Hamangia culture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hamangia culture is a Late
 The Hamangia culture began around 5250/5200 BC and lasted until around 4550/4500 BC. It was absorbed by the expanding Boian culture in its transition towards the Gumelniţa.
Its cultural links with
The Hamangia culture began around 5250/5200 BC and lasted until around 4550/4500 BC. It was absorbed by the expanding Boian culture in its transition towards the Gumelniţa.
Its cultural links with
Unitate şi diversitate în culturile neolitice de la dunărea de jos = Unity and diversity of Neolithic cultures along the lower Danube
''Revista Pontica'' vol. 30 (1997), pp. 105-116.
File:Human-sized clay head found at Varna necropolis.png, Life-sized clay head, c. 4500 BC
File:Hamangia Muzeul din Constanta.JPG, Male and female figurines
File:坐着的女人塑像.JPG, Female figurine, "The Sitting Woman"
File:Durankulak-Golemija ostrov-Hamangia IV vessels.jpg, Pottery
File:08 ENEOLIT-Ceramik.tif, Pottery
File:Female figurines, clay, ivory, bone, 4900-4600 BC, AM Varna, Varm51.jpg, Figurines
File:Durankulak-nekropola Hamangia.tif, Anthropomorphic pottery
File:2006 0814Hamangia Histria Museum20060298.jpg, Figurine
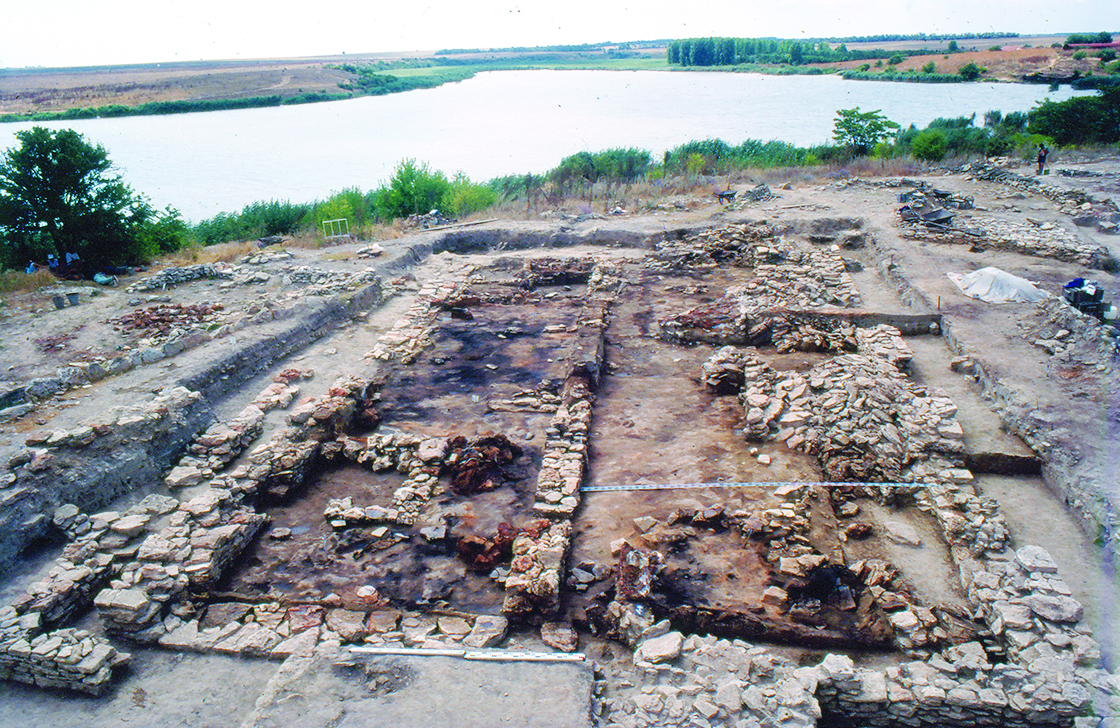
 Settlements consist of rectangular houses with one or two rooms, built of
Settlements consist of rectangular houses with one or two rooms, built of
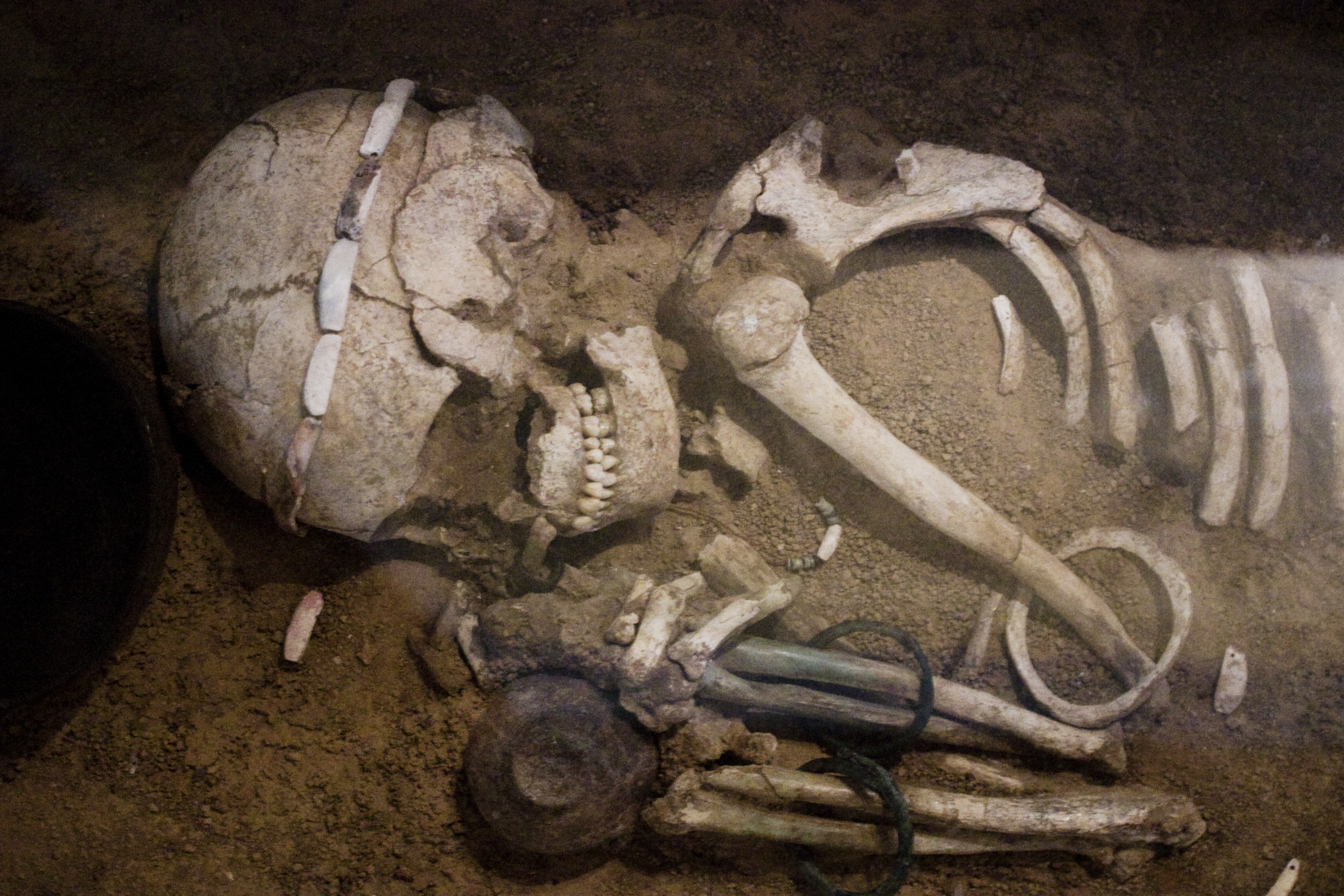 Crouched or extended inhumation in cemeteries. Grave-goods tend to be without pottery in Hamangia I. Grave-goods include flint, worked shells, bone tools and shell-ornaments.
