History Of Charlottetown on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
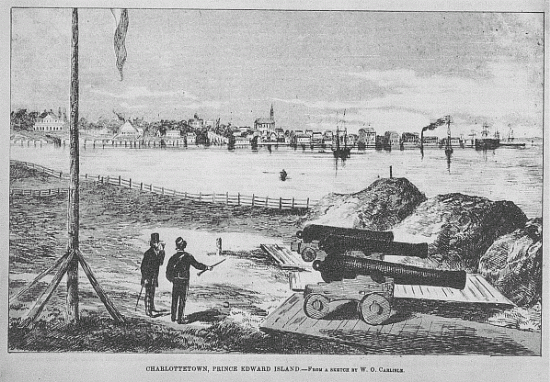 The History of Charlottetown can be traced back to the original French military settlement established on the site in 1720. Over the years
The History of Charlottetown can be traced back to the original French military settlement established on the site in 1720. Over the years
Historical Biographies, Nova Scotia: Charles des Champs de BoishĂŠbert (1729-1797)
/ref> In August 1758, at the height of the
 Between September 1 and September 7, 1864, Charlottetown hosted what is now termed the
Between September 1 and September 7, 1864, Charlottetown hosted what is now termed the
 Religion played a central role in the development of Charlottetown's institutions with non-denominational (i.e.
Religion played a central role in the development of Charlottetown's institutions with non-denominational (i.e.  In 1959, the suburban village of Spring Park was amalgamated into the city, extending the city's northern boundary from Kirkwood Drive to Hermitage Creek and included the campus of St. Dunstan's University.
To commemorate the centennial of the
In 1959, the suburban village of Spring Park was amalgamated into the city, extending the city's northern boundary from Kirkwood Drive to Hermitage Creek and included the campus of St. Dunstan's University.
To commemorate the centennial of the  Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, Charlottetown witnessed increased commercial office and retail development. A waterfront hotel and convention centre was completed in 1982 and helped to encourage diversification and renewal in the area, leading to several residential complexes and downtown shopping facilities. The abandonment of rail service in the province by
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, Charlottetown witnessed increased commercial office and retail development. A waterfront hotel and convention centre was completed in 1982 and helped to encourage diversification and renewal in the area, leading to several residential complexes and downtown shopping facilities. The abandonment of rail service in the province by
 The History of Charlottetown can be traced back to the original French military settlement established on the site in 1720. Over the years
The History of Charlottetown can be traced back to the original French military settlement established on the site in 1720. Over the years Charlottetown
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island, and the county seat of Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte, Charlottetown was an unincorporated town until it was incorporated as a city in ...
has grown to become the largest and most important city on Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has seve ...
.
18th century
The first European settlers in the area wereFrench
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
; personnel from Fortress Louisbourg
The Fortress of Louisbourg (french: Forteresse de Louisbourg) is a National Historic Site and the location of a one-quarter partial reconstruction of an 18th-century French fortress at Louisbourg on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia. Its two sie ...
founded a settlement in 1720 named '' Port-la-Joye'' on the southwestern part of the harbour opposite the present-day city. This settlement was led by Michel Haché-Gallant, who used his sloop to ferry Acadian settlers from Louisbourg.
During King George's War
King George's War (1744–1748) is the name given to the military operations in North America that formed part of the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748). It was the third of the four French and Indian Wars. It took place primarily in t ...
, the British had taken over the island. French officer Jean-Baptiste Nicolas Roch de Ramezay
Jean-Baptiste Nicolas Roch, ''Seigneur de Ramezay'', (4 September 1708, in Montreal, New France – 7 May 1777, in Blaye, France; officer of the marines and colonial administrator for New France during the 18th century. Joining at age 11, as an ...
sent 500 men to attack the British troops in the Battle at Port-la-Joye
The Battle at Port-la-Joye (also known as the ''Port-la-Joye Massacre'') was a battle in King George's War that took place with British against French troops and Mi'kmaq militia on the banks of present-day Hillsborough River, Prince Edward Is ...
. The French were successful in killing or taking prisoner forty British troops./ref> In August 1758, at the height of the
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
, a British fleet took control of the settlement and the rest of the island, promptly deporting those French settlers that they could find (this being fully three years after the original Acadian Expulsion
The Expulsion of the Acadians, also known as the Great Upheaval, the Great Expulsion, the Great Deportation, and the Deportation of the Acadians (french: Le Grand Dérangement or ), was the forced removal, by the British, of the Acadian pe ...
in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
). British forces built Fort Amherst
Fort Amherst, in Medway, South East England, was constructed in 1756 at the southern end of the Brompton lines of defence to protect the southeastern approaches to Chatham Dockyard and the River Medway against a French invasion. Fort Amherst ...
near the site of the abandoned Port-la-Joye settlement to protect the entrance to the harbour.
