
The history of Asia can be seen as the collective history of several distinct peripheral coastal regions such as
East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
,
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
,
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
and the
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
linked by the interior mass of the Eurasian
steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate gras ...
. See
History of the Middle East and
History of the Indian Subcontinent for further details.
The coastal periphery was the home to some of the world's earliest known civilizations and religions, with each of the three regions developing early civilizations around fertile river valleys. These valleys were fertile because the soil there was rich and could bear many root crops. The civilizations in
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
,
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
shared many similarities and likely exchanged technologies and ideas such as mathematics and the wheel. Other notions such as that of writing likely developed individually in each area. Cities, states, and then empires developed in these lowlands.
The steppe region had long been inhabited by mounted nomads, and from the central steppes, they could reach all areas of the Asian continent. The northern part of the continent, covering much of
Siberia was also inaccessible to the steppe nomads due to the dense forests and the
tundra. These areas in Siberia were very sparsely populated.
The centre and periphery were kept separate by mountains and deserts. The
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
,
Himalaya,
Karakum Desert
The Karakum Desert, also spelled Kara-Kum and Gara-Gum ( tk, Garagum, ; rus, Караку́мы, Karakumy, kərɐˈkumɨ), is a desert in Central Asia. Its name in Turkic languages means "black sand": "" means sand; "" is a contraction of : " ...
, and
Gobi Desert formed barriers that the steppe horsemen could only cross with difficulty. While technologically and culturally the city dwellers were more advanced, they could do little militarily to defend against the mounted hordes of the steppe. However, the lowlands did not have enough open grasslands to support a large horsebound force. Thus the nomads who conquered states in the Middle East were soon forced to adapt to the local societies.
The
spread of Islam waved the
Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
and the
Timurid Renaissance, which later influenced the age of
Islamic gunpowder empires.
Asia's history features major developments seen in other parts of the world, as well as events that have affected those other regions. These include the trade of the
Silk Road, which spread cultures, languages, religions, and diseases throughout Afro-Eurasian trade. Another major advancement was the innovation of
gunpowder in medieval China, later developed by the Gunpowder empires, mainly by the
Mughals and
Safavids, which led to advanced warfare through the use of guns.
Prehistory

A report by archaeologist Rakesh Tewari on Lahuradewa,
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
shows new C14 datings that range between 9000 and 8000 BCE associated with rice, making Lahuradewa the earliest Neolithic site in entire South Asia.
[
] Settled life emerged on the subcontinent in the western margins of the
Indus River alluvium approximately 9,000 years ago, evolving gradually into the
Indus Valley Civilisation of the third millennium BCE.
Göbekli Tepe is a
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
site in the
Southeastern Anatolia Region of
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
. Dated to the
Pre-Pottery Neolithic, between 9500 and 8000 BCE, the site comprises a number of large circular structures supported by massive stone pillars – the world's oldest known
megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
s.
The
prehistoric Beifudi site near Yixian in
Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
Province, China, contains relics of a culture contemporaneous with the
Cishan and
Xinglongwa cultures of about 8000–7000 BCE, neolithic cultures east of the
Taihang Mountains, filling in an archaeological gap between the two Northern Chinese cultures. The total excavated area is more than 1,200 square meters and the collection of neolithic findings at the site consists of two phases.
[
]
Around 5500 BCE the
Halafian
The Halaf culture is a prehistoric period which lasted between about 6100 BC and 5100 BC. The period is a continuous development out of the earlier Pottery Neolithic and is located primarily in the fertile valley of the Khabur River (Nahr al-K ...
culture appeared in
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
,
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
,
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
,
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, and northern
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, based upon dryland agriculture.
In southern Mesopotamia were the alluvial plains of
Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
and
Elam. Since there was little rainfall,
irrigation systems were necessary. The
Ubaid culture flourished from 5500 BCE.
Ancient
Bronze Age

The
Chalcolithic period (or Copper Age) began about 4500 BCE, then the
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
began about 3500 BCE, replacing the Neolithic cultures.
The
Indus Valley civilization (IVC) was a Bronze Age civilization (3300–1300 BCE; mature period 2600–1900 BCE) which was centered mostly in the western part of the Indian Subcontinent; it is considered that an early form of Hinduism was performed during this civilization. Some of the great cities of this civilization include
Harappa and
Mohenjo-daro, which had a high level of town planning and arts. The cause of the destruction of these regions around 1700 BCE is debatable, although evidence suggests it was caused by natural disasters (especially flooding). This era marks
Vedic period in India, which lasted from roughly 1500 to 500 BCE. During this period, the
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
language developed and the
Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute th ...
were written, epic hymns that told tales of gods and wars. This was the basis for the Vedic religion, which would eventually sophisticate and develop into
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
.
China and
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
were also centres of metalworking. Dating back to the Neolithic Age, the first bronze drums, called the Dong Son drums have been uncovered in and around the Red River Delta regions of Vietnam and Southern China. These relate to the prehistoric Dong Son Culture of Vietnam.
Song Da bronze drum's surface, Dong Son culture, Vietnam
In Ban Chiang, Thailand (Southeast Asia), bronze artifacts have been discovered dating to 2100 BCE.
In Nyaunggan, Burma bronze tools have been excavated along with ceramics and stone artifacts. Dating is still currently broad (3500–500 BCE).
Iron and Axial Age
The Iron Age saw the widespread use of iron tools, weaponry, and armor throughout the major civilizations of Asia.
Middle East

The
Achaemenid dynasty of the
Persian Empire, founded by
Cyrus the Great, ruled an area from
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
and
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
to the
Indus River and Central Asia during the 6th to 4th centuries BCE. Persian politics included a tolerance for other cultures, a highly
centralized government
A centralized government (also united government) is one in which both executive and legislative power is concentrated centrally at the higher level as opposed to it being more distributed at various lower level governments. In a national conte ...
, and significant infrastructure developments. Later, in
Darius the Great's rule, the territories were integrated, a bureaucracy was developed, nobility were assigned military positions, tax collection was carefully organized, and spies were used to ensure the loyalty of regional officials. The primary religion of Persia at this time was
Zoroastrianism, developed by the philosopher
Zoroaster. It introduced an early form of
monotheism to the area. The religion banned animal sacrifice and the use of intoxicants in rituals; and introduced the concept of spiritual salvation through personal moral action, an
end time, and both
general
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". O ...
and
Particular judgment with a
heaven or
hell. These concepts would heavily influence later emperors and the masses. More importantly, Zoroastrianism would be an important precursor for the
Abrahamic religions such as Christianity, Islam, or Judaism. The Persian Empire was successful in establishing peace and stability throughout the Middle East and were a major influence in art, politics (affecting Hellenistic leaders), and religion.
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
conquered this dynasty in the 4th century BCE, creating the brief
Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
. He was unable to establish stability and after his death, Persia broke into small, weak dynasties including the
Seleucid Empire, followed by the
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conqu ...
. By the end of the Classical age, Persia had been reconsolidated into the
Sassanid Empire, also known as the second Persian Empire.
The
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
would later control parts of Western Asia. The
Seleucid,
Parthian and
Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
dynasties of Persia dominated Western Asia for centuries.
India
The Maurya and Gupta empires are called the Golden Age of India and were marked by extensive inventions and discoveries in science, technology, art, religion, and philosophy that crystallized the elements of what is generally known as Indian culture. The religions of
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
, which began in Indian sub-continent, were an important influence on South, East and Southeast Asia.

By 600 BCE, India had been divided into 17 regional states that would occasionally feud amongst themselves. In 327 BCE,
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
came to India with a vision of conquering the whole world. He crossed northwestern India and created the province
Bactria but could not move further because his army wanted to go back to their family. Shortly prior, the soldier
Chandragupta Maurya began to take control of the Ganges river and soon established the
Maurya Empire. The Maurya Empire (Sanskrit: मौर्य राजवंश, Maurya Rājavaṃśa) was the geographically extensive and powerful empire in ancient India, ruled by the Mauryan dynasty from 321 to 185 BCE. It was one of the world's largest empires in its time, stretching to the
Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
in the north, what is now
Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
in the east, probably beyond modern
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
in the west, and annexing
Balochistan and much of what is now
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, at its greatest extent. South of Mauryan empire was the
Tamilakam an independent country dominated by three dynasties, the
Pandyans,
Cholas and
Cheras. The government established by Chandragupta was led by an autocratic king, who primarily relied on the military to assert his power. It also applied the use of a bureaucracy and even sponsored a postal service. Chandragupta's grandson,
Ashoka, greatly extended the empire by conquering most of modern-day India (save for the southern tip). He eventually converted to Buddhism, though, and began a peaceful life where he promoted the religion as well as humane methods throughout India. The Maurya Empire would disintegrate soon after Ashoka's death and was conquered by the Kushan invaders from the northwest, establishing the
Kushan Empire. Their conversion to Buddhism caused the religion to be associated with foreigners and therefore a decline in its popularity occurred.
The Kushan Empire would fall apart by 220 CE, creating more political turmoil in India. Then in 320, the
Gupta Empire (Sanskrit: गुप्त राजवंश, Gupta Rājavanśha) was established and covered much of the Indian Subcontinent. Founded by
Maharaja Sri-Gupta, the dynasty was the model of a classical civilization. Gupta kings united the area primarily through negotiation of local leaders and families as well as strategical intermarriage. Their rule covered less land than the Maurya Empire, but established the greatest stability. In 535, the empire ended when India was overrun by the
Hunas.
Classical China
=Zhou dynasty
=
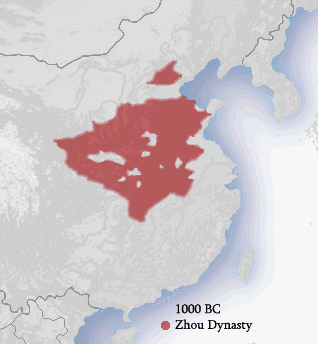
Since 1029 BCE, the
Zhou dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by th ...
( ), had existed in China and it would continue to until 258 BCE. The Zhou dynasty had been using a
feudal system
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structu ...
by giving power to local nobility and relying on their loyalty in order to control its large territory. As a result, the Chinese government at this time tended to be very decentralized and weak, and there was often little the emperor could do to resolve national issues. Nonetheless, the government was able to retain its position with the creation of the
Mandate of Heaven, which could establish an emperor as divinely chosen to rule. The Zhou additionally discouraged the
human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherei ...
of the preceding eras and unified the
Chinese language
Chinese (, especially when referring to written Chinese) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people (or approximately 16% of the ...
. Finally, the Zhou government encouraged settlers to move into the
Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
valley, thus creating the Chinese Middle Kingdom.
But by 500 BCE, its political stability began to decline due to repeated nomadic incursions and internal conflict derived from the fighting princes and families. This was lessened by the many philosophical movements, starting with the life of
Confucius. His philosophical writings (called
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a Religious Confucianism, religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, ...
) concerning the respect of elders and of the state would later be popularly used in the Han dynasty. Additionally,
Laozi's concepts of
Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
, including
yin and yang and the innate duality and balance of nature and the universe, became popular throughout this period. Nevertheless, the Zhou dynasty eventually disintegrated as the local nobles began to gain more power and their conflict devolved into the
Warring States period, from 402 to 201 BCE.
=Qin dynasty
=
One leader eventually came on top,
Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; 259–210 BC) was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of a unified China. Rather than maintain the title of " king" ( ''wáng'') borne by the previous Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Empero ...
(, ''Shǐ Huángdì''), who overthrew the last Zhou emperor and established the Qin dynasty. The
Qin dynasty (Chinese: 秦朝; pinyin: Qín Cháo) was the first ruling dynasty of Imperial China, lasting from 221 to 207 BCE. The new Emperor abolished the feudal system and directly appointed a bureaucracy that would rely on him for power. Huang's imperial forces crushed any regional resistance, and they furthered the Chinese empire by expanding down to the
South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Ph ...
and northern
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
. Greater organization brought a uniform tax system, a national census, regulated road building (and cart width), standard measurements, standard coinage, and an official written and spoken language. Further reforms included new irrigation projects, the encouragement of
silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from th ...
manufacturing, and (most famously) the beginning of the construction of the Great Wall of China—designed to keep out the nomadic raiders who'd constantly badger the Chinese people. However, Shi Huang was infamous for his tyranny, forcing laborers to build the Wall, ordering heavy taxes, and severely punishing all who opposed him. He oppressed Confucians and promoted
Legalism, the idea that people were inherently evil, and that a strong, forceful government was needed to control them. Legalism was infused with realistic, logical views and rejected the pleasures of educated conversation as frivolous. All of this made Shi Huang extremely unpopular with the people. As the Qin began to weaken, various factions began to fight for control of China.
=Han dynasty
=

