Harald III of Norway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Harald Sigurdsson (; – 25 September 1066), also known as Harald III of Norway and given the epithet ''Hardrada'' (; modern no, Hardråde, roughly translated as "stern counsel" or "hard ruler") in the
vol. 3
p. x. While Judith Jesch has argued for 'severe' as the best translation,Judith Jesch, 'Norse Historical Traditions and Historia Gruffud vab Kenan: Magnus Berfoettr and Haraldr Harfagri', in ''Gruffudd ap Cynan: A Collaborative Biography'', edited by K. L. Maund (Cambridge, 1996), pp. 117–147 (p. 139 n. 62). Alison Finlay and
The Early Kings of Norway, the Issue of Agnatic Succession, and the Settlement of Iceland
, ''Viator'', 47 (2016), 171–188 (pp. 1–18 in open-access text, at p. 7); . However, in a number of independent sources associated with the
 Harald was born in Ringerike, NorwayHjardar & Vike (2011) p. 284 in 1015 (or possibly 1016) to
Harald was born in Ringerike, NorwayHjardar & Vike (2011) p. 284 in 1015 (or possibly 1016) to
 After a few years in Kievan Rus', Harald and his force of around 500 men moved on south to
After a few years in Kievan Rus', Harald and his force of around 500 men moved on south to
 Harald became extremely rich during his time in the east, and secured the wealth collected in Constantinople by shipments to Kievan Rus' for safekeeping (with Yaroslav the Wise acting as safekeeper for his fortune). The sagas note that aside from the significant spoils of battle he had retained, he had participated three times in ''polutasvarf'' (loosely translated as "palace-plunder"), a term which implies either the pillaging of the palace exchequer on the death of the emperor, or perhaps the disbursement of funds to the Varangians by the new emperor in order to ensure their loyalty. It is likely that the money Harald made while serving in Constantinople allowed him to fund his claim for the crown of Norway.DeVries (1999) p. 39 If he participated in ''polutasvarf'' three times, these occasions must have been the deaths of
Harald became extremely rich during his time in the east, and secured the wealth collected in Constantinople by shipments to Kievan Rus' for safekeeping (with Yaroslav the Wise acting as safekeeper for his fortune). The sagas note that aside from the significant spoils of battle he had retained, he had participated three times in ''polutasvarf'' (loosely translated as "palace-plunder"), a term which implies either the pillaging of the palace exchequer on the death of the emperor, or perhaps the disbursement of funds to the Varangians by the new emperor in order to ensure their loyalty. It is likely that the money Harald made while serving in Constantinople allowed him to fund his claim for the crown of Norway.DeVries (1999) p. 39 If he participated in ''polutasvarf'' three times, these occasions must have been the deaths of
 Having heard of Sweyn's defeat by Magnus, Harald met up with his fellow exile in Sweden (who was also his nephew), as well as with the Swedish king Anund Jacob, and the three joined forces against Magnus. Their first military exploit consisted of raiding the Danish coast. The purpose of that was to impress the natives by demonstrating that Magnus offered them no protection, and thus leading them to submit to Harald and Sweyn. Learning about their actions, Magnus knew that their next target would be Norway. Harald may have planned to be taken as king of his father's petty kingdom, and thereafter claim the rest of the country.Tjønn (2010) p. 94 In any case, the people were unwilling to turn against Magnus, and on hearing news of Harald's schemes, Magnus (abroad at the time) went home to Norway with his entire army. Instead of going to war, Magnus's advisors recommended the young king not fight his uncle, and a compromise was reached in 1046 in which Harald would rule Norway (not Denmark) jointly with Magnus (although Magnus would have precedence). Notably, Harald also had to agree to share half of his wealth with Magnus, who at the time was effectively bankrupt and badly in need of funds. During their short co-rule, Harald and Magnus had separate courts and kept to themselves, and their only recorded meetings nearly ended in physical clashes.
In 1047, Magnus and Harald went to Denmark with their
Having heard of Sweyn's defeat by Magnus, Harald met up with his fellow exile in Sweden (who was also his nephew), as well as with the Swedish king Anund Jacob, and the three joined forces against Magnus. Their first military exploit consisted of raiding the Danish coast. The purpose of that was to impress the natives by demonstrating that Magnus offered them no protection, and thus leading them to submit to Harald and Sweyn. Learning about their actions, Magnus knew that their next target would be Norway. Harald may have planned to be taken as king of his father's petty kingdom, and thereafter claim the rest of the country.Tjønn (2010) p. 94 In any case, the people were unwilling to turn against Magnus, and on hearing news of Harald's schemes, Magnus (abroad at the time) went home to Norway with his entire army. Instead of going to war, Magnus's advisors recommended the young king not fight his uncle, and a compromise was reached in 1046 in which Harald would rule Norway (not Denmark) jointly with Magnus (although Magnus would have precedence). Notably, Harald also had to agree to share half of his wealth with Magnus, who at the time was effectively bankrupt and badly in need of funds. During their short co-rule, Harald and Magnus had separate courts and kept to themselves, and their only recorded meetings nearly ended in physical clashes.
In 1047, Magnus and Harald went to Denmark with their
 The second, more significant battle, a naval encounter, was the Battle of Niså on 9 August 1062. As Harald had not been able to conquer Denmark despite his raids, he wanted to win a decisive victory over Sweyn. He eventually set out from Norway with a great army and a fleet of around 300 ships. Sweyn had also prepared for the battle, which had been preassigned a time and place. Sweyn did not appear at the agreed time, and Harald thus sent home his non-professional soldiers (''bóndaherrin''), which had made up half of his forces. When the dismissed ships were out of reach, Sweyn's fleet finally appeared, possibly also with 300 ships. The battle resulted in great bloodshed as Harald defeated the Danes (70 Danish ships were reportedly left "empty"), but many ships and men managed to escape, including Sweyn. During the battle, Harald actively shot with his bow, like most others in the early phase of the battle.
Fatigue and the huge cost of the indecisive battles eventually led Harald to seek peace with Sweyn, and in 1064 (or 1065 according to ''Morkinskinna'') the two kings agreed on an unconditional peace agreement. By the agreement, they retained their respective kingdoms with the former boundaries, and there would be no payments of reparations. In the subsequent winter of 1065, Harald travelled through his realm and accused the farmers of withholding taxes from him. In response, he acted with brutality, and had people maimed and killed as a warning to those who disobeyed him. Harald maintained control of his nation through the use of his hird, a private standing army maintained by Norwegian lords. Harald's contribution to the strengthening of Norway's monarchy was the enforcement of a policy that only the king could retain a hird, thus centralising power away from local warlords.
The second, more significant battle, a naval encounter, was the Battle of Niså on 9 August 1062. As Harald had not been able to conquer Denmark despite his raids, he wanted to win a decisive victory over Sweyn. He eventually set out from Norway with a great army and a fleet of around 300 ships. Sweyn had also prepared for the battle, which had been preassigned a time and place. Sweyn did not appear at the agreed time, and Harald thus sent home his non-professional soldiers (''bóndaherrin''), which had made up half of his forces. When the dismissed ships were out of reach, Sweyn's fleet finally appeared, possibly also with 300 ships. The battle resulted in great bloodshed as Harald defeated the Danes (70 Danish ships were reportedly left "empty"), but many ships and men managed to escape, including Sweyn. During the battle, Harald actively shot with his bow, like most others in the early phase of the battle.
Fatigue and the huge cost of the indecisive battles eventually led Harald to seek peace with Sweyn, and in 1064 (or 1065 according to ''Morkinskinna'') the two kings agreed on an unconditional peace agreement. By the agreement, they retained their respective kingdoms with the former boundaries, and there would be no payments of reparations. In the subsequent winter of 1065, Harald travelled through his realm and accused the farmers of withholding taxes from him. In response, he acted with brutality, and had people maimed and killed as a warning to those who disobeyed him. Harald maintained control of his nation through the use of his hird, a private standing army maintained by Norwegian lords. Harald's contribution to the strengthening of Norway's monarchy was the enforcement of a policy that only the king could retain a hird, thus centralising power away from local warlords.
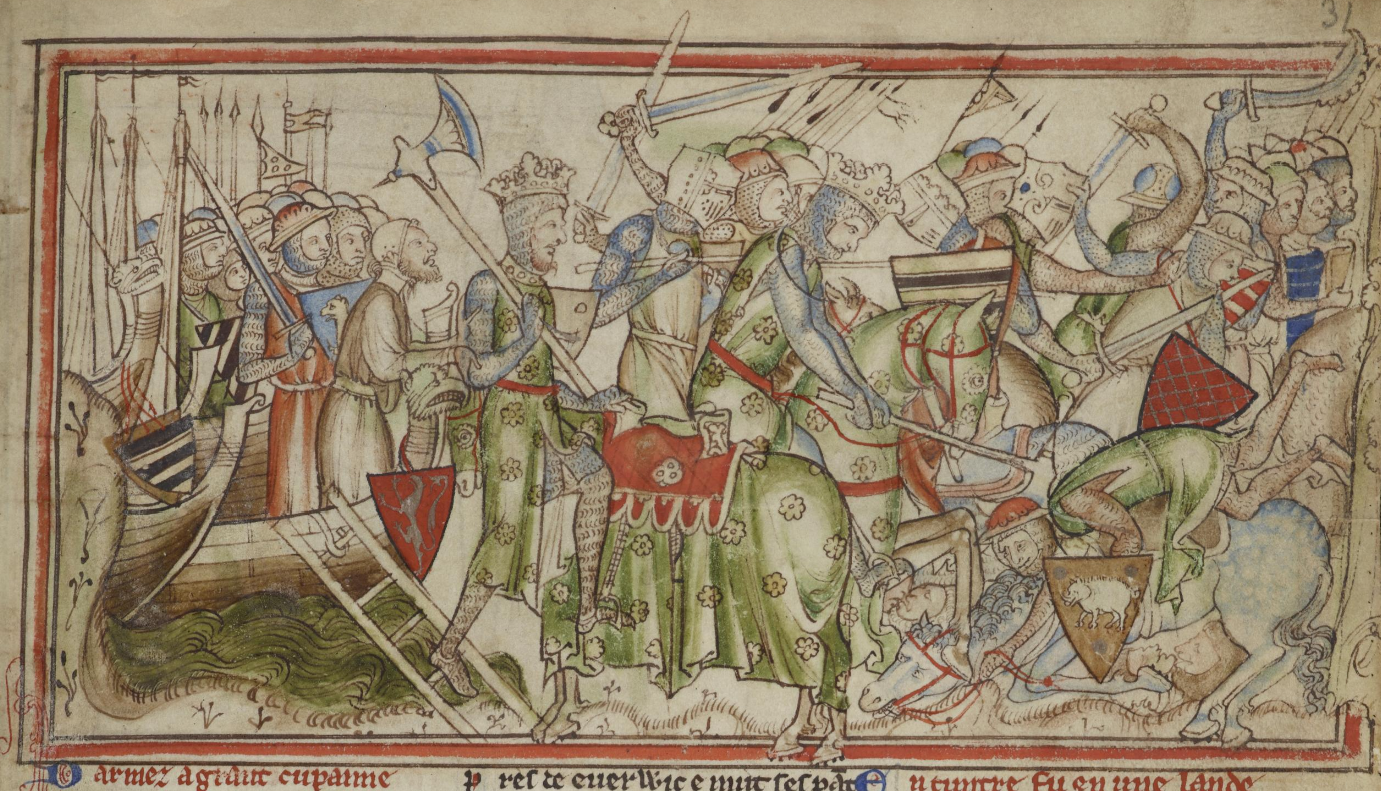 In March or April 1066, Harald began assembling his fleet at Solund, in the Sognefjord, a process completed by the start of September 1066; it included his flagship, ''Ormen'', or "Serpent". Before leaving Norway, he had Magnus proclaimed king of Norway, and left Tora behind, taking with him Elisiv, his daughters, and
In March or April 1066, Harald began assembling his fleet at Solund, in the Sognefjord, a process completed by the start of September 1066; it included his flagship, ''Ormen'', or "Serpent". Before leaving Norway, he had Magnus proclaimed king of Norway, and left Tora behind, taking with him Elisiv, his daughters, and
