Heating on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A central heating system provides warmth to a number of spaces within a building from one main source of heat. It is a component of
 Electrical heating systems occur less commonly and are practical only with low-cost electricity or when ground source heat pumps are used. Considering the combined system of
Electrical heating systems occur less commonly and are practical only with low-cost electricity or when ground source heat pumps are used. Considering the combined system of
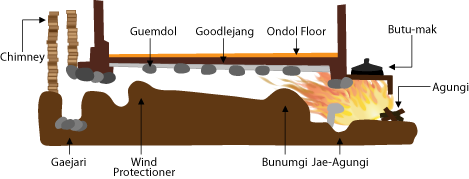 Use of the ''
Use of the ''
 William Strutt designed a new mill building in
William Strutt designed a new mill building in
 The English writer
The English writer
 Early hot water systems were used in
Early hot water systems were used in  Perkins' 1832 apparatus distributed water at 200 degrees
Perkins' 1832 apparatus distributed water at 200 degrees

 An expansion tank contains compressed gas, separated from the sealed-system water by a diaphragm. This allows for normal variations of pressure in the system. A safety valve allows water to escape from the system when pressure becomes too high, and a valve can open to replenish water from the normal water supply if the pressure drops too low. Sealed systems offer an alternative to open-vent systems, in which steam can escape from the system, and gets replaced from the building's water supply via a feed and central storage system.
Heating systems in the United Kingdom and in other parts of Europe commonly combine the needs of space heating with domestic hot-water heating. These systems occur less commonly in the USA. In this case, the heated water in a sealed system flows through a heat exchanger in a hot-water tank or hot-water cylinder where it heats water from the regular potable water supply for use at hot-water taps or appliances such as
An expansion tank contains compressed gas, separated from the sealed-system water by a diaphragm. This allows for normal variations of pressure in the system. A safety valve allows water to escape from the system when pressure becomes too high, and a valve can open to replenish water from the normal water supply if the pressure drops too low. Sealed systems offer an alternative to open-vent systems, in which steam can escape from the system, and gets replaced from the building's water supply via a feed and central storage system.
Heating systems in the United Kingdom and in other parts of Europe commonly combine the needs of space heating with domestic hot-water heating. These systems occur less commonly in the USA. In this case, the heated water in a sealed system flows through a heat exchanger in a hot-water tank or hot-water cylinder where it heats water from the regular potable water supply for use at hot-water taps or appliances such as
 In mild climates an air source heat pump can be used to air condition the building during hot weather, and to warm the building using heat extracted from outdoor air in cold weather. Air-source heat pumps are generally uneconomic for outdoor temperatures much below freezing. In colder climates,
In mild climates an air source heat pump can be used to air condition the building during hot weather, and to warm the building using heat extracted from outdoor air in cold weather. Air-source heat pumps are generally uneconomic for outdoor temperatures much below freezing. In colder climates,
EERE Consumer's Guide: Selecting Heating Fuel and System Types
/ref> Oil storage tanks, especially underground storage tanks, can also impact the environment. Even if a building's heating system was converted from oil long ago, oil may still be impacting the environment by contaminating soil and groundwater. Building owners can find themselves liable to remove buried tanks and the remediation costs.
BBC Wales History – Life before central heating
{{HVAC Plumbing Residential heating Greek inventions Ancient Greek technology Ancient Roman technology de:Gebäudeheizung#Zentralheizung
heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality ...
(short: HVAC) systems, which can both cool and warm interior spaces.
A central heating system has a furnace that converts fuel or electricity to heat. The heat is circulated through the building either by fans forcing heated air through ducts, circulation of low-pressure steam to radiators in each heated room, or pumps that circulate hot water through room radiators. Primary energy sources may be fuels like coal or wood, oil, kerosene, natural gas, or electricity.
Compared with systems such as fireplaces and wood stoves, a central heating plant offers improved uniformity of temperature control over a building, usually including automatic control of the furnace. Large homes or buildings may be divided into individually controllable zones with their own temperature controls. Automatic fuel (and sometimes ash) handling provides improved convenience over separate fireplaces. Where a system includes ducts for air circulation, central air conditioning can be added to the system. A central heating system may take up considerable space in a home or other building, and may require supply and return ductwork to be installed at the time of construction.