The
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
(simplified Chinese: 汉朝; traditional Chinese: 漢朝; pinyin: Hàn Cháo; 206 BCE – 220 CE) was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms (220–265 CE). Spanning over four centuries, the period of the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history. One of the Han dynasty's greatest emperors,
Emperor Wu of Han, established a peace throughout China comparable to the
Pax Romana seen in the Mediterranean a hundred years later. To this day, China's majority ethnic group refers to itself as the "Han people". The Han dynasty was established when two peasants succeeded in rising up against Shi Huang's significantly weaker successor-son. The new Han government retained the centralization and bureaucracy of the Qin, but greatly reduced the repression seen before. They expanded their territory into
Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
,
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
, and
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, creating an even larger empire than the Qin.
The Han developed contacts with the Persian Empire in the Middle East and the Romans, through the
Silk Road, with which they were able to trade many commodities—primarily silk. Many ancient civilizations were influenced by the
Silk Road, which connected China,
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, the Middle East and Europe. Han emperors like Wu also promoted Confucianism as the national "religion" (although it is debated by theologians as to whether it is defined as such or as a philosophy). Shrines devoted to Confucius were built and Confucian philosophy was taught to all scholars who entered the Chinese bureaucracy. The bureaucracy was further improved with the introduction of an examination system that selected scholars of high merit. These bureaucrats were often upper-class people educated in special schools, but whose power was often checked by the lower-class brought into the bureaucracy through their skill. The Chinese imperial bureaucracy was very effective and highly respected by all in the realm and would last over 2,000 years. The Han government was highly organized and it commanded the military, judicial law (which used a system of courts and strict laws), agricultural production, the economy, and the general lives of its people. The government also promoted intellectual philosophy, scientific research, and detailed historical records.
However, despite all of this impressive stability, central power began to lose control by the turn of the
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
. As the Han dynasty declined, many factors continued to pummel it into submission until China was left in a state of chaos. By 100 CE, philosophical activity slowed, and corruption ran rampant in the bureaucracy. Local landlords began to take control as the scholars neglected their duties, and this resulted in heavy taxation of the peasantry. Taoists began to gain significant ground and protested the decline. They started to proclaim magical powers and promised to save China with them; the Taoist
Yellow Turban Rebellion in 184 (led by rebels in yellow scarves) failed but was able to weaken the government. The aforementioned Huns combined with diseases killed up to half of the population and officially ended the Han dynasty by 220. The ensuing period of chaos was so terrible it lasted for three centuries, where many weak regional rulers and dynasties failed to establish order in China. This period of chaos and attempts at order is commonly known as that of the
Six Dynasties
Six Dynasties (; 220–589 or 222–589) is a collective term for six Han-ruled Chinese dynasties that existed from the early 3rd century AD to the late 6th century AD. The Six Dynasties period overlapped with the era of the Sixteen Kingdoms ...
. The first part of this included the
Three Kingdoms which started in 220 and describes the brief and weak successor "dynasties" that followed the Han. In 265, the
Jin dynasty of China was started and this soon split into two different empires in control of northwestern and southeastern China. In 420, the conquest and abdication of those two dynasties resulted in the first of the
Southern and Northern dynasties. The Northern and Southern dynasties passed through until finally, by 557, the
Northern Zhou dynasty ruled the north and the
Chen dynasty ruled the south.
Medieval
During this period, the
Eastern world
The Eastern world, also known as the East or historically the Orient, is an umbrella term for various cultures or social structures, nations and philosophical systems, which vary depending on the context. It most often includes at least ...
empires continued to expand through trade, migration and conquests of neighboring areas. Gunpowder was widely used as early as the 11th century and they were using moveable type printing five hundred years before Gutenberg created his press. Buddhism, Taoism, Confucianism were the dominant philosophies of the Far East during the Middle Ages. Marco Polo was not the first Westerner to travel to the Orient and return with amazing stories of this different culture, but his accounts published in the late 13th and early 14th centuries were the first to be widely read throughout Europe.
Western Asia (Middle East)

The Arabian peninsula and the surrounding
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
and
Near East regions saw dramatic change during the Medieval era caused primarily by the spread of
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
and the establishment of the Arabian Empires.
In the 5th century, the Middle East was separated into small, weak states; the two most prominent were the
Sassanian Empire of the
Persians in what is now
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, and the Byzantine Empire in
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
(modern-day
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
). The Byzantines and Sassanians fought with each other continually, a reflection of the rivalry between the Roman Empire and the Persian Empire seen during the previous five hundred years. The fighting weakened both states, leaving the stage open to a new power. Meanwhile, the nomadic
Bedouin tribes who dominated the Arabian desert saw a period of tribal stability, greater trade networking and a familiarity with Abrahamic religions or monotheism.
While the
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
Roman and
Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
Persian empires were both weakened by the
Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628, a new power in the form of
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
grew in the Middle East under
Muhammad in Medina. In a series of rapid
Muslim conquests, the
Rashidun army, led by the
Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
s and skilled military commanders such as
Khalid ibn al-Walid, swept through most of the Middle East, taking more than half of Byzantine territory in the
Arab–Byzantine wars and completely engulfing Persia in the
Muslim conquest of Persia
The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.
The ...
. It would be the Arab
Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
s of the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
that would first unify the entire Middle East as a distinct region and create the dominant
ethnic identity that persists today. These Caliphates included the
Rashidun Caliphate,
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
,
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttal ...
, and later the
Seljuq Empire.

After Muhammad introduced Islam, it jump-started Middle Eastern culture into an
Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
, inspiring achievements in
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
, the revival of old advances in science and technology, and the formation of a distinct way of life. Muslims saved and spread Greek advances in
medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
,
algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics.
Elementary ...
,
geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
,
astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
,
anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having i ...
, and
ethics
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concer ...
that would later finds it way back to Western Europe.
The dominance of the Arabs came to a sudden end in the mid-11th century with the arrival of the
Seljuq Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
, migrating south from the Turkic homelands in Central Asia. They conquered Persia, Iraq (capturing Baghdad in 1055), Syria, Palestine, and the
Hejaz. This was followed by a series of Christian Western Europe invasions. The fragmentation of the Middle East allowed joined forces, mainly from England, France, and the emerging
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
, to enter the region. In 1099 the knights of the
First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ...
captured
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
and founded the
Kingdom of Jerusalem, which survived until 1187, when
Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt an ...
retook the city. Smaller crusader fiefdoms survived until 1291. In the early 13th century, a new wave of invaders, the armies of the
Mongol Empire, swept through the region, sacking Baghdad in the
Siege of Baghdad (1258)
The siege of Baghdad was a siege that took place in Baghdad in 1258, lasting for 13 days from January 29, 1258 until February 10, 1258. The siege, laid by Ilkhanate Mongol forces and allied troops, involved the investment, capture, and sac ...
and advancing as far south as the border of
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
in what became known as the
Mongol conquests. The Mongols eventually retreated in 1335, but the chaos that ensued throughout the empire deposed the Seljuq Turks. In 1401, the region was further plagued by the Turko-Mongol,
Timur, and his ferocious raids. By then, another group of Turks had arisen as well, the
Ottomans.
Central Asia
Mongol Empire
The
Mongol Empire conquered a large part of Asia in the 13th century, an area extending from China to Europe. Medieval Asia was the kingdom of the Khans. Never before had any person controlled as much land as
Genghis Khan. He built his power unifying separate Mongol tribes before expanding his kingdom south and west. He and his grandson, Kublai Khan, controlled lands in China, Burma, Central Asia, Russia, Iran, the Middle East, and Eastern Europe. Genghis Khan was a Khagan who tolerated nearly every religion.
South Asia/Indian Subcontinent
India

The Indian early medieval age, 600 to 1200, is defined by regional kingdoms and cultural diversity. When
Harsha of
Kannauj, who ruled much of the Indo-Gangetic Plain from 606 to 647, attempted to expand southwards, he was defeated by the
Chalukya
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynast ...
ruler of the Deccan. When his successor attempted to expand eastwards, he was defeated by the
Pala Pala may refer to:
Places
Chad
*Pala, Chad, the capital of the region of Mayo-Kebbi Ouest
Estonia
*Pala, Kose Parish, village in Kose Parish, Harju County
*Pala, Kuusalu Parish, village in Kuusalu Parish, Harju County
* Pala, Järva County, vil ...
king of
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
. When the Chalukyas attempted to expand southwards, they were defeated by the
Pallavas from farther south, who in turn were opposed by the
Pandyas and the
Cholas from still farther south. The Cholas could under the rule of
Raja Raja Chola defeat their rivals and rise to a regional power. Cholas expanded northward and defeated
Eastern Chalukya
Eastern Chalukyas, also known as the Chalukyas of Vengi, were a dynasty that ruled parts of South India between the 7th and 12th centuries. They started out as governors of the Chalukyas of Badami in the Deccan region. Subsequently, they beca ...
,
Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom mentioned in classical Indian literature
** Kalinga script, an ancient writin ...
and the
Pala Pala may refer to:
Places
Chad
*Pala, Chad, the capital of the region of Mayo-Kebbi Ouest
Estonia
*Pala, Kose Parish, village in Kose Parish, Harju County
*Pala, Kuusalu Parish, village in Kuusalu Parish, Harju County
* Pala, Järva County, vil ...
. Under
Rajendra Chola the Cholas created the first notable navy of Indian subcontinent. The
Chola navy extended the influence of Chola empire to
southeast asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
. During this time, pastoral peoples whose land had been cleared to make way for the growing agricultural economy were accommodated within caste society, as were new non-traditional ruling classes.
The
Muslim conquest in the Indian subcontinent mainly took place from the 12th century onwards, though earlier Muslim conquests include the limited inroads into modern Afghanistan and Pakistan and the Umayyad campaigns in India, during the time of the Rajput kingdoms in the 8th century.
Major economic and military powers like the
Delhi Sultanate and
Bengal Sultanate, were seen to be established. The search of their wealth led the
Voyages of Christopher Columbus.
The Vijayanagara Empire based in the Deccan Plateau region of South India, was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, patronized by saint Vidyaranya, the 12th Shankaracharya of Sringeri in Karnataka. The empire rose to prominence as a result of attempts by the southern powers to resist and ward off Turkic Islamic invasions by the end of the 13th century. At its peak, it subjugated almost all of South India's rulers and pushed the sultans of the Deccan beyond the Tungabhadra-Krishna river region. After annexing modern day Odisha (ancient Kalinga) from the Gajapati Kingdom, became a notable power. The Kingdome lasted until 1646 after a major military defeat in the Battle of Talikota in 1565 by the combined armies of the Deccan sultanates.
East Asia
China
China saw the rise and fall of the Sui, Tang, Song, and Yuan dynasties and therefore improvements in its bureaucracy, the spread of
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
, and the advent of
Neo-Confucianism. It was an unsurpassed era for Chinese ceramics and painting. Medieval architectural masterpieces the Great South Gate in Todaiji, Japan, and the Tien-ning Temple in Peking, China are some of the surviving constructs from this era.
=Sui dynasty
=
A new powerful dynasty began to rise in the 580s, amongst the divided factions of China. This was started when an aristocrat named Yang Jian married his daughter into the Northern Zhou dynasty. He proclaimed himself
Emperor Wen of Sui and appeased the nomadic military by abandoning the Confucian scholar-gentry. Emperor Wen soon led the conquest of the southern Chen dynasty and united China once more under the
Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and la ...
. The emperor lowered taxes and constructed granaries that he used to prevent famine and control the market. Later Wen's son would murder him for the throne and declare himself
Emperor Yang of Sui. Emperor Yang revived the Confucian scholars and the bureaucracy, much to anger of the aristocrats and nomadic military leaders. Yang became an excessive leader who overused China's resources for personal luxury and perpetuated exhaustive attempts to conquer Goguryeo. His military failures and neglect of the empire forced his own ministers to assassinate him in 618, ending the Sui dynasty.
=Tang dynasty
=

