hydrogen emission on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hydrogen is the
 The
The

 *
*
 Compounds of hydrogen are often called
Compounds of hydrogen are often called
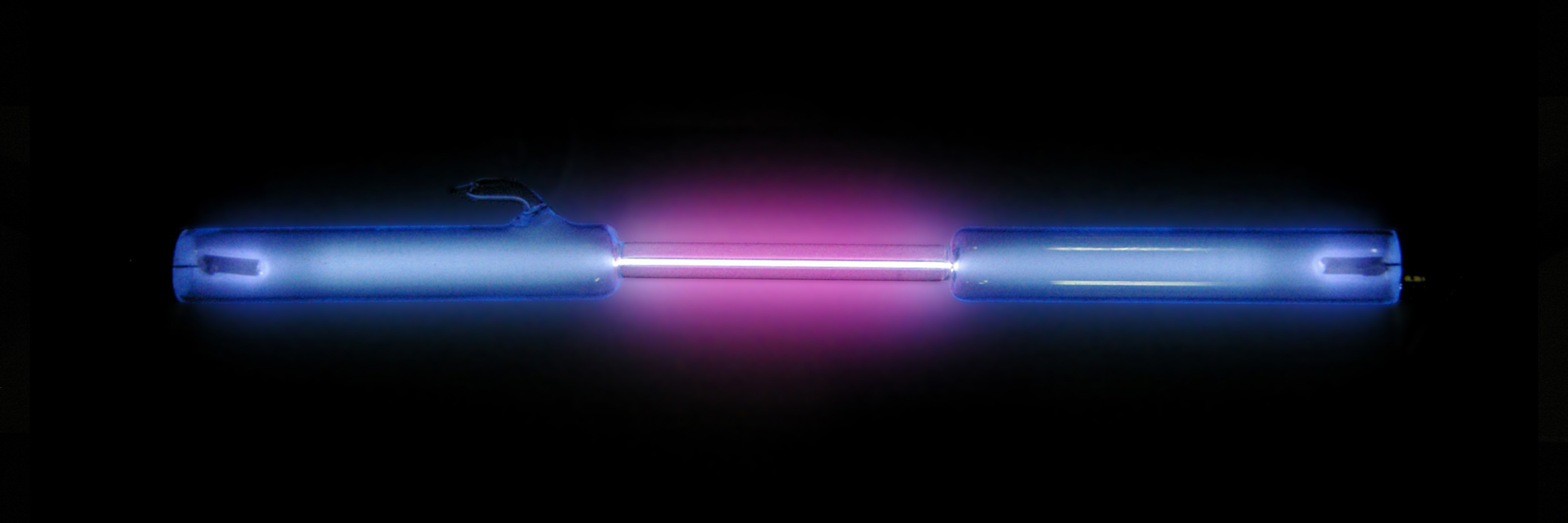


 Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes, denoted , and . Other, highly unstable nuclei ( to ) have been synthesized in the laboratory but not observed in nature.
* is the most common hydrogen isotope, with an abundance of more than 99.98%. Because the
Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes, denoted , and . Other, highly unstable nuclei ( to ) have been synthesized in the laboratory but not observed in nature.
* is the most common hydrogen isotope, with an abundance of more than 99.98%. Because the
 Because of its simple atomic structure, consisting only of a proton and an electron, the hydrogen atom, together with the spectrum of light produced from it or absorbed by it, has been central to the development of the theory of
Because of its simple atomic structure, consisting only of a proton and an electron, the hydrogen atom, together with the spectrum of light produced from it or absorbed by it, has been central to the development of the theory of
 Hydrogen, as atomic H, is the most Natural abundance, abundant
Hydrogen, as atomic H, is the most Natural abundance, abundant
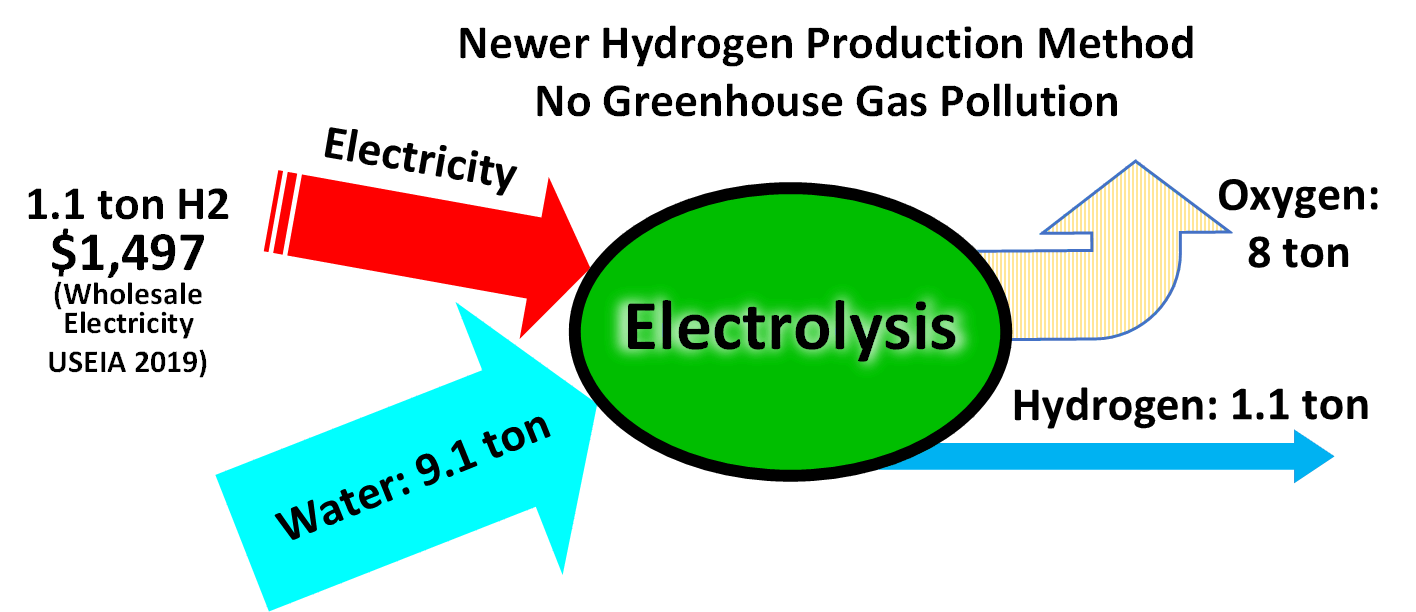 The
The
 Hydrogen production using natural gas methane pyrolysis is a one-step process that produces no greenhouse gases. Developing volume production using this method is the key to enabling faster carbon reduction by using hydrogen in industrial processes, fuel cell electric heavy truck transportation, and in gas turbine electric power generation. Methane pyrolysis is performed by having methane bubbled up through a molten metal catalyst containing dissolved nickel at . This causes the methane to break down into hydrogen gas and solid
Hydrogen production using natural gas methane pyrolysis is a one-step process that produces no greenhouse gases. Developing volume production using this method is the key to enabling faster carbon reduction by using hydrogen in industrial processes, fuel cell electric heavy truck transportation, and in gas turbine electric power generation. Methane pyrolysis is performed by having methane bubbled up through a molten metal catalyst containing dissolved nickel at . This causes the methane to break down into hydrogen gas and solid
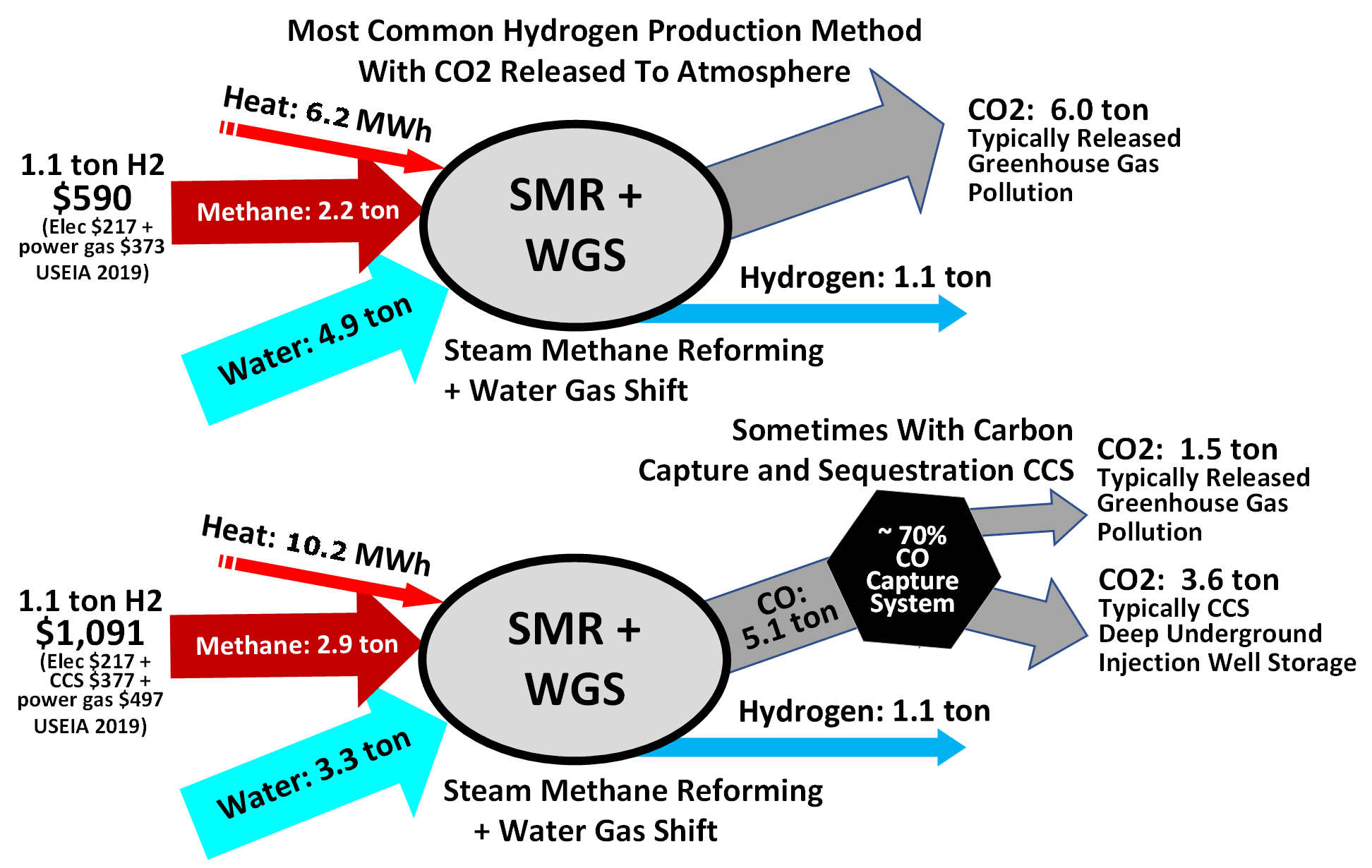 Hydrogen is often produced by reacting water with methane and carbon monoxide, which causes the removal of hydrogen from hydrocarbons at very high temperatures, with 48% of hydrogen production coming from
Hydrogen is often produced by reacting water with methane and carbon monoxide, which causes the removal of hydrogen from hydrocarbons at very high temperatures, with 48% of hydrogen production coming from
''carrier'' of energy rather than an energy resource, because there is no naturally occurring source of hydrogen in useful quantities.
Hydrogen can be burned to produce heat or combined with oxygen in
Basic Hydrogen Calculations of Quantum Mechanics
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
{{Authority control Hydrogen, Chemical elements Reactive nonmetals Diatomic nonmetals Nuclear fusion fuels Airship technology Reducing agents Refrigerants Gaseous signaling molecules E-number additives
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
with the symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
H and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements to be established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used standards are those of the International Union ...
hydrogen is a gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
of diatomic molecule
Diatomic molecules () are molecules composed of only two atoms, of the same or different chemical elements. If a diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen () or oxygen (), then it is said to be homonuclear. Ot ...
s having the formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwee ...
. It is colorless, odorless
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, it ...
, taste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception produced or stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste receptor ...
less, non-toxic, and highly combustible
A combustible material is something that can burn (i.e., ''combust'') in air. A combustible material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable mat ...
. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. Acc ...
, constituting roughly 75% of all normal Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson
* ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keith Rennie, and Andrew Airlie
* ''Norma ...
matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic partic ...
.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe. Dark matter is called "dark" because it does not appear to interact with the electromagnetic field, which means it does not ab ...
and dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univer ...
. Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
s such as the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
are mainly composed of hydrogen in the . Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
and organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ...
s. For the most common isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) ...
