Hand Pump on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

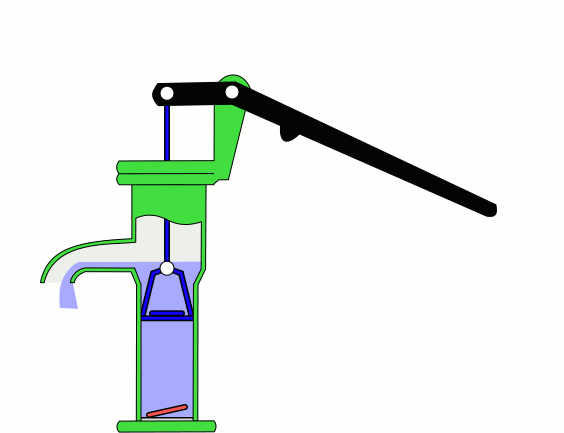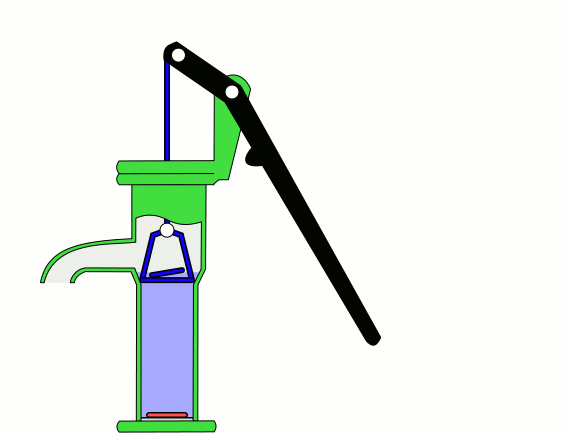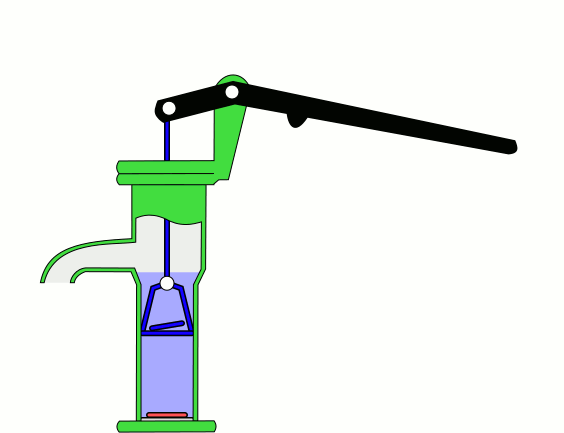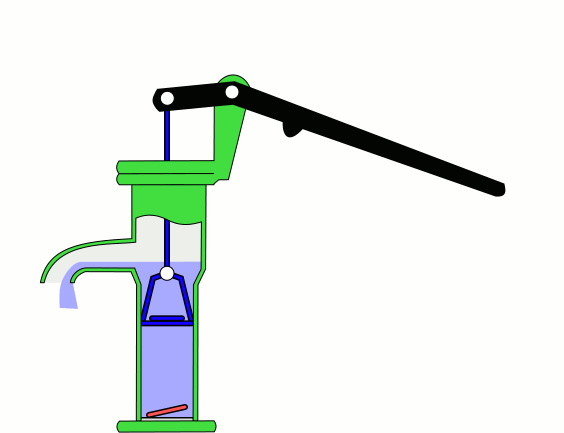 Hand pumps are manually operated
Hand pumps are manually operated
 One sort of pump once common worldwide was a hand-powered water pump, or 'pitcher pump'. It was commonly installed over community
One sort of pump once common worldwide was a hand-powered water pump, or 'pitcher pump'. It was commonly installed over community
Sustaining Rural Water Systems:The Case of Mali
Autumn 1997, Retrieved on 25 April 2011 The project is notable in its attempt to bring responsibility for the upkeep of the pumps to the villages themselves. The complexity of the pumps is a fundamental problem for all programs of this kind, as well as the quality of the pumps given the heavy demands of a village. A 1994 study, also Bank funded, of the endurance of hand pumps in Africa showed that only 41 to 51 percent of hand pumps were still functioning. The Mali Rural Supply Project did positively affect the longevity of hand pumps by doing the following: establishing local depots of spare parts, training individuals to maintain pumps, scheduling inspections from officials of the project, forming local committees and recruiting volunteers. Much attention has been given to the benefits of the use of hand pumps in developing nations, as opposed to more traditional methods. In communities reliant on groundwater, through a borehole or well, the utilization of a bucket and rope system has hygienic issues. The bucket and rope system is not compatible with the use of a cover slab, which can prevent pollution of groundwater. In addition, unwashed hands can contaminate the bucket and rope. Hand pumps avoid these issues and are therefore preferable. However, villagers did not stop using traditional means of gathering water during this project. This was especially true when rain provided villagers with shallow water sources. These shallow wells were often easier to access than the wells with hand pumps. When faced with the option of using near surface water or traveling to the hand pumps, many villagers chose the former. In addition, animal contamination and the mixing of groundwater and surface water were factors in sub- par sanitation. Another issue that faced the project was the fact that the pumps could only provide a maximum of 20 liters of water per person day, which required an unrealistic staggering of water retrieval. In addition, many depots withdrew support after the donated inventory ran out, the contracts given to consultants eventually closed, and maintenance was not kept up to a high standard. A June 2008 study, conducted by the World Bank, Review of Effectiveness of Rural Water Supply Schemes in India, showed that approximately 45 percent of rural piped water projects focused on breakdown maintenance instead of scheduled maintenance. In addition, about 20% were reported to be in “serious or somewhat serious neglect of maintenance.”
File:A beautiful hand pump in village Bado, Sindh.jpg, A hand pump in village Bado, near Shikarpur
 Hand pumps are manually operated
Hand pumps are manually operated pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they ...
s; they use human power and mechanical advantage
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for ...
