Hampton Roads on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hampton Roads is the name of both a body of water in the United States that serves as a wide channel for the James, Nansemond and Elizabeth rivers between Old Point Comfort and
Sewell's Point
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to t ...
where the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
flows into the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, and the surrounding metropolitan region located in the southeastern Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
and northeastern North Carolina
North Carolina () is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 28th largest and List of states and territories of the United ...
portions of the Tidewater Region.
Comprising the Virginia Beach–Norfolk–Newport News, VA–NC, metropolitan area and an extended combined statistical area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan statistical area, metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and ...
that includes the Elizabeth City, North Carolina, micropolitan statistical area and Kill Devil Hills, North Carolina, micropolitan statistical area, Hampton Roads is known for its large military presence, ice-free harbor, shipyards, coal piers, and miles of waterfront property and beaches, all of which contribute to the diversity and stability of the region's economy.
The body of water known as Hampton Roads is one of the world's largest natural harbors (more accurately a roadstead or "roads"). It incorporates the mouths of the Elizabeth, Nansemond, and James rivers, together with several smaller rivers, and empties into the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
near its mouth leading to the Atlantic Ocean.
The land area includes a collection of cities, counties, and towns on the Virginia Peninsula and in South Hampton Roads. Some of the outlying areas further from the harbor may or may not be included as part of "Hampton Roads", depending upon the organization or usage. For example, as defined for federal economic purposes, the Hampton Roads metropolitan statistical area ( MSA) includes two counties in northeastern North Carolina
North Carolina () is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 28th largest and List of states and territories of the United ...
and two counties in Virginia's Middle Peninsula. The Virginia Beach–Norfolk–Newport News, VA–NC, MSA has a population of 1,799,674, making it the 37th-largest metropolitan area in the United States. The Combined Statistical Area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan statistical area, metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and ...
includes four additional counties in North Carolina, pushing the regional population to nearly 1.9 million residents, the 32nd-largest CSA in the country.
The area is home to hundreds of historical sites and attractions. The harbor was the key to Hampton Roads' growth, both on land and in water-related activities and events. While the harbor and its tributaries were (and still are) important transportation conduits, at the same time they presented obstacles to land-based commerce and travel.
Creating and maintaining adequate infrastructure has long been a major challenge. The Hampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel
The Hampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel (HRBT) is a -long Hampton Roads crossing for Interstate 64 and U.S. Route 60. It is a four-lane facility comprising bridges, trestles, man-made islands, and tunnels under the main shipping channels for Hampton ...
(HRBT) and the Monitor–Merrimac Memorial Bridge–Tunnel
The Monitor–Merrimac Memorial Bridge–Tunnel (MMMBT) is the 4.6 mile-long (7.4 km) Hampton Roads crossing for Interstate 664 in the southeastern portion of Virginia in the United States. It is a four-lane bridge–tunnel composed of bri ...
(MMMBT) are major harbor crossings of the Hampton Roads Beltway interstate, which links the large population centers of Hampton Roads. In 2009, the Hampton Roads Transportation Authority
The Hampton Roads Transportation Accountability Commission (HRTAC) is a political subdivision of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States that has the responsibility for funding several major traffic projects in the Hampton Roads area. ...
(HRTA) was abolished by the Virginia General Assembly less than two years after its creation. In 2014, the Hampton Roads Transportation Accountability Commission was established to oversee the Hampton Roads Transportation Fund.
Etymology
The term "Hampton Roads" is a centuries-old designation that originated when the region was a strugglingEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
outpost nearly four hundred years ago.
The word "Hampton" honors one of the founders of the Virginia Company of London and a great supporter of the colonization of Virginia, Henry Wriothesley, 3rd Earl of Southampton
Henry Wriothesley, 3rd Earl of Southampton, (pronunciation uncertain: "Rezley", "Rizely" (archaic), (present-day) and have been suggested; 6 October 1573 – 10 November 1624) was the only son of Henry Wriothesley, 2nd Earl of So ...
. The early administrative center of the new colony was known as Elizabeth Cittie Elizabeth City (or Elizabeth Cittie as it was then called) was one of four incorporations established in the Virginia Colony in 1619 by the proprietor, the Virginia Company of London, acting in accordance with instructions issued by Sir George Yeard ...
, named for Princess Elizabeth, the daughter of King James I, and formally designated by the Virginia Company in 1619. The town at the center of Elizabeth Cittie became known as "Hampton", and a nearby waterway was designated Hampton Creek (also known as Hampton River).
Other references to the Earl include the area to the north across the bay (in what is now the Eastern Shore) which became known as Northampton
Northampton () is a market town and civil parish in the East Midlands of England, on the River Nene, north-west of London and south-east of Birmingham. The county town of Northamptonshire, Northampton is one of the largest towns in England ...
, and an area south of the James River which became Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Po ...
. As with Hampton, both of these names remain in use today.
The term "Roads" (short for roadstead) indicates the safety of a port; as applied to a body of water, it is "a partly sheltered area of water near a shore in which vessels may ride at anchor". Examples of other roadsteads are Castle Roads
Castle Roads is the primary channel by which vessels enter Castle Harbour, Bermuda, from the Atlantic Ocean. Although little used, today, except by pleasure boats, Castle Harbour was once an important anchorage, and an access route used by ships ...
, in another of the Virginia Company's settlements, Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
, and Lahaina Roads
Lahaina Roads, also called the Lahaina Roadstead, is an anchorage in the ʻAuʻau Channel lying off the town of Lahaina on the island of Maui in the Hawaiian archipelago and U.S. state of Hawaii. It lies in the lee of the West Maui Mountains ...
, in Hawaii.
In 1755, the Virginia General Assembly
The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, the first elected legislative assembly in the New World, and was established on July 30, 16 ...
recorded the name "Hampton Roads" as the channel linking the James, Elizabeth, and Nansemond rivers with the Chesapeake Bay.
Hampton Roads is among the world's largest natural harbors. It is the northernmost major East Coast port of the United States which is ice-free year round. (This status is claimed with the notable exception of the extraordinarily cold winter of 1917, which was the entire U.S.'s coldest year on record.)
Over time, the entire region has come to be known as "Hampton Roads", a label more specific than its other moniker, "Tidewater Virginia", which includes the whole coastal region of the state. The U.S. Postal Service changed the area's postmark from "Tidewater Virginia" to "Hampton Roads, Virginia" beginning in 1983.
In January 2019, ABC News affiliate WVEC reported that the area was considering a rebranding under the Greater Norfolk Area banner according to a post from an Instagram page Oceanfront9.
Definitions

Counties and independent cities
The U.S. Census Bureau defines the "Virginia Beach–Norfolk–Newport News, VA–NC, MSA" as 19 county-level jurisdictions—six counties and ten independent cities in Virginia, and three counties in North Carolina. While the borders of what locals call "Hampton Roads" may not perfectly align with the definition of the MSA, Hampton Roads is most often the name used for the metropolitan area. "Virginia Beach–Norfolk–Newport News, VA–NC, MSA" is a U.S.Metropolitan Statistical Area
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally incorporated as a city or tow ...
(MSA). According to the 2010 Census, its population is 1,676,822 and the 2014 estimated population is 1,716,624.
''Since a state constitutional change in 1871, all cities in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
are independent cities
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity (such as a province).
Historical precursors
In the Holy Roman Empire, and to a degree in its successor state ...
and they are not legally located in a county. The OMB considers these independent cities to be county-equivalents for the purpose of defining MSAs in Virginia. Each MSA is listed by its counties, then cities, in alphabetical order and not by size.''
In Virginia
The MSA consists of these locations in Virginia: Counties * Gloucester County * Isle of Wight County * James City County *Mathews County
Mathews County is a county located in the U.S. state of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 8,533. Its county seat is Mathews.
Located on the Middle Peninsula, Mathews County is included in the Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newpor ...
* Southampton County
Southampton County is a county located on the southern border of the Commonwealth of Virginia. North Carolina is to the south. As of the 2020 census, the population was 17,996. Its county seat is Courtland.
History
In the early 17th centu ...
* York County
Cities
* City of Chesapeake
* City of Franklin
* City of Hampton
* City of Newport News
Newport News () is an independent city in the U.S. state of Virginia. At the 2020 census, the population was 186,247. Located in the Hampton Roads region, it is the 5th most populous city in Virginia and 140th most populous city in the Uni ...
* City of Norfolk
* City of Poquoson
* City of Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most ...
* City of Suffolk
* City of Virginia Beach
* City of Williamsburg
In North Carolina
The MSA also includes the following locations in North Carolina: * Camden County * Currituck County * Gates CountyEvolution of Hampton Roads
The Hampton Roads metropolitan area was first defined in 1950 as the "Norfolk–Portsmouth Metropolitan Statistical Area". It comprised the independent cities of Norfolk, Portsmouth andSouth Norfolk
South Norfolk is a Non-metropolitan district, local government district in Norfolk, England. Its council is based in Long Stratton. The population of the Local Authority District was 124,012 as taken at the United Kingdom census, 2011, 2011 ...
and the counties of Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
and Princess Anne
Anne, Princess Royal (Anne Elizabeth Alice Louise; born 15 August 1950), is a member of the British royal family. She is the second child and only daughter of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, and the only sister of ...
. In 1952, Virginia Beach separated from Princess Anne County.
In 1963, Virginia Beach and Princess Anne County merged, retaining the name Virginia Beach. The city was added to the MSA that year, while South Norfolk lost its metropolitan status. Also in 1963, Norfolk County and the City of South Norfolk merged to create the city of Chesapeake.
In 1970, Chesapeake was added to the MSA, while Virginia Beach became a primary city.
In 1973, Currituck County, North Carolina was added to the MSA.
In 1983, the "Newport News–Hampton Metropolitan Statistical Area", comprising the cities of Newport News, Hampton, Poquoson and Williamsburg, and the counties of Gloucester, James City and York, was combined with the Norfolk–Virginia Beach–Portsmouth MSA and renamed the "Norfolk–Virginia Beach–Newport News MSA".
In 1993, Isle of Wight, Mathews and Surry counties were added. Although Virginia Beach had passed Norfolk as the state's largest city by 1990, it was not made the first primary city of the MSA until 2010.
As a result of the 2010 Census, Gates County, North Carolina was added to the MSA, while Surry County, Virginia was removed.
Combined Statistical Area
The Virginia Beach–Norfolk, VA–NC,Combined Statistical Area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan statistical area, metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and ...
additionally includes the Elizabeth City, NC, Micropolitan Statistical Area, comprising:
* Pasquotank County
* Perquimans County
Perquimans County ()
, from the North Carolina Collection's website at the
, from the North Carolina Collection's website at the
Kill Devil Hills, North Carolina, Micropolitan Statistical Area, comprising:
* Dare County
As of the 2010 census, the total population of this
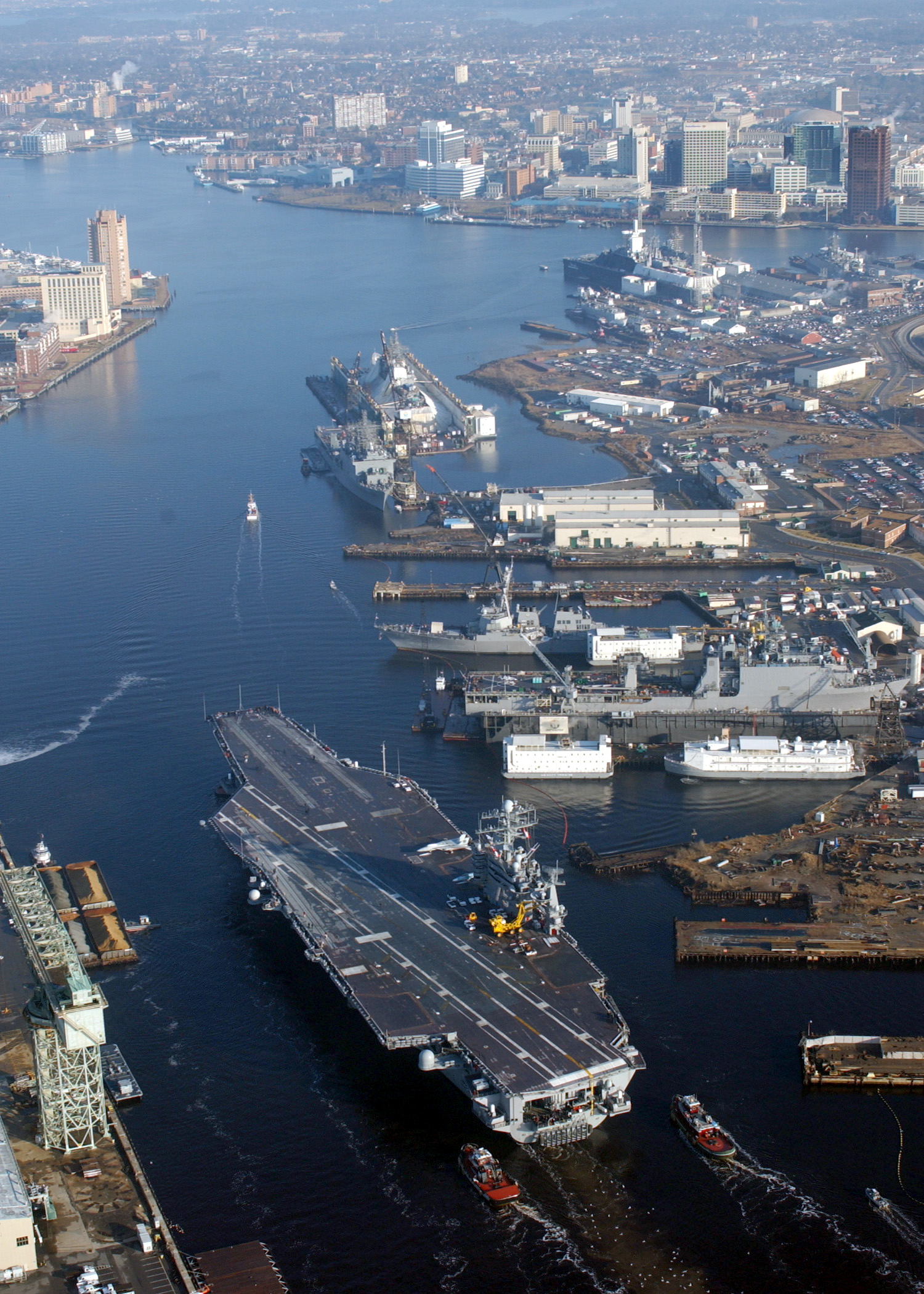 The water area known as Hampton Roads is a wide channel through which the waters of the James River, Nansemond River, and Elizabeth River pass (between Old Point Comfort to the north and
The water area known as Hampton Roads is a wide channel through which the waters of the James River, Nansemond River, and Elizabeth River pass (between Old Point Comfort to the north and  The Hampton Roads area consists of nine independent cities (which are not part of any county).
The Hampton Roads area consists of nine independent cities (which are not part of any county).
Coast Guard 5th District
in Portsmouth :
Coast Guard Base Portsmouth
in Portsmouth :* Coast Guard Training Center Yorktown, in York County :* Fleet Training Center Dam Neck, in Virginia Beach :* Fort Eustis, in Newport News :* Fort Monroe, in Hampton (closed in September 2011) :* Joint Expeditionary Base East, in Virginia Beach :* Lafayette River Complex (LRC), in Norfolk :* Langley Air Force Base, in Hampton :* Naval Air Station Oceana, in Virginia Beach :* Naval Amphibious Base Little Creek, in Virginia Beach :* Naval Auxiliary Landing Field Fentress, in Chesapeake :* Naval Medical Center Portsmouth, in Portsmouth :* Naval Station Norfolk, in Norfolk :*
 Hampton Roads has become known as the "world's greatest natural harbor." The port is located only from open ocean on one of the world's deepest, natural ice-free harbors. Since 1989, Hampton Roads has been the mid-Atlantic leader in U.S. waterborne foreign commerce and is ranked second nationally behind the Port of South Louisiana based on export tonnage. When import and export tonnage are combined, the Port of Hampton Roads ranks as the third largest port in the country (following the ports of New Orleans/South Louisiana and Houston). In 1996, Hampton Roads was ranked ninth among major U.S. ports in vessel port calls with approximately 2,700. In addition, this port is the U.S. leader in coal exports. The coal loading facilities in the Port of Hampton Roads are able to load in excess of 65 million tons annually, giving the port the largest, most efficient and modern coal loading facilities in the world.