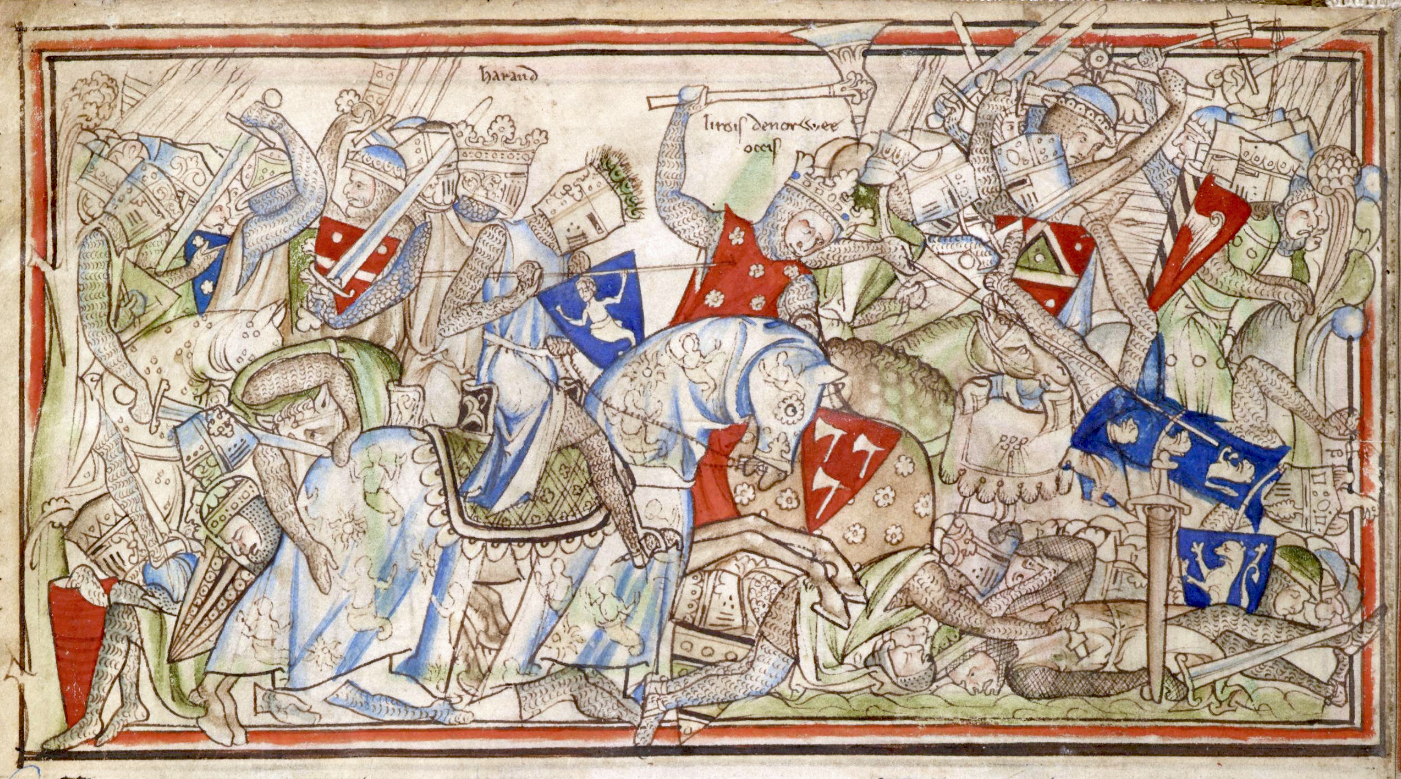 Early on 25 September, Harald and Tostig departed their landing place at Riccall with most of their forces, but left a third of their forces behind. They brought only light armour, as they expected to just meet the citizens of York, as they had agreed the day before, at Stamford Bridge to decide on who should manage the town under Harald. Once there Harald saw Godwinson's forces approaching, heavily armed and armoured, and greatly outnumbering Harald's. Although (according to non-saga sources) the English forces were held up at the bridge for some time by a single gigantic Norwegian, allowing Harald and Tostig to regroup into a shield-wall formation, Harald's army was in the end heavily beaten. Harald was struck in the throat by an arrow and killed early in the battle, later termed the
Early on 25 September, Harald and Tostig departed their landing place at Riccall with most of their forces, but left a third of their forces behind. They brought only light armour, as they expected to just meet the citizens of York, as they had agreed the day before, at Stamford Bridge to decide on who should manage the town under Harald. Once there Harald saw Godwinson's forces approaching, heavily armed and armoured, and greatly outnumbering Harald's. Although (according to non-saga sources) the English forces were held up at the bridge for some time by a single gigantic Norwegian, allowing Harald and Tostig to regroup into a shield-wall formation, Harald's army was in the end heavily beaten. Harald was struck in the throat by an arrow and killed early in the battle, later termed the
 A year after his death at Stamford Bridge, Harald's body was moved to Norway and buried at the Mary Church in Nidaros (Trondheim). About a hundred years after his burial, his body was reinterred at the
A year after his death at Stamford Bridge, Harald's body was moved to Norway and buried at the Mary Church in Nidaros (Trondheim). About a hundred years after his burial, his body was reinterred at the
Haraldr Sigurðarson's arrival in Rus' and his participation in the campaign against Poland in 1031
Saga of Harald Hardrade
by
Ágrip (af Nóregskonungasögum)
(), in Old Norse with English translation
An Account of the Ancient History of the Norwegian Kings
by
Morkinskinna
(), in Old Norse
Fagrskinna
(), in Old Norse
Flateyjarbók
(14th/15th century), in Icelandic {{DEFAULTSORT:Hardrada, Harald 1010s births 1066 deaths 11th-century Norwegian monarchs Christian monarchs Deaths by arrow wounds House of Hardrada Manglabitai Monarchs killed in action Norwegian exiles Pretenders to the Danish throne Pretenders to the English throne Royal reburials Uprising of Peter Delyan Varangian Guard Vikings killed in battle
saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated on the Game Boy in 1989 as the creation of Akitoshi Kawazu at Square. It has since continued across multiple platforms, from the Super NES to th ...
s, was King of Norway
The Norwegian monarch is the head of state of Norway, which is a constitutional and hereditary monarchy with a parliamentary system. The Norwegian monarchy can trace its line back to the reign of Harald Fairhair and the previous petty kingd ...
from 1046 to 1066. Additionally, he unsuccessfully claimed both the Danish throne until 1064 and the English throne
The Throne of England is the throne of the Monarch of England. "Throne of England" also refers metonymically to the office of monarch, and monarchy itself.Gordon, Delahay. (1760) ''A General History of the Lives, Trials, and Executions of All th ...
in 1066. Before becoming king, Harald had spent around fifteen years in exile as a mercenary
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any ...
and military commander in Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas o ...
and as a chief of the Varangian Guard
The Varangian Guard ( el, Τάγμα τῶν Βαράγγων, ''Tágma tōn Varángōn'') was an elite unit of the Byzantine Army from the tenth to the fourteenth century who served as personal bodyguards to the Byzantine emperors. The Varang ...
in the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
.
When he was fifteen years old, in 1030, Harald fought in the Battle of Stiklestad
The Battle of Stiklestad ( no, Slaget på Stiklestad, non, Stiklarstaðir) in 1030 is one of the most famous battles in the history of Norway. In this battle, King Olaf II of Norway () was killed. During the pontificate of Pope Alexander III ...
together with his half-brother Olaf Haraldsson (later Saint Olaf). Olaf sought to reclaim the Norwegian throne, which he had lost to the Danish king Cnut the Great
Cnut (; ang, Cnut cyning; non, Knútr inn ríki ; or , no, Knut den mektige, sv, Knut den Store. died 12 November 1035), also known as Cnut the Great and Canute, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norw ...
two years prior. In the battle, Olaf and Harald were defeated by forces loyal to Cnut, and Harald was forced into exile to Kievan Rus' (the sagas' ). He thereafter spent some time in the army of Grand Prince Yaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav the Wise or Yaroslav I Vladimirovich; russian: Ярослав Мудрый, ; uk, Ярослав Мудрий; non, Jarizleifr Valdamarsson; la, Iaroslaus Sapiens () was the Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death. He was al ...
, eventually obtaining rank as a captain, until he moved on to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
with his companions around 1034. In Constantinople, he soon rose to become the commander of the Byzantine Varangian Guard
The Varangian Guard ( el, Τάγμα τῶν Βαράγγων, ''Tágma tōn Varángōn'') was an elite unit of the Byzantine Army from the tenth to the fourteenth century who served as personal bodyguards to the Byzantine emperors. The Varang ...
, and saw action on the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
, in Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, possibly in the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
and in Constantinople itself, where he became involved in the imperial dynastic disputes. Harald amassed considerable wealth during his time in the Byzantine Empire, which he shipped to Yaroslav in Kievan Rus' for safekeeping. He finally left the Byzantine Empire in 1042, and arrived back in Kievan Rus' in order to prepare his campaign of reclaiming the Norwegian throne. Possibly to Harald's knowledge, in his absence the Norwegian throne had been restored from the Danes to Olaf's illegitimate son Magnus the Good
Magnus Olafsson (Old Norse: ''Magnús Óláfsson''; Norwegian and Danish: ''Magnus Olavsson''; – 25 October 1047), better known as Magnus the Good (Old Norse: ''Magnús góði'', Norwegian and Danish: ''Magnus den gode''), was King of Norwa ...
.
In 1046, Harald joined forces with Magnus's rival in Denmark (Magnus had also become king of Denmark), the pretender
A pretender is someone who claims to be the rightful ruler of a country although not recognized as such by the current government. The term is often used to suggest that a claim is not legitimate.Curley Jr., Walter J. P. ''Monarchs-in-Waiting'' ...
Sweyn II of Denmark, and started raiding the Danish coast. Magnus, unwilling to fight his uncle, agreed to share the kingship with Harald, since Harald in turn would share his wealth with him. The co-rule ended abruptly the next year as Magnus died, and Harald thus became the sole ruler of Norway. Domestically, Harald crushed all local and regional opposition, and outlined the territorial unification of Norway under a national governance. Harald's reign was probably one of relative peace and stability, and he instituted a viable coin economy and foreign trade. Probably seeking to restore Cnut's "North Sea Empire
The North Sea Empire, also known as the Anglo-Scandinavian Empire, was the personal union of the kingdoms of England, Denmark and Norway for most of the period between 1013 and 1042 towards the end of the Viking Age. This ephemeral Norse-ruled ...
", Harald also claimed the Danish throne, and spent nearly every year until 1064 raiding the Danish coast and fighting his former ally, Sweyn. Although the campaigns were successful, he was never able to conquer Denmark.
Not long after Harald had renounced his claim to Denmark, the former Earl of Northumbria
Earl of Northumbria or Ealdorman of Northumbria was a title in the late Anglo-Saxon, Anglo-Scandinavian and early Anglo-Norman period in England. The ealdordom was a successor of the Norse Kingdom of York. In the seventh century, the Anglo-Saxo ...
, Tostig Godwinson
Tostig Godwinson ( 102925 September 1066) was an Anglo-Saxon Earl of Northumbria and brother of King Harold Godwinson. After being exiled by his brother, Tostig supported the Norwegian king Harald Hardrada's invasion of England, and was killed ...
, brother of the newly chosen (but reigning not for long) English king Harold Godwinson (also known as Harold of Wessex), pledged his allegiance to Harald and invited him to claim the English throne. Harald went along and invaded northern England with 10,000 troops and 300 longships in September 1066, raided the coast and defeated English regional forces of Northumbria and Mercia in the Battle of Fulford
The Battle of Fulford was fought on the outskirts of the village of Fulford just south of York in England, on 20 September 1066, when King Harald III of Norway, also known as ''Harald Hardrada'' ("harðráði" in Old Norse, meaning "hard rule ...
near York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
on 20 September 1066. Although initially successful, Harald was defeated and killed in a surprise attack by Harold Godwinson's forces in the Battle of Stamford Bridge
The Battle of Stamford Bridge ( ang, Gefeoht æt Stanfordbrycge) took place at the village of Stamford Bridge, East Riding of Yorkshire, in England, on 25 September 1066, between an English army under King Harold Godwinson and an invading No ...
on 25 September 1066, which wiped out almost his entire army. Modern historians have often considered Harald's death, which brought an end to his invasion, as the end of the Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the Germ ...