Crouched or extended inhumation in cemeteries. Grave-goods tend to be without pottery in Hamangia I. Grave-goods include flint, worked shells, bone tools and shell-ornaments.
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several par ...
archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between these ...
of Dobruja (Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
) between the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Ro ...
and Muntenia
Muntenia (, also known in English as Greater Wallachia) is a historical region of Romania, part of Wallachia (also, sometimes considered Wallachia proper, as ''Muntenia'', ''Țara Românească'', and the seldom used ''Valahia'' are synonyms in ...
in the south. It is named after the site of Baia-Hamangia __NOTOC__
Baia is a commune in Tulcea County, Northern Dobruja, Romania.
Villages
The commune includes five villages:
* Baia (''Hamangia'' until 1929, tr, Hamamci)
* Camena
* Caugagia ( tr, Kavgaci)
* Ceamurlia de Sus (''Yeni Kazak'' until ca. 1 ...
, discovered in 1952 along Golovița Lake.
Genesis and successor
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
suggest that it was the result of a recent settlement by people from Anatolia, unlike the neighbouring cultures, which appear descended from earlier Neolithic settlement.M. NicaUnitate şi diversitate în culturile neolitice de la dunărea de jos = Unity and diversity of Neolithic cultures along the lower Danube
''Revista Pontica'' vol. 30 (1997), pp. 105-116.