to move fluids or air from one place to another. They are widely used in every country in the world for a variety of industrial, marine, irrigation and leisure activities. There are many different types of hand pump available, mainly operating on a piston, diaphragm or rotary vane principle with a check valve on the entry and exit ports to the chamber operating in opposing directions. Most hand pumps are either piston pumps or plunger pump
A plunger pump is a type of positive displacement pump where the high-pressure seal is stationary and a smooth cylindrical plunger slides through the seal. This makes them different from piston pumps and allows them to be used at higher pressures. ...
s, and are positive displacement.
Hand pumps are commonly used in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
for both community supply and self-supply of water and can be installed on borehole
A borehole is a narrow shaft bored in the ground, either vertically or horizontally. A borehole may be constructed for many different purposes, including the extraction of water ( drilled water well and tube well), other liquids (such as petrol ...
s or hand-dug wells.
History
 One sort of pump once common worldwide was a hand-powered water pump, or 'pitcher pump'. It was commonly installed over community
One sort of pump once common worldwide was a hand-powered water pump, or 'pitcher pump'. It was commonly installed over community water well
A well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, or drilling to access liquid resources, usually water. The oldest and most common kind of well is a water well, to access groundwater in underground aquifers. T ...
s in the days before piped water supplies.
In parts of Britain and Ireland, it was often called ''the parish pump''. Though such community pumps are no longer common, people still used the expression ''parish pump'' to describe a place or forum where matters of local interest are discussed.
Because water from pitcher pumps is drawn directly from the soil, it is more prone to contamination. If such water is not filtered and purified, consumption of it might lead to gastrointestinal or other water-borne diseases. A notorious case is the 1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak
Events
January–March
* January 4 – The McDonald Islands are discovered by Captain William McDonald aboard the ''Samarang''.
* January 6 – The fictional detective Sherlock Holmes is perhaps born.
* January 9 – The Teu ...
. At the time it was not known how cholera was transmitted, but physician John Snow
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology, in part because of his work in tracing the ...
suspected contaminated water and had the handle of the public pump he suspected removed; the outbreak then subsided.
Modern hand-operated community pumps are considered the most sustainable low-cost option for safe water supply in resource-poor settings, often in rural areas in developing countries. A hand pump opens access to deeper groundwater that is often not polluted and also improves the safety of a well by protecting the water source from contaminated buckets. Pumps such as the Afridev pump are designed to be cheap to build and install, and easy to maintain with simple parts. However, scarcity of spare parts for these type of pumps in some regions of Africa has diminished their utility for these areas.
