H2S radar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 H2S was the first airborne, ground scanning radar system. It was developed for the
H2S was the first airborne, ground scanning radar system. It was developed for the
 In October 1941, Dee attended a meeting of the RAF Bomber Command where the night targeting issue was discussed. Dee mentioned the recent discoveries using AIS. On 1 November, Dee performed an experiment in which he used an AIS radar mounted on a Blenheim to scan the ground. Using this display he was able to pick up the outline of a town away while flying at altitude.
The commanders were impressed and, on 1 January 1942, the TRE set up a team under Bernard Lovell to develop an S-band airborne targeting radar based on AIS. An initial order for 1,500 sets was placed. It was clear even at this point that a Plan Position Indicator (PPI) display would be desirable, but this would require a complex scanning parabolic antenna, compared to the very simple set of fixed antennas used in the A-scope system. It was decided to test both systems. In March, it was decided that both H2S and a new centimetric Air-Surface-Vessel radar (ASV) radar, ASV Mk. III, would be built using the same components, simplifying production.
In early tests in April, the superiority of the scanning PPI system was evident, and all work on the older A-scope version ended. H2S performed its first experimental flight on 23 April 1942, with the radar mounted in a
In October 1941, Dee attended a meeting of the RAF Bomber Command where the night targeting issue was discussed. Dee mentioned the recent discoveries using AIS. On 1 November, Dee performed an experiment in which he used an AIS radar mounted on a Blenheim to scan the ground. Using this display he was able to pick up the outline of a town away while flying at altitude.
The commanders were impressed and, on 1 January 1942, the TRE set up a team under Bernard Lovell to develop an S-band airborne targeting radar based on AIS. An initial order for 1,500 sets was placed. It was clear even at this point that a Plan Position Indicator (PPI) display would be desirable, but this would require a complex scanning parabolic antenna, compared to the very simple set of fixed antennas used in the A-scope system. It was decided to test both systems. In March, it was decided that both H2S and a new centimetric Air-Surface-Vessel radar (ASV) radar, ASV Mk. III, would be built using the same components, simplifying production.
In early tests in April, the superiority of the scanning PPI system was evident, and all work on the older A-scope version ended. H2S performed its first experimental flight on 23 April 1942, with the radar mounted in a  Then disaster occurred; on 7 June 1942, the Halifax performing H2S tests crashed, killing everyone on board and destroying the prototype H2S. One of the dead was Alan Blumlein, the chief designer, and his loss was a huge blow to the programme. Also killed in the crash were Blumlein's colleagues Cecil Oswald Browne and Frank Blythen; a TRE scientist Geoffrey S. Hensby, and seven RAF personnel.
Then disaster occurred; on 7 June 1942, the Halifax performing H2S tests crashed, killing everyone on board and destroying the prototype H2S. One of the dead was Alan Blumlein, the chief designer, and his loss was a huge blow to the programme. Also killed in the crash were Blumlein's colleagues Cecil Oswald Browne and Frank Blythen; a TRE scientist Geoffrey S. Hensby, and seven RAF personnel.
 As development continued, a great debate broke out in the Air Ministry and RAF about the relative merits of the H2S system. While the ability to bomb in all weather at great distances was obviously useful to Bomber Command, the loss of an H2S aircraft would potentially reveal the secret of the magnetron to the Germans. Churchill's science advisor, Frederick Lindemann, wanted the design team to build H2S around the
As development continued, a great debate broke out in the Air Ministry and RAF about the relative merits of the H2S system. While the ability to bomb in all weather at great distances was obviously useful to Bomber Command, the loss of an H2S aircraft would potentially reveal the secret of the magnetron to the Germans. Churchill's science advisor, Frederick Lindemann, wanted the design team to build H2S around the
 The Air Ministry radar groups had originally formed up at
The Air Ministry radar groups had originally formed up at
 Despite all the problems, on 3 July 1942 Churchill held a meeting with his military commanders and the H2S group, where he surprised the radar designers by demanding the delivery of 200 H2S sets by 15 October 1942. The H2S design team was under great pressure, but they were given priority on resources. The pressure also gave them an excellent argument to convince Lord Cherwell that the klystron-based H2S program finally be dropped.
TRE failed to meet the 15 October deadline; by 1 January 1943, only twelve
Despite all the problems, on 3 July 1942 Churchill held a meeting with his military commanders and the H2S group, where he surprised the radar designers by demanding the delivery of 200 H2S sets by 15 October 1942. The H2S design team was under great pressure, but they were given priority on resources. The pressure also gave them an excellent argument to convince Lord Cherwell that the klystron-based H2S program finally be dropped.
TRE failed to meet the 15 October deadline; by 1 January 1943, only twelve
 The original H2S sets were essentially prototype units that were hand-built to equip the Pathfinders with all possible speed. Among the many problems with the rushed service entry was that the developers were forced to use existing plug-and-socket designs to connect the various units of the complete set together. There were no bulkhead mounting male connectors available at this time, and consequently many of the male free connectors at the ends of cable runs carried exposed lethal voltages. While installations of the prototypes progressed, work was underway on a true production version, the Mk. II, which would go on to be the most numerous version built. This was largely identical to the Mk. I's with the exception of various packaging and electronics details intended to make them easier to build.
Bomber Command started general use of H2S in summer 1943. On the night of 24 July, the RAF began
The original H2S sets were essentially prototype units that were hand-built to equip the Pathfinders with all possible speed. Among the many problems with the rushed service entry was that the developers were forced to use existing plug-and-socket designs to connect the various units of the complete set together. There were no bulkhead mounting male connectors available at this time, and consequently many of the male free connectors at the ends of cable runs carried exposed lethal voltages. While installations of the prototypes progressed, work was underway on a true production version, the Mk. II, which would go on to be the most numerous version built. This was largely identical to the Mk. I's with the exception of various packaging and electronics details intended to make them easier to build.
Bomber Command started general use of H2S in summer 1943. On the night of 24 July, the RAF began
 It was noted on even the earliest flights of ''V9977'' that a number of basic features of the H2S made it difficult to use. Attempts to fix these began even before H2S entered service, but a number of problems greatly delayed their entry. Added as they became available, this produced a profusion of different Marks, detailed below.
Late in April 1942, during a test flight of ''V9977'', the prototype unit was shown to Flight Lieutenant E. Dickie, a navigator. Dickie pointed out that
It was noted on even the earliest flights of ''V9977'' that a number of basic features of the H2S made it difficult to use. Attempts to fix these began even before H2S entered service, but a number of problems greatly delayed their entry. Added as they became available, this produced a profusion of different Marks, detailed below.
Late in April 1942, during a test flight of ''V9977'', the prototype unit was shown to Flight Lieutenant E. Dickie, a navigator. Dickie pointed out that
 Radar operates by sending out very short pulses of a radio signal from a transmitter, then turning the transmitter off and listening for echoes in a receiver. The output of the receiver is sent to an oscilloscope's brightness input, so strong echoes cause a spot on the screen to light up. To make the spots correspond to locations in space, the oscilloscope quickly scans from the centre to the outside of the display; echoes that return later in time are produced further out on the display, indicating a further distance from the aircraft. The times are synchronized by using the transmission pulse to trigger the scan.
In the case of H2S, the echoes are returned from the ground and objects on it. That means the very first signal that would normally be received would be from the ground directly beneath the aircraft, as this is the closest to the aircraft. Since the echo from this location took some time to return to the aircraft, the time needed to travel to the ground and back at the aircraft's current altitude, the H2S display naturally had an empty area around the centre of the display, with its radius representing the altitude of the aircraft. This was known as the ''centre-zero''. Normally the operator used a dial that delayed the start of the sweep in order to reduce the size of this centre-zero, and thereby increase the amount of the screen used for the ground display.
When the centre-zero was not entirely dialled out, operators noticed that fleeting echoes were visible within this circle, and quickly concluded these were from other aircraft. This presented a simple way to see enemy night fighters as long as they were below the bomber and not far enough away that they would be hidden in the ground return. German night fighters normally approached from below as it helped silhouette the target aircraft against the Moon, and the lack of a gun position in that location made it safe to approach from that direction. This left them ideally positioned for detection by H2S. However, the display was very small, and this blank area on the screen only a small portion of that, so seeing these returns was difficult.
In early 1943 German night fighter operations were improving. Between January and April 1943 Bomber Command lost a total of 584 aircraft to the defences. Although this represented only 4% of the sorties, this was nevertheless worrying because the increasing daylight length during the summer meant that the defences would inevitably be more effective. Several systems were already under development to help the bombers defend themselves, including the Monica radar (a simple adaptation of the original AI Mk. IV radar from the RAF's own night fighters) and the
Radar operates by sending out very short pulses of a radio signal from a transmitter, then turning the transmitter off and listening for echoes in a receiver. The output of the receiver is sent to an oscilloscope's brightness input, so strong echoes cause a spot on the screen to light up. To make the spots correspond to locations in space, the oscilloscope quickly scans from the centre to the outside of the display; echoes that return later in time are produced further out on the display, indicating a further distance from the aircraft. The times are synchronized by using the transmission pulse to trigger the scan.
In the case of H2S, the echoes are returned from the ground and objects on it. That means the very first signal that would normally be received would be from the ground directly beneath the aircraft, as this is the closest to the aircraft. Since the echo from this location took some time to return to the aircraft, the time needed to travel to the ground and back at the aircraft's current altitude, the H2S display naturally had an empty area around the centre of the display, with its radius representing the altitude of the aircraft. This was known as the ''centre-zero''. Normally the operator used a dial that delayed the start of the sweep in order to reduce the size of this centre-zero, and thereby increase the amount of the screen used for the ground display.
When the centre-zero was not entirely dialled out, operators noticed that fleeting echoes were visible within this circle, and quickly concluded these were from other aircraft. This presented a simple way to see enemy night fighters as long as they were below the bomber and not far enough away that they would be hidden in the ground return. German night fighters normally approached from below as it helped silhouette the target aircraft against the Moon, and the lack of a gun position in that location made it safe to approach from that direction. This left them ideally positioned for detection by H2S. However, the display was very small, and this blank area on the screen only a small portion of that, so seeing these returns was difficult.