of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and ...
has one proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
, one electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no kn ...
, and no neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons beh ...
s.
In the early universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. Acc ...
, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 years later during the recombination epoch, when the plasma
Plasma or plasm may refer to:
Science
* Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter
* Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral
* Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics
Biology
* Blood pla ...
had cooled enough for electrons
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
to remain bound to protons.
Hydrogen is nonmetallic
In chemistry, a nonmetal is a chemical element that generally lacks a predominance of metallic properties; they range from colorless gases (like hydrogen) to shiny solids (like carbon, as graphite). The electrons in nonmetals behave differentl ...
(except it becomes metallic
Metallic may be a reference to:
*Metal
* Metalloid, metal-like substance
*Metallic bonding, type of chemical bonding
* Metallicity, in astronomy the proportion of elements other than helium and hydrogen in an object
*Metallic color, a color that ...
at extremely high pressures) and readily forms a single covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
with most nonmetallic elements, forming compounds such as water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
and nearly all organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ...
s. Hydrogen plays a particularly important role in acid–base reaction
An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their applica ...
s because these reactions usually involve the exchange of protons between soluble molecules. In ionic compound
In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound composed of ions held together by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonding. The compound is neutral overall, but consists of positively charged ions called cations and negatively charged i ...
s, hydrogen can take the form of a negative charge (i.e., anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
) where it is known as a hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of ...
, or as a positively charged (i.e., cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
) species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
denoted by the symbol . The cation is simply a proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
(symbol p) but its behavior in aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be re ...
s and in ionic compound
In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound composed of ions held together by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonding. The compound is neutral overall, but consists of positively charged ions called cations and negatively charged i ...
s involves screening
Screening may refer to:
* Screening cultures, a type a medical test that is done to find an infection
* Screening (economics), a strategy of combating adverse selection (includes sorting resumes to select employees)
* Screening (environmental), a ...
of its electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respe ...
by nearby polar
Polar may refer to:
Geography
Polar may refer to:
* Geographical pole, either of two fixed points on the surface of a rotating body or planet, at 90 degrees from the equator, based on the axis around which a body rotates
* Polar climate, the c ...
molecules or anions. Because hydrogen is the only neutral atom for which the Schrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a quantum-mechanical system. It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of the ...
can be solved analytically, the study of its energetics and chemical bonding has played a key role in the development of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
.
Hydrogen gas was first artificially produced in the early 16th century by the reaction of acids on metals. In 1766–1781, Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish ( ; 10 October 1731 – 24 February 1810) was an English natural philosopher and scientist who was an important experimental and theoretical chemist and physicist. He is noted for his discovery of hydrogen, which he termed "infl ...
was the first to recognize that hydrogen gas was a discrete substance, and that it produces water when burned, the property for which it was later named: in Greek, hydrogen means "water-former".
Industrial production
Industrial production is a measure of output of the industrial sector of the economy. The industrial sector includes manufacturing, mining, and utilities. Although these sectors contribute only a small portion of gross domestic product (GDP), the ...
is mainly from steam reforming
Steam reforming or steam methane reforming (SMR) is a method for producing syngas (hydrogen and carbon monoxide) by reaction of hydrocarbons with water. Commonly natural gas is the feedstock. The main purpose of this technology is hydrogen product ...
of natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, oil reforming, or coal gasification Coal gasification is the process of producing syngas—a mixture consisting primarily of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and water vapour (H2O)—from coal and water, air and/or oxygen.