Types
Suction and lift hand pumps
Suction and lift are important considerations when pumping fluids. Suction is the vertical distance between the fluid to be pumped and the centre of the pump, while lift is the vertical distance between the pump and the delivery point. The depth from which a hand pump will suck is limited by atmospheric pressure to an operating depth of less than 7 meters. The height to which a hand pump will lift is governed by the ability of the pump and the operator to lift the weight in the delivery pipe. Thus the same pump and operator will be able to achieve a greater lift with a smaller diameter pipe than they could with a larger diameter pipe. In addition to their use in drawing water from shallow groundwater sources for water supplies, another version of the hand-powered suction pump, with low lift and high delivery, was developed in the later 19th century for use as a ship's bilge pump (for smaller coastal vessels) and as a building site contractor's pump. It was known as a deluge pump. One manufacturer who illustrated this product from the late 1880s onwards into the early 20th century was Goulds Manufacturing Co.Force Pump
Where it is necessary to raise water to a height above that to which a suction or lift pump will operate effectively (about 7 metres), or to raise the pressure so that it will exit a nozzle with a strong force, such as through a fire hose, a force pump may be used. As with a suction pump, in its manual form it relies on an operator to pump a handle. The difference is however that after the water is sucked through the lower valve (as a result of raising the piston that is attached to the handle), its means of exit is via a pipe or nozzle in the side of the main cylinder. The water, once it has been drawn up above the lower valve and trapped there, is forced out the exit when the piston or plunger is pushed down again on the next stroke.Siphon
A siphon (or syphon) at its simplest is a bent tube, with one end placed in the water to be moved, and the other end into the vessel to receive the water. The receiving vessel must be at a lower level than the supplying vessel. Water will always try to find its lowest level. Using this principle, very simple pumps with plastic or rubber bulb with flap valve at each end are used for emptying fuel or water cans into tanks. Once the bulb is full, the fluid will flow without further effort from the higher to the lower container. Many hand pumps will allow the passage of fluid through them in the direction of flow and diaphragm pumps are particularly good at this. Thus where the levels are correct large volumes of liquid such as swimming pools can be emptied with very little effort and no expensive energy use.Chain pump
A chain pump is made of an endless chain carrying a series of discs that descend into the water, and then ascend inside a tube, carrying with them a large quantity of water. They are a simply made, old hand-powered pumping technology In the 18th century they were used as ship's bilge pumps.Direct action
Direct action hand pumps have a pumping rod that is moved up and down, directly by the user, discharging water. Direct action handpumps are easy to install and maintain but are limited to the maximum column of water a person can physically lift of up to 15 m. Examples of direct action pumps include the canzee pump and the EMAS pump.Deep wells
Deep well hand pumps are used for high lifts of more than 15 m. The weight of the column of water is too great to be lifted directly and some form of mechanical advantage system such as a lever or flywheel is used. High lift pumps need to be stronger and sturdier to cope with the extra stresses. The installation, maintenance and repair of deep well hand pumps is more complicated than with other hand pumps. A deep well hand pump theoretically has no limit to which it can extract water. In practice, the depth is limited by the physical power a human being can exert in lifting the column of water, which is around 30 mDiaphragm
Diaphragm pumps have the advantage that they pump relatively lightly due to the lack of pulling rods and are corrosion resistant. Their disadvantage is that they need a specific length of tubing and high quality rubber diaphragms, which are costly and are relatively inefficient due to the extra work needed to deform the diaphragm. Rubber diaphragms will eventually leak and need to be replaced. Because this is usually complicated and costly, diaphragm pumps operating in poor rural areas are often abandoned once the diaphragm wears out.Progressive cavity
Progressive cavity pumps consist of a single helix rotor inserted into a double helix stator. As the rotor is turned, the voids in the stator are screwed upwards along the axis of rotation. Progressive cavity pumps can have complicated gearing mechanisms and are difficult for local pump technicians to maintain and repair. A rope and washer pump is a type of progressive cavity hand pump.Range of lift
The range of lift of different types of hand pumps is given below:Hand pumps and access to clean water
In November 2002, the United Nations Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights asserted that access to clean, safe water goes beyond the classification of water as an economic commodity. The committee stressed the fundamental right of sufficient access to clean water for both domestic and personal use. “The human right to water is indispensable for leading a life in human dignity.” With this in mind, manufacturers of water pumps, like those produced by GOAZ Development in Malaysia, have a wide range of potential customers: governments, non- governmental organizations, women’s groups, community groups and other organizations of various types interested to developing access to groundwater.Village level operation and maintenance
