handwriting recognition on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Handwriting recognition (HWR), also known as handwritten text recognition (HTR), is the ability of a computer to receive and interpret intelligible handwritten input from sources such as
Handwriting recognition (HWR), also known as handwritten text recognition (HTR), is the ability of a computer to receive and interpret intelligible handwritten input from sources such as
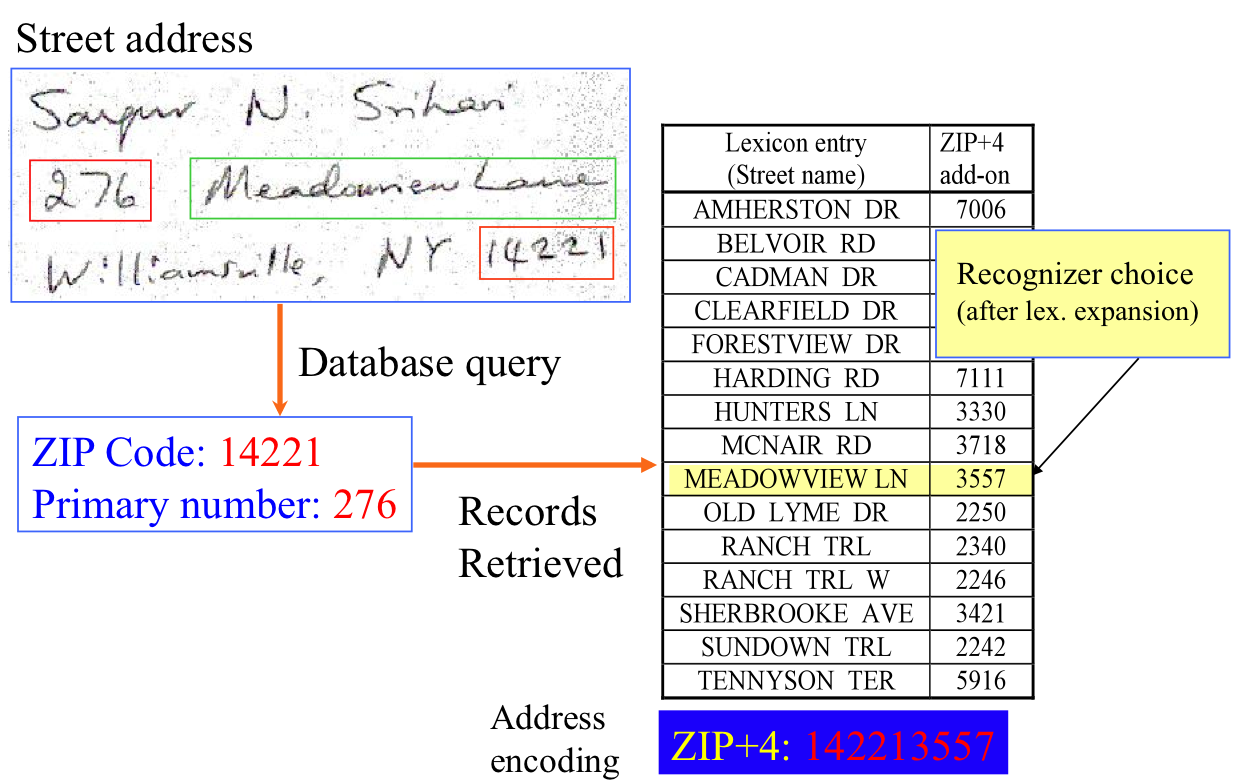 Handwriting recognition has an active community of academics studying it. The biggest conferences for handwriting recognition are the International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition (ICFHR), held in even-numbered years, and the
Handwriting recognition has an active community of academics studying it. The biggest conferences for handwriting recognition are the International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition (ICFHR), held in even-numbered years, and the
Annotated bibliography of references to gesture and pen computingNotes on the History of Pen-based Computing
– video on
 Handwriting recognition (HWR), also known as handwritten text recognition (HTR), is the ability of a computer to receive and interpret intelligible handwritten input from sources such as
Handwriting recognition (HWR), also known as handwritten text recognition (HTR), is the ability of a computer to receive and interpret intelligible handwritten input from sources such as paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distribu ...
documents, photograph
A photograph (also known as a photo, image, or picture) is an image created by light falling on a photosensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic image sensor, such as a CCD or a CMOS chip. Most photographs are now create ...
s, touch-screens and other devices. The image of the written text may be sensed "off line" from a piece of paper by optical scanning (optical character recognition
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronic or mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a sc ...
