Huntorf on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Compressed-air energy storage (CAES) is a way to
Compressed-air energy storage (CAES) is a way to
Wind Drives Growing Use of Batteries
'' The New York Times'', July 28, 2010, p. B1. The first utility-scale CAES project has been built in Huntorf, Germany, and is still operational. The Huntorf plant was initially developed as a load balancer for fossil fuel-generated electricity, the global shift towards
Global Clean Energy: A Storage Solution Is in the Air
''
Electricity Storage and Renewables: Costs and Markets to 2030
, page 55. '' International Renewable Energy Agency'', Abu Dhabi. A 110-megawatt plant with a capacity of 26 hours (2,860 MWh energy) was built in McIntosh, Alabama (1991). The Alabama facility's $65 million cost equals $590 per kW of capacity and about $23 per kW-hr of storage capacity. It uses a 19 million cubic foot solution mined salt cavern to store air at up to 1100 psi. Although the compression phase is approximately 82% efficient, the expansion phase requires the combustion of natural gas at one-third the rate of a gas turbine producing the same amount of electricity at 54% efficiency. The US Department of Energy awarded $24.9 million in matching funds for phase one of a 300 MW, $356 million
 Air engines have been used since the 19th century to power mine locomotives, pumps, drills and trams, via centralized, city-level distribution. Racecars use compressed air to start their internal combustion engine (ICE), and large Diesel engines may have starting pneumatic motors.
Air engines have been used since the 19th century to power mine locomotives, pumps, drills and trams, via centralized, city-level distribution. Racecars use compressed air to start their internal combustion engine (ICE), and large Diesel engines may have starting pneumatic motors.
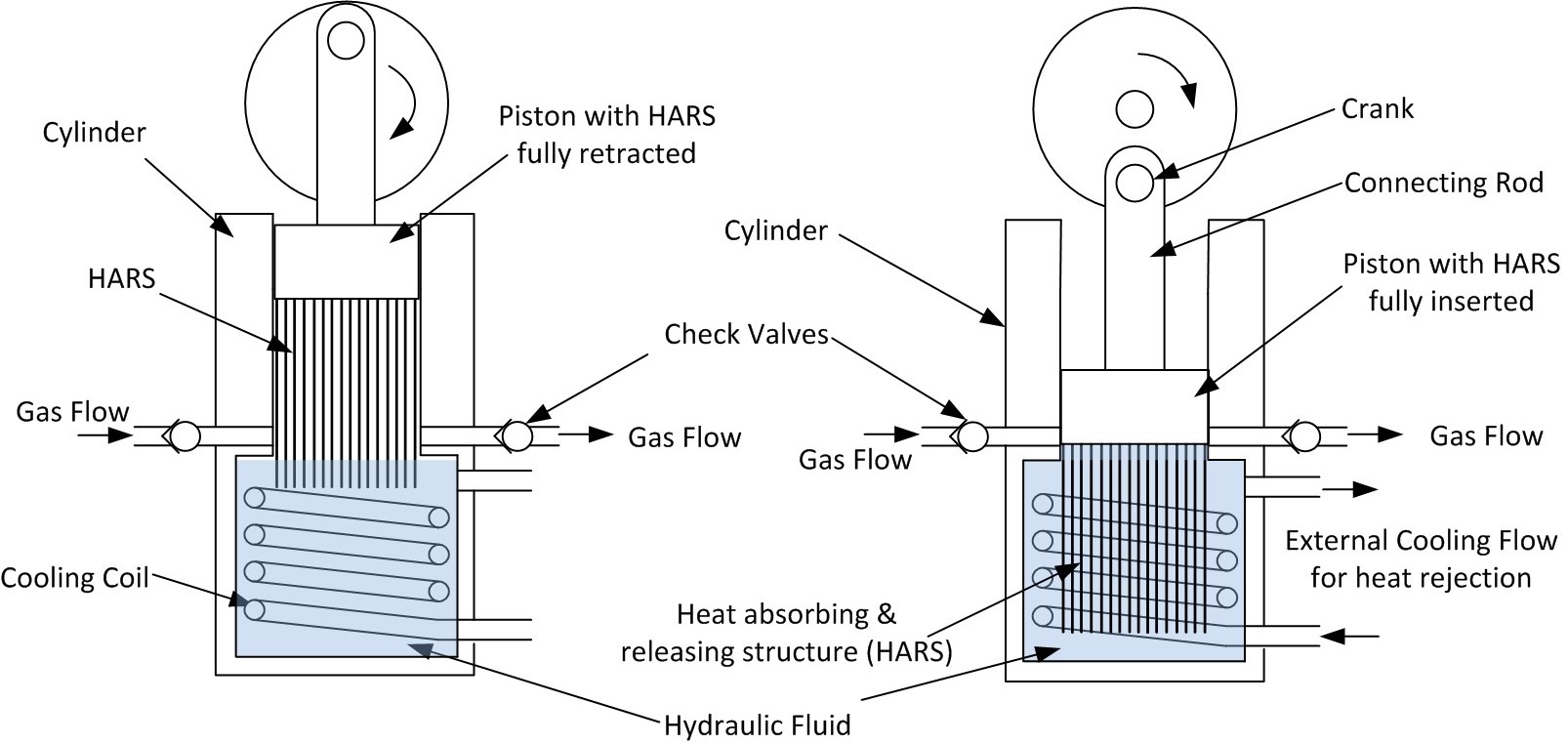 A number of methods of nearly isothermal compression are being developed. Fluid Mechanics has a system with a heat absorbing and releasing structure (HARS) attached to a reciprocating piston. Light Sail injects a water spray into a reciprocating cylinder. SustainX uses an air-water foam mix inside a semi-custom, 120 rpm compressor/expander. All these systems ensure that the air is compressed with high thermal diffusivity compared to the speed of compression. Typically these compressors can run at speeds up to 1000 rpm. To ensure high thermal diffusivity, the average distance a gas molecule is from a heat-absorbing surface is about 0.5 mm. These nearly isothermal compressors can also be used as nearly isothermal expanders and are being developed to improve the round-trip efficiency of CAES.