VLOM, meaning Village Level Operation and Maintenance, is a term first used during the UNDP and World Bank Rural Water Supply Hand Pumps Project. This project lasted from 1981 to 1991, and studied the availability and maintenance of hand pump systems. 40 kinds of hand pumps were analyzed in laboratories, and the performance of 2700 hand pumps was analyzed in the field. The study established that centralized maintenance structure was a cause of many problems in hand pump programs, and that maintenance at the village level is best. The VLOM concept was initially applied to hardware, with the following aims: the possibility of maintenance by village workers, having spare parts manufactured within the country to make sure spare parts are available, endurance in the field, and cost effectiveness. With time, more emphasis was placed on maintenance management. Thus, the “M” came to represent “management of maintenance.” Therefore, greater community choice of service, who will service, and financial accountability by the community to the caretakers of the pump have gained more importance within the VLOM concept. The Swiss Centre Resource Centre and Consultancies for Development, Skat, continues to work on design and support structure for hand pump development as the host of Secretariat of the Rural Water Supply Network (RWSN).Hand pump development projects
An example of a Bank funded project that highlights many issues of hand pumps is the 1992 Mali Rural Supply Project. The project brought approximately 230 rural villages inclined towards periods of drought, and 228,000 people access to safe water.World Bank, Operations Evaluation DepartmenSustaining Rural Water Systems:The Case of Mali
Autumn 1997, Retrieved on 25 April 2011 The project is notable in its attempt to bring responsibility for the upkeep of the pumps to the villages themselves. The complexity of the pumps is a fundamental problem for all programs of this kind, as well as the quality of the pumps given the heavy demands of a village. A 1994 study, also Bank funded, of the endurance of hand pumps in Africa showed that only 41 to 51 percent of hand pumps were still functioning. The Mali Rural Supply Project did positively affect the longevity of hand pumps by doing the following: establishing local depots of spare parts, training individuals to maintain pumps, scheduling inspections from officials of the project, forming local committees and recruiting volunteers. Much attention has been given to the benefits of the use of hand pumps in developing nations, as opposed to more traditional methods. In communities reliant on groundwater, through a borehole or well, the utilization of a bucket and rope system has hygienic issues. The bucket and rope system is not compatible with the use of a cover slab, which can prevent pollution of groundwater. In addition, unwashed hands can contaminate the bucket and rope. Hand pumps avoid these issues and are therefore preferable. However, villagers did not stop using traditional means of gathering water during this project. This was especially true when rain provided villagers with shallow water sources. These shallow wells were often easier to access than the wells with hand pumps. When faced with the option of using near surface water or traveling to the hand pumps, many villagers chose the former. In addition, animal contamination and the mixing of groundwater and surface water were factors in sub- par sanitation. Another issue that faced the project was the fact that the pumps could only provide a maximum of 20 liters of water per person day, which required an unrealistic staggering of water retrieval. In addition, many depots withdrew support after the donated inventory ran out, the contracts given to consultants eventually closed, and maintenance was not kept up to a high standard. A June 2008 study, conducted by the World Bank, Review of Effectiveness of Rural Water Supply Schemes in India, showed that approximately 45 percent of rural piped water projects focused on breakdown maintenance instead of scheduled maintenance. In addition, about 20% were reported to be in “serious or somewhat serious neglect of maintenance.”
Hand pump affordability in rural developing areas
Whether or not a project to use hand pumps in a developing country is an affordable alternative certainly depends on who or what organization pays the bill. However, the example of a 1992 Ethiopia aid project illustrates what the cost would be for the locals who benefit from the project. This example relates to isolated, rural communities in the rural South. 165 Afridevs hand pumps were imported from India. Each cost approximately US$700, including clearing, transportation and installation. These pumps serve around 55 households each. At that time, the World Bank established that the average per capita income in Ethiopia was $120. A hand pump, first produced by researchers at theUniversity of Waterloo
The University of Waterloo (UWaterloo, UW, or Waterloo) is a public research university with a main campus in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is on of land adjacent to "Uptown" Waterloo and Waterloo Park. The university also operates ...
and then refined at the University of Malaya, has been designed with local access to parts in mind. Materials readily available, like a rope covered in chicken fat or leather belt, can be used to ensure maintenance. GOAZ Development sells these pumps from $160 to $300. Therefore, 11% of one’s annual income would go towards accessing clean water. This is over twice as much as the 5% that the World Bank stated should be the maximum amount paid by a family.
