HMS Hermes (1913) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
HMS ''Hermes'' was a
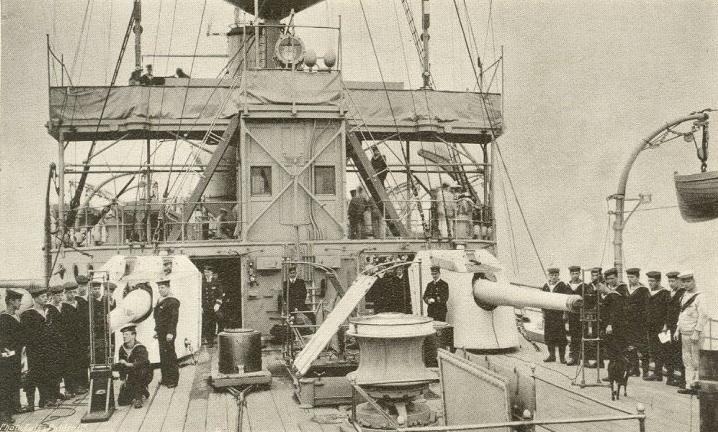 ''Hermes'' was designed to displace . The ship had an
''Hermes'' was designed to displace . The ship had an
 ''Hermes'', named after the Greek god
''Hermes'', named after the Greek god
/ref> Her wreck lies upside down in approximately of water at coordinates . In January 2017, two English divers were charged with failing to declare items removed from the wreck of ''Hermes'', in contravention of the
Highflyer class in World War I
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hermes Highflyer-class cruisers Ships built in Govan 1898 ships Seaplane carriers of the Royal Navy World War I aircraft carriers of the United Kingdom Ships sunk by German submarines in World War I World War I shipwrecks in the English Channel Maritime incidents in October 1914
protected cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of naval cruiser of the late-19th century, gained their description because an armoured deck offered protection for vital machine-spaces from fragments caused by shells exploding above them. Protected cruisers re ...
built for the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
in the 1890s. She spent much of her early career as flagship for various foreign stations before returning home in 1913 to be assigned to the reserve
Reserve or reserves may refer to:
Places
* Reserve, Kansas, a US city
* Reserve, Louisiana, a census-designated place in St. John the Baptist Parish
* Reserve, Montana, a census-designated place in Sheridan County
* Reserve, New Mexico, a US vi ...
Third Fleet. The ship was modified later that year as the first experimental seaplane carrier
A seaplane tender is a boat or ship that supports the operation of seaplanes. Some of these vessels, known as seaplane carriers, could not only carry seaplanes but also provided all the facilities needed for their operation; these ships are rega ...
in the Royal Navy. In that year's annual fleet manoeuvers, she was used to evaluate how aircraft could cooperate with the fleet and if aircraft could be operated successfully at sea for an extended time. The trials were a success and ''Hermes'' was paid off
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in ...
in December at their conclusion. She was recommissioned at the beginning of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in August 1914 for service as an aircraft ferry and depot ship
A depot ship is an auxiliary ship used as a mobile or fixed base for submarines, destroyers, minesweepers, fast attack craft, landing craft, or other small ships with similarly limited space for maintenance equipment and crew dining, berthing and ...
for the Royal Naval Air Service. She was torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, s ...
ed and sunk by a German submarine in the Straits of Dover that October, with the loss of 21 lives.
Design and description
 ''Hermes'' was designed to displace . The ship had an
''Hermes'' was designed to displace . The ship had an overall length
The overall length (OAL) of an ammunition cartridge is a measurement from the base of the brass shell casing to the tip of the bullet, seated into the brass casing. Cartridge overall length, or "COL", is important to safe functioning of reloads i ...
of , a beam of and a draught of . She was powered by two 4-cylinder triple-expansion steam engines, each driving one shaft, which produced a total of designed to give a maximum speed of . ''Hermes'' reached a speed of from , during her sea trials
A sea trial is the testing phase of a watercraft (including boats, ships, and submarines). It is also referred to as a "shakedown cruise" by many naval personnel. It is usually the last phase of construction and takes place on open water, and i ...
. The engines were powered by 18 Belleville boiler
There have been a vast number of designs of steam boiler, particularly towards the end of the 19th century when the technology was evolving rapidly. A great many of these took the names of their originators or primary manufacturers, rather than a m ...
s.Chesneau & Kolesnik, p. 79 She carried a maximum of of coal and her complement consisted of 470 officers and ratings.Friedman 2012, p. 336
Her main armament consisted of 11 quick-firing (QF) Mk I guns. One gun was mounted on the forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase " be ...
and two others were positioned on the quarterdeck. The remaining eight guns were placed port and starboard amidships
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water (mostly though not necessarily on the sea). Some remain current, while many date from the 17th ...