In early 1943 German night fighter operations were improving. Between January and April 1943 Bomber Command lost a total of 584 aircraft to the defences. Although this represented only 4% of the sorties, this was nevertheless worrying because the increasing daylight length during the summer meant that the defences would inevitably be more effective. Several systems were already under development to help the bombers defend themselves, including the Monica radar (a simple adaptation of the original AI Mk. IV radar from the RAF's own night fighters) and the 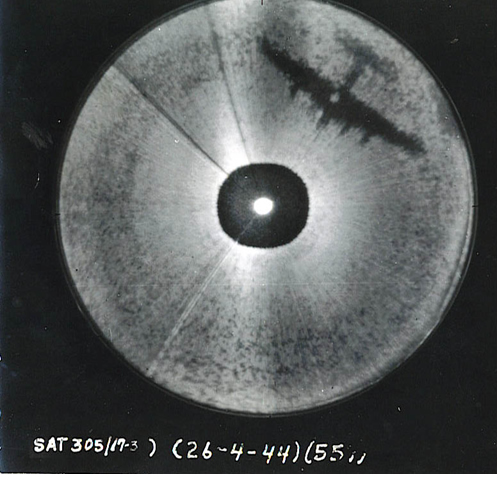 When the photos reached the desk of Bomber Command's Deputy Commander-in-Chief Robert Saundby, he immediately sent a message to the Air Ministry demanding that they be installed with all possible speed. The new display, given the official title Type 182 and nicknamed "Mousetrap", was on the assembly line by August 1943. At this point, the team received a message demanding they immediately stop using the name Mousetrap as that was the name of an upcoming secret mission. They were officially allocated the new name "Fishpond", a choice that was made official by a telegram from Churchill on 9 July. The first operational units went into service in October 1943, and by the spring of 1944, most of Bomber Command's aircraft carried it. Two hundred examples of the prototype model were produced before a slightly modified version was introduced, the Type 182A. This version had the range fixed at , with the side-effect that if the aircraft flew below this altitude the ground appeared as a ring of noise on the display.
The Type 182 display was normally located at the radio operator's station, not the navigator's. This reduced the navigator's workload while also simplifying communications when a target was seen; the radio operator could easily communicate with the crew or send messages to other aircraft. Normally a number of blips would be seen, as other aircraft in the
When the photos reached the desk of Bomber Command's Deputy Commander-in-Chief Robert Saundby, he immediately sent a message to the Air Ministry demanding that they be installed with all possible speed. The new display, given the official title Type 182 and nicknamed "Mousetrap", was on the assembly line by August 1943. At this point, the team received a message demanding they immediately stop using the name Mousetrap as that was the name of an upcoming secret mission. They were officially allocated the new name "Fishpond", a choice that was made official by a telegram from Churchill on 9 July. The first operational units went into service in October 1943, and by the spring of 1944, most of Bomber Command's aircraft carried it. Two hundred examples of the prototype model were produced before a slightly modified version was introduced, the Type 182A. This version had the range fixed at , with the side-effect that if the aircraft flew below this altitude the ground appeared as a ring of noise on the display.
The Type 182 display was normally located at the radio operator's station, not the navigator's. This reduced the navigator's workload while also simplifying communications when a target was seen; the radio operator could easily communicate with the crew or send messages to other aircraft. Normally a number of blips would be seen, as other aircraft in the
 After
After
Sitzungsprotokolle der Arbeitsgemeinschaft Rotterdam
minutes of the meetings of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Rotterdam (AGR) *
* ttp://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1945/1945%20-%201767.html ''Bomber's Radar – General Survey of the Three Primary Systems Used by Bomber Command''– ''Flight'' article of September 1945
H2S Equipment (AP2890L) operators manual
Air Ministry, July 1944 {{RAF WWII Strategic Bombing Aircraft radars World War II radars World War II British electronics Military radars of the United Kingdom British inventions Military equipment introduced from 1940 to 1944
 H2S was the first airborne, ground scanning radar system. It was developed for the
H2S was the first airborne, ground scanning radar system. It was developed for the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
's Bomber Command
Bomber Command is an organisational military unit, generally subordinate to the air force of a country. The best known were in Britain and the United States. A Bomber Command is generally used for strategic bombing (although at times, e.g. during t ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
to identify targets on the ground for night and all-weather bombing. This allowed attacks outside the range of the various radio navigation
Radio navigation or radionavigation is the application of radio frequencies to determine a position of an object on the Earth, either the vessel or an obstruction. Like radiolocation, it is a type of radiodetermination.
The basic principles a ...
aids like Gee or Oboe
The oboe ( ) is a type of double reed woodwind instrument. Oboes are usually made of wood, but may also be made of synthetic materials, such as plastic, resin, or hybrid composites. The most common oboe plays in the treble or soprano range.
...
, which were limited to about . It was also widely used as a general navigation system, allowing landmarks to be identified at long range.
In March 1941, experiments with an early airborne interception radar based on the 9.1 cm wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
, (3 GHz) cavity magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-power vacuum tube used in early radar systems and currently in microwave ovens and linear particle accelerators. It generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field whi ...
revealed that different objects have very different radar signature
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, Marine radar, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor v ...
s; water, open land and built-up areas of cities and towns all produced distinct returns. In January 1942, a new team was set up to combine the magnetron with a new scanning antenna and plan-position indicator display. The prototype's first use in April confirmed that a map of the area below the aircraft could be produced using radar. The first systems went into service in early 1943 as the H2S Mk. I and H2S Mk. II, as well as ASV Mark III
Radar, Air-to-Surface Vessel, Mark III, or ASV Mk. III for short, was a surface search radar system used by RAF Coastal Command during World War II. It was a slightly modified version of the H2S radar used by RAF Bomber Command, with minor changes ...
.
On its second operational mission on 2/3 February 1943, an H2S was captured almost intact by German forces, and a second unit a week later. Combined with intelligence gathered from the surviving crew, they learned it was a mapping system and were able to determine its method of operation. When they pieced one together from parts and saw the display of Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
, near panic broke out in the ''Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
''. This led to the introduction of the FuG 350 ''Naxos'' radar detector in late 1943, which enabled ''Luftwaffe'' night fighter
A night fighter (also known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor for a period of time after the Second World War) is a fighter aircraft adapted for use at night or in other times of bad visibility. Night fighters began to be used i ...
s to home on the transmissions of H2S. The British learned of Naxos and a great debate ensued over the use of H2S. However, calculations showed that losses during this period were actually less than before.
After it was found the resolution of the early sets was too low to be useful over large cities like Berlin, in 1943 work started on a version operating in the X band at 3 cm (10 GHz), the H2S Mk. III. Almost simultaneously, its American equivalent was introduced as the 10 GHz H2X radar in October of that year. A wide variety of Mk. III's were produced before the Mk. IIIG was selected as the late-war standard. Development continued through the late-war Mk. IV to the 1950s era Mk. IX that equipped the V bomber fleet and the English Electric Canberra
The English Electric Canberra is a British first-generation, jet-powered medium bomber. It was developed by English Electric during the mid- to late 1940s in response to a 1944 Air Ministry requirement for a successor to the wartime de Havil ...
. In the V-force, Mk. IXA was tied into both the bombsight and navigation system to provide a complete long-range Navigation and Bombing System (NBS). In this form, H2S was last used operationally during the Falklands War in 1982 on the Avro Vulcan
The Avro Vulcan (later Hawker Siddeley Vulcan from July 1963) is a jet-powered, tailless, delta-wing, high-altitude, strategic bomber, which was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) from 1956 until 1984. Aircraft manufacturer A.V. Roe an ...
. Some H2S Mk. IX units remained in service on the Handley Page Victor
The Handley Page Victor is a British jet-powered strategic bomber developed and produced by Handley Page during the Cold War. It was the third and final '' V bomber'' to be operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF), the other two being the Avr ...
aircraft until 1993, providing fifty years of service.
Etymology of "H2S"
The radar was originally called "BN" (Blind Navigation), but it quickly became "H2S". The genesis of this remains somewhat contentious, with different sources claiming it meant "Height to Slope"; or "Home Sweet Home". The "S" was already being used by the airborne interception radar team as a deliberately confusing acronym for its operating wavelength in the " " range, which ultimately gave name to the S band. It is widely reported that it was named after hydrogen sulphide (chemical formula H2S, in connection with its rotten smell), because the inventor realized that had he simply pointed the radar downward instead of towards the sky, he would have a new use for radar, ground tracking instead of for identifying air targets and that it was simply "rotten" that he had not thought of it sooner. The "rotten" connection, with a twist, is propounded by R. V. Jones, director of theAir Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force, that existed from 1918 to 1964. It was under the political authority of the Secretary of State ...
's scientific intelligence unit. He relates the tale that, due to a misunderstanding between the original developers and Lord Cherwell, science advisor to Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
, development of the technology was delayed as the engineers thought that Lord Cherwell did not like the idea. Later, when Cherwell asked how the project was progressing, he was most upset to hear that it had been put on hold, and repeatedly declared about the delay that "it stinks". The engineers called the resumed project "H2S" and later, when Cherwell inquired as to what H2S stood for, no one dared tell Cherwell that it was named after his phrase. Instead, they pretended, on the spot, that it meant "Home Sweet Home", which was the meaning that Cherwell related to others (including Jones).
Development
Genesis
After theBattle of Britain
The Battle of Britain, also known as the Air Battle for England (german: die Luftschlacht um England), was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) of the Royal Navy defende ...
, RAF Bomber Command began night attacks against German cities. Although Bomber Command had reported good results from the raids, the Butt Report
The Butt Report, released on 18 August 1941, was a report prepared during World War II, revealing the widespread failure of RAF Bomber Command aircraft to hit their targets.
At the start of the war, Bomber Command had no real means of determini ...
showed only one bomb in twenty landed within of the target, half the bombs fell on open country, and in some cases, the bombing was seen to fall as far as from the target.
Radio electronics promised some improvement and the Telecommunications Research Establishment
The Telecommunications Research Establishment (TRE) was the main United Kingdom research and development organization for radio navigation, radar, infra-red detection for heat seeking missiles, and related work for the Royal Air Force (RAF) ...