Charlottetown was selected as the site for the county seat of Queens County in the colonial survey of 1764 by Captain Samuel Holland
Samuel Johannes Holland (1728 – 28 December 1801) was a Dutch-born Royal Engineer and first Surveyor General of British North America.
Life in the Netherlands
Holland was born in 1728 in Deventer, the Netherlands. He was baptised on 22 S ...
of the Royal Engineers. A year later, Charlottetown was made the colonial capital of St. John's Island. Further surveys conducted between 1768–1771 established the street grid and public squares which can be seen in the city's historic district. The town was named in honour of Queen Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Sophia Charlotte; 19 May 1744 – 17 November 1818) was Queen of Great Britain and of Ireland as the wife of King George III from their marriage on 8 September 1761 until the union of the two kingdoms ...
, consort __NOTOC__
Consort may refer to:
Music
* "The Consort" (Rufus Wainwright song), from the 2000 album ''Poses''
* Consort of instruments, term for instrumental ensembles
* Consort song (musical), a characteristic English song form, late 16th–earl ...
of King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
.
On November 17, 1775, the colony's new capital was ransacked by Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
-based privateers, participants in the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
. During the attack, the colonial seal was stolen and several prisoners, including Phillips Callbeck
Phillips Callbeck ( – January 28, 1790) was a merchant, lawyer and political figure in St. John's Island (later Prince Edward Island). He served as administrator for the island from 1775 to 1780.
Callbeck is believed to have been born and educ ...
and Thomas Wright, were taken to Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As part of the Boston metropolitan area, the cities population of the 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the fourth most populous city in the state, behind Boston, ...
and later released.
In 1793, land had been set aside by Governor Fanning on the western limits of the community for use by the "Administrator of Government" (the Governor), and as such it became known informally as "Fanning's Bank" or just "Fanning Bank".
On November 29, 1798, St. John's Island was renamed to Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has seve ...
in honour of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn
Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn, (Edward Augustus; 2 November 1767 – 23 January 1820) was the fourth son and fifth child of King George III. His only legitimate child became Queen Victoria.
Prince Edward was created Duke of Kent an ...
who was the Commander-in-Chief, North America
The office of Commander-in-Chief, North America was a military position of the British Army. Established in 1755 in the early years of the Seven Years' War, holders of the post were generally responsible for land-based military personnel and ac ...
.
19th century
In 1805, the local British garrison constructed a harbour defence called "Fort Edward" to the west of the capital's waterfront and the "Prince Edward Battery" manned this facility. In 1835, "Government House
Government House is the name of many of the official residences of governors-general, governors and lieutenant-governors in the Commonwealth and the remaining colonies of the British Empire. The name is also used in some other countries.
Gover ...
" was constructed at Fanning Bank as a residence for the colony's Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
. Today, it serves as the official residence for the Lieutenant Governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ...
.
Between 1843 and 1847, a new legislative building was constructed in the community. Named " Province House", the completion of this structure was an important milestone in the history of the capital and it is still in use today as the provincial legislature and is currently the second-oldest legislative seat in Canada.
On April 17, 1855, Charlottetown was incorporated as a city, holding its first council meeting on August 11 that year. The community had 6,500 residents at the time of incorporation.
Charlottetown Conference
The Charlottetown Conference (Canada's Conference) was held in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island for representatives from colonies of British North America to discuss Canadian Confederation. The conference took place between September 1 thro ...
. Although many of the meetings and negotiations which would lead to Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Canada, Dom ...
were held in Province House, various social events spilled over into the surrounding community.
On June 14, 1873 the "Government House Farm" at Fanning Bank was designated a municipal park, named Victoria Park Victoria Park may refer to:
Places Australia
* Victoria Park Nature Reserve, a protected area in Northern Rivers region, New South Wales
* Victoria Park, Adelaide, a park and racecourse
* Victoria Park, Brisbane, a public park and former golf ...
in honour of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
. Prince Edward Island entered Confederation on July 1, 1873.
Aside from being the seat of colonial government, the community came to be noted during the early nineteenth century for shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
and its lumber industry as well as being a fishing port. The shipbuilding industry declined in the latter part of the nineteenth century. In August 1874, the Prince Edward Island Railway
The Prince Edward Island Railway (PEIR) was a historic Canadian railway in Prince Edward Island (PEI). The railway ran tip-to-tip on the island, from Tignish in the west to Elmira in the east, with major spurs serving Borden-Carleton's train fer ...
opened its main line between Charlottetown and Summerside. The railway, along with the shipping industry, would continue to drive industrial development on the waterfront for several decades to come.
