Hygrophorus Eburneus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Hygrophorus eburneus'', commonly known as the ivory waxy cap or the cowboy's handkerchief, is a species of
 The
The
 When they are viewed in mass, such as with a
When they are viewed in mass, such as with a
p. 250
Retrieved 2010-08-25.
 Several
Several
Mushroom Observer
Images {{Good article Edible fungi Fungi of Africa Fungi of Europe Fungi of North America eburneus Taxa named by Jean Baptiste François Pierre Bulliard
edible mushroom
Edible mushrooms are the fleshy and edible fruit bodies of several species of macrofungi (fungi which bear fruiting structures that are large enough to be seen with the naked eye). They can appear either below ground (hypogeous) or above ground ...
in the waxgill family of fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
. It is widespread in Europe and North America, and has also been collected in northern Africa. The fruit bodies
The sporocarp (also known as fruiting body, fruit body or fruitbody) of fungi is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne. The fruitbody is part of the sexual phase of a fungal life cyc ...
are medium-sized, pure white, and when wet are covered in a layer of slime thick enough to make the mushroom difficult to pick up. The gills
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
are broadly attached to the stem
Stem or STEM may refer to:
Plant structures
* Plant stem, a plant's aboveground axis, made of vascular tissue, off which leaves and flowers hang
* Stipe (botany), a stalk to support some other structure
* Stipe (mycology), the stem of a mushro ...
or running down it; as the family name suggests, they feel waxy when rubbed between the fingers. Like all ''Hygrophorus'' species, the fungus is mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza (from Greek μύκης ', "fungus", and ῥίζα ', "root"; pl. mycorrhizae, mycorrhiza or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant ...
l—a symbiotic
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
association whereby the underground fungal mycelia
Mycelium (plural mycelia) is a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrates. A typical single spore germinates in ...
penetrate and exchange nutrients with tree roots. They are common in a variety of forest types, where they grow on the ground in thickets or grassy areas. ''Hygrophorus eburneus'' is the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
of the genus ''Hygrophorus''. A number of biologically active chemicals have been purified from the fruit bodies of the fungus, including fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, fr ...
s with bactericidal
A bactericide or bacteriocide, sometimes abbreviated Bcidal, is a substance which kills bacteria. Bactericides are disinfectants, antiseptics, or antibiotics.
However, material surfaces can also have bactericidal properties based solely on their ...
and fungicidal
Fungicides are biocidal chemical compounds or biological organisms used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. A fungistatic inhibits their growth. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in critical losses of yield, quality, ...
activity.
Taxonomy
The species was first named as ''Agaricus eburneus'' by French botanist Jean Bulliard in 1783.Elias Fries
Elias Magnus Fries (15 August 1794 – 8 February 1878) was a Swedish mycologist and botanist.
Career
Fries was born at Femsjö (Hylte Municipality), Småland, the son of the pastor there. He attended school in Växjö.
He acquired an ...
divided the large genus ''Agaricus'' into a number of "tribes" (taxonomically
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given ...
equivalent to modern sections
Section, Sectioning or Sectioned may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Section (music), a complete, but not independent, musical idea
* Section (typography), a subdivision, especially of a chapter, in books and documents
** Section sig ...
) in his ''Systema Mycologicum I'', and classified ''A. eburneus'' in the tribe ''Limacium''. When In 1836, Fries first defined the genus ''Hygrophorus
''Hygrophorus'' is a genus of agarics (gilled mushrooms) in the family Hygrophoraceae. Called "woodwaxes" in the UK or "waxy caps" (together with ''Hygrocybe'' species) in North America, basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are typically fleshy, often wi ...
'' in his ''Epicrisis Systematis Mycologici'', ''H. eburneus'' was included. The fungus has also been named ''Limacium eburneum'' by Paul Kummer
Paul Kummer (22 August 1834 – 6 December 1912) was a minister, teacher, and scientist in Zerbst, Germany, known chiefly for his contribution to mycological nomenclature. Earlier classification of agarics by pioneering fungal taxonomist Elias Ma ...
in 1871, when he raised the tribes of Fries to the rank of genus, and ''Gymnopus eburneus'' by Samuel Frederick Gray
Samuel Frederick Gray (10 December 1766 – 12 April 1828) was a British botanist, mycologist, and pharmacologist. He was the father of the zoologists John Edward Gray and George Robert Gray.