) or intelligent word recognition. Alternatively, the movements of the pen tip may be sensed "on line", for example by a pen-based computer screen surface, a generally easier task as there are more clues available. A handwriting recognition system handles formatting, performs correct segmentation into characters, and finds the most plausible words.
Offline recognition
Offline handwriting recognition involves the automatic conversion of text in an image into letter codes that are usable within computer and text-processing applications. The data obtained by this form is regarded as a static representation of handwriting. Offline handwriting recognition is comparatively difficult, as different people have different handwriting styles. And, as of today, OCR engines are primarily focused on machine printed text and ICR for hand "printed" (written in capital letters) text.Traditional techniques
Character extraction
Offline character recognition often involves scanning a form or document. This means the individual characters contained in the scanned image will need to be extracted. Tools exist that are capable of performing this step. However, there are several common imperfections in this step. The most common is when characters that are connected are returned as a single sub-image containing both characters. This causes a major problem in the recognition stage. Yet many algorithms are available that reduce the risk of connected characters.Character recognition
After individual characters have been extracted, a recognition engine is used to identify the corresponding computer character. Several different recognition techniques are currently available.= Feature extraction
= Feature extraction works in a similar fashion to neural network recognizers. However, programmers must manually determine the properties they feel are important. This approach gives the recognizer more control over the properties used in identification. Yet any system using this approach requires substantially more development time than a neural network because the properties are not learned automatically.Modern techniques
Where traditional techniques focus on segmenting individual characters for recognition, modern techniques focus on recognizing all the characters in a segmented line of text. Particularly they focus onmachine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
techniques that are able to learn visual features, avoiding the limiting feature engineering previously used. State-of-the-art methods use convolutional networks to extract visual features over several overlapping windows of a text line image which a recurrent neural network uses to produce character probabilities.
Online recognition
Online handwriting recognition involves the automatic conversion of text as it is written on a special digitizer orPDA
PDA may refer to:
Science and technology
* Patron-driven acquisition, a mechanism for libraries to purchase books
*Personal digital assistant, a mobile device
* Photodiode array, a type of detector
* Polydiacetylenes, a family of conducting po ...
, where a sensor picks up the pen-tip movements as well as pen-up/pen-down switching. This kind of data is known as digital ink and can be regarded as a digital representation of handwriting. The obtained signal is converted into letter codes that are usable within computer and text-processing applications.
The elements of an online handwriting recognition interface typically include:
* a pen or stylus for the user to write with.
* a touch sensitive surface, which may be integrated with, or adjacent to, an output display.
* a software application which interprets the movements of the stylus across the writing surface, translating the resulting strokes into digital text.
The process of online handwriting recognition can be broken down into a few general steps:
* preprocessing,
* feature extraction and
* classification
The purpose of preprocessing is to discard irrelevant information in the input data, that can negatively affect the recognition. This concerns speed and accuracy. Preprocessing usually consists of binarization, normalization, sampling, smoothing and denoising. The second step is feature extraction. Out of the two- or higher-dimensional vector field received from the preprocessing algorithms, higher-dimensional data is extracted. The purpose of this step is to highlight important information for the recognition model. This data may include information like pen pressure, velocity or the changes of writing direction. The last big step is classification. In this step, various models are used to map the extracted features to different classes and thus identifying the characters or words the features represent.
Hardware
Commercial products incorporating handwriting recognition as a replacement for keyboard input were introduced in the early 1980s. Examples include handwriting terminals such as the Pencept Penpad and the Inforite point-of-sale terminal. With the advent of the large consumer market for personal computers, several commercial products were introduced to replace the keyboard and mouse on a personal computer with a single pointing/handwriting system, such as those from Pencept, CIC and others. The first commercially available tablet-type portable computer was the GRiDPad from GRiD Systems, released in September 1989. Its operating system was based onMS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few o ...
.
In the early 1990s, hardware makers including NCR, IBM and EO released tablet computer
A tablet computer, commonly shortened to tablet, is a mobile device, typically with a mobile operating system and touchscreen display processing circuitry, and a rechargeable battery in a single, thin and flat package. Tablets, being com ...
s running the PenPoint
The PenPoint OS was a product of GO Corporation and was one of the earliest operating systems written specifically for graphical tablets and personal digital assistants. It ran on AT&T Corporation's EO Personal Communicator as well as a number ...
operating system developed by GO Corp. PenPoint used handwriting recognition and gestures throughout and provided the facilities to third-party software. IBM's tablet computer was the first to use the ThinkPad name and used IBM's handwriting recognition. This recognition system was later ported to Microsoft Windows for Pen Computing, and IBM's Pen for OS/2. None of these were commercially successful.
