Hypsipyle Sauve Thoas BnF Français 599 Fol on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 The Roman poets
The Roman poets
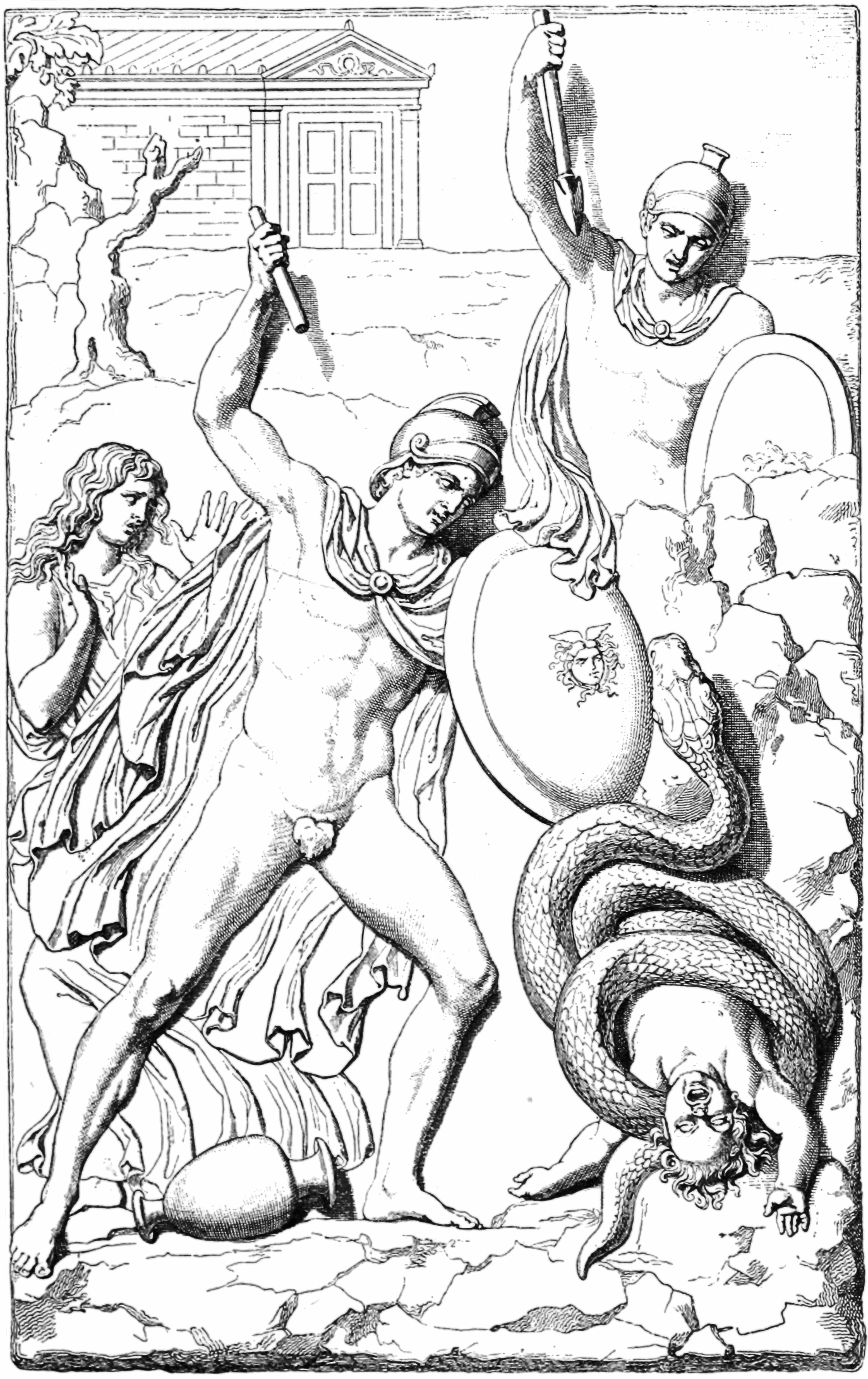 Hypsipyle became involved in the story of the infant
Hypsipyle became involved in the story of the infant
3.6.4
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
*
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
*
Internet Archive
* Bravo, Jorge J., III, ''Excavations at Nemea IV: The Shrine of Opheltes'', Univ of California Press, 2018. . *
Online version at Harvard University Press
. * Collard, Christopher and Martin Cropp, ''Euripides Fragments: Oedipus-Chrysippus: Other Fragments'',
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Fletcher, Judith, "Lemnian Infamy and Masculine Glory in Apollonios' ''Argonautica''" in ''Celebrity, Fame, and Infamy in the Hellenistic World'', edited by Riemer A. Faber, University of Toronto Press, 2020. . * Gantz, Timothy, ''Early Greek Myth: A Guide to Literary and Artistic Sources'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996, Two volumes: (Vol. 1), (Vol. 2). * Grimal, Pierre, ''The Dictionary of Classical Mythology'', Wiley-Blackwell, 1996. . * Hard, Robin, ''The Routledge Handbook of Greek Mythology: Based on H.J. Rose's "Handbook of Greek Mythology"'', Psychology Press, 2004,
Google Books
*
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
*
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Hyginus, Gaius Julius, ''
Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Online version at Harvard University Press
* ''
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Pepin, Ronald E., ''The Vatican Mythographers'', Fordham University Press, 2008. . *
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
*
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Smith, William, ''
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Sommerstein, Alan H., ''Aeschylus: Fragments.'' Edited and translated by Alan H. Sommerstein.
Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1991. * Tripp, Edward, ''Crowell's Handbook of Classical Mythology'', Thomas Y. Crowell Co; First edition (June 1970). . * Valerius Flaccus, Gaius, ''Argonautica'', translated by J. H. Mozley,
Online version at Harvard University Press
{{Authority control Princesses in Greek mythology Queens in Greek mythology Characters in the Argonautica Lemnian characters in Greek mythology Nemea] Fictional Greek and Roman slaves Deeds of Aphrodite
 In
In Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
, Hypsipyle (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
: Ὑψιπύλη) was a queen of Lemnos
Lemnos or Limnos ( el, Λήμνος; grc, Λῆμνος) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean region. The p ...
, and the daughter of King Thoas of Lemnos, and the granddaughter of Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
and Ariadne
Ariadne (; grc-gre, Ἀριάδνη; la, Ariadne) was a Cretan princess in Greek mythology. She was mostly associated with mazes and labyrinths because of her involvement in the myths of the Minotaur and Theseus. She is best known for having ...
. When the women of Lemnos killed all the males on the island, Hypsipyle saved her father Thoas. She ruled Lemnos when the Argonauts
The Argonauts (; Ancient Greek: ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, '' Argo'', ...
visited the island, and had two sons by Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea. He w ...
, the leader of the Argonauts. Later the women of Lemnos discovered that Thoas had been saved by Hypsipyle and she was sold as a slave to Lycurgus
Lycurgus or Lykourgos () may refer to:
People
* Lycurgus (king of Sparta) (third century BC)
* Lycurgus (lawgiver) (eighth century BC), creator of constitution of Sparta
* Lycurgus of Athens (fourth century BC), one of the 'ten notable orators' ...
, the king of Nemea
Nemea (; grc, Νεμέα; grc-x-ionic, Νεμέη) is an ancient site in the northeastern part of the Peloponnese, in Greece. Formerly part of the territory of Cleonae in ancient Argolis, it is today situated in the regional unit of Corinthia ...
, where she became the nurse of the king's infant son Opheltes
In Greek mythology, Opheltes (Ancient Greek: Ὀφέλτης), also called Archemorus (Αρχέμορος, Beginning of Doom), was a son of Lycurgus (of Nemea), Lycurgus of Nemea. His mother is variously given as Eurydice (Greek myth), Eurydice, ...
, who was killed by a serpent while in her care. She is eventually freed from her servitude by her sons.
Family
Hypsipyle's father was Thoas, who was the son ofDionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
and Ariadne
Ariadne (; grc-gre, Ἀριάδνη; la, Ariadne) was a Cretan princess in Greek mythology. She was mostly associated with mazes and labyrinths because of her involvement in the myths of the Minotaur and Theseus. She is best known for having ...
. According to the ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odysse ...
'', Hypsipyle was the mother, by Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea. He w ...
, of Euneus In Greek mythology, Euneus ( Ancient Greek: Εὔνηος) was a son of Jason and Queen Hypsipyle of Lemnos; he had a twin brother whose name is variously given as Nebrophonus, Thoas or Deipylus.
Mythology
The children were separated from the ...
. Later sources say that Hypsipyle had, in addition to Euneus, a second son by Jason. In Euripides' partially preserved play ''Hypsipyle
In Greek mythology, Hypsipyle (Ancient Greek: Ὑψιπύλη) was a queen of Lemnos, and the daughter of King Thoas of Lemnos, and the granddaughter of Dionysus and Ariadne. When the women of Lemnos killed all the males on the island, Hypsipyle ...
'', she and Jason had twin sons: Euneus and Thoas. According to Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
, the second son was Nebrophonus, while according to Hyginus
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of Caesar Augustus. He was elected superintendent of the Palatine library by Augustus according to Suetonius' ''De Grammatic ...
, the second son was Deipylus, Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the th ...
says simply that Hypsipyle bore Jason twins, without naming them.
The Lemnian crime and the rescue of Thoas
The women of Lemnos killed all the males on the island, except for Thoas, who was saved by Hypsipyle. Traces of the story can be found in the ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odysse ...
'' (c. 8th century), where Lemnos is referred to as the "city of godlike Thoas", and Euneus In Greek mythology, Euneus ( Ancient Greek: Εὔνηος) was a son of Jason and Queen Hypsipyle of Lemnos; he had a twin brother whose name is variously given as Nebrophonus, Thoas or Deipylus.
Mythology
The children were separated from the ...
, Jason's son by Hypsipyle, is mentioned. As early as Aeschylus the story was famous: "the Lemnian holds first place among evils in story: it has long been told with groans as an abominable calamity. Men compare each new horror to Lemnian troubles." And by the time of the mid-5th-century BC historian Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
, the story had given rise to the proverbial phrase "Lemnian crime" used to mean any cruel deed. Aeschylus probably dealt with it in his' lost tragedies ''Hypsipyle'' and ''Lemniai'' (late 6th century-early 5th century BC). The lyric poet
Modern lyric poetry is a formal type of poetry which expresses personal emotions or feelings, typically spoken in the first person.
It is not equivalent to song lyrics, though song lyrics are often in the lyric mode, and it is also ''not'' equi ...
Pindar
Pindar (; grc-gre, Πίνδαρος , ; la, Pindarus; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar is ...
(late 6th century-early 5th century BC) mentions "the race of the Lemnian women, who killed their husbands."
''Hypsipyle''
There is a brief mention of the story inEuripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful e ...
' partially preserved play ''Hypsipyle
In Greek mythology, Hypsipyle (Ancient Greek: Ὑψιπύλη) was a queen of Lemnos, and the daughter of King Thoas of Lemnos, and the granddaughter of Dionysus and Ariadne. When the women of Lemnos killed all the males on the island, Hypsipyle ...