Background
He was the son of Samuel Gray, a London s ...
in 1821. ''H. eburneus'' is the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
of the genus ''Hygrophorus'', and is classified in the section ''Hygrophorus'', subsection ''Hygrophorus''. This includes species with non-amyloid
Amyloids are aggregates of proteins characterised by a Fibril, fibrillar morphology of 7–13 Nanometer, nm in diameter, a beta sheet (β-sheet) Secondary structure of proteins, secondary structure (known as cross-β) and ability to be Staining, ...
, smooth spores
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, f ...
, and divergent hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one or ...
e in the tissue of the hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some ...
. Other species in this subsection include '' H. eburneiformis'', '' H. coccus'', '' H. ponderatus'', '' H. chrysaspis'', and '' H. glutinosus''.
The mushroom is commonly known as the "ivory waxy cap", the "white waxy cap", or the "cowboy's handkerchief". The specific epithet
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
''eburneus'' is a Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
adjective meaning "of ivory".
Description
 The
The cap
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. Caps typically have a visor, or no brim at all. They are popular in casual and informal se ...
of ''H. eburneus'' is broad, with a shape ranging from convex to flattened, sometimes with an umbo (a raised area in the center of the cap). In age the cap margin sometimes becomes elevated and the center of the cap depressed. The cap is pure white, and depending on the moisture in the environment, may be glutinous
Domestication syndrome refers to two sets of phenotypic traits that are common to either domesticated animals, or domesticated plants. These traits were identified by Charles Darwin in '' The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication. ...
to sticky. The cap surface is smooth, the margin is even and in young specimens, rolled inward and covered with short fibrils. The flesh
Flesh is any aggregation of soft tissues of an organism. Various multicellular organisms have soft tissues that may be called "flesh". In mammals, including humans, ''flesh'' encompasses muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as mu ...
is white, thick in the center of the cap but thinning toward the margin. The odor and taste are mild. The gills
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
are somewhat arcuate-decurrent, meaning they are shaped like a bow, curving upward and then running down the stem for a short distance. In terms of spacing, they are subdistant to distant, so that space can be seen between them. The gills are moderately broad, broadest near the stem, narrowed in front, pure white, slightly yellowish or buff
Buff or BUFF may refer to:
People
* Buff (surname), a list of people
* Buff (nickname), a list of people
* Johnny Buff, ring name of American world champion boxer John Lisky (1888–1955)
* Buff Bagwell, a ring name of American professional wr ...
with age or when dried. The stem
Stem or STEM may refer to:
Plant structures
* Plant stem, a plant's aboveground axis, made of vascular tissue, off which leaves and flowers hang
* Stipe (botany), a stalk to support some other structure
* Stipe (mycology), the stem of a mushro ...
is long, thick, equal in width throughout its length to somewhat tapered downward or with a greatly attenuated base, and glutinous. Its surface is silky beneath the gluten. The top of the stem is covered with short fibrils, pure white, sometimes becoming grayish or dirty with age. It is initially stuffed with cotton-like mycelia
Mycelium (plural mycelia) is a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrates. A typical single spore germinates in ...
, then later becomes hollow. The caps of dried fruit bodies will typically remain white, while the stems will dry darker, especially if they are initially waterlogged.Smith, 1947, pp. 253–55.
Microscopic characteristics
 When they are viewed in mass, such as with a
When they are viewed in mass, such as with a spore print
300px, Making a spore print of the mushroom ''Volvariella volvacea'' shown in composite: (photo lower half) mushroom cap laid on white and dark paper; (photo upper half) cap removed after 24 hours showing pinkish-tan spore print. A 3.5-centimeter ...
, the spores
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, f ...
appear white. Observing with a light microscope reveals additional details: spores are ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation.
An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the ...
, smooth, and measure 6–8 by 3.5–5 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
. They are pale yellow in Melzer's reagent
Melzer's reagent (also known as Melzer's iodine reagent, Melzer's solution or informally as Melzer's) is a chemical reagent used by mycologists to assist with the identification of fungi, and by phytopathologists for fungi that are plant pathogens ...
