Haplogroup E-M96 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Haplogroup E-M96 is a
Phylogeographic refinement and large scale genotyping of human Y chromosome haplogroup E provide new insights into the dispersal of early pastoralists in the African continent
/ref> A Eurasian center of origin and dispersal for haplogroup E has also been hypothesized by Cabrera et al. (2018) based on the similar age of the clade's parent haplogroup DE and the mtDNA haplogroup L3. According to this hypothesis, after an initial Out-of-Africa migration of early
 One of various Pre-Pottery Neolithic B fossils that were analysed for ancient DNA was found to carry the paternal haplogroup E(xE2,E1a,E1b1a1a1c2c3b1,E1b1b1b1a1,E1b1b1b2b) (1/7; ~14%).
One of various Pre-Pottery Neolithic B fossils that were analysed for ancient DNA was found to carry the paternal haplogroup E(xE2,E1a,E1b1a1a1c2c3b1,E1b1b1b1a1,E1b1b1b2b) (1/7; ~14%).
/ref> Sampling bias does not allow for meaningful percentages, but the presences of the haplogroup is solidly attested.
Supplementary Data
* *. Published online April 2, 2008. See als
Supplementary Material.
*. Published online 9 March 2005 * *
Map of E1b1b1 distribution in EuropeDistribution of E1b1a/E3a in AfricaFrequency Distributions of Y-DNA Haplogroup E and its subclades - with Video Tutorial
Haplogroup E-V38 Y-DNA Project at FTDNAE-M243 Y-DNA Project at FTDNAHaplozone::The E-M35 Phylogeny Project (former E3b Project)Jewish E-M243 Project at FTDNA
E
human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of s ...
. It is one of the two main branches of the older and ancestral haplogroup DE
Haplogroup DE is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is defined by the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutations, or UEPs, M1(YAP), M145(P205), M203, P144, P153, P165, P167, P183. DE is unique because it is distributed in several geogra ...
, the other main branch being haplogroup D. The E-M96 clade is divided into two main subclades
In genetics, a subclade is a subgroup of a haplogroup.
Naming convention
Although human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and Y chromosome DNA (Y-DNA) haplogroups and subclades are named in a similar manner, their names belong to completely separate syst ...
: the more common E-P147, and the less common E-M75.
Origins
Underhill (2001) proposed that haplogroup E may have arisen in East Africa. Some authors as Chandrasekar (2007), accept the earlier position of Hammer (1997) that Haplogroup E may have originated in West Asia, given that: * E is a clade of Haplogroup DE, with the other major clade, haplogroup D, being exclusively distributed in Asia. * DE is a clade within M168 with the other two major clades, C and F, considered to have already a Eurasian origin. However, several discoveries made since the Hammer articles are thought to make an Asian origin less likely: # Underhill and Kivisild (2007) demonstrated that C and F have a common ancestor meaning that DE has only one sibling which is non-African. # DE* is found in both Asia and Africa, meaning that not only one, but several siblings of D are found in Asia and Africa. # Karafet (2008), in which Hammer is a co-author, significantly rearranged time estimates leading to "new interpretations on the geographical origin of ancient sub-clades". Amongst other things this article proposed a much older age for haplogroup E-M96 than had been considered previously, giving it a similar age to Haplogroup D, and DE itself, meaning that there is no longer any strong reason to see it as an offshoot of DE which must have happened long after DE came into existence and had entered Asia. In 2015 Poznik and Underhill have claimed haplogroup E, arose outside Africa, arguing that, "This model of geographical segregation within the CT clade requires just one continental haplogroup exchange (E to Africa), rather than three (D, C, and F out of Africa). The timing of this putative return to Africa, between the emergence of haplogroup E and its differentiation within Africa by 58 kya, is consistent with proposals, based on non–Y chromosome data, of abundant gene flow between Africa and Arabia 50–80 kya." In 2015 Trobetta et al. suggested an East African origin for haplogroup E, stating: "our phylogeographic analysis, based on thousands of samples worldwide, suggests that the radiation of haplogroup E started about 58 ka, somewhere in sub-Saharan Africa, with a higher posterior probability (0.73) for an eastern African origin."Trombetta et al. 2015Phylogeographic refinement and large scale genotyping of human Y chromosome haplogroup E provide new insights into the dispersal of early pastoralists in the African continent
/ref> A Eurasian center of origin and dispersal for haplogroup E has also been hypothesized by Cabrera et al. (2018) based on the similar age of the clade's parent haplogroup DE and the mtDNA haplogroup L3. According to this hypothesis, after an initial Out-of-Africa migration of early
anatomically modern human
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
s around 125 kya, E-carrying males are thus proposed to have back-migrated from the paternal haplogroup's place of origin in Eurasia around 70 kya along with females bearing the maternal haplogroup L3, which the study also hypothesizes to have originated in Eurasia. These new Eurasian lineages were then suggested to have largely replaced the old autochthonous male and female African lineages.