'' (c. 410 BC), in an exchange between Hypsipyle and her son Euneus:
::Hypsipyle
:Alas, the flight that I fled, my son—if you only knew it—from sea-girt Lemnos, because I did not cut off my father’s grey head!
::Euneus
:Did they really order you to kill your father?
::Hypsipyle
:I am gripped by fear of those evil events—O my son, like Gorgons they slew their husbands in their beds!
Apollonius of Rhodes' ''Argonautica''
The earliest extant telling of the story in detail occurs in the 3rd-century BC ''Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' ( el, Ἀργοναυτικά , translit=Argonautika) is a Greek epic poem written by Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only surviving Hellenistic epic, the ''Argonautica'' tells the myth of the voyage of Jason a ...
'' by Apollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius of Rhodes ( grc, Ἀπολλώνιος Ῥόδιος ''Apollṓnios Rhódios''; la, Apollonius Rhodius; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek author, best known for the ''Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and t ...
. According to this account, the women of Lemnos had long neglected the worship of Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols include ...
, and because of this the goddess caused their husbands to spurn them in favor of captive Thracian women. In revenge, the women massacred all the males on the island, except for the "aged" Thoas, whom Hypsipyle put into a "hollow chest," setting him adrift on the open sea. Fishermen pulled him ashore on the island of Sicinus
Sikinos ( el, Σίκινος) is a Greek island and municipality in the Cyclades. It is located midway between the islands of Ios and Folegandros. Sikinos is part of the Thira regional unit.
It was known as Oenoe or Oinoe ( grc, Οἰνόη, I ...
. The Lemnian women took over all the previous work of the men, cattle-herding, plowing, and warfare.
Valerius Flaccus' ''Argonautica''
The 1st-century AD Latin poet Valerius Flaccus, in his ''Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' ( el, Ἀργοναυτικά , translit=Argonautika) is a Greek epic poem written by Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only surviving Hellenistic epic, the ''Argonautica'' tells the myth of the voyage of Jason a ...
'', gives a different reason for Aphrodite (Venus) causing the Lemnian men to reject their wives. He says it was because of the goddess' anger with her husband, the god Hephaestus
Hephaestus (; eight spellings; grc-gre, Ἥφαιστος, Hḗphaistos) is the Greek god of blacksmiths, metalworking, carpenters, craftsmen, artisans, sculptors, metallurgy, fire (compare, however, with Hestia), and volcanoes.Walter Burk ...
(Vulcan)—who had a home on Lemnos—for his having caught her in a tryst with Ares (Mars). He also gives a more detailed account of Thoas' rescue and escape. During the night of the massacre, Hypsipyle woke Thoas, covered his head, and took him to Dionysus' temple where she hid him. The next morning, Hypsipyle disguised Thoas as the temples' cult statue of Dionysus, placed him on the ritual chariot (used to parade the statue). She then took Thoas through the streets of the city, crying aloud that the god's statue had been polluted by the night's bloody murders, and needed to be cleansed in the sea. By this subterfuge, and with the god Dionysus' help, Thoas was safely hid outside the city. But fearing discovery, Hypsipyle finds an old abandoned boat, in which Thoas put to sea, eventually reaching the land of the Taurians, where "Diana put a sword in his hand, and didst appoint him warden of thy cheerless altar". And the women of Lemnos bestow on Hypsipyle "the throne and sceptre of her father as by right".
Other accounts
Other accounts tell similar stories, with variations. According to the 1st-century AD Latin poetStatius
Publius Papinius Statius (Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; ; ) was a Greco-Roman poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving Latin poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the ''Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetry, ...
, Hypsipyle hid Thoas on a ship, while according to the late 1st-century BC Latin mythographer Hyginus
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of Caesar Augustus. He was elected superintendent of the Palatine library by Augustus according to Suetonius' ''De Grammatic ...
, who identifies Thoas with the Thoas who was the Taurian king, Hypsipyle put Thoas onto a ship which a storm carried to the "island Taurica".
According to the Greek mythographer Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
(first or second century AD), the women of Lemnos were rejected by their husbands because Aphrodite had caused them to omit a foul odor. Apollodorus also gives a different ending to the story: while Thoas was saved when Hypsipyle hid him, when, sometime later, the Lemnian women discovered that Thoas had escaped the initial slaughter, they killed Thoas, and sold Hypsipyle into slavery.
Affair with Jason
The first adventure (usually) ofJason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea. He w ...
and the Argonauts
The Argonauts (; Ancient Greek: ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, '' Argo'', ...
, on their quest for the Golden Fleece
In Greek mythology, the Golden Fleece ( el, Χρυσόμαλλον δέρας, ''Chrysómallon déras'') is the fleece of the golden-woolled,, ''Khrusómallos''. winged ram, Chrysomallos, that rescued Phrixus and brought him to Colchis, where P ...
, is their visit to the island of Lemnos
Lemnos or Limnos ( el, Λήμνος; grc, Λῆμνος) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean region. The p ...
, where Hypsipyle was then queen. The story seems at least as old as the ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odysse ...
'', since Euneus In Greek mythology, Euneus ( Ancient Greek: Εὔνηος) was a son of Jason and Queen Hypsipyle of Lemnos; he had a twin brother whose name is variously given as Nebrophonus, Thoas or Deipylus.