Historically, coal ...
. A small percentage is also produced using more energy-intensive methods such as the electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water, also known as electrochemical water splitting, is the process of using electricity to decompose water into oxygen and hydrogen gas by electrolysis. Hydrogen gas released in this way can be used as hydrogen fuel, or remi ...
. Most hydrogen is used near the site of its production, the two largest uses being fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
processing (e.g., hydrocracking
In petrochemistry, petroleum geology and organic chemistry, cracking is the process whereby complex organic molecules such as kerogens or long-chain hydrocarbons are broken down into simpler molecules such as light hydrocarbons, by the breaking of ...
) and ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
production, mostly for the fertilizer market. It can be burned to produce heat or combined with oxygen in fuel cells
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
to generate electricity directly, with water being the only emissions at the point of usage. Hydrogen atoms (but not gaseous molecules) are problematic in metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
because they can embrittle many metals.
Properties
Combustion
Hydrogen gas (dihydrogen or molecular hydrogen) is highly flammable: : (572 kJ/2 mol = 286 kJ/mol = 141.865 MJ/kg)286 kJ/mol: energy per mole of the combustible material (molecular hydrogen). Theenthalpy of combustion
The heating value (or energy value or calorific value) of a substance, usually a fuel or food (see food energy), is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it.
The ''calorific value'' is the total energy relea ...
is −286 kJ/mol.
Hydrogen gas forms explosive mixtures with air in concentrations from 4–74% and with chlorine at 5–95%. The explosive reactions may be triggered by spark, heat, or sunlight. The hydrogen autoignition temperature
The autoignition temperature or kindling point of a substance is the lowest temperature in which it spontaneously ignites in a normal atmosphere without an external source of ignition, such as a flame or spark. This temperature is required to su ...
, the temperature of spontaneous ignition in air, is .
Flame
Pure hydrogen-oxygen flames emitultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
light and with high oxygen mix are nearly invisible to the naked eye, as illustrated by the faint plume of the Space Shuttle Main Engine
The Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-25, also known as the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME), is a liquid-fuel cryogenic rocket engine that was used on NASA's Space Shuttle and is currently used on the Space Launch System (SLS).
Designed and manufacture ...
, compared to the highly visible plume of a Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster
The Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster (SRB) was the first solid-propellant rocket to be used for primary propulsion on a vehicle used for human spaceflight. A pair of these provided 85% of the Space Shuttle's thrust at liftoff and for the first ...
, which uses an ammonium perchlorate composite. The detection of a burning hydrogen leak may require a flame detector
A flame detector is a sensor designed to detect and respond to the presence of a flame or fire, allowing flame detection. Responses to a detected flame depend on the installation, but can include sounding an alarm, deactivating a fuel line (such as ...
; such leaks can be very dangerous. Hydrogen flames in other conditions are blue, resembling blue natural gas flames. The destruction of the Hindenburg airship was a notorious example of hydrogen combustion and the cause is still debated. The visible flames in the photographs were the result of carbon compounds in the airship skin burning.
Reactants
is unreactive compared to diatomic elements such ashalogens
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
or oxygen. The thermodynamic basis of this low reactivity is the very strong H–H bond, with a bond dissociation energy
The bond-dissociation energy (BDE, ''D''0, or ''DH°'') is one measure of the strength of a chemical bond . It can be defined as the standard enthalpy change when is cleaved by homolysis to give fragments A and B, which are usually radical s ...
of 435.7 kJ/mol. The kinetic basis of the low reactivity is the nonpolar nature of and its weak polarizability. It spontaneously reacts with chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate betwee ...
and fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
to form hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride ga ...
and hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock i ...
, respectively. The reactivity of is strongly affected by the presence of metal catalysts. Thus, while mixtures of with or air combust readily when heated to at least 500 °C by a spark or flame, they do not react at room temperature in the absence of a catalyst.
Electron energy levels
ground state
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. ...
energy level
A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The te ...
of the electron in a hydrogen atom is −13.6 eV, which is equivalent to an ultraviolet photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always ...
of roughly 91 nm wavelength.
The energy levels of hydrogen can be calculated fairly accurately using the Bohr model
In atomic physics, the Bohr model or Rutherford–Bohr model, presented by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford in 1913, is a system consisting of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons—similar to the structure of the Solar Syste ...
of the atom, which conceptualizes the electron as "orbiting" the proton in analogy to the Earth's orbit of the Sun. However, the atomic electron and proton are held together by electromagnetic force
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of ...
, while planets and celestial objects are held by gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
. Because of the discretization of angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed syst ...
postulated in early quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
by Bohr, the electron in the Bohr model can only occupy certain allowed distances from the proton, and therefore only certain allowed energies.
A more accurate description of the hydrogen atom comes from a purely quantum mechanical treatment that uses the Schrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a quantum-mechanical system. It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of the ...
, Dirac equation
In particle physics, the Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation derived by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. In its free form, or including electromagnetic interactions, it describes all spin- massive particles, called "Dirac part ...
or Feynman
Richard Phillips Feynman (; May 11, 1918 – February 15, 1988) was an American theoretical physicist, known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics, the physics of the superflu ...
path integral formulation
The path integral formulation is a description in quantum mechanics that generalizes the action principle of classical mechanics. It replaces the classical notion of a single, unique classical trajectory for a system with a sum, or functional in ...
to calculate the probability density
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), or density of a continuous random variable, is a function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the set of possible values taken by the random variable) can ...
of the electron around the proton. The most complicated treatments allow for the small effects of special relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates:
# The laws o ...
and vacuum polarization
In quantum field theory, and specifically quantum electrodynamics, vacuum polarization describes a process in which a background electromagnetic field produces virtual electron–positron pairs that change the distribution of charges and curr ...
. In the quantum mechanical treatment, the electron in a ground state hydrogen atom has no angular momentum at all—illustrating how the "planetary orbit" differs from electron motion.
Spin isomers
Molecular exists as two spin isomers, i.e. compounds that differ only in the spin states of their nuclei. In the orthohydrogen form, the spins of the two nuclei are parallel, forming a spintriplet state
In quantum mechanics, a triplet is a quantum state of a system with a spin of quantum number =1, such that there are three allowed values of the spin component, = −1, 0, and +1.
Spin, in the context of quantum mechanics, is not a mechanical ...
having a total molecular spin ; in the parahydrogen form the spins are antiparallel and form a spin singlet state
In quantum mechanics, a singlet state usually refers to a system in which all electrons are paired. The term 'singlet' originally meant a linked set of particles whose net angular momentum is zero, that is, whose overall spin quantum number s=0. A ...
having spin . The equilibrium ratio of ortho- to para-hydrogen depends on temperature. At room temperature or warmer, equilibrium hydrogen gas contains about 25% of the para form and 75% of the ortho form. The ortho form is an excited state
In quantum mechanics, an excited state of a system (such as an atom, molecule or nucleus) is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state (that is, more energy than the absolute minimum). Excitation refers to a ...
, having higher energy than the para form by 1.455 kJ/mol, and it converts to the para form over the course of several minutes when cooled to low temperature. The thermal properties of the forms differ because they differ in their allowed rotational quantum states, resulting in different thermal properties such as the heat capacity.
The ortho-to-para ratio in is an important consideration in the liquefaction
In materials science, liquefaction is a process that generates a liquid from a solid or a gas or that generates a non-liquid phase which behaves in accordance with fluid dynamics.
It occurs both naturally and artificially. As an example of the ...
and storage of liquid hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully li ...