(TRE) developed a radio navigation system called " Gee" and then a second known as "Oboe
The oboe ( ) is a type of double reed woodwind instrument. Oboes are usually made of wood, but may also be made of synthetic materials, such as plastic, resin, or hybrid composites. The most common oboe plays in the treble or soprano range.
...
". Both were based on transmitter stations in the UK which sent out synchronized signals. In the case of Gee, an oscilloscope in the aircraft measured the time difference between two signals to determine location. Oboe used a transponder
In telecommunications, a transponder is a device that, upon receiving a signal, emits a different signal in response. The term is a blend of ''transmitter'' and ''responder''.
In air navigation or radio frequency identification, a flight trans ...
in the aircraft to reflect the signals back to the UK where operators carried out the same measurements on much larger displays to produce more accurate values. In both cases, the ground-based portion of the system limited range to a line-of-sight, about for aircraft flying at typical mission altitudes. This was useful against targets in the Ruhr, but not the heart of Germany.
Taffy Bowen had noticed during his early 1.5 m wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
AI radar experiments before the war that the radar returns from fields, cities and other areas were different. This was due to geometry; objects with vertical sides, like buildings or ships, produced much stronger returns than flat objects like the ground or sea. During early tests of the AI system, the operator would often see coastlines at very long distances, and the development team used this as an ''ad hoc'' navigation system on several occasions. Bowen had suggested developing a targeting radar based on this principle, but the matter had been forgotten.
In 1940, John Randall and Harry Boot
Henry Albert Howard Boot (29 July 1917 – 8 February 1983) was an English physicist who with Sir John Randall and James Sayers developed the cavity magnetron, which was one of the keys to the Allied victory in the Second World War.
Biography ...
, PhD students at the University of Birmingham
The University of Birmingham (informally Birmingham University) is a Public university, public research university located in Edgbaston, Birmingham, United Kingdom. It received its royal charter in 1900 as a successor to Queen's College, Birmingha ...
, devised a new microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ra ...
-frequency vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
known as the cavity magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-power vacuum tube used in early radar systems and currently in microwave ovens and linear particle accelerators. It generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field whi ...
that output thousands of watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James ...
s of radio signal at 3 cm wavelength. At this wavelength, the antennas were only a few centimeters long, making radar much easier to fit to an aircraft. The mapping idea resurfaced in March 1941 when Philip Dee
Philip Ivor Dee CBE FRS FRSE (8 April 1904, Stroud – 17 April 1983, Glasgow) was a British nuclear physicist. He was responsible for the development of airborne radar during the Second World War. Glasgow University named the Philip Ivor Dee Me ...
's group was developing a new AI radar, christened "AIS" in reference to its "sentimetric" wavelength. During tests in a Blenheim, the team noticed the same sort of effects Bowen had earlier. However, the set's wavelength, over ten times shorter than the original 1.5 m AI sets, provided much greater resolution and allowed them to pick out individual objects on the ground.
Work begins
 In October 1941, Dee attended a meeting of the RAF Bomber Command where the night targeting issue was discussed. Dee mentioned the recent discoveries using AIS. On 1 November, Dee performed an experiment in which he used an AIS radar mounted on a Blenheim to scan the ground. Using this display he was able to pick up the outline of a town away while flying at altitude.
The commanders were impressed and, on 1 January 1942, the TRE set up a team under Bernard Lovell to develop an S-band airborne targeting radar based on AIS. An initial order for 1,500 sets was placed. It was clear even at this point that a Plan Position Indicator (PPI) display would be desirable, but this would require a complex scanning parabolic antenna, compared to the very simple set of fixed antennas used in the A-scope system. It was decided to test both systems. In March, it was decided that both H2S and a new centimetric Air-Surface-Vessel radar (ASV) radar, ASV Mk. III, would be built using the same components, simplifying production.
In early tests in April, the superiority of the scanning PPI system was evident, and all work on the older A-scope version ended. H2S performed its first experimental flight on 23 April 1942, with the radar mounted in a
In October 1941, Dee attended a meeting of the RAF Bomber Command where the night targeting issue was discussed. Dee mentioned the recent discoveries using AIS. On 1 November, Dee performed an experiment in which he used an AIS radar mounted on a Blenheim to scan the ground. Using this display he was able to pick up the outline of a town away while flying at altitude.
The commanders were impressed and, on 1 January 1942, the TRE set up a team under Bernard Lovell to develop an S-band airborne targeting radar based on AIS. An initial order for 1,500 sets was placed. It was clear even at this point that a Plan Position Indicator (PPI) display would be desirable, but this would require a complex scanning parabolic antenna, compared to the very simple set of fixed antennas used in the A-scope system. It was decided to test both systems. In March, it was decided that both H2S and a new centimetric Air-Surface-Vessel radar (ASV) radar, ASV Mk. III, would be built using the same components, simplifying production.
In early tests in April, the superiority of the scanning PPI system was evident, and all work on the older A-scope version ended. H2S performed its first experimental flight on 23 April 1942, with the radar mounted in a Handley Page Halifax
The Handley Page Halifax is a British Royal Air Force (RAF) four-engined heavy bomber of the Second World War. It was developed by Handley Page to the same specification as the contemporary twin-engine Avro Manchester.
The Halifax has its orig ...
bomber, '' V9977''. The scanning unit was installed in the aircraft's belly using the position previously occupied by the mid-under turret, which was by that time seldom installed. The rotating scanner mounting was designed and manufactured by Nash & Thompson
Nash & Thompson was a British engineering firm that developed and produced hydraulically operated gun turrets for aircraft. As part of Parnall Aircraft it was also an important manufacturer of hydraulic-powered radar scanners used on radar sys ...
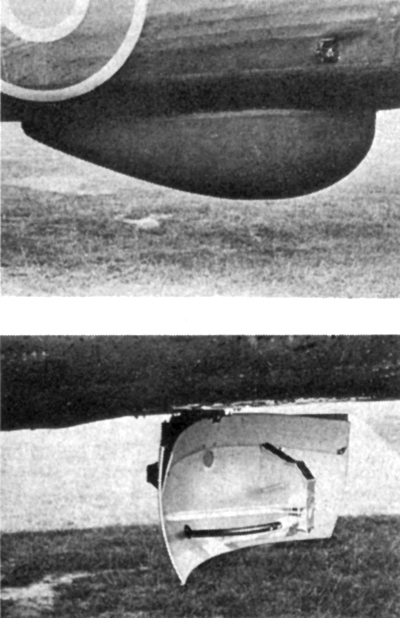
. The scanning aerial was covered by a distinctive streamlined
Streamlines, streaklines and pathlines are field lines in a fluid flow.
They differ only when the flow changes with time, that is, when the flow is not steady.
Considering a velocity vector field in three-dimensional space in the framework of ...
radome
A radome (a portmanteau of radar and dome) is a structural, weatherproof enclosure that protects a radar antenna. The radome is constructed of material transparent to radio waves. Radomes protect the antenna from weather and conceal antenna e ...
.
One problem was that the returns from closer objects were much stronger than more distant objects, due to the radar equation. This made the area directly under the bomber much brighter than the surroundings if the signal was not adjusted to account for this. The solution was to adjust the broadcast power according to the cosecant-squared rule, so-called after the mathematical function
In mathematics, a function from a set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words map, mapping, transformation, correspondence, and operator are often used synonymously. The set is called the domain of the functi ...
that defined the effective change in gain. The change was originally produced by fixing an angled metal plate on part of the parabolic reflector of the aerial, as may be seen in the picture of the aerial on a Halifax bomber. Later reflectors were actually shaped with a cosecant-squared curvature, no longer a perfect parabolic section.
 Then disaster occurred; on 7 June 1942, the Halifax performing H2S tests crashed, killing everyone on board and destroying the prototype H2S. One of the dead was Alan Blumlein, the chief designer, and his loss was a huge blow to the programme. Also killed in the crash were Blumlein's colleagues Cecil Oswald Browne and Frank Blythen; a TRE scientist Geoffrey S. Hensby, and seven RAF personnel.
Then disaster occurred; on 7 June 1942, the Halifax performing H2S tests crashed, killing everyone on board and destroying the prototype H2S. One of the dead was Alan Blumlein, the chief designer, and his loss was a huge blow to the programme. Also killed in the crash were Blumlein's colleagues Cecil Oswald Browne and Frank Blythen; a TRE scientist Geoffrey S. Hensby, and seven RAF personnel.
Magnetron debate
 As development continued, a great debate broke out in the Air Ministry and RAF about the relative merits of the H2S system. While the ability to bomb in all weather at great distances was obviously useful to Bomber Command, the loss of an H2S aircraft would potentially reveal the secret of the magnetron to the Germans. Churchill's science advisor, Frederick Lindemann, wanted the design team to build H2S around the
As development continued, a great debate broke out in the Air Ministry and RAF about the relative merits of the H2S system. While the ability to bomb in all weather at great distances was obviously useful to Bomber Command, the loss of an H2S aircraft would potentially reveal the secret of the magnetron to the Germans. Churchill's science advisor, Frederick Lindemann, wanted the design team to build H2S around the klystron
A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian,Pond, Norman H. "The Tube Guys". Russ Cochran, 2008 p.31-40 which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequen ...
rather than the magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-power vacuum tube used in early radar systems and currently in microwave ovens and linear particle accelerators. It generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field while ...
.
Unlike a klystron, which is made mostly of glass and fragile metal parts, the magnetron was built out of a single block of copper that would be extremely difficult to destroy with any reasonable demolition charge. If a magnetron was recovered by the Germans, they would immediately understand its operation and potentially develop countermeasures. Since the magnetron was also being designed for use in night fighter
A night fighter (also known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor for a period of time after the Second World War) is a fighter aircraft adapted for use at night or in other times of bad visibility. Night fighters began to be used i ...
s and Coastal Command
RAF Coastal Command was a formation within the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was founded in 1936, when the RAF was restructured into Fighter, Bomber and Coastal Commands and played an important role during the Second World War. Maritime Aviation ...
, the loss of the secret would not only provide the Germans with ample early warning to build detectors, but also allow them to develop their own effective airborne radars.
