Heart Valve on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A heart valve is a

 The heart valves and the chambers are lined with
The heart valves and the chambers are lined with
 ;Relationship between pressure and flow in open valves
The pressure drop, , across an open heart valve relates to the flow rate, Q, through the valve:
:
If:
* Inflow energy conserved
* Stagnant region behind leaflets
* Outflow momentum conserved
* Flat velocity profile
;Valves with a single degree of freedom
Usually, the aortic and mitral valves are incorporated in valve studies within a single degree of freedom. These relationships are based on the idea of the valve being a structure with a single degree of freedom. These relationships are based on the
;Relationship between pressure and flow in open valves
The pressure drop, , across an open heart valve relates to the flow rate, Q, through the valve:
:
If:
* Inflow energy conserved
* Stagnant region behind leaflets
* Outflow momentum conserved
* Flat velocity profile
;Valves with a single degree of freedom
Usually, the aortic and mitral valves are incorporated in valve studies within a single degree of freedom. These relationships are based on the idea of the valve being a structure with a single degree of freedom. These relationships are based on the
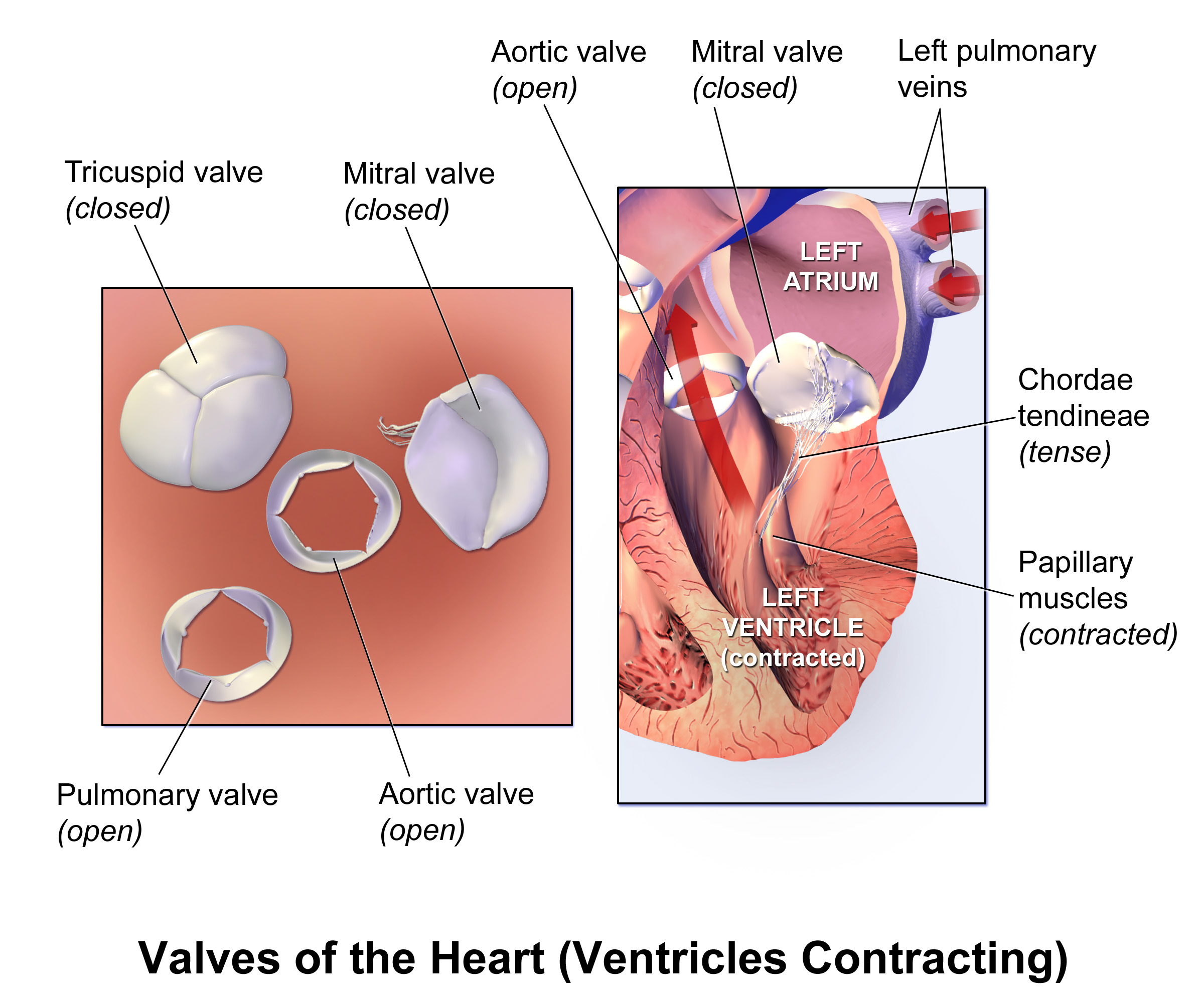 Function of heart valves
*
Function of heart valves
*
Mitral Valve Repair at The Mount Sinai Hospital – "Mitral Valve Anatomy"
* ttps://www.pcronline.com/eurointervention/Y_issue/volume-12/supplement-y/20/transcatheter-mitral-valve-implantation-tendyne.html Transcatheter mitral valve implantation: Tendyne {{Authority control Cardiac anatomy
one-way valve
A check valve, non-return valve, reflux valve, retention valve, foot valve, or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid ( liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction.
Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have ...
that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously m ...
through the heart. A heart valve opens or closes according to differential blood pressure on each side.
The four valves in the mammalian heart are two atrioventricular valves separating the upper atria from the lower ventricles – the mitral valve in the left heart, and the tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ven ...
in the right heart. The other two valves are at the entrance to the arteries leaving the heart these are the semilunar valves – the aortic valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. Th ...
at the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes o ...
, and the pulmonary valve
The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) is a valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and has three cusps. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar v ...
at the pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
.
The heart also has a coronary sinus
In anatomy, the coronary sinus () is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle (myocardium). It delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium, as do the superior and inferior vena ...
valve, and an inferior vena cava valve, not discussed here.
Structure
 The heart valves and the chambers are lined with
The heart valves and the chambers are lined with endocardium
The endocardium is the innermost layer of tissue that lines the chambers of the heart. Its cells are embryologically and biologically similar to the endothelial cells that line blood vessels. The endocardium also provides protection to the v ...
. Heart valves separate the atria from the ventricles, or the ventricles from a blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
. Heart valves are situated around the fibrous rings of the cardiac skeleton
In cardiology, the cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high-density homogeneous structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves of the heart, and influences the forces exerted by and through t ...
. The valves incorporate flaps called leaflets or cusps, similar to a duckbill valve
A duckbill valve is a check valve, usually manufactured from rubber or synthetic elastomer, and has 2 (or more) flaps, usually shaped like the beak of a duck. It is commonly used in medical applications to prevent contamination due to backflow.
...
or flutter valve
A flutter valve (also known as the Heimlich valve after its inventor, Henry Heimlich) is a one-way valve used in respiratory medicine to prevent air from travelling back along a chest tube. One can also use a chest drainage management system, w ...
, which are pushed open to allow blood flow and which then close together to seal and prevent backflow. The mitral valve has two cusps, whereas the others have three. There are nodules at the tips of the cusps that make the seal tighter.
The pulmonary valve
The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) is a valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and has three cusps. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar v ...
has left, right, and anterior cusps. The aortic valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. Th ...
has left, right, and posterior cusps. The tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ven ...
has anterior, posterior, and septal cusps; and the mitral valve has just anterior and posterior cusps.
The valves of the human heart can be grouped in two sets:
* Two atrioventricular valves
A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart v ...
to prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles into the atria:
** Tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ven ...
or right atrioventricular valve, between the right atrium and right ventricle
** Mitral valve or bicuspid valve, between the left atrium and left ventricle
* Two semilunar valves
A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart v ...
to prevent the backflow of blood into the ventricle:
** Pulmonary valve
The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) is a valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and has three cusps. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar v ...
, located at the opening between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk
** Aortic valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. Th ...
, located at the opening between the left ventricle and the aorta.
Atrioventricular valves
The atrioventricular valves are the mitral valve, and thetricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ven ...
, which are situated between the atria and the ventricles, and prevent backflow from the ventricles into the atria during systole. They are anchored to the walls of the ventricles by chordae tendineae
The chordae tendineae (tendinous cords), colloquially known as the heart strings, are inelastic cords of fibrous connective tissue that connect the papillary muscles to the tricuspid valve and the mitral valve in the heart.
Structure
The chorda ...
, which prevent them from inverting.