It is little surprise therefore that the Hampton Roads region's economic base is largely port-related, including shipbuilding, ship repair, naval installations, cargo transfer and storage, and manufacturing related to the processing of imports and exports. Associated with the ports' military role are almost 50,000 federal civilian employees.
The harbor of Hampton Roads is an important highway of commerce, especially for the cities of
Hampton Roads has become known as the "world's greatest natural harbor." The port is located only from open ocean on one of the world's deepest, natural ice-free harbors. Since 1989, Hampton Roads has been the mid-Atlantic leader in U.S. waterborne foreign commerce and is ranked second nationally behind the Port of South Louisiana based on export tonnage. When import and export tonnage are combined, the Port of Hampton Roads ranks as the third largest port in the country (following the ports of New Orleans/South Louisiana and Houston). In 1996, Hampton Roads was ranked ninth among major U.S. ports in vessel port calls with approximately 2,700. In addition, this port is the U.S. leader in coal exports. The coal loading facilities in the Port of Hampton Roads are able to load in excess of 65 million tons annually, giving the port the largest, most efficient and modern coal loading facilities in the world.
It is little surprise therefore that the Hampton Roads region's economic base is largely port-related, including shipbuilding, ship repair, naval installations, cargo transfer and storage, and manufacturing related to the processing of imports and exports. Associated with the ports' military role are almost 50,000 federal civilian employees.
The harbor of Hampton Roads is an important highway of commerce, especially for the cities of  Massive coal piers and loading facilities were established in the late 19th and early 20th century by the
Massive coal piers and loading facilities were established in the late 19th and early 20th century by the

Combined Statistical Area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan statistical area, metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and ...
was 1,779,243, with a 2013 estimate of 1,810,266, a growth of 1.74%. It is currently the 32nd largest in the country and the largest based in Virginia. Among all metropolitan areas in Virginia, only the Northern Virginia portion of the Washington–Arlington–Alexandria, DC–VA–MD–WV, MSA is larger.
Geography
The metropolitan area and water area is in the Tidewater region, a low-lying plains region composed of southeastern portions ofVirginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
and northeastern portions of North Carolina
North Carolina () is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 28th largest and List of states and territories of the United ...
.
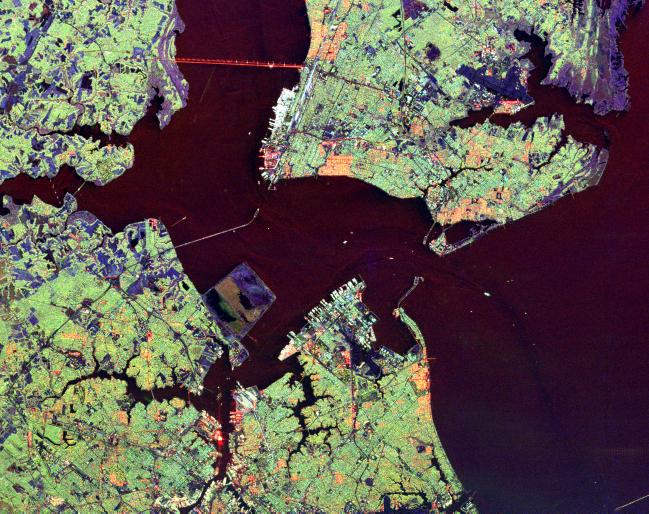
 The water area known as Hampton Roads is a wide channel through which the waters of the James River, Nansemond River, and Elizabeth River pass (between Old Point Comfort to the north and
The water area known as Hampton Roads is a wide channel through which the waters of the James River, Nansemond River, and Elizabeth River pass (between Old Point Comfort to the north and Sewell's Point
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to t ...
to the south) into the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
and the Atlantic Ocean.
Norfolk and Hampton Roads are among the worst-hit parts of the United States by the effects of global warming. As of 2016, the region is a few decades ahead in feeling the effects of sea-level rise compared to many American coastal areas.
The geology and topography of the Hampton Roads region is influenced by the Chesapeake Bay impact crater, one of three factors contributing to the sinking of Hampton Roads at a rate between per century.
The region has extensive natural areas, including of Atlantic Ocean and Chesapeake Bay beaches, the Great Dismal Swamp, picturesque rivers, state parks, wildlife refuges, and botanical gardens. Inland from the bay, the region includes Lake Drummond, one of only two natural lakes in Virginia, and miles of waterfront property along the various rivers and waterways. The region's native flora is consistent with that of the Southeast Coastal Plain and the lower Southeast Maritime Forest.
The land area that constitutes Hampton Roads varies depending upon perspective and purpose. Most of Hampton Roads' land is geographically divided into 2 smaller regions: the eastern portion of the Virginia Peninsula (the Peninsula) and South Hampton Roads (locally known as "the Southside"), which are separated by the harbor. When speaking of communities of Hampton Roads, virtually all sources include the seven major cities, two smaller ones, and three counties within those two subregions.
In addition, the Middle Peninsula counties of Gloucester and Mathews, while not part of the geographical Hampton Roads area, are included in the metropolitan region's population, as is a small portion of northeastern North Carolina ( Currituck County). Due to a peculiarity in the drawing of the Virginia-North Carolina border, Knott's Island in that county is connected to Virginia by land, but is only accessible to other parts of North Carolina by water via a ferry system.
Each of the following current cities, counties and towns is included by at least one of the three organizations that define Hampton Roads:
 The Hampton Roads area consists of nine independent cities (which are not part of any county).
The Hampton Roads area consists of nine independent cities (which are not part of any county). Chesapeake Chesapeake often refers to:
*Chesapeake people, a Native American tribe also known as the Chesepian
* The Chesapeake, a.k.a. Chesapeake Bay
*Delmarva Peninsula, also known as the Chesapeake Peninsula
Chesapeake may also refer to:
Populated plac ...
, Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
, Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most d ...
, Suffolk
Suffolk () is a ceremonial county of England in East Anglia. It borders Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south; the North Sea lies to the east. The county town is Ipswich; other important towns include ...
, and Virginia Beach
Virginia Beach is an independent city located on the southeastern coast of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. The population was 459,470 at the 2020 census. Although mostly suburban in character, it is the most populous ci ...
cover the Southside of Hampton Roads while Hampton, Newport News, Poquoson, and Williamsburg are on the Peninsula. Franklin borders Suffolk but the Census Bureau does not consider it part of the metro area.
The metro area has one county in North Carolina, Currituck. The remaining counties, in Virginia, include Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Is ...
and Surry on the Southside, James City and York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
on the Virginia Peninsula, and Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east o ...
and Mathews on the Middle Peninsula. While Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Po ...
is adjacent to Surry, Isle of Wight, and the City of Suffolk, the Census Bureau does not consider it part of the metro area.
Five incorporated towns are in the metro area, including Claremont in Surry County, Dendron in Surry County, Smithfield in Isle of Wight County, Surry, Surry County's seat, and Windsor in Isle of Wight County. (Two other incorporated towns, Boykins and Courtland, are in Southampton County, and therefore, like the county within which they are located, are not part of the federally defined metropolitan area).
Other unincorporated towns and communities in the metropolitan area that are not within its cities include Gloucester Courthouse and Gloucester Point
Gloucester Point is a census-designated place (CDP) in Gloucester County, Virginia, United States. The population was 9,402 at the 2010 census. It is home to the College of William & Mary's Virginia Institute of Marine Science, a graduate school ...
in Gloucester County, Isle of Wight Courthouse, Rushmere, Rescue
Rescue comprises responsive operations that usually involve the saving of life, or the urgent treatment of injuries after an accident or a dangerous situation.
Tools used might include search and rescue dogs, mounted search and rescue ...
, Carrollton, Benns Church, and Walters in Isle of Wight County, Yorktown, Grafton, Seaford, and Tabb in York County, Jamestown, Ford's Colony, Grove, Lightfoot, Toano, and Norge
Norge is Norwegian (bokmål), Danish and Swedish for Norway.
It may also refer to:
People
* Kaare Norge (born 1963), Danish guitarist
* Norge Luis Vera (born 1971), Cuban baseball player
Places
* 11871 Norge, asteroid
Toponyms:
*Norge, Okla ...
in James City County, Moyock, Knotts Island
Knotts Island is a marshy island and a small unincorporated community. The island is shared by Currituck County, North Carolina and Virginia Beach, Virginia, United States, bounded by the Currituck Sound, North Landing River, Back Bay, and Knotts ...
, and Currituck in Currituck County, North Carolina.
The Hampton Roads MSA, with a population of about 1.7 million, is the seventh-largest metropolitan area in the Southeastern United States
The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical List of regions in the United States, region of the United States. It is located broadly on the eastern portion of the south ...
, after the Washington metropolitan area; Miami–Fort Lauderdale–Pompano Beach, FL, MSA; Atlanta–Sandy Springs–Marietta, GA, MSA, Tampa–St. Petersburg–Clearwater, FL, MSA; Orlando–Kissimmee, FL, MSA; and Charlotte–Gastonia-Rock Hill, NC–SC, MSA.
History

17th–19th centuries
The first colonists arrived in 1607 when English Captain Christopher Newport landed atCape Henry
Cape Henry is a cape on the Atlantic shore of Virginia located in the northeast corner of Virginia Beach. It is the southern boundary of the entrance to the long estuary of the Chesapeake Bay.
Across the mouth of the bay to the north is Cape Ch ...
, today's City of Virginia Beach, an event now called the "First Landing." However, his party moved on, in search of a more defensible area upriver, mindful of competitors such as the Spanish, who had built a failed settlement on the Virginia Peninsula known as the Ajacán Mission.
After exploring the James River, they established the first successful English colony in the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
on Jamestown Island on May 14, 1607. Association for the Preservation of Virginia Antiquities: ''Jamestown History'' But the low, marshy site proved unhealthy and most of the colonists died, before a new Governor, Lord De La Warr
Earl De La Warr ( ) is a title in the Peerage of Great Britain. It was created in 1761 for John West, 7th Baron De La Warr.
The Earl holds the subsidiary titles of Viscount Cantelupe (1761) in the Peerage of Great Britain, Baron De La Warr ...
(Delaware) arrived with John Rolfe, who would establish the Virginia tobacco industry.
The harbor and rivers of Hampton Roads were immediately recognized as prime locations for commerce, shipbuilding and military installations, with the fortifications at Old Point Comfort established as early as 1610, and Gosport Navy Yard (later Norfolk Naval Shipyard) in 1767. The decisive battle of the Revolution was won at Yorktown in 1781, and the first naval action of the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
took place in Hampton Roads, when a Royal Naval vessel was seized by the American privateer ''Dash''. Later the entrance from Chesapeake Bay was equipped with new fortifications ( Fort Monroe and Fort Wool), much of the building work being supervised by a young military engineer Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nor ...
.
During the American Civil War (1861–1865), the historic Battle of Hampton Roads
The Battle of Hampton Roads, also referred to as the Battle of the ''Monitor'' and ''Virginia'' (rebuilt and renamed from the USS ''Merrimack'') or the Battle of Ironclads, was a naval battle during the American Civil War.
It was fought over t ...
between the first American ironclad warship
An ironclad is a steam engine, steam-propelled warship protected by Wrought iron, iron or steel iron armor, armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships ...
s, the and the CSS ''Virginia'', took place off Sewell's Point
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to t ...
in 1862. The battle was inconclusive, but Union forces later took control of Hampton Roads, Norfolk, and the lower James River, though they were thwarted from venturing further upstream by a strong Confederate battery at Drewry's Bluff. Also in 1862, Fort Monroe was the launching place for Union General George McClellan's massive advance up the Virginia Peninsula, which almost reached the Confederate capital Richmond
Richmond most often refers to:
* Richmond, Virginia, the capital of Virginia, United States
* Richmond, London, a part of London
* Richmond, North Yorkshire, a town in England
* Richmond, British Columbia, a city in Canada
* Richmond, Californi ...
, before the Seven Days Battles forced him back. In 1865, as the Confederacy was near collapse, President Abraham Lincoln met with three senior Confederates at Hampton Roads in an unsuccessful bid for a negotiated peace.
Some former slaves had been camped near Fort Monroe, where they were declared to be Contraband of war, instead of being returned to their former owners. Booker T. Washington
Booker Taliaferro Washington (April 5, 1856November 14, 1915) was an American educator, author, orator, and adviser to several presidents of the United States. Between 1890 and 1915, Washington was the dominant leader in the African-American c ...
was among the freedmen who attended the local school, which evolved into the present-day Hampton University
Hampton University is a private, historically black, research university in Hampton, Virginia. Founded in 1868 as Hampton Agricultural and Industrial School, it was established by Black and White leaders of the American Missionary Association a ...
.
20th century
TheJamestown Exposition
The Jamestown Exposition was one of the many world's fairs and expositions that were popular in the United States in the early part of the 20th century. Commemorating the 300th anniversary of the founding of Jamestown in the Virginia Colony, it ...
for the 300th anniversary of the 1607 founding of Jamestown was held at Sewell's Point
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to t ...
in a rural section of Norfolk County in 1907.
President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
arrived by water in the harbor of Hampton Roads, as did other notable persons such as Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has pr ...
and Henry Huttleston Rogers, who both arrived aboard the latter's steam yacht '' Kanawha''. A major naval display was featured, and the U.S. Great White Fleet
The Great White Fleet was the popular nickname for the group of United States Navy battleships which completed a journey around the globe from December 16, 1907 to February 22, 1909 by order of President Theodore Roosevelt. Its mission was ...
made an appearance. The leaders of the U.S. Navy apparently did not fail to note the ideal harbor conditions, as was later proved.
Beginning in 1917, as the United States became involved in World War I under President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
, formerly rural Sewell's Point
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to t ...
became the site of what grew to become the largest Naval Base in the world which was established by the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
and is now known as the Naval Station Norfolk.
Twice in the 20th century, inhabitants mostly African American were displaced when land along the northern side of the Peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on a ...
primarily in York County west of Yorktown was taken in large tracts for military use during World War I and World War II, creating the present-day U.S. Naval Weapons Station Yorktown, which includes Cheatham Annex, and a former Seabee base which became Camp Peary.
Communities including "the Reservation", Halstead's Point, Penniman, Bigler's Mill, and Magruder were all lost
Lost may refer to getting lost, or to:
Geography
* Lost, Aberdeenshire, a hamlet in Scotland
*Lake Okeechobee Scenic Trail, or LOST, a hiking and cycling trail in Florida, US
History
*Abbreviation of lost work, any work which is known to have bee ...
and absorbed into the large military bases.
Although some left the area entirely, many of the displaced families chose to relocate nearby to Grove, an unincorporated town in southeastern James City County where many generations of some of those families now reside. From a population estimated at only 37 in 1895, Grove had grown to an estimated 1,100 families by the end of the 20th century. (To its north, Grove actually borders the Naval Weapons Station property and on its extreme east, a portion of the U.S. Army's land at Fort Eustis extends across Skiffe's Creek, although there is no direct access to either base).