.
Epithets
Harald's most famous epithet is Old Norse ''harðráði'', which has been translated variously as 'hard in counsel', 'tyrannical', 'tyrant', 'hard-ruler', 'ruthless', 'savage in counsel', 'tough', and 'severe'.Snorri Sturluson, ''Heimskringla'', trans. by Alison Finlay and Anthony Faulkes, 3 vols (London: Viking Society for Northern Research, 2011–15) (second edition 2016–)vol. 3
p. x. While Judith Jesch has argued for 'severe' as the best translation,Judith Jesch, 'Norse Historical Traditions and Historia Gruffud vab Kenan: Magnus Berfoettr and Haraldr Harfagri', in ''Gruffudd ap Cynan: A Collaborative Biography'', edited by K. L. Maund (Cambridge, 1996), pp. 117–147 (p. 139 n. 62). Alison Finlay and
Anthony Faulkes
Anthony or Antony is a masculine given name, derived from the ''Antonii'', a ''gens'' ( Roman family name) to which Mark Antony (''Marcus Antonius'') belonged. According to Plutarch, the Antonii gens were Heracleidae, being descendants of Anton, ...
prefer 'resolute'. ''Harðráði'' has traditionally been Anglicised as 'Hardrada', though Judith Jesch characterises this form as 'a bastard Anglicisation of the original epithet in an oblique case
In grammar, an oblique ( abbreviated ; from la, casus obliquus) or objective case (abbr. ) is a nominal case other than the nominative case, and sometimes, the vocative.
A noun or pronoun in the oblique case can generally appear in any role ex ...
'. This epithet predominates in the later Icelandic saga-tradition.Sverrir jakobsson,The Early Kings of Norway, the Issue of Agnatic Succession, and the Settlement of Iceland
, ''Viator'', 47 (2016), 171–188 (pp. 1–18 in open-access text, at p. 7); . However, in a number of independent sources associated with the
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isl ...
, mostly earlier than the Icelandic sagas, Harald is given epithets deriving from Old Norse ''hárfagri'' (literally 'hair-beautiful'). These sources include:
* Manuscript D of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of A ...
'' ('Harold Harfagera', under the year 1066) and the related histories by Orderic Vitalis
Orderic Vitalis ( la, Ordericus Vitalis; 16 February 1075 – ) was an English chronicler and Benedictine monk who wrote one of the great contemporary chronicles of 11th- and 12th-century Normandy and Anglo-Norman England. Modern historia ...
('Harafagh', re events in 1066), John of Worcester
John of Worcester (died c. 1140) was an English monk and chronicler who worked at Worcester Priory. He is usually held to be the author of the ''Chronicon ex chronicis''.
''Chronicon ex chronicis''
The ''Chronicon ex chronicis'' is a world wi ...
('Harvagra', s.aa. 1066 and 1098), and William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury ( la, Willelmus Malmesbiriensis; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as " ...
(''Gesta regum Anglorum
The ''Gesta Regum Anglorum'' ( Latin for "Deeds of the Kings of the English"), originally titled ("On the Deeds of the Kings of the English") and also anglicized as or , is an early-12th-century history of the kings of England by William of Ma ...
'', 'Harvagre', regarding 1066).
* Marianus Scotus of Mainz ('Arbach', d. 1082/1083).
* The ''Life'' of Gruffydd ap Cynan
Gruffudd ap Cynan ( 1137), sometimes written as Gruffydd ap Cynan, was King of Gwynedd from 1081 until his death in 1137. In the course of a long and eventful life, he became a key figure in Welsh resistance to Norman rule, and was rememb ...
('Haralld Harfagyr', later twelfth century).
In Icelandic sagas the name ''Harald Fairhair'' is more famously associated with an earlier Norwegian king, and twentieth-century historians assumed that the name was attached to Harald Hardrada in error by Insular historians. However, recognising the independence of some of the Insular sources, historians have since favoured the idea that Harald Hardrada was widely known as Harald Fairhair, and indeed now doubt that the earlier Harald Fairhair existed in any form resembling the later saga-accounts.
Sverrir Jakobsson Sverre, Sverrir or Sverri is a Nordic name from the Old Norse ''Sverrir'', meaning "wild, swinging, spinning". It is a common name in Norway, Iceland and the Faroe Islands; it is less common in Denmark and Sweden. It can also be a surname. Sverre ma ...
has suggested that 'fairhair' 'might be the name by which King Harald wished himself to be known. It must have been his opponents who gave him the epithet "severe" (ON. ''harðráði''), by which he is generally known in thirteenth-century Old Norse kings' sagas'.
Early life
 Harald was born in Ringerike, NorwayHjardar & Vike (2011) p. 284 in 1015 (or possibly 1016) to
Harald was born in Ringerike, NorwayHjardar & Vike (2011) p. 284 in 1015 (or possibly 1016) to Åsta Gudbrandsdatter
Åsta Gudbrandsdatter (c. 975/980 – c. 1020/1030) was the mother of two Norwegian kings, King Olaf II of Norway and King Harald III of Norway. The primary source for the life of Åsta is Snorri Sturluson's saga Heimskringla, a 13th-century ...
and her second husband Sigurd Syr. Sigurd was a petty king of Ringerike, and among the strongest and wealthiest chieftains in the Uplands
Upland or Uplands may refer to:
Geography
*Hill, an area of higher land, generally
*Highland, an area of higher land divided into low and high points
*Upland and lowland, conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level
*I ...
. Through his mother Åsta, Harald was the youngest of King Olaf II of Norway
Olaf II Haraldsson ( – 29 July 1030), later known as Saint Olaf (and traditionally as St. Olave), was King of Norway from 1015 to 1028. Son of Harald Grenske, a petty king in Vestfold, Norway, he was posthumously given the title '' Rex Per ...
/ Olaf Haraldsson's (later Saint Olaf) three half-brothers. In his youth, Harald displayed traits of a typical rebel with big ambitions, and admired Olaf as his role model. He thus differed from his two older brothers, who were more similar to their father, down-to-earth and mostly concerned with maintaining the farm.
The Icelandic sagas, in particular Snorri Sturluson
Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of th ...
in ''Heimskringla
''Heimskringla'' () is the best known of the Old Norse kings' sagas. It was written in Old Norse in Iceland by the poet and historian Snorre Sturlason (1178/79–1241) 1230. The name ''Heimskringla'' was first used in the 17th century, derive ...
'', claim that Sigurd, like Olaf's father, was a great-grandson of King Harald Fairhair
Harald Fairhair no, Harald hårfagre Modern Icelandic: ( – ) was a Norwegian king. According to traditions current in Norway and Iceland in the eleventh and twelfth centuries, he reigned from 872 to 930 and was the first King of No ...
in the male line. Most modern scholars believe that the ancestors attributed to Harald Hardrada's father, along with other parts of the Fairhair genealogy, are inventions reflecting the political and social expectations of the time of the authors (around two centuries after Harald Hardrada's lifetime) rather than historical reality. Harald Hardrada's alleged descent from Harald Fairhair is not mentioned and played no part during Harald Hardrada's own time, which seems odd considering that it would have provided significant legitimacy in connection with his claim to the Norwegian throne.
Following a revolt in 1028, Harald's brother Olaf was forced into exile until he returned to Norway in early 1030. On hearing news of Olaf's planned return, Harald gathered 600 men from the Uplands to meet Olaf and his men upon their arrival in the east of Norway. After a friendly welcome, Olaf went on to gather an army and eventually fight in the Battle of Stiklestad
The Battle of Stiklestad ( no, Slaget på Stiklestad, non, Stiklarstaðir) in 1030 is one of the most famous battles in the history of Norway. In this battle, King Olaf II of Norway () was killed. During the pontificate of Pope Alexander III ...
on 29 July 1030, in which Harald took part on his brother's side. The battle was part of an attempt to restore Olaf to the Norwegian throne, which had been captured by the Danish king Cnut the Great
Cnut (; ang, Cnut cyning; non, Knútr inn ríki ; or , no, Knut den mektige, sv, Knut den Store. died 12 November 1035), also known as Cnut the Great and Canute, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norw ...
(Canute). The battle resulted in defeat for the brothers at the hands of those Norwegians who were loyal to Cnut, and Olaf was killed while Harald was badly wounded.Blöndal & Benedikz (2007) p. 54 Harald was nonetheless remarked to have shown considerable military talent during the battle.
Exile in the East
To Kievan Rus'
After the defeat at the Battle of Stiklestad, Harald managed to escape with the aid of Rögnvald Brusason (later Earl of Orkney) to a remote farm inEastern Norway
Eastern Norway ( nb, Østlandet, nn, Austlandet) is the geographical region of the south-eastern part of Norway. It consists of the counties Vestfold og Telemark, Viken, Oslo and Innlandet.
Eastern Norway is by far the most populous region ...
. He stayed there for some time to heal his wounds, and thereafter (possibly up to a month later) journeyed north over the mountains to Sweden. A year after the Battle of Stiklestad, Harald arrived in Kievan Rus' (referred to in the sagas as '' Garðaríki'' or ''Svíþjóð hin mikla''). He likely spent at least part of his time in the town of Staraya Ladoga
Staraya Ladoga (russian: Ста́рая Ла́дога, p=ˈstarəjə ˈladəɡə, lit=Old Ladoga), known as Ladoga until 1704, is a rural locality (a '' selo'') in Volkhovsky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located on the Volkhov River ne ...
(''Aldeigjuborg''), arriving there in the first half of 1031. Harald and his men were welcomed by Grand Prince Yaroslav the Wise
Yaroslav the Wise or Yaroslav I Vladimirovich; russian: Ярослав Мудрый, ; uk, Ярослав Мудрий; non, Jarizleifr Valdamarsson; la, Iaroslaus Sapiens () was the Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019 until his death. He was al ...
, whose wife Ingegerd was a distant relative of Harald. Badly in need of military leaders, Yaroslav recognised a military potential in Harald and made him a captain of his forces. Harald's brother Olaf Haraldsson had previously been in exile to Yaroslav Yaroslav () is a Slavic given name. Its variant spelling is Jaroslav and Iaroslav, and its feminine form is Yaroslava. The surname derived from the name is Yaroslavsky and its variants. All may refer to:
Historical figures
* Yaroslav I the Wise ( ...
following the revolt in 1028, and '' Morkinskinna'' says that Yaroslav embraced Harald first and foremost because he was the brother of Olaf. Harald took part in Yaroslav's campaign against the Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
in 1031, and possibly also fought against other 1030s Kievan enemies and rivals such as the Chud
Chud or Chude ( orv, чудь, in Finnic languages: tšuudi, čuđit) is a term historically applied in the early East Slavic annals to several Finnic peoples in the area of what is now Estonia, Karelia and Northwestern Russia.
Arguably, th ...
es in Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, an ...
, and the Byzantines, as well as the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
and other steppe nomad people.
In Byzantine service
 After a few years in Kievan Rus', Harald and his force of around 500 men moved on south to
After a few years in Kievan Rus', Harald and his force of around 500 men moved on south to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
('' Miklagard''), the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantino ...
(later known as the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
), probably in 1033 or 1034, where they joined the Varangian Guard
The Varangian Guard ( el, Τάγμα τῶν Βαράγγων, ''Tágma tōn Varángōn'') was an elite unit of the Byzantine Army from the tenth to the fourteenth century who served as personal bodyguards to the Byzantine emperors. The Varang ...
. Although the ''Flateyjarbók
''Flateyjarbók'' (; "Book of Flatey") is an important medieval Icelandic manuscript. It is also known as GkS 1005 fol. and by the Latin name ''Codex Flateyensis''. It was commissioned by Jón Hákonarson and produced by the priests and scribes ...