Overview
Central heating differs from space heating in that the heat generation occurs in one place, such as a furnace room orbasement
A basement or cellar is one or more Storey, floors of a building that are completely or partly below the storey, ground floor. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the Furnace (house heating), furnace, ...
in a house or a mechanical room in a large building (though not necessarily at the geometrically "central" point). The heat is distributed throughout the building, typically by forced-air through ductwork, by water circulating through pipes, or by steam fed through pipes. The most common method of heat generation involves the combustion of fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels ma ...
in a furnace or boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central ...
.
In much of the temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
zone, most detached housing has had central heating installed since before the Second World War. Where coal was readily available (i.e. the anthracite coal region
The Coal Region is a region of Northeastern Pennsylvania. It is known for being home to the largest known deposits of anthracite coal in the world with an estimated reserve of seven billion short tons.
The region is typically defined as compris ...
in northeast Pennsylvania) coal-fired steam or hot water systems were common. Later in the 20th century, these were updated to burn fuel oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil, marine fuel oil (MFO), b ...
or gas, eliminating the need for a large coal storage bin near the boiler and the need to remove and discard coal ashes.
A cheaper alternative to hot water or steam heat is forced hot air. A furnace burns fuel oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil, marine fuel oil (MFO), b ...
or gas, which heats air in a heat exchanger, and blower fans circulate the warmed air through a network of ducts to the rooms in the building. This system is cheaper because the air moves through a series of ducts instead of pipes, and does not require a pipe fitter to install. The space between floor joists can be boxed in and used as some of the ductwork, further lowering costs.
thermal power station
A thermal power station is a type of power station in which heat energy is converted to electrical energy. In a steam-generating cycle heat is used to boil water in a large pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam, which drives a stea ...
and electric resistance heating, the overall efficiency will be less than for direct use of fossil fuel for space heating.
Some other buildings utilize central solar heating
Central solar heating is the provision of central heating and hot water from solar energy by a system in which the water is heated centrally by arrays of solar thermal collectors (central solar heating plants - CSHPs) and distributed through dis ...
, in which case the distribution system normally uses water circulation.
Alternatives to such systems are gas heater
A gas heater is a space heater used to heat a room or outdoor area by burning natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, propane or butane.
Indoor household gas heaters can be broadly categorized in one of two ways: ''flued'' or ''non-flued,'' or '' ...
s and district heating
District heating (also known as heat networks or teleheating) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating ...
. District heating uses the waste heat
Waste heat is heat that is produced by a machine, or other process that uses energy, as a byproduct of doing work. All such processes give off some waste heat as a fundamental result of the laws of thermodynamics. Waste heat has lower utilit ...
from an industrial process or electrical generating plant to provide heat for neighboring buildings. Similar to cogeneration
Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time.
Cogeneration is a more efficient use of fuel or heat, because otherwise- wasted heat from elec ...
, this requires underground piping to circulate hot water or steam.
History
Ancient Korea
 Use of the ''
Use of the ''ondol
Ondol (; , Hangul: 온돌, 溫堗, ) or gudeul (Hangul: 구들, ) in Korean traditional architecture, is underfloor heating that uses direct heat transfer from wood smoke to heat the underside of a thick masonry floor. In modern usage it refe ...
'' has been found at archaeological sites in present-day North Korea. A Neolithic Age
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
archaeological site, circa 5000 BC, discovered in Unggi
Sonbong County, formerly called Unggi ( Chosŏn'gŭl: 웅기, Hancha: 雄基), is a subdivision of the North Korean city of Rason. It is located at the northeastern extreme of North Korea, bordering Russia and China. It lies on Unggi Bay, an ext ...
, Hamgyeongbuk-do
"North Hamgyeong Province" or "''Hamgyeongbuk-do''" () is, according to South Korean law, a province of the Republic of Korea, as the South Korean government formally claims to be the legitimate government of whole of Korea. The area constitu ...
, in present-day North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
, shows a clear vestige of gudeul in the excavated dwelling ().
The main components of the traditional ''ondol'' are an '' agungi'' (firebox
Firebox may refer to:
* Firebox (steam engine), the area where the fuel is burned in a steam engine
* Firebox (architecture), the part of a fireplace where fuel is combusted
*Firebox Records, a Finnish 8101705801record label
* Firebox.com, an elect ...
or stove
A stove or range is a device that burns fuel or uses electricity to generate heat inside or on top of the apparatus, to be used for general warming or cooking. It has evolved highly over time, with cast-iron and induction versions being develope ...