Colonial Williamsburg
It was the dream of an Episcopal priest to save his 18th-century church building by turning Williamsburg into the world's largest living museum. Williamsburg replaced Jamestown at the very end of the 17th century after a disastrous fire. It was the capital of the colony and the new State of Virginia from 1699 to 1780. The capital was moved to Richmond in 1780. Williamsburg became a "sleepy" small town. During the Civil War theBattle of Williamsburg
The Battle of Williamsburg, also known as the Battle of Fort Magruder, took place on May 5, 1862, in York County, James City County, and Williamsburg, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the first p ...
was fought nearby during the Peninsula Campaign in the spring months of 1862. The decaying town was not located along any major waterway and did not have railroad access until 1881. Perhaps due to the secure inland location originally known as Middle Plantation Williamsburg missed growth and economic expansion in the 19th century. The main economic engines were The College of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William I ...
and Eastern State Hospital. The College of William and Mary was chartered by the Crown and is the only pre-Independence college to have kept it. In addition to the city's historic past, quite a few buildings of antiquity from the 18th century were still extant, although time was taking a toll by the early 20th century. The Reverend Dr. W.A.R. Goodwin
William Archer Rutherfoord Goodwin (June 18, 1869 – September 7, 1939) (or W.A.R. Goodwin as he preferred or "the Doctor" as commonly used to his annoyance) was an Episcopal priest, historian, and author. As the rector of Bruton Parish Church, ...
of Bruton Parish Church motive was to only to save historic church building which was secured by 1907. He subsequently served in Rochester, New York
Rochester () is a City (New York), city in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, the county seat, seat of Monroe County, New York, Monroe County, and the fourth-most populous in the state after New York City, Buffalo, New York, Buffalo, ...
for many years. Upon returning to Williamsburg in 1923 he realized that many of the other colonial-era buildings were deteriorating and their existence was at risk.
Goodwin dreamt of a much larger restoration of the colonial town. A cleric of modest means, he first sought support and financing from a number of sources before successfully drawing the interests before receiving major financial support from Standard Oil
Standard Oil Company, Inc., was an American oil production, transportation, refining, and marketing company that operated from 1870 to 1911. At its height, Standard Oil was the largest petroleum company in the world, and its success made its co- ...
heir and philanthropist John D. Rockefeller Jr.
John Davison Rockefeller Jr. (January 29, 1874 – May 11, 1960) was an American financier and philanthropist, and the only son of Standard Oil co-founder John D. Rockefeller.
He was involved in the development of the vast office complex in M ...
and his wife Abby Aldrich Rockefeller
Abigail Greene Aldrich Rockefeller (October 26, 1874 – April 5, 1948) was an American socialite and philanthropist. She was a prominent member of the Rockefeller family through her marriage to financier and philanthropist John D. Rockefeller ...
. The result is the creation of Colonial Williamsburg
Colonial Williamsburg is a living-history museum and private foundation presenting a part of the historic district in the city of Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. The Colonial Williamsburg Foundation has 7300 employees at this location ...
with extensive restoration of buildings such as the Wren Building of the College of William & Mary and the Governor's Palace, and the transformation of downtown Williamsburg area into Historic District of restored buildings. Many 19th century buildings were removed.
By the 1930s, Colonial Williamsburg had become the centerpiece of the Historic Triangle of Colonial Virginia. These were, of course, Jamestown, where the colony started, Williamsburg, and Yorktown, where independence from Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
was won. The three points were joined by the U.S. National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational properti ...
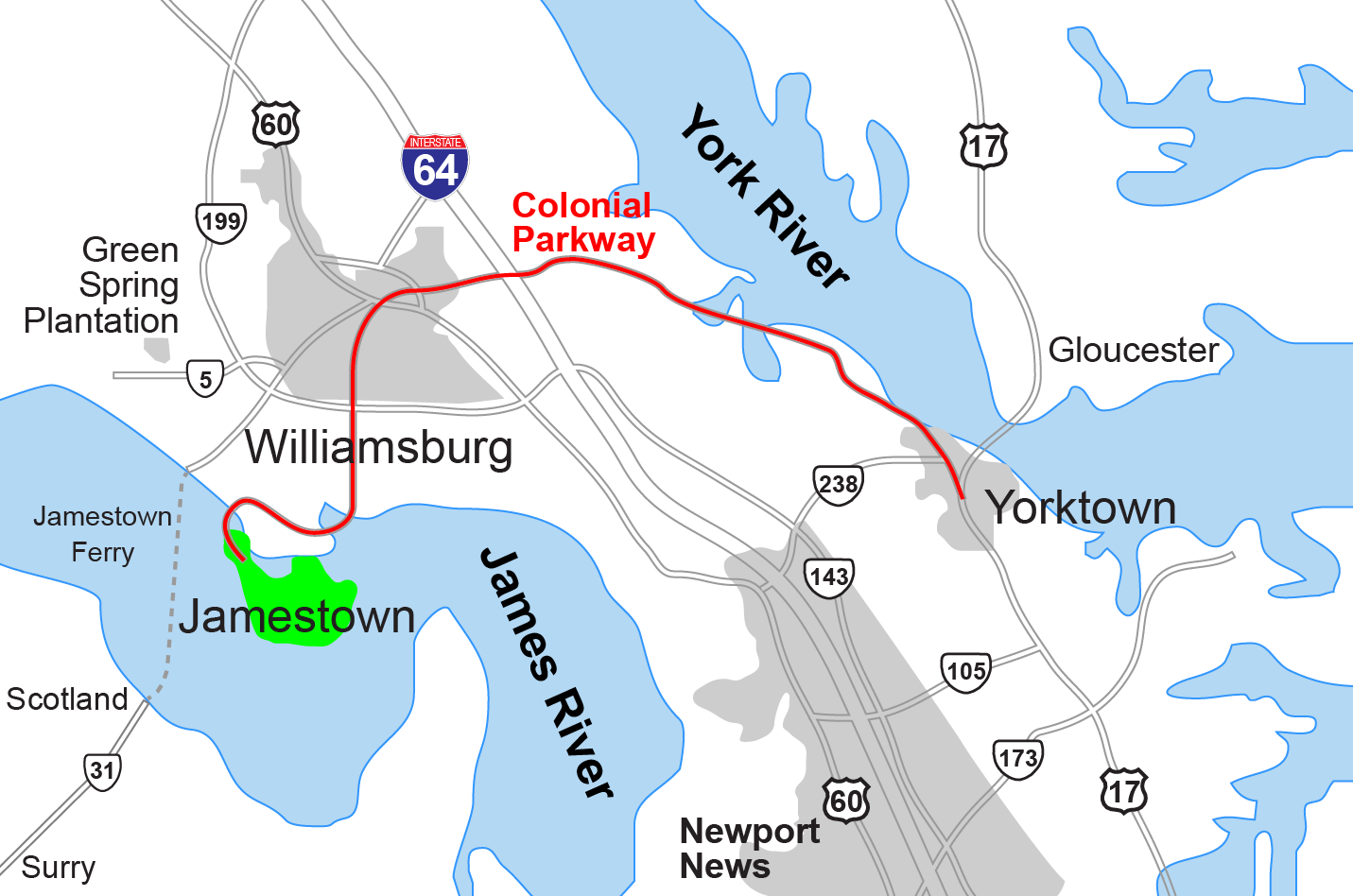
's Colonial Parkway
Colonial Parkway is a scenic parkway linking the three points of Virginia's Historic Triangle, Jamestown, Williamsburg, and Yorktown. It is part of the National Park Service's Colonial National Historical Park. Virginia's official state c ...
, a remarkable accomplishment in course of 27 years. The Historic Triangle area of the Hampton Roads region became one of the largest tourist attractions in Virginia.
In Dr. Goodwin's words: "Williamsburg is Jamestown continued, and Yorktown is Williamsburg vindicated."
Government
The area consists of ten independent cities and six counties. Each independent city has the powers and responsibilities of a county, including maintaining roads, courts, schools, and public safety. Some cities share these responsibilities with an adjoining county. Incorporated towns located within counties in Virginia operate with some level of autonomy, with some larger Towns exercising more autonomy than others. The localities come together to consult on regional issues. Virginia defines regional planning districts by law. District members are usually independent cities and counties. Localities around the state may belong to more than one Planning District, as their constituents may have interests which cross over individual planning district boundaries. The Hampton Roads Planning District Commission (HRPDC) currently includes 16 cities and counties and one incorporated town in Virginia, representing over 1.7 million people. The 17 jurisdictions include: * the Cities of Chesapeake, Franklin, Hampton, Newport News, Norfolk, Poquoson, Portsmouth, Suffolk, Virginia Beach, and Williamsburg, * the Counties of Gloucester, Isle of Wight, James City, Southampton, Surry, and York * the Town of Smithfield There are incorporated towns in three of the counties (Isle of Wight, Southampton and Surry) within the district. The differences between the service area of the HRPDC and the federally defined metropolitan statistical area (MSA) are: * Southampton County and the City of Franklin are not in the MSA. * Mathews County is in the MSA but not the HRPDC. * The MSA includes Currituck County and Gates County, North Carolina, but the HRPDC does not. The Federal government has two major research laboratories in the area. NASA-Langley, on the northeast edge of Hampton near Poquoson, is the home of a variety of aeronautics research, including several one-of-a-kind wind tunnels. The Department of Energy'sThomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility
Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF), commonly called Jefferson Lab or JLab, is a US National Laboratory located in Newport News, Virginia. Its stated mission is "to provide forefront scientific facilities, opportunities an ...
(known as 'Jefferson Lab') conducts cutting edge physics research in Newport News; the lab hosts the Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility (CEBAF) and a kilowatt-class free-electron laser.
U.S. Military
The military has a large presence in the region. Area military facilities (alphabetically) include: :* Camp Allen, in Norfolk :* Camp Peary, in York County :Coast Guard 5th District
in Portsmouth :
Coast Guard Base Portsmouth
in Portsmouth :* Coast Guard Training Center Yorktown, in York County :* Fleet Training Center Dam Neck, in Virginia Beach :* Fort Eustis, in Newport News :* Fort Monroe, in Hampton (closed in September 2011) :* Joint Expeditionary Base East, in Virginia Beach :* Lafayette River Complex (LRC), in Norfolk :* Langley Air Force Base, in Hampton :* Naval Air Station Oceana, in Virginia Beach :* Naval Amphibious Base Little Creek, in Virginia Beach :* Naval Auxiliary Landing Field Fentress, in Chesapeake :* Naval Medical Center Portsmouth, in Portsmouth :* Naval Station Norfolk, in Norfolk :*
Naval Support Activity Hampton Roads
Naval Support Activity Hampton Roads (NSA HR) is a United States Navy Echelon 4 regional support commander that is responsible to Navy Region Mid-Atlantic for the operation and maintenance of the installation of the same name that it is headquarte ...
, in Chesapeake
:* Naval Consolidated Brig, Chesapeake
:* Naval Support Activity Northwest Annex, in Chesapeake
:* Naval Weapons Station Yorktown, in York County
:* Norfolk Naval Shipyard, in Portsmouth (not to be confused with Portsmouth Naval Shipyard, in Kittery, Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
)
:* Saint Julian's Creek Naval Depot Annex, in Chesapeake
Economy
Hampton Roads is home to two ''Fortune'' 500 companies. Representing the retail and shipbuilding industry, these two companies are located inChesapeake Chesapeake often refers to:
*Chesapeake people, a Native American tribe also known as the Chesepian
* The Chesapeake, a.k.a. Chesapeake Bay
*Delmarva Peninsula, also known as the Chesapeake Peninsula
Chesapeake may also refer to:
Populated plac ...
and Newport News.
;2021 ''Fortune'' 500 Corporations
* 111 Dollar Tree
Dollar Tree, Inc. is an American multi-price-point chain of discount variety stores. Headquartered in Chesapeake, Virginia, it is a ''Fortune'' 500 company and operates 15,115 stores throughout the 48 contiguous U.S. states and Canada. Its s ...
* 327 Huntington Ingalls Industries
 Hampton Roads has become known as the "world's greatest natural harbor." The port is located only from open ocean on one of the world's deepest, natural ice-free harbors. Since 1989, Hampton Roads has been the mid-Atlantic leader in U.S. waterborne foreign commerce and is ranked second nationally behind the Port of South Louisiana based on export tonnage. When import and export tonnage are combined, the Port of Hampton Roads ranks as the third largest port in the country (following the ports of New Orleans/South Louisiana and Houston). In 1996, Hampton Roads was ranked ninth among major U.S. ports in vessel port calls with approximately 2,700. In addition, this port is the U.S. leader in coal exports. The coal loading facilities in the Port of Hampton Roads are able to load in excess of 65 million tons annually, giving the port the largest, most efficient and modern coal loading facilities in the world.
It is little surprise therefore that the Hampton Roads region's economic base is largely port-related, including shipbuilding, ship repair, naval installations, cargo transfer and storage, and manufacturing related to the processing of imports and exports. Associated with the ports' military role are almost 50,000 federal civilian employees.
The harbor of Hampton Roads is an important highway of commerce, especially for the cities of
Hampton Roads has become known as the "world's greatest natural harbor." The port is located only from open ocean on one of the world's deepest, natural ice-free harbors. Since 1989, Hampton Roads has been the mid-Atlantic leader in U.S. waterborne foreign commerce and is ranked second nationally behind the Port of South Louisiana based on export tonnage. When import and export tonnage are combined, the Port of Hampton Roads ranks as the third largest port in the country (following the ports of New Orleans/South Louisiana and Houston). In 1996, Hampton Roads was ranked ninth among major U.S. ports in vessel port calls with approximately 2,700. In addition, this port is the U.S. leader in coal exports. The coal loading facilities in the Port of Hampton Roads are able to load in excess of 65 million tons annually, giving the port the largest, most efficient and modern coal loading facilities in the world.
It is little surprise therefore that the Hampton Roads region's economic base is largely port-related, including shipbuilding, ship repair, naval installations, cargo transfer and storage, and manufacturing related to the processing of imports and exports. Associated with the ports' military role are almost 50,000 federal civilian employees.
The harbor of Hampton Roads is an important highway of commerce, especially for the cities of Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
, Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most d ...
, and Newport News.
Huntington Ingalls Industries (formerly Newport News Shipbuilding and Drydock Company), was created in 2008 as a spinoff of Northrop Grumman Newport News and is the world's largest shipyard. It is located a short distance up the James River. In Portsmouth, a few miles up the Elizabeth River, the historic Norfolk Naval Shipyard is located. BAE Systems, formerly known as NORSHIPCO, operates from sites in the City of Norfolk. There are also several smaller shipyards, numerous docks and terminals.
 Massive coal piers and loading facilities were established in the late 19th and early 20th century by the
Massive coal piers and loading facilities were established in the late 19th and early 20th century by the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway
The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P. Huntington, it reached from Virginia's capital city of Richmond t ...
(C&O), Norfolk and Western Railway
The Norfolk and Western Railway , commonly called the N&W, was a US class I railroad, formed by more than 200 railroad mergers between 1838 and 1982. It was headquartered in Roanoke, Virginia, for most of its existence. Its motto was "Precis ...
(N&W), and Virginian Railway
The Virginian Railway was a Class I railroad located in Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. The VGN was created to transport high quality "smokeless" bituminous coal from southern West Virginia to port at Hampton Roads.
Histor ...
(VGN). The latter two were predecessors of the Norfolk Southern Railway
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad in the United States formed in 1982 with the merger of Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. With headquarters in Atlanta, the company operates 19,420 route miles (31 ...
, a Class I railroad which has its headquarters in Norfolk, and continues to export coal from a large facility at Lambert's Point
Lamberts Point is a point of land on the east shore of the Elizabeth River near the downtown area of the independent city of Norfolk in the South Hampton Roads region of eastern Virginia, United States. It includes a large coal exporting facili ...
on the Elizabeth River. CSX Transportation now serves the former C&O facility at Newport News. (The VGN's former coal facility at Sewell's Point
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to t ...
has been gone since the 1960s, and the property is now part of the expansive Norfolk Navy Base
Naval Station Norfolk is a United States Navy base in Norfolk, Virginia, that is the headquarters and home port of the U.S. Navy's Fleet Forces Command. The installation occupies about of waterfront space and of pier and wharf space of the Ham ...
).
Federal impact
Almost 80% of the region's economy is derived from federal sources. This includes the large military presence, but also NASA and facilities of the Departments of Energy, Transportation, Commerce and Veterans Affairs. The region also receives a substantial impact in government student loans and grants, university research grants, and federal aid to cities. The Hampton Roads area has the largest concentration of military bases and facilities of any metropolitan area in the world. Nearly one-fourth of the nation's active-duty military personnel are stationed in Hampton Roads, and 45% of the region's $81B gross regional output is Defense-related. All five military services' operating forces are there, as well as several major command headquarters: Hampton Roads is a chief rendezvous of theUnited States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
, and the area is home to the Allied Command Transformation, which is the only major military command of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
) on U.S. soil. Langley Air Force Base is home to Air Combat Command
Air Combat Command (ACC) is one of nine Major Commands (MAJCOMs) in the United States Air Force, reporting to Headquarters, United States Air Force (HAF) at the Pentagon. It is the primary provider of air combat forces for the Air Force, and i ...