'' maintains that Harald at first sought to keep his royal identity a secret, most sources agree that Harald and his men's reputation was well known in the east at the time. While the Varangian Guard was primarily meant to function as the emperor's bodyguard, Harald was found fighting on "nearly every frontier" of the empire. He first saw action in campaigns against Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
pirates in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
, and then in inland towns in Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
/ Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
that had supported the pirates. By this time, he had, according to Snorri Sturluson
Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of th ...
(a contemporary Icelandic historian, poet, and politician), become the "leader over all the Varangians". By 1035, the Byzantines had pushed the Arabs out of Asia Minor to the east and southeast, and Harald took part in campaigns that went as far east as the Tigris River
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the P ...
and Euphrates River
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, where according to his skald
A skald, or skáld (Old Norse: , later ; , meaning "poet"), is one of the often named poets who composed skaldic poetry, one of the two kinds of Old Norse poetry, the other being Eddic poetry, which is anonymous. Skaldic poems were traditional ...
(poet) Þjóðólfr Arnórsson
Þjóðólfr Arnórsson (Old Norse: ; Modern Icelandic: ; Modern Norwegian: ) was an 11th-century Icelandic skáld, who spent his career as a court poet to the Norwegian kings Magnus the Good and Harald Hardrada and is thought to have died wit ...
(recounted in the sagas) he participated in the capture of eighty Arab strongholds, a number which historians Sigfus Blöndal and Benedikt Benedikz see no particular reason to question. Although not holding independent command of an army as the sagas imply, it is not unlikely that King Harald and the Varangians at times could have been sent off to capture a castle or town. During the first four years of the reign of Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as ...
Michael IV the Paphlagonian
Michael IV the Paphlagonian ( el, , ''Mikhaēl ho Paphlagōn''; c. 1010 – 10 December 1041) was Byzantine Emperor from 11 April 1034 to his death on 10 December 1041.
The son of a peasant, Michael worked as a money changer until he was fou ...
, Harald probably also fought in campaigns against the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
.Blöndal & Benedikz (2007) p. 63
Thereafter, Harald is reported in the sagas to have gone to Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
and fought in battles in the area. Although the sagas place this after his expedition to Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, historian Kelly DeVries has questioned that chronology.DeVries (1999) p. 30 Whether his trip was of a military or peaceful nature would depend on whether it took place before or after the 1036 peace treaty between Michael IV and the Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dyna ...
Caliph Ma'ad al-Mustansir Billah (in reality the Caliph's mother, originally a Byzantine Christian, since the Caliph was a minor), although it is considered unlikely to have been made before. Modern historians have speculated that Harald may have been in a party sent to escort pilgrims to Jerusalem (possibly including members of the Imperial family) following the peace agreement, as it was also agreed that the Byzantines were allowed to repair the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
. Furthermore, this may in turn have presented Harald with opportunities to fight against bandits who preyed on Christian pilgrims.
In 1038, Harald joined the Byzantines in their expedition to Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
,DeVries (1999) p. 31Tjønn (2010) p. 47 in George Maniakes
George Maniakes (, transliterated as Georgios Maniaces, Maniakis, or Maniaches, , ; died 1043) was a prominent general of the Byzantine Empire of Byzantine Greek origin
during the 11 ...
's (the sagas' "Gyrge") attempt to reconquer the island from the Muslim Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia ...
s, who had established the Emirate of Sicily
The Emirate of Sicily ( ar, إِمَارَة صِقِلِّيَة, ʾImārat Ṣiqilliya) was an Islamic kingdom that ruled the island of Sicily from 831 to 1091. Its capital was Palermo (Arabic: ''Balarm''), which during this period became ...
on the island. During the campaign, Harald fought alongside Norman mercenaries such as William Iron Arm
William I of Hauteville (before 1010 – 1046), known as William Iron Arm,Guillaume Bras-de-fer in French, Guglielmo Braccio di Ferro in Italian and Gugghiermu Vrazzu di Ferru in Sicilian. was a Norman adventurer who was the founder of the ...
. According to Snorri Sturluson, Harald captured four towns on Sicily. In 1041, when the Byzantine expedition to Sicily was over, a Lombard-Norman revolt erupted in southern Italy, and Harald led the Varangian Guard in multiple battles. Harald fought with the Catepan of Italy, Michael Dokeianos
Michael Dokeianos ( el, Μιχαήλ Δοκειανός), erroneously called Doukeianos by some modern writers, was a Byzantine nobleman and military leader, who married into the Komnenos family. He was active in Sicily under George Maniakes befo ...
with initial success, but the Normans, led by their former ally William Iron Arm, defeated the Byzantines in the Battle of Olivento
The Battle of Olivento was fought on 17 March 1041 between the Byzantine Empire and the Normans of southern Italy and their Lombard allies near the Olivento river, between the actual Basilicata and Apulia, southern Italy.
History
The battle h ...
in March, and in the Battle of Montemaggiore
The Battle of Montemaggiore (or Monte Maggiore) was fought on 4 May 1041, on the river Ofanto near Cannae in Byzantine Italy, between Lombard- Norman rebel forces and the Byzantine Empire. The Norman William Iron Arm led the offence, which was ...
in May. After the defeat, Harald and the Varangian Guard were called back to Constantinople, following Maniakes' imprisonment by the emperor and the onset of other more pressing issues. Harald and the Varangians were thereafter sent to fight in the southeastern European frontier in Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, where they arrived in late 1041. There, he fought in the army of Emperor Michael IV in the Battle of Ostrovo
The Battle of Ostrovo occurred in 1041 near Ostrovo, an area close to the lake of the same name in modern Northern Greece. History
In 1040 Peter Delyan, an illegitimate relative of Samuel, the Bulgarian Tsar, led an uprising against the Byza ...
of the 1041 campaign against the Bulgarian uprising led by Peter Delyan, which later gained Harald the nickname the "Bulgar-burner" (''Bolgara brennir'') by his skald.
Harald was not affected by Maniakes' conflict with Emperor Michael IV, and received honours and respect upon his return to Constantinople. In a Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
book written in the 1070s, the '' Strategikon of Kekaumenos'', Araltes (i.e. Harald) is said to have won the favour of the emperor. The book says that the Byzantine emperor first appointed him '' manglabites'' (possibly identified with the title ''protospatharios
''Prōtospatharios'' ( el, πρωτοσπαθάριος) was one of the highest court dignities of the middle Byzantine period (8th to 12th centuries), awarded to senior generals and provincial governors, as well as to foreign princes.
History
Th ...
''), a soldier of the imperial guard, after the Sicilian campaign.Bibikov (2004) p. 21 Following the campaign against the Bulgarians, in which Harald again served with distinction, he received the rank while at Mosynopolis
Mosynopolis ( el, Μοσυνόπολις), of which only ruins now remain in Greek Thrace, was a city in the Roman province of Rhodope, which was known until the 9th century as Maximianopolis (Μαξιμιανούπολις) or, to distinguish ...
of '' spatharokandidatos'', identified by DeVries as a promotion to the possibly third highest Byzantine rank, but by Mikhail Bibikov as a lesser rank than ''protospatharios'' that was ordinarily awarded to foreign allies to the emperor. The ''Strategikon'' indicates that the ranks awarded to Harald were rather low, since Harald reportedly was "not angry for just having been appointed to ''manglabites'' or ''spatharokandidatos''". According to his skald Þjóðólfr Arnórsson, Harald had participated in eighteen greater battles during his Byzantine service. Harald's favour at the imperial court quickly declined after the death of Michael IV in December 1041, which was followed by conflicts between the new emperor Michael V Michael V may refer to:
*Michael V Kalaphates (1015–1042), Byzantine Emperor
*Coptic Pope Michael V of Alexandria (fl. 1145–1146)
*Michael V.
Beethoven Del Valle Bunagan (born December 17, 1969), known professionally as Michael V. and a ...
and the powerful empress Zoe.
During the turmoil, Harald was arrested and imprisoned, but the sources disagree on the grounds. The sagas state that Harald was arrested for defrauding the emperor of his treasure, as well as for requesting marriageDeVries (1999) pp. 34–35 with an apparently fictional niece or granddaughter of Zoe, called Maria (his suit supposedly being turned down by the empress because she wanted to marry Harald herself). William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury ( la, Willelmus Malmesbiriensis; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as " ...
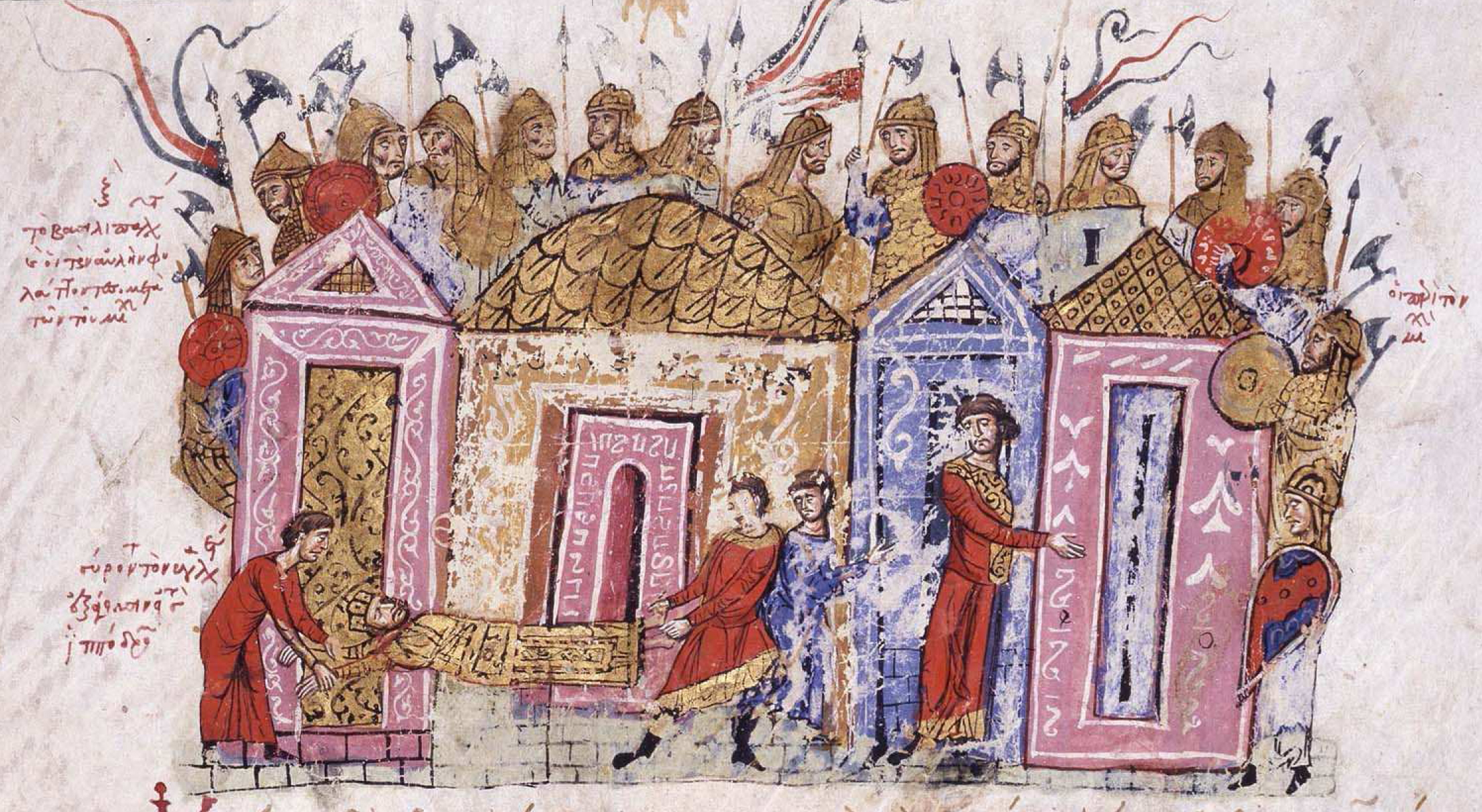
states that Harald was arrested for defiling a noble woman, while according to Saxo Grammaticus he was imprisoned for murder. DeVries suggests that the new emperor may have feared Harald because of his loyalty to the previous emperor. The sources also disagree on how Harald got out of prison, but he may have been helped by someone outside to escape in the midst of the revolt that had begun against the new emperor. While some of the Varangians helped guard the emperor, Harald became the leader of the Varangians who supported the revolt. The emperor was in the end dragged out of his sanctuary, blinded and exiled to a monastery, and the sagas claim that it was Harald himself who blinded Michael V (or at least claimed to have done so).DeVries (1999) pp. 35–38
Back to Kievan Rus'
 Harald became extremely rich during his time in the east, and secured the wealth collected in Constantinople by shipments to Kievan Rus' for safekeeping (with Yaroslav the Wise acting as safekeeper for his fortune). The sagas note that aside from the significant spoils of battle he had retained, he had participated three times in ''polutasvarf'' (loosely translated as "palace-plunder"), a term which implies either the pillaging of the palace exchequer on the death of the emperor, or perhaps the disbursement of funds to the Varangians by the new emperor in order to ensure their loyalty. It is likely that the money Harald made while serving in Constantinople allowed him to fund his claim for the crown of Norway.DeVries (1999) p. 39 If he participated in ''polutasvarf'' three times, these occasions must have been the deaths of
Harald became extremely rich during his time in the east, and secured the wealth collected in Constantinople by shipments to Kievan Rus' for safekeeping (with Yaroslav the Wise acting as safekeeper for his fortune). The sagas note that aside from the significant spoils of battle he had retained, he had participated three times in ''polutasvarf'' (loosely translated as "palace-plunder"), a term which implies either the pillaging of the palace exchequer on the death of the emperor, or perhaps the disbursement of funds to the Varangians by the new emperor in order to ensure their loyalty. It is likely that the money Harald made while serving in Constantinople allowed him to fund his claim for the crown of Norway.DeVries (1999) p. 39 If he participated in ''polutasvarf'' three times, these occasions must have been the deaths of Romanos III
Romanos III Argyros ( el, Ρωμανός Αργυρός; Latinized Romanus III Argyrus; 968 – 11 April 1034), or Argyropoulos was Byzantine Emperor from 1028 until his death. He was a Byzantine noble and senior official in Constantinople wh ...