A 2019 study by Haber et al. supports an African origin for haplogroup E (based on an analysis of the Y-chromosomal phylogenetic structure, haplogroup divergence times, and the recently discovered haplogroup D0 found in three Nigerians, an additional branch of the DE lineage diverging early from the D branch). The authors support an African origin for DE (parent haplogroup of E) with E and D0 also originating in Africa, along with the migration out of Africa of the three lineages (C, D and FT) that now form the vast majority of non-African Y chromosomes. The early divergence dates found in the study for DE, E, and D0 (all dated from about 71-76 kya), which are determined to predate the migration out-of-Africa of the ancestors of Eurasians (dated to ca. 50-60 kya), are also considered by the authors to support an African origin for those haplogroups.
Distribution
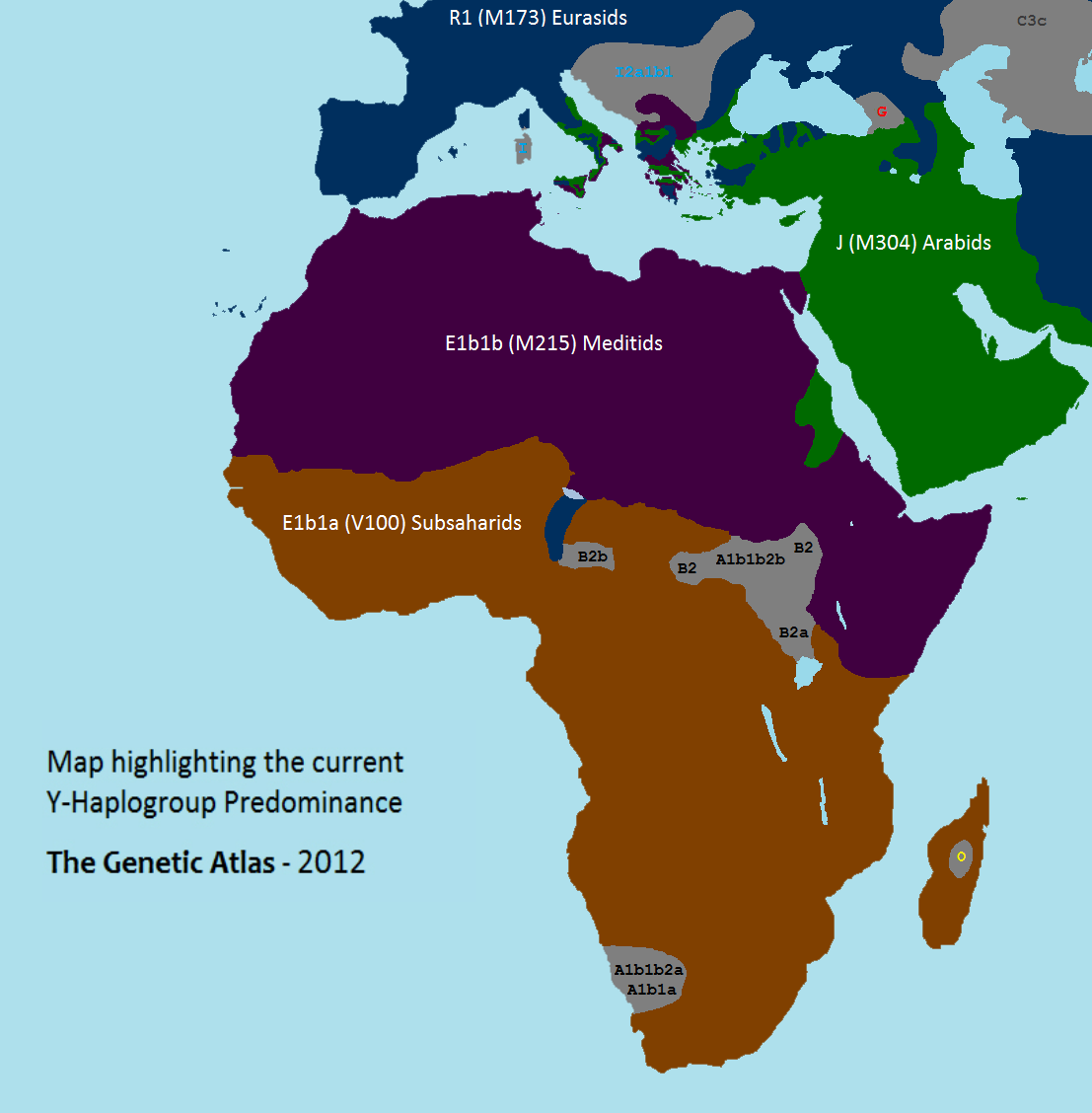
Most members of haplogroup E-M96 belong to one of its identified subclades, and the E-M96(xE-P147, E-M75) is rare. E1a and E-M75 are found almost exclusively inAfrica
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. By looking at the major subclade frequencies, five broad regions of Africa can be defined: East, Central, North, Southern and West. The division can be distinguished by the prevalence of E-M2 in East, Central, Southern and West Africa, E-M78 in East Africa and E-M81 in North Africa. E-M2 is the most prevalent subclade of E in Africa. It is observed at high frequencies in all African regions from moderate to high. E-M215 (especially its subclades M78 and M81) is found at high frequencies in North East Africa
Northeast Africa, or ''Northeastern Africa'' or Northern East Africa as it was known in the past, is a geographic regional term used to refer to the countries of Africa situated in and around the Red Sea. The region is intermediate between North ...