(ACC). The Norfolk Navy Base
Naval Station Norfolk is a United States Navy base in Norfolk, Virginia, that is the headquarters and home port of the U.S. Navy's Fleet Forces Command. The installation occupies about of waterfront space and of pier and wharf space of the Ham ...
is located at Sewell's Point
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to t ...
near the mouth, on the site used for the tercentennial Jamestown Exposition
The Jamestown Exposition was one of the many world's fairs and expositions that were popular in the United States in the early part of the 20th century. Commemorating the 300th anniversary of the founding of Jamestown in the Virginia Colony, it ...
in 1907. For a width of the Federal government during 1902 through 1905 increased its minimum depth at low water from , and the channel has now been dredged to a depth of in some places.

NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
's Langley Research Center
The Langley Research Center (LaRC or NASA Langley), located in Hampton, Virginia, United States of America, is the oldest of NASA's field centers. It directly borders Langley Air Force Base and the Back River on the Chesapeake Bay. LaRC has f ...
, located on the Peninsula adjacent to Langley Air Force Base in Hampton, is home to scientific and aerospace technology research. The Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility
Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF), commonly called Jefferson Lab or JLab, is a US National Laboratory located in Newport News, Virginia. Its stated mission is "to provide forefront scientific facilities, opportunities an ...
(commonly known as Jefferson Lab) is located nearby in Newport News.
Commercial growth
The area's experiences with commercial and retail centers began early in 1918. Afton Square, located in the Cradock naval community of Portsmouth, was the first planned shopping center in the US and has served as template for future developments throughout the nation. Hampton Roads experienced tremendous growth during and after World War II. In the 1950s, a trend in retail was the shopping center, a group of stores along a common sidewalk adjacent to off-street parking, usually in a suburban location. In 1959, one of the largest shopping centers on the east coast of the US was opened at the northeast corner of Military Highway and Virginia Beach Boulevard on property which had formally been used as an airfield. The newJANAF Shopping Center
The JANAF Shopping Yard, commonly known as JANAF, is a suburban shopping center located in Norfolk, Virginia. Opening in 1959,Pembroke Mall. The mall opened in 1966, and became Hampton Road's newest indoor shopping destination. The Virginia Peninsula had its first indoor shopping mall in 1973, with 
 Several older malls such as Pembroke and Military Circle have since their grand openings been renovated, and others have been closed and torn down. Newmarket North Mall is now NetCenter, a business center.
Several older malls such as Pembroke and Military Circle have since their grand openings been renovated, and others have been closed and torn down. Newmarket North Mall is now NetCenter, a business center.
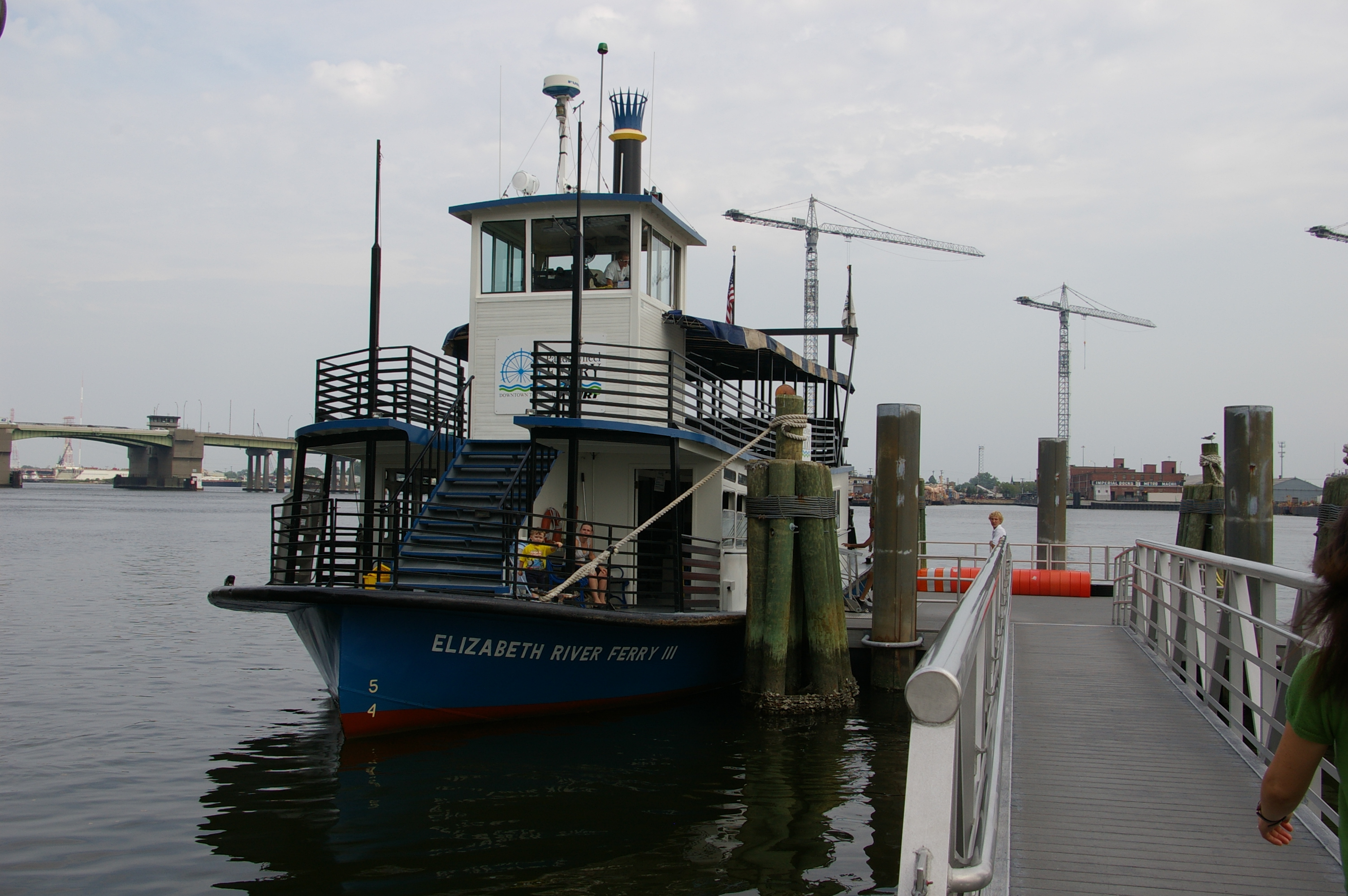 Historically, from the earliest times, the harbor was the key to the Hampton Roads area's growth, both on land and in water-related activities and events. The harbor and its tributary waterways were (and still are) both important transportation conduits and obstacles to other land-based commerce and travel. Yet, the community leaders learned to overcome them.
In modern times, the region has faced increasing transportation challenges as it has become largely urbanized, with additional traffic needs. In the 21st century, the conflicts between traffic on vital waterways and land-based travel continue to present the area's leaders with extraordinary transportation challenges, both for additional capacity, and as the existing infrastructure, much of it originally built with toll revenues, has aged without an adequate source of funding to repair or build replacements. The now-closed
Historically, from the earliest times, the harbor was the key to the Hampton Roads area's growth, both on land and in water-related activities and events. The harbor and its tributary waterways were (and still are) both important transportation conduits and obstacles to other land-based commerce and travel. Yet, the community leaders learned to overcome them.
In modern times, the region has faced increasing transportation challenges as it has become largely urbanized, with additional traffic needs. In the 21st century, the conflicts between traffic on vital waterways and land-based travel continue to present the area's leaders with extraordinary transportation challenges, both for additional capacity, and as the existing infrastructure, much of it originally built with toll revenues, has aged without an adequate source of funding to repair or build replacements. The now-closed  Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport, located in Newport News, and Norfolk International Airport, in Norfolk, both cater to passengers from Hampton Roads. The primary airport for the Virginia Peninsula is the Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport. The Airport experienced a 4th year of record, double-digit growth through 2011, making it one of the fastest growing airports in the country. In 2012 however, the airport lost its biggest carrier and has seen massive declines in passenger service, culminating in layoffs of police officers and many other staff.
Norfolk International Airport , serves the region. The airport is located near Chesapeake Bay, along the city limits of
Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport, located in Newport News, and Norfolk International Airport, in Norfolk, both cater to passengers from Hampton Roads. The primary airport for the Virginia Peninsula is the Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport. The Airport experienced a 4th year of record, double-digit growth through 2011, making it one of the fastest growing airports in the country. In 2012 however, the airport lost its biggest carrier and has seen massive declines in passenger service, culminating in layoffs of police officers and many other staff.
Norfolk International Airport , serves the region. The airport is located near Chesapeake Bay, along the city limits of  The Hampton Roads area has an extensive network of
The Hampton Roads area has an extensive network of
 In 1998, a flag representing the Hampton Roads region was adopted. The design of the flag was created by a contest. The winner, sixteen-year-old Andrew J. Wall of Frank W. Cox High School in Virginia Beach, raised the new regional flag for the first time on the mast of a ship moored in the harbor.
As conceived by student Andrew Wall and embellished by the selection committee, his flag is highly symbolic:
:The ring of sixteen white stars stands for the cities and counties that comprise the region of Hampton Roads. The blue upper panel refers to the sea and sky, recalling the first European settlers at Jamestown in 1607, the first battle between ironclad ships in 1862, the importance of shipbuilding and ship repair in the area, as well as maritime commerce, fishing, recreational boating, and the major military and government installations around the area's shores. Agriculture, the environment, tourism, industry, and a healthy quality of life are suggested by the lower panel of green. The wavy white central band with three crests suggests past, present, and future. The wave also recalls the surf and sand dunes of the area as seen from the sea. Water is the central theme. It touches all the components and binds them together.
In 1998, a flag representing the Hampton Roads region was adopted. The design of the flag was created by a contest. The winner, sixteen-year-old Andrew J. Wall of Frank W. Cox High School in Virginia Beach, raised the new regional flag for the first time on the mast of a ship moored in the harbor.
As conceived by student Andrew Wall and embellished by the selection committee, his flag is highly symbolic:
:The ring of sixteen white stars stands for the cities and counties that comprise the region of Hampton Roads. The blue upper panel refers to the sea and sky, recalling the first European settlers at Jamestown in 1607, the first battle between ironclad ships in 1862, the importance of shipbuilding and ship repair in the area, as well as maritime commerce, fishing, recreational boating, and the major military and government installations around the area's shores. Agriculture, the environment, tourism, industry, and a healthy quality of life are suggested by the lower panel of green. The wavy white central band with three crests suggests past, present, and future. The wave also recalls the surf and sand dunes of the area as seen from the sea. Water is the central theme. It touches all the components and binds them together.
 Also in downtown Norfolk and inside Nauticus is the Hampton Roads Naval Museum, an official U.S. Navy museum that focuses on the 220 plus year history of the Navy within the region.
The Children's Museum of Virginia in
Also in downtown Norfolk and inside Nauticus is the Hampton Roads Naval Museum, an official U.S. Navy museum that focuses on the 220 plus year history of the Navy within the region.
The Children's Museum of Virginia in
 Area residents also have options for training for technical professions. The Apprentice School was founded in 1919 and offers four/five-year programs in mechanical and technical fields associated with the shipbuilding industry. Graduates from the Apprentice School go on to work at the Newport News Shipbuilding. Technology-focused ECPI University has campuses in Virginia Beach and Newport News while ITT Technical Institute has a campus in Norfolk.
Area residents also have options for training for technical professions. The Apprentice School was founded in 1919 and offers four/five-year programs in mechanical and technical fields associated with the shipbuilding industry. Graduates from the Apprentice School go on to work at the Newport News Shipbuilding. Technology-focused ECPI University has campuses in Virginia Beach and Newport News while ITT Technical Institute has a campus in Norfolk.
Nielsen Reports 1.1% increase in U.S. Television Households for the 2006–2007 Season
." Nielsen Media Research. September 23, 2006. Retrieved on September 28, 2007. The major network television affiliates are
Hampton Roads Planning District Commission
Hampton Roads Transportation Planning Organization
Hampton Roads Transportation Accountability Commission
Hampton Roads Chamber
Hampton Roads Sports Commission
Hampton Roads Economic Development Alliance
Hampton Roads Military and Federal Facilities Alliance
Hampton Roads Sanitation District
Hampton Roads Housing Consortium
Norfolk City Historical Society
contains essays
– Norfolk Public Library
{{Authority control Bodies of water of Virginia James River (Virginia) Ports and harbors of Virginia Regions of Virginia Roadsteads Northeast megalopolis
Coliseum Mall
The Colosseum ( ; it, Colosseo ) is an oval amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphitheatre ever built, and is still the largest standing amphitheatre in the world ...
. Coliseum Mall drew so much traffic from Interstate 64, that a towering flyover was built at the Mercury Boulevard and Coliseum Drive intersection, to accommodate eastbound mall traffic, from the Mercury Boulevard interchange. Coliseum Mall was demolished to make way for the open air mixed-use development Peninsula Town Center
Peninsula Town Center is an open air mixed-use development located in the Coliseum Central Business improvement district of Hampton, Virginia in the Hampton Roads region. The Town Center is located on the site of the original Coliseum Mall, an ...
. Also in the 1970s, Tower Mall was built in Portsmouth, but was torn down and turned into the Victory Crossing shopping development. In Norfolk, Military Circle Mall
Military Circle Mall, known as The Gallery at Military Circle Mall from 2002 to 2015, is a soon to be demolished enclosed shopping mall in Norfolk, Virginia. The mall opened in 1970. In October 2016 the Virginia Beach City Council rejected plans f ...
on Military Highway was built across Virginia Beach Boulevard from the large JANAF Shopping Center with its own high-rise hotel right in the center. In 1981, Greenbrier Mall
Greenbrier Mall is a nearly regional mall in Chesapeake, Virginia, United States in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. The mall has a hillside terrain, with entries on both upper and lower levels. It serves communities on the east coast in t ...
gave Chesapeake a shopping mall of its own as well, and Virginia Beach got the massive Lynnhaven Mall the same year.
Chesapeake Square Mall was constructed in Chesapeake, Virginia in 1989, near the border of Suffolk, Virginia, and has spawned a number of shopping centers in the surrounding areas. MacArthur Center
MacArthur Center is a shopping mall in Norfolk, Virginia, in the center of the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. Built by the Taubman Company, the mall is owned by Starwood Capital Group since October 2014.
The mall currently features a large Dilla ...
opened in March 1999, which made downtown Norfolk a prime shoppers destination, with the region's first Nordstrom
Nordstrom, Inc. () is an American luxury department store chain headquartered in Seattle, Washington, and founded by John W. Nordstrom and Carl F. Wallin in 1901. The original Wallin & Nordstrom store operated exclusively as a shoe store, and ...
department store anchor. MacArthur Center is compared to other downtown malls, such as Baltimore's Harborplace
Harborplace is a shopping complex on the Inner Harbor in Baltimore, Maryland.
Description
The property is composed of 2 two-story pavilions: the Pratt Street Pavilion and the Light Street Pavilion. Each of these buildings contains many stores an ...
, Indianapolis' Circle Centre Mall, Atlanta's Lenox Square
Lenox Square is a shopping mall in the Buckhead district of Atlanta, Georgia. With 198 tenants and of gross leasable area, it is the third-largest mall in Georgia. The mall is currently owned and managed by Simon Property Group, and is consid ...
Mall and most comparably to The Fashion Centre at Pentagon City near Washington, D.C., in Arlington, Virginia
Arlington County is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. The county is situated in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from the District of Columbia, of which it was once a part. The county ...
.
Currently, Virginia Beach's Lynnhaven Mall is the region's largest shopping center with nearly 180 stores, and is one of the region's biggest tourist draws, with the Virginia Beach Oceanfront, Colonial Williamsburg
Colonial Williamsburg is a living-history museum and private foundation presenting a part of the historic district in the city of Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. The Colonial Williamsburg Foundation has 7300 employees at this location ...