Mythology
The children were separated from the ...
is said to be a son of Jason and Hypsipyle, and was dealt with in Aeschylus' lost tragedies ''Hypsipyle'' and ''Lemniai'', although the only surviving detail is that the Lemnian women "in arms" refused to allow the Argonauts to land until they agreed to mate with them. Pindar
Pindar (; grc-gre, Πίνδαρος , ; la, Pindarus; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar is ...
refers to the visit, mentioning the Argonauts engaging in athletic contests, receiving garments made by the Lemnian women as prizes, and sharing the women's beds. In Sophocles
Sophocles (; grc, Σοφοκλῆς, , Sophoklễs; 497/6 – winter 406/5 BC)Sommerstein (2002), p. 41. is one of three ancient Greek tragedians, at least one of whose plays has survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or co ...
' lost play ''Lemniai'', there was apparently a battle between the Argonauts and the Lemnian women. The story also played a part in Euripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful e ...
' partially preserved play ''Hypsipyle'', where Hypsipyle is reunited with her twin sons by Jason, Euneus and Thoas, and learns, to her sorrow, of Jason's death.
Apollonius of Rhodes' ''Argonautica''
The first complete account of the Argonauts encounter with Hypsipyle on Lemnos is given inApollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius of Rhodes ( grc, Ἀπολλώνιος Ῥόδιος ''Apollṓnios Rhódios''; la, Apollonius Rhodius; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek author, best known for the ''Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and t ...
' ''Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' ( el, Ἀργοναυτικά , translit=Argonautika) is a Greek epic poem written by Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only surviving Hellenistic epic, the ''Argonautica'' tells the myth of the voyage of Jason a ...
''. According to Apollonius of Rhodes' version of the story, when the Argonauts first arrive, Hypsipyle and the women, fearing that the Argonauts' were Thracians coming to attack them, put on amour and rush to the beach, to defend their island. However the Argonauts herald Aethalides
In Greek mythology, Aethalides (; Ancient Greek: Αἰθαλίδης) was a son of Hermes and Eupolemeia, a daughter of King Myrmidon of Phthia.
Mythology
Aethalides was the herald of the Argonauts, and had received from his father the facu ...
was able to persuade Hypsipyle to allow the Argonauts to stay for one night on the island.
The next day, sitting on her father's throne, Hypsipyle spoke to the assembled women of the Island:
:My friends, come, let us give these men gifts to their liking, such things as men ought to take with them on a ship, provisions and sweet wine, so that they might forever remain outside our walls, lest out of need they may come among us and get to know us all too accurately, and an evil report may travel far and wide. For we have done a terrible deed, and it will not be at all heart-cheering to them either, if they were to learn of it.
However, Hypsipyle's old nurse Polyxo said that, rather than live in continual fear of attack, they should take the Argonauts as their mates and protectors. All the women agreed to this plan, and so Hypsipyle received the Argonauts as welcome guests.
Hypsipyle told Jason the Lemnian women's story, saying that because of Aphrodite, the men of Lemnos had come to hate their wives, expelling them from their homes, and replacing them with Thracian girls captured on their frequent raids on nearby Thrace. Finally, after enduring terrible hardship, the women found the courage to take action. But Hypsipyle did not tell of the massacre, instead she deceived Jason, saying that one day when the men were returning from a raid, the women refused to allow the men to reenter the city, so the men took their sons and resettled in Thrace. Hypsipyle then asked Jason and his men to stay and take up residence on the island.
So the Argonauts stayed for a while on the island, residing with the women in their homes, including Jason, who lived with Hypsipyle in her palace. But finally, at the urging of Heracles
Heracles ( ; grc-gre, Ἡρακλῆς, , glory/fame of Hera), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive ...
, who had remained apart, the Argonauts agreed to leave the women, and continue their quest for the Golden Fleece.
Hypsipyle told Jason that "her father's scepter will be waiting" for him should he return to the island, but that she does not think that he will, and asked him to promise to remember her always, and to tell her what she should do with any children of his she might bear. And Jason told her to send any son, when grown, to Jason's parents in Iolcus
Iolcus (; also rendered ''Iolkos'' ; grc, Ἰωλκός and Ἰαωλκός; grc-x-doric, Ἰαλκός; ell, Ιωλκός) is an ancient city, a modern village and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local gove ...
. Jason took with him a "sacred purple robe", given to him by Hypsipyle, which had been made by the Graces
In Greek mythology, the Charites ( ), singular ''Charis'', or Graces, were three or more goddesses of charm, beauty, nature, human creativity, goodwill, and fertility. Hesiod names three – Aglaea ("Shining"), Euphrosyne ("Joy"), and Thali ...
for Dionysus, who gave it to his son Thoas, who in turn gave it to Hypsipyle.
Later accounts
 The Roman poets
The Roman poets Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the th ...
, Valerius Flaccus, and Statius
Publius Papinius Statius (Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; ; ) was a Greco-Roman poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving Latin poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the ''Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetry, ...
, all wrote about the affair of Hypsipyle and Jason. Their accounts are all similar to that of Apollonius of Rhodes, with a few variations and additional details.
In his ''Heroides
The ''Heroides'' (''The Heroines''), or ''Epistulae Heroidum'' (''Letters of Heroines''), is a collection of fifteen epistolary
Epistolary means "in the form of a letter or letters", and may refer to:
* Epistolary ( la, epistolarium), a Christi ...
'' 6, Ovid has Hypsipyle, in an angry letter, rebuke Jason for having forsaken her for Medea
In Greek mythology, Medea (; grc, Μήδεια, ''Mēdeia'', perhaps implying "planner / schemer") is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, a niece of Circe and the granddaughter of the sun god Helios. Medea figures in the myth of Jason an ...