A number of methods of nearly isothermal compression are being developed. Fluid Mechanics has a system with a heat absorbing and releasing structure (HARS) attached to a reciprocating piston. Light Sail injects a water spray into a reciprocating cylinder. SustainX uses an air-water foam mix inside a semi-custom, 120 rpm compressor/expander. All these systems ensure that the air is compressed with high thermal diffusivity compared to the speed of compression. Typically these compressors can run at speeds up to 1000 rpm. To ensure high thermal diffusivity, the average distance a gas molecule is from a heat-absorbing surface is about 0.5 mm. These nearly isothermal compressors can also be used as nearly isothermal expanders and are being developed to improve the round-trip efficiency of CAES.
Part 1
(Special supplement, Scientific American, 1921)
(
Cities to Store Wind Power for Later Use
January 4, 2006
Power storage: Trapped wind
* ttps://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9D0CEEDE103DF93AA1575AC0A967958260&sec=&spon=&pagewanted=print New York Times Article: Technology; Using Compressed Air To Store Up Electricity
Compressed Air Energy Storage, Entropy and Efficiency
{{DEFAULTSORT:Compressed-Air Energy Storage Energy storage *
store energy
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production.
A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
Energy comes in ...
for later use using compressed air
Compressed air is air kept under a pressure that is greater than atmospheric pressure. Compressed air is an important medium for transfer of energy in industrial processes, and is used for power tools such as air hammers, drills, wrenches, and o ...
. At a utility scale, energy generated during periods of low demand can be released during peak load periods.Wild, Matthew, LWind Drives Growing Use of Batteries
'' The New York Times'', July 28, 2010, p. B1. The first utility-scale CAES project has been built in Huntorf, Germany, and is still operational. The Huntorf plant was initially developed as a load balancer for fossil fuel-generated electricity, the global shift towards
renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
renewed interest in CAES systems, to help highly intermittent energy sources like photovoltaics and wind satisfy fluctuating electricity demands.Lund, Henrik. The role of compressed air energy storage (CAES) in future sustainable energy systems. Energy Conversion and Management.