) accessible from an adjoining room (typically kitchen or master bedroom), a raised masonry
Masonry is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term ''masonry'' can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are bricks, building ...
floor underlain by horizontal smoke passages, and a vertical, freestanding chimney
A chimney is an architectural ventilation structure made of masonry, clay or metal that isolates hot toxic exhaust gases or smoke produced by a boiler, stove, furnace, incinerator, or fireplace from human living areas. Chimneys are typ ...
on the opposite exterior wall providing a draft. The heated floor, supported by stone piers or baffles to distribute the smoke, is covered by stone slabs, clay and an impervious layer such as oiled paper.
Early ''ondol''s began as ''gudeul'' that provided the heating for a home and for cooking. When a fire was lit in the furnace to cook rice for dinner, the flame would extend horizontally because the flue entry was beside the furnace. This arrangement was essential, as it would not allow the smoke to travel upward, which would cause the flame to go out too soon. As the flame would pass through the flue entrance, it would be guided through the network of passages with the smoke. Entire rooms would be built on the furnace flue to create ondol floored rooms.
Ondol had traditionally been used as a living space for sitting, eating, sleeping and other pastimes in most Korean homes before the 1960s. Koreans are accustomed to sitting and sleeping on the floor, and working and eating at low tables instead of raised tables with chairs. The furnace burned mainly rice paddy straws, agricultural crop waste, biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bio ...
or any kind of dried firewood. For short-term cooking, rice paddy straws or crop waste was preferred, while long hours of cooking and floor heating needed longer-burning firewood. Unlike modern-day water heaters, the fuel was either sporadically or regularly burned (two to five times a day), depending on frequency of cooking and seasonal weather conditions.
Ancient Rome and Greece
The ancient Greeks originally developed central heating. Thetemple of Ephesus
The Temple of Artemis or Artemision ( gr, Ἀρτεμίσιον; tr, Artemis Tapınağı), also known as the Temple of Diana, was a Greek temple dedicated to an ancient, local form of the goddess Artemis (identified with Diana, a Roman g ...
was heated by flues
A flue is a duct, pipe, or opening in a chimney for conveying exhaust gases from a fireplace, furnace, water heater, boiler, or generator to the outdoors. Historically the term flue meant the chimney itself. In the United States, they are ...
planted in the ground and circulating the heat which was generated by fire. Some buildings in the Roman Empire used central heating systems, conducting air heated by furnaces
A furnace is a structure in which heat is produced with the help of combustion.
Furnace may also refer to:
Appliances Buildings
* Furnace (central heating): a furnace , or a heater or boiler , used to generate heat for buildings
* Boiler, used t ...
through empty spaces under the floors and out of pipes
Pipe(s), PIPE(S) or piping may refer to:
Objects
* Pipe (fluid conveyance), a hollow cylinder following certain dimension rules
** Piping, the use of pipes in industry
* Smoking pipe
** Tobacco pipe
* Half-pipe and quarter pipe, semi-circula ...
(called ''caliducts'') in the walls—a system known as a ''hypocaust
A hypocaust ( la, hypocaustum) is a system of central heating in a building that produces and circulates hot air below the floor of a room, and may also warm the walls with a series of pipes through which the hot air passes. This air can warm th ...
''.
The Roman hypocaust continued to be used on a smaller scale during late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English h ...
and by the Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
, while later Muslim builders employed a simpler system of underfloor pipes.
After the collapse of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
, overwhelmingly across Europe, heating reverted to more primitive fireplaces for almost a thousand years.
In the early medieval Alpine upland, a simpler central heating system where heat travelled through underfloor channels from the furnace room replaced the Roman hypocaust at some places. In Reichenau Abbey
Reichenau Abbey was a Benedictine monastery on Reichenau Island (known in Latin as Augia Dives). It was founded in 724 by the itinerant Saint Pirmin, who is said to have fled Spain ahead of the Moorish invaders, with patronage that included Charl ...
a network of interconnected underfloor channels heated the 300 m² large assembly room of the monks during the winter months. The degree of efficiency of the system has been calculated at 90%.
In the 13th century, the Cistercian
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint B ...
monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedic ...
s revived central heating in Christian Europe using river diversions combined with indoor wood-fired furnaces. The well-preserved Royal Monastery of Our Lady of the Wheel (founded 1202) on the Ebro River in the Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to s ...
region of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
provides an excellent example of such an application.