Gallery
Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
.
File:Pump-tah.jpg, Hand-operated, reciprocating, positive displacement, water pump in Košice
Košice ( , ; german: Kaschau ; hu, Kassa ; pl, Коszyce) is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of a ...
- Ťahanovce, Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
(walking beam pump).
File:DrawingWater.jpg, A child drawing water from a ''hand pump'', Oklahoma City
Oklahoma City (), officially the City of Oklahoma City, and often shortened to OKC, is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The county seat of Oklahoma County, it ranks 20th among United States cities in population, and ...
, Oklahoma, USA 1939.
File:Pumping water in Wilder, Fentress County TN 1942.gif, The sole water supply of this section of Wilder, Tennessee
Wilder is an unincorporated community in Fentress County, Tennessee, United States. The community is in the Cumberland Mountains near Cookeville, Tennessee.
History Early development
Wilder was a planned company town, intended to provide housin ...
, USA 1942.
File:La Russell Water Pump.jpg, A 1904 community ''hand pump'' surviving modern encroachment in 2010 on the middle of Main Street at La Russell, Missouri, USA.
File:Village Pump at Thorpe Abbotts.jpg, The covered Village Pump in Thorpe Abbots, Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
, England
File:Fotothek df pk 0000135 002.jpg, Hand pump in use during reconstruction of Germany after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
File:BerlinWaterPump.jpg, Hand-operated, water pump in Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
, Germany
File:Afridev.jpg, A rural handpump in Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast� ...
.
File:01 Bruges - Fontaine - JPG1.jpg, A city handpump in Bruges, Belgium
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the country by population.
The area of the whole city a ...
.
File:Well Pekkatori Raahe 20160731.jpg, Hand pump in Raahe
Raahe (; sv, Brahestad; ) is a town and municipality of Finland. Founded by Swedish statesman and Governor General of Finland Count Per Brahe the Younger in 1649, it is one of 10 historic wooden towns (or town centers) remaining in Finland. Exam ...
, Finland
File:Handschwengelpumpe Lobstädter Straße Leipzig 06.JPG, Hand pump in Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
, Germany
File:Retro Hand Pump.JPG, Hand Pump carved by Bijay Boghani in chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. C ...
File:Old hand water pump.jpg, Old hand water pump (c. 1924) at the Colored School in Alapaha, Georgia, US; typical of the period and the area
File:Ebenezer, GA, US (06).jpg, Hand pump at Ebenezer, Georgia
Ebenezer, also known as New Ebenezer, is a ghost town in Effingham County, Georgia, United States, along the banks of Ebenezer Creek. It was listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places as Ebenezer Townsite and Jerusalem Lutheran Chur ...
, USA
File:Handpump Repairing service in Bohardih Bilaspur Chhattisgarh.jpg, An India Mark II handpump in Bohardih, near Bilaspur, Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prad ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
.
See also
*Ram Pump
A plunger pump is a type of positive displacement pump where the high-pressure seal is stationary and a smooth cylindrical plunger slides through the seal. This makes them different from piston pumps and allows them to be used at higher pressures. ...
*Bush pump
The bush pump, also known as the Zimbabwe bush pump, is a positive displacement pump based on lever action used to extract water from a bore hole well. It is the standard hand pump in Zimbabwe, and is used in Zimbabwe and Namibia. There are appr ...
*Drinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, ...
* India Mark II
*Rope pump
A rope pump is a kind of pump where a loose hanging rope is lowered into a well and drawn up through a long pipe with the bottom immersed in water. On the rope, round disks or knots matching the diameter of the pipe are attached which pull the wat ...
*Treadle pump A treadle pump is a human-powered suction pump that sits on top of a well and is used for irrigation. It is designed to lift water from a depth of seven metres or less. The pumping is activated by stepping up and down on a treadle, which are levers ...
*Water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Th ...
*Water well
A well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, or drilling to access liquid resources, usually water. The oldest and most common kind of well is a water well, to access groundwater in underground aquifers. T ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hand Pump Pumps Appropriate technology Water supply Human power