and North Africa and is the only subclade that is found in Europe and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
at significant frequencies. E-M215 is common among Afro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic su ...
speakers in the Near East and North Africa as well as among some Nilo-Saharan and Niger–Congo speakers in North East Africa
Northeast Africa, or ''Northeastern Africa'' or Northern East Africa as it was known in the past, is a geographic regional term used to refer to the countries of Africa situated in and around the Red Sea. The region is intermediate between North ...
and Sudan. E-M215 is far less common in West, Central, and Southern Africa, though it has been observed among some Khoisan speakers and among Niger–Congo speakers in Senegambia, Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ) ...
, Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to th ...
, Ghana, Gabon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda
Rwanda (; rw, u Rwanda ), officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of Central Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equat ...
, Namibia, and South Africa.
 One of various Pre-Pottery Neolithic B fossils that were analysed for ancient DNA was found to carry the paternal haplogroup E(xE2,E1a,E1b1a1a1c2c3b1,E1b1b1b1a1,E1b1b1b2b) (1/7; ~14%).
One of various Pre-Pottery Neolithic B fossils that were analysed for ancient DNA was found to carry the paternal haplogroup E(xE2,E1a,E1b1a1a1c2c3b1,E1b1b1b1a1,E1b1b1b2b) (1/7; ~14%).
Subclades
E-M96*
Paragroup
Paragroup is a term used in population genetics to describe lineages within a haplogroup that are not defined by any additional unique markers.
In human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups, paragroups are typically represented by an asterisk (*) placed ...
E-M96* refers to lineages belonging to the E clade but which cannot be classified into any known branch. E(xE1-P147, E2-M75) - that is, E which has tested negative for both P147 and M75 - has been reported in 2 Amharas
Amharas ( am, አማራ, Āmara; gez, ዐምሐራ, ʾÄməḥära) are a Semitic-speaking ethnic group which is indigenous to Ethiopia, traditionally inhabiting parts of the northwest Highlands of Ethiopia, particularly inhabiting the Amhar ...
from Ethiopia, in 2 men from Saudi Arabia, and in a single Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
* Black Association for Nationa ...
-speaking male from South Africa. E(xE1a-M33, E1b1-P2, E2-M75) was reported among several Southern African populations and in an Egyptian man; E(xE1a-M33, E1b1a1-M2, E1b1b-M215, E2-M75) has been observed amongst pygmies and Bantu from Cameroon and Gabon; and E(xE1a-M33, E1b1a1-M2, E1b1b1-M35, E2-M75) has been found in several Lebanese, in Burkina Faso, and a Fulbe man from Niger.
Recently it was discovered that 3 East African men previously classified only as E*-M96 could be assigned to a new branch, E-V44, which is a sister branch to E1-P147; E-P147 and E-V44 share the V3725 mutation, making E2-M75 and E-V3725 the two known primary branches of E. It is not known whether or not some (or all) other E*(xE1, E2) would fall into V44 as well.
E-P147
E-P147 (also known as E1) is by far the most numerous and widely distributed branch of E-M96. It has two primary branches: E-M132 (E1a) and E-P177 (E1b). Within Haplogroup E-P177,Haplogroup E-P2
E-P2, also known as E1b1, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. This paternal clade had an ancient presence in the Middle East, and is now primarily distributed in Africa where it's believed to have originated, with lower frequencies in the Midd ...