. The basidia
A basidium () is a microscopic sporangium (a spore-producing structure) found on the hymenophore of fruiting bodies of basidiomycete fungi which are also called tertiary mycelium, developed from secondary mycelium. Tertiary mycelium is highly-c ...
(spore-bearing cells) are 42–52 by 6-8 μm, and four-spored. There are no pleurocystidia
A cystidium (plural cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that ar ...
or cheilocystidia
A cystidium (plural cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that ar ...
. The gill tissue is made of branching hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one or ...
e about 7–12 μm wide. The cap cuticle
The pileipellis is the uppermost layer of hyphae in the pileus of a fungal fruit body. It covers the trama, the fleshy tissue of the fruit body. The pileipellis is more or less synonymous with the cuticle, but the cuticle generally describes th ...
is made of gelatinous, narrow (3–6 μm) hyphae which are repent (bent over) but typically with some erect free ends. Clamp connection
A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain fungi. It is a characteristic feature of Basidiomycetes fungi. It is created to ensure that each cell, or segment of hypha separated by septa (cross walls), rece ...
s are present in the hyphae.
Edibility
The mushroom isedible
An edible item is any item that is safe for humans to eat. "Edible" is differentiated from "eatable" because it does not indicate how an item tastes, only whether it is fit to be eaten. Nonpoisonous items found in nature – such as some mushroo ...
, although it may not be appealing to many due to its sliminess. In China, a yak milk beverage is made with ''H. eburneus'' and yak
The domestic yak (''Bos grunniens''), also known as the Tartary ox, grunting ox or hairy cattle, is a species of long-haired domesticated cattle found throughout the Himalayan region of the Indian subcontinent, the Tibetan Plateau, Kachin Sta ...
milk, by lactic acid fermentation
Lactic acid fermentation is a metabolic process by which glucose or other six-carbon sugars (also, disaccharides of six-carbon sugars, e.g. sucrose or lactose) are converted into cellular energy and the metabolite lactate, which is lactic acid ...
with ''Lactobacillus bulgaricus
''Lactobacillus delbrueckii'' subsp. ''bulgaricus'' (until 2014 known as ''Lactobacillus bulgaricus'') is one of over 200 published species in the ''Lactobacillus'' genome complex (LGC) and is the main bacterium used for the production of yogurt. ...
'', ''Streptococcus thermophilus
''Streptococcus thermophilus'' also known as ''Streptococcus salivarius ''subsp.'' thermophilus'' is a gram-positive bacterium, and a fermentative facultative anaerobe, of the '' viridans'' group. It tests negative for cytochrome, oxidase, and ...
'' and ''Lactobacillus acidophilus
''Lactobacillus acidophilus'' (New Latin 'acid-loving milk-bacillus') is a rod-shaped, Gram-positive, homofermentative, anaerobic microbe first isolated from infant feces in the year 1900. The species is most commonly found in humans, specifically ...
'' as mixed starter.
Similar species
A lookalike species of ''Hygrophorus eburneus'' is '' H. piceae'', which differs by having a less slimy cap, dry to slightly viscid stem, and frequent association with spruce. '' H. gliocyclus'' is just as slimy, but has a cream-colored cap, thicker stalk, and grows with pine. The "snow white waxy cap" ('' H. borealis'') is also similar in appearance, but has a smaller cap diameter of up to —and is not slimy. ''Hygrophorus cossus
''Hygrophorus cossus'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Hygrophorus
''Hygrophorus'' is a genus of agarics (gilled mushrooms) in the family Hygrophoraceae. Called "woodwaxes" in the UK or "waxy caps" (together with ''Hygrocybe'' species) ...
'', which typically grows with ''Quercus
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably '' ...
'' species, differs in its pale pinkish-buff cap and gills, and has a distinct sour odor; also, ''H. cossus'' does not have a potassium hydroxide reaction
Reaction may refer to a process or to a response to an action, event, or exposure:
Physics and chemistry
*Chemical reaction
*Nuclear reaction
*Reaction (physics), as defined by Newton's third law
*Chain reaction (disambiguation).