Fortunately, one of Yang's most respectable advisors, Li Yuan, was able to claim the throne quickly, preventing a chaotic collapse. He proclaimed himself
Emperor Gaozu, and established the
Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
in 623. The Tang saw expansion of China through conquest to Tibet in the west,
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
in the south, and Manchuria in the north. Tang emperors also improved the education of scholars in the Chinese bureaucracy. A Ministry of Rites was established and the examination system was improved to better qualify scholars for their jobs. In addition, Buddhism became popular in China with two different strains between the peasantry and the elite, the
Pure Land and
Zen strains, respectively. Greatly supporting the spread of Buddhism was
Empress Wu, who additionally claimed an unofficial "Zhou dynasty" and displayed China's tolerance of a woman ruler, which was rare at the time. However, Buddhism would also experience some backlash, especially from Confucianists and Taoists. This would usually involve criticism about how it was costing the state money, since the government was unable to tax Buddhist monasteries, and additionally sent many grants and gifts to them.
The Tang dynasty began to decline under the rule of
Emperor Xuanzong, who began to neglect the economy and military and caused unrest amongst the court officials due to the excessive influence of his concubine,
Yang Guifei, and her family. This eventually sparked a revolt in 755. Although the revolt failed, subduing it required involvement with the unruly nomadic tribes outside of China and distributing more power to local leaders—leaving the government and economy in a degraded state. The Tang dynasty officially ended in 907 and various factions led by the aforementioned nomadic tribes and local leaders would fight for control of China in the
Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen conc ...
.
=Liao, Song and Jin dynasties
=
By 960, most of China proper had been reunited under the
Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
, although it lost territories in the north and could not defeat one of the nomadic tribes there—the
Liao dynasty
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yelü ...
of the highly sinicized
Khitan people. From then on, the Song would have to pay tribute to avoid invasion and thus set the precedent for other nomadic kingdoms to oppress them. The Song also saw the revival of Confucianism in the form of
Neo-Confucianism. This had the effect of putting the Confucian scholars at a higher status than aristocrats or Buddhists and also intensified the reduction of power in women. The infamous practice of
foot binding developed in this period as a result. Eventually the Liao dynasty in the north was overthrown by the
Jin dynasty of the Manchu-related
Jurchen people. The new Jin kingdom
invaded northern China, leaving the Song to flee farther south and creating the
Southern Song dynasty in 1126. There, cultural life flourished.
=Yuan dynasty
=

By 1227, the Mongols had conquered the
Western Xia kingdom northwest of China. Soon the Mongols incurred upon the Jin empire of the Jurchens. Chinese cities were soon besieged by the Mongol hordes that showed little mercy for those who resisted and the Southern Song Chinese were quickly losing territory. In 1271 the current great khan,
Kublai Khan, claimed himself Emperor of China and officially established the Yuan dynasty. By 1290, all of China was under control of the Mongols, marking the first time they were ever completely conquered by a foreign invader; the new capital was established at
Khanbaliq (modern-day
Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the Capital city, capital of the China, People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's Li ...
). Kublai Khan segregated Mongol culture from Chinese culture by discouraging interactions between the two peoples, separating living spaces and places of worship, and reserving top administrative positions to Mongols, thus preventing Confucian scholars to continue the bureaucratic system. Nevertheless, Kublai remained fascinated with Chinese thinking, surrounding himself with Chinese Buddhist, Taoist, or Confucian advisors.
Mongol women displayed a contrasting independent nature compared to the Chinese women who continued to be suppressed. Mongol women often rode out on hunts or even to war. Kublai's wife,
Chabi, was a perfect example of this; Chabi advised her husband on several political and diplomatic matters; she convinced him that the Chinese were to be respected and well-treated in order to make them easier to rule. However, this was not enough to affect Chinese women's position, and the increasingly Neo-Confucian successors of Kublai further repressed Chinese and even Mongol women.
The Black Death, which would later ravage Western Europe, had its beginnings in Asia, where it wiped out large populations in China in 1331.
Korea
= Three Kingdoms of Korea
=

The three Kingdoms of Korea involves
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
in north,
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder J ...
in southwest, and
Silla
Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms o ...
in southeast Korean peninsula. These three kingdoms act as a bridge of cultures between China and Japan. Thanks to them, Japan was able to accept Chinese splendid cultures.
Prince Shōtoku of Japan had been taught by two teachers. One was from
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder J ...
, the other was from
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
. Once Japan invaded
Silla
Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms o ...
, Goguryeo helped Silla to defeat Japan.
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder J ...
met the earliest heyday of them. Its heyday was the 5th century AD. Its capital was
Seoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
. During its heyday, the kingdom made colonies overseas. Liaodong, China and Kyushu, Japan were the colonies of
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder J ...
during its short heyday.
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
was the strongest kingdom of all. They sometimes called themselves as an Empire. Its heyday was 6th century. King Gwanggaeto widened its territory to north. So Goguryeo dominated from Korean peninsula to Manchuria. And his son,
King Jangsu
Jangsu of Goguryeo (394–491, r. 413–491) was the 20th monarch of Goguryeo, the northernmost of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. He was born in 394 as the eldest son of Gwanggaeto. He became the crown prince in 408, and upon his father's death ...
widened its territory to south. He occupied
Seoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
, and moved its capital to
Pyeongyang. Goguryeo almost occupied three quarters of South Korean peninsula thanks to king Jangsu who widened the kingdom's territory to south.
Silla
Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms o ...
met the latest heyday. King Jinheung went north and occupied
Seoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
. But it was short.
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder J ...
became stronger and attacked Silla. Baekje occupied more than 40 cities of Silla. So Silla could hardly survive.
China's Sui dynasty invaded
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
and
Goguryeo–Sui War occurred between Korea and China.
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
won against China and
Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and la ...
fell. After then,
Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
reinvaded
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
and helped
Silla
Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms o ...
to unify the peninsula.
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
,
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder J ...
, and Japan helped each other against Tang-Silla alliance, but
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.
Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder J ...
and
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
fell. Unfortunately,
Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
betrayed
Silla
Silla or Shilla (57 BCE – 935 CE) ( , Old Korean: Syera, Old Japanese: Siraki2) was a Korean kingdom located on the southern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula. Silla, along with Baekje and Goguryeo, formed the Three Kingdoms o ...
and invaded Korean peninsula in order to occupy the whole Korean peninsula (
Silla-Tang war). Silla advocated 'Unification of Three Korea', so people of fallen Baekje and Goguryeo helped Silla against Chinese invasion. Eventually Silla could beat China and unified the peninsula. This war helped Korean people to unite mentally.
=North-South States Period
=


The rest of
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
people established
Balhae and won the war against Tang in later 7th century AD.
Balhae is the north state, and
Later Silla
Unified Silla, or Late Silla (, ), is the name often applied to the Korean kingdom of Silla, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, after 668 CE. In the 7th century, a Silla–Tang alliance conquered Baekje and the southern part of Goguryeo in the ...
was the south state. Balhae was a quite strong kingdom as their ancestor Goguryeo did. Finally, the Emperor of Tang dynasty admits Balhae as 'A strong country in the East'. They liked to trade with Japan, China, and Silla. Balhae and Later Silla sent a lot of international students to China. And Arabian merchants came into Korean peninsula, so Korea became known as 'Silla' in the western countries. Silla improved Korean writing system called Idu letters. Idu affected
Katakana of Japan.
Liao dynasty
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yelü ...
invaded
Balhae in early 10th century, so
Balhae fell.
=Later Three Kingdoms of Korea
=
The unified Korean kingdom, Later Silla divided into three kingdoms again because of the corrupt central government. It involves
Later Goguryeo
Taebong (; ) was a state established by Gung Ye () on the Korean Peninsula in 901 during the Later Three Kingdoms.
Name
The state's initial name was Goryeo, after the official name of Goguryeo, a previous state in Manchuria and the northe ...
(also as known as "Taebong"),
Later Baekje
Hubaekje or Later Baekje (, ) was one of the Later Three Kingdoms of Korea, along with Taebong and Silla. Later Baekje was a Korean dynastic kingdom founded by the disaffected Silla general Gyeon Hwon in 900, whom led the local gentry and ...
, and Later Silla. The general of
Later Goguryeo
Taebong (; ) was a state established by Gung Ye () on the Korean Peninsula in 901 during the Later Three Kingdoms.
Name
The state's initial name was Goryeo, after the official name of Goguryeo, a previous state in Manchuria and the northe ...
, Wang Geon took the throne and changed the name of kingdom into
Goryeo, which was derived by the ancient strong kingdom,
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
, and Goryeo reunified the peninsula.
=Goryeo
=
 Goryeo
Goryeo reunited the Korean peninsula during the later three kingdoms period and named itself as 'Empire'. But nowadays, Goryeo is known as a kingdom. The name 'Goryeo' was derived from
Goguryeo
Goguryeo (37 BC–668 AD) ( ) also called Goryeo (), was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled mos ...
, and the name
Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
was derived from Goryeo. Goryeo adopted people from fallen
Balhae. They also widened their territory to north by defending Liao dynasty and attacking the
Jurchen people. Goryeo developed a splendid culture. The first metal type printed book
Jikji was also from Korea. The
Goryeo ware
Goryeo ware ( ko, 고려도자기, translit=Goryeo dojagi, also known as ''Goryeo cheong-ja'') refers to all types of Korean pottery and porcelain produced during the Goryeo dynasty, from 918 to 1392, but most often refers to celadon (greenware).
...
is one of the most famous legacies of this kingdom. Goryeo imported Chinese government system and developed into their own ways.
During this period, laws were codified and a civil service system was introduced. Buddhism flourished and spread throughout the peninsula. The
Tripitaka Koreana
The (lit. ) or ("Eighty-Thousand ''Tripiṭaka''") is a Korean collection of the (Buddhist scriptures, and the Sanskrit word for "three baskets"), carved onto 81,258 wooden printing blocks in the 13th century.
It is the oldest intact vers ...
is 81,258 books total. It was made to keep Korea safe against the Mongolian invasion. It is now a UNESCO world heritage. Goryeo won the battle against
Liao dynasty
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yelü ...
. Then, the
Mongolian Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Eu ...
invaded Goryeo. Goryeo did not disappear but it had to obey Mongolians. After 80 years, in 14th century, the Mongolian dynasty Yuan lost power, King Gongmin tried to free themselves against Mongol although his wife was also Mongolian. At the 14th century,
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
wanted Goryeo to obey China. But Goryeo didn't. They decided to invade China. Going to China, the general of Goryeo, Lee Sung-Gae came back and destroyed Goryeo. Then, in 1392, he established new dynasty,
Joseon. And he became
Taejo of Joseon, which means the first king of
Joseon.
Japan