The chordae tendineae are attached to papillary muscle
The papillary muscles are muscles located in the ventricles of the heart. They attach to the cusps of the atrioventricular valves (also known as the mitral and tricuspid valves) via the chordae tendineae and contract to prevent inversion or pro ...
s that cause tension to better hold the valve. Together, the papillary muscles and the chordae tendineae are known as the subvalvular apparatus. The function of the subvalvular apparatus is to keep the valves from prolapsing into the atria when they close. The subvalvular apparatus has no effect on the opening and closure of the valves, however, which is caused entirely by the pressure gradient across the valve. The peculiar insertion of chords on the leaflet free margin, however, provides systolic stress sharing between chords according to their different thickness.
The closure of the AV valves is heard as ''lub'', the first heart sound (S1). The closure of the SL valves is heard as ''dub'', the second heart sound (S2).
The mitral valve is also called the bicuspid valve because it contains two leaflets or cusps. The mitral valve gets its name from the resemblance to a bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is c ...
's mitre
The mitre (Commonwealth English) (; Greek: μίτρα, "headband" or "turban") or miter (American English; see spelling differences), is a type of headgear now known as the traditional, ceremonial headdress of bishops and certain abbots in ...
(a type of hat). It is on the left side of the heart and allows the blood to flow from the left atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two at ...
into the left ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the uppe ...
.
During diastole
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventri ...
, a normally-functioning mitral valve opens as a result of increased pressure from the left atrium as it fills with blood (preloading). As atrial pressure increases above that of the left ventricle, the mitral valve opens. Opening facilitates the passive flow of blood into the left ventricle. Diastole ends with atrial contraction, which ejects the final 30% of blood that is transferred from the left atrium to the left ventricle. This amount of blood is known as the end diastolic volume (EDV), and the mitral valve closes at the end of atrial contraction to prevent a reversal of blood flow.
The tricuspid valve has three leaflets or cusps and is on the right side of the heart. It is between the right atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two at ...
and the right ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the uppe ...
, and stops the backflow of blood between the two.
Semilunar valves
The aortic and pulmonary valves are located at the base of the aorta and thepulmonary trunk
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
respectively. These are also called the "semilunar valves". These two arteries receive blood from the ventricles and their semilunar valves permit blood to be forced into the arteries, and prevent backflow from the arteries into the ventricles. These valves do not have chordae tendineae, and are more similar to the valves in veins than they are to the atrioventricular valves. The closure of the semilunar valves causes the second heart sound.
The aortic valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. Th ...
, which has three cusps, lies between the left ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the uppe ...
and the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes o ...
. During ventricular systole, pressure rises in the left ventricle and when it is greater than the pressure in the aorta, the aortic valve opens, allowing blood to exit the left ventricle into the aorta. When ventricular systole ends, pressure in the left ventricle rapidly drops and the pressure in the aorta forces the aortic valve to close. The closure of the aortic valve contributes the A2 component of the second heart sound.
The pulmonary valve
The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) is a valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and has three cusps. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar v ...
(sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) lies between the right ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the uppe ...
and the pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
, and has three cusps. Similar to the aortic valve, the pulmonary valve opens in ventricular systole, when the pressure in the right ventricle rises above the pressure in the pulmonary artery. At the end of ventricular systole, when the pressure in the right ventricle falls rapidly, the pressure in the pulmonary artery will close the pulmonary valve. The closure of the pulmonary valve contributes the P2 component of the second heart sound. The right heart is a low-pressure system, so the P2 component of the second heart sound is usually softer than the A2 component of the second heart sound. However, it is physiologically normal in some young people to hear both components separated during inhalation.
Development
In the developing heart, the valves between the atria and ventricles, the bicuspid and the tricuspid valves, develop on either side of theatrioventricular canal
The proper development of the atrioventricular canal into its prospective components (The heart septum and associated valves) to create a clear division between the four compartments of the heart and ensure proper blood movement through the heart, ...
s. The upward extension of the bases of the ventricles causes the canal to become invaginated into the ventricle cavities. The invaginated margins form the rudiments of the lateral cusps of the AV valves. The middle and septal cusps develop from the downward extension of the septum intermedium.
The semilunar valves (the pulmonary and aortic valves) are formed from four thickenings at the cardiac end of the truncus arteriosus
The truncus arteriosus is a structure that is present during embryonic development. It is an arterial trunk that originates from both ventricles of the heart that later divides into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk.
Structure
The truncus arterio ...
. These thickenings are called endocardial cushion
Endocardial cushions, or atrioventricular cushions, refer to a subset of cells in the development of the heart that play a vital role in the proper formation of the heart septa.