: the conversion from ortho to para is exothermic
In thermodynamics, an exothermic process () is a thermodynamic process or reaction that releases energy from the system to its surroundings, usually in the form of heat, but also in a form of light (e.g. a spark, flame, or flash), electricity (e ...
and produces enough heat to evaporate a most of the liquid if not converted first to parahydrogen during the cooling process. Catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
s for the ortho-para interconversion, such as ferric oxide
Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Fe2O3. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4), which also occurs naturally a ...
and activated carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, is a form of carbon commonly used to filter contaminants from water and air, among many other uses. It is processed (activated) to have small, low-volume pores that increase the surface area avail ...
compounds, are used during hydrogen cooling to avoid this loss of liquid.
Phases

 *
* Gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
eous hydrogen
* Liquid hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully li ...
* Slush hydrogen Slush hydrogen is a combination of liquid hydrogen and solid hydrogen at the triple point with a lower temperature and a higher density than liquid hydrogen. It is commonly formed by repeating a freeze-thaw process. This is most easily done by bring ...
* Solid hydrogen
Solid hydrogen is the solid state of the element hydrogen, achieved by decreasing the temperature below hydrogen's melting point of . It was collected for the first time by James Dewar in 1899 and published with the title "Sur la solidification de ...
* Metallic hydrogen
Metallic hydrogen is a phase of hydrogen in which it behaves like an electrical conductor. This phase was predicted in 1935 on theoretical grounds by Eugene Wigner and Hillard Bell Huntington.
At high pressure and temperatures, metallic hydrogen c ...
* Plasma
Plasma or plasm may refer to:
Science
* Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter
* Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral
* Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics
Biology
* Blood pla ...
hydrogen
Compounds
Covalent and organic compounds
While is not very reactive under standard conditions, it does form compounds with most elements. Hydrogen can form compounds with elements that are moreelectronegative
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the d ...
, such as halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
s (F, Cl, Br, I), or oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
; in these compounds hydrogen takes on a partial positive charge. When bonded to a more electronegative element, particularly fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reacti ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
, or nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
, hydrogen can participate in a form of medium-strength noncovalent bonding with another electronegative element with a lone pair, a phenomenon called hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
ing that is critical to the stability of many biological molecules. Hydrogen also forms compounds with less electronegative elements, such as metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
s and metalloid
A metalloid is a type of chemical element which has a preponderance of material property, properties in between, or that are a mixture of, those of metals and nonmetals. There is no standard definition of a metalloid and no complete agreement on ...
s, where it takes on a partial negative charge. These compounds are often known as hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of ...
s.
Hydrogen forms a vast array of compounds with carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
called the hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
s, and an even vaster array with heteroatoms
In chemistry, a heteroatom () is, strictly, any atom that is not carbon or hydrogen.
Organic chemistry
In practice, the term is usually used more specifically to indicate that non-carbon atoms have replaced carbon in the backbone of the molecula ...
that, because of their general association with living things, are called organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ...
s. The study of their properties is known as organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; ...
and their study in the context of living organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and ...
s is known as biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
. By some definitions, "organic" compounds are only required to contain carbon. However, most of them also contain hydrogen, and because it is the carbon-hydrogen bond that gives this class of compounds most of its particular chemical characteristics, carbon-hydrogen bonds are required in some definitions of the word "organic" in chemistry. Millions of hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
s are known, and they are usually formed by complicated pathways that seldom involve elemental hydrogen.
Hydrogen is highly soluble in many rare earth and transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...
s and is soluble in both nanocrystalline and amorphous metal
An amorphous metal (also known as metallic glass, glassy metal, or shiny metal) is a solid metallic material, usually an alloy, with disordered atomic-scale structure. Most metals are crystalline in their solid state, which means they have a high ...
s. Hydrogen solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubil ...
in metals is influenced by local distortions or impurities in the crystal lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by
: \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 + n ...
. These properties may be useful when hydrogen is purified by passage through hot palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself na ...
disks, but the gas's high solubility is a metallurgical problem, contributing to the embrittlement
Embrittlement is a significant decrease of ductility of a material, which makes the material Brittleness, brittle. Embrittlement is used to describe any phenomena where the environment compromises a stressed material's mechanical performance, such ...
of many metals, complicating the design of pipelines and storage tanks.
Hydrides
 Compounds of hydrogen are often called
Compounds of hydrogen are often called hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of ...
s, a term that is used fairly loosely. The term "hydride" suggests that the H atom has acquired a negative or anionic character, denoted , and is used when hydrogen forms a compound with a more electropositive
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the d ...
element. The existence of the hydride anion
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of ...
, suggested by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1916 for group 1 and 2 salt-like hydrides, was demonstrated by Moers in 1920 by the electrolysis of molten lithium hydride
Lithium hydride is an inorganic compound with the formula Li H. This alkali metal hydride is a colorless solid, although commercial samples are grey. Characteristic of a salt-like (ionic) hydride, it has a high melting point, and it is not solub ...
(LiH), producing a stoichiometric
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equal ...
quantity of hydrogen at the anode. For hydrides other than group 1 and 2 metals, the term is quite misleading, considering the low electronegativity of hydrogen. An exception in group 2 hydrides is , which is polymeric. In lithium aluminium hydride
Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li Al H4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic ...
, the anion carries hydridic centers firmly attached to the Al(III).
Although hydrides can be formed with almost all main-group elements, the number and combination of possible compounds varies widely; for example, more than 100 binary borane hydrides are known, but only one binary aluminium hydride. Binary indium
Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. Indium is the softest metal that is not an alkali metal. It is a silvery-white metal that resembles tin in appearance. It is a post-transition metal that makes up 0.21 parts p ...
hydride has not yet been identified, although larger complexes exist.
In inorganic chemistry
Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disci ...
, hydrides can also serve as bridging ligand
In coordination chemistry, a bridging ligand is a ligand that connects two or more atoms, usually metal ions. The ligand may be atomic or polyatomic. Virtually all complex organic compounds can serve as bridging ligands, so the term is usually r ...
s that link two metal centers in a coordination complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many ...
. This function is particularly common in group 13 element
The Group 13 network ( pl, Trzynastka, Yiddish: ''דאָס דרײַצענטל'') was a Jewish Nazi collaborationist organization in the Warsaw Ghetto during the German occupation of Poland in World War II. The rise and fall of the Group ...
s, especially in borane
Trihydridoboron, also known as borane or borine, is an unstable and highly reactive molecule with the chemical formula . The preparation of borane carbonyl, BH3(CO), played an important role in exploring the chemistry of boranes, as it indicated ...
s (boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has th ...
hydrides) and aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
complexes, as well as in clustered carborane
Carboranes are electron-delocalized (non-classically bonded) clusters composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms.Grimes, R. N., ''Carboranes 3rd Ed.'', Elsevier, Amsterdam and New York (2016), . Like many of the related boron hydrides, these c ...
s.
Protons and acids
Oxidation of hydrogen removes its electron and gives , which contains no electrons and anucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
which is usually composed of one proton. That is why is often called a proton. This species is central to discussion of acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
s. Under the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory
The Brønsted–Lowry theory (also called proton theory of acids and bases) is an acid–base reaction theory which was proposed independently by Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923. The fundamental concept of this theory ...
, acids are proton donors, while bases are proton acceptors.
A bare proton, , cannot exist in solution or in ionic crystals because of its unstoppable attraction to other atoms or molecules with electrons. Except at the high temperatures associated with plasmas, such protons cannot be removed from the electron cloud
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any spe ...
s of atoms and molecules, and will remain attached to them. However, the term 'proton' is sometimes used loosely and metaphorically to refer to positively charged or cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
ic hydrogen attached to other species in this fashion, and as such is denoted "" without any implication that any single protons exist freely as a species.
To avoid the implication of the naked "solvated proton" in solution, acidic aqueous solutions are sometimes considered to contain a less unlikely fictitious species, termed the "hydronium
In chemistry, hydronium (hydroxonium in traditional British English) is the common name for the aqueous cation , the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid is d ...
ion" (). However, even in this case, such solvated hydrogen cations are more realistically conceived as being organized into clusters that form species closer to . Other oxonium ion
In chemistry, an oxonium ion is any cation containing an oxygen atom that has three bonds and 1+ formal charge. The simplest oxonium ion is the hydronium ion ().