Advancements in electronics allowed the computing power necessary for handwriting recognition to fit into a smaller form factor than tablet computers, and handwriting recognition is often used as an input method for hand-held PDA
PDA may refer to:
Science and technology
* Patron-driven acquisition, a mechanism for libraries to purchase books
*Personal digital assistant, a mobile device
* Photodiode array, a type of detector
* Polydiacetylenes, a family of conducting po ...
s. The first PDA to provide written input was the Apple Newton, which exposed the public to the advantage of a streamlined user interface. However, the device was not a commercial success, owing to the unreliability of the software, which tried to learn a user's writing patterns. By the time of the release of the Newton OS 2.0, wherein the handwriting recognition was greatly improved, including unique features still not found in current recognition systems such as modeless error correction, the largely negative first impression had been made. After discontinuation of Apple Newton, the feature was incorporated in Mac OS X 10.2 and later as Inkwell.
Palm
Palm most commonly refers to:
* Palm of the hand, the central region of the front of the hand
* Palm plants, of family Arecaceae
**List of Arecaceae genera
* Several other plants known as "palm"
Palm or Palms may also refer to:
Music
* Palm (ba ...
later launched a successful series of PDA
PDA may refer to:
Science and technology
* Patron-driven acquisition, a mechanism for libraries to purchase books
*Personal digital assistant, a mobile device
* Photodiode array, a type of detector
* Polydiacetylenes, a family of conducting po ...
s based on the Graffiti
Graffiti (plural; singular ''graffiti'' or ''graffito'', the latter rarely used except in archeology) is art that is written, painted or drawn on a wall or other surface, usually without permission and within public view. Graffiti ranges from s ...
recognition system. Graffiti improved usability by defining a set of "unistrokes", or one-stroke forms, for each character. This narrowed the possibility for erroneous input, although memorization of the stroke patterns did increase the learning curve for the user. The Graffiti handwriting recognition was found to infringe on a patent held by Xerox, and Palm replaced Graffiti with a licensed version of the CIC handwriting recognition which, while also supporting unistroke forms, pre-dated the Xerox patent. The court finding of infringement was reversed on appeal, and then reversed again on a later appeal. The parties involved subsequently negotiated a settlement concerning this and other patents.
A Tablet PC is a notebook computer with a digitizer tablet and a stylus, which allows a user to handwrite text on the unit's screen. The operating system recognizes the handwriting and converts it into text. Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years before, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of ...
and Windows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, ...
include personalization features that learn a user's writing patterns or vocabulary for English, Japanese, Chinese Traditional, Chinese Simplified and Korean. The features include a "personalization wizard" that prompts for samples of a user's handwriting and uses them to retrain the system for higher accuracy recognition. This system is distinct from the less advanced handwriting recognition system employed in its Windows Mobile
Windows Mobile is a discontinued family of mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones and personal digital assistants.
Its origin dated back to Windows CE in 1996, though Windows Mobile itself first appeared in 2000 as Pock ...
OS for PDAs.
Although handwriting recognition is an input form that the public has become accustomed to, it has not achieved widespread use in either desktop computers or laptops. It is still generally accepted that keyboard
Keyboard may refer to:
Text input
* Keyboard, part of a typewriter
* Computer keyboard
** Keyboard layout, the software control of computer keyboards and their mapping
** Keyboard technology, computer keyboard hardware and firmware
Music
* Mu ...
input is both faster and more reliable. , many PDAs offer handwriting input, sometimes even accepting natural cursive handwriting, but accuracy is still a problem, and some people still find even a simple on-screen keyboard
A virtual keyboard is a software component that allows the input of characters without the need for physical keys. The interaction with the virtual keyboard happens mostly via a touchscreen interface, but can also take place in a different form ...
more efficient.
Software
Early software could understand print handwriting where the characters were separated; however, cursive handwriting with connected characters presented Sayre's Paradox, a difficulty involving character segmentation. In 1962 Shelia Guberman, then in Moscow, wrote the first applied pattern recognition program. Commercial examples came from companies such as Communications Intelligence Corporation and IBM. In the early 1990s, two companies – ParaGraph International and Lexicus – came up with systems that could understand cursive handwriting recognition. ParaGraph was based in Russia and founded by computer scientist Stepan Pachikov while Lexicus was founded by Ronjon Nag and Chris Kortge who were students at Stanford University. The ParaGraph CalliGrapher system was deployed in the Apple Newton systems, and Lexicus Longhand system was made available commercially for the PenPoint and Windows operating system. Lexicus was acquired by Motorola in 1993 and went on to develop Chinese handwriting recognition and predictive text systems for Motorola. ParaGraph was acquired in 1997 by SGI and its handwriting recognition team formed a P&I division, later acquired from SGI by Vadem. Microsoft has acquired CalliGrapher handwriting recognition and other digital ink technologies developed by P&I from Vadem in 1999. Wolfram Mathematica (8.0 or later) also provides a handwriting or text recognition function TextRecognize.Research
 Handwriting recognition has an active community of academics studying it. The biggest conferences for handwriting recognition are the International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition (ICFHR), held in even-numbered years, and the
Handwriting recognition has an active community of academics studying it. The biggest conferences for handwriting recognition are the International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition (ICFHR), held in even-numbered years, and the International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition The International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR) is an international academic conference which is held every two years in a different city. It is about character and symbol recognition, printed/handwritten text recognition, ...