, Busch Gardens Williamsburg
Busch Gardens Williamsburg (formerly known as Busch Gardens Europe and Busch Gardens: The Old Country) is a amusement park located in James City County near Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. Located approximately northwest of Virginia ...
and MacArthur Center.
For a long time, the indoor shopping malls were seen as largely competitive with small shopping centers and traditional downtown type areas. However, in the 1990s and since, the "big-box store
A big-box store (also hyperstore, supercenter, superstore, or megastore) is a physically large retail establishment, usually part of a chain of stores. The term sometimes also refers, by extension, to the company that operates the store. The te ...
s" on the Peninsula and Southside, such as Wal-mart, Home Depot, and Target have been creating a new competitive atmosphere for the shopping malls of Hampton Roads.
 Several older malls such as Pembroke and Military Circle have since their grand openings been renovated, and others have been closed and torn down. Newmarket North Mall is now NetCenter, a business center.
Several older malls such as Pembroke and Military Circle have since their grand openings been renovated, and others have been closed and torn down. Newmarket North Mall is now NetCenter, a business center. Coliseum Mall
The Colosseum ( ; it, Colosseo ) is an oval amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphitheatre ever built, and is still the largest standing amphitheatre in the world ...
, in Hampton, has been redeveloped as Peninsula Town Center
Peninsula Town Center is an open air mixed-use development located in the Coliseum Central Business improvement district of Hampton, Virginia in the Hampton Roads region. The Town Center is located on the site of the original Coliseum Mall, an ...
in a new style, in step with the latest commercial real estate trend: the nationwide establishment of " lifestyle centers". Additional malls which have closed include Mercury Mall in Hampton (converted to Mercury Plaza Shopping Center in the mid-1980s, then completely torn down in 2001), and Tower Mall in Portsmouth (Built in the early 1970s, then torn down in 2001).
America's first region
In late 2006, the Hampton Roads Partnership, a non-profit organization representing 17 localities (ten cities, six counties, and one town), all local universities and major military commands as well as leading businesses in southeastern Virginia, commenced a campaign aimed at branding the land area of Hampton Roads as "America's First Region". The new title is based on events in 1607 when English Captain Christopher Newport's three ships – the '' Susan Constant'', '' Godspeed'', and ''Discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discove ...
'' landed at Cape Henry
Cape Henry is a cape on the Atlantic shore of Virginia located in the northeast corner of Virginia Beach. It is the southern boundary of the entrance to the long estuary of the Chesapeake Bay.
Across the mouth of the bay to the north is Cape Ch ...
along the Atlantic Coast in what is today Virginia Beach. After 18 days of exploring the area, the ships and their crews arrived at Jamestown Island where they established the first English speaking settlement to survive in the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
on May 14, 1607.
Because the region's east–west boundaries (now the City of Virginia Beach and James City County) have not changed since 1607, the Partnership felt justified in labeling Hampton Roads "America's First Region". It unveiled the new brand before 800 people at the annual meeting of the Hampton Roads Chamber of Commerce on December 13, 2006. A video shown that afternoon included endorsements from mayors and county board of supervisors chairs representing Hampton, Norfolk, Virginia Beach, Williamsburg and James City County as well as the Governor of Virginia
The governor of the Commonwealth of Virginia serves as the head of government of Virginia for a four-year term. The incumbent, Glenn Youngkin, was sworn in on January 15, 2022.
Oath of office
On inauguration day, the Governor-elect takes th ...
, Timothy Kaine.
The mission of Hampton Roads Economic Development Alliance (HREDA) is a non-profit organization dedicated to business attraction—marketing the Hampton Roads region as the preferred location for business investment and expansion. HREDA represents the cities of Chesapeake, Hampton, Newport News, Norfolk, Poquoson, Portsmouth, Suffolk, Virginia Beach, Williamsburg and Franklin, as well as the counties of Gloucester, James City, Isle of Wight, York, and Southampton.
Transportation
 Historically, from the earliest times, the harbor was the key to the Hampton Roads area's growth, both on land and in water-related activities and events. The harbor and its tributary waterways were (and still are) both important transportation conduits and obstacles to other land-based commerce and travel. Yet, the community leaders learned to overcome them.
In modern times, the region has faced increasing transportation challenges as it has become largely urbanized, with additional traffic needs. In the 21st century, the conflicts between traffic on vital waterways and land-based travel continue to present the area's leaders with extraordinary transportation challenges, both for additional capacity, and as the existing infrastructure, much of it originally built with toll revenues, has aged without an adequate source of funding to repair or build replacements. The now-closed
Historically, from the earliest times, the harbor was the key to the Hampton Roads area's growth, both on land and in water-related activities and events. The harbor and its tributary waterways were (and still are) both important transportation conduits and obstacles to other land-based commerce and travel. Yet, the community leaders learned to overcome them.
In modern times, the region has faced increasing transportation challenges as it has become largely urbanized, with additional traffic needs. In the 21st century, the conflicts between traffic on vital waterways and land-based travel continue to present the area's leaders with extraordinary transportation challenges, both for additional capacity, and as the existing infrastructure, much of it originally built with toll revenues, has aged without an adequate source of funding to repair or build replacements. The now-closed Kings Highway Bridge
Kings Highway Bridge was located on the Nansemond River in the independent city of Suffolk, Virginia, United States. Built in 1928, it carried traffic on the Kings Highway, also known as State Route 125, for over 75 years.
The drawbridge w ...
in Suffolk
Suffolk () is a ceremonial county of England in East Anglia. It borders Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south; the North Sea lies to the east. The county town is Ipswich; other important towns include ...
and the Jordan Bridge
The Jordan Bridge, officially named the South Norfolk Jordan Bridge, is a tolled highway fixed bridge which carries State Route 337 over the Southern Branch Elizabeth River between the City of Portsmouth into the City of Chesapeake in South ...
closed by neighboring Chesapeake Chesapeake often refers to:
*Chesapeake people, a Native American tribe also known as the Chesepian
* The Chesapeake, a.k.a. Chesapeake Bay
*Delmarva Peninsula, also known as the Chesapeake Peninsula
Chesapeake may also refer to:
Populated plac ...
in 2008 were each built in the 1920s. These were considered locally prime examples of this situation.
In 2007, the new Hampton Roads Transportation Authority
The Hampton Roads Transportation Accountability Commission (HRTAC) is a political subdivision of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States that has the responsibility for funding several major traffic projects in the Hampton Roads area. ...
(HRTA) was formed under a controversial state law to levy various additional taxes to generate funding for major regional transportation projects, including a long-sought and costly additional crossing of the harbor of Hampton Roads (The Hampton Roads Bridge Tunnel, Monitor-Merrimac Bridge Tunnel, and the James River Bridge are the existing crossings). As of March 2008, although its projects were considered to be needed, the agency's future was in some question while its controversial sources of funding were being reconsidered in light of a Virginia Supreme Court decision.
 Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport, located in Newport News, and Norfolk International Airport, in Norfolk, both cater to passengers from Hampton Roads. The primary airport for the Virginia Peninsula is the Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport. The Airport experienced a 4th year of record, double-digit growth through 2011, making it one of the fastest growing airports in the country. In 2012 however, the airport lost its biggest carrier and has seen massive declines in passenger service, culminating in layoffs of police officers and many other staff.
Norfolk International Airport , serves the region. The airport is located near Chesapeake Bay, along the city limits of
Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport, located in Newport News, and Norfolk International Airport, in Norfolk, both cater to passengers from Hampton Roads. The primary airport for the Virginia Peninsula is the Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport. The Airport experienced a 4th year of record, double-digit growth through 2011, making it one of the fastest growing airports in the country. In 2012 however, the airport lost its biggest carrier and has seen massive declines in passenger service, culminating in layoffs of police officers and many other staff.
Norfolk International Airport , serves the region. The airport is located near Chesapeake Bay, along the city limits of Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
and Virginia Beach
Virginia Beach is an independent city located on the southeastern coast of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. The population was 459,470 at the 2020 census. Although mostly suburban in character, it is the most populous ci ...
. Seven airlines provide nonstop services to twenty five destinations. ORF had 3,703,664 passengers take off or land at its facility and 68,778,934 pounds of cargo were processed through its facilities.
The Hampton Roads Executive Airport (KPVG), located on US460/US58, is the state's 3rd busiest General Aviation airport and hosts the largest number of general aviation aircraft of any Virginia airport. The airport offers flight training, avionics services, as well as major and minor airframe and powerplant repairs. There is also a sit-down restaurant in the terminal.
The Chesapeake Regional Airport (KCPK) provides similar general aviation services and is located in the city of Chesapeake. Additionally, many local general aviation pilots fly from the nearby Suffolk (KSFQ), Wakefield (KAKQ) and Franklin (KFKN) airports.
Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada. ...
serves the region with Northeast Regional
The ''Northeast Regional'' is an intercity rail service operated by Amtrak in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic United States. In the past it has been known as the ''NortheastDirect'', ''Acela Regional'', or ''Regional''. It is Amtrak's busi ...
trains to its Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
, Williamsburg and Newport News stations. The lines run west to Richmond
Richmond most often refers to:
* Richmond, Virginia, the capital of Virginia, United States
* Richmond, London, a part of London
* Richmond, North Yorkshire, a town in England
* Richmond, British Columbia, a city in Canada
* Richmond, Californi ...
then north to Washington, D.C. and major cities north to Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
. Connecting buses are available between the Norfolk and Newport News stations and from both stations to Virginia Beach. A high-speed rail connection at Richmond to both the Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston through Providence, New Haven, Stamford, New York City, Philadelphia, Wilmington, ...
and the Southeast High Speed Rail Corridor are also under study.
Intercity bus
An intercity bus service ( North American English) or intercity coach service (British English and Commonwealth English), also called a long-distance, express, over-the-road, commercial, long-haul, or highway bus or coach service, is a public ...
service is provided by Greyhound Lines
Greyhound Lines, Inc. (commonly known as simply Greyhound) operates the largest intercity bus service in North America, including Greyhound Mexico. It also operates charter bus services, Amtrak Thruway services, commuter bus services, and ...
(Carolina Trailways) with bus stations in Newport News, Hampton, and Norfolk. Transportation within Hampton Roads is served by a regional bus service, Hampton Roads Transit
Hampton Roads Transit (HRT), incorporated on October 1, 1999, began through the voluntary merger of PENTRAN (Peninsula Transportation District Commission) on the Virginia Peninsula and TRT ( Tidewater Regional Transit a.k.a. Tidewater Transit Di ...
. Local routes serving Williamsburg, James City County, and upper York County is operated by Williamsburg Area Transit Authority
Williamsburg Area Transit Authority (WATA) is a multi-jurisdiction transportation agency providing transit bus and ADA Paratransit services in the City of Williamsburg, James City County, York County in the Historic Triangle area and Surry Cou ...
.
A light rail service known as The Tide was constructed in Norfolk. It began service in August 2011. Operated by Hampton Roads Transit, it is the first light rail service in the state. It is projected to have a daily ridership of between 7,130 and 11,400 passengers a day. There has also been a light rail study in the Hampton – Newport News areas. In the 2016 election, a referendum was on the ballot in Virginia Beach to kill the planned, and mainly state-funded extension of the Tide to the commercial center of Virginia Beach and ultimately to the oceanfront. The ballot initiative won, cancelling the project. The transit authority and the state were left with new light rail cars and major infrastructure for the extension to be disposed of. There are no further plans for light rail mass transit initiatives within Virginia Beach.
 The Hampton Roads area has an extensive network of
The Hampton Roads area has an extensive network of Interstate Highway
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. T ...
s, including the Interstate 64, the major east–west route to and from the area, and its spurs and bypasses of I-264, I-464, I-564, and I-664
Interstate 664 (I-664) is an auxiliary Interstate Highway in the US state of Virginia. The Interstate runs from I-64 and I-264 in Chesapeake north to I-64 in Hampton. I-664 forms the west side of the Hampton Roads Beltway, a circumferen ...
.
The Hampton Roads Beltway extends on a long loop through the region, crossing the harbor on two toll-free bridge–tunnel
A bridge–tunnel is a persistent, unbroken road or rail connection across water that uses a combination of bridges and tunnels, and sometimes causeways, and does not involve intermittent connections such as drawbridges or ferries.
Bridge–tun ...
facilities. These crossings are the Hampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel
The Hampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel (HRBT) is a -long Hampton Roads crossing for Interstate 64 and U.S. Route 60. It is a four-lane facility comprising bridges, trestles, man-made islands, and tunnels under the main shipping channels for Hampton ...
between Phoebus in Hampton and Willoughby Spit in Norfolk and the Monitor–Merrimac Memorial Bridge–Tunnel
The Monitor–Merrimac Memorial Bridge–Tunnel (MMMBT) is the 4.6 mile-long (7.4 km) Hampton Roads crossing for Interstate 664 in the southeastern portion of Virginia in the United States. It is a four-lane bridge–tunnel composed of bri ...
between Newport News and Suffolk. The Beltway connects with another Interstate highway and three arterial U.S. Highways at Bower's Hill
Bower's Hill is a community located in the independent city of Chesapeake, Virginia (formerly Norfolk County) in the United States. It is located in the South Hampton Roads region at the northeastern edge of the Great Dismal Swamp, an area consi ...
near the northeastern edge of the Great Dismal Swamp. Other major east–west routes are U.S. Route 58, U.S. Route 60, and U.S. Route 460. The major north–south routes are U.S. Route 13 and U.S. Route 17.
There are also two other tunnels in the area, the Midtown Tunnel, and the Downtown Tunnel joining Portsmouth and Norfolk, as well as the -long Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel, a toll facility which links the region with Virginia's Eastern Shore which carries US 13. The original Downtown Tunnel in conjunction with the Berkley Bridge were considered a single bridge and tunnel complex when completed in 1952, perhaps stimulating the innovative bridge-tunnel design using man-made island
An artificial island is an island that has been constructed by people rather than formed by natural means. Artificial islands may vary in size from small islets reclaimed solely to support a single pillar of a building or structure to those tha ...
s when the Hampton Roads Bridge-Tunnel was planned, first opening in 1957. The George P. Coleman Memorial Bridge
The George P. Coleman Memorial Bridge (known locally as simply the Coleman Bridge) is a double swing bridge that spans the York River between Yorktown and Gloucester Point, in the United States state of Virginia. It connects the Peninsula and ...
is a major toll bridge connecting U.S. Highway 17 on the Peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on a ...
at Yorktown with Virginia's Middle Peninsula region. Another major crossing of waterways is the James River Bridge
The James River Bridge (JRB) is a four-lane divided highway lift bridge across the James River in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Owned and operated by the Virginia Department of Transportation, it carries U.S. Route 17 (US 17), US 258, ...
, carrying US 17
U.S. Route 17 or U.S. Highway 17 (US 17), also known as the Coastal Highway, is a north–south United States Highway that spans in the southeastern United States. It runs close to the Atlantic Coast for much of its length, with ...
US 258
U.S. Route 258 (US 258) is a spur of US 58 in the U.S. states of North Carolina and Virginia. The U.S. Highway runs from US 17 Business and NC 24 Business in Jacksonville, North Carolina north to Virginia State Route 143 (SR 143) at Fort Mo ...
, and SR 32 from Newport News to Isle of Wight County.
The region is notable in that it has 2 types of public transport services via ferries. A passenger ferry is operated on the Elizabeth River between downtown areas of Norfolk and Portsmouth by HRT. The Jamestown Ferry (also known as the Jamestown-Scotland Ferry) is an automobile ferry system on the James River connecting Jamestown in James City County with Scotland in Surry County. It carries State Route 31. Operated by VDOT, it is the only 24-hour state-run ferry operation in Virginia and has over 90 employees. It operates four ferryboats, the ''Pocahontas'', the ''Williamsburg'', the ''Surry'', and the ''Virginia''. The facility is toll-free.
Demographics
According to the 2010 Census, the overall racial composition of Hampton Roads was as follows: * White or Caucasian: 59.6% * Black or African American: 31.3% * American Indian: 0.4% * Asian: 3.5% * Some other race: 1.7% *Two or more races
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultur ...