=Asuka period
=
Japan's medieval history began with the
Asuka period
The was a period in the history of Japan lasting from 538 to 710 (or 592 to 645), although its beginning could be said to overlap with the preceding Kofun period. The Yamato polity evolved greatly during the Asuka period, which is named after ...
, from around 600 to 710. The time was characterized by the
Taika Reform and imperial centralization, both of which were a direct result of growing Chinese contact and influences. In 603,
Prince Shōtoku of the
Yamato dynasty began significant political and cultural changes. He issued the
Seventeen-article constitution
The is, according to the '' Nihon Shoki'' of 720, a document authored by Prince Shōtoku in 604. It was adopted in the reign of Empress Suiko. The emphasis of the document is not so much on the basic laws by which the state was to be governed, suc ...
in 604, centralizing power towards the emperor (under the title ''tenno'', or heavenly sovereign) and removing the power to levy taxes from provincial lords. Shōtoku was also a patron of Buddhism and he encouraged building temples competitively.
=Nara period
=
Shōtoku's reforms transitioned Japan to the
Nara period (c. 710 to c. 794), with the moving of the Japanese capital to
Nara in
Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island s ...
. This period saw the culmination of Chinese-style writing, etiquette, and architecture in Japan along with Confucian ideals to supplement the already present Buddhism. Peasants revered both Confucian scholars and Buddhist monks. However, in the wake of the
735–737 Japanese smallpox epidemic
The was a major smallpox epidemic caused by the Variola major virus that afflicted much of Japan. Killing approximately one third (around 1 million individuals) of the entire Japanese population, the epidemic had significant social, economic, and ...
, Buddhism gained the status of state religion and the government ordered the construction of numerous Buddhist temples, monasteries, and statues. The lavish spending combined with the fact that many aristocrats did not pay taxes, put a heavy burden on peasantry that caused poverty and famine. Eventually the Buddhist position got out of control, threatening to seize imperial power and causing
Emperor Kanmu
, or Kammu, was the 50th emperor of Japan, Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 桓武天皇 (50) retrieved 2013-8-22. according to the traditional order of succession. Kanmu reigned from 781 to 806, and it was during his reign that the s ...
to move the capital to
Heian-kyō to avoid a Buddhist takeover. This marked the beginning of the
Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japan ...
and the end of Taika reform.
=Heian period
=
With the Heian period (from 794 to 1185) came a decline of imperial power. Chinese influence also declined, as a result of its correlation with imperial centralization and the
heavenly mandate, which came to be regarded as ineffective. By 838, the Japanese court discontinued its embassies in China; only traders and Buddhist monks continued to travel to China. Buddhism itself came to be considered more Japanese than Chinese, and persisted to be popular in Japan. Buddhists monks and monasteries continued their attempts to gather personal power in courts, along with aristocrats. One particular noble family that dominated influence in the imperial bureaucracy was the
Fujiwara clan
was a powerful family of imperial regents in Japan, descending from the Nakatomi clan and, as legend held, through them their ancestral god Ame-no-Koyane. The Fujiwara prospered since the ancient times and dominated the imperial court until th ...
. During this time cultural life in the imperial court flourished. There was a focus on beauty and social interaction and writing and literature was considered refined. Noblewomen were cultured the same as noblemen, dabbling in creative works and politics. A prime example of both Japanese literature and women's role in high-class culture at this time was ''
The Tale of Genji'', written by the
lady-in-waiting Murasaki Shikibu
was a Japanese novelist, poet and lady-in-waiting at the Imperial court in the Heian period. She is best known as the author of '' The Tale of Genji,'' widely considered to be one of the world's first novels, written in Japanese between abo ...
. Popularization of wooden palaces and
shōji sliding doors amongst the nobility also occurred.
Loss of imperial power also led to the rise of provincial warrior elites. Small lords began to function independently. They administered laws, supervised public works projects, and collected revenue for themselves instead of the imperial court. Regional lords also began to build their own armies. These warriors were loyal only their local lords and not the emperor, although the imperial government increasingly called them in to protect the capital. The regional warrior class developed into the
samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retainers of the '' daimyo'' (the great feudal landholders). They ...
, which created its own culture: including specialized weapons such as the
katana
A is a Japanese sword characterized by a curved, single-edged blade with a circular or squared guard and long grip to accommodate two hands. Developed later than the ''tachi'', it was used by samurai in feudal Japan and worn with the edge ...
and a form of chivalry,
bushido. The imperial government's loss of control in the second half of the Heian period allowed banditry to grow, requiring both feudal lords and Buddhist monasteries to procure warriors for protection. As imperial control over Japan declined, feudal lords also became more independent and seceded from the empire. These feudal states squandered the peasants living in them, reducing the farmers to an almost
serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which develop ...
status. Peasants were also rigidly restricted from rising to the samurai class, being physically set off by dress and weapon restrictions. As a result of their oppression, many peasants turned to Buddhism as a hope for reward in the afterlife for upright behavior.
With the increase of feudalism, families in the imperial court began to depend on alliances with regional lords. The Fujiwara clan declined from power, replaced by a rivalry between the
Taira clan
The Taira was one of the four most important clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian, Kamakura and Muromachi Periods of Japanese history – the others being the Fujiwara, the Tachibana, and the Minamoto. The clan is divide ...
and the
Minamoto clan. This rivalry grew into the
Genpei War in the early 1180s. This war saw the use of both samurai and peasant soldiers. For the samurai, battle was ritual and they often easily cut down the poorly trained peasantry. The Minamoto clan proved successful due to their rural alliances. Once the Taira was destroyed, the Minamoto established a military government called the
shogunate (or bakufu), centered in
Kamakura.
=Kamakura period
=
The end of the Genpei War and the establishment of the
Kamakura shogunate
The was the feudal military government of Japan during the Kamakura period from 1185 to 1333. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Kamakura-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 459.
The Kamakura shogunate was established by Minamoto no ...
marked the end of the Heian period and the beginning of the
Kamakura period
The is a period of Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura by the first ''shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the Genpei War, which saw the struggle b ...
in 1185, solidifying feudal Japan.
Southeast Asia
Khmers