The H2S design team did not believe the klystron could do the job, and tests of an H2S built with klystrons showed a drop in output power by a factor of 20 to 30. At the same altitude, the klystron powered versions were able to detect a town at while the magnetron version was capable of . There appeared to be no way to improve this, so it would have to be the magnetron, or nothing. The H2S team also protested that it would take the Germans two years to develop a centimetric radar once the cavity magnetron fell into their hands, and that there was no reason to believe they were not working on the technology already. The first concern would prove correct; although a magnetron was captured in early 1943, the war ended before German examples were in production.
In the midst of the debate, Isidor Isaac Rabi
Isidor Isaac Rabi (; born Israel Isaac Rabi, July 29, 1898 – January 11, 1988) was an American physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1944 for his discovery of nuclear magnetic resonance, which is used in magnetic resonance ima ...
of the American Radiation Laboratory visited the TRE offices on 5 and 6 July 1942. According to Lovell, he stated that the H2S device provided to them during the Tizard Mission
The Tizard Mission, officially the British Technical and Scientific Mission, was a British delegation that visited the United States during WWII to obtain the industrial resources to exploit the military potential of the research and development ( ...
was "unscientific and unworkable" and expressed his feelings that the only use of it would be to hand the magnetron to the Germans. Years later, Lovell attempted to discover the reasons for this negative report, but he found that no one recalled Rabi being so negative. The only explanation that anyone had was that problems getting the sets working were taken out of context. Taffy Bowen had noted that he had significant trouble getting the sets to do anything in the US; in testing against Springfield, Hartford and Boston, the display simply did not show anything.
By September, a prototype version suitable for operational use was ready. In spite of all the concerns, on 15 September Churchill personally released the magnetron for use by Bomber Command. While the debate raged, it had been noticed that German submarines had been fitted with a new radar detector
A radar detector is an electronic device used by motorists to detect if their speed is being monitored by police or law enforcement using a radar gun. Most radar detectors are used so the driver can reduce the car's speed before being ticketed ...
, later known to be the FuMB 1 ''Metox 600A'', which allowed them to detect Coastal Command's ASV sets operating on the older 1.5 m band. In September the decision was made to prioritize construction for the ASV Mk. III. It was felt the chance that a magnetron falling into German hands from a patrol aircraft was vanishingly small.
Emergency relocation
 The Air Ministry radar groups had originally formed up at
The Air Ministry radar groups had originally formed up at Bawdsey Manor
Bawdsey Manor stands at a prominent position at the mouth of the River Deben close to the village of Bawdsey in Suffolk, England, about northeast of London.
Built in 1886, it was enlarged in 1895 as the principal residence of Sir William C ...
on the eastern coast of England. When the war began in 1939, this location was considered too exposed to a potential German attack, and a pre-arranged move to the University of Dundee
, mottoeng = "My soul doth magnify the Lord"
, established = 1967 – gained independent university status by Royal Charter1897 – Constituent college of the University of St Andrews1881 – University College
, ...
was carried out almost overnight. On arrival, it was found nothing was prepared and there was little room for the teams to work in. Worse, the team working on airborne radars ended up at a tiny private airstrip in Perth, Scotland that was entirely unsuitable for development.
It took some time before the nature of the problem was finally accepted by management and a search began for a new location. In late 1939, the Airborne team moved to RAF St Athan
Ministry of Defence St Athan or MOD St Athan (Welsh: Maes awyr Sain Tathan), formerly known as RAF St Athan, is a large Ministry of Defence unit near the village of St Athan in the Vale of Glamorgan, southern Wales. It was the designated site for ...
, about from Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingd ...
. Although this location should have been ideal, they found themselves in a disused hangar with no heating, and work became almost impossible as the weather turned cold. The main research teams remained in Dundee during this period.
The ongoing search for a more suitable location for all the teams led to the selection of Swanage on the southern coast of the UK. The rest of the original radar group moved there in May 1940, the AI group arriving the day before them. The AI group, located in shacks on the shoreline near Worth Matravers
Worth Matravers () is a village and civil parish in the English county of Dorset. The village is situated on the cliffs west of Swanage. It comprises limestone cottages and farm houses and is built around a pond, which is a regular feature on pos ...
, was particularly exposed and only a short distance from German-occupied Cherbourg. While the move was taking place, A.P. Rowe took the opportunity to set up a second airborne group working with magnetrons, sidelining Bowen's group. Bowen was soon forced out of the TRE and sent on the Tizard Mission that summer.
On 25 May 1942, Combined Operations Headquarters
Combined Operations Headquarters was a department of the British War Office set up during Second World War to harass the Germans on the European continent by means of raids carried out by use of combined naval and army forces.
History
The comm ...
carried out Operation Biting
Operation Biting, also known as the Bruneval Raid, was a British Combined Operations raid on a German coastal radar installation at Bruneval in northern France, during the Second World War, on the night .
Several of these installations were id ...
to capture a Würzburg radar
The low-UHF band Würzburg radar was the primary ground-based tracking radar for the Wehrmacht's Luftwaffe and Kriegsmarine (German Navy) during World War II. Initial development took place before the war and the apparatus entered service in 1940 ...
that had been photographed near the French coast. This led to concerns that the Germans might launch a similar raid on British installations. When reports were received that "seventeen train loads" of paratroopers had been stationed near Cherbourg, directly across the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
from Christchurch
Christchurch ( ; mi, Ōtautahi) is the largest city in the South Island of New Zealand and the seat of the Canterbury Region. Christchurch lies on the South Island's east coast, just north of Banks Peninsula on Pegasus Bay. The Avon Rive ...
, near panic broke out in the Air Ministry, and yet another emergency move was made. The team ended up at Malvern College about to the north. This provided ample office space but little in the way of housing and introduced yet more delays in the development program.
Operational use
Service entry
 Despite all the problems, on 3 July 1942 Churchill held a meeting with his military commanders and the H2S group, where he surprised the radar designers by demanding the delivery of 200 H2S sets by 15 October 1942. The H2S design team was under great pressure, but they were given priority on resources. The pressure also gave them an excellent argument to convince Lord Cherwell that the klystron-based H2S program finally be dropped.
TRE failed to meet the 15 October deadline; by 1 January 1943, only twelve
Despite all the problems, on 3 July 1942 Churchill held a meeting with his military commanders and the H2S group, where he surprised the radar designers by demanding the delivery of 200 H2S sets by 15 October 1942. The H2S design team was under great pressure, but they were given priority on resources. The pressure also gave them an excellent argument to convince Lord Cherwell that the klystron-based H2S program finally be dropped.
TRE failed to meet the 15 October deadline; by 1 January 1943, only twelve Stirling
Stirling (; sco, Stirlin; gd, Sruighlea ) is a city in central Scotland, northeast of Glasgow and north-west of Edinburgh. The market town, surrounded by rich farmland, grew up connecting the royal citadel, the medieval old town with its me ...
and twelve Halifax bombers had been fitted with H2S. On the night of 30 January 1943, thirteen Stirlings and Halifaxes of the "Pathfinder" force used H2S to drop incendiaries or flares on a target in Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
. One hundred Lancasters following the Pathfinders used the flares as the target for their bombsights. The results were considered "satisfactory". Similar raids were carried out against Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The ...
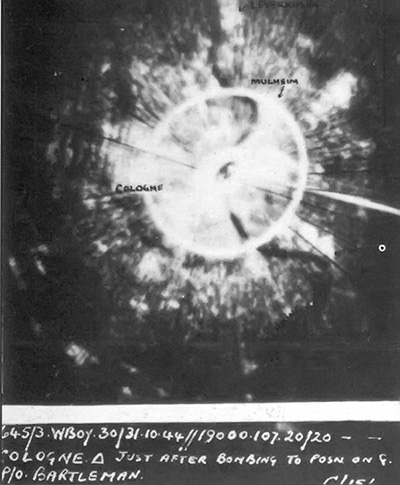
the next night, and Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
on the night of 2/3 February.
On 21 February, the decision was made to equip all Bomber Command aircraft with H2S, not only as a bombing aid but also as a navigation aid. In early operations, H2S had proved able to detect coastlines at such a great distance that it could be used as a long-range navigation system, allowing the aircraft to fly in all weather. To aid the navigator, the bomb aimer had the task of operating the H2S during these periods. To further improve operations, on 12 March it was decided that Bomber Command would receive more of the available spares, as it was believed that they would need to make up for higher casualty rates. Previously, every equipped squadron was required to hold 100% spares for all parts, and there simply were not enough to go around.
H2S Mk. II, production version
 The original H2S sets were essentially prototype units that were hand-built to equip the Pathfinders with all possible speed. Among the many problems with the rushed service entry was that the developers were forced to use existing plug-and-socket designs to connect the various units of the complete set together. There were no bulkhead mounting male connectors available at this time, and consequently many of the male free connectors at the ends of cable runs carried exposed lethal voltages. While installations of the prototypes progressed, work was underway on a true production version, the Mk. II, which would go on to be the most numerous version built. This was largely identical to the Mk. I's with the exception of various packaging and electronics details intended to make them easier to build.
Bomber Command started general use of H2S in summer 1943. On the night of 24 July, the RAF began
The original H2S sets were essentially prototype units that were hand-built to equip the Pathfinders with all possible speed. Among the many problems with the rushed service entry was that the developers were forced to use existing plug-and-socket designs to connect the various units of the complete set together. There were no bulkhead mounting male connectors available at this time, and consequently many of the male free connectors at the ends of cable runs carried exposed lethal voltages. While installations of the prototypes progressed, work was underway on a true production version, the Mk. II, which would go on to be the most numerous version built. This was largely identical to the Mk. I's with the exception of various packaging and electronics details intended to make them easier to build.
Bomber Command started general use of H2S in summer 1943. On the night of 24 July, the RAF began Operation Gomorrah
The Allied bombing of Hamburg during World War II included numerous attacks on civilians and civic infrastructure. As a large city and industrial centre, Hamburg's shipyards, U-boat pens, and the Hamburg-Harburg area oil refineries were attack ...