: 3.4%
In addition, 5.4% of the population were Hispanic or Latino (of any race). 57.2% of the population were of non-Hispanic White background.
Culture
The area is most often associated with the larger American South. People who have grown up in the Hampton Roads area have a unique Tidewater accent which sounds different from a stereotypical Southern accent. Vowels have a longer pronunciation than in a regular southern accent.Flag
Sites of interest
Parks and recreation
TheNorfolk Botanical Garden
The Norfolk Botanical Garden (158 acres) is a botanical garden with arboretum located at 6700 Azalea Garden Road, Norfolk, Virginia.
History
The Norfolk Botanical Garden was founded through the collaboration between Norfolk City Manager Thoma ...
, opened in 1939, is a botanical garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
and arboretum
An arboretum (plural: arboreta) in a general sense is a botanical collection composed exclusively of trees of a variety of species. Originally mostly created as a section in a larger garden or park for specimens of mostly non-local species, man ...
located near the Norfolk International Airport. It is open year-round.
The Virginia Zoological Park, opened in 1900, is a zoo
A zoo (short for zoological garden; also called an animal park or menagerie) is a facility in which animals are kept within enclosures for public exhibition and often bred for conservation purposes.
The term ''zoological garden'' refers to z ...
with hundreds of animals on display, including the critically endangered Siberian tiger
The Siberian tiger or Amur tiger is a population of the tiger subspecies '' Panthera tigris tigris'' native to the Russian Far East, Northeast China and possibly North Korea. It once ranged throughout the Korean Peninsula, but currently inh ...
and threatened white rhino
The white rhinoceros, white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum'') is the largest extant species of rhinoceros. It has a wide mouth used for grazing and is the most social of all rhino species. The white rhinoceros consists ...
.
First Landing State Park and False Cape State Park are both located in coastal areas in Virginia Beach. Both offer camping facilities, cabins, and outdoor recreation activities in addition to nature and history tours. First Landing is the site of Cape Henry
Cape Henry is a cape on the Atlantic shore of Virginia located in the northeast corner of Virginia Beach. It is the southern boundary of the entrance to the long estuary of the Chesapeake Bay.
Across the mouth of the bay to the north is Cape Ch ...
while False Cape is located at the southeastern end of Virginia Beach.
Newport News Park
Newport News Park, in Newport News, Virginia, is the largest park in the system of municipal parks maintained by the Newport News Department of Parks, Recreation and Tourism. At 8,065 acres (32.63 km²), it is one of largest city-run parks in ...
is located in the northern part of the city of Newport News. The city's golf course also lies within the park along with camping and outdoor activities. There are over of trails in the Newport News Park complex. The park has a 5.3-mile (8.5-km) multi-use bike path. The park offers bicycle and helmet rental, and requires helmet use by children under 14. Newport News Park also offers an archery range, disc golf course, and an "aeromodel flying field" for remote-controlled aircraft, complete with a runway.
The region also has amusement parks which attract tourists and locals alike. The Virginia Beach Oceanfront has Atlantic Fun Park (formerly called "Virginia Beach Amusement Park"). Virginia Beach also has Ocean Breeze Waterpark, Shipwreck Golf, and Motor World
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power gene ...
which were formerly combined into one as "Ocean Breeze Fun Park". As separate parks, they provide miniature golf, go-karts, water slides, pools, climbing wall, paintball area, and kiddie rides. Busch Gardens Williamsburg
Busch Gardens Williamsburg (formerly known as Busch Gardens Europe and Busch Gardens: The Old Country) is a amusement park located in James City County near Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. Located approximately northwest of Virginia ...
and Water Country USA are the major theme parks in Williamsburg.
Historic Triangle
The Historic Triangle is located on the Virginia Peninsula and includes the colonial communities of Jamestown, Williamsburg, and Yorktown. The sites are linked by a scenic roadway, theNational Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational properti ...
's Colonial Parkway
Colonial Parkway is a scenic parkway linking the three points of Virginia's Historic Triangle, Jamestown, Williamsburg, and Yorktown. It is part of the National Park Service's Colonial National Historical Park. Virginia's official state c ...
.
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (histor ...
was the first permanent English settlement in the Americas. It was established by the Virginia Company of London as "James Fort" on May 4, 1607, and was considered permanent after brief abandonment in 1610. It followed several failed attempts, including the Lost Colony of Roanoke. Jamestown served as the capital of the colony of Virginia for 83 years, from 1616 until 1699.
Historic Jamestowne
Historic Jamestown is the cultural heritage site that was the location of the 1607 James Fort and the later 17th-century town of Jamestown in America. It is located on Jamestown Island, on the James River at Jamestown, Virginia and operated as ...
is the archaeological site on Jamestown Island and is a cooperative effort by Jamestown National Historic Site (part of Colonial National Historical Park) and Preservation Virginia. Jamestown Settlement, a living history interpretive site, is operated by the Jamestown Yorktown Foundation, a state agency of the Commonwealth of Virginia.
Williamsburg was founded in 1632 as Middle Plantation, a fortified settlement on high ground between the James and York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
rivers. The city served as the capital of the Colony of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (histor ...
from 1699 to 1780 and was the center of political events in Virginia leading to the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
. The College of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William I ...
, established in 1693, is the second-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and the only one of the nine colonial colleges located in the South; its alumni include three U.S. presidents as well as many other important figures in the nation's early history.
The city's tourism-based economy is driven by Colonial Williamsburg
Colonial Williamsburg is a living-history museum and private foundation presenting a part of the historic district in the city of Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. The Colonial Williamsburg Foundation has 7300 employees at this location ...
, the restored Historic Area of the city. Modern Williamsburg is also a college town, inhabited in large part by William & Mary students and staff.
Yorktown is one of the eight original shires formed in colonial Virginia in 1682. The town is most famous as the site of the siege and subsequent surrender of General Charles Cornwallis to General George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
and the French Fleet during the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
on October 19, 1781. Although the war would last for another year, this British defeat at Yorktown effectively ended the war. Yorktown also figured prominently in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
(1861–1865), serving as a major port to supply both northern and southern towns, depending upon who held Yorktown at the time. It is the eastern terminus of the Colonial Parkway
Colonial Parkway is a scenic parkway linking the three points of Virginia's Historic Triangle, Jamestown, Williamsburg, and Yorktown. It is part of the National Park Service's Colonial National Historical Park. Virginia's official state c ...
connecting these locations. Yorktown is also the eastern terminus of the TransAmerica Trail
U.S. Bicycle Route 76 (USBR 76) is a cross-country bicycle route east of Colorado in the United States. It is one of the two original U.S. Bicycle Routes, the other being U.S. Bicycle Route 1. USBR 76 runs from the Midwestern state of Kansas t ...
, a bicycle touring route created by the Adventure Cycling Association.
=Peninsula museums
= The Mariners' Museum, founded in 1930 by Archer and Anna Huntington, is an institution dedicated to bringing maritime history to the world. It is currently home to the USS ''Monitor'' Center where 210 tons of artifacts recovered from the USS ''Monitor'' are held, including thegun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanis ...
. The museum also consists of a 550-acre park and the Mariners' Lake
The Mariners' Lake is a reservoir which was created as part of the natural park on the grounds of the Mariners' Museum and Park located in the independent city of Newport News in the Hampton Roads region of southeastern Virginia.
The museum was ...
, through which is the five-mile Noland Trail. The permanent collection at the museum totals about 32,000 objects, equally divided between works of art and three-dimensional objects. The Mariners' Museum Library and Archive, now located in the Trible Library at Christopher Newport University, consists of over 78,000 books, 800,000 photographs, films and negatives, and over one million archival pieces, making it the largest maritime library in the Western Hemisphere.
The Virginia War Museum
The Virginia War Museum is located in Huntington Park on Warwick Blvd., Newport News, Virginia. The museum contains exhibits on American military history from 1775 to the present.Virginia War Museum. "Virginia War Museum" brochure, Winter 2007 ...
covers American military history. The museum's collection includes, weapons, vehicles, artifacts, uniforms and posters from various periods of American history. Highlights of the museum's collection include a section of the Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall (german: Berliner Mauer, ) was a guarded concrete barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and East Germany (GDR). Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the gover ...
and the outer wall from Dachau Concentration Camp
,
, commandant = List of commandants
, known for =
, location = Upper Bavaria, Southern Germany
, built by = Germany
, operated by = ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS)
, original use = Political prison
, construction ...
.
The Virginia Living Museum
The Virginia Living Museum is an open-air museum located in Newport News, Virginia that has many living exhibits of Virginia's indigenous species. The exhibits include aspects of an aquarium, science center, aviary, botanical preserve and pl ...
, first established in 1966, combines the elements of a native wildlife park, science museum, aquarium, botanical preserve, and planetarium. The exhibits are themed on the geographic regions of Virginia, from the Appalachian Mountains to the offshore waters of the Atlantic Ocean, and includes more than 245 different animal species.
The Peninsula Fine Arts Center in Newport News contains a rotating gallery of art exhibits. The center also contains a Studio Art School of private and group instruction for all ages. It maintains a permanent "Hands on For Kids" gallery designed for children and families to interact in what the center describes as "a fun, educational environment that encourages participation with art materials and concepts."
The Hampton University
Hampton University is a private, historically black, research university in Hampton, Virginia. Founded in 1868 as Hampton Agricultural and Industrial School, it was established by Black and White leaders of the American Missionary Association a ...
museum was established in 1868 in the heart of the historic Hampton University campus. The museum is the oldest African American museum in the United States and one of the oldest museums in the State of Virginia. It contains over 9,000 objects, including African American fine arts, traditional African, Native American, Native Hawaiian, Pacific Island, and Asian art.
The Charles H. Taylor Arts Center is Hampton's public access arts center. It offers a series of changing visual art exhibitions as well as a quarterly schedule of classes, workshops and educational programs.
The Downing-Gross Cultural Arts Center in SE Newport News contains a community-based art gallery, as well as arts classrooms and the Ella Fitzgerald Theater.
The Casemate Museum (where former Confederate President Jefferson Davis was imprisoned) is at Fort Monroe in the historic Phoebus area at Old Point Comfort in Hampton.
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
Langley Research Center
The Langley Research Center (LaRC or NASA Langley), located in Hampton, Virginia, United States of America, is the oldest of NASA's field centers. It directly borders Langley Air Force Base and the Back River on the Chesapeake Bay. LaRC has f ...
is in Hampton, the original training ground for the Mercury Seven, Gemini, and Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
Astronauts
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally r ...
. Visitors are able to learn about the region's aviation history at the Virginia Air and Space Center
The Virginia Air and Space Science Center is a museum and educational facility in Hampton, Virginia that also serves as the visitors center for NASA's Langley Research Center and Langley Air Force Base. The museum also features an IMAX digit ...
in Hampton.
Air Power Park is an outdoor on-site display of various aircraft and a space capsule. It is located on Mercury Boulevard at the intersection of LaSalle Blvd, near the AF Base.
The Biblical Art Gallery at Ivy Farms Baptist Church is Virginia's largest collection of pre-1900s religious art.
=South Hampton Roads
= TheChrysler Museum of Art
The Chrysler Museum of Art is an art museum on the border between downtown and the Ghent district of Norfolk, Virginia. The museum was founded in 1933 as the Norfolk Museum of Arts and Sciences. In 1971, automotive heir, Walter P. Chrysler Jr. ...
, located in the Ghent district
The Ghent District is a historic neighborhood in Norfolk, Virginia. It comprises Ghent, West Ghent, and Ghent Square. Other portions of surrounding neighborhoods are often attributed to Ghent as an extension of its commerce including Chelsea, Nor ...
of Norfolk, is the region's foremost art museum and is considered by ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' to be the finest in the state. Of particular note is the extensive glass collection and American neoclassical marble sculptures.
Nauticus
Nauticus is a maritime-themed science center and museum located on the downtown waterfront in Norfolk, Virginia, also known as the National Maritime Center.
History
Nauticus was incorporated under the National Maritime Center Authority in Febru ...
, the National Maritime Center, opened on the downtown waterfront in 1994. It features hands-on exhibits, interactive theaters, aquaria, digital high-definition films and an extensive variety of educational programs. Since 2000, Nauticus has been home to the battleship , one of the last battleships to be built in the United States. It served briefly in World War II and later in the Korean and Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Iraq were carried out in two key phases: ...
s. The General Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was ...
Memorial, located in the 19th-century Norfolk court house and city hall in downtown, contains the tombs of the late General and his wife, a museum and a vast research library, personal belongings (including his famous corncob pipe) and a short film that chronicles the life of the famous General of the Army.
 Also in downtown Norfolk and inside Nauticus is the Hampton Roads Naval Museum, an official U.S. Navy museum that focuses on the 220 plus year history of the Navy within the region.
The Children's Museum of Virginia in
Also in downtown Norfolk and inside Nauticus is the Hampton Roads Naval Museum, an official U.S. Navy museum that focuses on the 220 plus year history of the Navy within the region.
The Children's Museum of Virginia in Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most d ...
has one of the largest collection of model electric trains and other toys.
The Norfolk Naval Shipyard in Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most d ...
is one of the oldest shipyards and has the first dry dock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, ...
on display.
The Great Dismal Swamp National Wildlife Refuge (in Suffolk and Chesapeake) is accessed from U.S. Route 17 in Chesapeake Chesapeake often refers to:
*Chesapeake people, a Native American tribe also known as the Chesepian
* The Chesapeake, a.k.a. Chesapeake Bay
*Delmarva Peninsula, also known as the Chesapeake Peninsula
Chesapeake may also refer to:
Populated plac ...
.
The Suffolk-Nansemond Museum is in the restored Seaboard and Virginian Railway
The Virginian Railway was a Class I railroad located in Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. The VGN was created to transport high quality "smokeless" bituminous coal from southern West Virginia to port at Hampton Roads.
Histor ...
passenger train station in Suffolk
Suffolk () is a ceremonial county of England in East Anglia. It borders Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south; the North Sea lies to the east. The county town is Ipswich; other important towns include ...
.
The Isle of Wight Museum is in Smithfield.
The Contemporary Art Center of Virginia located in Virginia Beach features the significant art of our time.
Music and venues
The Hampton Roads region has a thriving music scene, with a heavy concentration thereof in the Virginia Beach, Chesapeake, and Norfolk areas. Many clubs, venues, and festivals exist within the region, all playing host to a wide variety of musical styles. There are a few hundred bands that play routinely in the region, spanning multiple genres. There are also twenty to thirty musical acts based in the region that perform throughout Hampton Roads and its surrounding areas on a "full-time" basis. In addition, plenty of well known acts have come from the area. Some of the major rock/pop artists include Bruce Hornsby, Gary "U.S." Bonds, Juice Newton,Mae
Mae is an American rock band that formed in Norfolk, Virginia in 2001. The band's name is an acronym for "Multi-sensory Aesthetic Experience", based on a course taken by drummer Jacob Marshall while a student at Old Dominion University.
History ...
, Seven Mary Three, Gene Vincent, Keller Williams
Keller Williams is an American singer, songwriter and musician who combines elements of bluegrass, folk, alternative rock, reggae, electronica/dance, jazz, funk, along with other assorted genres. He is often described as a 'one-man jam-ban ...
, and Steve Earle
Stephen Fain Earle (; born January 17, 1955) is an American singer-songwriter, record producer, author, and actor. Earle began his career as a songwriter in Nashville and released his first EP in 1982. Initially working in the country music ...
. Ella Fitzgerald
Ella Jane Fitzgerald (April 25, 1917June 15, 1996) was an American jazz singer, sometimes referred to as the "First Lady of Song", "Queen of Jazz", and "Lady Ella". She was noted for her purity of tone, impeccable diction, phrasing, timing, in ...
is the most recognizable jazz musician from the area. Robert Cray and Ruth Brown are both prominent blues and R&B artists. Tommy Newsom is another famous jazz musician. Many prominent rap and hip hop artists come from the area including Chad Hugo, Clipse, Magoo, Missy Elliott
Melissa Arnette Elliott (born July 1, 1971), better known as Missy Elliott or Missy “Misdemeanor” Elliot, is an American rapper, singer, songwriter, and record producer. She embarked on her music career with R&B girl group Sista in the earl ...