In 802,
Jayavarman II
Jayavarman II ( km, ជ័យវរ្ម័នទី២; c. 770 – 850) (reigned c. 802–850) was a Khmer prince who founded and became the ruler of the Khmer Empire (Cambodia) after unifying the Khmer civilization. The Khmer Empire was the ...
consolidated his rule over neighboring peoples and declared himself
chakravartin, or "universal ruler". The Khmer Empire effectively dominated all
Mainland Southeast Asia from the early 9th until the 15th century, during which time they developed a sophisticated monumental architecture of most exquisite expression and mastery of composition at
Angkor.
Vietnam
The history of Vietnam can be traced back to around 20,000 years ago, as the first modern humans arrived and settled on this land, known as the Hoabinhians, which can be traced back to the modern-day Negritos. Archaeological findings from 1965, which are still under research, show the remains of two hominins closely related to the Sinanthropus, dating as far back as the Middle Pleistocene era, roughly half a million years ago.
Pre-historic Vietnam was home to some of the world's earliest civilizations and societies—making them one of the world's first people who had practiced agriculture.
3] The Red River valley formed a natural geographic and economic unit, bounded to the north and west by mountains and jungles, to the east by the sea and to the south by the Red River Delta.
The need to have a single authority to prevent floods of the Red River, to cooperate in constructing hydraulic systems, trade exchange, and to repel invaders, led to the creation of the first legendary Vietnamese states approximately 2879 BC. While in the later times, ongoing research from archaeologists have suggested that the Vietnamese Đông Sơn culture were traceable back to Northern Vietnam, Guangxi and Laos around 700 BC.
6]
Vietnam's long coastal and narrowed lands, rugged mountainous terrains, with two major deltas, were soon home to several different ancient cultures and civilizations. In the north, the Dongsonian culture and its indigenous chiefdoms of Van Lang and Au Lac started to flourish by 500 BC. In Central, Sa Huynh culture of Austronesian Chamic peoples also thrived. Both were swept by the Chinese Han dynasty expansion from the north - the Han conquest of Nanyue brought parts of Vietnam under the Chinese rule in 111 BC. Traditional Chinese became the official language as well as the later developed independent Nôm script of Vietnamese.
In 40 BC, the Trưng Sisters led the first uprising of indigenous tribes and peoples against Chinese domination. The rebellion was however defeated, but as the Han dynasty began to weaken by late 2nd century and China (中国) started to descend into state of turmoil, the indigenous peoples of Vietnam rose again and some became free. In 192 AD, the Cham of Central Vietnam revolted against the Chinese and subsequently became independent kingdom of Champa, while the Red River Delta saw loosening Northern control. At that time, with the introduction of Buddhism and Hinduism by the second century AD, Vietnam was the first place in Southeast Asia which shared influences of both Indian and Sino cultures, and the rise of first Indianized kingdoms Champa and Funan.
During these 1,000 years there were many uprisings against Sino domination, and at certain periods Vietnam was independently governed under the Trưng Sisters, Early Lý, Khúc and Dương Đình Nghệ—although their triumphs and reigns were temporary.
When Ngô Quyền (King of Vietnam, 938–944) restored sovereign power in the country with the victory at the battle of Bach Dang River, the next millennium was advanced by the accomplishments of successive local dynasties: Ngô, Đinh, Early Lê, Lý, Trần, Hồ, Later Trần, Later Lê, Mạc, Trịnh, Nguyễn, Tây Sơn and again Nguyễn. Nôm script of the Vietnamese started to develop and become more sophisticated, with literature being published and written in Nôm. At various points during the imperial dynasties, Vietnam was ravaged and divided by civil wars and witnessed interventions by the Song, Yuan, Cham, Ming, Siamese, Qing, French, and Imperial Japan.
The Ming Empire conquered the Red River valley for a while before native Vietnamese regained control and the French Empire reduced Vietnam to a French dependency for nearly a century, followed by brief but brutal occupation by the Japanese Empire. During the French period, widespread brutality, inequality and cultural remnants of Hán-Nôm were being destroyed, with the French wishing to rid the Vietnamese of their Confucian legacy from the 1880s. French was the official language during this period. The Vietnamese Latin script, seen to be a Latin transliteration of Hán-Nôm, superseded the Hán-Nôm logographic scripts and became the main mode of written as well as spoken language since the 20th century.
Japan invaded in 1940, creating deep resentment that fuelled resistance to post-World War II military-political efforts by the returning power of France, and the US who had viewed themselves as fighters for liberty and democracy against the red waves of communism.
9] In the Vietnamese Proxy War, the US or the Western Bloc supported South Vietnam and the Soviet Union or the Communist Bloc supported North Vietnam. Political upheaval, a period of intense fighting and war, followed by Communist insurrection and victory further put an end to the monarchy after World War II, and the country was proclaimed a communist Socialist Republic. Vietnam suffered heavy sanctions as well as political and economic isolation following brutal wars with China and Cambodia in the successive years. Following that era, the Đổi Mới (renovation/innovation) reformations were enacted. The forces of market liberalisation and globalisation has shaped Vietnam's economic and political circumstances since.
Early modern
The
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
began to expand into Asia from the 17th century, and would eventually take control of all of
Siberia and most of Central Asia by the end of the 19th century. The
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
controlled Anatolia, the Middle East, North Africa and the Balkans from the 16th century onwards. In the 17th century, the
Manchu conquered China and established the
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
. In the 16th century, the
Mughal Empire controlled much of India and initiated the second golden age for India. China was the largest economy in the world for much of the time, followed by India until the 18th century.
Ming China
By 1368,
Zhu Yuanzhang had claimed himself
Hongwu Emperor and established the Ming dynasty of China. Immediately, the new emperor and his followers drove the Mongols and their culture out of China and beyond the Great Wall. The new emperor was somewhat suspicious of the scholars that dominated China's bureaucracy, for he had been born a peasant and was uneducated. Nevertheless, Confucian scholars were necessary to China's bureaucracy and were reestablished as well as reforms that would improve the exam systems and make them more important in entering the bureaucracy than ever before. The exams became more rigorous, cut down harshly on cheating, and those who excelled were more highly appraised. Finally, Hongwu also directed more power towards the role of emperor so as to end the corrupt influences of the bureaucrats.
Society and economy
The Hongwu emperor, perhaps for his sympathy of the common-folk, had built many irrigation systems and other public projects that provided help for the peasant farmers. They were also allowed to cultivate and claim unoccupied land without having to pay any taxes and labor demands were lowered. However, none of this was able to stop the rising landlord class that gained many privileges from the government and slowly gained control of the peasantry. Moneylenders foreclosed on peasant debt in exchange for mortgages and bought up farmer land, forcing them to become the landlords' tenants or to wander elsewhere for work. Also during this time,
Neo-Confucianism intensified even more than the previous two dynasties (the Song and Yuan). Focus on the superiority of elders over youth, men over women, and teachers over students resulted in minor discrimination of the "inferior" classes. The fine arts grew in the Ming era, with improved techniques in brush painting that depicted scenes of court, city or country life; people such as scholars or travelers; or the beauty of mountains, lakes, or marshes. The Chinese novel fully developed in this era, with such classics written such as ''
Water Margin'', ''
Journey to the West'', and ''
Jin Ping Mei''.
Economics grew rapidly in the Ming dynasty as well. The introduction of American crops such as
maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
,
sweet potatoes, and
peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small an ...
s allowed for cultivation of crops in infertile land and helped prevent famine. The population boom that began in the Song dynasty accelerated until China's population went from 80 or 90 million to 150 million in three centuries, culminating in 1600. This paralleled the market economy that was growing both internally and externally. Silk, tea, ceramics, and lacquer-ware were produced by artisans that traded them in Asia and to Europeans. Westerners began to trade (with some Chinese-assigned limits), primarily in the port-towns of
Macau and
Canton. Although merchants benefited greatly from this, land remained the primary symbol of wealth in China and traders' riches were often put into acquiring more land. Therefore, little of these riches were used in private enterprises that could've allowed for China to develop the
market economy that often accompanied the highly-successful Western countries.
Foreign interests

In the interest of national glory, the Chinese began sending impressive
junk ships across the
South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Ph ...
and the
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
. From 1403 to 1433, the
Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (; pronounced ; 2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), personal name Zhu Di (), was the third Emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 1424.
Zhu Di was the fourth son of the Hongwu Emperor, the founder of the Ming dyn ...
commissioned
expeditions led by the admiral
Zheng He, a Muslim
eunuch from China. Chinese junks carrying hundreds of soldiers, goods, and animals for zoos, traveled to Southeast Asia, Persia, southern Arabia, and east Africa to show off Chinese power. Their prowess exceeded that of current Europeans at the time, and had these expeditions not ended, the world economy may be different from today. In 1433, the Chinese government decided that the cost of a navy was an unnecessary expense. The Chinese navy was slowly dismantled and focus on interior reform and military defense began. It was China's longstanding priority that they protect themselves from nomads and they have accordingly returned to it. The growing limits on the Chinese navy would leave them vulnerable to foreign invasion by sea later on.

As was inevitable, Westerners arrived on the Chinese east coast, primarily
Jesuit missionaries which reached the mainland in 1582. They attempted to
convert the Chinese people to Christianity by first converting the top of the social hierarchy and allowing the lower classes to subsequently convert. To further gain support, many Jesuits adopted Chinese dress, customs, and language. Some Chinese scholars were interested in certain Western teachings and especially in Western technology. By the 1580s, Jesuit scholars like
Matteo Ricci and
Adam Schall amazed the Chinese elite with technological advances such as European clocks, improved calendars and cannons, and the accurate prediction of eclipses. Although some the scholar-gentry converted, many were suspicious of the Westerners whom they called "barbarians" and even resented them for the embarrassment they received at the hand of Western correction. Nevertheless, a small group of Jesuit scholars remained at the court to impress the emperor and his advisors.
Decline
Near the end of the 1500s, the extremely centralized government that gave so much power to the emperor had begun to fail as more incompetent rulers took the mantle. Along with these weak rulers came increasingly corrupt officials who took advantage of the decline. Once more the public projects fell into disrepair due to neglect by the bureaucracy and resulted in floods, drought, and famine that rocked the peasantry. The famine soon became so terrible that some peasants resorted to selling their children to slavery to save them from starvation, or to eating bark, the feces of geese, or
other people. Many landlords abused the situation by building large estates where desperate farmers would work and be exploited. In turn, many of these farmers resorted to flight, banditry, and open rebellion.
All of this corresponded with the usual dynastic decline of China seen before, as well as the growing foreign threats. In the mid-16th century, Japanese and ethnic Chinese pirates began to raid the southern coast, and neither the bureaucracy nor the military were able to stop them. The threat of the northern
Manchu people also grew. The Manchu were an already large state north of China, when in the early 17th century a local leader named
Nurhaci suddenly united them under the
Eight Banners—armies that the opposing families were organized into. The Manchus adopted many Chinese customs, specifically taking after their bureaucracy. Nevertheless, the Manchus still remained a Chinese
vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerai ...
. In 1644 Chinese administration became so weak, the 16th and last emperor, the
Chongzhen Emperor
The Chongzhen Emperor (; 6 February 1611 – 25 April 1644), personal name Zhu Youjian (), courtesy name Deyue (),Wang Yuan (王源),''Ju ye tang wen ji'' (《居業堂文集》), vol. 19. "聞之張景蔚親見烈皇帝神主題御諱字德� ...
, did not respond to the severity of an ensuing rebellion by local dissenters until the enemy had invaded the
Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples including the Zhongshan Park, the sacrifi ...
(his personal estate). He soon hanged himself in the imperial gardens. For a brief amount of time, the
Shun dynasty was claimed, until a loyalist Ming official called support from the Manchus to put down the new dynasty. The Shun dynasty ended within a year and the Manchu were now within the Great Wall. Taking advantage of the situation, the Manchus marched on the Chinese capital of Beijing.
Within two decades all of China belonged to the Manchu and the
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
was established.
Korea: Joseon dynasty (1392–1897)

In early-modern Korea, the 500-year-old kingdom,
Goryeo fell and new dynasty
Joseon rose in August 5, 1392.
Taejo of Joseon changed the country's name from
Goryeo to
Joseon.
Sejong the Great created
Hangul
The Korean alphabet, known as Hangul, . Hangul may also be written as following South Korea's standard Romanization. ( ) in South Korea and Chosŏn'gŭl in North Korea, is the modern official writing system for the Korean language. The l ...
, the modern Korean alphabet, in 1443; likewise the Joseon dynasty saw several improvements in science and technology, like Sun Clocks, Water Clocks, Rain-Measuring systems, Star Maps, and detailed records of Korean small villages. The ninth king,
Seongjong accomplished the first complete Korean
law code
A code of law, also called a law code or legal code, is a systematic collection of statutes. It is a type of legislation that purports to exhaustively cover a complete system of laws or a particular area of law as it existed at the time the cod ...
in 1485. So the culture and people's lives were improved again.
In 1592, Japan under
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Cour ...
invaded Korea. That war is
Imjin war
The Imjin River ( in South Korea) or Rimjin River ( in North Korea) is the 7th largest river in Korea. It flows from north to south, crossing the Demilitarized Zone and joining the Han River downstream of Seoul, near the Yellow Sea. The rive ...
. Before that war, Joseon was in a long peace like PAX ROMANA. So Joseon was not ready for the war. Joseon had lost again and again. Japanese army conquered
Seoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
. The whole
Korean peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
was in danger. But
Yi Sun-sin, the most renowned general of Korea, defeated Japanese fleet in southern Korea coast even 13 ships VS 133 ships. This incredible battle is called "
Battle of Myeongnyang". After that,
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
helped Joseon, and Japan lost the battle. So Toyotomi Hideyoshi's campaign in Korea failed, and the
Tokugawa Shogunate has later began. Korea was hurt a lot at
Imjin war
The Imjin River ( in South Korea) or Rimjin River ( in North Korea) is the 7th largest river in Korea. It flows from north to south, crossing the Demilitarized Zone and joining the Han River downstream of Seoul, near the Yellow Sea. The rive ...
. Not long after, Manchurian people invaded Joseon again. It is called
Qing invasion of Joseon. The first invasion was for sake. Because Qing was at war between Ming, so Ming's alliance with Joseon was threatening. And the second invasion was for Joseon to obey Qing. After that, Qing defeated Ming and took the whole Chinese territories. Joseon also had to obey Qing because Joseon lose the second war against Qing.
After the Qing invasion, the princes of the Joseon dynasty lived their childhood in China. The son of King Injo met
Adam Schall in Beijing. So he wanted to introduce western technologies to Korean people when he becomes a king. Unfortunately, he died before he could take the throne. After then, the alternative prince became the 17th king of the Joseon dynasty,
Hyojong, trying to revenge for his kingdom and fallen Ming dynasty to Qing. Later kings such as
Yeongjo
Yeongjo of Joseon (31 October 1694 – 22 April 1776), personal name Yi Geum (Korean: 이금, Hanja: 李昑), was the 21st monarch of the Joseon dynasty of Korea. He was the second son of King Sukjong, by his concubine Royal Noble Consort Suk ...
and
Jeongjo
Jeongjo of Joseon (28 October 1752 – 18 August 1800), personal name Yi San (Korean: 이산; Hanja: 李祘), sometimes called Jeongjo the Great (Korean: 정조대왕; Hanja: 正祖大王), was the 22nd monarch of the Joseon dynasty of Korea. ...
tried to improve their people's lives and stop the governors' unreasonable competition. From the 17th century to the 18th century, Joseon sent diplomats and artists to Japan more than 10 times. This group was called 'Tongshinsa'. They were sent to Japan to teach Japan about advanced Korean culture. Japanese people liked to receive poems from Korean nobles. At that time, Korea was more powerful than Japan. But that relationship between Joseon and Japan was reversed after the 19th century. Because Japan became more powerful than Korea and China, either. So Joseon sent diplomats called 'Sooshinsa' to learn Japanese advanced technologies. After king Jeongjo's death, some noble families controlled the whole kingdom in the early 19th century. At the end of that period, Western people invaded Joseon. In 1876, Joseon was set free from Qing so they did not have to obey Qing. But Japanese Empire was happy because Joseon became a perfect independent kingdom. So Japan could intervene in the kingdom more. After this, Joseon traded with the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and sent 'Sooshinsa' to Japan, 'Youngshinsa' to Qing, and 'Bobingsa' to the US and Europe. These groups took many modern things to the Korean peninsula.
Japan: Tokugawa or Edo period (1603–1867)