, a large attack on Hamburg. By that time, H2S had been fitted to Lancasters, which became a backbone of Bomber Command. With the target marked by Pathfinders using H2S, RAF bombers hit the city with high explosive and incendiary bombs. They returned on 25 and 27 July, with the USAAF
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
performing two daylight attacks in between the three RAF raids. Large parts of the city were burned to the ground by a firestorm
A firestorm is a conflagration which attains such intensity that it creates and sustains its own wind system. It is most commonly a natural phenomenon, created during some of the largest bushfires and wildfires. Although the term has been used ...
. About 45,000 people, mostly civilians, were killed.
The Mk. II was soon upgraded to the Mk. IIA version, which differed from the Mk. II only in the detail of the scanner antenna; IIA replaced the original dipole antenna at the scanner's focal point with a feed horn
A feed horn (or feedhorn) is a small horn antenna used to couple a waveguide to e.g. a parabolic dish antenna or offset dish antenna for reception or transmission of microwave. A typical application is the use for satellite television recep ...
that sent the signal back to the receiver in a waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound, with minimal loss of energy by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Without the physical constraint of a waveguide, wave intensities de ...
, eliminating the lossy coaxial cable of the earlier model.
Scanning improvements
 It was noted on even the earliest flights of ''V9977'' that a number of basic features of the H2S made it difficult to use. Attempts to fix these began even before H2S entered service, but a number of problems greatly delayed their entry. Added as they became available, this produced a profusion of different Marks, detailed below.
Late in April 1942, during a test flight of ''V9977'', the prototype unit was shown to Flight Lieutenant E. Dickie, a navigator. Dickie pointed out that
It was noted on even the earliest flights of ''V9977'' that a number of basic features of the H2S made it difficult to use. Attempts to fix these began even before H2S entered service, but a number of problems greatly delayed their entry. Added as they became available, this produced a profusion of different Marks, detailed below.
Late in April 1942, during a test flight of ''V9977'', the prototype unit was shown to Flight Lieutenant E. Dickie, a navigator. Dickie pointed out that navigational chart
A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a sea area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land (topographic map), natural features of the seabed, details of the coa ...
s were always produced with north at the top, while the PPI display of H2S had the top of the display representing whatever direction the aircraft was flying. He suggested that this would cause significant problems during navigation. This had not been considered before because H2S had been developed as a bombing aid. Now that it was also used as an important navigation aid, this was a major issue. This led to a crash program at EMI
EMI Group Limited (originally an initialism for Electric and Musical Industries, also referred to as EMI Records Ltd. or simply EMI) was a British Transnational corporation, transnational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in March 1 ...
to modify the prototype sets with a system to correct this problem. This was solved with the introduction of a selsyn (or "servo") connected to the aircraft's gyrocompass
A gyrocompass is a type of non-magnetic compass which is based on a fast-spinning disc and the rotation of the Earth (or another planetary body if used elsewhere in the universe) to find geographical direction automatically. The use of a gyroc ...
, whose output modified the scan rotation. A further addition produced a bright line on the display indicating the direction of travel.
A later modification allowed the heading indicator display to be manually controlled by the operator. This was used in concert with the Mark XIV bomb sight
The Mark XIV Bomb Sight was a bombsight developed by Royal Air Force (RAF) Bomber Command during the Second World War. It was also known as the Blackett sight after its primary inventor, P. M. S. Blackett. Production of a slightly modified ve ...
to accurately correct for any wind blowing the aircraft off the bomb line. The indicator was set to an initial angle provided by the bomb aimer, and from then the navigator could see any residual drift on his display and call out corrections to the pilot, and to the bomb aimer who would update his settings in the bombsight. This basic idea was later expanded to allow the navigator's measurements to be automatically sent back to the bombsight, meaning the bomb aimer no longer had to do this during the approach. Since the other settings, like altitude and airspeed, were already automatically fed in from the aircraft instruments, this left only the selection of the elevation of the target over sea level to be set manually, which could be done before the mission.
The other problem was that when the aircraft rolled, the signal hit the ground only on the lower side of the aircraft, filling one side of the display with a solid signal while the other side was blank. This was particularly annoying because it was during the last minute of the approach to the target that the navigator would be giving course corrections to the pilot, rendering the display unusable every time the pilot responded. This problem was solved through the introduction of a mechanical stabilizer that kept the scanning system level with respect to the ground. A preliminary version was ready by September 1943, but several problems were noted, and it was not until 5 November that the decision was made to move it into production. By this time development of the 3 cm version of H2S was underway, and Nash & Thompson promised to have versions of the stabilizer for both 10 and 3 cm units available by 15 December 1943.
A final problem related to the geometry of the signals returned by the radar. As the scanning angle increased, the time taken for the signal to return did not increase linearly, but hyperbolically. As a result, returns close to the aircraft were fairly similar to what would be seen on a map, but those further from the aircraft were increasingly compressed in range. At the shortest range setting, , this was not a serious problem, but at the longest, , this made the display very difficult to understand. This led F. C. Williams to develop a new time base generator A time base generator (also timebase or time base) is a special type of function generator, an electronic circuit that generates a varying voltage to produce a particular waveform. Time base generators produce very high frequency sawtooth waves spec ...
that also output a hyperbolic signal, fixing this problem. This was called the "scan corrected indicator", or display Type 184.
All of these concepts were being worked on largely in parallel, and at a meeting in March 1944, it was learned that only low rates of production could be expected through the end of the year. By that time the new 3 cm sets were being introduced as well, and this led to a profusion of various Marks featuring one or more of these additional corrections. These delays had not been expected, and Lovell later noted:
Fishpond
 Radar operates by sending out very short pulses of a radio signal from a transmitter, then turning the transmitter off and listening for echoes in a receiver. The output of the receiver is sent to an oscilloscope's brightness input, so strong echoes cause a spot on the screen to light up. To make the spots correspond to locations in space, the oscilloscope quickly scans from the centre to the outside of the display; echoes that return later in time are produced further out on the display, indicating a further distance from the aircraft. The times are synchronized by using the transmission pulse to trigger the scan.
In the case of H2S, the echoes are returned from the ground and objects on it. That means the very first signal that would normally be received would be from the ground directly beneath the aircraft, as this is the closest to the aircraft. Since the echo from this location took some time to return to the aircraft, the time needed to travel to the ground and back at the aircraft's current altitude, the H2S display naturally had an empty area around the centre of the display, with its radius representing the altitude of the aircraft. This was known as the ''centre-zero''. Normally the operator used a dial that delayed the start of the sweep in order to reduce the size of this centre-zero, and thereby increase the amount of the screen used for the ground display.
When the centre-zero was not entirely dialled out, operators noticed that fleeting echoes were visible within this circle, and quickly concluded these were from other aircraft. This presented a simple way to see enemy night fighters as long as they were below the bomber and not far enough away that they would be hidden in the ground return. German night fighters normally approached from below as it helped silhouette the target aircraft against the Moon, and the lack of a gun position in that location made it safe to approach from that direction. This left them ideally positioned for detection by H2S. However, the display was very small, and this blank area on the screen only a small portion of that, so seeing these returns was difficult.
In early 1943 German night fighter operations were improving. Between January and April 1943 Bomber Command lost a total of 584 aircraft to the defences. Although this represented only 4% of the sorties, this was nevertheless worrying because the increasing daylight length during the summer meant that the defences would inevitably be more effective. Several systems were already under development to help the bombers defend themselves, including the Monica radar (a simple adaptation of the original AI Mk. IV radar from the RAF's own night fighters) and the
Radar operates by sending out very short pulses of a radio signal from a transmitter, then turning the transmitter off and listening for echoes in a receiver. The output of the receiver is sent to an oscilloscope's brightness input, so strong echoes cause a spot on the screen to light up. To make the spots correspond to locations in space, the oscilloscope quickly scans from the centre to the outside of the display; echoes that return later in time are produced further out on the display, indicating a further distance from the aircraft. The times are synchronized by using the transmission pulse to trigger the scan.
In the case of H2S, the echoes are returned from the ground and objects on it. That means the very first signal that would normally be received would be from the ground directly beneath the aircraft, as this is the closest to the aircraft. Since the echo from this location took some time to return to the aircraft, the time needed to travel to the ground and back at the aircraft's current altitude, the H2S display naturally had an empty area around the centre of the display, with its radius representing the altitude of the aircraft. This was known as the ''centre-zero''. Normally the operator used a dial that delayed the start of the sweep in order to reduce the size of this centre-zero, and thereby increase the amount of the screen used for the ground display.
When the centre-zero was not entirely dialled out, operators noticed that fleeting echoes were visible within this circle, and quickly concluded these were from other aircraft. This presented a simple way to see enemy night fighters as long as they were below the bomber and not far enough away that they would be hidden in the ground return. German night fighters normally approached from below as it helped silhouette the target aircraft against the Moon, and the lack of a gun position in that location made it safe to approach from that direction. This left them ideally positioned for detection by H2S. However, the display was very small, and this blank area on the screen only a small portion of that, so seeing these returns was difficult.
In early 1943 German night fighter operations were improving. Between January and April 1943 Bomber Command lost a total of 584 aircraft to the defences. Although this represented only 4% of the sorties, this was nevertheless worrying because the increasing daylight length during the summer meant that the defences would inevitably be more effective. Several systems were already under development to help the bombers defend themselves, including the Monica radar (a simple adaptation of the original AI Mk. IV radar from the RAF's own night fighters) and the Automatic Gun-Laying Turret
The Automatic Gun-Laying Turret (AGLT), also known as the Frazer-Nash FN121, was a radar-directed, rear gun turret fitted to some British bombers from 1944. AGLT incorporated both a low-power tail warning radar and fire-control system, which cou ...
(AGLT), which was intended to automate defensive fire. However, the former proved almost useless in practice, and it was already clear the latter would not be available at least until 1944.
Dudley Saward, the Bomber Command liaison with the radar teams, visited the Malvern site on 18 April to view progress on the microwave radars and mentioned the problem to Lovell. He was particularly frustrated by a raid carried out the night before on 16/17 April on the Škoda Works
The Škoda Works ( cs, Škodovy závody, ) was one of the largest European industrial conglomerates of the 20th century, founded by Czech engineer Emil Škoda in 1859 in Plzeň, then in the Kingdom of Bohemia, Austrian Empire. It is the predece ...