They develop on the atrioventricular canal and conotruncal region of ...
s. The truncus arteriosus is originally a single outflow tract from the embryonic heart that will later split to become the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
. Before it has split, four thickenings occur. There are anterior, posterior, and two lateral thickenings. A septum begins to form between what will later become the ascending aorta and pulmonary tract. As the septum forms, the two lateral thickenings are split, so that the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk have three thickenings each (an anterior or posterior, and half of each of the lateral thickenings). The thickenings are the origins of the three cusps of the semilunar valves. The valves are visible as unique structures by the ninth week. As they mature, they rotate slightly as the outward vessels spiral, and move slightly closer to the heart.
Physiology
In general, the motion of the heart valves is determined using the Navier–Stokes equation, using boundary conditions of the blood pressures, pericardial fluid, and external loading as the constraints. The motion of the heart valves is used as a boundary condition in the Navier–Stokes equation in determining the fluid dynamics of blood ejection from the left and right ventricles into the aorta and the lung.Euler equations
200px, Leonhard Euler (1707–1783)
In mathematics and physics, many topics are named in honor of Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler (1707–1783), who made many important discoveries and innovations. Many of these items named after Euler include ...
.
Equations for the aortic valve in this case:
:
:
:
:
where:
: ''u'' = axial velocity
: ''p'' = pressure
: ''A'' = cross sectional area of valve
: ''L'' = axial length of valve
: Λ(''t'') = single degree of freedom; when
:
Atrioventricular valve
Clinical significance
Valvular heart disease
Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart (the aortic and mitral valves on the left side of heart and the pulmonic and tricuspid valves on the right side of heart). These ...
is a general term referring to dysfunction of the valves, and is primarily in two forms, either ''regurgitation'', (also ''insufficiency'', or ''incompetence'') where a dysfunctional valve lets blood flow in the wrong direction, or ''stenosis'', when a valve is narrow.
Regurgitation occurs when a valve becomes insufficient and malfunctions, allowing some blood to flow in the wrong direction. This insufficiency can affect any of the valves as in aortic insufficiency
Aortic regurgitation (AR), also known as aortic insufficiency (AI), is the leaking of the aortic valve of the heart that causes blood to flow in the reverse direction during ventricular diastole, from the aorta into the left ventricle. As a conseq ...
, mitral insufficiency
Mitral regurgitation (MR), also known as mitral insufficiency or mitral incompetence, is a form of valvular heart disease in which the mitral valve is insufficient and does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood.
, pulmonary insufficiency
Pulmonary (or pulmonic) insufficiency (or incompetence, or regurgitation) is a condition in which the pulmonary valve is incompetent and allows backflow from the pulmonary artery to the right ventricle of the heart during diastole. While a small ...
and tricuspid insufficiency
Tricuspid regurgitation (TR), also called tricuspid insufficiency, is a type of valvular heart disease in which the tricuspid valve of the heart, located between the right atrium and right ventricle, does not close completely when the right ventr ...
. The other form of valvular heart disease is stenosis, a narrowing of the valve. This is a result of the valve becoming thickened and any of the heart valves can be affected, as in mitral valve stenosis
Mitral stenosis is a valvular heart disease characterized by the narrowing of the opening of the mitral valve of the heart. It is almost always caused by rheumatic valvular heart disease. Normally, the mitral valve is about 5 cm2 during d ...
, tricuspid valve stenosis, pulmonary valve stenosis
Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) is a heart valve disorder. Blood going from the heart to the lungs goes through the pulmonary valve, whose purpose is to prevent blood from flowing back to the heart. In pulmonary valve stenosis this opening is too n ...
and aortic valve stenosis. Stenosis of the mitral valve is a common complication of rheumatic fever. Inflammation of the valves can be caused by infective endocarditis
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the inner surface of the heart, usually the valves. Signs and symptoms may include fever, small areas of bleeding into the skin, heart murmur, feeling tired, and low red blood cell count. Complications ...
, usually a bacterial infection but can sometimes be caused by other organisms. Bacteria can more readily attach to damaged valves. Another type of endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the ...
which doesn't provoke an inflammatory response, is nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis. This is commonly found on previously undamaged valves. A major valvular heart disease is mitral valve prolapse, which is a weakening of connective tissue called myxomatous degeneration
A myxoma (New Latin from Greek 'muxa' for mucus) is a myxoid tumor of primitive connective tissue. It is most commonly found in the heart (and is the most common primary tumor of the heart in adults) but can also occur in other locations.
Type ...
of the valve. This sees the displacement of a thickened mitral valve cusp into the left atrium during systole.