Modern central heating systems
The three main methods of central heating were developed in the late 18th to mid-19th centuries.Hot air
Derby
Derby ( ) is a city and unitary authority area in Derbyshire, England. It lies on the banks of the River Derwent in the south of Derbyshire, which is in the East Midlands Region. It was traditionally the county town of Derbyshire. Derby g ...
with a central hot air furnace in 1793, although the idea had been already proposed by John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society.
John Evelyn's diary, or m ...
almost a hundred years earlier. Strutt's design consisted of a large stove that heated air brought from the outside by a large underground passage. The air was ventilated through the building by large central ducts.
In 1807, he collaborated with another eminent engineer, Charles Sylvester
Charles Sylvester (1774–1828) was a chemist and inventor born in Sheffield, in the Kingdom of Great Britain. He worked on galvanization, public building heating and sanitation, and railroad friction amongst other things. A book, ''Industrial M ...
, on the construction of a new building to house Derby's Royal Infirmary. Sylvester was instrumental in applying Strutt's novel heating system for the new hospital. He published his ideas in ''The Philosophy of Domestic Economy; as exemplified in the mode of Warming, Ventilating, Washing, Drying, & Cooking, ... in the Derbyshire General Infirmary'' in 1819. Sylvester documented the new ways of heating hospitals that were included in the design, and the healthier features such as self-cleaning and air-refreshing toilets. The infirmary's novel heating system allowed the patients to breathe fresh heated air whilst old air was channeled up to a glass and iron dome at the centre.
Their designs proved very influential. They were widely copied in the new mills of the Midlands
The Midlands (also referred to as Central England) are a part of England that broadly correspond to the Kingdom of Mercia of the Early Middle Ages, bordered by Wales, Northern England and Southern England. The Midlands were important in the In ...
and were constantly improved, reaching maturity with the work of de Chabannes on the ventilation of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
in the 1810s. This system remained the standard for heating small buildings for the rest of the century.
Steam
 The English writer
The English writer Hugh Plat
Sir Hugh Plat (1552–1608) was an English writer on agriculture and inventor, known from his works ''The Jewell House of Art and Nature'' (1594) and his major work on gardening ''Floraes Paradise'' (1608).
Biography
Hugh Plat was born in the ...
proposed a steam-based central heating system for a greenhouse in 1594, although this was an isolated occurrence and was not followed up until the 18th century. Colonel Coke devised a system of pipes that would carry steam around the house from a central boiler, but it was James Watt
James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was ...
the Scottish inventor who was the first to build a working system in his house.
A central boiler supplied high-pressure steam that then distributed the heat within the building through a system of pipes embedded in the columns. He implemented the system on a much larger scale at a textile factory in Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The ...
. Robertson Buchanan wrote the definitive description of these installations in his treatises published in 1807 and 1815. Thomas Tredgold
Thomas Tredgold (1788–1829) was an English engineer and author, known for his early work on railroad construction. His definition of civil engineering formed the basis of the charter of the Institution of Civil Engineers.
Biography
He was ...
's work ''Principles of Warming and Ventilating Public Buildings'', delineated the method of the application of hot steam heating to smaller, non-industrial buildings. This method had superseded the hot air systems by the late 19th century.
Hot water
 Early hot water systems were used in
Early hot water systems were used in Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom ...
for heating the Thermæ. Another early hot water system was developed in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
for central heating of the Summer Palace
The Summer Palace () is a vast ensemble of lakes, gardens and palaces in Beijing. It was an imperial garden in the Qing dynasty. Inside includes Longevity Hill () Kunming Lake and Seventeen Hole Bridge. It covers an expanse of , three-quarte ...
(1710–1714) of Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
. Slightly later, in 1716, came the first use of water in Sweden to distribute heating in buildings. Mårten Triewald
Mårten Triewald FRS (18 November 1691 – 8 August 1747), sometimes referred to as Mårten Triewald the Younger, was a Swedish merchant, engineer and amateur physicist.
Mårten Triewald was the son of Mårten Triewald the Elder, a farrier ...
, a Swedish engineer, used this method for a greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.These ...
at Newcastle upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne ( RP: , ), or simply Newcastle, is a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. The city is located on the River Tyne's northern bank and forms the largest part of the Tyneside built-up area. Newcastle is ...