, Nicole Wray, Pharrell Williams, Quan, Teddy Riley, and Timbaland.
The region has a number of venues hosting live music and performances. Several of the larger (in order of maximum seating capacity) are:
* Veterans United Home Loans Amphitheater in Virginia Beach (seating 20,000)
* Norfolk Scope Arena in Norfolk (seating 13,800)
* Hampton Coliseum
Hampton Coliseum is a multi-purpose arena in Hampton, Virginia. Construction began on May 24, 1968. The venue held its first event on December 1, 1969, with the nearby College of William & Mary playing North Carolina State University in a coll ...
in Hampton (seating 13,800)
* Kaplan Arena in Williamsburg (seating 10,175)
* Ted Constant Convocation Center
Chartway Arena at the Ted Constant Convocation Center is a , multi-purpose arena in Norfolk, Virginia, United States, on the campus of Old Dominion University. It is operated by Spectra Venue Management. Chartway Arena is part of the University Vi ...
at Old Dominion University in Norfolk (seating 9,500)
* Portsmouth Pavilion in Portsmouth (seating 7,500)
* Le Palais Royal Theatre at Busch Gardens Williamsburg
Busch Gardens Williamsburg (formerly known as Busch Gardens Europe and Busch Gardens: The Old Country) is a amusement park located in James City County near Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. Located approximately northwest of Virginia ...
in James City County (seating 5,600)
* Ferguson Center for the Arts in Newport News (seating 1,725 and 453 in 2 separate concert halls)
* Lake Matoaka Amphitheatre at The College of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William I ...
in Williamsburg (seating 1,700)
* The NorVa in Norfolk (standing 1,500)
Dozens of much smaller commercial establishments offer live music and other entertainment such as comedy shows and mystery dinner-theater throughout the region.
Other notable Hampton Roads "firsts"
America's first free public schools, the Syms and Eaton free schools (later combined as Syms-Eaton Academy), were established in Hampton in 1634 and 1659 respectively. The Syms-Eaton Academy was later renamed Hampton Academy and in 1852 became part of the public school system, thus Hampton High School lays claim to being the oldest public school in the United States. The trust fund created from the Syms and Eaton donations has remained intact since the 17th century and was incorporated into support for the Hampton public school system. In 1957, theHampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel
The Hampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel (HRBT) is a -long Hampton Roads crossing for Interstate 64 and U.S. Route 60. It is a four-lane facility comprising bridges, trestles, man-made islands, and tunnels under the main shipping channels for Hampton ...
was the first bridge–tunnel
A bridge–tunnel is a persistent, unbroken road or rail connection across water that uses a combination of bridges and tunnels, and sometimes causeways, and does not involve intermittent connections such as drawbridges or ferries.
Bridge–tun ...
complex in the world, to be followed by the area's much longer Chesapeake Bay Bridge–Tunnel in 1963. This was followed by the Monitor–Merrimac Memorial Bridge–Tunnel
The Monitor–Merrimac Memorial Bridge–Tunnel (MMMBT) is the 4.6 mile-long (7.4 km) Hampton Roads crossing for Interstate 664 in the southeastern portion of Virginia in the United States. It is a four-lane bridge–tunnel composed of bri ...
in 1992.
Education
Hampton Roads' individual cities and counties administer their own K-12 education for their localities. In addition to public education, area residents have many private and religious school options. The area also has a number of higher education options for area residents. Some offer only associates and technical degrees and certificates, while others award advanced degrees, including doctorates. Some are publicly funded, but the region also has a number of private and for-profit colleges. Additionally, a number of universities have established satellite campuses in the region.Higher education
Public universities: TheCollege of William and Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William ...
in Williamsburg was founded in 1693 and has served as the second oldest institution of higher education in the United States. Old Dominion University, founded as the Norfolk Division of the College of William and Mary in 1930, became an independent institution in 1962 and now offers degrees in 68 undergraduate and 95 (60 masters/35 doctoral) graduate degree programs. Norfolk's Eastern Virginia Medical School
Eastern Virginia Medical School (EVMS) is a public medical school in Norfolk, Virginia. Founded by grassroots efforts in the Southeastern part of Virginia known as Hampton Roads, EVMS is not affiliated with an undergraduate institution and co ...
, founded as a community medical school by the surrounding jurisdictions in 1973, is noted for its research into reproductive medicine and is located in the region's major medical complex in the Ghent district
The Ghent District is a historic neighborhood in Norfolk, Virginia. It comprises Ghent, West Ghent, and Ghent Square. Other portions of surrounding neighborhoods are often attributed to Ghent as an extension of its commerce including Chelsea, Nor ...
. Norfolk State University
Norfolk State University (NSU) is a public historically black university in Norfolk, Virginia. It is a member of the Thurgood Marshall College Fund and Virginia High-Tech Partnership.
History
The institution was founded on September 18, 193 ...
is the largest majority black university in Virginia and offers degrees in a wide variety of liberal arts
Liberal arts education (from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as La ...
. Christopher Newport University serves as a public university and is located in Newport News.
Private universities:
Regent University, a private university founded by Christian evangelist, television host and leader Pat Robertson, has historically focused on graduate education but is attempting to establish an undergraduate program as well. Atlantic University, associated with the Edgar Cayce organization's Association for Research and Enlightenment
The Association for Research and Enlightenment (A.R.E.), also known as Edgar Cayce's A.R.E., is a non-profit organization founded in 1931 by clairvoyant Edgar Cayce to explore spirituality, holistic health, and other psychic topics, as well as pr ...
(ARE), offers instruction in New Age subjects and an M.A. in Transpersonal Studies. Virginia Wesleyan University is a small private liberal arts
Liberal arts education (from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as La ...
college on the border of Norfolk and Virginia Beach. Hampton University
Hampton University is a private, historically black, research university in Hampton, Virginia. Founded in 1868 as Hampton Agricultural and Industrial School, it was established by Black and White leaders of the American Missionary Association a ...
, a private HBCU
Historically black colleges and universities (HBCUs) are institutions of higher education in the United States that were established before the Civil Rights Act of 1964 with the intention of primarily serving the African-American community. M ...
university, has a long history serving Hampton.
Universities with satellite campuses:
Several universities based outside Hampton Roads offer a limited selection of classes in the area. Virginia Tech
Virginia Tech (formally the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University and informally VT, or VPI) is a public land-grant research university with its main campus in Blacksburg, Virginia. It also has educational facilities in six re ...
and University of Virginia
The University of Virginia (UVA) is a public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia. Founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson, the university is ranked among the top academic institutions in the United States, with highly selective ad ...
have established a joint teaching center in Newport News. George Washington University
, mottoeng = "God is Our Trust"
, established =
, type = Private federally chartered research university
, academic_affiliations =
, endowment = $2.8 billion (2022)
, presi ...
and Averett University also maintain campuses there. Troy State University, Florida International University
Florida International University (FIU) is a public research university with its main campus in Miami-Dade County. Founded in 1965, the school opened its doors to students in 1972. FIU has grown to become the third-largest university in Florid ...
, and Saint Leo University offer classes, primarily connected to one or more of the area's military bases.
University consortia:
The National Institute of Aerospace (NIA) is a consortium of member universities: Georgia Tech, Hampton University
Hampton University is a private, historically black, research university in Hampton, Virginia. Founded in 1868 as Hampton Agricultural and Industrial School, it was established by Black and White leaders of the American Missionary Association a ...
, North Carolina A&T
North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University (also known as North Carolina A&T State University, North Carolina A&T, N.C. A&T, or simply A&T) is a public, historically black land-grant research university in Greensboro, North Carol ...
, North Carolina State, Old Dominion University, University of Virginia
The University of Virginia (UVA) is a public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia. Founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson, the university is ranked among the top academic institutions in the United States, with highly selective ad ...
, Virginia Tech
Virginia Tech (formally the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University and informally VT, or VPI) is a public land-grant research university with its main campus in Blacksburg, Virginia. It also has educational facilities in six re ...
, the College of William and Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William ...
, and Christopher Newport University. Their unique approach allows students pursuing M.S. and PhD degrees the opportunity to take classes from any member university taught at the institute.
Technical education:
 Area residents also have options for training for technical professions. The Apprentice School was founded in 1919 and offers four/five-year programs in mechanical and technical fields associated with the shipbuilding industry. Graduates from the Apprentice School go on to work at the Newport News Shipbuilding. Technology-focused ECPI University has campuses in Virginia Beach and Newport News while ITT Technical Institute has a campus in Norfolk.
Area residents also have options for training for technical professions. The Apprentice School was founded in 1919 and offers four/five-year programs in mechanical and technical fields associated with the shipbuilding industry. Graduates from the Apprentice School go on to work at the Newport News Shipbuilding. Technology-focused ECPI University has campuses in Virginia Beach and Newport News while ITT Technical Institute has a campus in Norfolk. Bryant & Stratton College
Bryant & Stratton College (BSC) is a private for-profit college with campuses in New York, Ohio, Virginia, and Wisconsin, as well as an online campus. Founded in 1854, the college offers associate degree programs at all campuses and bachelor's ...
has campuses in Virginia Beach Town Center
Virginia Beach Town Center is a group of offices, hotels, stores, and restaurants in Virginia Beach, Virginia.
Location
The Virginia Beach Town Center is located in the Central Business District of Virginia Beach across the street from Pembrok ...
and Peninsula Town Center
Peninsula Town Center is an open air mixed-use development located in the Coliseum Central Business improvement district of Hampton, Virginia in the Hampton Roads region. The Town Center is located on the site of the original Coliseum Mall, an ...
. The Culinary Institute of Virginia is located in Norfolk. The Art Institute of Virginia Beach offers programs in the media arts, design and culinary arts fields.
Two-year colleges:
Three institutions in the Virginia Community College System offer affordable higher education options for area residents. Tidewater Community College
Tidewater Community College (TCC) is a public community college in South Hampton Roads, Virginia, with campuses in Chesapeake, Norfolk, Portsmouth, Suffolk, and Virginia Beach. It is part of the Virginia Community College System and is accredited ...
in Norfolk, Virginia Beach, Chesapeake, and Portsmouth, Paul D. Camp Community College
Paul D. Camp Community College (PDCCC) is a public community college in Franklin, Virginia. Founded in 1970, it is one of 23 schools in the Virginia Community College System. The college is named after a local advocate of education, who, along ...
in Suffolk, Franklin, and Smithfield, and Virginia Peninsula Community College
Virginia Peninsula Community College (VPCC) is a public community college with two campuses in Virginia, one in Hampton and the other in James City County. It also has two education centers The Southeast Higher Education Center in Newport News ...
in Hampton and Williamsburg offer two-year degrees and specialized training programs.
Religious education
Bible training schools include Hampton University and Regent University, but also Canaan Theological College & Seminary, Bethel College and Victory Baptist Bible College and Seminary in Hampton, Tabernacle Baptist Bible College & Theological Seminary, Central Baptist Theological Seminary in Virginia Beach, Providence Bible College & Theological Seminary in Norfolk and the Hampton Roads campus of theJohn Leland Center for Theological Studies
__NOTOC__
The John Leland Center for Theological Studies is a Baptist theological institute in Arlington, Virginia, with several satellite locations elsewhere in Virginia. Leland is partnered with the Baptist General Association of Virginia and t ...
.
Media
Newspapers
Three daily newspapers serve Hampton Roads: '' The Virginian-Pilot'' in the Southside, the '' Daily Press'' on the Peninsula, and the six days a week ''Suffolk News-Herald
The ''Suffolk News-Herald'' is a newspaper serving Suffolk, Virginia, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North Ameri ...
'' that serves Suffolk and Franklin. Smaller publications include the Williamsburg-James City County area's twice-weekly '' Virginia Gazette'' (the state's oldest newspaper), the ''New Journal and Guide
The ''New Journal and Guide'' is a regional weekly newspaper based in Norfolk, Virginia, and serving the Hampton Roads area. The weekly focuses on local and national African-American news, sports, and issues and has been in circulation since 1900 ...
'', and ''Inside Business
''For the business newspaper based in the United States, see Inside Business (newspaper)''
''Inside Business'' was an Australian television program broadcast on ABC1. Making its debut on 4 August 2002, it presented analysis of the financial worl ...
'', the area's only business newspaper.
Newspapers serving the Hampton Roads area include:
* '' Daily Press'' – Newport News
* '' The Virginian-Pilot'' – Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
* ''Suffolk News-Herald
The ''Suffolk News-Herald'' is a newspaper serving Suffolk, Virginia, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North Ameri ...
'' – Suffolk
Suffolk () is a ceremonial county of England in East Anglia. It borders Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south; the North Sea lies to the east. The county town is Ipswich; other important towns include ...
* '' The Flat Hat'' – student newspaper of the College of William & Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William I ...
* ''Inside Business
''For the business newspaper based in the United States, see Inside Business (newspaper)''
''Inside Business'' was an Australian television program broadcast on ABC1. Making its debut on 4 August 2002, it presented analysis of the financial worl ...
'' – Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
(business news)
* ''The New Journal and Guide
The ''New Journal and Guide'' is a regional weekly newspaper based in Norfolk, Virginia, and serving the Hampton Roads area. The weekly focuses on local and national African-American news, sports, and issues and has been in circulation since 1900 ...
'' – Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
* ''Tidewater News
''Tidewater News'' is a newspaper based in Franklin, Virginia covering Franklin, Southampton County and Isle of Wight County
Isle of Wight County is a county located in the Hampton Roads region of the U.S. state of Virginia. It was named af ...
'' – Franklin
* '' The Virginia Gazette'' – Williamsburg
Magazines
''Coastal Virginia Magazine'' is one of the region's city and lifestyle magazine. The publication is published eight times a year and covers all of Hampton Roads and the Eastern Shore of Virginia. ''Coastal Virginia Magazine'' was formerly known as ''Hampton Roads Magazine''. ''Hampton Roads Times'' serves as an online magazine for the region. ''Suffolk Living Magazine'' is another of the region's city and lifestyle magazines. The publication is published four times a year and covers the City of Suffolk. Suffolk Publications also produces Virginia-Carolina Boomers, a regional guide for Boomers in the area, which comes out twice a year.Television
The Hampton Roads designated market area (DMA) is the 42nd largest in the U.S. with 712,790 homes (0.64% of the total U.S.).Holmes, Gary.Nielsen Reports 1.1% increase in U.S. Television Households for the 2006–2007 Season
." Nielsen Media Research. September 23, 2006. Retrieved on September 28, 2007. The major network television affiliates are
WTKR-TV
WTKR (channel 3) is a television station licensed to Norfolk, Virginia, United States, serving the Hampton Roads area as an affiliate of CBS. It is owned by E. W. Scripps Company alongside Portsmouth-licensed CW affiliate WGNT (channel 27). ...
3 ( CBS), WAVY
WAVY-TV (channel 10) is a television station licensed to Portsmouth, Virginia, United States, serving the Hampton Roads area as an affiliate of NBC. It is owned by Nexstar Media Group alongside Virginia Beach–licensed Fox affiliate WVBT (chann ...
10 ( NBC), WVEC-TV 13 ( ABC), WGNT 27 ( CW), WTVZ 33 ( MyNetworkTV), WVBT 43 ( Fox), and WPXV 49 ( Ion Television). WHRO-TV 15 serves as the region's primary member station of the Public Broadcasting Service
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educa ...
(PBS); WUND 2 – an Edenton, North Carolina-based satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioiso ...
of PBS North Carolina, a state network of PBS member stations owned by the University of North Carolina
The University of North Carolina is the multi-campus public university system for the state of North Carolina. Overseeing the state's 16 public universities and the NC School of Science and Mathematics, it is commonly referred to as the UNC S ...
– serves as a secondary PBS outlet for the area. Area residents also can receive independent stations, such as WSKY broadcasting on channel 4 from the Outer Banks of North Carolina, WGBS-LD
WGBS-LD, virtual channel 7 ( VHF digital channel 12), is a low-powered Retro TV- affiliated television station licensed to Carrollton, Virginia, United States and serving the Greater Hampton Roads area. The station is owned by Joan Wright.