. They had a maximum range of approximately with their shells. Eight quick-firing (QF) 12-pounder 12 cwt guns were fitted for defence against torpedo boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of ...
s. One additional 12-pounder 8 cwt gun could be dismounted for service ashore. ''Hermes'' also carried six 3-pounder Hotchkiss guns and two submerged 18-inch torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
s.
The ship's protective deck armour ranged in thickness from . The engine hatches were protected by of armour. The main guns were fitted with 3-inch gun shields and the conning tower had armour 6 inches thick.
Construction and service
 ''Hermes'', named after the Greek god
''Hermes'', named after the Greek god Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, wikt:Ἑρμῆς, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travelle ...
,Silverstone, p. 238 was laid down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship.
Keel laying is one o ...
by Fairfield Shipbuilding & Engineering
The Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company, Limited was a Scottish shipbuilding company in the Govan area on the Clyde in Glasgow. Fairfields, as it is often known, was a major warship builder, turning out many vessels for the Royal Navy ...
at their shipyard in Govan
Govan ( ; Cumbric?: ''Gwovan'?''; Scots: ''Gouan''; Scottish Gaelic: ''Baile a' Ghobhainn'') is a district, parish, and former burgh now part of south-west City of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated west of Glasgow city centre, on the south ba ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
on 30 April 1897, and launched on 7 April 1898, when she was named by Lady Kelvin. She was completed on 5 October 1899, and commissioned for service on the North America and West Indies Station
The North America and West Indies Station was a formation or command of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy stationed in North American waters from 1745 to 1956. The North American Station was separate from the Jamaica Station until 1830 when the ...
by Captain Frank Hannam Henderson. She visited Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
and the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
in January 1900, and two months later arrived in Nassau, Bahamas with her shaft broken and boilers damaged. Towed to Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
by , she then underwent repairs in the dockyard at Kingston, Jamaica. She served as the flagship of the North America and West Indies Station until late 1901 when she returned home to have her troublesome Belleville boilers replaced with Babcock & Wilcox boilers. The work was undertaken by Harland & Wolff
Harland & Wolff is a British shipbuilding company based in Belfast, Northern Ireland. It specialises in ship repair, shipbuilding and offshore construction. Harland & Wolff is famous for having built the majority of the ocean liners for the W ...
at Belfast
Belfast ( , ; from ga, Béal Feirste , meaning 'mouth of the sand-bank ford') is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdom ...
, where she arrived from Devonport in May 1902, in tow of the special service vessel HMS ''Traveller''.
She was assigned to the Channel Fleet until 1905 when she was reduced to reserve at Portsmouth Royal Dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is l ...
. The ship was recommissioned the following year as the flagship of the East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around ...
station, but she became the flagship of the Cape of Good Hope Station
The Commander-in-Chief, Africa was the last title of a Royal Navy's formation commander located in South Africa from 1795 to 1939. Under varying titles, it was one of the longest-lived formations of the Royal Navy. It was also often known as the C ...
in 1907. ''Hermes'' returned home in March 1913 and was reduced to reserve as part of the Nore Command
The Commander-in-Chief, The Nore, was an operational commander of the Royal Navy. His subordinate units, establishments, and staff were sometimes informally known as the Nore Station or Nore Command. The Nore is a sandbank at the mouth of the Th ...