. Jean Simon Bonnemain (1743–1830), a French architect, introduced the technique to industry on a cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-contro ...
, at Château du Pêcq, near Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
.
However, these scattered attempts were isolated and mainly confined in their application to greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.These ...
s. Tredgold originally dismissed its use as impractical, but changed his mind in 1836, when the technology went into a phase of rapid development.
Early systems had used low pressure water systems, which required very large pipes. One of the first modern hot water central heating systems to remedy this deficiency was installed by Angier March Perkins in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
in the 1830s. At that time central heating was coming into fashion in Britain, with steam or hot air systems generally being used.
 Perkins' 1832 apparatus distributed water at 200 degrees
Perkins' 1832 apparatus distributed water at 200 degrees Celsius
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius scale (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the Kelvin scale. The d ...
(392 °F) through small diameter pipes at high pressure. A crucial invention to make the system viable was the thread screwed joint, that allowed the joint between the pipes to bear a similar pressure to the pipe itself. He also separated the boiler from the heat source to reduce the risk of explosion. The first unit was installed in the home of Governor of the Bank of England John Horsley Palmer so that he could grow grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus '' Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years a ...
s in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
's cold climate.
His systems were installed in factories and churches across the country, many of them remaining in usable condition for over 150 years. His system was also adapted for use by bakers in the heating of their ovens and in the making of paper from wood pulp.
Franz San Galli, a Prussian-born Russian businessman living in St. Petersburg, invented the radiator
Radiators are heat exchangers used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics.
A radiator is always ...
between 1855 and 1857, which was a major step in the final shaping of modern central heating. The Victorian cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron– carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuri ...
radiator became widespread by the end of the 19th century as companies, such as the American Radiator Company, expanded the market for low cost radiators in the US and Europe.
Energy sources
The energy source selected for a central heating system varies by region. The primary energy source is selected on the basis of cost, convenience, efficiency and reliability. The energy cost of heating is one of the main costs of operating a building in a cold climate. Some central heating plants can switch fuels for reasons of economy and convenience; for example, a home owner may install a wood-fired furnace with electrical backup for occasional unattended operation.Solid fuel
Solid fuel refers to various forms of solid material that can be burnt to release energy, providing heat and light through the process of combustion. Solid fuels can be contrasted with liquid fuels and gaseous fuels. Common examples of solid fuel ...
s such as wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
, peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and ...
or coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
can be stockpiled at the point of use, but are inconvenient to handle and difficult to automatically control. Wood fuel is still used where the supply is plentiful and the occupants of the building don't mind the work involved in hauling in fuel, removing ashes, and tending the fire. Pellet fuel systems can automatically stoke the fire, but still need manual removal of ash. Coal was once an important residential heating fuel but today is uncommon, and smokeless fuel
Smokeless fuel is a type of solid fuel which either does not emit visible smoke, or emits minimal amounts, during combustion. These types of fuel are becoming increasingly popular in areas which ban the use of coal and other fuels such as unseaso ...
is preferred as a substitute in open fireplaces or stoves.
Liquid fuels are petroleum products such as heating oil
Heating oil is any petroleum product or other oil used for heating; a fuel oil. Most commonly, it refers to low viscosity grades of fuel oil used for furnaces or boilers use for home heating and in other buildings. Home heating oil is often ...
and kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning " wax", and was re ...
. These are still widely applied where other heat sources are unavailable. Fuel oil can be automatically fired in a central heating system and requires no ash removal and little maintenance of the combustion system. However, the variable price of oil on world markets leads to erratic and high prices compared to some other energy sources. Institutional heating systems (office buildings or schools, for example) can use low-grade, inexpensive bunker fuel to run their heating plants, but capital cost is high compared to more easily managed liquid fuels.
Natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
is a widespread heating fuel in North America and northern Europe. Gas burners are automatically controlled and require no ash removal and little maintenance. However, not all areas have access to a natural gas distribution system. Liquefied petroleum gas
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG or LP gas) is a fuel gas which contains a flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases, specifically propane, propylene, butylene, isobutane and n-butane.
LPG is used as a fuel gas in heating appliances, cookin ...
or propane can be stored at the point of use and periodically replenished by a truck-mounted mobile tank.