, whom she says "intrudes upon my marriage-bed". She says that Jason spent two years on Lemnos, and that, although he promised her "thine own will I ever be", and told her of his hope to share in the parenting of their offspring then in her womb, she now knows that Jason has taken up with Medea, and calls all these words of Jason "lies".
In his ''Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' ( el, Ἀργοναυτικά , translit=Argonautika) is a Greek epic poem written by Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only surviving Hellenistic epic, the ''Argonautica'' tells the myth of the voyage of Jason a ...
'', Valerius Flaccus, when the Argonauts are making ready to leave Lemnos, has a "weeping" Hypsipyle say to Jason: "So quickly, at the first clear sky, dost thou resolve to unfurl thy sails, O dearer to me than mine own father? ... Is it then to the sky and to the waves that hindered thy course that we owed thy tarrying?" She then gives Jason a "tunic of woven handiwork", and her father's sword "with its renowned emblem", "the flaming gift of Aetna's god", (i.e Vulcan), asking him to "forget not the land that first folded you to its peaceful bosom; and from Colchis' conquered shores bring back hither thy sails, I pray thee, by this Jason whom thou leavest in my womb."
Statius
Publius Papinius Statius (Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; ; ) was a Greco-Roman poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving Latin poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the ''Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetry, ...
in his Thebaid
The Thebaid or Thebais ( grc-gre, Θηβαΐς, ''Thēbaïs'') was a region in ancient Egypt, comprising the 13 southernmost nomes of Upper Egypt, from Abydos to Aswan.
Pharaonic history
The Thebaid acquired its name from its proximity to ...
'' has Hypsipyle say that her union with Jason "was not by my will", calling Jason her "ungentle guest", and her twin offspring by Jason, "memorials of a forced bed". She describes Jason as a "brute ... uncaring for his children and pledged word!".
Nurse of Opheltes
 Hypsipyle became involved in the story of the infant
Hypsipyle became involved in the story of the infant Opheltes
In Greek mythology, Opheltes (Ancient Greek: Ὀφέλτης), also called Archemorus (Αρχέμορος, Beginning of Doom), was a son of Lycurgus (of Nemea), Lycurgus of Nemea. His mother is variously given as Eurydice (Greek myth), Eurydice, ...
, the Seven against Thebes
The Seven against Thebes were seven champions in Greek mythology who made war on Thebes. They were chosen by Adrastus, the king of Argos, to be the captains of an Argive army whose purpose was to restore Oedipus' son Polynices to the Theban th ...
, and the origin of the Nemean Games
The Nemean Games ( grc-gre, Νέμεα or Νέμεια) were one of the four Panhellenic Games of Ancient Greece, and were held at Nemea every two years (or every third).
With the Isthmian Games, the Nemean Games were held both the year before ...
. On their way to Thebes, the Seven, in need of water, stop at Nemea
Nemea (; grc, Νεμέα; grc-x-ionic, Νεμέη) is an ancient site in the northeastern part of the Peloponnese, in Greece. Formerly part of the territory of Cleonae in ancient Argolis, it is today situated in the regional unit of Corinthia ...
, where they encounter Hypsipyle. Because of the discovery of her having saved Thoas, Hypsipyle has been sold into slavery to the parents of Opheltes, becoming his nursemaid. While helping the Seven to get water, Hypsipyle sets Opheltes down, and he is killed by a serpent. The Seven kill the serpent, and the seer Amphiaraus
In Greek mythology, Amphiaraus or Amphiaraos (; Ancient Greek: Ἀμφιάραος, Ἀμφιάρεως, "very sacred") was the son of Oicles, a seer, and one of the leaders of the Seven against Thebes. Amphiaraus at first refused to go with Adra ...
, one of the Seven, renames the child Archemorus, meaning the "Beginning of Doom", interpreting the child's death as a harbinger of the Seven's own impending doom at Thebes. The Seven save Hypsipyle from being put to death and hold funeral games in the child's honor, which become the origin of the Nemean Games. Hypsipyle's sons arrive, compete in the funeral games, and rescue Hypsipyle from her captivity.
''Hypsipyle''
The earliest involvement of Hypsipyle in the Opheltes/Archemorus story occurs in Euripides' ''Hypsipyle
In Greek mythology, Hypsipyle (Ancient Greek: Ὑψιπύλη) was a queen of Lemnos, and the daughter of King Thoas of Lemnos, and the granddaughter of Dionysus and Ariadne. When the women of Lemnos killed all the males on the island, Hypsipyle ...
'', and may well have been an Euripidean invention. After fleeing Lemnos, Hypsipyle was captured by pirates and sold as a slave to Lycurgus, the priest of Zeus at Nemea
Nemea (; grc, Νεμέα; grc-x-ionic, Νεμέη) is an ancient site in the northeastern part of the Peloponnese, in Greece. Formerly part of the territory of Cleonae in ancient Argolis, it is today situated in the regional unit of Corinthia ...
, where she has become the nurse to Lycurgus and Eurydice's son Opheltes
In Greek mythology, Opheltes (Ancient Greek: Ὀφέλτης), also called Archemorus (Αρχέμορος, Beginning of Doom), was a son of Lycurgus (of Nemea), Lycurgus of Nemea. His mother is variously given as Eurydice (Greek myth), Eurydice, ...
.
As the action of the play begins, Hypsipyle's twin sons by Jason, Euneus and Thoas, arrive seeking shelter for the night. The sons have been separated from Hypsipyle since infancy, so neither recognizes the other. When Jason left Lemnos he had taken his sons to Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia (country), Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians a ...