The province's first health care facility, the Charlottetown Hospital
The Charlottetown Hospital is a former acute care hospital that was located in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island. It was the first public hospital established in the province.
The facility was established in 1879 under the leadership of Peter ...
, was opened by the Diocese of Charlottetown
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Charlottetown ( la, Dioecesis Carolinapolitana) is a diocese of the Catholic Church in Canada. It is a suffragan diocese comprising the entire province of Prince Edward Island.
Originally carved from the Archdiocese ...
in 1879, which was followed by the publicly operated Prince Edward Island Hospital
The Prince Edward Island Hospital is a former acute care hospital that was located in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island. It was the first public general hospital established in the province and the largest such facility throughout its history.
...
in 1884.
In 1885 the municipality saw its status upgraded to become a city.
20th century
 Religion played a central role in the development of Charlottetown's institutions with non-denominational (i.e.
Religion played a central role in the development of Charlottetown's institutions with non-denominational (i.e. Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
) and Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
public schools (Catholic Queen Square, Notre Dame, and St. Josephs. vs Protestant West Kent and Prince Street), hospitals (Prince Edward Island Hospital vs. Charlottetown Hospital), and post-secondary institutions (Prince of Wales College
Prince of Wales College (PWC) is a former university college, which was located in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada. PWC merged with St. Dunstan's University in 1969 to form the University of Prince Edward Island.
PWC traces its hist ...
vs. St. Dunstan's University :''St. Andrew's College, Prince Edward Island'' redirects to here.
St. Dunstan's University (SDU) is a former university which was located on the northern outskirts of Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada. SDU merged with Prince of Wales C ...
) being instituted. St. Dunstan's was originally developed as a seminary for training priests, and the Maritime Christian College was founded in 1960 to train preachers for the Christian churches and churches of Christ
The group of churches known as the Christian Churches and Churches of Christ is a fellowship of congregations within the Restoration Movement (also known as the Stone-Campbell Movement and the Reformation of the 19th Century) that have no forma ...
in Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has seve ...
and the Maritime Provinces
The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% of Ca ...
.
As with most communities in North America, the automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, pe ...
shaped Charlottetown's development in the latter half of the twentieth century, when outlying farms in rural areas of Brighton, Spring Park, and Parkdale saw increased housing developments.
The Charlottetown airfield in the nearby rural community of Sherwood
Sherwood may refer to:
Places Australia
*Sherwood, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane
*Sherwood, South Australia, a locality
*Shire of Sherwood, a former local government area of Queensland
*Electoral district of Sherwood, an electoral district from ...
was upgraded as part of the British Commonwealth Air Training Plan
The British Commonwealth Air Training Plan (BCATP), or Empire Air Training Scheme (EATS) often referred to as simply "The Plan", was a massive, joint military aircrew training program created by the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and New Zea ...
and operated for the duration of World War II as RCAF Station Charlottetown
RCAF Station Charlottetown was a Royal Canadian Air Force station located in Sherwood, Prince Edward Island. Today's Charlottetown Airport maintains a remnant of the airfield's runways near its general aviation terminal, but all buildings and most ...
, in conjunction with RCAF Station Mount Pleasant
RCAF Station Mount Pleasant was a Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) station in Mount Pleasant, Prince Edward Island, Mount Pleasant, Prince Edward Island, Canada. Two of its runways remain in use by members of the Experimental Aircraft Associatio ...
and RCAF Station Summerside
Canadian Forces Base Summerside (CFB Summerside) was an air force base located in St. Eleanors, Prince Edward Island, Canada, now part of the city of Summerside.
RCAF Station Summerside World War II
The airfield was constructed by the Royal Ca ...
. After the war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
the airfield was designated Charlottetown Airport
Charlottetown Airport is located north of Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada. The airport is currently run by the Charlottetown Airport Authority, is owned by Transport Canada and forms part of the National Airports System.
The airp ...
. Charlottetown's shipyards also saw extensive use during World War II, being used for refits and upgrades to numerous Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the Navy, naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack s ...
warships. Further post-war development saw residential properties continue to expand in adjacent outlying areas, particularly in the neighbouring farming communities of Sherwood, West Royalty, and East Royalty.
 In 1959, the suburban village of Spring Park was amalgamated into the city, extending the city's northern boundary from Kirkwood Drive to Hermitage Creek and included the campus of St. Dunstan's University.
To commemorate the centennial of the
In 1959, the suburban village of Spring Park was amalgamated into the city, extending the city's northern boundary from Kirkwood Drive to Hermitage Creek and included the campus of St. Dunstan's University.