Some areas have low cost electric power, making electric heating economically practical. Electric heating can either be purely resistance-type heating or make use of a heat pump
A heat pump is a device that can heat a building (or part of a building) by transferring thermal energy from the outside using a refrigeration cycle. Many heat pumps can also operate in the opposite direction, cooling the building by removing ...
system to take advantage of low-grade heat in the air or ground.
A district heating
District heating (also known as heat networks or teleheating) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating ...
system uses centrally located boilers or water heaters and circulates heat energy to individual customers by circulating hot water or steam. This has the advantage of a central highly efficient energy converter that can use the best available pollution controls, and that is professionally operated. The district heating system can use heat sources impractical to deploy to individual homes, such as heavy oil, wood byproducts, or (hypothetically) nuclear fission. The distribution network is more costly to build than for gas or electric heating, and so is only found in densely populated areas or compact communities.
Not all central heating systems require purchased energy. A few buildings are served by local geothermal heat, using hot water or steam from a local well to provide building heat. Such areas are uncommon. A passive solar
In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, reflect, and distribute solar energy, in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. This is called passive solar design because, unli ...
system requires no purchased fuel but needs to be carefully designed for the site.
Calculating output of heater required
Heater outputs are measured in kilowatts or BTUs per hour. For placement in a house, the heater, and the level of output required for the house, needs to be calculated. This calculation is achieved by recording a variety of factors – namely, what is above and below the room you wish to heat, how many windows there are, the type of external walls in the property and a variety of other factors that will determine the level of heat output that is required to adequately heat the space. This calculation is called a heat loss calculation and can be done with a BTU Calculator. Depending on the outcome of this calculation, the heater can be exactly matched to the house.Billing
Heat output can be measured by Heat cost allocators, so that each unit can be individually billed even though there is only one centralized system.Types of central heating
Water heating
Circulating hot water can be used for central heating. Sometimes these systems are called hydronic heating systems. Common components of a central heating system using water-circulation include: * A supply of fuel, electric power ordistrict heating
District heating (also known as heat networks or teleheating) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating ...
supply lines
* A boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central ...
(or a heat exchanger for district heating) which heats water in the system
* Pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they ...
to circulate the water
* Radiators through which the heated water passes in order to release heat into rooms.
The circulating water systems use a closed loop; the same water is heated and then reheated. A sealed system provides a form of central heating in which the water used for heating circulates independently of the building's normal water supply.

 An expansion tank contains compressed gas, separated from the sealed-system water by a diaphragm. This allows for normal variations of pressure in the system. A safety valve allows water to escape from the system when pressure becomes too high, and a valve can open to replenish water from the normal water supply if the pressure drops too low. Sealed systems offer an alternative to open-vent systems, in which steam can escape from the system, and gets replaced from the building's water supply via a feed and central storage system.
Heating systems in the United Kingdom and in other parts of Europe commonly combine the needs of space heating with domestic hot-water heating. These systems occur less commonly in the USA. In this case, the heated water in a sealed system flows through a heat exchanger in a hot-water tank or hot-water cylinder where it heats water from the regular potable water supply for use at hot-water taps or appliances such as
An expansion tank contains compressed gas, separated from the sealed-system water by a diaphragm. This allows for normal variations of pressure in the system. A safety valve allows water to escape from the system when pressure becomes too high, and a valve can open to replenish water from the normal water supply if the pressure drops too low. Sealed systems offer an alternative to open-vent systems, in which steam can escape from the system, and gets replaced from the building's water supply via a feed and central storage system.
Heating systems in the United Kingdom and in other parts of Europe commonly combine the needs of space heating with domestic hot-water heating. These systems occur less commonly in the USA. In this case, the heated water in a sealed system flows through a heat exchanger in a hot-water tank or hot-water cylinder where it heats water from the regular potable water supply for use at hot-water taps or appliances such as washing machine
A washing machine (laundry machine, clothes washer, washer, or simply wash) is a home appliance used to wash laundry. The term is mostly applied to machines that use water as opposed to dry cleaning (which uses alternative cleaning fluids and ...
s or dishwashers.
Hydronic radiant floor heating systems use a boiler or district heating to heat water and a pump to circulate the hot water in plastic pipes installed in a concrete slab. The pipes, embedded in the floor, carry heated water that conducts warmth to the surface of the floor, where it broadcasts heat energy to the room above. Hydronic heating systems are also used with antifreeze solutions in ice and snow melt systems for walkways, parking lots and streets. They are more commonly used in commercial and whole house radiant floor heat projects, whereas electric radiant heat systems are more commonly used in smaller "spot warming" applications.