. After he died, Jason's fellow argonaut Orpheus
Orpheus (; Ancient Greek: Ὀρφεύς, classical pronunciation: ; french: Orphée) is a Thracian bard, legendary musician and prophet in ancient Greek religion. He was also a renowned poet and, according to the legend, travelled with Jaso ...
took the boys to Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
, where he raised them. They eventually met Hypsipyles' father Thoas, who took them back to Lemnos. From there they embarked on a search for their mother.
The Seven against Thebes have also just arrived and encounter Hypsipyle. Amphiaraus tells Hypsipyle that they need water for a sacrifice, and she leads the Seven to a spring. Hypsipyle brings Opheltes with her, and somehow, in a moment of neglect, Opheltes is killed by a serpent. The child's mother Eurydice is about to have Hypsipyle put to death, when Amphiaraus arrives and Hypsipyle pleads with him to speak in her defense. Amphiaraus tells Euridice that the child's death was destined, proposes that funeral games be held in Opheltes' honor, and is able to convince Euridice to spare Hypsipyle's life. Funeral games are held, and Hypsypyle's sons participate, as a result of which, a recognition and reunion between Hypsipyle and her sons is effected, who then manage to free Hypsipyle from her servitude.
The surviving fragments of Euripides' play do not make it clear how the recognition between Hypsipyle and her sons was brought about, but two later accounts may have been based on the play. According to the Second Vatican Mythographer The so-called Vatican Mythographers ( la, Mythographi Vaticani) are the anonymous authors of three Latin mythographical texts found together in a single medieval manuscript, Vatican Reg. lat. 1401. The name is that used by Angelo Mai when he publi ...
, after the sons won the foot-race, at the funeral games, their names and parents were announced, and in this way their identities were revealed. The Cyzicene epigrams The Cyzicene epigrams are a collection of nineteen numbered Greek epigrams, each accompanied by a short prose preamble, which, together with a one-sentence introduction, constitute the third and shortest book of the ''Palatine Anthology''. The epigr ...
, the third book of the ''Palatine Anthology
The ''Palatine Anthology'' (or ''Anthologia Palatina''), sometimes abbreviated ''AP'', is the collection of Greek poems and epigrams discovered in 1606 in the Palatine Library in Heidelberg. It is based on the lost collection of Constantinus Ceph ...
'', describes a depiction, on a temple in Cyzicus
Cyzicus (; grc, Κύζικος ''Kúzikos''; ota, آیدینجق, ''Aydıncıḳ'') was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peni ...
, of Euneus and Thoas showing Hypsipyle a gold ornament ("the golden vine") as proof of their identities.
Hyginus
According toHyginus
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of Caesar Augustus. He was elected superintendent of the Palatine library by Augustus according to Suetonius' ''De Grammatic ...
, when the women of Lemnos discovered Hypsipyle's deception, they tried to kill her, but, as in Euripides' play, she fled the island and was captured by pirates who sold her as a slave (although Hyginus' Latin text—probably in error—says she was sold to "King Lycus", rather than Lycurgus).
Hyginus also tells of an oracle that had warned that Opheltes should not be put on the ground until he had learned to walk, and says that, to avoid setting the child directly on the ground, she put him on a bed of wild celery where he is killed by a serpent who guarded the spring. Hyginus connects this with the tradition of the celery crowns awarded to the winners at the Nemean games
The Nemean Games ( grc-gre, Νέμεα or Νέμεια) were one of the four Panhellenic Games of Ancient Greece, and were held at Nemea every two years (or every third).
With the Isthmian Games, the Nemean Games were held both the year before ...
. According to Hyginus, as in Euripides, the Seven intercede on Hypsipyle's behalf, but with Lycurgus, rather than Eurydice.
The ''Thebaid''
Statius
Publius Papinius Statius (Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; ; ) was a Greco-Roman poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving Latin poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the ''Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetry, ...
, in his epic poem, the ''Thebaid
The Thebaid or Thebais ( grc-gre, Θηβαΐς, ''Thēbaïs'') was a region in ancient Egypt, comprising the 13 southernmost nomes of Upper Egypt, from Abydos to Aswan.
Pharaonic history
The Thebaid acquired its name from its proximity to ...
''—which tells the story of the Seven against Thebes—preserves the most complete account of the myth of Hypsipyle and Opheltes. As in Hyginus' account, when the Lemnian women discovered that Thoas had been saved, Hypsipyle fled the island, but was captured by pirates, and sold as a slave to Lycurgus, who is both the king of Nemea (as in Hyginus) and the priest of Zeus (as in Euripides).
As in Euripides, Hypsipyle, who has become the nurse of Lycurgus and Eurydice's son Opheltes, encounters the Seven against Thebes, who are in urgent need of water. However in Statius' account, Hypsipyle does not take Opheltes with her to the spring, instead, in her haste to provide water for the Seven, she leaves the child behind, lying on the ground, "lest she be too slow a guide". Hypsipyle takes the Seven to the spring, and when they have drunk their fill, they ask Hypsipyle to tell them who she is. Then, over the course of 471 lines of the ''Thebaid'', Hypsipyle tells the Seven her story: the massacre of the men by the Lemnian women, her saving her father Thoas, the visit to Lemnos by the Argonauts, her twin sons, Euneus and Thoas, by Jason, and how she came to be the nurse of Opheltes. Meanwhile, with Hypsipyle long delayed at the spring telling her story, and "oblivious (so the gods would have it) of her absent charge", Opheltes has fallen asleep in the grass, and though unnoticed, he is killed by an unwitting swish of the tale of the enormous serpent who guards Zeus' sacred grove.