(ICDAR), held in odd-numbered years. Both of these conferences are endorsed by the IEEE and IAPR
The International Association for Pattern Recognition (IAPR), founded in 1978 by Purdue University computer scientist King-Sun Fu, is an international association of non-profit, scientific, or professional organizations (being national, multi-natio ...
.
In 2021, the ICDAR proceedings will be published by LNCS, Springer.
Active areas of research include:
* Online recognition
* Offline recognition
* Signature verification
* Postal address interpretation
* Bank-Check processing
* Writer recognition
Handwritten biometric recognition is the process of identifying the author of a given text from the handwriting style. Handwritten biometric recognition belongs to behavioural biometric systems because it is based on something that the user has l ...
Results since 2009
Since 2009, the recurrent neural networks and deepfeedforward
Feedforward is the provision of context of what one wants to communicate prior to that communication. In purposeful activity, feedforward creates an expectation which the actor anticipates. When expected experience occurs, this provides confirmato ...
neural networks developed in the research group of Jürgen Schmidhuber
Jürgen Schmidhuber (born 17 January 1963) is a German computer scientist most noted for his work in the field of artificial intelligence, deep learning and artificial neural networks. He is a co-director of the Dalle Molle Institute for Artific ...
at the Swiss AI Lab IDSIA have won several international handwriting competitions. In particular, the bi-directional and multi-dimensional Long short-term memory
Long short-term memory (LSTM) is an artificial neural network used in the fields of artificial intelligence and deep learning. Unlike standard feedforward neural networks, LSTM has feedback connections. Such a recurrent neural network (RNN) c ...
(LSTM) of Alex Graves et al. won three competitions in connected handwriting recognition at the 2009 International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), without any prior knowledge about the three different languages (French, Arabic, Persian) to be learned. Recent GPU-based deep learning
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with representation learning. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised.
...
methods for feedforward networks by Dan Ciresan and colleagues at IDSIA won the ICDAR 2011 offline Chinese handwriting recognition contest; their neural networks also were the first artificial pattern recognizers to achieve human-competitive performance on the famous MNIST handwritten digits problem of Yann LeCun
Yann André LeCun ( , ; originally spelled Le Cun; born 8 July 1960) is a French computer scientist working primarily in the fields of machine learning, computer vision, mobile robotics and computational neuroscience. He is the Silver Professo ...
and colleagues at NYU
New York University (NYU) is a private research university in New York City. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded by a group of New Yorkers led by then-Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin.
In 1832, the ...
.
See also
*AI effect
:''For the magnitude of effect of a pesticide, see Pesticide application. Of change in farming practices, see Agricultural intensification.''
The AI effect occurs when onlookers discount the behavior of an artificial intelligence program by argu ...
* Applications of artificial intelligence
* Electronic signature
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is data that is logically associated with other data and which is used by the signatory to sign the associated data. This type of signature has the same legal standing as a handwritten signature as long as ...
* Handwriting movement analysis
* Intelligent character recognition
In computer science, intelligent character recognition (ICR) is an advanced optical character recognition (OCR) or — rather more specific — handwriting recognition system that allows fonts and different styles of handwriting to be learned by a ...
* Live Ink Character Recognition Solution
* Neocognitron
* Optical character recognition
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronic or mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a sc ...
* Pen computing
* Sketch recognition
* Stylus (computing)
In computing, a stylus (or stylus pen) is a small pen-shaped instrument whose tip position on a computer monitor can be detected. It is used to draw, or make selections by tapping. While devices with touchscreens such as newer computers, mobile ...
* Tablet PC
Lists
* Outline of artificial intelligence *List of emerging technologies
This is a list of emerging technologies, in-development technical innovations with significant potential in their applications. The criteria for this list is that the technology must:
# Exist in some way; purely hypothetical technologies ca ...
References
External links
Annotated bibliography of references to gesture and pen computing
– video on
YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second mo ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Handwriting Recognition
Applications of artificial intelligence
Pointing-device text input
Machine learning task