Alkyloxonium
Hydronium is one of a series of oxonium ions with the formula R''n''H ...
s are found when water is in acidic solution with other solvents.
Although exotic on Earth, one of the most common ions in the universe is the ion, known as protonated molecular hydrogen
The trihydrogen cation or protonated molecular hydrogen is a cation (positive ion) with chemical formula, formula , consisting of three hydrogen nuclei (protons) sharing two electrons.
The trihydrogen cation is one of the most abundant ions in t ...
or the trihydrogen cation.
Isotopes


 Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes, denoted , and . Other, highly unstable nuclei ( to ) have been synthesized in the laboratory but not observed in nature.
* is the most common hydrogen isotope, with an abundance of more than 99.98%. Because the
Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes, denoted , and . Other, highly unstable nuclei ( to ) have been synthesized in the laboratory but not observed in nature.
* is the most common hydrogen isotope, with an abundance of more than 99.98%. Because the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
of this isotope consists of only a single proton, it is given the descriptive but rarely used formal name '' protium''. It is unique among all stable isotopes in having no neutrons; see diproton
Although there are nine known isotopes of helium (2He) ( standard atomic weight: ), only helium-3 () and helium-4 () are stable. All radioisotopes are short-lived, the longest-lived being with a half-life of . The least stable is , with a half- ...
for a discussion of why others do not exist.
* , the other stable hydrogen isotope, is known as ''deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium ato ...
'' and contains one proton and one neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons beh ...
in the nucleus. All deuterium in the universe is thought to have been produced at the time of the Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
, and has endured since that time. Deuterium is not radioactive, and does not represent a significant toxicity hazard. Water enriched in molecules that include deuterium instead of normal hydrogen is called heavy water. Deuterium and its compounds are used as a non-radioactive label in chemical experiments and in solvents for -NMR spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. The sample is placed in a magnetic fiel ...
. Heavy water is used as a neutron moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely mo ...
and coolant for nuclear reactors. Deuterium is also a potential fuel for commercial nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles ( neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifest ...
.
* is known as ''tritium
Tritium ( or , ) or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with half-life about 12 years. The nucleus of tritium (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus o ...
'' and contains one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. It is radioactive, decaying into helium-3
Helium-3 (3He see also helion) is a light, stable isotope of helium with two protons and one neutron (the most common isotope, helium-4, having two protons and two neutrons in contrast). Other than protium (ordinary hydrogen), helium-3 is the ...
through beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For ...
with a half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
of 12.32 years. It is so radioactive that it can be used in luminous paint
Luminous paint or luminescent paint is paint that exhibits luminescence. In other words, it gives off Visible spectrum, visible light through fluorescence, phosphorescence, or radioluminescence. There are three types of luminous paints: fluoresc ...
, making it useful in such things as watches. The glass prevents the small amount of radiation from getting out. Small amounts of tritium are produced naturally by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric gases; tritium has also been released during nuclear weapons tests
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected b ...
. It is used in nuclear fusion reactions, as a tracer in isotope geochemistry
Isotope geochemistry is an aspect of geology based upon the study of natural variations in the relative abundances of isotopes of various elements. Variations in isotopic abundance are measured by isotope ratio mass spectrometry, and can reveal ...
, and in specialized self-powered lighting
Tritium radioluminescence is the use of gaseous tritium, a radioactive isotope of hydrogen, to create visible light. Tritium emits electrons through beta decay and, when they interact with a phosphor material, light is emitted through the proces ...
devices. Tritium has also been used in chemical and biological labeling experiments as a radiolabel
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tr ...
.
Unique among the elements, distinct names are assigned to its isotopes in common use today. During the early study of radioactivity, various heavy radioactive isotopes were given their own names, but such names are no longer used, except for deuterium and tritium. The symbols D and T (instead of and ) are sometimes used for deuterium and tritium, but the symbol P is already in use for phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
and thus is not available for protium. In its nomenclatural
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal conventions of everyday speech to the internationally ag ...
guidelines, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
(IUPAC) allows any of D, T, , and to be used, although and are preferred.
The exotic atom
An exotic atom is an otherwise normal atom in which one or more sub-atomic particles have been replaced by other particles of the same charge. For example, electrons may be replaced by other negatively charged particles such as muons (muonic atoms) ...
muonium
Muonium is an exotic atom made up of an antimuon and an electron,
which was discovered in 1960 by Vernon W. Hughes
and is given the chemical symbol Mu. During the muon's lifetime, muonium can undergo chemical reactions. Due to the mass diffe ...
(symbol Mu), composed of an antimuon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of , but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As wit ...
and an electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no kn ...
, can also be considered a light radioisotope of hydrogen. Because muons decay with lifetime , muonium is too unstable to exhibit observable chemistry. Nevertheless, muonium compounds are important test cases for quantum simulation, due to the mass difference between the antimuon and the proton, and IUPAC nomenclature incorporates such hypothetical compounds as muonium chloride (MuCl) and sodium muonide (NaMu), analogous to hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride ga ...
and sodium hydride
Sodium hydride is the chemical compound with the empirical formula Na H. This alkali metal hydride is primarily used as a strong yet combustible base in organic synthesis. NaH is a saline (salt-like) hydride, composed of Na+ and H− ions, in co ...
respectively.
Thermal and physical properties
Table of thermal and physical properties of hydrogen (H2) at atmospheric pressure:History
Discovery and use
In 1671,Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of ...
discovered and described the reaction between iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
filings and dilute acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
s, which results in the production of hydrogen gas.
In 1766, Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish ( ; 10 October 1731 – 24 February 1810) was an English natural philosopher and scientist who was an important experimental and theoretical chemist and physicist. He is noted for his discovery of hydrogen, which he termed "infl ...
was the first to recognize hydrogen gas as a discrete substance, by naming the gas from a metal-acid reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ...
"inflammable air". He speculated that "inflammable air" was in fact identical to the hypothetical substance called "phlogiston
The phlogiston theory is a superseded scientific theory that postulated the existence of a fire-like element called phlogiston () contained within combustible bodies and released during combustion. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''burni ...
" and further finding in 1781 that the gas produces water when burned. He is usually given credit for the discovery of hydrogen as an element. In 1783, Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794), When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and th ...
gave the element the name hydrogen (from the Greek ὑδρο- ''hydro'' meaning "water" and -γενής ''genes'' meaning "former") when he and Laplace
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace (; ; 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827) was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics, statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He summarized ...
reproduced Cavendish's finding that water is produced when hydrogen is burned.
Lavoisier produced hydrogen for his experiments on mass conservation by reacting a flux of steam with metallic iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
through an incandescent iron tube heated in a fire. Anaerobic oxidation of iron by the protons of water at high temperature can be schematically represented by the set of following reactions:
:1)
:2)
:3)
Many metals such as zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name ''zirconium'' is taken from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian '' zargun'' (zircon; ''zar-gun'', ...
undergo a similar reaction with water leading to the production of hydrogen.
Hydrogen was liquefied for the first time by James Dewar
Sir James Dewar (20 September 1842 – 27 March 1923) was a British chemist and physicist. He is best known for his invention of the vacuum flask, which he used in conjunction with research into the liquefaction of gases. He also studied ato ...
in 1898 by using regenerative cooling
Regenerative cooling is a method of cooling gases in which compressed gas is cooled by allowing it to expand and thereby take heat from the surroundings. The cooled expanded gas then passes through a heat exchanger where it cools the incoming comp ...
and his invention, the vacuum flask
A vacuum flask (also known as a Dewar flask, Dewar bottle or thermos) is an insulating storage vessel that greatly lengthens the time over which its contents remain hotter or cooler than the flask's surroundings. Invented by Sir James Dewa ...