Hypsipyle is again saved, by the Seven, from execution, but here, as in Hyginus, it is the king who is restrained. As in Euripides, Hypsipyles' sons Thoas and Euneus, who are searching for their mother, arrive at the palace. In Statius' poem, Hypsipyle is able to identify her sons by means of the swords they carry, which belonged to Jason, and bear the mark of Jason's ship the Argo
In Greek mythology the ''Argo'' (; in Greek: ) was a ship built with the help of the gods that Jason and the Argonauts sailed from Iolcos to Colchis to retrieve the Golden Fleece. The ship has gone on to be used as a motif in a variety of sour ...
on them, and a joyous reunion ensues.
Apollodorus
Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
, generally follows Euripides' account of the story, but differs at two points. According to Apollodorus, it was the Lemnian women themselves who, having discovered that Thoas had been spared, sold Hypsipyle into slavery. Also according to Apollodorus, as in Statius' account, Hypsipyle left Opheltes behind when she led the Seven to the spring.Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
3.6.4
In literature
*In his work, ''Inferno
Inferno may refer to:
* Hell, an afterlife place of suffering
* Conflagration, a large uncontrolled fire
Film
* ''L'Inferno'', a 1911 Italian film
* Inferno (1953 film), ''Inferno'' (1953 film), a film noir by Roy Ward Baker
* Inferno (1973 fi ...
'', the 14th-century Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
poet Dante Alighieri
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: '' ...
placed Jason in the eighth circle of Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hell ...
, along with seducers and panderers, for his deception and abandonment of Hypsipyle.
*In the ''Purgatorio
''Purgatorio'' (; Italian for "Purgatory") is the second part of Dante's ''Divine Comedy'', following the ''Inferno'' and preceding the '' Paradiso''. The poem was written in the early 14th century. It is an allegory telling of the climb of Da ...
'', Dante's guide Virgil notes that Hypsipyle is among the virtuous pagans in Limbo
In Catholic theology, Limbo (Latin '' limbus'', edge or boundary, referring to the edge of Hell) is the afterlife condition of those who die in original sin without being assigned to the Hell of the Damned. Medieval theologians of Western Euro ...
(Canto 22.112)
Notes
References
*Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; grc-gre, Αἰσχύλος ; c. 525/524 – c. 456/455 BC) was an ancient Greek tragedian, and is often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek ...
, ''Libation Bearers
The ''Oresteia'' ( grc, Ὀρέστεια) is a trilogy of Greek tragedies written by Aeschylus in the 5th century BCE, concerning the murder of Agamemnon by Clytemnestra, the murder of Clytemnestra by Orestes, the trial of Orestes, the end of t ...
'' in ''Aeschylus, with an English translation by Herbert Weir Smyth, Ph. D. in two volumes.'' Vol 2. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
. 1926Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
*
Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
, ''Apollodorus, The Library, with an English Translation by Sir James George Frazer, F.B.A., F.R.S. in 2 Volumes.'' Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1921Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
*
Apollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius of Rhodes ( grc, Ἀπολλώνιος Ῥόδιος ''Apollṓnios Rhódios''; la, Apollonius Rhodius; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek author, best known for the ''Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and t ...
, ''Apollonius Rhodius: the Argonautica'', translated by Robert Cooper Seaton, W. Heinemann, 1912Internet Archive
* Bravo, Jorge J., III, ''Excavations at Nemea IV: The Shrine of Opheltes'', Univ of California Press, 2018. . *
Callimachus
Callimachus (; ) was an ancient Greek poet, scholar and librarian who was active in Alexandria during the 3rd century BC. A representative of Ancient Greek literature of the Hellenistic period, he wrote over 800 literary works in a wide variety ...
, Musaeus Musaeus, Musaios ( grc, Μουσαῖος) or Musäus may refer to:
Greek poets
* Musaeus of Athens, legendary polymath, considered by the Greeks to be one of their earliest poets (mentioned by Socrates in Plato's Apology)
* Musaeus of Ephesus, liv ...
, ''Aetia, Iambi, Hecale and Other Fragments, Hero and Leander'', edited and translated by C. A. Trypanis, T. Gelzer, Cedric H. Whitman, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 421, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
, 1973Online version at Harvard University Press
. * Collard, Christopher and Martin Cropp, ''Euripides Fragments: Oedipus-Chrysippus: Other Fragments'',
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 506. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
, 2008. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Fletcher, Judith, "Lemnian Infamy and Masculine Glory in Apollonios' ''Argonautica''" in ''Celebrity, Fame, and Infamy in the Hellenistic World'', edited by Riemer A. Faber, University of Toronto Press, 2020. . * Gantz, Timothy, ''Early Greek Myth: A Guide to Literary and Artistic Sources'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996, Two volumes: (Vol. 1), (Vol. 2). * Grimal, Pierre, ''The Dictionary of Classical Mythology'', Wiley-Blackwell, 1996. . * Hard, Robin, ''The Routledge Handbook of Greek Mythology: Based on H.J. Rose's "Handbook of Greek Mythology"'', Psychology Press, 2004,
Google Books
*
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
; ''Histories'', A. D. Godley
Alfred Denis Godley (22 January 1856 – 27 June 1925) was an Anglo-Irish classical scholar and author of humorous poems. From 1910 to 1920 he was Public Orator at the University of Oxford, a post that involved composing citations in Latin for ...
(translator), Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
, 1920; Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
*
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
, ''The Iliad with an English Translation by A.T. Murray, Ph.D. in two volumes''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
; London, William Heinemann, Ltd. 1924Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Hyginus, Gaius Julius, ''
Fabulae
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of Caesar Augustus. He was elected superintendent of the Palatine library by Augustus according to Suetonius' ''De Grammati ...