, Michael IV, and Michael V, in which Harald would have opportunities, beyond his legitimate revenues, to carry off immense wealth.
After Zoe had been restored to the throne in June 1042 together with Constantine IX, Harald requested to be allowed to return to Norway. Although Zoe refused to allow this, Harald managed to escape into the Bosphorus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
with two ships and some loyal followers. Although the second ship was destroyed by the Byzantine cross-strait iron chains, Harald's ship sailed safely into the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
after successfully manoeuvring over the barrier. Despite this, Kekaumenos lauds the "loyalty and love" Harald had for the empire, which he reportedly maintained even after he returned to Norway and became king. Following his escape from Constantinople, Harald arrived back in Kievan Rus' later in 1042. During his second stay there, he married Elisabeth (referred to in Scandinavian sources as Ellisif), daughter of Yaroslav the Wise and granddaughter of the Swedish king Olof Skötkonung
Olof Skötkonung, (Old Norse: ''Óláfr skautkonungr'') sometimes stylized as ''Olaf the Swede'' (c. 980–1022), was King of Sweden, son of Eric the Victorious and, according to Icelandic sources, Sigrid the Haughty. He succeeded his father ...
. Shortly after Harald's arrival in Kiev, Yaroslav attacked Constantinople, and it is considered likely that Harald provided him with valuable information about the state of the empire.Tjønn (2010) p. 77
It is possible that the marriage with Elisiv had been agreed to already during Harald's first time in Rus', or that they at least had been acquainted. During his service in the Byzantine Empire, Harald composed a love poem which included the verse "Yet the goddess in Gardarike / will not accept my gold rings"Henriksen (2011) (whom Snorri Sturluson identifies with Elisiv), although ''Morkinskinna'' claims that Harald had to remind Yaroslav of the promised marriage when he returned to Kiev.DeVries (1999) pp. 26–27 According to the same source, Harald had spoken with Yaroslav during his first time in Rus', requesting to marry Elisiv, only to be rejected because he was not yet wealthy enough. It is in any case significant that Harald was allowed to marry the daughter of Yaroslav, since his other children were married to figures such as Henry I of France, Andrew I of Hungary
Andrew I the White or the Catholic ( hu, I. Fehér or ; 1015 – before 6 December 1060) was King of Hungary from 1046 to 1060. He descended from a younger branch of the Árpád dynasty. After spending fifteen years in exile, he ascended ...
and the daughter of Constantine IX.
King of Norway
Return to Scandinavia
Seeking to regain for himself the kingdom lost by his half-brother Olaf Haraldsson, Harald began his journey westwards in early 1045, departing fromNovgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ...
(''Holmgard'') to Staraya Ladoga (''Aldeigjuborg'') where he obtained a ship. His journey went through Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga (; rus, Ла́дожское о́зеро, r=Ladozhskoye ozero, p=ˈladəʂskəjə ˈozʲɪrə or rus, Ла́дога, r=Ladoga, p=ˈladəɡə, fi, Laatokka arlier in Finnish ''Nevajärvi'' ; vep, Ladog, Ladoganjärv) is a fresh ...
, down the Neva River
The Neva (russian: Нева́, ) is a river in northwestern Russia flowing from Lake Ladoga through the western part of Leningrad Oblast (historical region of Ingria) to the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Despite its modest length of , it ...
, and then into the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and ...
and the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
. He arrived in Sigtuna
Sigtuna () is a locality situated in Sigtuna Municipality, Stockholm County, Sweden with 8,444 inhabitants in 2010. It is the namesake of the municipality even though the seat is in Märsta.
Sigtuna is for historical reasons often still referr ...
in Sweden, probably at the end of 1045 or in early 1046. When he arrived in Sweden, according to the skald Tjodolv Arnorsson, his ship was unbalanced by its heavy load of gold. In Harald's absence, the throne of Norway had been restored to Magnus the Good
Magnus Olafsson (Old Norse: ''Magnús Óláfsson''; Norwegian and Danish: ''Magnus Olavsson''; – 25 October 1047), better known as Magnus the Good (Old Norse: ''Magnús góði'', Norwegian and Danish: ''Magnus den gode''), was King of Norwa ...
, an illegitimate son of Olaf. Harald may actually have known this, and it could have been the reason why Harald wanted to return to Norway in the first place. Since Cnut the Great's sons had chosen to abandon Norway and instead fight over England, and his sons and successors Harold Harefoot and Harthacnut
Harthacnut ( da, Hardeknud; "Tough-knot"; – 8 June 1042), traditionally Hardicanute, sometimes referred to as Canute III, was King of Denmark from 1035 to 1042 and King of the English from 1040 to 1042.
Harthacnut was the son of King ...
had died young, Magnus's position as king had been secured. No domestic threats or insurrections are recorded to have occurred during his eleven-year reign.DeVries (1999) p. 40 After the death of Harthacnut, which had left the Danish throne vacant, Magnus had in addition been selected to be the king of Denmark, and managed to defeat the Danish royal pretender Sweyn Estridsson
Sweyn Estridsson Ulfsson ( on, Sveinn Ástríðarson, da, Svend Estridsen; – 28 April 1076) was King of Denmark (being Sweyn II) from 1047 until his death in 1076. He was the son of Ulf Thorgilsson and Estrid Svendsdatter, and the grandson ...
.
 Having heard of Sweyn's defeat by Magnus, Harald met up with his fellow exile in Sweden (who was also his nephew), as well as with the Swedish king Anund Jacob, and the three joined forces against Magnus. Their first military exploit consisted of raiding the Danish coast. The purpose of that was to impress the natives by demonstrating that Magnus offered them no protection, and thus leading them to submit to Harald and Sweyn. Learning about their actions, Magnus knew that their next target would be Norway. Harald may have planned to be taken as king of his father's petty kingdom, and thereafter claim the rest of the country.Tjønn (2010) p. 94 In any case, the people were unwilling to turn against Magnus, and on hearing news of Harald's schemes, Magnus (abroad at the time) went home to Norway with his entire army. Instead of going to war, Magnus's advisors recommended the young king not fight his uncle, and a compromise was reached in 1046 in which Harald would rule Norway (not Denmark) jointly with Magnus (although Magnus would have precedence). Notably, Harald also had to agree to share half of his wealth with Magnus, who at the time was effectively bankrupt and badly in need of funds. During their short co-rule, Harald and Magnus had separate courts and kept to themselves, and their only recorded meetings nearly ended in physical clashes.
In 1047, Magnus and Harald went to Denmark with their
Having heard of Sweyn's defeat by Magnus, Harald met up with his fellow exile in Sweden (who was also his nephew), as well as with the Swedish king Anund Jacob, and the three joined forces against Magnus. Their first military exploit consisted of raiding the Danish coast. The purpose of that was to impress the natives by demonstrating that Magnus offered them no protection, and thus leading them to submit to Harald and Sweyn. Learning about their actions, Magnus knew that their next target would be Norway. Harald may have planned to be taken as king of his father's petty kingdom, and thereafter claim the rest of the country.Tjønn (2010) p. 94 In any case, the people were unwilling to turn against Magnus, and on hearing news of Harald's schemes, Magnus (abroad at the time) went home to Norway with his entire army. Instead of going to war, Magnus's advisors recommended the young king not fight his uncle, and a compromise was reached in 1046 in which Harald would rule Norway (not Denmark) jointly with Magnus (although Magnus would have precedence). Notably, Harald also had to agree to share half of his wealth with Magnus, who at the time was effectively bankrupt and badly in need of funds. During their short co-rule, Harald and Magnus had separate courts and kept to themselves, and their only recorded meetings nearly ended in physical clashes.
In 1047, Magnus and Harald went to Denmark with their leidang The institution known as ''leiðangr'' (Old Norse), ''leidang'' ( Norwegian), ''leding'' ( Danish), ''ledung'' ( Swedish), ''expeditio'' (Latin) or sometimes lething (English), was a form of conscription ( mass levy) to organize coastal fleets for s ...
forces. Later that year in Jylland
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of ...
, less than a year into their co-rule, Magnus died without an heir. Before his death, he had decided that Sweyn was to inherit Denmark and Harald to inherit Norway. On hearing the news of Magnus's death, Harald quickly gathered the local leaders in Norway and declared himself king of Norway as well as of Denmark. Although Magnus had appointed Sweyn his successor as king of Denmark, Harald immediately announced his plans to gather an army and oust his former ally from the country. In response, the army and the chieftains, headed by Einar Thambarskelfir
Einar Eindridesson Thambarskelfir (c. 980–c. 1050) (Old Norse: ''Einarr Þambarskelfir'', Modern Norwegian: ''Einar Tambarskjelve'') was an influential Norwegian noble and politician during the 11th century. He headed the feudal lords in t ...
, opposed any plans of invading Denmark. Although Harald himself objected to bringing the body of Magnus back to Norway, the Norwegian army prepared to transport his body to Nidaros
Nidaros, Niðarós or Niðaróss () was the medieval name of Trondheim when it was the capital of Norway's first Christian kings. It was named for its position at the mouth (Old Norse: ''óss'') of the River Nid (the present-day Nidelva).
Althou ...
(now Trondheim
Trondheim ( , , ; sma, Tråante), historically Kaupangen, Nidaros and Trondhjem (), is a city and municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. As of 2020, it had a population of 205,332, was the third most populous municipality in Norway, an ...
), where they buried him next to Saint Olaf in late 1047.Tjønn (2010) p. 103 Einar, an opponent of Harald, claimed that "to follow Magnus dead was better than to follow any other king alive".
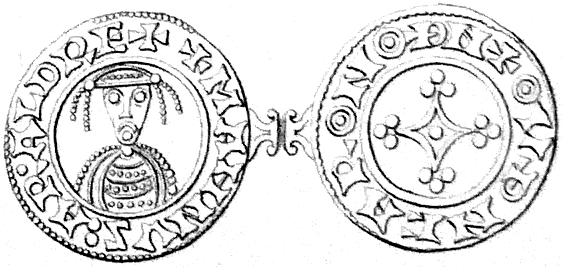
Under Harald's rule, Norway introduced a royal monopoly on the minting of coins. The coins minted under Harald's rule appear to have been accepted as a commonly used currency (as opposed to continued use of primarily foreign-minted coins). Minting of coins likely provided a substantial part of Harald's annual revenues. Minting of coinage collapsed in Norway in the late 14th century.