. He produced solid hydrogen
Solid hydrogen is the solid state of the element hydrogen, achieved by decreasing the temperature below hydrogen's melting point of . It was collected for the first time by James Dewar in 1899 and published with the title "Sur la solidification de ...
the next year. Deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium ato ...
was discovered in December 1931 by Harold Urey
Harold Clayton Urey ( ; April 29, 1893 – January 5, 1981) was an American physical chemist whose pioneering work on isotopes earned him the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1934 for the discovery of deuterium. He played a significant role in the d ...
, and tritium
Tritium ( or , ) or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with half-life about 12 years. The nucleus of tritium (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus o ...
was prepared in 1934 by Ernest Rutherford
Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson, (30 August 1871 – 19 October 1937) was a New Zealand physicist who came to be known as the father of nuclear physics.
''Encyclopædia Britannica'' considers him to be the greatest ...
, Mark Oliphant
Sir Marcus Laurence Elwin Oliphant, (8 October 1901 – 14 July 2000) was an Australian physicist and humanitarian who played an important role in the first experimental demonstration of nuclear fusion and in the development of nuclear weapon ...
, and Paul Harteck
Paul Karl Maria Harteck (20 July 190222 January 1985) was an Austrian physical chemist. In 1945 under Operation Epsilon in "the big sweep" throughout Germany, Harteck was arrested by the allied British and American Armed Forces for suspicion of ...
. Heavy water, which consists of deuterium in the place of regular hydrogen, was discovered by Urey's group in 1932. François Isaac de Rivaz
François Isaac de Rivaz (Paris, December 19, 1752 – Sion, July 30, 1828) was a French-born Swiss inventor and a politician. He invented a hydrogen-powered internal combustion engine with electric ignition and described it in a French paten ...
built the first de Rivaz engine The de Rivaz engine was a pioneering reciprocating engine designed and developed from 1804 by the Franco-Swiss inventor Isaac de Rivaz. The engine has a claim to be the world's first internal combustion engine and contained some features of modern ...
, an internal combustion engine powered by a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen in 1806. Edward Daniel Clarke invented the hydrogen gas blowpipe in 1819. The Döbereiner's lamp and limelight were invented in 1823.
The first hydrogen-filled balloon was invented by Jacques Charles in 1783. Hydrogen provided the lift for the first reliable form of air-travel following the 1852 invention of the first hydrogen-lifted airship by Henri Giffard. German count Ferdinand von Zeppelin promoted the idea of rigid airships lifted by hydrogen that later were called Zeppelins; the first of which had its maiden flight in 1900. Regularly scheduled flights started in 1910 and by the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, they had carried 35,000 passengers without a serious incident. Hydrogen-lifted airships were used as observation platforms and bombers during the war.
The first non-stop transatlantic crossing was made by the British airship ''R34 (airship), R34'' in 1919. Regular passenger service resumed in the 1920s and the discovery of helium reserves in the United States promised increased safety, but the U.S. government refused to sell the gas for this purpose. Therefore, was used in the LZ 129 Hindenburg, ''Hindenburg'' airship, which was destroyed in a midair fire over New Jersey on 6 May 1937. The incident was broadcast live on radio and filmed. Ignition of leaking hydrogen is widely assumed to be the cause, but later investigations pointed to the ignition of the aluminium, aluminized fabric coating by static electricity. But the damage to hydrogen's reputation as a lifting gas was already done and commercial hydrogen airship travel Rigid airship#Demise, ceased. Hydrogen is still used, in preference to non-flammable but more expensive helium, as a lifting gas for Weather balloon#Materials and equipment, weather balloons.
In the same year, the first hydrogen-cooled turbogenerator went into service with gaseous hydrogen as a coolant in the rotor and the stator in 1937 at Dayton, Ohio, Dayton, Ohio, by the Dayton Power & Light Co.; because of the thermal conductivity and very low viscosity of hydrogen gas, thus lower drag than air, this is the most common type in its field today for large generators (typically 60 MW and bigger; smaller generators are usually air cooling, air-cooled).
The nickel hydrogen battery was used for the first time in 1977 aboard the U.S. Navy's Navigation technology satellite-2 (NTS-2). For example, the International Space Station, ISS, 2001 Mars Odyssey, Mars Odyssey and the Mars Global Surveyor are equipped with nickel-hydrogen batteries. In the dark part of its orbit, the Hubble Space Telescope is also powered by nickel-hydrogen batteries, which were finally replaced in May 2009, more than 19 years after launch and 13 years beyond their design life.
Role in quantum theory
atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and ...
ic structure. Furthermore, study of the corresponding simplicity of the hydrogen molecule and the corresponding cation H2+, brought understanding of the nature of the chemical bond, which followed shortly after the quantum mechanical treatment of the hydrogen atom had been developed in the mid-1920s.
One of the first quantum effects to be explicitly noticed (but not understood at the time) was a Maxwell observation involving hydrogen, half a century before full Quantum mechanics, quantum mechanical theory arrived. Maxwell observed that the specific heat capacity of unaccountably departs from that of a diatomic gas below room temperature and begins to increasingly resemble that of a monatomic gas at cryogenic temperatures. According to quantum theory, this behavior arises from the spacing of the (quantized) rotational energy levels, which are particularly wide-spaced in because of its low mass. These widely spaced levels inhibit equal partition of heat energy into rotational motion in hydrogen at low temperatures. Diatomic gases composed of heavier atoms do not have such widely spaced levels and do not exhibit the same effect.
Antihydrogen () is the antimatter counterpart to hydrogen. It consists of an antiproton with a positron. Antihydrogen is the only type of antimatter atom to have been produced .
Cosmic prevalence and distribution
 Hydrogen, as atomic H, is the most Natural abundance, abundant
Hydrogen, as atomic H, is the most Natural abundance, abundant chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
in the universe, making up 75 percent of Baryon, normal matter by mass and more than 90 percent by number of atoms. (Most of the mass of the universe, however, is not in the form of chemical-element type matter, but rather is postulated to occur as yet-undetected forms of mass such as dark matter
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe. Dark matter is called "dark" because it does not appear to interact with the electromagnetic field, which means it does not ab ...
and dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univer ...
.) This element is found in great abundance in stars and gas giant planets. Molecular clouds of are associated with star formation. Hydrogen plays a vital role in powering stars through the proton-proton reaction in case of stars with very low to approximately 1 mass of the Sun and the CNO cycle of nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles ( neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifest ...
in case of stars more massive than our Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
.
States
Throughout the universe, hydrogen is mostly found in theatom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and ...
ic and plasma
Plasma or plasm may refer to:
Science
* Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter
* Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral
* Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics
Biology
* Blood pla ...
states, with properties quite distinct from those of molecular hydrogen. As a plasma, hydrogen's electron and proton are not bound together, resulting in very high electrical conductivity and high emissivity (producing the light from the Sun and other stars). The charged particles are highly influenced by magnetic and electric fields. For example, in the solar wind they interact with the Earth's magnetosphere giving rise to Birkeland currents and the Aurora (phenomenon), aurora.
Hydrogen is found in the neutral atomic state in the interstellar medium because the atoms seldom collide and combine. They are the source of the hydrogen line, 21-cm hydrogen line at 1420 MHz that is detected in order to probe primordial hydrogen. The large amount of neutral hydrogen found in the damped Lyman-alpha systems is thought to dominate the Physical cosmology, cosmological baryonic density of the universe up to a redshift of ''z'' = 4.
Under ordinary conditions on Earth, elemental hydrogen exists as the diatomic gas, . Hydrogen gas is very rare in the Earth's atmosphere (1 part per million, ppm by volume) because of its light weight, which enables it to atmospheric escape, escape from the atmosphere more rapidly than heavier gases. However, hydrogen is the third most abundant element on the Earth's surface, mostly in the form of chemical compounds such as hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
s and water.