In early-modern Japan following the
Sengoku period
The was a period in History of Japan, Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615.
The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the Feudalism, feudal system of Japan under the ...
of "warring states", central government had been largely reestablished by
Oda Nobunaga and
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Cour ...
during the
Azuchi–Momoyama period. After the
Battle of Sekigahara in 1600, central authority fell to
Tokugawa Ieyasu who completed this process and received the title of ''
shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamaku ...
'' in 1603.
Society in the Japanese "
Tokugawa period" (see
Edo society), unlike the shogunates before it, was based on the strict class
hierarchy originally established by
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Cour ...
. The ''
daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominall ...
s'' (feudal lords) were at the top, followed by the warrior-caste of
samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retainers of the '' daimyo'' (the great feudal landholders). They ...
, with the farmers, artisans, and merchants ranking below. The country was strictly closed to foreigners with few exceptions with the ''
Sakoku'' policy. Literacy rose in the two centuries of isolation.
In some parts of the country, particularly smaller regions, ''daimyōs'' and samurai were more or less identical, since ''daimyōs'' might be trained as samurai, and samurai might act as local lords. Otherwise, the largely inflexible nature of this
social stratification system unleashed disruptive forces over time. Taxes on the
peasantry were set at fixed amounts which did not account for inflation or other changes in monetary value. As a result, the tax revenues collected by the samurai landowners were worth less and less over time. This often led to numerous confrontations between noble but impoverished samurai and well-to-do peasants. None, however, proved compelling enough to seriously challenge the established order until the arrival of foreign powers.
India
In the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, the Mughal Empire ruled most of India in the early 18th century. During emperor
Shah Jahan and his son
Aurangzeb's Islamic
sharia reigns, the empire reached its architectural and economic zenith, and became the world's largest economy, worth over 25% of world GDP. In the mid-18th century it was a major
proto-industrializing region.
Following major events such as the
Nader Shah's invasion of the Mughal Empire,
Battle of Plassey,
Battle of Buxar and the long
Anglo-Mysore Wars
The Anglo-Mysore Wars were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company (represented chiefly by the neighbouring Madras Pres ...
, most of South Asia was colonised and governed by the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, thus establishing the
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
. The "classic period" ended with the death of
Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb,
although the dynasty continued for another 150 years. During this period, the Empire was marked by a highly centralized administration connecting the different regions. All the significant monuments of the Mughals, their most visible legacy, date to this period which was characterised by the expansion of Persian cultural influence in the Indian subcontinent, with brilliant literary, artistic, and architectural results. The Maratha Empire was located in the south west of present-day India and expanded greatly under the rule of the
Peshwa
The Peshwa (Pronunciation: e(ː)ʃʋaː was the appointed (later becoming hereditary) prime minister of the Maratha Empire of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, the Peshwas served as subordinates to the Chhatrapati (the Maratha king); later ...
s, the prime ministers of the Maratha empire. In 1761, the Maratha army lost the
Third Battle of Panipat against
Ahmad shah Durrani king of Afghanistan which halted imperial expansion and the empire was then divided into a confederacy of Maratha states.
British and Dutch colonization
The European economic and naval powers pushed into Asia, first to do trading, and then to take over major colonies. The Dutch led the way followed by the British. Portugal had arrived first, but was too weak to maintain its small holdings and was largely pushed out, retaining only
Goa and
Macau. The British set up a private organization, the
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
, which handled both trade and Imperial control of much of India.
The
commercial colonization of India commenced in 1757, after the
Battle of Plassey, when the
Nawab of Bengal surrendered his dominions to the British East India Company, in 1765, when the company was granted the ''diwani'', or the right to collect revenue, in
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
and
Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
, or in 1772, when the company established a capital in
Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, commer ...
, appointed its first
Governor-General,
Warren Hastings, and became directly involved in governance.
The
Maratha states, following the
Anglo-Maratha wars, eventually lost to the
British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
in 1818 with the
Third Anglo-Maratha War. The rule lasted until 1858, when, after the
Indian rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the for ...
and consequent of the
Government of India Act 1858, the
British government assumed the task of directly administering India in the new
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
.
In 1819
Stamford Raffles established
Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
as a key trading post for Britain in their rivalry with the Dutch. However, their rivalry cooled in 1824 when an
Anglo-Dutch treaty demarcated their respective interests in Southeast Asia. From the 1850s onwards, the pace of colonization shifted to a significantly higher gear.
The
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
(1800) and
British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
(1858) were dissolved by their respective governments, who took over the direct administration of the colonies. Only
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
was spared the experience of foreign rule, although, Thailand itself was also greatly affected by the power politics of the Western powers. Colonial rule had a profound effect on Southeast Asia. While the colonial powers profited much from the region's vast resources and large market, colonial rule did develop the region to a varying extent.
Late modern
Central Asia: The Great Game, Russia vs Great Britain
 The Great Game
The Great Game was a political and diplomatic confrontation between Great Britain and Russia over
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
and neighbouring territories in
Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
. It lasted from 1828 to 1907. There was no war, but there were many threats. Russia was fearful of British commercial and military inroads into
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, and Britain was fearful of Russia threatening its largest and most important possession, India. This resulted in an atmosphere of distrust and the constant threat of war between the two empires. Britain made it a high priority to protect all the approaches to India, and the "great game" is primarily how the British did this in terms of a possible Russian threat. Historians with access to the archives have concluded that Russia had no plans involving India, as the Russians repeatedly stated.
The Great Game began in 1838 when Britain decided to gain control over the
Emirate of Afghanistan and make it a protectorate, and to use the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, the
Persian Empire, the
Khanate of Khiva, and the Emirate of Bukhara as buffer states between both empires. This would protect India and also key British sea trade routes by stopping Russia from gaining a port on the Persian Gulf or the Indian Ocean. Russia proposed Afghanistan as the neutral zone, and the final result was diving up Afghanistan with a neutral zone in the middle between Russian areas in the north and British in the South. Important episodes included the failed
First Anglo-Afghan War
The First Anglo-Afghan War ( fa, جنگ اول افغان و انگلیس) was fought between the British Empire and the Emirate of Kabul from 1838 to 1842. The British initially successfully invaded the country taking sides in a succession di ...
of 1838, the
First Anglo-Sikh War of 1845, the
Second Anglo-Sikh War of 1848, the
Second Anglo-Afghan War of 1878, and the annexation of
Kokand by Russia. The 1901 novel
''Kim'' by
Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)'' The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
made the term popular and introduced the new implication of great power rivalry. It became even more popular after the 1979 advent of the
Soviet–Afghan War.
[Seymour Becker, "The ‘great game’: The history of an evocative phrase." ''Asian Affairs'' 43.1 (2012): 61-80.]
Qing China

By 1644, the northern
Manchu people had conquered
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
and established a foreign dynasty—the
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
—once more. The Manchu Qing emperors, especially Confucian scholar
Kangxi, remained largely conservative—retaining the bureaucracy and the scholars within it, as well as the Confucian ideals present in Chinese society. However, changes in the economy and new attempts at resolving certain issues occurred too. These included increased trade with Western countries that brought large amounts of silver into the Chinese economy in exchange for tea,
porcelain, and silk textiles. This allowed for a new merchant-class, the
compradors, to develop. In addition, repairs were done on existing
dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes ...
, canals, roadways, and
irrigation works. This, combined with the lowering of taxes and government-assigned labor, was supposed to calm peasant unrest. However, the Qing failed to control the growing landlord class which had begun to exploit the peasantry and abuse their position.
By the late 18th century, both internal and external issues began to arise in Qing China's politics, society, and economy. The exam system with which scholars were assigned into the bureaucracy became increasingly corrupt; bribes and other forms of cheating allowed for inexperienced and inept scholars to enter the bureaucracy and this eventually caused rampant neglect of the peasantry, military, and the previously mentioned infrastructure projects. Poverty and banditry steadily rose, especially in rural areas, and mass migrations looking for work throughout China occurred. The perpetually conservative government refused to make reforms that could resolve these issues.
Opium War
China saw its status reduced by what it perceived as parasitic trade with Westerners. Originally, European traders were at a disadvantage because the Chinese cared little for their goods, while European demand for Chinese commodities such as tea and porcelain only grew. In order to tip the trade imbalance in their favor, British merchants began to sell Indian
opium to the Chinese. Not only did this sap Chinese bullion reserves, it also led to widespread drug addiction amongst the
bureaucracy and society in general. A ban was placed on opium as early as 1729 by the
Yongzheng Emperor, but little was done to enforce it. By the early 19th century, under the new
Daoguang Emperor, the government began serious efforts to eradicate opium from Chinese society. Leading this endeavour were respected scholar-officials including
Imperial Commissioner Lin Zexu.
After Lin
destroyed more than 20,000 chests of opium in the summer of 1839, Europeans demanded compensation for what they saw as unwarranted Chinese interference in their affairs. When it was not paid, the British declared war later the same year, starting what became known as the
First Opium War. The outdated Chinese
junks were no match for the advanced British gunboats, and soon the
Yangzi River region came under threat of British bombardment and invasion. The emperor had no choice but to sue for peace, resulting in the exile of Lin and the making of the
Treaty of Nanking, which ceded the British control of
Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a List of cities in China, city and Special administrative regions of China, special ...
and opened up trade and diplomacy with other European countries, including Germany, France, and the USA.
Inner Manchuria
Northeast China came under influence of Russia with the building of the
Chinese Eastern Railway through
Harbin to
Vladivostok. The
Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent form ...
replaced Russian influence in the region as a result of the
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
in 1904–1905, and Japan laid the
South Manchurian Railway
The South Manchuria Railway ( ja, 南満州鉄道, translit=Minamimanshū Tetsudō; ), officially , Mantetsu ( ja, 満鉄, translit=Mantetsu) or Mantie () for short, was a large of the Empire of Japan whose primary function was the operatio ...
in 1906 to
Port Arthur. During the
Warlord Era in China,
Zhang Zuolin established himself in Northeast China, but was murdered by the Japanese for being too independent. The former Chinese emperor,
Puyi, was then placed on the throne to lead a Japanese puppet state of
Manchukuo. In August 1945, the Soviet Union invaded the region. From 1945 to 1948, Northeast China was a base area for Mao Zedong's
People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the China, People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five Military branch, service branches: the People's ...
in the
Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on main ...
. With the encouragement of the Kremlin, the area was used as a staging ground during the Civil War for the
Chinese Communists, who were victorious in 1949 and have controlled ever since.
Joseon