Invasions of Denmark
Harald also wanted to re-establish Magnus's rule over Denmark, and in the long term probably sought to restore Cnut the Great's "North Sea Empire
The North Sea Empire, also known as the Anglo-Scandinavian Empire, was the personal union of the kingdoms of England, Denmark and Norway for most of the period between 1013 and 1042 towards the end of the Viking Age. This ephemeral Norse-ruled ...
" in its entirety. While his first proposal to invade Denmark fell through, the next year Harald embarked on what would turn into constant warfare against Sweyn, from 1048 almost yearly until 1064. Similar to his campaigns (then together with Sweyn) against Magnus's rule in Denmark, most of his campaigns against Sweyn consisted of swift and violent raids on the Danish coasts. In 1048, he plundered Jutland
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of ...
, and in 1049 he pillaged and burned Hedeby
Hedeby (, Old Norse ''Heiðabýr'', German ''Haithabu'') was an important Danish Viking Age (8th to the 11th centuries) trading settlement near the southern end of the Jutland Peninsula, now in the Schleswig-Flensburg district of Schleswig-Holst ...
, at the time the most important Danish trade center, and one of the best protected and most populous towns in Scandinavia. Hedeby as a civil town never recovered from Harald's destruction, and was left completely desolate when what remained was looted by Slavic tribes
This is a list of Slavic peoples and Slavic tribes reported in Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, that is, before the year AD 1500.
Ancestors
*Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers)
** Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of Ba ...
in 1066. One of two conventional battles was set to be fought between the two kings later the same year, but, according to Saxo Grammaticus, Sweyn's smaller army was so frightened when approached by the Norwegians that they chose to jump in the water trying to escape; most drowned. Although Harald was victorious in most of the engagements, he was never successful in occupying Denmark.
 The second, more significant battle, a naval encounter, was the Battle of Niså on 9 August 1062. As Harald had not been able to conquer Denmark despite his raids, he wanted to win a decisive victory over Sweyn. He eventually set out from Norway with a great army and a fleet of around 300 ships. Sweyn had also prepared for the battle, which had been preassigned a time and place. Sweyn did not appear at the agreed time, and Harald thus sent home his non-professional soldiers (''bóndaherrin''), which had made up half of his forces. When the dismissed ships were out of reach, Sweyn's fleet finally appeared, possibly also with 300 ships. The battle resulted in great bloodshed as Harald defeated the Danes (70 Danish ships were reportedly left "empty"), but many ships and men managed to escape, including Sweyn. During the battle, Harald actively shot with his bow, like most others in the early phase of the battle.
Fatigue and the huge cost of the indecisive battles eventually led Harald to seek peace with Sweyn, and in 1064 (or 1065 according to ''Morkinskinna'') the two kings agreed on an unconditional peace agreement. By the agreement, they retained their respective kingdoms with the former boundaries, and there would be no payments of reparations. In the subsequent winter of 1065, Harald travelled through his realm and accused the farmers of withholding taxes from him. In response, he acted with brutality, and had people maimed and killed as a warning to those who disobeyed him. Harald maintained control of his nation through the use of his hird, a private standing army maintained by Norwegian lords. Harald's contribution to the strengthening of Norway's monarchy was the enforcement of a policy that only the king could retain a hird, thus centralising power away from local warlords.
The second, more significant battle, a naval encounter, was the Battle of Niså on 9 August 1062. As Harald had not been able to conquer Denmark despite his raids, he wanted to win a decisive victory over Sweyn. He eventually set out from Norway with a great army and a fleet of around 300 ships. Sweyn had also prepared for the battle, which had been preassigned a time and place. Sweyn did not appear at the agreed time, and Harald thus sent home his non-professional soldiers (''bóndaherrin''), which had made up half of his forces. When the dismissed ships were out of reach, Sweyn's fleet finally appeared, possibly also with 300 ships. The battle resulted in great bloodshed as Harald defeated the Danes (70 Danish ships were reportedly left "empty"), but many ships and men managed to escape, including Sweyn. During the battle, Harald actively shot with his bow, like most others in the early phase of the battle.
Fatigue and the huge cost of the indecisive battles eventually led Harald to seek peace with Sweyn, and in 1064 (or 1065 according to ''Morkinskinna'') the two kings agreed on an unconditional peace agreement. By the agreement, they retained their respective kingdoms with the former boundaries, and there would be no payments of reparations. In the subsequent winter of 1065, Harald travelled through his realm and accused the farmers of withholding taxes from him. In response, he acted with brutality, and had people maimed and killed as a warning to those who disobeyed him. Harald maintained control of his nation through the use of his hird, a private standing army maintained by Norwegian lords. Harald's contribution to the strengthening of Norway's monarchy was the enforcement of a policy that only the king could retain a hird, thus centralising power away from local warlords.
Domestic opposition
According to historianKnut Helle
Knut Helle (19 December 1930 – 27 June 2015) was a Norwegian historian. A professor at the University of Bergen from 1973 to 2000, he specialized in the late medieval history of Norway. He has contributed to several large works.
Early life, ...
, Harald completed the first phase of what he has termed the "national territorial unification of Norway".Moseng et al. (2019) p. 79 Having forced his way to the kingship, Harald would have to convince the aristocracy that he was the right person to rule Norway alone. To establish domestic alliances, he married Tora Torbergsdatter of one of the most powerful Norwegian families. The primary opposition to Harald's rule would be the descendants of Haakon Sigurdsson
Haakon Sigurdsson ( non, Hákon Sigurðarson , no, Håkon Sigurdsson; 937–995), known as Haakon Jarl (Old Norse: ''Hákon jarl''), was the ''de facto'' ruler of Norway from about 975 to 995. Sometimes he is styled as Haakon the Powerful ( n ...
, from the powerful dynasty of Earls of Lade
The Earls of Lade ( no, ladejarler) were a dynasty of Norse '' jarls'' from Lade (Old Norse: ''Hlaðir''), who ruled what is now Trøndelag and Hålogaland from the 9th century to the 11th century.
The seat of the Earls of Lade was at Lade ...
who had controlled Northern Norway
Northern Norway ( nb, Nord-Norge, , nn, Nord-Noreg; se, Davvi-Norga) is a geographical region of Norway, consisting of the two northernmost counties Nordland and Troms og Finnmark, in total about 35% of the Norwegian mainland. Some of the lar ...
and Trøndelag
Trøndelag (; sma, Trööndelage) is a county in the central part of Norway. It was created in 1687, then named Trondhjem County ( no, Trondhjems Amt); in 1804 the county was split into Nord-Trøndelag and Sør-Trøndelag by the King of Denma ...
with much autonomy under the Norwegian king. Haakon had even ruled the whole of Norway (nominally under the Danish king) from 975 until 995, when he was killed during the takeover by Olaf Tryggvasson
Olaf Tryggvason (960s – 9 September 1000) was King of Norway from 995 to 1000. He was the son of Tryggvi Olafsson, king of Viken ( Vingulmark, and Rånrike), and, according to later sagas, the great-grandson of Harald Fairhair, first King o ...
. Even after Haakon's death, his offspring held a certain degree of sovereignty in the north, and by Harald's early reign the family was headed by Einar Thambarskelfir
Einar Eindridesson Thambarskelfir (c. 980–c. 1050) (Old Norse: ''Einarr Þambarskelfir'', Modern Norwegian: ''Einar Tambarskjelve'') was an influential Norwegian noble and politician during the 11th century. He headed the feudal lords in t ...
, who was married to Haakon's daughter. While the family had maintained good relations with Magnus, Harald's absolutism and consolidation of the kingship soon led to conflict with Einar.
It was from his power-struggle with the Norwegian aristocracy that Harald got himself the reputation that gave him the nickname "Hardrada", or "the hard ruler". Although the relationship between Harald and Einar was poor from the start, confrontation did not occur before Harald went north to his court in Nidaros. One time in Nidaros, Einar arrived at Harald's court, and in a display of power was accompanied by "eight or nine longships and almost five hundred men", obviously seeking confrontation. Harald was not provoked by the incident. Although the sources differ on the circumstances, the next event nonetheless led to the murder of Einar by Harald's men, which threatened to throw Norway into a state of civil war. Although the remaining descendants of Haakon Sigurdsson considered rebellion against the king, Harald eventually managed to negotiate peace with them, and secured the family's submission for the remainder of his reign. By the death of Einar and his son around 1050, the Earls of Lade had outplayed their role as a base of opposition, and Trøndelag was definitely subordinated to Harald's national kingdom.
Before the Battle of Niså, Harald had been joined by Haakon Ivarsson, who distinguished himself in the battle and gained Harald's favour. Harald reportedly even considered giving Haakon the title of Earl, and Haakon was greatly upset when Harald later backed down from his promise. With a strong hold over the Uplands, Haakon was additionally given the earldom of Värmland
Värmland () also known as Wermeland, is a '' landskap'' (historical province) in west-central Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Dalsland, Dalarna, Västmanland, and Närke, and is bounded by Norway in the west. Latin name versions are '' ...
by the Swedish king Stenkil
Stenkil (Old Norse: ''Steinkell'') was a King of Sweden who ruled c. 1060 until 1066. He succeeded Emund the Old and became the first king from the House of Stenkil. He is praised as a devout Christian, but with an accommodating stance towards ...
. In early 1064, Haakon entered the Uplands and collected their taxes, the region thus effectively threatened to renounce their loyalty to Harald in response. The revolt of Haakon and the farmers in the Uplands may have been the main reason why Harald finally had been willing to enter a peace agreement with Sweyn Estridsson. After the agreement, Harald went to Oslo and sent tax collectors to the Uplands, only to find that the farmers would withhold their taxes until Haakon arrived. In response, Harald entered Sweden with an army and quickly defeated Haakon. Still facing opposition from the farmers, Harald embarked on a campaign to crush the areas that had withheld their taxes. Due to the remote location of the region in the interior of the country, the Uplands had never been an integrated part of the Norwegian king's realm. Using harsh measures, Harald burned down farms and small villages, and had people maimed and killed. Starting in Romerike, his campaign continued into Hedmark, Hadeland
Hadeland () is a traditional district in the southeastern part of Norway. It is centered on the southern part of the large lake Randsfjorden in Innlandet and Viken counties. The district consists of the municipalities Gran in Innlandet county ...
and Ringerike. Since the regions contained several rich rural communities, Harald strengthened his economic position by confiscating farming estates. By the end of 1065 there was probably peace in Norway, as any opposition had either been killed, chased into exile or silenced.
Policies
Harald's reign was marked by his background as a military commander, as he often solved disputes with a brute force. One of hisskald
A skald, or skáld (Old Norse: , later ; , meaning "poet"), is one of the often named poets who composed skaldic poetry, one of the two kinds of Old Norse poetry, the other being Eddic poetry, which is anonymous. Skaldic poems were traditional ...
s even boasted about how Harald broke settlements he had made, in his battles in the Mediterranean. While the sagas largely focus on Harald's war with Sweyn and the invasion of England, little is said about his domestic policies. Modern historians have taken this as a sign that, despite his absolutism, his reign was one of peace and progress for Norway. Harald is considered to have instituted good economic policies, as he developed a Norwegian currency and a viable coin economy, which in turn allowed Norway to participate in international trade. He initiated trade with Kievan Rus' and the Byzantine Empire through his connections, as well as with Scotland and Ireland. According to the later sagas, Harald founded Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
, where he spent much time.