A molecular form called protonated molecular hydrogen () is found in the interstellar medium, where it is generated by ionization of molecular hydrogen from cosmic rays. This ion has also been observed in the upper atmosphere of the planet Jupiter. The ion is relatively stable in the environment of outer space due to the low temperature and density. is one of the most abundant ions in the universe, and it plays a notable role in the chemistry of the interstellar medium. Neutral triatomic hydrogen can exist only in an excited form and is unstable. By contrast, the positive hydrogen molecular ion () is a rare molecule in the universe.
Production
is produced in chemistry and biology laboratories, often as a by-product of other reactions; in industry for the hydrogenation of Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated substrates; and in nature as a means of expelling redox, reducing equivalents in biochemical reactions.Water electrolysis
 The
The electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water, also known as electrochemical water splitting, is the process of using electricity to decompose water into oxygen and hydrogen gas by electrolysis. Hydrogen gas released in this way can be used as hydrogen fuel, or remi ...
is a simple method of producing hydrogen. A current is run through the water, and gaseous oxygen forms at the anode while gaseous hydrogen forms at the cathode. Typically the cathode is made from platinum or another inert metal when producing hydrogen for storage. If, however, the gas is to be burnt on site, oxygen is desirable to assist the combustion, and so both electrodes would be made from inert metals. (Iron, for instance, would oxidize, and thus decrease the amount of oxygen given off.) The theoretical maximum efficiency (electricity used vs. energetic value of hydrogen produced) is in the range 88–94%.
:
Methane pyrolysis
 Hydrogen production using natural gas methane pyrolysis is a one-step process that produces no greenhouse gases. Developing volume production using this method is the key to enabling faster carbon reduction by using hydrogen in industrial processes, fuel cell electric heavy truck transportation, and in gas turbine electric power generation. Methane pyrolysis is performed by having methane bubbled up through a molten metal catalyst containing dissolved nickel at . This causes the methane to break down into hydrogen gas and solid
Hydrogen production using natural gas methane pyrolysis is a one-step process that produces no greenhouse gases. Developing volume production using this method is the key to enabling faster carbon reduction by using hydrogen in industrial processes, fuel cell electric heavy truck transportation, and in gas turbine electric power generation. Methane pyrolysis is performed by having methane bubbled up through a molten metal catalyst containing dissolved nickel at . This causes the methane to break down into hydrogen gas and solid carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
, with no other byproducts.
: (ΔH° = 74 kJ/mol)
The industrial quality solid carbon may be sold as manufacturing feedstock or permanently landfilled; it is not released into the atmosphere and does not cause ground water pollution in landfill. Methane pyrolysis is in development and considered suitable for commercial bulk hydrogen production. Volume production is being evaluated in the BASF "methane pyrolysis at scale" pilot plant. Further research continues in several laboratories, including at Karlsruhe Liquid-metal Laboratory (KALLA) and the chemical engineering laboratory at University of California – Santa Barbara
Other industrial methods
 Hydrogen is often produced by reacting water with methane and carbon monoxide, which causes the removal of hydrogen from hydrocarbons at very high temperatures, with 48% of hydrogen production coming from
Hydrogen is often produced by reacting water with methane and carbon monoxide, which causes the removal of hydrogen from hydrocarbons at very high temperatures, with 48% of hydrogen production coming from steam reforming
Steam reforming or steam methane reforming (SMR) is a method for producing syngas (hydrogen and carbon monoxide) by reaction of hydrocarbons with water. Commonly natural gas is the feedstock. The main purpose of this technology is hydrogen product ...
. The water vapor is then reacted with the carbon monoxide produced by steam reforming to oxidize it to carbon dioxide and turn the water into hydrogen. Commercial bulk hydrogen is usually produced by the steam reforming of natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
with release of atmospheric greenhouse gas or with capture using CCS and climate change mitigation. Steam reforming is also known as the Bosch reaction, Bosch process and is widely used for the industrial preparation of hydrogen.
At high temperatures (1000–1400 K, 700–1100 °C or 1300–2000 °F), steam (water vapor) reacts with methane to yield carbon monoxide and .
:
This reaction is favored at low pressures but is nonetheless conducted at high pressures (2.0 MPa, 20 atm or 600 inHg). This is because high-pressure is the most marketable product, and pressure swing adsorption (PSA) purification systems work better at higher pressures. The product mixture is known as "synthesis gas" because it is often used directly for the production of methanol and related compounds. Hydrocarbons other than methane can be used to produce synthesis gas with varying product ratios. One of the many complications to this highly optimized technology is the formation of coke or carbon:
:
Consequently, steam reforming typically employs an excess of . Additional hydrogen can be recovered from the steam by use of carbon monoxide through the water gas shift reaction, especially with an iron oxide catalyst. This reaction is also a common industrial source of carbon dioxide:
:
Other important methods for CO and production include partial oxidation of hydrocarbons:
:
and the coal reaction, which can serve as a prelude to the shift reaction above:
:
Hydrogen is sometimes produced and consumed in the same industrial process, without being separated. In the Haber process for the Ammonia production, production of ammonia, hydrogen is generated from natural gas. Electrolysis of brine to yield chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate betwee ...
also produces hydrogen as a co-product.
Olefin production units may produce substantial quantities of byproduct hydrogen particularly from cracking light feedstocks like ethane or propane.
Metal-acid
Many metals react with water to produce , but the rate of hydrogen evolution depends on the metal, the pH, and the presence alloying agents. Most commonly, hydrogen evolution is induced by acids. The alkali and alkaline earth metals, aluminium, zinc, manganese, and iron react readily with aqueous acids. This reaction is the basis of the Kipp's apparatus, which once was used as a laboratory gas source: : In the absence of acid, the evolution of is slower. Because iron is widely used structural material, its anaerobic corrosion is of technological significance: : Many metals, such asaluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
, are slow to react with water because they form passivated coatings of oxides. An alloy of aluminium and gallium, however, does react with water. At high pH, aluminium can produce :
:
Some metal-containing compounds react with acids to evolve . Under anaerobic conditions, ferrous hydroxide () can be oxidized by the protons of water to form magnetite and . This process is described by the Schikorr reaction:
:
This process occurs during the anaerobic corrosion of iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
and steel in Anoxic waters, oxygen-free groundwater and in reducing soils below the water table.
Thermochemical
More than 200 thermochemical cycles can be used for water splitting. Many of these cycles such as the iron oxide cycle, cerium(IV) oxide–cerium(III) oxide cycle, zinc zinc-oxide cycle, sulfur-iodine cycle, copper-chlorine cycle and hybrid sulfur cycle have been evaluated for their commercial potential to produce hydrogen and oxygen from water and heat without using electricity. A number of laboratories (including in France, Germany, Greece, Japan, and the United States) are developing thermochemical methods to produce hydrogen from solar energy and water.Serpentinization reaction
In deep geological conditions prevailing far away from the Earth's atmosphere, hydrogen () is produced during the process of Serpentinization#Hydrogen production by anaerobic oxidation of fayalite ferrous ions, serpentinization. In this process, water protons () are reduced by ferrous () ions provided by fayalite (). The reaction forms magnetite (), quartz (), and hydrogen (): : :''fayalite + water → magnetite + quartz + hydrogen'' This reaction closely resembles the Schikorr reaction observed in anaerobic oxidation of ferrous hydroxide in contact with water.Applications
Petrochemical industry
Large quantities of are used in the "upgrading" of fossil fuels. Key consumers of include hydrodealkylation, hydrodesulfurization, andhydrocracking
In petrochemistry, petroleum geology and organic chemistry, cracking is the process whereby complex organic molecules such as kerogens or long-chain hydrocarbons are broken down into simpler molecules such as light hydrocarbons, by the breaking of ...