Biology and me ...
on the stem as does ''H. eburneus''. The "white slime mushroom" ('' Limacella illinita'') has non-waxy gills that are free from attachment to the stalk.Roody, 1997p. 250
Retrieved 2010-08-25.
Habitat and distribution
The fruit bodies of ''H. eburneus'' grow on the soil, mostly inconiferous woods
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
, thickets and grassy areas. The fungus prefers soil that is moist, mesic, loam
Loam (in geology and soil science) is soil composed mostly of sand (particle size > ), silt (particle size > ), and a smaller amount of clay (particle size < ). By weight, its mineral composition is about 40–40–20% concentration of sand–sil ...
y and calcareous
Calcareous () is an adjective meaning "mostly or partly composed of calcium carbonate", in other words, containing lime or being chalky. The term is used in a wide variety of scientific disciplines.
In zoology
''Calcareous'' is used as an adje ...
.
The fungus is widely distributed in North America. It is also found in Europe (Poland and Portugal), Israel and North Africa.
Bioactive compounds
 Several
Several fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, fr ...
s with bactericidal
A bactericide or bacteriocide, sometimes abbreviated Bcidal, is a substance which kills bacteria. Bactericides are disinfectants, antiseptics, or antibiotics.
However, material surfaces can also have bactericidal properties based solely on their ...
and fungicidal
Fungicides are biocidal chemical compounds or biological organisms used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. A fungistatic inhibits their growth. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in critical losses of yield, quality, ...
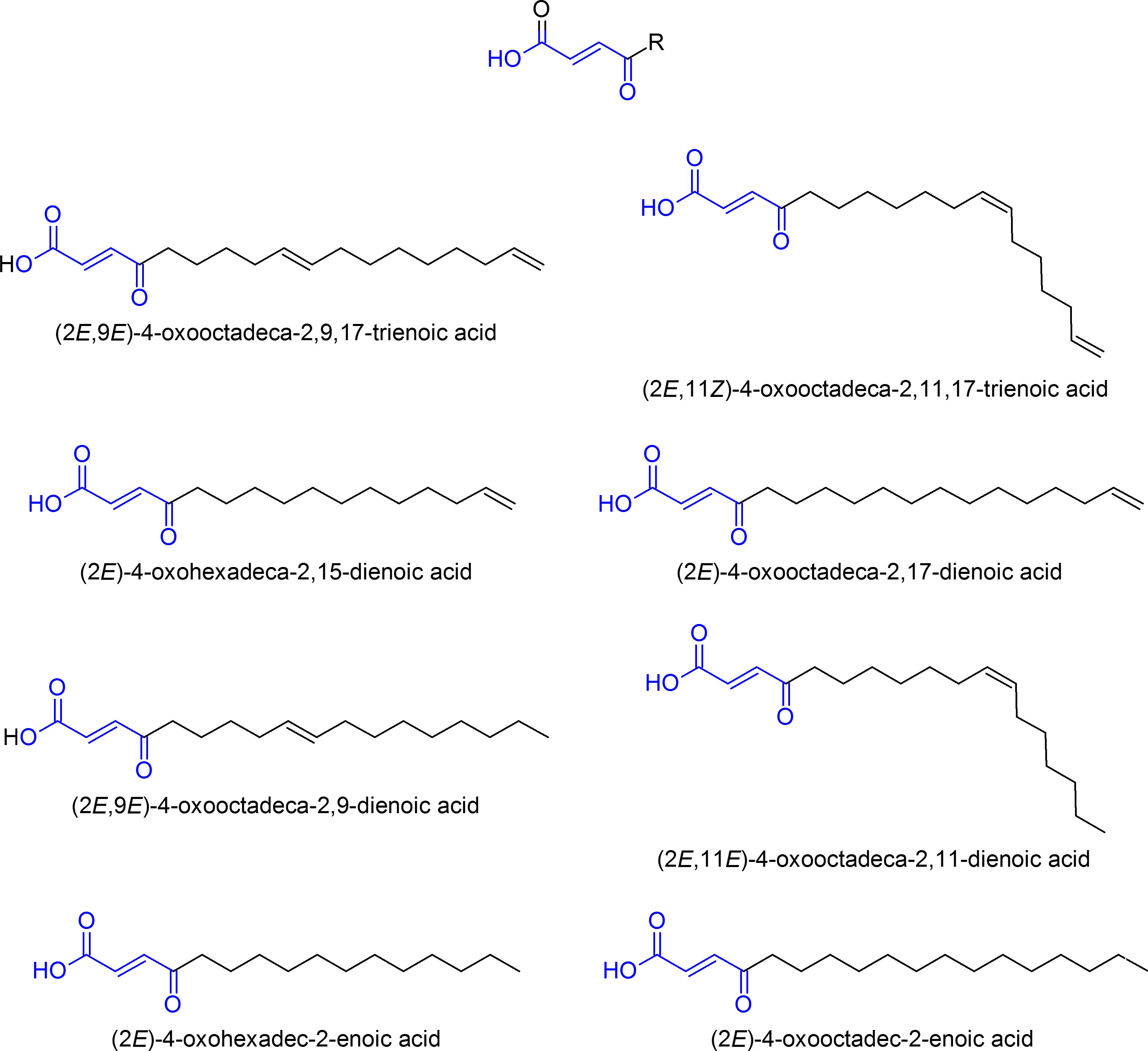
activity have been isolated and identified from the fruit bodies of ''H. eburneus''. The bioactive fatty acids are built upon a chemical structure called γ-oxocrotonate. The following gamma-oxocrotonate derivatives
The derivative of a function is the rate of change of the function's output relative to its input value.
Derivative may also refer to:
In mathematics and economics
* Brzozowski derivative in the theory of formal languages
* Formal derivative, an ...