, where 11.3% of the attacking force was lost due to enemy action and all other issues. Mentioning the problems with Monica and especially the AGLT, Saward told Lovell:
Lovell was aware that this was indeed possible. The team promised they could build a sample of a special display that was effectively the opposite of the main mapping display; instead of adjusting the display so the centre-zero was eliminated and thus provide maximum screen space to the map, this new display would adjust the size of the centre-zero until it filled the display, thus making the returns from other aircraft easier to see. They only asked that the "whole affair was to be kept quiet to avoid difficulties".
Saward supplied an electronics technician, Sergeant Walker, and two mechanics, all of whom arrived the next day and immediately set about building a display in Halifax ''BB360''. The basic idea was to use the delay timer that reduced the size of the centre-zero as a switch; the existing display would receive returns exactly as it had before, with everything before that timer being suppressed, while a new display would receive everything before that time, and could be adjusted so the centre-zero filled the display. This would result in one display showing everything in the air, and a second providing a ground map exactly as before. The first experimental system flew on 27 May with a Mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
providing a target. The Mosquito clearly appeared on the display, and photographs of the display caused much excitement.
 When the photos reached the desk of Bomber Command's Deputy Commander-in-Chief Robert Saundby, he immediately sent a message to the Air Ministry demanding that they be installed with all possible speed. The new display, given the official title Type 182 and nicknamed "Mousetrap", was on the assembly line by August 1943. At this point, the team received a message demanding they immediately stop using the name Mousetrap as that was the name of an upcoming secret mission. They were officially allocated the new name "Fishpond", a choice that was made official by a telegram from Churchill on 9 July. The first operational units went into service in October 1943, and by the spring of 1944, most of Bomber Command's aircraft carried it. Two hundred examples of the prototype model were produced before a slightly modified version was introduced, the Type 182A. This version had the range fixed at , with the side-effect that if the aircraft flew below this altitude the ground appeared as a ring of noise on the display.
The Type 182 display was normally located at the radio operator's station, not the navigator's. This reduced the navigator's workload while also simplifying communications when a target was seen; the radio operator could easily communicate with the crew or send messages to other aircraft. Normally a number of blips would be seen, as other aircraft in the
When the photos reached the desk of Bomber Command's Deputy Commander-in-Chief Robert Saundby, he immediately sent a message to the Air Ministry demanding that they be installed with all possible speed. The new display, given the official title Type 182 and nicknamed "Mousetrap", was on the assembly line by August 1943. At this point, the team received a message demanding they immediately stop using the name Mousetrap as that was the name of an upcoming secret mission. They were officially allocated the new name "Fishpond", a choice that was made official by a telegram from Churchill on 9 July. The first operational units went into service in October 1943, and by the spring of 1944, most of Bomber Command's aircraft carried it. Two hundred examples of the prototype model were produced before a slightly modified version was introduced, the Type 182A. This version had the range fixed at , with the side-effect that if the aircraft flew below this altitude the ground appeared as a ring of noise on the display.
The Type 182 display was normally located at the radio operator's station, not the navigator's. This reduced the navigator's workload while also simplifying communications when a target was seen; the radio operator could easily communicate with the crew or send messages to other aircraft. Normally a number of blips would be seen, as other aircraft in the bomber stream
The bomber stream was a saturation attack tactic developed by the Royal Air Force (RAF) Bomber Command to overwhelm the nighttime German aerial defences of the Kammhuber Line during World War II.
The Kammhuber Line consisted of three layers of ...
made excellent returns. These remained largely stationary on the display as they were all flying roughly the same path, so enemy fighters were easy to see as dots moving around within the pattern of returns. If it was suspected a blip was approaching the bomber, they would change their heading and see if the blip followed; if it did, immediate defensive manoeuvring started.
X band
The resolution of any radar is a function of the wavelength used and the size of the antenna. In the case of H2S, the antenna size was a function of the bomber's turret opening, and when combined with the 10 cm wavelength, this led to a resolution of 8 degrees in arc. This was much coarser than desired, both for mapping purposes and for Coastal Command's desires to easily detect submarine conning towers. On 6 February 1943, work began on an X band version of the electronics, operating at 3 cm. This would improve resolution to 3 degrees when used with the same antenna. When priority was given to Bomber Command, Coastal Command responded by producing specifications for a far more advanced ASV system operating at 1.25 cm, but this was not completed by the end of the war. Work on 3 cm magnetrons had been ongoing for some time, and an AIS unit with such a device had been fitted to the nose ofRAF Defford
Royal Air Force Defford or more simply RAF Defford is a former Royal Air Force station located northwest of Defford, Worcestershire, England.
History
Second World War
At the outbreak of the Second World War, Croome Court and its surrounding ...
's Boeing 247
The Boeing Model 247 is an early United States airliner, and one of the first such aircraft to incorporate advances such as all-metal ( anodized aluminum) semimonocoque construction, a fully cantilevered wing, and retractable landing gear.
-D, '' DZ203'' as early as 1942. This aircraft had originally been supplied by the Canadian Defence Research Board to test US models of AI radar, and since then had been widely used in the development of several versions of AI, ASV and H2S. George Beeching had been assigned the task of fitting H2S to the Stirling, and in early 1943 he managed to obtain a single 3 cm magnetron from Herbert Skinner's AI group working on the Boeing. He had it working in the H2S electronics in a benchtop set on 7 March 1943, and then quickly fit it to Stirling ''N3724'' to make its first flight on 11 March. Testing showed the unit had very short range, and could not be used effectively over altitude. Further work was delayed by the need to fit the existing 10 cm sets to operational aircraft.
Bomber Command began a series of large-scale raids on Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
on the nights of 23/24 August, 31 August/1 September and 3/4 September 1943. H2S was found to be largely useless on these missions; the city was so large that picking out features proved very difficult. On 5 September, Saward visited the H2S team and showed them photographs of the PPI displays from H2S over Berlin. On the range setting, used during the bomb run, returns covered the entire display and there were no clear outlines of large objects on which to navigate. This was a surprise given the excellent results over Hamburg. After much argument among teams within the TRE on how to address this problem, on 14 September the team began working on an official version of H2S working in the X band.
By this time the American MIT Radiation Laboratory
The Radiation Laboratory, commonly called the Rad Lab, was a microwave and radar research laboratory located at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was first created in October 1940 and operated until 31 ...
facility was also entering the fray. They had decided to move directly to the 3 cm wavelength, calling their unit H2X
H2X, officially known as the AN/APS-15, was an American ground scanning radar system used for blind bombing during World War II. It was a development of the British H2S radar, the first ground mapping radar to be used in combat. It was also kno ...
. It was being deployed on American bombers by October 1943. By June there was an ongoing debate in the UK whether to continue the development of their own 3 cm H2S sets or simply use the American units when they became available. The suggestion was made that the existing H2S Mk. II units should be converted to X band, and the Americans should work on 3 cm ASV instead. This was followed by a 7 June meeting in which TRE management decided to press for three squadrons of 3 cm H2S by the end of the year. Lovell's team considered this to be basically impossible. Instead, they hatched a private plan to build and install a total of six sets which would equip Pathfinder Force Lancasters by the end of October.
Work continued on what was now known as H2S Mk. III, and an experimental set was first used over Berlin on the night of 18/19 November 1943. In comparison to the first mission with the Mk. I sets, the results using Mk. III were described as "most outstanding". Mk. III was rushed into production and saw its first real operational use on 2 December.
From this point until the end of the war, the Mk. III became the backbone of the Bomber Command fleet, and a large variety of versions were introduced. The first modification was the out-of-sequence Mk. IIIB, which added the range corrected Type 184 display unit from the IIC models, but lacked roll stabilization. Stabilization was added in the next version to see service, the Mk. IIIA. The new "whirligig" scanner was added to the Mk. IIIA to produce Mk. IIIC, while the original scanner with a higher power magnetron produced the Mk. IIID. The Type 216 display, using magnetic deflection, which was much easier to mass-produce, was added to the original IIIA to produce the Mk. IIIE, while the whirligig was added to the same unit to make the Mk. IIIF.
By the middle of 1944, the war in Europe was clearly entering its final stages, and the RAF began making plans to begin attacks on Japan with the Tiger Force group. In order to equip these aircraft, which would need both targeting and long-range navigation, a conversion system for the earlier Mk. II units was introduced. Based on non-stabilized IIC units, the Mk. IIIG used a new magnetron and receiver for 3 cm operation like the other Mk. III systems. The primary goal was to use it for long-range navigation, as opposed to bomb aiming. The final Mk. IIIH was IIIG with the Type 216 display.
Rotterdam Gerät
Before H2S was deployed in 1943, there was an intense debate over whether to use it due to the possibility of it being lost to the Germans. As it turned out, this occurred almost immediately. On its second combat mission, during the raid on Cologne on the night of 2/3 February 1943, shortly after crossing the coast one of the Stirlings carrying H2S was shot down nearRotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"Ne ...
by Reinhold Knacke. The device immediately attracted the attention of Wolfgang Martini
''Wolfgang Martini'' (September 20, 1891 – January 6, 1963) was a Career Officer in the German Air Force and largely responsible for promoting early radar development and utilization in that country.
Early career
While attending the Gymnasium ...
's technicians, who managed to salvage everything except for the PPI display.
Giving it the name ''Rotterdam Gerät'' (Rotterdam apparatus), a group formed to exploit the device and met for the first time on 23 February 1943 at Telefunken
Telefunken was a German radio and television apparatus company, founded in Berlin in 1903, as a joint venture of Siemens & Halske and the ''Allgemeine Elektrizitäts-Gesellschaft'' (AEG) ('General electricity company').
The name "Telefunken" ap ...
's offices in Berlin. A second example, also with a destroyed PPI, was captured on 1 March, ironically from a bomber that was part of a group attacking and greatly damaging Telefunken's offices, destroying the first example in the process.