Art
The Hamangia culture attracted and attracts the attention of many art historians because of its exceptional clay figures.Pottery
Painted vessels with complex geometrical patterns based on spiral-motifs are typical. The shapes include: bowls and cylindric glasses (most of them with arched walls). They are decorated with dots, straight parallel lines and zig-zags, which make Hamangia pottery very original.Figurines
Pottery figurines are normally extremely stylized and show standing naked faceless women with emphasized breasts and buttocks. Two figurines known as "The Thinker" and "The Sitting woman" are considered masterpieces of Neolithic art.Gallery
Settlements
 Settlements consist of rectangular houses with one or two rooms, built of
Settlements consist of rectangular houses with one or two rooms, built of wattle and daub
Wattle and daub is a composite building method used for making walls and buildings, in which a woven lattice of wooden strips called wattle is daubed with a sticky material usually made of some combination of wet soil, clay, sand, animal dung ...
, sometimes with stone foundations (in Durankulak
Durankulak ( bg, Дуранкулак ) is a village in northeastern Bulgaria, part of Shabla Municipality, Dobrich Province. Located in the historical region of Southern Dobruja, Durankulak is the north-easternmost inhabited place in Bulgaria ...
). They are normally arranged on a rectangular grid and may form small tells. Settlements are located along the coast, on the coast of lakes, on lower or middle river terraces.
Important sites
*TheDurankulak lake
Durankulak ( bg, Дуранкулак ) is a village in northeastern Bulgaria, part of Shabla Municipality, Dobrich Province. Located in the historical region of Southern Dobruja, Durankulak is the north-easternmost inhabited place in Bulgaria a ...
settlement, now Archaeological Complex Durankulak
Durankulak is a prehistoric archaeological site on the Golemija ostrov (Big Island) in Durankulak lake, Bulgaria. Prehistoric settlement commenced on the small island approximately 7000 BP and lasted for thousands of years.
The first inhabitant ...
, commenced on a small island, approximately 7000 BC and around 4700/4600 BC the stone architecture was already in general use and became a characteristic phenomenon that was unique in Europe.
*Cernavodă
Cernavodă () is a town in Constanța County, Northern Dobruja, Romania with a population of 20,514.
The town's name is derived from the Bulgarian ''černa voda'' (черна вода in Cyrillic), meaning 'black water'. This name is regarded ...
, the necropolis
A necropolis (plural necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'', literally meaning "city of the dead".
The term usually im ...
where the famous statues "The Thinker" and "The Sitting Woman" were discovered
*The eponymous site of Baia-Hamangia __NOTOC__
Baia is a commune in Tulcea County, Northern Dobruja, Romania.
Villages
The commune includes five villages:
* Baia (''Hamangia'' until 1929, tr, Hamamci)
* Camena
* Caugagia ( tr, Kavgaci)
* Ceamurlia de Sus (''Yeni Kazak'' until ca. 1 ...
, discovered in 1953 along Lake Golovița, close to the Black Sea coast, in the Romanian province of Dobrogea.
Inhumation
 Crouched or extended inhumation in cemeteries. Grave-goods tend to be without pottery in Hamangia I. Grave-goods include flint, worked shells, bone tools and shell-ornaments.
Crouched or extended inhumation in cemeteries. Grave-goods tend to be without pottery in Hamangia I. Grave-goods include flint, worked shells, bone tools and shell-ornaments.
See also
*Cycladic art
The ancient Cycladic culture flourished in the islands of the Aegean Sea from c. 3300 to 1100 BCE. Along with the Minoan civilization and Mycenaean Greece, the Cycladic people are counted among the three major Aegean cultures. Cycladic art therefo ...
*Varna culture
The Varna culture is a Chalcolithic culture of northeastern Bulgaria, dated ca. 4500 BC, contemporary and closely related with Gumelnița in southern Romania, often considered as local variants.
It is characterized by polychrome pottery and r ...
*Vinča culture
The Vinča culture (), also known as Turdaș culture or Turdaș–Vinča culture, is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southeast Europe, dated to the period 5700–4500 BC or 5300–4700/4500 BC.. Named for its type site, Vinča-Belo Brdo ...
* Cucuteni-Trypillia culture
* Old Europe
*Prehistory of Southeastern Europe
The prehistory of Southeastern Europe, defined roughly as the territory of the wider Southeast Europe (including the territories of the modern countries of Albania,
Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Greece, Kosovo, Moldova, Monte ...
*History of Bulgaria
The history of Bulgaria can be traced from the first settlements on the lands of Bulgaria, modern Bulgaria to its formation as a nation-state, and includes the history of the Bulgarians, Bulgarian people and their origin. The earliest evidence of ...
* Prehistoric Romania
*Prehistoric art
In the history of art, prehistoric art is all art produced in preliterate, Prehistory, prehistorical cultures beginning somewhere in very late geological history, and generally continuing until that culture either develops writing or other met ...
* List of Stone Age art
References
External links
{{Prehistoric technology Archaeological cultures in Romania Archaeological cultures in Bulgaria Archaeological cultures of Eastern Europe Prehistory of Southeastern Europe Prehistoric art Stone Age Europe Prehistoric Bulgaria