Steam heating
A steam heating system takes advantage of the high latent heat which is given off when steam condenses to liquid water. In a steam heating system, each room is equipped with a radiator which is connected to a source of low-pressure steam (a boiler). Steam entering the radiator condenses and gives up its latent heat, returning to liquid water. The radiator in turn heats the air of the room, and provides some directradiant heat
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of particles in matter. Thermal radiation is generated when heat from the movement of charges in the material (electrons and protons in common forms of matter) is ...
. The condensate water returns to the boiler either by gravity or with the assistance of a pump. Some systems use only a single pipe for combined steam and condensate return. Since trapped air prevents proper circulation, such systems have vent valves to allow air to be purged. In domestic and small commercial buildings, the steam is generated at relatively low pressure, less than 15 psig (200 kPa).
Steam heating systems are rarely installed in new single-family residential construction owing to the cost of the piping installation. Pipes must be carefully sloped to prevent trapped condensate blockage. Compared to other methods of heating, it is more difficult to control the output of a steam system. However, steam can be sent, for example, between buildings on a campus to allow use of an efficient central boiler and low cost fuel. Tall buildings take advantage of the low density of steam to avoid the excessive pressure required to circulate hot water from a basement-mounted boiler. In industrial systems, process steam
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
*Business process, activities that produce a specific se ...
used for power generation or other purposes can also be tapped for space heating. Steam for heating systems may also be obtained from heat recovery boilers using otherwise wasted heat from industrial processes.
Electric heating
Electric heating or resistance heating converts electricity directly to heat. Electric heat is often more expensive than heat produced by combustion appliances like natural gas, propane, and oil. Electric resistance heat can be provided by baseboard heaters, space heaters, radiant heaters, furnaces, wall heaters, or thermal storage systems. Electric heaters are usually part of a fan coil which is part of a central air conditioner. They circulate heat by blowing air across theheating element
A heating element converts electrical energy into heat through the process of Joule heating. Electric current through the element encounters resistance, resulting in heating of the element. Unlike the Peltier effect, this process is indepen ...
which is supplied to the furnace through return air ducts. Blowers in electric furnaces move air over one to five resistance coils or elements which are usually rated at five kilowatts. The heating elements activate one at a time to avoid overloading the electrical system. Overheating is prevented by a safety switch called a limit controller or limit switch. This limit controller may shut the furnace off if the blower fails or if something is blocking the air flow. The heated air is then sent back through the home through supply ducts.
In larger commercial applications, central heating is provided through an air handler
An air handler, or air handling unit (often abbreviated to AHU), is a device used to regulate and circulate air as part of a heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning ( HVAC) system. An air handler is usually a large metal box containing a blow ...
which incorporates similar components as a furnace but on a larger scale.
A data furnace uses computers to convert electricity into heat while simultaneously processing data.
Heat pumps
 In mild climates an air source heat pump can be used to air condition the building during hot weather, and to warm the building using heat extracted from outdoor air in cold weather. Air-source heat pumps are generally uneconomic for outdoor temperatures much below freezing. In colder climates,
In mild climates an air source heat pump can be used to air condition the building during hot weather, and to warm the building using heat extracted from outdoor air in cold weather. Air-source heat pumps are generally uneconomic for outdoor temperatures much below freezing. In colder climates, geothermal heat pump
A ground source heat pump (also geothermal heat pump) is a heating/cooling system for buildings that uses a type of heat pump to transfer heat to or from the ground, taking advantage of the relative constancy of temperatures of the earth through ...
s can be used to extract heat from the ground. For economy, these systems are designed for average low winter temperatures and use supplemental heating for extreme low temperature conditions. The advantage of the heat pump is that it reduces the purchased energy required for building heating; often geothermal source systems also supply domestic hot water. Even in places where fossil fuels provide most electricity, a geothermal system may offset greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane ...
production since most of the heat is supplied from the surrounding environment, with only 15–30% as electrical consumption.