have been identified from the mushroom: (2''E'',9''E'')-4-oxooctadeca-2,9,17-trienoic acid, (2''E'',11''Z'')-4-oxooctadeca-2,11,17-trienoic acid, (''E'')-4-oxohexadeca-2,15-dienoic acid, (''E'')-4-oxooctadeca-2,17-dienoic acid, (2''E'',9''E'')-4-oxooctadeca-2,9-dienoic acid, (2''E'',11''Z'')-4-oxooctadeca-2,11-dienoic acid, (''E'')-4-oxohexadec-2-enoic acid, and (''E'')-4-oxooctadec-2-enoic acid. The compound (''E'')-4-oxohexadec-2-enoic acid has been investigated for potential use as a fungicide against the oomycete
Oomycota forms a distinct phylogenetic lineage of fungus-like eukaryotic microorganisms, called oomycetes (). They are filamentous and heterotrophic, and can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction of an oospore is the resul ...
species ''Phytophthora infestans
''Phytophthora infestans'' is an oomycete or water mold, a fungus-like microorganism that causes the serious potato and tomato disease known as late blight or potato blight. Early blight, caused by ''Alternaria solani'', is also often called "pot ...
'', a causal agent of potato and tomato late blight disease.
Additional secondary metabolites
Secondary metabolites, also called specialised metabolites, toxins, secondary products, or natural products, are organic compounds produced by any lifeform, e.g. bacteria, fungi, animals, or plants, which are not directly involved in the nor ...
discovered in ''H. eburneus'' include the ceramide
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of N-acetylsphingosine and a fatty acid. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up ...
compound named ''hygrophamide'' ((2''S'',3''R'',4''R'',2''R'')-2-(2'-hydroxy-9''Z''-ene-tetracosanoylamino)-octadecane-1,3,4-triol), and the β-carboline
β-Carboline (9''H''- pyrido ,4-''b'' ndole) represents the basic chemical structure for more than one hundred alkaloids and synthetic compounds. The effects of these substances depend on their respective substituent. Natural β-carbolines prima ...
alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
s known as ''harmane'' and ''norharmane''. The report of discovery of the latter two compounds in 2008 represents their first known occurrence in fungal fruit bodies.
See also
* List of ''Hygrophorus'' speciesReferences
Literature cited
* *External links
* *Mushroom Observer
Images {{Good article Edible fungi Fungi of Africa Fungi of Europe Fungi of North America eburneus Taxa named by Jean Baptiste François Pierre Bulliard