Disease of the heart valves can be congenital, such as aortic regurgitation
Aortic regurgitation (AR), also known as aortic insufficiency (AI), is the leaking of the aortic valve of the heart that causes blood to flow in the reverse direction during ventricular diastole, from the aorta into the left ventricle. As a conseq ...
or acquired, for example infective endocarditis
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the inner surface of the heart, usually the valves. Signs and symptoms may include fever, small areas of bleeding into the skin, heart murmur, feeling tired, and low red blood cell count. Complications ...
. Different forms are associated with cardiovascular disease, connective tissue disorder
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds togeth ...
s and hypertension. The symptoms of the disease will depend on the affected valve, the type of disease, and the severity of the disease. For example, valvular disease of the aortic valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. Th ...
, such as aortic stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse ov ...
or aortic regurgitation
Aortic regurgitation (AR), also known as aortic insufficiency (AI), is the leaking of the aortic valve of the heart that causes blood to flow in the reverse direction during ventricular diastole, from the aorta into the left ventricle. As a conseq ...
, may cause breathlessness, whereas valvular diseases of the tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ven ...
may lead to dysfunction of the liver and jaundice. When valvular heart disease results from infectious causes, such as infective endocarditis
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the inner surface of the heart, usually the valves. Signs and symptoms may include fever, small areas of bleeding into the skin, heart murmur, feeling tired, and low red blood cell count. Complications ...
, an affected person may have a fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
and unique signs such as splinter haemorrhages of the nails, Janeway lesions, Osler nodes and Roth spots. A particularly feared complication of valvular disease is the creation of emboli
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule ( fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas (gas embolism), amniotic fluid ( amni ...
because of turbulent blood flow, and the development of heart failure.
Valvular heart disease is diagnosed by echocardiography, which is a form of ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
. Damaged and defective heart valves can be repaired, or replaced with artificial heart valve
An artificial heart valve is a one-way valve implanted into a person's heart to replace a heart valve that is not functioning properly ( valvular heart disease). Artificial heart valves can be separated into three broad classes: mechanical he ...
s. Infectious causes may also require treatment with antibiotics.
Congenital heart disease
The most common form of valvular anomaly is acongenital heart defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascul ...
(CHD), called a bicuspid aortic valve
Bicuspid aortic valve (aka BAV) is a form of heart disease in which two of the leaflets of the aortic valve fuse during development in the womb resulting in a two-leaflet (bicuspid) valve instead of the normal three-leaflet (tricuspid) valve. BA ...
. This results from the fusing of two of the cusps during embryonic development forming a bicuspid valve instead of a tricuspid valve. This condition is often undiagnosed until calcific aortic stenosis has developed, and this usually happens around ten years earlier than would otherwise develop.Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Materials'' 12, 476–78 (2013).
Less common CHD's are tricuspid
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ven ...
and pulmonary atresia
Pulmonary atresia is a congenital malformation of the pulmonary valve in which the valve orifice fails to develop. The valve is completely closed thereby obstructing the outflow of blood from the heart to the lungs. The pulmonary valve is located ...
, and Ebstein's anomaly
Ebstein's anomaly is a congenital heart defect in which the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve are displaced towards the apex of the right ventricle of the heart. It is classified as a critical congenital heart defect accounting ...
. Tricuspid atresia is the complete absence of the tricuspid valve which can lead to an underdeveloped or absent right ventricle. Pulmonary atresia is the complete closure of the pulmonary valve. Ebstein's anomaly is the displacement of the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve causing a larger atrium and a smaller ventricle than normal.
History
 Function of heart valves
*
Function of heart valves
* Artificial heart valve
An artificial heart valve is a one-way valve implanted into a person's heart to replace a heart valve that is not functioning properly ( valvular heart disease). Artificial heart valves can be separated into three broad classes: mechanical he ...
* Pericardial heart valves
The pericardial heart valve was invented by Marian Ionescu, a British surgeon working at the General Infirmary in Leeds, England. He created this artificial bioprosthetic heart valve as a three-cusp structure made of chemically treated bovine peri ...
* Bjork–Shiley valve
References
External links
Mitral Valve Repair at The Mount Sinai Hospital – "Mitral Valve Anatomy"
* ttps://www.pcronline.com/eurointervention/Y_issue/volume-12/supplement-y/20/transcatheter-mitral-valve-implantation-tendyne.html Transcatheter mitral valve implantation: Tendyne {{Authority control Cardiac anatomy