One ongoing challenge in large-scale design is the management of thermal energy since the compression of air leads to an unwanted temperature increase that not only reduces operational efficiency but can also lead to damage. The main difference between various architectures lies in thermal engineering. On the other hand, small-scale systems have long been used as propulsion of mine locomotives. Contrasted with traditional batteries, systems can store energy for longer periods of time and have less upkeep.
Types
Compression of air creates heat; the air is warmer after compression. Expansion removes heat. If no extra heat is added, the air will be much colder after expansion. If the heat generated during compression can be stored and used during expansion, the efficiency of the storage improves considerably.Gies, EricaGlobal Clean Energy: A Storage Solution Is in the Air
''
International Herald Tribune
The ''International Herald Tribune'' (''IHT'') was a daily English-language newspaper published in Paris, France for international English-speaking readers. It had the aim of becoming "the world's first global newspaper" and could fairly be said ...
'', October 1, 2012. Retrieved from NYTimes.com website, March 19, 2013. There are several ways in which a CAES system can deal with heat. Air storage can be adiabatic, diabatic, isothermal, or near-isothermal.
Adiabatic
Adiabatic storage continues to store the energy produced by compression and returns it to the air as it is expanded to generate power. This is a subject of an ongoing study, with no utility-scale plants as of 2015. The theoreticalefficiency
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time in doing something or in producing a desired result. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without ...
of adiabatic storage approaches 100% with perfect insulation, but in practice, round trip efficiency is expected to be 70%. Heat can be stored in a solid such as concrete or stone, or in a fluid such as hot oil (up to 300 °C) or molten salt solutions (600 °C). Storing the heat in hot water may yield an efficiency around 65%.
Packed beds have been proposed as thermal storage units for A-* " systems. A study numerically simulated an adiabatic compressed air energy storage system using packed bed
In chemical processing, a packed bed is a hollow tube, pipe, or other vessel that is filled with a packing material. The packing can be randomly filled with small objects like Raschig rings or else it can be a specifically designed structured ...
thermal energy storage. The efficiency of the simulated system under continuous operation was calculated to be between 70.5% and 71%.
Diabatic
Diabatic storage dissipates much of the heat of compression withintercooler
An intercooler is a heat exchanger used to cool a gas after compression. Often found in turbocharged engines, intercoolers are also used in air compressors, air conditioners, refrigeration and gas turbines.
Internal combustion engines
Mo ...
s (thus approaching isothermal compression) into the atmosphere as waste, essentially wasting the energy used to perform the work of compression. Upon removal from storage, the temperature of this compressed air is ''the one indicator'' of the amount of stored energy that remains in this air. Consequently, if the air temperature is low for the energy recovery process, the air must be substantially re-heated prior to expansion in the turbine to power a generator. This reheating can be accomplished with a natural gas-fired burner for utility-grade storage or with a heated metal mass. As recovery is often most needed when renewable sources are quiescent, the fuel must be burned to make up for the ''wasted'' heat. This degrades the efficiency of the storage-recovery cycle. While this approach is relatively simple, the burning of fuel adds to the cost of the recovered electrical energy and compromises the ecological benefits associated with most renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
sources. Nevertheless, this is thus far the only system that has been implemented commercially.
The McIntosh, Alabama CAES plant requires 2.5 MJ of electricity and 1.2 MJ lower heating value (LHV) of gas for each MJ of energy output, corresponding to an energy recovery efficiency of about 27%. A General Electric 7FA 2x1 combined cycle
A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas turb ...
plant, one of the most efficient natural gas plants in operation, uses 1.85 MJ (LHV) of gas per MJ generated, a 54% thermal efficiency.
Isothermal
Isothermal compression and expansion approaches attempt to maintainoperating temperature
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the de ...
by constant heat exchange to the environment. In a reciprocating compressor, this can be achieved by using a finned piston and low cycle speeds. Current challenges in effective heat exchangers mean that they are only practical for low power levels. The theoretical efficiency of isothermal energy storage approaches 100% for perfect heat transfer to the environment. In practice, neither of these perfect thermodynamic cycles is obtainable, as some heat losses are unavoidable, leading to a near-isothermal process.