When it became the 19th century, the king of
Joseon was powerless. Because the noble family of the king's wife got the power and ruled the country by their way. The 26th king of Joseon dynasty,
Gojong's father,
Heungseon Daewongun wanted the king be powerful again. Even he wasn't the king. As the father of young king, he destroyed noble families and corrupt organizations. So the royal family got the power again. But he wanted to rebuild
Gyeongbokgung palace in order to show the royal power to people. So he was criticized by people because he spent enormous money and
inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
occurred because of that. So his son, the real king
Gojong got power.
Korean Empire
The 26th king of
Joseon, Gojong changed the nation's name to ''Daehan Jeguk''. It means the
Korean Empire. And he also promoted himself as an emperor. The new empire accepted more western technology and strengthened military power. And
Korean Empire was going to become a
Neutral Nation
The Neutral Confederacy (also Neutral Nation, Neutral people, or ''Attawandaron'' by neighbouring tribes) were an Iroquoian people who lived in what is now southwestern and south-central Ontario in Canada, North America. They lived throughout ...
. Unfortunately, in the
Russo-Japanese war
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
, Japan ignored this, and eventually Japan won against
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
, and started to invade Korea. Japan first stole the right of diplomacy from Korean Empire illegally. But every western country ignored this invasion because they knew Japan became a strong country as they defeated Russian Empire. So emperor Gojong sent diplomats to a Dutch city known as
The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
to let everyone know that Japan stole the Empire's right illegally. But it was failed. Because the diplomats couldn't go into the conference room. Japan kicked Gojong off on the grounds that this reason. 3 years after, In 1910, Korean Empire became a part of Empire of Japan. It was the first time ever after invasion of Han dynasty in 108 BC.
Contemporary

The European powers had control of other parts of Asia by the early 20th century, such as
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
,
French Indochina
French Indochina (previously spelled as French Indo-China),; vi, Đông Dương thuộc Pháp, , lit. 'East Ocean under French Control; km, ឥណ្ឌូចិនបារាំង, ; th, อินโดจีนฝรั่งเศส, ...
,
Spanish East Indies, and Portuguese
Macau and
Goa. The
Great Game between Russia and Britain was the struggle for power in the Central Asian region in the nineteenth century. The
Trans-Siberian Railway, crossing Asia by train, was complete by 1916. Parts of Asia remained free from European control, although not influence, such as
Persia,
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
and most of China. In the twentieth century,
Imperial Japan expanded into China and Southeast Asia during the
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. After the war, many Asian countries became independent from European powers. During the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, the northern parts of Asia were communist controlled with the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
and People's Republic of China, while western allies formed pacts such as
CENTO and
SEATO. Conflicts such as the
Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top:{ ...
,
Vietnam War and
Soviet invasion of Afghanistan were fought between communists and anti-communists. In the decades after the Second World War, a massive restructuring plan drove Japan to become the world's second-largest economy, a phenomenon known as the
Japanese post-war economic miracle. The
Arab–Israeli conflict
The Arab–Israeli conflict is an ongoing intercommunal phenomenon involving political tension, military conflicts, and other disputes between Arab countries and Israel, which escalated during the 20th century, but had mostly faded out by th ...
has dominated much of the recent history of the Middle East. After the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
's collapse in 1991, there were many new independent nations in Central Asia.
China
Prior to
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, China faced a civil war between
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also Romanization of Chinese, romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the List of national founde ...
's Communist party and
Chiang Kai-shek's nationalist party; the nationalists appeared to be in the lead. However, once the
Japanese invaded in 1937, the two parties were forced to form a temporary cease-fire in order to defend China. The nationalists faced many military failures that caused them to lose territory and subsequently, respect from the Chinese masses. In contrast, the communists' use of guerilla warfare (led by
Lin Biao) proved effective against the Japanese's conventional methods and put the Communist Party on top by 1945. They also gained popularity for the reforms they were already applying in controlled areas, including land redistribution, education reforms, and widespread health care. For the next four years, the nationalists would be forced to retreat to the small island east of Fujian province, known as
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
(formerly known as Formosa), where they remain today. In mainland China,
People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
was established by the Communist Party, with
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also Romanization of Chinese, romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the List of national founde ...
as its
state chairman.
The communist government in China was defined by the party
cadres. These hard-line officers controlled the
People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the China, People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five Military branch, service branches: the People's ...
, which itself controlled large amounts of the bureaucracy. This system was further controlled by the
Central Committee, which additionally supported the state chairman who was considered the head of the government. The People's Republic's foreign policies included the repressing of
secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics l ...
attempts in Mongolia and Tibet and supporting of
North Korea and
North Vietnam in the
Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top:{ ...
and
Vietnam War, respectively. By 1960 China and the USSR became adversaries, battling worldwide for control of local communist movements.
Today China plays important roles in world economics and politics. China today is the world's second largest economy and the second fastest growing economy.
Indian Subcontinent
From the mid-18th century to the mid-19th century, large regions of India were gradually annexed by the
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
, a chartered company acting as a sovereign power on behalf of the British government. Dissatisfaction with
company rule in India
Company rule in India (sometimes, Company ''Raj'', from hi, rāj, lit=rule) refers to the rule of the British East India Company on the Indian subcontinent. This is variously taken to have commenced in 1757, after the Battle of Plassey, whe ...
led to the
Indian Rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the for ...
, which rocked parts of north and central India, and led to the dissolution of the company. India was afterwards ruled directly by the
British Crown, in the
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
. After
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, a nationwide struggle for independence was launched by the
Indian National Congress, led by
Mahatma Gandhi, and noted for
nonviolence. Later, the
All-India Muslim League would advocate for a separate Muslim-majority
nation state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may ...
.
In August 1947, the British Indian Empire was
partitioned into the
Union of India and
Dominion of Pakistan
Between 14 August 1947 and 23 March 1956, Pakistan was an independent federal dominion in the Commonwealth of Nations, created by the passing of the Indian Independence Act 1947 by the British parliament, which also created the Dominion of ...
. In particular, the partition of
Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
and Bengal led to rioting between Hindus, Muslims, and Sikhs in these provinces and spread to other nearby regions, leaving some 500,000 dead. The police and army units were largely ineffective. The British officers were gone, and the units were beginning to tolerate if not actually indulge in violence against their religious enemies.
[Philip Ziegler, ''Mountbatten''(1985) p. 401.] Also, this period saw one of the largest mass migrations anywhere in modern history, with a total of 12 million Hindus, Sikhs and Muslims moving between the newly created nations of India and Pakistan (which gained independence on 15 and 14 August 1947 respectively).
In 1971,
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
, formerly
East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Myanmar, wit ...
and
East Bengal
ur,
, common_name = East Bengal
, status = Province of the Dominion of Pakistan
, p1 = Bengal Presidency
, flag_p1 = Flag of British Bengal.svg
, s1 = Ea ...
, seceded from Pakistan
through an
armed conflict sparked by the rise of the
Bengali nationalist and
self-determination movement.
Korea

