succession of regimes in Guinea, unsuccessfully running against President La ...
, the leader of the opposition party Rally of the Guinean People
The Rally of the Guinean People (french: Rassemblement du Peuple Guinéen, sometimes translated as ''Guinean People's Assembly''; RPG) is a political party in Guinea. The RPG was the ruling party in the country from 2010 to 2021 and was recently ...
(RGP), was officially declared the winner of a 7 November run-off in Guinea's presidential election. He had promised to reform the security sector and review mining contracts if elected.
On the night of 18 July 2011, President Condé's residence was attacked in an attempted coup. The attack included a fierce firefight and rocket propelled grenades. The president was unharmed. Sixteen people have been charged with the attempted assassination. Most of those indicted are close associates of Konaté.
The National Assembly of Guinea
The unicameral ''Assemblée nationale'' or National Assembly is Guinea's legislative body. Since the country's birth in 1958, it has experienced political turmoil, and elections have been called at irregular intervals, and only since 1995 have th ...
, the country's legislative body, has not met since 2008 when it was dissolved after the military coup in December. Elections
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operate ...
have been postponed many times since 2007 and, most recently, were scheduled for 8 July 2012. In April 2012, President Condé postponed the elections indefinitely, citing the need to ensure that they were "transparent and democratic".
In February 2013, a plane carrying the head of the Guinean armed forces, General Kelefa Diallo, and nine other military officials, crashed on its way to the Liberian capital, Monrovia
Monrovia () is the capital city of the West African country of Liberia. Founded in 1822, it is located on Cape Mesurado on the Atlantic coast and as of the 2008 census had 1,010,970 residents, home to 29% of Liberiaâs total population. As the ...
.
2013 protests
The opposition coalition withdrew from the electoral process in mid-February, mainly due to President Conde's insistence on using a suspicious South African firm Waymark Infotech to draw up the registered voter list. In late February 2013, political violence erupted in Guinea after protesters took to the streets to voice their concerns over the transparency of the upcoming May 2013 elections. The demonstrations were fueled by the opposition coalition's decision to step down from the electoral process in protest at the lack of transparency in the preparations for elections. Nine people were killed during the protests, while around 220 were injured, and many of the deaths and injuries were caused by security forces using live fire on protesters. The political violence also led to inter-ethnic clashes between theFula
Fula may refer to:
*Fula people (or Fulani, FulÉe)
*Fula language (or Pulaar, Fulfulde, Fulani)
**The Fula variety known as the Pulaar language
**The Fula variety known as the Pular language
**The Fula variety known as Maasina Fulfulde
*Al-Fula ...
and Malinke
Maninka (also known as Malinke), or more precisely Eastern Maninka, is the name of several closely related languages and dialects of the southeastern Manding subgroup of the Mande language family. It is the mother tongue of the Malinké peop ...
peoples, the latter forming the base of support for President Condé, with the former consisting mainly of the opposition.
On 26 March 2013 the opposition party backed out of the negotiation with the government over the upcoming 12 May election. The opposition claimed that the government has not respected them, and have not kept any promises they agreed to. This is expected to lead to more protests and fighting in the streets of Guinea.
2014 Ebola outbreak
Beginning in July 2014, Guinea suffered the most severe recordedoutbreak
In epidemiology, an outbreak is a sudden increase in occurrences of a disease when cases are in excess of normal expectancy for the location or season. It may affect a small and localized group or impact upon thousands of people across an entire ...
of Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becom ...
in history, which rapidly spread to neighbouring countries Liberia and Sierra Leone. The epidemic was over by June 2016.
2020 elections
In October 2020, president Alpha Condé wonpresidential elections
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The pr ...
. Condé had been in power since 2010 and he won the third term. Opposition did not accept the results because of allegations of fraud. The president said a constitutional referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
in March 2020 allowed him to run despite a two-term limit. After the election there were violent protests across the country.
Coup d'état 2021
On September 5, 2021, Alpha Condé was deposed by the military.National Committee of Reconciliation and Development
The National Committee of Reconciliation and Development (french: Comité national du rassemblement et du développement, CNRD) is the ruling Military junta, military junta of Guinea since 5 September 2021.
Historical background
The CNRD seized ...
headed by Mamady Doumbouya
Mamady Doumbouya (N'Ko: , born 4 March 1980) is a Guinean military officer serving as the interim president of Guinea since 1 October 2021. Doumbouya led a coup d'état on 5 September 2021 that overthrew the previous president, Alpha Condé. He ...
, Guinea's new interim president, took power. On 1 October 2021, Colonel Mamady Doumbouya, who led the last month's coup in Guinea, was sworn in as interim president of Guinea.
See also
*List of heads of government of Guinea
This article lists the prime ministers of Guinea, since the establishment of the office of Prime Minister in 1972.
List
Key
;''Political parties''
*
*
*
*
;''Other factions''
*
*
Officeholders
Notes
Timeline
See also
* Guinea
** List ...
* List of heads of state of Guinea
* Politics of Guinea
Politics of Guinea takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Guinea is both head of state and head of government of Guinea. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legisla ...
* Conakry history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
and timeline
A timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale representi ...
General:
* History of West Africa
The history of West Africa has been divided into its prehistory, the Iron Age in Africa, the major polities flourishing, the colonial period, and finally the post-independence era, in which the current nations were formed. West Africa is west o ...
Further reading
* Chafer, Tony. ''The End of Empire in French West Africa: France's Successful Decolonization''. Berg (2002). * Davidson, Basil. "Guinea, Past And Present" ''History Today'' (June 1959) 9#6 pp 392â398. Covers 1800 to 1959. * O'Toole, Thomas and Bah-Lalya, Ibrahima. ''Historical Dictionary of Guinea'' (3rd ed. Scarecrow Press. 1995)online
References
External links
* Elizabeth BluntCivil war fears in Guinea
''BBC News''. October 23, 2000.
Guinea head blames neighbours
''BBC News''. January 6, 2001.
Stopping Guineaâs slide
International Crisis Group
The International Crisis Group (ICG; also known as the Crisis Group) is a transnational non-profit, non-governmental organisation founded in 1995. It is a think tank, used by policymakers and academics, performing research and analysis on global ...
, Africa Report No. 94. June 14, 2005.
* Adama SowChancen und Risiken von NGOs â Die Gewerkschaften in Guinea während der Unruhen 2007
â EPU Research Papers: Issue 03/07, Stadtschlaining 2007 * André R. Lewin
Sékou Touréâs âNoâ
''African Geopolitics.'' 2005.
Bad government, bad neighbour
''The Economist''. July 21, 2005.
* {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Guinea Guinea (colonial)
Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, ð¤ð¤ð¤²ð¤«, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ßß߬ߣßß«, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...