Harald also continued to advance Christianity in Norway, and archaeological excavations show that churches were built and improved during his reign. He also imported bishops, priests and monks from abroad, especially from Kievan Rus' and the Byzantine Empire. A slightly different form of Christianity was thus introduced in Norway from the rest of northern Europe, although the East–West Schism
The East–West Schism (also known as the Great Schism or Schism of 1054) is the ongoing break of communion between the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches since 1054. It is estimated that, immediately after the schism occurred, a ...
had not yet taken place. Since the clergy was not ordained
Ordination is the process by which individuals are consecrated, that is, set apart and elevated from the laity class to the clergy, who are thus then authorized (usually by the denominational hierarchy composed of other clergy) to perform ...
in England or France, it nonetheless caused controversy when Harald was visited by papal legates. The protests by the legates led Harald to throw the Catholic clergy out of his court, and he reportedly stated to the legates that "he did not know of any other archbishop or lord of Norway than the king himself".DeVries (1999) pp. 47–48 Norwegian historian Halvdan Koht has remarked that the "words seemed as if spoken by a Byzantine despot". It is possible that Harald maintained contacts with Byzantine emperors after he became king, which could suggest a background for his church policies.
Northern explorations
Once he had returned to Norway, Harald seems to have displayed an interest in exploring his own realm, as for instance the '' Morkinskinna'' recounts Harald's trip into the Uplands. Harald is also said to have explored the seas beyond his kingdom, as the contemporaryAdam of Bremen
Adam of Bremen ( la, Adamus Bremensis; german: Adam von Bremen) (before 1050 – 12 October 1081/1085) was a German medieval chronicler. He lived and worked in the second half of the eleventh century. Adam is most famous for his chronicle ''Gest ...
reports of such naval expeditions conducted by Harald:DeVries (1999) p. 49
Kelly DeVries has suggested that Harald "may even have known of and sought out the legendary land called Vinland
Vinland, Vineland, or Winland ( non, Vínland ᚠᛁᚾᛚᛅᚾᛏ) was an area of coastal North America explored by Vikings. Leif Erikson landed there around 1000 AD, nearly five centuries before the voyages of Christopher Columbus and John ...
, which Viking sailors had discovered only a short time before", which Adam mentions earlier in the same passage to have been widely reported in Denmark and Norway. H. H. Lamb has on the other hand proposed that the land he reached may have been either Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Nor ...
or Novaya Zemlya
Novaya Zemlya (, also , ; rus, Но́вая Земля́, p=ˈnovəjə zʲɪmˈlʲa, ) is an archipelago in northern Russia. It is situated in the Arctic Ocean, in the extreme northeast of Europe, with Cape Flissingsky, on the northern island, ...
.
Invasion of England
Background and preparations
Accepting he could not conquer Denmark, Harald switched attention to England; his claim was based on a 1038 agreement between Magnus and its previous ruler,Harthacnut
Harthacnut ( da, Hardeknud; "Tough-knot"; – 8 June 1042), traditionally Hardicanute, sometimes referred to as Canute III, was King of Denmark from 1035 to 1042 and King of the English from 1040 to 1042.
Harthacnut was the son of King ...
, who died childless in 1042. The agreement stated that if either die, the other would inherit his lands; however, it was unlikely Magnus assumed he would gain the English throne without fighting. Harthacnut himself preferred his brother, Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ; la, Eduardus Confessor , ; ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was one of the last Anglo-Saxon English kings. Usually considered the last king of the House of Wessex, he ruled from 1042 to 1066.
Edward was the son of Æt ...
, who became king with the backing of Earl Godwin
Godwin of Wessex ( ang, Godwine; – 15 April 1053) was an English nobleman who became one of the most powerful earls in England under the Danish king Cnut the Great (King of England from 1016 to 1035) and his successors. Cnut made Godwin the ...
, father of Harold Godwinson
Harold Godwinson ( – 14 October 1066), also called Harold II, was the last crowned Anglo-Saxon English king. Harold reigned from 6 January 1066 until his death at the Battle of Hastings, fighting the Norman invaders led by William the ...
. Plans by Magnus to invade England in 1045 were suspended, while he dealt with an uprising by Sweyn of Denmark.
After Magnus died in 1047, Harald took over his claim; however, Edward kept potential enemies happy by hinting they might succeed him; in addition to Harald, these included Sweyn, and William, Duke of Normandy
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
. In 1058, a fleet under Harald's son Magnus
Magnus, meaning "Great" in Latin, was used as cognomen of Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus in the first century BC. The best-known use of the name during the Roman Empire is for the fourth-century Western Roman Emperor Magnus Maximus. The name gained wid ...
supported a large scale Welsh raid into England, although details are limited. This may have shown Harald that he could not simultaneously fight Denmark and England; this became crucial when Edward died in January 1066, and Harold Godwinson proclaimed king of England.
Harold's brother Tostig Godwinson
Tostig Godwinson ( 102925 September 1066) was an Anglo-Saxon Earl of Northumbria and brother of King Harold Godwinson. After being exiled by his brother, Tostig supported the Norwegian king Harald Hardrada's invasion of England, and was killed ...
, formerly Earl of Northumbria
Earl of Northumbria or Ealdorman of Northumbria was a title in the late Anglo-Saxon, Anglo-Scandinavian and early Anglo-Norman period in England. The ealdordom was a successor of the Norse Kingdom of York. In the seventh century, the Anglo-Saxo ...
, now appeared on the scene; hoping to regain his titles and lands, he reportedly approached both William and Sweyn Estridsson for their support. However, since Northern England was the most suitable landing place for a Norwegian invasion, he was more valuable to Harald. Details are limited, but it is suggested Tostig sent a fellow exile, Copsi
Copsi (or Copsig; ang, Cōpsige; died 1067) was a Northumbrian magnate in late Anglo-Saxon England. He was a supporter of Tostig, and was exiled along with him in 1065. Copsi soon fled to Orkney (then a part of Norway). The next year (1066), h ...
g, to meet with Harald in Norway and agree plans, while he remained in France. If correct, this would also have allowed Tostig to increase both their chances by simultaneously supporting an invasion by William, who also claimed the throne.
 In March or April 1066, Harald began assembling his fleet at Solund, in the Sognefjord, a process completed by the start of September 1066; it included his flagship, ''Ormen'', or "Serpent". Before leaving Norway, he had Magnus proclaimed king of Norway, and left Tora behind, taking with him Elisiv, his daughters, and
In March or April 1066, Harald began assembling his fleet at Solund, in the Sognefjord, a process completed by the start of September 1066; it included his flagship, ''Ormen'', or "Serpent". Before leaving Norway, he had Magnus proclaimed king of Norway, and left Tora behind, taking with him Elisiv, his daughters, and Olaf
Olaf or Olav (, , or British ; Old Norse: ''Áleifr'', ''Ólafr'', ''Óleifr'', ''Anleifr'') is a Scandinavian and German given name. It is presumably of Proto-Norse origin, reconstructed as ''*Anu-laibaz'', from ''anu'' "ancestor, grand-father" ...
. En route, he stopped at the Norwegian-held islands of Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the n ...
and Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
, where he collected additional troops, including Paul and Erlend Thorfinnsson, the Earls of Orkney. At Dunfermline
Dunfermline (; sco, Dunfaurlin, gd, Dùn Phàrlain) is a city, parish and former Royal Burgh, in Fife, Scotland, on high ground from the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. The city currently has an estimated population of 58,508. Acco ...
, he met Tostig's ally, Malcolm III of Scotland, who gave him around 2,000 Scottish soldiers.
Although possible he also met Tostig there, most sources suggest they linked up at Tynemouth
Tynemouth () is a coastal town in the metropolitan borough of North Tyneside, North East England. It is located on the north side of the mouth of the River Tyne, hence its name. It is 8 mi (13 km) east-northeast of Newcastle upon Tyn ...
, on 8 September, Harald bringing around 10–15,000 men, on 240–300 longship
Longships were a type of specialised Scandinavian warships that have a long history in Scandinavia, with their existence being archaeologically proven and documented from at least the fourth century BC. Originally invented and used by the Nor ...
s. Tostig had only 12 ships, his connections being far more significant. The chronicler, John of Worcester
John of Worcester (died c. 1140) was an English monk and chronicler who worked at Worcester Priory. He is usually held to be the author of the ''Chronicon ex chronicis''.
''Chronicon ex chronicis''
The ''Chronicon ex chronicis'' is a world wi ...
, suggests he left Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
in May or June, raiding the heartland of Harold's estates in southern England, from the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Is ...
to Sandwich
A sandwich is a food typically consisting of vegetables, sliced cheese or meat, placed on or between slices of bread, or more generally any dish wherein bread serves as a container or wrapper for another food type. The sandwich began as a po ...
. Having made it seem an attack from Normandy was imminent, he then sailed north, while his brother and most of his troops remained in the south, waiting for William.
Early raids, invasion, and Battle of Fulford
After embarking from Tynemouth, Harald and Tostig probably landed at theRiver Tees
The River Tees (), in Northern England, rises on the eastern slope of Cross Fell in the North Pennines and flows eastwards for to reach the North Sea between Hartlepool and Redcar near Middlesbrough. The modern day history of the river has bee ...
. They then entered Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
, and started plundering the coast. They encountered the first resistance at Scarborough, where Harald's demand for surrender was opposed. In the end, Harald resorted to burning down the town and this action led to other Northumbrian towns surrendering to him. After further raiding, Harald and Tostig sailed up the Humber, disembarking at Riccall
Riccall is a village and civil parish situated in the Selby District of North Yorkshire, England, lying to the north of Selby and south of York.
It was historically part of the East Riding of Yorkshire until 1974.
According to the 2011 c ...
on 20 September. News of the early raids had reached the earls Morcar of Northumbria
Morcar (or Morkere) ( ang, Mōrcǣr) (died after 1087) was the son of Ælfgār (earl of Mercia) and brother of Ēadwine. He was the earl of Northumbria from 1065 to 1066, when he was replaced by William the Conqueror with Copsi.
Dispute with ...
and Edwin of Mercia
Edwin (Old English: ''Ēadwine'') (died 1071) was the elder brother of Morcar, Earl of Northumbria, son of Ælfgār, Earl of Mercia and grandson of Leofric, Earl of Mercia. He succeeded to his father's title and responsibilities on Ælfgār's d ...
, and they fought against Harald's invading army south of York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
at the Battle of Fulford
The Battle of Fulford was fought on the outskirts of the village of Fulford just south of York in England, on 20 September 1066, when King Harald III of Norway, also known as ''Harald Hardrada'' ("harðráði" in Old Norse, meaning "hard rule ...
, also on 20 September. The battle was a decisive victory for Harald and Tostig, and led York to surrender to their forces on 24 September. This would be the last time a Scandinavian army defeated English forces. The same day as York surrendered to Harald and Tostig, Harold Godwinson arrived with his army in Tadcaster
Tadcaster is a market town and civil parish in the Selby district of North Yorkshire, England, east of the Great North Road, north-east of Leeds, and south-west of York. Its historical importance from Roman times onward was largely as the ...
, just from the anchored Norwegian fleet at Riccall. From there, he probably scouted the Norwegian fleet, preparing a surprise attack. As Harald had left no forces in York, Harold Godwinson marched right through the town to Stamford Bridge.
Battle of Stamford Bridge
 Early on 25 September, Harald and Tostig departed their landing place at Riccall with most of their forces, but left a third of their forces behind. They brought only light armour, as they expected to just meet the citizens of York, as they had agreed the day before, at Stamford Bridge to decide on who should manage the town under Harald. Once there Harald saw Godwinson's forces approaching, heavily armed and armoured, and greatly outnumbering Harald's. Although (according to non-saga sources) the English forces were held up at the bridge for some time by a single gigantic Norwegian, allowing Harald and Tostig to regroup into a shield-wall formation, Harald's army was in the end heavily beaten. Harald was struck in the throat by an arrow and killed early in the battle, later termed the
Early on 25 September, Harald and Tostig departed their landing place at Riccall with most of their forces, but left a third of their forces behind. They brought only light armour, as they expected to just meet the citizens of York, as they had agreed the day before, at Stamford Bridge to decide on who should manage the town under Harald. Once there Harald saw Godwinson's forces approaching, heavily armed and armoured, and greatly outnumbering Harald's. Although (according to non-saga sources) the English forces were held up at the bridge for some time by a single gigantic Norwegian, allowing Harald and Tostig to regroup into a shield-wall formation, Harald's army was in the end heavily beaten. Harald was struck in the throat by an arrow and killed early in the battle, later termed the Battle of Stamford Bridge
The Battle of Stamford Bridge ( ang, Gefeoht æt Stanfordbrycge) took place at the village of Stamford Bridge, East Riding of Yorkshire, in England, on 25 September 1066, between an English army under King Harold Godwinson and an invading No ...