During the period when the
Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top:{ ...
occurred, Korea divided into North and South.
Syngman Rhee
Syngman Rhee (, ; 26 March 1875 – 19 July 1965) was a South Korean politician who served as the first president of South Korea from 1948 to 1960.
Rhee was also the first and last president of the Provisional Government of the Republic of Ko ...
became the first president of
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, and
Kim Il-sung became the supreme leader of
North Korea. After the war, the president of South Korea, Syngman Rhee tries to become a dictator. So the
April Revolution occurred, eventually
Syngman Rhee
Syngman Rhee (, ; 26 March 1875 – 19 July 1965) was a South Korean politician who served as the first president of South Korea from 1948 to 1960.
Rhee was also the first and last president of the Provisional Government of the Republic of Ko ...
was exiled from his country.
In 1963,
Park Chung-hee was empowered with a military coup d'état. He dispatched
Republic of Korea Army to
Vietnam War. And during this age, the economy of
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
outran that of
North Korea.
Although
Park Chung-hee improved the nation's economy, he was a dictator, so people didn't like him. Eventually, he is murdered by
Kim Jae-gyu
Kim Jae-gyu (Hangul: 김재규, April 9, 1924 – May 24, 1980) was a South Korean politician, army lieutenant general and the director of the Korean Central Intelligence Agency. He assassinated South Korean President Park Chung-hee— ...
. In 1979,
Chun Doo-hwan was empowered by another coup d’état by military. He oppressed the resistances in the city of
Gwangju. That event is called 'Gwangju Uprising'. Despite the Gwangju Uprising,
Chun Doo-hwan became the president. But the people resisted again in 1987. This movement is called '
June Struggle'. As a result of
Gwangju Uprising
The Gwangju Uprising was a popular uprising in the city of Gwangju, South Korea, from May 18 to May 27, 1980, which pitted local, armed citizens against soldiers and police of the South Korean government. The event is sometimes called 5·18 ( ...
and
June Struggle, South Korea finally became a democratic republic in 1987.
Roh Tae-woo (1988–93),
Kim Young-sam (1993–98), Kim Dae-jung (1998–2003), Roh Moo-hyun (2003–2008), Lee Myung-bak (2008–2013), Park Geun-hye (2013–2017), Moon Jae-in (2017–) were elected as a president in order after 1987. In 1960,
North Korea was far wealthier than
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
. But in 1970, South Korea begins to outrun the North Korean economy. In 2018, South Korea is ranked #10 in world GDP ranking.
See also
* Ancient Asian history
* History of Southeast Asia
*
* Prehistoric Asia
References
Bibliography
*
* Cotterell, Arthur. ''Asia: A Concise History'' (2011)
* Cotterell, Arthur. ''Western Power in Asia: Its Slow Rise and Swift Fall, 1415 - 1999'' (2009) popular history
excerpt* Curtin, Philip D. ''The World and the West: The European Challenge and the Overseas Response in the Age of Empire'' (2002)
* Embree, Ainslie T., and Carol Gluck, eds. '' Asia in Western and World History: A Guide for Teaching'' (M.E. Sharpe, 1997).
* Embree, Ainslie T., ed. ''Encyclopedia of Asian history'' (1988)
vol. 1 onlinevol 2 onlinevol 3 onlinevol 4 online
* Fairbank, John K., Edwin O. Reischauer. '' A History of East Asian Civilization: Volume One : East Asia the Great Tradition'' and ''A History of East Asian Civilization: Volume Two : East Asia the Modern transformation'' (1966
Online free to borrow
* Moffett, Samuel Hugh. ''A History of Christianity in Asia, Vol. II: 1500–1900'' (2003
excerpt
* Murphey, Rhoads. ''A History of Asia'' (8th ed, 2019
excerpt
als
Online
* Paine, S. C. M. ''The Wars for Asia, 1911-1949'' (2014
excerpt
*
* Stearns, Peter N., and William L. Langer. ''The Encyclopedia of World History: Ancient, Medieval, and Modern'' (2001)
Regions
* Adshead, Samuel Adrian Miles. ''Central Asia in world history'' (Springer, 2016).
* Best, Antony. ''The International History of East Asia, 1900-1968: Trade, Ideology and the Quest for Order'' (2010
online
* Catchpole, Brian. ''A map history of modern China'' (1976), new maps & diagrams
* Clyde, Paul Herbert. ''International-Rivalries-In-Manchuria-1689-1928'' (2nd ed. 1928
online free
* Clyde, Paul H, and Burton H. Beers. ''The Far East, a history of the Western impact and the Eastern response, 1830-1975'' (6th ed. 1975) 575pp
**Clyde, Paul Hibbert. ''The Far East: A History of the Impact of the West on Eastern Asia'' (3rd ed. 1948
online free
836pp
* Ebrey, Patricia Buckley, Anne Walthall and James Palais. ''East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History'' (2006); 639pp; also in 2-vol edition split at 1600.
* Fenby, Jonatham ''The Penguin History of Modern China: The Fall and Rise of a Great Power 1850 to the Present'' (3rd ed. 2019) popular history.
* Gilbert, Marc Jason. ''South Asia in World History'' (Oxford UP, 2017)
* Goldin, Peter B. ''Central Asia in World History'' (Oxford UP, 2011)
* Holcombe, Charles. ''A History of East Asia: From the Origins of Civilization to the Twenty-First Century'' (2010).
* Huffman, James L. ''Japan in World History'' (Oxford, 2010)
* Jansen, Marius B. ''Japan and China: From War to Peace, 1894-1972'' (1975)
* Karl, Rebecca E. "Creating Asia: China in the world at the beginning of the twentieth century." ''American Historical Review'' 103.4 (1998): 1096–1118
online
* Lockard, Craig. ''Southeast Asia in world history'' (Oxford UP, 2009).
* Ludden, David. ''India and South Asia: A Short History'' (2013).
* Mansfield, Peter, and Nicolas Pelham, ''A History of the Middle East'' (4th ed, 2013).
* Park, Hye Jeong. "East Asian Odyssey Towards One Region: The Problem of East Asia as a Historiographical Category." ''History Compass'' 12.12 (2014): 889–900
online
* Ropp, Paul S. ''China in World History'' (Oxford UP, 2010)
Economic history
* Allen, G.C. ''A Short Economic History Of Modern Japan 1867-1937'' (1945
online
als
1981 edition free to borrow
* Cowan, C.D. ed. ''The economic development of China and Japan: studies in economic history and political economy'' (1964
online free to borrow
* Hansen, Valerie. ''The Silk Road: A New History'' (Oxford University Press, 2012).
* Jones, Eric. ''The European miracle: environments, economies and geopolitics in the history of Europe and Asia. (Cambridge UP, 2003).
* Lockwood, William W. ''The economic development of Japan; growth and structural change'' (1970
online free to borrow
* Pomeranz, Kenneth. ''The Great Divergence: China, Europe, and the Making of the Modern World Economy.'' (2001)
* Schulz-Forberg, Hagen, ed. ''A Global Conceptual History of Asia, 1860–1940'' (2015)
* Smith, Alan K. ''Creating a World Economy: Merchant Capital, Colonialism, and World Trade, 1400-1825'' (Routledge, 2019).
* Von Glahn, Richard. ''The Economic History of China'' (2016)
Relations with Europe
* Belk, Russell. "China’s global trade history: A western perspective." Journal of China Marketing 6.1 (2016): 1-22 [1 online].
* Hoffman, Philip T. ''Why did Europe conquer the world?'' (Princeton UP, 2017).\
* Ji, Fengyuan. "The West and China: discourses, agendas and change." ''Critical Discourse Studies'' 14.4 (2017): 325-340.
* Lach, Donald F. ''Asia in the Making of Europe'' (3 vol. U of Chicago Press, 1994).
* Lach, Donald F. ''Southeast Asia in the eyes of Europe: the sixteenth century'' (U of Chicago Press, 1968).
* Lach, Donald F., and Edwin J. Van Kley. "Asia in the eyes of Europe: the seventeenth century." ''The Seventeenth Century'' 5.1 (1990): 93-109.
* Lach, Donald F. ''China in the eyes of Europe: the Sixteenth Century'' (U of Chicago Press, 1968).
* Lee, Christina H., ed. ''Western visions of the Far East in a Transpacific Age, 1522-1657'' (Routledge, 2016).
* Nayar, Pramod K. "Marvelous excesses: English travel writing and India, 1608–1727." ''Journal of British Studies'' 44.2 (2005): 213-238.
* Pettigrew, William A., and Mahesh Gopalan, eds. ''The East India Company, 1600-1857: Essays on Anglo-Indian Connection'' (Routledge, 2016).
* Smith, Alan K. ''Creating a World Economy: Merchant Capital, Colonialism, and World Trade, 1400-1825'' (Routledge, 2019).
* Steensgaard, Niels. "European shipping to Asia 1497–1700." ''Scandinavian Economic History Review'' 18.1 (1970): 1–11.
{{History by continent
History of Asia,
 A report by archaeologist Rakesh Tewari on Lahuradewa,
A report by archaeologist Rakesh Tewari on Lahuradewa,  The Achaemenid dynasty of the Persian Empire, founded by Cyrus the Great, ruled an area from
The Achaemenid dynasty of the Persian Empire, founded by Cyrus the Great, ruled an area from  Since 1029 BCE, the
Since 1029 BCE, the  The Arabian peninsula and the surrounding
The Arabian peninsula and the surrounding  After Muhammad introduced Islam, it jump-started Middle Eastern culture into an
After Muhammad introduced Islam, it jump-started Middle Eastern culture into an  The Indian early medieval age, 600 to 1200, is defined by regional kingdoms and cultural diversity. When Harsha of Kannauj, who ruled much of the Indo-Gangetic Plain from 606 to 647, attempted to expand southwards, he was defeated by the
The Indian early medieval age, 600 to 1200, is defined by regional kingdoms and cultural diversity. When Harsha of Kannauj, who ruled much of the Indo-Gangetic Plain from 606 to 647, attempted to expand southwards, he was defeated by the  Fortunately, one of Yang's most respectable advisors, Li Yuan, was able to claim the throne quickly, preventing a chaotic collapse. He proclaimed himself Emperor Gaozu, and established the
Fortunately, one of Yang's most respectable advisors, Li Yuan, was able to claim the throne quickly, preventing a chaotic collapse. He proclaimed himself Emperor Gaozu, and established the  By 1227, the Mongols had conquered the Western Xia kingdom northwest of China. Soon the Mongols incurred upon the Jin empire of the Jurchens. Chinese cities were soon besieged by the Mongol hordes that showed little mercy for those who resisted and the Southern Song Chinese were quickly losing territory. In 1271 the current great khan, Kublai Khan, claimed himself Emperor of China and officially established the Yuan dynasty. By 1290, all of China was under control of the Mongols, marking the first time they were ever completely conquered by a foreign invader; the new capital was established at Khanbaliq (modern-day
By 1227, the Mongols had conquered the Western Xia kingdom northwest of China. Soon the Mongols incurred upon the Jin empire of the Jurchens. Chinese cities were soon besieged by the Mongol hordes that showed little mercy for those who resisted and the Southern Song Chinese were quickly losing territory. In 1271 the current great khan, Kublai Khan, claimed himself Emperor of China and officially established the Yuan dynasty. By 1290, all of China was under control of the Mongols, marking the first time they were ever completely conquered by a foreign invader; the new capital was established at Khanbaliq (modern-day 
 The rest of
The rest of  Goryeo reunited the Korean peninsula during the later three kingdoms period and named itself as 'Empire'. But nowadays, Goryeo is known as a kingdom. The name 'Goryeo' was derived from
Goryeo reunited the Korean peninsula during the later three kingdoms period and named itself as 'Empire'. But nowadays, Goryeo is known as a kingdom. The name 'Goryeo' was derived from 
 In 802,
In 802,  In the interest of national glory, the Chinese began sending impressive junk ships across the
In the interest of national glory, the Chinese began sending impressive junk ships across the  As was inevitable, Westerners arrived on the Chinese east coast, primarily Jesuit missionaries which reached the mainland in 1582. They attempted to convert the Chinese people to Christianity by first converting the top of the social hierarchy and allowing the lower classes to subsequently convert. To further gain support, many Jesuits adopted Chinese dress, customs, and language. Some Chinese scholars were interested in certain Western teachings and especially in Western technology. By the 1580s, Jesuit scholars like Matteo Ricci and Adam Schall amazed the Chinese elite with technological advances such as European clocks, improved calendars and cannons, and the accurate prediction of eclipses. Although some the scholar-gentry converted, many were suspicious of the Westerners whom they called "barbarians" and even resented them for the embarrassment they received at the hand of Western correction. Nevertheless, a small group of Jesuit scholars remained at the court to impress the emperor and his advisors.
As was inevitable, Westerners arrived on the Chinese east coast, primarily Jesuit missionaries which reached the mainland in 1582. They attempted to convert the Chinese people to Christianity by first converting the top of the social hierarchy and allowing the lower classes to subsequently convert. To further gain support, many Jesuits adopted Chinese dress, customs, and language. Some Chinese scholars were interested in certain Western teachings and especially in Western technology. By the 1580s, Jesuit scholars like Matteo Ricci and Adam Schall amazed the Chinese elite with technological advances such as European clocks, improved calendars and cannons, and the accurate prediction of eclipses. Although some the scholar-gentry converted, many were suspicious of the Westerners whom they called "barbarians" and even resented them for the embarrassment they received at the hand of Western correction. Nevertheless, a small group of Jesuit scholars remained at the court to impress the emperor and his advisors.
 In early-modern Korea, the 500-year-old kingdom, Goryeo fell and new dynasty Joseon rose in August 5, 1392. Taejo of Joseon changed the country's name from Goryeo to Joseon. Sejong the Great created
In early-modern Korea, the 500-year-old kingdom, Goryeo fell and new dynasty Joseon rose in August 5, 1392. Taejo of Joseon changed the country's name from Goryeo to Joseon. Sejong the Great created  In early-modern Japan following the
In early-modern Japan following the  The Great Game was a political and diplomatic confrontation between Great Britain and Russia over
The Great Game was a political and diplomatic confrontation between Great Britain and Russia over  By 1644, the northern Manchu people had conquered
By 1644, the northern Manchu people had conquered 
 When it became the 19th century, the king of Joseon was powerless. Because the noble family of the king's wife got the power and ruled the country by their way. The 26th king of Joseon dynasty, Gojong's father, Heungseon Daewongun wanted the king be powerful again. Even he wasn't the king. As the father of young king, he destroyed noble families and corrupt organizations. So the royal family got the power again. But he wanted to rebuild Gyeongbokgung palace in order to show the royal power to people. So he was criticized by people because he spent enormous money and
When it became the 19th century, the king of Joseon was powerless. Because the noble family of the king's wife got the power and ruled the country by their way. The 26th king of Joseon dynasty, Gojong's father, Heungseon Daewongun wanted the king be powerful again. Even he wasn't the king. As the father of young king, he destroyed noble families and corrupt organizations. So the royal family got the power again. But he wanted to rebuild Gyeongbokgung palace in order to show the royal power to people. So he was criticized by people because he spent enormous money and  The European powers had control of other parts of Asia by the early 20th century, such as
The European powers had control of other parts of Asia by the early 20th century, such as  During the period when the
During the period when the