Near-isothermal
Near-isothermal compression (and expansion) is a process in which a gas is compressed in very close proximity to a large incompressible thermal mass such as a heat absorbing and releasing structure (HARS) or a water spray. A HARS is usually made up of a series of parallel fins. As the gas is compressed, the heat of compression is rapidly transferred to the thermal mass, so the gas temperature is stabilized. An external cooling circuit is then used to maintain the temperature of the thermal mass. The isothermal efficiency (Z) is a measure of where the process lies between an adiabatic and isothermal process. If the efficiency is 0%, then it is totally adiabatic; with an efficiency of 100%, it is totally isothermal. Typically with a near-isothermal process, an isothermal efficiency of 90-95% can be expected.Other
One implementation of isothermal CAES uses high, medium, and low pressure pistons in series. Each stage is followed by an airblast venturi pump that draws ambient air over an air-to-air (or air-to-seawater) heat exchanger between each expansion stage. Early compressed air torpedo designs used a similar approach, substituting seawater for air. The venturi warms the exhaust of the preceding stage and admits this preheated air to the following stage. This approach was widely adopted in various compressed air vehicles such asH. K. Porter, Inc.
H.K. Porter, Inc. (Porter) manufactured light-duty railroad locomotives in the US, starting in 1866. The company became the largest producer of industrial locomotives, and built almost eight thousand of them. The last locomotive was built in ...
's mining locomotives and trams.
Here the heat of compression is effectively stored in the atmosphere (or sea) and returned later on.
Compressors and expanders
Compression can be done with electrically powered turbo-compressors and expansion withturbo-expander
A turboexpander, also referred to as a turbo-expander or an expansion turbine, is a centrifugal or axial-flow turbine, through which a high-pressure gas is expanded to produce work that is often used to drive a Gas compressor, compressor or electr ...
s or air engines driving electrical generators to produce electricity.
Storage
Air storage vessels vary in the thermodynamic conditions of the storage and on the technology used: # Constant volume storage (solution mined caverns, aboveground vessels, aquifers, automotive applications, etc.) # Constant pressure storage (underwater pressure vessels, hybrid pumped hydro - compressed air storage)Constant-volume storage
This storage system uses a chamber with specific boundaries to store large amounts of air. This means from a thermodynamic point of view that this system is a constant-volume and variable-pressure system. This causes some operational problems for the compressors and turbines, so the pressure variations have to be kept below a certain limit as do the stresses induced on the storage vessels. The storage vessel is often a cavern created bysolution mining
In-situ leaching (ISL), also called in-situ recovery (ISR) or solution mining, is a mining process used to recover minerals such as copper and uranium through boreholes drilled into a deposit, '' in situ''. In situ leach works by artificially d ...
(salt is dissolved in water for extraction) or by utilizing an abandoned mine
An abandoned mine is a mine or quarry which is no longer producing or operational and, there is no responsible party to finance the cost to address the remediation and/or restoration of the mine feature/site. Terms and definitions vary though the ...
; use of porous and permeable rock formations (rocks that have interconnected holes, through which liquid or air can pass), such as those in which reservoirs of natural gas are found, has also been studied.
In some cases, an above-ground pipeline was tested as a storage system, giving some good results. Obviously, the cost of the system is higher, but it can be placed wherever the designer chooses, whereas an underground system needs some particular geologic formations (salt domes, aquifers, depleted gas fields, etc.).