(E1b1) – a subclade of E-P177 – is not only the most frequent variant of E-M96, but is also the most common Y-DNA lineage in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. It is also the only subclade of E-M96 found in significant numbers in West Asia and Europe.
A prolific primary branch of E-P2, Haplogroup E-M215 (E1b1b) is distributed in high frequencies from East Africa, through North Africa into Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
and Southern Europe. It is also found at significant levels among populations native to Southern Africa and throughout Western Europe.
E-M75
E-M75 is present throughout Subequatorial Africa, particularly in theAfrican Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in the wo ...
and Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, ...
. The highest concentration of the haplogroup has been found among the Alur (66.67%), Hema (38.89%), Rimaibe (27.03%), Mbuti (25.00%), Daba (22.22%), Eviya (20.83%), Zulu (20.69%), and Kenyan Bantus
The Bantu peoples, or Bantu, are an ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. They are native to 24 countries spread over a vast area from Central Africa to Southeast Africa and into Southern A ...
(17.24%).
Haplogroup E-M75(xM41,M54) has been found in 6% (1/18) of Dama from Namibia, 4% (1/26) of Ganda
Ganda may refer to:
Places
* Ganda, Angola
* Ganda, Tibet, China
* Ganda, the ancient Latin name of Ghent, a city in Belgium
Other uses
* Baganda or Ganda, a people of Uganda
** Luganda or Ganda language, a language of Uganda
* ''Ganda'' and "Ga ...
from Uganda, 3% (1/39) of Mandinka Mandinka, Mandika, Mandinkha, Mandinko, or Mandingo may refer to:
Media
* ''Mandingo'' (novel), a bestselling novel published in 1957
* ''Mandingo'' (film), a 1975 film based on the eponymous 1957 novel
* ''Mandingo (play)'', a play by Jack Kir ...
from Gambia/Senegal, and 2% (1/49) of Shona from Zimbabwe.
Family Tree DNA
FamilyTreeDNA is a division of Gene by Gene, a commercial genetic testing company based in Houston, Texas. FamilyTreeDNA offers analysis of autosomal DNA, Y-DNA, and mitochondrial DNA to individuals for genealogical purpose. With a database of m ...
shows numerous persons of Haplogroup E-M75 claiming origins from the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
(most from Saudi Arabia, but also from Bahrain, Kuwait, Yemen, and United Arab Emirates).Family Tree DNA public haplotree, Haplogroup E-M75/ref> Sampling bias does not allow for meaningful percentages, but the presences of the haplogroup is solidly attested.
Phylogenetics
Phylogenetic history
Prior to 2002, there were in academic literature at least seven naming systems for the Y-Chromosome Phylogenetic tree. This led to considerable confusion. In 2002, the major research groups came together and formed the Y-Chromosome Consortium (YCC). They published a joint paper that created a single new tree that all agreed to use. Later, a group of citizen scientists with an interest in population genetics and genetic genealogy formed a working group to create an amateur tree aiming at being above all timely. The table below brings together all of these works at the point of the landmark 2002 YCC Tree. This allows a researcher reviewing older published literature to quickly move between nomenclatures.Research publications
The following research teams per their publications were represented in the creation of the YCC tree.Phylogenetic trees
This phylogenetic tree of haplogroup subclades is based on the Y-Chromosome Consortium (YCC) Tree, the ISOGG Y-DNA Haplogroup Tree, and subsequent published research.Prominent members of E
*Skanderbeg
, reign = 28 November 1443 – 17 January 1468
, predecessor = Gjon Kastrioti
, successor = Gjon Kastrioti II
, spouse = Donika Arianiti
, issue = Gjon Kastrioti II
, royal house = Kastrioti
, father ...
* Giuseppe Garibaldi
* Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
* Napoleon
* Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
* Nicolas Cage
* Franz Kafka
* Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of hi ...
* Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and then ...
* Zinedine Zidane
* The Wright brothers
* Nelson Mandela
* Desmond Tutu
Desmond Mpilo Tutu (7 October 193126 December 2021) was a South African Anglican bishop and theologian
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic dis ...
* Ramesses III
See also
Genetics
Y-DNA E subclades
Y-DNA backbone tree
Notes
Sources for conversion tables
* * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * Also seSupplementary Data
* *. Published online April 2, 2008. See als
Supplementary Material.
*. Published online 9 March 2005 * *
External links
{{Commons category, Haplogroup E of Y-DNAPhylogenetic tree and distribution maps of Y-DNA haplogroup E
Projects
Haplogroup E-V38 Y-DNA Project at FTDNA
E