, in a state of ''berserker
In the Old Norse written corpus, berserker were those who were said to have fought in a trance-like fury, a characteristic which later gave rise to the modern English word '' berserk'' (meaning "furiously violent or out of control"). Berserkers ...
gang'', having worn no body armour and fought aggressively with both hands around his sword.
When the battle was almost over, some reserve forces from Riccall led by Eystein Orre finally appeared, but they were exhausted as they had run all the way. Eystein picked up Harald's fallen banner, the "Landwaster" (''Landøyðan''), and initiated a final counter-attack. Although they for a moment appeared to almost breach the English line, Eystein was suddenly killed, which left the rest of the men to flee from the battlefield.Hjardar & Vike (2011) p. 291 Among those left at Riccall after the battle, who were allowed to return home peacefully by the English forces, was Harald's son Olaf. Although sources state that Harald's remaining army only filled 20–25 ships on the return to Norway, it is likely that this number only accounts for the Norwegian forces. Most of the forces from Scotland and Orkney probably remained at Riccall throughout the battle (the earls Paul and Erlend Thorfinnsson are certainly known to have been stationed there the entire time), and has not been counted in the traditional figure.
Harold Godwinson's victory was short-lived, as only a few weeks later he was defeated by William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
and killed at the Battle of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings nrf, Batâle dé Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman Conque ...
. The fact that Harold had to make a forced march to fight Hardrada at Stamford Bridge and then move at utmost speed south to meet the Norman invasion, all in less than three weeks, is widely seen as a primary factor in William's victory at Hastings.
Personal life
Harald is described by Snorri Sturluson to have been physically "larger than other men and stronger". It is said that he had light hair, a light beard, and a long "upper beard" (moustache), and that one of his eyebrows was somewhat higher situated than the other. He also reportedly had big hands and feet, and could measure five ells in height. It is not known whether Snorri's description of Harald's physical appearance actually represents historical facts. The tall stature of Harald is also substantiated by a story that relates that before the Battle of Stamford Bridge, Harold Godwinson offered Tostig back the earldom of Northumbria, and Harald "six feet of the ground of England, or perhaps more seeing that he is taller than most men" (according to Henry of Huntingdon) or "six feet of English ground, or seven feet as he was taller than other men" (according to Snorri Sturluson). Harald himself composedskaldic poetry
A skald, or skáld (Old Norse: , later ; , meaning "poet"), is one of the often named poets who composed skaldic poetry, one of the two kinds of Old Norse poetry, the other being Eddic poetry, which is anonymous. Skaldic poems were traditional ...
. According to Lee M. Hollander
Lee Milton Hollander (November 8, 1880 – October 19, 1972) was an American philologist who specialized in Old Norse studies. Hollander was for many years head of the Department of Germanic Languages at the University of Texas at Austin. ...
, composing poetry was normal for Norwegian kings, but Harald was the only one who "showed a decided talent." According to one poem, Harald had mastered a number of activities that were considered sports in the Viking Age, in addition to poetry, brewing, horse riding, swimming, skiing, shooting, rowing and playing the harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orc ...
. The sagas state that Harald and his Varangians at least once took a break during the siege of a town to enjoy sports.
With regards to religion, Harald had, according to DeVries, a "religious inclination towards Christianity" and was "publicly close to the Christian Church", although he was influenced by the Eastern Christian culture of Kievan Rus' (Garderike) and the Byzantine Empire, having spent most of his life there. He was clearly interested in advancing Christianity in Norway, which can be seen by the continued building and improvement of churches throughout his reign. Despite this, DeVries notes that Harald's "personal morality appears not to have matched the Christian ideal", citing his marriage arrangements.
Issue
Harald married Elisiv of Kiev (c. 1025 – after 1066) around 1044/45, and they had an unknown number, possibly several children. According to Snorri Sturluson, they had two daughters:DeVries (1999) p. 48 * Ingegerd (). Married first to the future Olaf I of Denmark, and after his death, to the future Philip of Sweden. * Maria (died 25 September 1066). Promised away for marriage to Eystein Orre (brother of Tora Torbergsdatter), but reportedly died on Orkney the same day that Harald (and Eystein) died at Stamford Bridge. According to the sagas, Harald married Tora Torbergsdatter (c. 1025 – after 1066) around 1048. Some modern historians have disputed this, since Harald in that case would be in a bigamous marriage, as he was still married to Elisiv. It is nonetheless possible that such a marriage could take place in Norway in the 11th century, and although Harald had two wives, only Elisiv is noted to have held the title of Queen. Harald and Tora had at least two children: * Magnus II (). Reigned as king of Norway from 1066 to 1069. * Olaf III (). Reigned as king of Norway from 1067 to 1093.Legacy
Burial
 A year after his death at Stamford Bridge, Harald's body was moved to Norway and buried at the Mary Church in Nidaros (Trondheim). About a hundred years after his burial, his body was reinterred at the
A year after his death at Stamford Bridge, Harald's body was moved to Norway and buried at the Mary Church in Nidaros (Trondheim). About a hundred years after his burial, his body was reinterred at the Helgeseter Priory
Helgeseter Priory or Elgeseter Priory (''Elgeseter kloster'') was a medieval era house of Augustinian Canons in what is now the neighborhood of Elgeseter in Trondheim, Norway.
History
The monastery was founded by Archbishop Eystein no later ...
, which was demolished in the 17th century. On 25 September 2006, the 940th anniversary of Harald's death, the newspaper ''Aftenposten
( in the masthead; ; Norwegian for "The Evening Post") is Norway's largest printed newspaper by circulation. It is based in Oslo. It sold 211,769 copies in 2015 (172,029 printed copies according to University of Bergen) and estimated 1.2 milli ...
'' published an article on the poor state of Norway's ancient royal burial sites, including that of Harald, which is reportedly located underneath a road built across the monastery site. In a follow-up article on 26 September, the Municipality of Trondheim revealed they would be examining the possibility of exhuming the king and reinterring him in Nidaros Cathedral
Nidaros Cathedral ( no, Nidarosdomen / Nidaros Domkirke) is a Church of Norway cathedral located in the city of Trondheim in Trøndelag county. It is built over the burial site of King Olav II (c. 995–1030, reigned 1015–1028), who became t ...
, currently the burial place of nine Norwegian kings, among them Magnus the Good and Magnus Haraldsson, Harald's predecessor and successor respectively. A month later it was reported that the proposal to exhume the king had been scrapped.
Modern memorials
Two monuments have been erected in honour of Harald in Oslo, the city which he is traditionally held to have founded. A bronze relief on granite by Lars Utne depicting Harald on horseback was raised on the eponymously named square ''Harald Hardrådes plass'' in 1905. In 1950, a large relief byAnne Grimdalen
Anne Grimdalen (1 November 1899 – 3 October 1961) was a Norwegian sculptor. She was born on the mountain farm Grimdalen in Skafså, Telemark, and later also lived and worked in the so-called ''Kunstnerdalen'' in Asker. She worked mainly wi ...
, also of Harald on horseback, was unveiled on the western façade of the Oslo City Hall
Oslo City Hall ( no, Oslo rådhus) is a municipal building in Oslo, the capital of Norway. It houses the city council, the city's administration and various other municipal organisations. The building as it stands today was constructed between ...
.
In popular culture
* Harald appears in a number of historical fiction books. In H. P. Lovecraft's novella ''The Call of Cthulhu'', one key character "lay in the Old Town of King Harold Haardrada, which kept alive the name of Oslo during all the centuries that the greater city masqueraded as 'Christiana'." Justin Hill's ''Viking Fire'' is the second in his ''Conquest Trilogy'', and tells the life of Harald in his own voice. He serves as the protagonist in two children's books by Henry Treece, ''The Last of the Vikings''/''The Last Viking'' (1964) and ''Swords from the North''/''The Northern Brothers'' (1967). He also appears as the protagonist in the trilogy ''The Last Viking'' (1980) by Poul and Karen Anderson, and in ''Byzantium'' (1989) by Michael Ennis, which chronicles Harald's career in the Byzantine Empire. * The alternative history book ''Crusader Gold
''Crusader Gold'' is an archaeological adventure novel by David Gibbins. First published in 2006, it is the second book in Gibbins's Jack Howard series. It has been published in more than 20 languages and was a New York Times bestseller.
Plot su ...
'' (2007) by marine archeologist David Gibbins
David Gibbins (born 1962) is an underwater archaeologist and a bestselling novelist.
Early life
Gibbins was born in 1962 in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada, to British parents who were academic scientists. He is related to the Victorian histo ...
features Harald as a key figure, as it follows him in acquiring the lost Menorah among his treasures during his service in the Byzantine Varangian Guard. Harald also makes an appearance in ''Meadowland'' (2005) by Tom Holt
Thomas Charles Louis Holt (born 13 September 1961) is a British novelist. In addition to fiction published under his own name, he writes fantasy under the pseudonym K. J. Parker.
Biography
Holt was born in London, the son of novelist Hazel H ...
.
* Harald's unorthodox departure from Constantinople is featured in music by the Finnish folk metal
Folk metal is a fusion genre of heavy metal music and traditional folk music that developed in Europe during the 1990s. It is characterised by the widespread use of folk instruments and, to a lesser extent, traditional singing styles (for exam ...
band Turisas
Turisas is a Finnish metal band from Hämeenlinna. They were founded in 1997 by Mathias Nygård and Jussi Wickström, and named after an ancient Finnish god of war.
Turisas are a folk metal band, incorporating elements of power metal and s ...
in the song "The Great Escape"; in addition, he is followed loosely throughout the story of the albums ''The Varangian Way
''The Varangian Way'' is the second full-length album by the Finnish folk metal band Turisas, released on May 27, 2007 through Century Media. It is a concept album that tells the story of a group of Scandinavians traveling the river routes of m ...
'' (2007) and '' Stand Up and Fight'' (2011).
* Harald is a playable character in the Mobile/PC Game Rise of Kingdoms
Rise or RISE may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* '' Rise: The Vieneo Province'', an internet-based virtual world
* Rise FM, a fictional radio station in the video game ''Grand Theft Auto 3''
* Rise Kujikawa, a vide ...
.
* Harald is a playable character as "Harald Hardrada" in the turn-based strategyPC Game Civilization VI
''Sid Meier's Civilization VI'' is a turn-based strategy 4X video game developed by Firaxis Games, published by 2K Games, and distributed by Take-Two Interactive. The mobile port was published by Aspyr Media. The latest entry into the ''Civili ...
. He is a leader presenting the Norwegian civilization.
Explanatory footnotes
Citations
General sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Haraldr Sigurðarson's arrival in Rus' and his participation in the campaign against Poland in 1031
Saga of Harald Hardrade
by
Snorri Sturluson
Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of th ...
(), English translation
Ágrip (af Nóregskonungasögum)
(), in Old Norse with English translation
An Account of the Ancient History of the Norwegian Kings
by
Theodoric the Monk
Theodoric the Monk ( la, Theodoricus monachus; also ''Tjodrik munk''; in Old Norse his name was most likely ''Þórir'') was a 12th-century Norwegian Benedictine monk, perhaps at the Nidarholm Abbey. He may be identical with either Bishop Tore o ...
(), English translation
Morkinskinna
(), in Old Norse
Fagrskinna
(), in Old Norse
Flateyjarbók
(14th/15th century), in Icelandic {{DEFAULTSORT:Hardrada, Harald 1010s births 1066 deaths 11th-century Norwegian monarchs Christian monarchs Deaths by arrow wounds House of Hardrada Manglabitai Monarchs killed in action Norwegian exiles Pretenders to the Danish throne Pretenders to the English throne Royal reburials Uprising of Peter Delyan Varangian Guard Vikings killed in battle