Constant-pressure storage
In this case, the storage vessel is kept at constant pressure, while the gas is contained in a variable-volume vessel. Many types of storage vessels have been proposed. However, the operating conditions follow the same principle: The storage vessel is positioned hundreds of meters underwater, and the hydrostatic pressure of the water column above the storage vessel maintains the pressure at the desired level. This configuration allows: * Improvement of the energy density of the storage system because all the air contained can be used (the pressure is constant in all charge conditions, full or empty, so the turbine has no problem exploiting it, while with constant-volume systems if the pressure goes below a safety limit the system needs to stop). * Improvement of the efficiency of the turbomachinery, which will work under constant-inlet conditions. * Use of various geographic locations for the positioning of the CAES plant (coastal lines, floating platforms, etc.). On the other hand, the cost of this storage system is higher due to the need to position the storage vessel on the bottom of the chosen water reservoir (often the sea or the ocean) and due to the cost of the vessel itself. A different approach consists of burying a large bag buried under several meters of sand instead of water. Plants operate on a peak-shaving daily cycle, charging at night and discharging during the day. Heating the compressed air using natural gas or geothermal heat to increase the amount of energy being extracted has been studied by thePacific Northwest National Laboratory
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) is one of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, managed by the Department of Energy's (DOE) Office of Science. The main campus of the laboratory is in Richland, Washington.
O ...
.
Compressed-air energy storage can also be employed on a smaller scale, such as exploited by air car
A compressed-air car is a compressed-air vehicle fueled by pressure vessels filled with compressed air. It is propelled by the release and expansion of the air within a motor adapted to compressed air. The car might be powered solely by air, or ...
s and air-driven locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
s, and can use high-strength (e.g., carbon-fiber) air-storage tanks. In order to retain the energy stored in compressed air, this tank should be thermally isolated from the environment; otherwise, the energy stored will escape in the form of heat, because compressing air raises its temperature.
History
Citywide compressed air energy systems have been built since 1870. Cities such as Paris, France; Birmingham, England; Dresden, Rixdorf and Offenbach, Germany andBuenos Aires, Argentina
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
installed such systems. Victor P (opp constructed the first systems to power clocks by sending a pulse of air every minute to change their pointer arms. They quickly evolved to deliver power to homes and industries. As of 1896, the Paris system had 2.2 MW of generation distributed at 550 kPa in 50 km of air pipes for motors in light and heavy industry. Usage was measured by cubic meters. The systems were the main source of house-delivered energy in those days and also powered the machines of dentists, seamstresses, printing facilities and bakeries.
The first utility-scale diabatic compressed air energy storage project was the 290 megawatt Huntorf
Compressed-air energy storage (CAES) is a way to store energy for later use using compressed air. At a utility scale, energy generated during periods of low demand can be released during peak load periods.Wild, Matthew, LWind Drives Growing Use ...
plant opened in 1978 in Germany using a salt dome with 580 MWh energy, 42% efficiency.IRENA (2017).Electricity Storage and Renewables: Costs and Markets to 2030
, page 55. '' International Renewable Energy Agency'', Abu Dhabi. A 110-megawatt plant with a capacity of 26 hours (2,860 MWh energy) was built in McIntosh, Alabama (1991). The Alabama facility's $65 million cost equals $590 per kW of capacity and about $23 per kW-hr of storage capacity. It uses a 19 million cubic foot solution mined salt cavern to store air at up to 1100 psi. Although the compression phase is approximately 82% efficient, the expansion phase requires the combustion of natural gas at one-third the rate of a gas turbine producing the same amount of electricity at 54% efficiency. The US Department of Energy awarded $24.9 million in matching funds for phase one of a 300 MW, $356 million
Pacific Gas and Electric Company
The Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E) is an American investor-owned utility (IOU). The company is headquartered in the Pacific Gas & Electric Building, in San Francisco, California. PG&E provides natural gas and electricity to 5.2 milli ...
installation utilizing a saline porous rock formation being developed near Bakersfield in Kern County, California. The goals of the project were to build and validate an advanced design (2009).
The US Department of Energy provided $29.4 million in funding to conduct preliminary work on a 150 MW salt-based project being developed by Iberdrola USA
Avangrid, Inc. (formerly Energy East and Iberdrola USA), is an energy services and delivery company. AVANGRID serves about 3.1 million customers throughout New England, Pennsylvania and New York in the United States.
History
In 2008 Iberdrola ...
in Watkins Glen, New York. The goal is to incorporate smart grid technology to balance renewable intermittent energy sources (2010).
General Compression completed construction of a 2 MW near-isothermal project in Gaines County, Texas; the world's third project (2012). The project uses no fuel. It appears to have stopped operating in 2016.