According to Lovell, interrogation of surviving members of the second crew revealed that:
Combined with their own display, a set was reassembled on the Humboldthain flak tower
Flak towers (german: link=no, Flaktürme) were large, above-ground, anti-aircraft gun blockhouse towers constructed by Nazi Germany. There were 8 flak tower complexes in the cities of Berlin (three), Hamburg (two), and Vienna (three) from 1940 on ...
in Berlin. When it was activated clear images of the city appeared on the display, causing considerable consternation for Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German politician, military leader and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which ruled Germany from 1933 to 1 ...
. A quickly adopted countermeasure was put in place by installing small corner reflectors around the city, producing bright spots on the display in areas that would otherwise be empty, like lakes and rivers. Producing the reflectors with the required angular accuracy proved to be a difficult problem, as did keeping them in the right positions in order to produce the right image.
Although the basic concept of the magnetron was immediately understood, a number of details of the system as a whole remained a mystery, and it was also realized that building a complete radar system using it would take some time. So for the short term, they gave "panic priority" to a ground-based jammer and a detector that would allow their night fighters to home in on the microwave signals. This development was slowed by the German electronic industry's decision to stop researching microwaves shortly before ''Rotterdam Gerät'' literally fell from the sky. Another serious problem was a lack of suitable crystal detector
A crystal detector is an obsolete electronic component used in some early 20th century radio receivers that consists of a piece of crystalline mineral which rectifies the alternating current radio signal. It was employed as a detector ( de ...
s that were key to the British receiver designs.
Several jammer systems were trialled. The first, known as ''Roderich'', was developed by Siemens. These used a transmitter mounted on a tower pointed at the ground, the reflections off the ground spreading the signal out in space where they were picked up by the H2S receivers. Roderich transmissions were timed roughly with the scanning speed of the H2S antenna, causing a pattern to appear similar to a pinwheel that made it difficult to see the ground between its pulses. However, their magnetron was only capable of 5 W of power, giving it very short range. They were so ineffective that they were abandoned in 1944. Another system, ''Roland'', used a 50 W klystron, but it was also considered unsuccessful and abandoned around March 1945. Another klystron-based system, ''Postklystron'', was designed by the Reichspost
''Reichspost'' (; "Imperial Mail") was the name of the postal service of Germany from 1866 to 1945.
''Deutsche Reichspost''
Upon the out break of the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 and the break-up of the German Confederation in the Peace of ...
and deployed around Leuna
Leuna is a town in Saxony-Anhalt, eastern Germany, south of Merseburg and Halle, on the river Saale.
The town is known for the ''Leunawerke'', at 13 km2 one of the biggest chemical industrial complexes in Germany, where a very wide range of ...
.
Two detector systems were ordered: a simple passive system that was essentially just a high-frequency receiver, which became ''Naxos'', and a much more sensitive system using its own magnetron as a local oscillator
In electronics, a local oscillator (LO) is an electronic oscillator used with a mixer to change the frequency of a signal. This frequency conversion process, also called heterodyning, produces the sum and difference frequencies from the frequenc ...
known as ''Korfu''. Both required crystal detectors in their receivers, and a crash program to develop them began. These began delivery in a few months, but proved difficult to mass-produce and extremely fragile in the field. This limited the availability of the ''Funkgerät'' (FuG) 350 Naxos radar detector
The Naxos radar warning receiver was a World War II German countermeasure to S band microwave radar produced by a cavity magnetron. Introduced in September 1943, it replaced Metox, which was incapable of detecting centimetric radar. Two versio ...
to a handful of operational examples, which enabled Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
night fighters to home on the transmissions of H2S. A U version of the same equipment was used to allow U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
s to detect microwave-frequency ASVs.
The RAF remained unaware of the Naxos until the spring of 1944 when a number of intelligence reports suggested the Germans had developed an H2S detector. By this time, the Germans had only a few dozen such detectors in service, but the reports reopened the longstanding debate between the supporters of H2S and those of UK-based navigation systems like Oboe. This corresponded with a period of increased losses among Bomber Command, and there were calls for the system to be abandoned. The matter was debated for months.
The issue was finally settled by a study by Saward. He noted that losses during the Naxos period were actually lower, down from 4% to 2% of the sorties. The drop corresponded with the introduction of Fishpond. Saward concluded that:
In July 1944, a Ju 88G-1 of 7 '' Staffel''/ NJG 2 flew the wrong way on a landing beacon and landed at RAF Woodbridge
Royal Air Force Woodbridge or RAF Woodbridge, is a former Royal Air Force station located east of Woodbridge in the county of Suffolk, England.
Constructed in 1943 as a Royal Air Force (RAF) military airfield during the Second World War to a ...
by accident. The crew were arrested before they could destroy their equipment, providing the British researchers with the latest version of the ''Lichtenstein'' SN-2 VHF-band radar, the Flensburg radar detector, and the FuG 25a Erstling IFF gear. Interrogation of the crew revealed that the Flensburg system detected the RAF bombers' Monica radar emissions and that it was used as a homing system. Naxos was not fitted, and the crew stated that it was only used for initial warning, not as a homing system. This was all to the great relief of everyone involved; Monica was already being replaced by Fishpond systems on most aircraft, and those aircraft with Monica were told to turn it off. H2S remained in use for the rest of the war.
As the British engineers had predicted, it took the Germans two years to complete the development of magnetron based radars. The first to reach operation in early 1945 was the FuG 240 ''Berlin'', an AI radar very similar to the British AI Mk. VIII. By this time the country was on the brink of defeat and ''Berlin'' never entered service. A small number were fitted experimentally, one of which was captured by the RAF in a shot-down Ju 88. Several other radars developed from the same basic systems were also introduced but saw limited or no service. One advancement made by the Germans during this period was a new type of antenna using a dielectric to shape the output, known in the UK as a ''polyrod''.
Continued developments
Improved computers
In a separate line of development, the RAF was working on a pair ofmechanical computer
A mechanical computer is a computer built from mechanical components such as levers and gears rather than electronic components. The most common examples are adding machines and mechanical counters, which use the turning of gears to increment out ...
s known as the Air Mileage Unit (AMU) and Air Position Indicator (API), which continually performed dead reckoning
In navigation, dead reckoning is the process of calculating current position of some moving object by using a previously determined position, or fix, and then incorporating estimates of speed, heading direction, and course over elapsed time. ...
calculations, greatly reducing navigator workload. This was fed by inputs similar to those for the Mk. XIV bomb sight, namely the estimated wind direction and speed, with the aircraft heading and speed fed in automatically from the aircraft instruments. The system output was a varying voltage that could be used to drive the Mk. XIV bomb sight.
In a development known as Mark IV, H2S was modified to also read these voltages, which offset the centre of the display by an amount proportional to the signals. This would counteract the motion of the aircraft, and "freeze" the display. When initially set up these calculations were never perfect, so some residual drift on the display was normally encountered. The navigator could then fine tune these settings with controls on the display, adjusting them until the image was perfectly still. These values then fed back into the AMU and API, producing highly accurate measurements of the winds aloft. The Mk. IVA used the larger whirligig scanner. None were available by the time the war ended.
K band
Further improvements in magnetron and receiver design during the war led to the ability to use even shorter wavelengths, and in the summer of 1943 the decision was made to begin development of versions operating in the K band at 1.25 cm. This would improve the resolution by more than a factor of two over the X band versions, and was especially interesting as a system for low-level bombing where the short local horizon limited the amount of territory visible on the display and would require guidance on smaller objects like particular buildings. The corollary of this improved resolution was that a K-band system would offer the same resolution as the X-band system with an antenna half the size. Such an antenna would fit on the Mosquito, and development of a scanner began. The Mosquito was already widely used for pinpoint target indicator operations, and fitting them with H2S would further increase their abilities. On 22 February 1944, the development group proposed rapidly fitting Mark IV to all Lancasters, and for higher-accuracy needs, developing either an X-band Whirligig, or a K-band with a smaller antenna. Instead, they were ordered to do both. The K-band work was given the name "Lion Tamer". The first test of the basic equipment took place on aVickers Wellington
The Vickers Wellington was a British twin-engined, long-range medium bomber. It was designed during the mid-1930s at Brooklands in Weybridge, Surrey. Led by Vickers-Armstrongs' chief designer Rex Pierson; a key feature of the aircraft is its ...
on 8 May 1944, and Lancaster ''ND823'' was equipped with the prototype Mark VI and flew on 25 June. However, a meeting on 16 June noted that the range of the K-band sets was not good, with tests in the US reaching only from altitude. Further, production was not ready for large-scale deliveries, and as Dee put it, "the present programme of 100 H2S Mark VI equipments should be regarded as an expression of faith."
Several new features became part of the Lion Tamer effort. Due to the much higher resolution of the K-band signals, a new display was needed because the dot produced on the older display was too large and overlapped details on either side. A solution was found in the Type 216 display, which featured ''sector scan'', which allowed the operator to select one of the eight compass rose
A compass rose, sometimes called a wind rose, rose of the winds or compass star, is a figure on a compass, map, nautical chart, or monument used to display the orientation of the cardinal directions (north, east, south, and west) and their i ...
points and the display expanded to show only that sector. This effectively doubled the resolution of the display. Meanwhile, work on the new mechanical computers for air navigation was progressing well. It was decided that the Mark VI should be able to connect to these systems. Eventually, all of these changes were rolled up into the proposed Mark VIII.
During the late summer of 1944, as the post- D-Day operations bogged down, there was renewed interest in using the K-band system to detect tactical targets like tanks. Lancaster ''JB558'' was fit with a 6-foot scanner and a K-band set and began tests at low altitudes between beginning in December 1944. The results were "immediately staggering", with the displays showing high-quality images of individual buildings, roads, railways and even small streams.
Similar experiments with the smaller 3-foot scanner were not so successful in this role. At a meeting on 16 December, it was decided to move ahead with Lancasters with 6-foot scanners and Mosquitos with 3-foot scanners. This meant the K-band equipment originally planned to be installed on the Pathfinder Force would be used on these aircraft instead. Pathfinder Force received the Mark IIIF X-band equipment instead.