Environmental aspects
From an energy-efficiency standpoint considerable heat gets lost or goes to waste if only a single room needs heating, since central heating has distribution losses and (in the case of forced-air systems particularly) may heat some unoccupied rooms without need. In such buildings which require isolated heating, one may wish to consider non-central systems such as individual room heaters, fireplaces or other devices. Alternatively, architects can design new buildings which can virtually eliminate the need for heating, such as those built to thePassive House
"Passive house" (german: Passivhaus) is a voluntary standard for energy efficiency in a building, which reduces the building's ecological footprint. It results in ultra-low energy buildings that require little energy for space heating or coo ...
standard.
However, if a building does need full heating, combustion central heating may offer a more environmentally friendly
Environment friendly processes, or environmental-friendly processes (also referred to as eco-friendly, nature-friendly, and green), are sustainability and marketing terms referring to goods and services, laws, guidelines and policies that cl ...
solution than electric resistance heating. This applies when electricity originates from a fossil fuel power station, with up to 60% of the energy in the fuel lost (unless utilized for district heating
District heating (also known as heat networks or teleheating) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating ...
) and about 6% in transmission losses. In Sweden proposals exist to phase out direct electric heating for this reason (see oil phase-out in Sweden
In 2005 the government of Sweden appointed a commission to draw up a comprehensive programme to reduce Sweden's dependence on petroleum, natural gas and other ‘ fossil raw materials’ by 2020. In June 2006 (less than three months before the 20 ...
). Nuclear, wind, solar and hydroelectric sources reduce this factor.
In contrast, hot-water central heating systems can use water heated in or close to the building using high-efficiency condensing boiler
Condensing boilers are water heaters typically used for heating systems that are fueled by gas or oil. When operated in the correct circumstances, a heating system can achieve high efficiency (greater than 90% on the higher heating value) by cond ...
s, biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration ...
s, or district heating
District heating (also known as heat networks or teleheating) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating ...
. Wet underfloor heating has proven ideal. This offers the option of relatively easy conversion in the future to use developing technologies such as heat pump
A heat pump is a device that can heat a building (or part of a building) by transferring thermal energy from the outside using a refrigeration cycle. Many heat pumps can also operate in the opposite direction, cooling the building by removing ...
s and solar combisystems, thereby also providing future-proofing.
Typical efficiencies for central heating (measured at the customer's purchase of energy) are:
* 65–97% for gas fired heating;
* 80–89% for oil-fired and
* 45–60% for coal-fired heating./ref> Oil storage tanks, especially underground storage tanks, can also impact the environment. Even if a building's heating system was converted from oil long ago, oil may still be impacting the environment by contaminating soil and groundwater. Building owners can find themselves liable to remove buried tanks and the remediation costs.
See also
*District heating
District heating (also known as heat networks or teleheating) is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating ...
* Energy conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (f ...
* Forced air
* Forced-air gas
* Geothermal systems
* Hearth
A hearth () is the place in a home where a fire is or was traditionally kept for home heating and for cooking, usually constituted by at least a horizontal hearthstone and often enclosed to varying degrees by any combination of reredos (a lo ...
* Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality ...
(HVAC)
* Hydronics
Hydronics () is the use of liquid water or gaseous water ( steam) or a water solution (usually glycol with water) as heat-transfer medium in heating and cooling systems. The name differentiates such systems from oil and refrigerant systems ...
* Oil heater
An oil heater, also known as an oil-filled heater, oil-filled radiator, or column heater, is a common form of convection heater used in domestic heating. Although filled with oil, it is electrically heated and does not involve burning any oi ...
* OpenTherm
OpenTherm (OT) is a standard communications protocol used in central heating systems for the communication between a central heating boiler and a thermostatic controller. As a standard, OpenTherm is independent of any single manufacturer. A cont ...
* Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
* Solar combisystem
* Thermostat
A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint (control system), setpoint.
Thermostats are used i ...
* Underfloor heating
* Water heating
Water heating is a heat transfer process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated t ...
* Wind energy
* Outdoor wood heaters
* Uniform Mechanical Code
The Uniform Mechanical Code (UMC) is a model code developed by the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials ( IAPMO) to govern the installation, inspection and maintenance of HVAC (heating, ventilating and air-conditionin ...
References
Sources
*Further reading
* Adams, Sean Patrick. ''Home Fires: How Americans Kept Warm in the 19th Century'' (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2014), 183 ppExternal links
BBC Wales History – Life before central heating
{{HVAC Plumbing Residential heating Greek inventions Ancient Greek technology Ancient Roman technology de:Gebäudeheizung#Zentralheizung