The first adiabatic project, a 200-megawatt facility called ADELE, was planned for construction in Germany (2013) with a target of 70% efficiency by using air at 100 bar presure. This project was delayed for undisclosed reasons until at least 2016.
Storelectric Ltd planned to build a 40 MW 100% renewable energy
100% renewable energy means getting all energy from renewable resources. The endeavor to use 100% renewable energy for electricity, heating, cooling and transport is motivated by climate change, pollution and other environmental issues, ...
pilot plant in Cheshire, UK, with 800 MWh storage capacity (2017).
Hydrostor completed the first commercial A-CAES system in Goderich, Ontario, supplying service with 2.2MW / 10MWh storage to the Ontario Grid (2019). It was the first A-CAES system to achieve commercial operation in decades.
The European Union-funded RICAS (adiabatic) project in Austria was to use crushed rock to store heat from the compression process to improve efficiency (2020). The system was expected to achieve 70-80% efficiency.
Apex planned a plant for Anderson County, Texas, to go online in 2016. This project has been delayed and until at least 2020.
Canadian company Hydrostor planned to build four Advance plants in Toronto, Goderich, Angas, and Rosamond (2020). Some included partial heat storage in water, improving efficiency to 65%.
A 60 MW / 300 MWh facility with 60% efficiency opened in Jiangsu, China, using a salt cavern (2022).
A 2.5 MW / 4 MWh compressed facility started operating in Sardinia, Italy (2022).
As of 2022 the Gem project at Rosamond in Kern County, California was planned to provide 500 MW / 4,000 MWh of storage. The Pecho project in San Luis Obispo, California
San Luis Obispo (; Spanish for " St. Louis the Bishop", ; Chumash: ''tiłhini'') is a city and county seat of San Luis Obispo County, in the U.S. state of California. Located on the Central Coast of California, San Luis Obispo is roughly halfwa ...
was planned to be 400 MW / 3,200 MWh. The Broken Hill
Broken Hill is an inland mining city in the far west of outback New South Wales, Australia. It is near the border with South Australia on the crossing of the Barrier Highway (A32) and the Silver City Highway (B79), in the Barrier Range. It is ...
project in New South Wales, Australia was 200 MW / 1,600 MWh.
In 2022 Zhangjiakou connected the world's first 100-MW "advanced" system to the grid in north China. It uses no fossil fuels, instead adopting supercritical thermal storage, supercritical heat exchange, high-load compression and expansion technologies. The plant can store 400 MWh, with 70.4% efficiency. A 350 MW / 1.4 GWh project started construction in Shangdong.
Storage thermodynamics
In order to achieve a near thermodynamically reversible process so that most of the energy is saved in the system and can be retrieved, and losses are kept negligible, a near reversibleisothermal process
In thermodynamics, an isothermal process is a type of thermodynamic process in which the temperature ''T'' of a system remains constant: Δ''T'' = 0. This typically occurs when a system is in contact with an outside thermal reservoir, and ...
or an isentropic process
In thermodynamics, an isentropic process is an idealized thermodynamic process that is both adiabatic and reversible. The work transfers of the system are frictionless, and there is no net transfer of heat or matter. Such an idealized process ...
is desired.
Isothermal storage
In an isothermal compression process, the gas in the system is kept at a constant temperature throughout. This necessarily requires an exchange of heat with the gas; otherwise, the temperature would rise during charging and drop during discharge. This heat exchange can be achieved by heat exchangers (intercooling) between subsequent stages in the compressor, regulator, and tank. To avoid wasted energy, the intercoolers must be optimized for high heat transfer and low-pressure drop. Smaller compressors can approximate isothermal compression even without intercooling, due to the relatively high ratio of surface area to volume of the compression chamber and the resulting improvement in heat dissipation from the compressor body itself. When one obtains perfect isothermal storage (and discharge), the process is said to be "reversible". This requires that the heat transfer between the surroundings and the gas occur over an infinitesimally small temperature difference. In that case, there is no exergy loss in the heat transfer process, and so the compression work can be completely recovered as expansion work: 100% storage efficiency. However, in practice, there is always a temperature difference in any heat transfer process, and so all practical energy storage obtains efficiencies lower than 100%. To estimate the compression/expansion work in an isothermal process, it may be assumed that the compressed air obeys the ideal gas law: : From a process from an initial state ''A'' to a final state ''B'', with absolute temperature constant, one finds the work required for compression (negative) or done by the expansion (positive), to be : where , and so . Here is the absolute pressure, is the (unknown) volume of gas compressed, is the volume of the vessel, is theamount of substance
In chemistry, the amount of substance ''n'' in a given sample of matter is defined as the quantity or number of discrete atomic-scale particles in it divided by the Avogadro constant ''N''A. The particles or entities may be molecules, atoms, ions, ...