Digi ...
broadcasting on channel 11 from Hampton, and WTPC 21, a TBN affiliate out of Virginia Beach.
Cable television
Cable television is a system of delivering television programming to consumers via radio frequency (RF) signals transmitted through coaxial cables, or in more recent systems, light pulses through fibre-optic cables. This contrasts with bro ...
service in most Hampton Roads localities is provided by Cox Communications
Cox Communications, Inc. (also known as Cox Cable and formerly Cox Broadcasting Corporation, Dimension Cable Services and Times-Mirror Cable) is an American digital cable television provider, telecommunications and home automation services. It i ...
. Suffolk, Franklin, Isle of Wight, and Southampton are served by Charter Communications. Verizon FiOS service is currently available in parts of the region and continues to expand, offering a non-satellite alternative to Cox. DirecTV
DirecTV (trademarked as DIRECTV) is an American multichannel video programming distributor based in El Segundo, California. Originally launched on June 17, 1994, its primary service is a digital satellite service serving the United States. I ...
and Dish Network are also popular as an alternative to cable television.
Radio
Norfolk is served by a variety of radio stations on the FM and AM dials, with towers located around the Hampton Roads area. These cater to many different interests, including news,talk radio
Talk radio is a radio format containing discussion about topical issues and consisting entirely or almost entirely of original spoken word content rather than outside music. Most shows are regularly hosted by a single individual, and often featu ...
, and sports, as well as an eclectic mix of musical interests.
Sports
The Virginia Beach-Norfolk, VA-NC Combined Statistical Area is the largest statistical area in the United States without a professional sports franchise in one of the five major North American sports leagues ( NFL, MLB, NBA, NHL, MLS).Team sports
Norfolk serves as home to two professional franchises, the Norfolk Tides of theInternational League
The International League (IL) is a Minor League Baseball league that operates in the United States. Along with the Pacific Coast League, it is one of two leagues playing at the Triple-A level, which is one grade below Major League Baseball ( ...
and the Norfolk Admirals Norfolk Admirals has been the name of two professional ice hockey franchises:
*Norfolk Admirals (AHL), a team which played in the American Hockey League from 2000 to 2015
*Norfolk Admirals (ECHL)
The Norfolk Admirals are a professional ice hocke ...
of the ECHL
The ECHL (formerly the East Coast Hockey League) is a mid-level professional ice hockey league based in Shrewsbury, New Jersey, with teams scattered across the United States and Canada. It is a tier below the American Hockey League (AHL).
The ...
. The Tides play at Harbor Park, seating 12,067 and opened in 1993. The Admirals play at Norfolk Scope Arena, seating 8,725 or 13,800 festival seating, which opened in 1971. Hampton Roads was formerly home to the ABA Virginia Squires
The Virginia Squires were a basketball team based in Norfolk, Virginia, and playing in several other Virginia cities. They were members of the American Basketball Association from 1970 to 1976.
The team originated in 1967 as the Oakland Oaks, ...
, alternating between Norfolk and Hampton, as well as Richmond and Roanoke. The Squires folded in 1976, after the league merged with the NBA.
Lionsbridge FC competes in USL League Two, the top pre-professional men's soccer league in North America. The club began play in 2018 and was named USL League Two Franchise of the Year in 2019. They play home games on the campus of Christopher Newport University. The Peninsula Pilots play in the Coastal Plain League, a summer baseball league. The Pilots play in Hampton at War Memorial Stadium seating 5,125 and opened in 1948.
On the collegiate level, four Division I programs—two on the Southside and two on the Peninsula—field teams in many sports, including football, basketball, and baseball; three currently play football in the second-tier FCS, while ODU recently moved up to the FBS football. The Southside boasts the Old Dominion Monarchs and the Norfolk State Spartans, both in Norfolk, while the Peninsula features the William & Mary Tribe
The William & Mary Tribe is a moniker for the College of William & Mary's athletic teams and the university's community more broadly.
William & Mary has won two team national championships (both in men's tennis), the AIAW championships in ...
in Williamsburg and Hampton Pirates in Hampton. W&M is a member of the Colonial Athletic Association
The Colonial Athletic Association (CAA) is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference affiliated with the National Collegiate Athletic Association, NCAA's NCAA Division I, Division I whose full members are located in East Coast ...
. Norfolk State and Hampton, both historically black institutions, compete in the Mid-Eastern Athletic Conference. ODU joined Conference USA
Conference USA (C-USA or CUSA) is an intercollegiate athletic conference whose current member institutions are located within the Southern United States. The conference participates in the NCAA's Division I in all sports. C-USA's offices are ...
, an FBS football conference, as a full FBS member in 2015. The area also has two Division III programs, one in each subregion—the Virginia Wesleyan Marlins on the border of Virginia Beach and Norfolk, and the Christopher Newport University Captains in Newport News. The Captains sponsor fourteen sports and currently compete in the USA South Athletic Conference
The USA South Athletic Conference (formerly the Dixie Intercollegiate Athletic Conference or the Dixie Conference) is an athletic conference which competes in the NCAA's Division III. Member schools are located in North Carolina and Virginia ...
, but will move to the Capital Athletic Conference
The Coast to Coast Athletic Conference (C2C; officially stylized as Coast-to-Coast Athletic Conference), formerly named Capital Athletic Conference (CAC), is an intercollegiate athletic conference affiliated with the NCAA's Division III. Member ...
in July 2013.
Virginia Beach serves as home to one soccer team, the Hampton Roads Piranhas
Hampton Roads Piranhas was an American women's soccer team, founded in 1995. The team was a member of the United Soccer Leagues W-League, the second tier of women's soccer in the United States and Canada. The team played in the Atlantic Division ...
, a women's team in the W-League, as the Virginia Beach Piranhas dissolved in 2014. The Piranhas play at the Virginia Beach Sportsplex. The Virginia Beach Sportsplex, seating 11,541 and opened in 1999, contains the central training site for the U.S. women's national field hockey
Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting ...
team. The Sportsplex was expanded to accommodate the Virginia Destroyers, a franchise in the United Football League which relocated from Orlando. The Destroyers played in Virginia Beach from 2011 to 2012, and won the 2011 league championship. The North American Sand Soccer Championships
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' is ...
, a beach soccer
Beach soccer, also known as beach football, sand football or beasal, is a variant of association football played on a beach or some form of sand.
Whilst football has been played informally on beaches, the introduction of ''beach soccer'' was a ...
tournament, is held annually on the beach in Virginia Beach.
The Norfolk Nighthawks
The Norfolk Nighthawks are a now-defunct charter member of the AF2. They played their home games at The Norfolk Scope Arena in Norfolk, Virginia. After a very impressive inaugural season, the Nighthawks never made it back to the playoffs and c ...
were a charter member of the Arena Football League
The Arena Football League (AFL) was a professional arena football league in the United States. It was founded in 1986, but played its first official games in the 1987 season, making it the third longest-running professional football league in ...
's minor league, af2. They ceased operations in 2003 after their fourth season. Also, the Virginia Beach Mariners of soccer's USL First Division
The USL First Division (usually referred to as USL-1) was a professional men's soccer league in the United States and Canada from 2005 to 2010.
During its existence, it formed the second tier of soccer in the United States soccer league system ...
were active from 1994 until 2006.
Hampton Roads is from the nearest major sports teams in Washington, D.C. and Raleigh, North Carolina
Raleigh (; ) is the capital city of the state of North Carolina and the seat of Wake County in the United States. It is the second-most populous city in North Carolina, after Charlotte. Raleigh is the tenth-most populous city in the Sout ...
. Another significant issue with the area as a sports market is internal transportation. The metropolitan area is split into two distinct parts by its eponymous harbor; as of 2012, the harbor has only three widely separated road crossings (the Hampton Roads Bridge-Tunnel, Monitor-Merrimac Memorial Bridge-Tunnel, and James River Bridge
The James River Bridge (JRB) is a four-lane divided highway lift bridge across the James River in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Owned and operated by the Virginia Department of Transportation, it carries U.S. Route 17 (US 17), US 258, ...
), each with two lanes of traffic in each direction. In addition, the area has two other major tunnels, plus several drawbridges on key highway corridors.
Hampton Roads previously hosted a successful franchise in the American Basketball Association
The American Basketball Association (ABA) was a major men's professional basketball league from 1967 to 1976. The ABA ceased to exist with the American Basketball Association–National Basketball Association merger in 1976, leading to four A ...
, although it was never a full-time home for that team. Its highest-ranking teams as of 2015 are the Norfolk Admirals Norfolk Admirals has been the name of two professional ice hockey franchises:
*Norfolk Admirals (AHL), a team which played in the American Hockey League from 2000 to 2015
*Norfolk Admirals (ECHL)
The Norfolk Admirals are a professional ice hocke ...
of the ECHL
The ECHL (formerly the East Coast Hockey League) is a mid-level professional ice hockey league based in Shrewsbury, New Jersey, with teams scattered across the United States and Canada. It is a tier below the American Hockey League (AHL).
The ...
, the Norfolk Tides of the IL, and Lionsbridge FC of USL League Two. Virginia is also the most populous state without a major league team playing within its borders, though its northern reaches are served by the Washington clubs — two of which, the NHL's Capitals
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
and NFL's Washington Commanders, have their operational headquarters and practice facilities in Virginia. Washington Commanders owner Daniel Snyder, through a separate company, owns two radio stations, WXTG and WXTG-FM, in the Norfolk market. The Hampton Roads television market is ranked 42nd in the U.S.
There have been several failed projects to attract major league teams to Hampton Roads:
* In 1997, Norfolk presented a proposal to bring an expansion hockey team to Hampton Roads, but that initiative failed. The team was going to be called the Hampton Roads Rhinos
The Hampton Roads Rhinos were a potential National Hockey League expansion team that was to begin play in the late-1990s in Norfolk, Virginia. The franchise would have been under the ownership of George Shinn and play in a proposed $142 million ...
.
* In 2002, Norfolk presented a proposal to bring the Charlotte Hornets basketball team to southeastern Virginia, but New Orleans won the bid for the team, renaming it the New Orleans Hornets.
* In 2004, Norfolk presented a proposal to bring the Montreal Expos
The Montreal Expos (french: link=no, Les Expos de Montréal) were a Canadian professional baseball team based in Montreal, Quebec. The Expos were the first Major League Baseball (MLB) franchise located outside the United States. They played in ...
baseball team to the metro area, but Washington, D.C. won the bid for the team, renaming it the Washington Nationals
The Washington Nationals are an American professional baseball team based in Washington, D.C.. They compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member of the National League (NL) East division. From 2005 to 2007, the team played in RFK Stadiu ...
.
* In 2012, there were talks of the Sacramento Kings of the NBA moving to a proposed new arena in Virginia Beach near the Oceanfront.
Individual sports
TheHampton Coliseum
Hampton Coliseum is a multi-purpose arena in Hampton, Virginia. Construction began on May 24, 1968. The venue held its first event on December 1, 1969, with the nearby College of William & Mary playing North Carolina State University in a coll ...
, seating 10,761 to 13,800 festival seating, hosts the annual Virginia Duals wrestling events, and the annual Hampton Jazz Festival. The arena opened in 1970 and has previously hosted Hampton University
Hampton University is a private, historically black, research university in Hampton, Virginia. Founded in 1868 as Hampton Agricultural and Industrial School, it was established by Black and White leaders of the American Missionary Association a ...
basketball along with NBA and NHL preseason exhibition games.
Virginia Beach is home to the East Coast Surfing Championships The East Coast Surfing Championships (ECSC) is an annual surfing contest held in Virginia Beach, Virginia on the oceanfront, and is one of the United States Surfing Federation’s major amateur events. The ECSC stretches over a four-day period ev ...
, an annual contest of more than 100 of the world's top professional surfers and an estimated 400 amateur surfers. This is North America's oldest surfing contest, and features combined cash prizes of $40,000.
Langley Speedway in Hampton, seating 6,500, hosts stock car races every weekend during spring, summer, and early fall.
The Kingsmill Championship
The Pure Silk Championship was a women's professional golf tournament on the LPGA Tour, played in Williamsburg, Virginia. The 72-hole tournament was held on the par-71 River Course at Kingsmill Resort, set at in 2013.
Previously known as t ...
, an event on the LPGA Tour, is contested annually on Mother's Day weekend at Kingsmill Resort near Williamsburg.
In 1998, 2001, 2006, 2010, and 2015 the Hampton Roads Sports Commission hosted the AAU Junior Olympics
The AAU Junior Olympic Games'' are the pinnacle competitions held annually by the US Amateur Athletic Union.
Overview
The AAU Junior Olympic Games are known as the largest national multi-sport event for youth in the United States. It has become t ...
.
Professional wrestling
Hampton Roads has hosted many professional wrestling events throughout the years. The Norfolk Scope has served as the site of these events, includingTotal Nonstop Action Wrestling
Impact Wrestling (stylized as ''IMPACT! Wrestling''), is an American professional wrestling promotion based in Nashville, Tennessee. It is a subsidiary of Anthem Sports & Entertainment.
Founded by Jeff and Jerry Jarrett in 2002, the prom ...
's Destination X, World Championship Wrestling
World Championship Wrestling, Inc. (WCW) was an American professional wrestling promotion founded by Ted Turner in 1988, after Turner Broadcasting System, through a subsidiary named Universal Wrestling Corporation, purchased the assets of Nati ...
's Starrcade (1988)
Starrcade '88: True Gritt was the sixth annual Starrcade professional wrestling pay-per-view (PPV) event produced under the National Wrestling Alliance (NWA) banner. It was the first Starrcade event produced by World Championship Wrestling (WCW), ...
, World War 3 1995 and 1996
File:1996 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: A bomb explodes at Centennial Olympic Park in Atlanta, set off by a radical anti-abortionist; The center fuel tank explodes on TWA Flight 800, causing the plane to crash and killing everyone o ...
, and WWF/WWE's The Great American Bash (2004) and the 2011 Slammy Awards. Norfolk Scope was also the site of an infamous episode of WCW Monday Nitro, where several members of the World Wrestling Federation
World Wrestling Entertainment, Inc., d/b/a as WWE, is an American professional wrestling promotion. A global integrated media and entertainment company, WWE has also branched out into other fields, including film, American football, and var ...
stable D-Generation X literally drove a tank to the entryway of the Scope, thus "invading" the competition. The Hampton Coliseum has also hosted many events, including '' RAW'', in April 1998, August 2005, May 2007, January 2008, and July 2011, as well as '' SmackDown!'' and for '' ECW on Sci Fi'' in December 2006. In January 2008, WWE broadcast its first television show taped in high definition from Hampton, Virginia.
The Hampton Roads area is also home to at least one professional wrestling promotion, Vanguard Championship Wrestling, which holds events throughout the region, and has a weekly television show on the local Fox affiliate.
See also
* 2003 Virginia earthquake *Colonial Williamsburg
Colonial Williamsburg is a living-history museum and private foundation presenting a part of the historic district in the city of Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. The Colonial Williamsburg Foundation has 7300 employees at this location ...
* Former counties, cities, and towns of Virginia
* Historic Triangle
* Jamestown, Virginia
* List of people from Hampton Roads
* List of tallest buildings in Norfolk, Virginia
The history of high-rises in Norfolk, Virginia, began in the early 1900s with the construction of such structures as the 12-story Royster Building in 1912.
The skyline of Downtown Norfolk remained relatively low to mid-rise until the 1960s whi ...
* South Hampton Roads
* Tidewater region
* Virginia Peninsula
* Virginia Port Authority
References
Sources
*External links
Hampton Roads Planning District Commission
Hampton Roads Transportation Planning Organization
Hampton Roads Transportation Accountability Commission
Hampton Roads Chamber
Hampton Roads Sports Commission
Hampton Roads Economic Development Alliance
Hampton Roads Military and Federal Facilities Alliance
Hampton Roads Sanitation District
Hampton Roads Housing Consortium
Norfolk City Historical Society
contains essays
– Norfolk Public Library
{{Authority control Bodies of water of Virginia James River (Virginia) Ports and harbors of Virginia Regions of Virginia Roadsteads Northeast megalopolis