Ultimately, only the Mosquitoes were ready before the war ended, and carried out a total of three target marking operations for the Pathfinder Force. When the war ended and the Lend-Lease program ended with it, the availability of the K-band magnetrons disappeared. Additionally, in high-altitude tests, it was noticed that the signal disappeared in clouds, an observation that would later give rise to weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar (WSR) and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, and estimate its type (rain, snow, hail etc.). Modern weather radars are mostly pulse- ...
systems, but in the meantime made the system less than useful. The Director of Radar in the Air Ministry decided to embargo all work on the K-band systems for security reasons.
H2D
Looking to further improve the navigational aspects of the system, some work was carried out on a system known as H2D, the D for "Doppler". The idea was that the Doppler shift of the signals due to the motion over the ground could be used to determine the ground speed. In still air, the maximum Doppler shift would be seen dead ahead, but in the presence of any winds aloft, the sideways component would cause the maximum point to shift to an angle, while the head or tail component would make the measured Doppler speed differ from the airspeed indicator. By comparing these measurements to the aircraft's airspeed and heading, the wind speed and direction could be accurately calculated. Testing began at RAF Defford on Wellington ''NB822'' in early 1944. It became apparent that the sensitivity of the unit was enough that ground traffic like trucks and trains became visible on the display. This is the first example of what is today known asmoving target indication
Moving target indication (MTI) is a mode of operation of a radar to discriminate a target against the clutter. It describes a variety of techniques used for finding moving objects, like an aircraft, and filter out unmoving ones, like hills or tree ...
, which would theoretically allow an aircraft to scan for targets across a wide area. A second aircraft, ''NB823'', joined the effort in June 1944, and then a third (unknown ID).
More rigorous testing demonstrated that the experimental set was only really useful when the aircraft was flying under and had a maximum effective detection range on the order of . Work to improve these numbers was slow going, and the project was eventually relegated to purely experimental with no plans to introduce a service version.
Post-war
 After
After VE day
Victory in Europe Day is the day celebrating the formal acceptance by the Allies of World War II of Germany's unconditional surrender of its armed forces on Tuesday, 8 May 1945, marking the official end of World War II in Europe in the Easter ...
, all models earlier than the Mk. IIIG were declared obsolete, and ongoing work on many of the newer versions ended. In place of the entire series from Mk. VI to VIII came the Mark IX, which was essentially a version of the 3 cm Mk. VIII designed specifically for use on the E3/45 jet bomber, which after becoming B3/45, would finally emerge as the English Electric Canberra
The English Electric Canberra is a British first-generation, jet-powered medium bomber. It was developed by English Electric during the mid- to late 1940s in response to a 1944 Air Ministry requirement for a successor to the wartime de Havil ...
.
In contrast to the earlier designs that were added to existing bombers in an external fairing, for E3/45 the radar was designed as an integral part of the aircraft. It was otherwise a relatively straightforward upgrade to the existing Mk. VIII with a much more powerful 200 kW magnetron and numerous other minor changes. A contract was awarded to EMI in 1946 as the Mark IX, but during development it was amended to also equip the much larger B14/46 bomber designs, the V-force
V Force was a reconnaissance, intelligence-gathering and guerrilla organisation established by the British against Japanese forces during the Burma Campaign in World War II.
Establishment and organisation
In April 1942, when the Japanese drove t ...
. These were essentially identical to the original concept, but used the larger "whirligig" reflector and became the Mk. IXA. Using the larger whirligig reflector and a slotted waveguide
A slot antenna consists of a metal surface, usually a flat plate, with one or more holes or slots cut out. When the plate is driven element, driven as an antenna (radio), antenna by an applied radio frequency current, the slot radiates electromagn ...
allowed the angular beamwidth to be reduced to 1.5 degrees, a great improvement over the World War II models.
The Mk. IX, later known as Mk. 9 when roman numerals were dropped, allowed the scanning rate to be set at 8, 16 or 32 RPM. Additionally, like the K-band models, the IX included the ability to perform a sector scan, limiting the movement of the scanner so instead of performing complete circles it scanned back and forth across a smaller angle. In this case, the idea was not to improve resolution but to provide much more rapid updates of the selected area, which was needed in order to account for the much higher speed of the aircraft. This was especially useful on the V-force, where the radar's location in the nose made it difficult to scan to the rear anyway, and at best some 60 to 90 degrees was always blocked. Further limiting the scan to 45 degrees, on-demand, was not a real loss.
The system also added the ability to perform ''offset bombing'', a relatively common addition to post-war bombing systems. It was found during operations that the target might not appear on the radar; in these cases, the navigator would select a nearby feature that would be visible, a bend in a river or a radio tower for instance, and measure the angle and distance between it and the target. They would then attempt to guide the aircraft so that the selected aiming feature was in the proper location relative to the centre of the display, by no means a simple task. Offset bombing allowed the navigator to dial these offsets into the display, which caused the entire display to move by that amount. The navigator then guided the aircraft so that the selected feature passed through the centre of the display, which was much easier to arrange.
Through the same period, the API was replaced by the more advanced Navigation and Bombing Computer (NBC), which, when combined with Mk. IX and Green Satin radar, formed the Navigation and Bombing System (NBS). Green Satin made highly accurate and completely automatic measurements of wind speed and direction, allowing the NBC to perform dead reckoning calculations with a very high degree of accuracy. This further automated the navigation process to the point where separate navigators and bomb aimers were no longer needed, and some aircraft were designed with a crew of only two.
Development proceeded at a slower rate due to post-war austerities. Flight testing of the smaller Mk. IX began in 1950 on an Avro Lincoln, followed by the Mk. IXA in 1951 on Handley Page Hastings or Avro Ashton aircraft. As this was too late for the Canberra, which entered service in 1951, early models had to be modified with a conventional glass nose for optical bombing. The Mk. IVA remained in service until 1956 when the Mk. IX finally entered service on the V-force.
The first use of NBS in combat was in 1956, when Vickers Valiants performed long-range strikes on the Egyptian Air Force at Cairo Airport. The system remained in service with the V bomber force (Valiant, Avro Vulcan
The Avro Vulcan (later Hawker Siddeley Vulcan from July 1963) is a jet-powered, tailless, delta-wing, high-altitude, strategic bomber, which was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) from 1956 until 1984. Aircraft manufacturer A.V. Roe an ...
and Handley Page Victor
The Handley Page Victor is a British jet-powered strategic bomber developed and produced by Handley Page during the Cold War. It was the third and final '' V bomber'' to be operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF), the other two being the Avr ...
) throughout their lifetime. The last use in combat was made by the Vulcans of the Operation Black Buck
Operations Black Buck 1 to Black Buck 7 were seven extremely long-range ground attack missions conducted during the 1982 Falklands War by Royal Air Force (RAF) Vulcan bombers of the RAF Waddington Wing, comprising aircraft from 44, 50 an ...
flights in 1982 during the Falklands War, which used the system as the primary navigation and bombing aid throughout the round trips to and from Ascension Island. Mk. IX was also used on the Handley Page Victor
The Handley Page Victor is a British jet-powered strategic bomber developed and produced by Handley Page during the Cold War. It was the third and final '' V bomber'' to be operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF), the other two being the Avr ...
, the last examples of which left service in 1993.
In 1950 a further requirement for more accurate conventional bombing was raised, demanding accuracy from an aircraft flying at and . This led to the early consideration of a version operating in the Q-band
The Q band is a range of frequencies contained in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Common usage places this range between 33 and 50 GHz, but may vary depending on the source using the term. The foregoing range corresponds ...
at 8 mm wavelength. An experimental version was constructed in 1951, but in practice the Mk. IX proved useful enough on its own and development was dropped.
Versions
''From Lovell:'' * Mark I – prototype versions fit to Pathfinder Force (TR3159) * Mark II – main production version with standard scanner (TR3191) * Mark IIA – replaced the scanner's dipole antenna with a horn and waveguide * Mark IIB – IIA with Fishpond displays * Mark IIC – IIB with Type 184 scan-corrected display, roll stabilized scanner, and improved antenna reflector that eliminated the metal fillet * Mark III – prototype 3 cm versions, six produced by December 1943 * Mark IIIA – III with Type 184 display and roll stabilized scanner * Mark IIIB – III with Type 184 display (introduced as an interim model before IIIA while stabilizer production improved) * Mark IIIC – IIIA with the 6-foot whirligig scanner * Mark IIID – IIIA with a more powerful magnetron * Mark IIIE – IIIA with the Type 216 display, new scanner and using a shorter pulse length * Mark IIIF – IIIE with whirligig scanner * Mark IIIG – IIC systems converted to 3 cm, lacking the stabilizer. Intended primarily for long-range navigation by Tiger Force * Mark IIIH – IIIG with Type 216 display * Mark IV – IIIA with altitude correction, links to AMU computer and Mk. XIV bombsight. Passed over in favour of Mk. IVA * Mark IVA – IV with whirligig scanner, standard model on Avro Lincoln bombers * Mark V – set aside for H2X but not used * Mark VI – IIIF operating at 1.25 cm wavelength, also with 28-inch scanner for Mosquitos. Also known as Lion Tamer. * Mark VII – updated Mark VI with links to the navigation system, cancelled with the ending of the war * Mark VIII – Mark IVA operating in the X-band, replacement for Mk. VII. Four produced. * Mark IX, IXA – Mk. VIII with 200 kW magnetron and many other improvements. Used on the V bombers.See also
*Naxos radar detector
The Naxos radar warning receiver was a World War II German countermeasure to S band microwave radar produced by a cavity magnetron. Introduced in September 1943, it replaced Metox, which was incapable of detecting centimetric radar. Two versio ...
, created by Germany to spot H2S transmissions
* List of World War II electronic warfare equipment
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
Sitzungsprotokolle der Arbeitsgemeinschaft Rotterdam
minutes of the meetings of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Rotterdam (AGR) *
External links
* ttp://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1945/1945%20-%201767.html ''Bomber's Radar – General Survey of the Three Primary Systems Used by Bomber Command''– ''Flight'' article of September 1945
H2S Equipment (AP2890L) operators manual
Air Ministry, July 1944 {{RAF WWII Strategic Bombing Aircraft radars World War II radars World War II British electronics Military radars of the United Kingdom British inventions Military equipment introduced from 1940 to 1944