'' in ''Apollodorus' ''Library'' and Hyginus' ''Fabulae'': Two Handbooks of Greek Mythology, Translated, with Introductions by R. Scott Smith and Stephen M. Trzaskoma'', Hackett Publishing Company, 2007. .
* Lloyd-Jones, Hugh, ''Sophocles: Fragments'', Edited and translated by Hugh Lloyd-Jones, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 483, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
, 1996. Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the th ...
, ''Heroides
The ''Heroides'' (''The Heroines''), or ''Epistulae Heroidum'' (''Letters of Heroines''), is a collection of fifteen epistolary
Epistolary means "in the form of a letter or letters", and may refer to:
* Epistolary ( la, epistolarium), a Christi ...
'' in ''Heroides. Amores.'' Translated by Grant Showerman. Revised by G. P. Goold. Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 41. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1977. Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the th ...
, ''Ibis
The ibises () (collective plural ibis; classical plurals ibides and ibes) are a group of long-legged wading birds in the family Threskiornithidae, that inhabit wetlands, forests and plains. "Ibis" derives from the Latin and Ancient Greek word f ...
'' in ''Art of Love. Cosmetics. Remedies for Love. Ibis. Walnut-tree. Sea Fishing. Consolation.'' Translated by J. H. Mozley. Revised by G. P. Goold. Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 232, Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1929Online version at Harvard University Press
* ''
The Oxford Classical Dictionary
The ''Oxford Classical Dictionary'' (''OCD'') is generally considered "the best one-volume dictionary on antiquity," an encyclopædic work in English consisting of articles relating to classical antiquity and its civilizations. It was first pub ...
'', second edition, Hammond, N.G.L. and Howard Hayes Scullard
Howard Hayes Scullard (9 February 1903 – 31 March 1983) was a British historian specialising in ancient history, notable for editing the ''Oxford Classical Dictionary'' and for his many published works.
Scullard's father was Herbert Hayes S ...
(editors), Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
, 1992. .
* Parada, Carlos, ''Genealogical Guide to Greek Mythology'', Jonsered, Paul Åströms Förlag, 1993. .
* Paton, W. R. (ed.), ''Greek Anthology, Volume I: Book 1: Christian Epigrams, Book 2: Description of the Statues in the Gymnasium of Zeuxippus, Book 3: Epigrams in the Temple of Apollonis at Cyzicus, Book 4: Prefaces to the Various Anthologies, Book 5: Erotic Epigrams'', translated by W. R. Paton. Revised by Michael A. Tueller, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 67, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
, 2014. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Pepin, Ronald E., ''The Vatican Mythographers'', Fordham University Press, 2008. . *
Pindar
Pindar (; grc-gre, Πίνδαρος , ; la, Pindarus; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar is ...
, ''Odes'', Diane Arnson Svarlien. 1990Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
*
Propertius
Sextus Propertius was a Latin elegiac poet of the Augustan age. He was born around 50–45 BC in Assisium and died shortly after 15 BC.
Propertius' surviving work comprises four books of ''Elegies'' ('). He was a friend of the poets Gallus a ...
, ''Elegies'' Edited and translated by G. P. Goold. Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
18. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1990.Online version at Harvard University Press
* Smith, William, ''
Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology
The ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'' (1849, originally published 1844 under a slightly different title) is an encyclopedia/biographical dictionary. Edited by William Smith, the dictionary spans three volumes and 3,700 p ...
'', London (1873)Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Sommerstein, Alan H., ''Aeschylus: Fragments.'' Edited and translated by Alan H. Sommerstein.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 505. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
, 2009. Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Statius
Publius Papinius Statius (Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; ; ) was a Greco-Roman poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving Latin poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the ''Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetry, ...
, ''Thebaid
The Thebaid or Thebais ( grc-gre, Θηβαΐς, ''Thēbaïs'') was a region in ancient Egypt, comprising the 13 southernmost nomes of Upper Egypt, from Abydos to Aswan.
Pharaonic history
The Thebaid acquired its name from its proximity to ...
, Volume I: Thebaid: Books 1-7'', edited and translated by D. R. Shackleton Bailey, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 207, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirem ...
, 2004. Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Stesichorus
Stesichorus (; grc-gre, Στησίχορος, ''Stēsichoros''; c. 630 – 555 BC) was a Greek lyric poet native of today's Calabria (Southern Italy). He is best known for telling epic stories in lyric metres, and for some ancient traditions abou ...
, Ibycus
Ibycus (; grc-gre, Ἴβυκος; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet, a citizen of Rhegium in Magna Graecia, probably active at Samos during the reign of the tyrant Polycrates and numbered by the scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria in the canonic ...
, Simonides
Simonides of Ceos (; grc-gre, Σιμωνίδης ὁ Κεῖος; c. 556–468 BC) was a Greek lyric poet, born in Ioulis on Kea (island), Ceos. The scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria included him in the canonical list of the nine lyric p ...
. ''Greek Lyric, Volume III: Stesichorus, Ibycus, Simonides, and Others''. Edited and translated by David A. Campbell. Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
br>476Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1991. * Tripp, Edward, ''Crowell's Handbook of Classical Mythology'', Thomas Y. Crowell Co; First edition (June 1970). . * Valerius Flaccus, Gaius, ''Argonautica'', translated by J. H. Mozley,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 286. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1928Online version at Harvard University Press
{{Authority control Princesses in Greek mythology Queens in Greek mythology Characters in the Argonautica Lemnian characters in Greek mythology Nemea] Fictional Greek and Roman slaves Deeds of Aphrodite