of gas (mol) and is the ideal gas constant
The molar gas constant (also known as the gas constant, universal gas constant, or ideal gas constant) is denoted by the symbol or . It is the molar equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per ...
.
If there is a constant pressure outside of the vessel, which is equal to the starting pressure , the positive work of the outer pressure reduces the exploitable energy (negative value). This adds a term to the equation above:
:
; Example
How much energy can be stored in a 1 m3 storage vessel at a pressure of , if the ambient pressure is . In this case, the process work is
: =
: = 7.0 MPa × 1 m3 × ln(0.1 MPa/7.0 MPa) + (7.0 MPa − 0.1 MPa) × 1 m3 = −22.8 MJ (equivalently 6.33 KWh).
The negative sign means that work is done on the gas by the surroundings. Process irreversibilities (such as in heat transfer) will result in less energy being recovered from the expansion process than is required for the compression process. If the environment is at a constant temperature, for example, the thermal resistance in the intercoolers will mean that the compression occurs at a temperature somewhat higher than the ambient temperature, and the expansion will occur at a temperature somewhat lower than the ambient temperature. So a perfect isothermal storage system is impossible to achieve.
Adiabatic (isentropic) storage
An adiabatic process is one where there is no heat transfer between the fluid and the surroundings: the system is insulated against heat transfer. If the process is furthermore internally reversible (frictionless, to the ideal limit), then it will additionally be isentropic. An adiabatic storage system does away with the intercooling during the compression process and simply allows the gas to heat up during compression and likewise cool down during expansion. This is attractive since the energy losses associated with the heat transfer are avoided, but the downside is that the storage vessel must be insulated against heat loss. It should also be mentioned that real compressors and turbines are not isentropic, but instead have an isentropic efficiency of around 85%. The result is that round-trip storage efficiency for adiabatic systems is also considerably less than perfect.Large storage system thermodynamics
Energy storage systems often use large caverns. This is the preferred system design due to the very large volume and thus the large quantity of energy that can be stored with only a small pressure change. The gas is compressed adiabatically with little temperature change (approaching a reversible isothermal system) and heat loss (approaching an isentropic system). This advantage is in addition to the low cost of constructing the gas storage system, using the underground walls to assist in containing the pressure. The cavern space can be insulated to improve efficiency. Undersea insulated airbags that have similar thermodynamic properties to large cavern storage have been suggested.Vehicle applications
Practical constraints in transportation
In order to use air storage in vehicles or aircraft for practical land or air transportation, the energy storage system must be compact and lightweight.Energy density
In physics, energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. It is sometimes confused with energy per unit mass which is properly called specific energy or .
Often only the ''useful'' or extract ...
and specific energy are the engineering terms that define these desired qualities.