the next month.Hobbs, p. 18
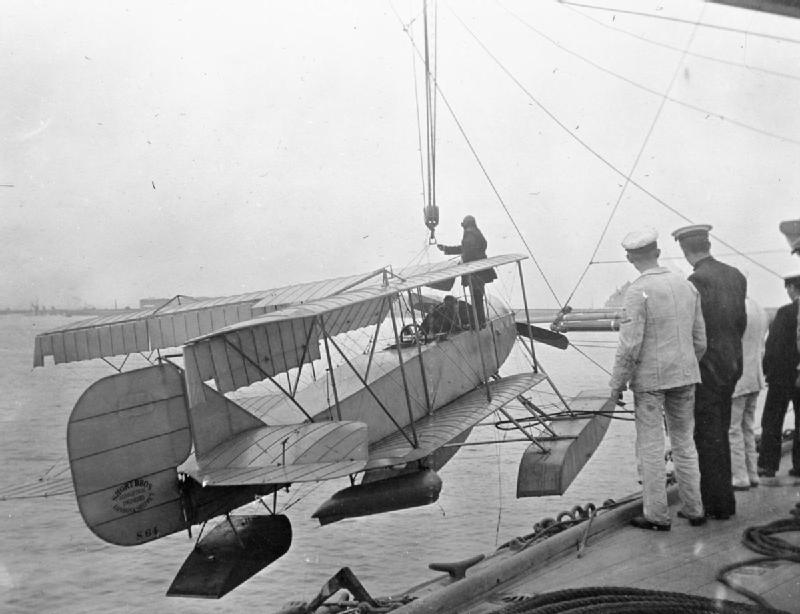
Work began to modify her to accommodate three seaplanes in April to evaluate the use of aircraft in support of the fleet. Her forward 6-inch gun was removed and a tracked launching platform was built over the forecastle. A canvas hangar
A hangar is a building or structure designed to hold aircraft or spacecraft. Hangars are built of metal, wood, or concrete. The word ''hangar'' comes from Middle French ''hanghart'' ("enclosure near a house"), of Germanic origin, from Frankish ...
was fitted at the aft end of the rails to shelter the aircraft from the weather and a derrick
A derrick is a lifting device composed at minimum of one guyed mast, as in a gin pole, which may be articulated over a load by adjusting its guys. Most derricks have at least two components, either a guyed mast or self-supporting tower, and ...
was rigged from the foremast
The mast of a sailing vessel is a tall spar, or arrangement of spars, erected more or less vertically on the centre-line of a ship or boat. Its purposes include carrying sails, spars, and derricks, and giving necessary height to a navigation ...
to lift the seaplane from the water. The guns on the quarterdeck were removed to allow for a seaplane to be stowed there in another hangar. A third aircraft could also be carried amidships, exposed to the elements. Three storage lockers were fitted with a total capacity of of petrol
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
in tins.Friedman 1988, p. 28
''Hermes'' was recommissioned on 7 May and loaded two unknown aircraft on 5 July, making nine flights with them before 14 July. For the trials she initially used a Borel Bo.11 and a Short Folder, but the Borel was damaged in a storm and replaced by a Caudron G.2 amphibian. This latter aircraft took off successfully while the ship was moving on 28 July, but the take-off platform only seems to have been used twice during this time. During the manoeuvers, she simulated a reconnaissance Zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp ...
for the Red Fleet, commanded by Vice Admiral John Jellicoe
Admiral of the Fleet John Rushworth Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, (5 December 1859 – 20 November 1935) was a Royal Navy officer. He fought in the Anglo-Egyptian War and the Boxer Rebellion and commanded the Grand Fleet at the Battle of Jutlan ...
. The Folder could only carry a small wireless transmitter because of weight limits and it would be launched to search for enemy ships and report back to Hermes which would retransmit its message with its more powerful transmitter. The aircraft made a total of about 30 flights before 6 October. The tests showed that aircraft required radio transmitters to usefully perform reconnaissance, that sustained use of aircraft at sea was possible and that handling aircraft aboard ship and on the sea imposed their own set of requirements that could not be met by converted land-based aircraft.
The ship was paid off on 30 December, but was recommissioned on 31 August 1914. Assigned to the Nore Command, she was used to ferry aircraft and stores to France. It is uncertain if the flying-off platform was reinstalled. On 30 October she arrived at Dunkirk with one load of seaplanes. The next morning, ''Hermes'' set out on the return journey but was recalled because a German submarine was reported in the area. Despite zigzagging at a speed of , she was torpedoed by at a range of . ''Hermes'' sank off Ruylingen Bank in the Straits of Dover with the loss of 21 of her crew.Roll of Honour, list of casualties/ref> Her wreck lies upside down in approximately of water at coordinates . In January 2017, two English divers were charged with failing to declare items removed from the wreck of ''Hermes'', in contravention of the
Protection of Military Remains Act 1986
Protection is any measure taken to guard a thing against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights. Although th ...
.
Notes
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * *External links
Highflyer class in World War I
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hermes Highflyer-class cruisers Ships built in Govan 1898 ships Seaplane carriers of the Royal Navy World War I aircraft carriers of the United Kingdom Ships sunk by German submarines in World War I World War I shipwrecks in the English Channel Maritime incidents in October 1914