. Many of these reactions can be classified as hydrogenolysis, i.e., the cleavage of bonds to carbon. Illustrative is the separation of sulfur from liquid fossil fuels:
:
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation, the addition of to various substrates is conducted on a large scale. The hydrogenation of to produce ammonia by the Haber–Bosch process consumes a few percent of the energy budget in the entire industry. The resulting ammonia is used to supply the majority of the protein consumed by humans. Hydrogenation is used to convert unsaturated fats and vegetable oil, oils to saturated fats and oils. The major application is the production of margarine. Methanol is produced by hydrogenation of carbon dioxide. It is similarly the source of hydrogen in the manufacture of hydrochloric acid. is also used as a reducing agent for the conversion of some ores to the metals.Coolant
Hydrogen is commonly used in power stations as a coolant in generators due to a number of favorable properties that are a direct result of its light diatomic molecules. These include low density, low viscosity, and the highest Specific heat capacity, specific heat and thermal conductivity of all gases.Energy carrier
Elemental hydrogen has been widely discussed in the context of energy, as a possible future carrier of energy on an economy-wide scale. Hydrogen is afuel cells
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
to generate electricity directly, with water being the only emissions at the point of usage. The overall lifecycle emissions of hydrogen depend on how it is produced. Nearly all of the world's current supply of hydrogen is created from fossil fuels. The main method is steam methane reforming, in which hydrogen is produced from a chemical reaction between steam and methane, the main component of natural gas. Producing one tonne of hydrogen through this process emits 6.6–9.3 tonnes of carbon dioxide. While carbon capture and storage can remove a large fraction of these emissions, the overall carbon footprint of hydrogen from natural gas is difficult to assess , in part because of emissions created in the production of the natural gas itself.
Electricity can be used to split water molecules, producing sustainable hydrogen provided the electricity was generated sustainably. However, this electrolysis process is currently more expensive than creating hydrogen from methane and the efficiency of energy conversion is inherently low. Hydrogen can be produced when there is a surplus of Variable renewable energy, variable renewable electricity, then stored and used to generate heat or to re-generate electricity. It can be further transformed into synthetic fuels such as ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
and methanol.
Innovation in Electrolysis of water, hydrogen electrolysers could make large-scale production of hydrogen from electricity more cost-competitive. There is potential for hydrogen to play a significant role in decarbonising energy systems because in certain sectors, replacing fossil fuels with direct use of electricity would be very difficult. Hydrogen fuel can produce the intense heat required for industrial production of steel, cement, glass, and chemicals. For steelmaking, hydrogen can function as a clean energy carrier and simultaneously as a low-carbon catalyst replacing coal-derived Coke (fuel), coke. Hydrogen used in transportation would burn relatively cleanly, with some NOx, emissions, but without carbon emissions. Disadvantages of hydrogen as an energy carrier include high costs of storage and distribution due to hydrogen's explosivity, its large volume compared to other fuels, and its tendency to make pipes brittle. The infrastructure costs associated with full conversion to a hydrogen economy would be substantial.
Semiconductor industry
Hydrogen is employed to saturate broken ("dangling") bonds of amorphous silicon and amorphous carbon that helps stabilizing material properties. It is also a potential electron donor in various oxide materials, including zinc oxide, ZnO, Tin dioxide, , Cadmium oxide, CdO, Magnesium oxide, MgO, Zirconium dioxide, , Hafnium(IV) oxide, , Lanthanum(III) oxide, , Yttrium(III) oxide, , Titanium dioxide, , Strontium titanate, , Lanthanum aluminate, , Silicon dioxide, , Aluminium oxide, , Zircon, , Hafnon, , and Strontium zirconate, .Aerospace
Liquid hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully li ...
and liquid oxygen together serve as cryogenic fuel in liquid-propellant rockets, as in the RS-25, Space Shuttle main engines.
Niche and evolving uses
*Shielding gas: Hydrogen is used as a shielding gas in welding methods such as atomic hydrogen welding. *Cryogenic research: Liquid is used in cryogenic research, including superconductivity studies. *Buoyant lifting: Because is lighter than air, having only 7% of the density of air, it was once widely used as a lifting gas in balloons and airships. *Leak detection: Pure or mixed with nitrogen (sometimes called forming gas), hydrogen is a tracer gas for Leak detection, detection of minute leaks. Applications can be found in the automotive, chemical, power generation, aerospace, and telecommunications industries. Hydrogen is an authorized food additive (E 949) that allows food package leak testing, as well as having anti-oxidizing properties. *Neutron moderation:Deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium ato ...
(hydrogen-2) is used in CANDU reactor, nuclear fission applications as a neutron moderator, moderator to slow neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons beh ...
s.
*Nuclear fusion fuel: Deuterium is used in nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles ( neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifest ...
reactions.
*Isotopic labeling: Deuterium compounds have applications in chemistry and biology in studies of Kinetic isotope effect, isotope effects on reaction rates.
*Rocket propellant: NASA has investigated the use of rocket propellant made from atomic hydrogen, boron or carbon that is frozen into solid molecular hydrogen particles that are suspended in liquid helium. Upon warming, the mixture vaporizes to allow the atomic species to recombine, heating the mixture to high temperature.
*Tritium uses: Tritium (hydrogen-3), produced in nuclear reactors, is used in the production of hydrogen bombs, as an isotopic label in the biosciences, and as a source of beta particle, beta radiation in Tritium radioluminescence, radioluminescent paint for instrument dials and emergency signage.
Biological reactions
is a product of some types of Fermentation (biochemistry), anaerobic metabolism and is produced by several microorganisms, usually via reactions catalysis, catalyzed byiron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
- or nickel-containing enzymes called hydrogenases. These enzymes catalyze the reversible redox reaction between and its component two protons and two electrons. Creation of hydrogen gas occurs in the transfer of reducing equivalents produced during pyruvate fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation to water. The natural cycle of hydrogen production and consumption by organisms is called the hydrogen cycle. Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the human body in terms of numbers of atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and ...
s of the element but, it is the 3rd most abundant element by mass, because hydrogen is so light. occurs in the breath of humans due to the metabolic activity of hydrogenase-containing microorganisms in the large intestine. The concentration in fasted people at rest is typically less than 5 parts per million (ppm) but can be 50 ppm when people with intestinal disorders consume molecules they cannot absorb during diagnostic hydrogen breath tests.
Hydrogen gas is produced by some bacteria and algae and is a natural component of flatus, as is methane, itself a hydrogen source of increasing importance.
Water splitting, in which water is decomposed into its component protons, electrons, and oxygen, occurs in the Light-dependent reactions, light reactions in all photosynthetic organisms. Some such organisms, including the alga ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' and cyanobacteria, have evolved a second step in the dark reactions in which protons and electrons are reduced to form gas by specialized hydrogenases in the chloroplast. Efforts have been undertaken to genetically modify cyanobacterial hydrogenases to efficiently synthesize gas even in the presence of oxygen. Efforts have also been undertaken with genetically modified Biological hydrogen production (Algae), alga in a bioreactor.
Safety and precautions
Hydrogen poses a number of hazards to human safety, from potential detonations and fires when mixed with air to being an asphyxiant in its pure,oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
-free form. In addition, liquid hydrogen is a cryogen and presents dangers (such as frostbite) associated with very cold liquids. Hydrogen dissolves in many metals and in addition to leaking out, may have adverse effects on them, such as hydrogen embrittlement, leading to cracks and explosions. Hydrogen gas leaking into external air may spontaneously ignite. Moreover, hydrogen fire, while being extremely hot, is almost invisible, and thus can lead to accidental burns.
Even interpreting the hydrogen data (including safety data) is confounded by a number of phenomena. Many physical and chemical properties of hydrogen depend on the Spin isomers of hydrogen, parahydrogen/orthohydrogen ratio (it often takes days or weeks at a given temperature to reach the equilibrium ratio, for which the data is usually given). Hydrogen detonation parameters, such as critical detonation pressure and temperature, strongly depend on the container geometry.
See also
* * * * * * * (for hydrogen) * *Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * Hydrogen safety covers the safe production, handling and useExternal links
Basic Hydrogen Calculations of Quantum Mechanics
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
{{Authority control Hydrogen, Chemical elements Reactive nonmetals Diatomic nonmetals Nuclear fusion fuels Airship technology Reducing agents Refrigerants Gaseous signaling molecules E-number additives