To commemorate the centennial of the Charlottetown Conference
The Charlottetown Conference (Canada's Conference) was held in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island for representatives from colonies of British North America to discuss Canadian Confederation. The conference took place between September 1 thro ...
, the ten provincial governments and the Government of Canada contributed to a national monument to the "Fathers of Confederation". The Confederation Centre of the Arts
Confederation Centre of the Arts (french: Centre des arts de la Confédération) is a cultural centre dedicated to the visual and performing arts located in the city of Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada.
History
Construction of Confeder ...
, which opened in 1964, as a gift to the residents of Prince Edward Island. The centre contains the Confederation Centre Art Gallery
The Confederation Centre Art Gallery (CCAG; french: Musée d’art du Centre de la Confédération) is an art museum that forms a part of the Confederation Centre of the Arts in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada. The art museum pavilion f ...
, a public library, and a mainstage theatre which has played to the Charlottetown Festival
The Charlottetown Festival is a seasonal Canadian musical theatre festival which runs from late May to mid-October every year since 1965.
Named after its host city Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island and its Charlottetown Conference, since its inc ...
every summer since.
In the 1960s, new public schools were constructed in the community, and in 1969 the city became home to the amalgamated University of Prince Edward Island
The University of Prince Edward Island (UPEI) is a public university in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada, and the only university in the province. Founded in 1969, the enabling legislation is the ''University Act, R.S.P.E.I 2000.''
H ...
(UPEI), located on the campus of the former St. Dunstan's University. Together with the federal Department of Agriculture and Agri-Food's Charlottetown Experimental Farm (also known as ''Ravenwood Farm''), these properties comprise a large green space surrounded by the city. The Prince of Wales College downtown campus became part of a new provincial community college system named Holland College
Holland College is the provincial community college for the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island (PEI). It is named after the British Army engineer and surveyor Captain Samuel Holland.
History
It was formed by the Government of Prince ...
, in honour of the island's famous surveyor. The P.E.I. Comprehensive Development Plan in the late 1960s greatly contributed to the expansion of the provincial government in Charlottetown for the next decade.
The Queen Elizabeth Hospital opened in 1982. In 1983, the national headquarters of the federal Department of Veterans Affairs
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is a Cabinet-level executive branch department of the federal government charged with providing life-long healthcare services to eligible military veterans at the 170 VA medical centers and ...
was moved to Charlottetown as part of a nationwide federal government decentralization programme. In 1986, UPEI saw further expansion with the opening of the Atlantic Veterinary College
The Atlantic Veterinary College (AVC) is an accredited and globally recognized veterinary school in the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine at University of Prince Edward Island, located in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada.
History
AVC ...
.
 Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, Charlottetown witnessed increased commercial office and retail development. A waterfront hotel and convention centre was completed in 1982 and helped to encourage diversification and renewal in the area, leading to several residential complexes and downtown shopping facilities. The abandonment of rail service in the province by
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, Charlottetown witnessed increased commercial office and retail development. A waterfront hotel and convention centre was completed in 1982 and helped to encourage diversification and renewal in the area, leading to several residential complexes and downtown shopping facilities. The abandonment of rail service in the province by CN Rail
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I railroad, Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern United States, M ...
in December 1989 led to the railway and industrial lands at the east end of the waterfront being transformed into parks and cultural attractions.
The late 1990s and 2000s witnessed a change in the retail landscape with the opening of big box stores on the site of former traditional shopping centres and in new developments in the northern suburbs, particularly the neighbourhood of West Royalty, which is a key road junction.
In 1995 Charlottetown underwent municipal amalgamation. The present city was created by merging Charlottetown with Sherwood
Sherwood may refer to:
Places Australia
*Sherwood, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane
*Sherwood, South Australia, a locality
*Shire of Sherwood, a former local government area of Queensland
*Electoral district of Sherwood, an electoral district from ...
, Parkdale, Winsloe, West Royalty, and East Royalty. Since amalgamation, the city occupies most of Queens Royalty and part of the townships Lot 33 and Lot 34.
The central business district continues to undergo incremental expansion as government and private sector office space is constructed and new institutional space is built or retrofitted, however retail space in the CBD has suffered as a result of outlying big box retail construction in recent years.
See also
*History of Prince Edward Island
The history of Prince Edward Island covers several historical periods, from the pre-Columbian era to the present day. Prior to the arrival of Europeans, the island formed a part of Mi'kma'ki, the lands of the Mi'kmaq people. The island was first ...
*List of historic places in Charlottetown
This article is a list of historic places in Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island entered on the Canadian Register of Historic Places, whether they are federal, provincial, or municipal.
List of historic places
...
References
{{History of Canada navbox History of Charlottetown