Specific energy, energy density, and efficiency
As explained in the thermodynamics of the gas storage section above, compressing air heats it, and expanding it cools it. Therefore, practical air engines require heat exchangers in order to avoid excessively high or low temperatures, and even so don't reach ideal constant temperature conditions or ideal thermal insulation. Nevertheless, as stated above, it is useful to describe the maximum energy storable using the isothermal case, which works out to about 100 kJ/m3 nbsp;ln(''P''''A''/''P''''B'') Thus if 1.0 m3 of air from the atmosphere is very slowly compressed into a 5 L bottle at , the potential energy stored is 530 kJ. A highly efficient air motor can transfer this into kinetic energy if it runs very slowly and manages to expand the air from its initial 20 MPa pressure down to 100 kPa (bottle completely "empty" at atmospheric pressure). Achieving high efficiency is a technical challenge both due to heat loss to the ambient and to unrecoverable internal gas heat. If the bottle above is emptied to 1 MPa, the extractable energy is about 300 kJ at the motor shaft. A standard 20 MPa, 5 L steel bottle has a mass of 7.5 kg, a superior one 5 kg. High-tensile strength fibers such as carbon fiber or Kevlar can weigh below 2 kg in this size, consistent with the legal safety codes. One cubic meter of air at 20 °C has a mass of 1.204 kg atstandard temperature and pressure
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements to be established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used standards are those of the International Union o ...
. Thus, ''theoretical'' specific energies are from roughly 70 kJ/kg at the motor shaft for a plain steel bottle to 180 kJ/kg for an advanced fiber-wound one, whereas practical ''achievable'' specific energies for the same containers would be from 40 to 100 kJ/kg.
Safety
As with most technologies, compressed air has safety concerns, mainly catastrophic tank rupture. Safety regulations make this a rare occurrence at the cost of higher weight and additional safety features such as pressure relief valves. Regulations may limit the legal working pressure to less than 40% of the rupture pressure for steel bottles ( safety factor of 2.5) and less than 20% for fiber-wound bottles ( safety factor of 5). Commercial designs adopt the ISO 11439 standard. High-pressure bottles are fairly strong so that they generally do not rupture in vehicle crashes.Comparison with batteries
Advanced fiber-reinforced bottles are comparable to therechargeable
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or prim ...
lead–acid battery in terms of energy density. Batteries provide nearly constant voltage over their entire charge level, whereas the pressure varies greatly while using a pressure vessel from full to empty. It is technically challenging to design air engines to maintain high efficiency and sufficient power over a wide range of pressures. Compressed air can transfer power at very high flux rates, which meets the principal acceleration and deceleration objectives of transportation systems, particularly for hybrid vehicles.
Compressed air systems have advantages over conventional batteries, including longer lifetimes of pressure vessel
A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure.
Construction methods and materials may be chosen to suit the pressure application, and will depend on the size o ...
s and lower material toxicity. Newer battery designs such as those based on lithium iron phosphate chemistry suffer from neither of these problems. Compressed air costs are potentially lower; however, advanced pressure vessels are costly to develop, and safety-test and at present are more expensive than mass-produced batteries.
As with electric storage technology, compressed air is only as "clean" as the source of the energy that it stores. Life cycle assessment addresses the question of overall emissions from a given energy storage technology combined with a given mix of generation on a power grid.
Engine
A pneumatic motor or compressed-air engine uses the expansion of compressed air to drive the pistons of an engine, turn theaxle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearing ...
, or to drive a turbine.
The following methods can increase efficiency:
* A continuous expansion turbine at high efficiency
* Multiple expansion stages
* Use of waste heat, notably in a hybrid heat engine design
* Use of environmental heat
A highly efficient arrangement uses high, medium and low pressure pistons in series, with each stage followed by an airblast venturi that draws ambient air over an air-to-air heat exchanger. This warms the exhaust of the preceding stage and admits this preheated air to the following stage. The only exhaust gas from each stage is cold air which can be as cold as ; the cold air may be used for air conditioning in a car.
Additional heat can be supplied by burning fuel as in 1904 for the Whitehead torpedo. This improves the range and speed available for a given tank volume at the cost of the additional fuel.
Cars
Since about 1990 several companies have claimed to be developing compressed air cars, but none is available. Typically the main claimed advantages are: no roadside pollution, low cost, use of cooking oil forlubrication
Lubrication is the process or technique of using a lubricant to reduce friction and wear and tear in a contact between two surfaces. The study of lubrication is a discipline in the field of tribology.
Lubrication mechanisms such as fluid-lubric ...
, and integrated air conditioning.
The time required to refill a depleted tank is important for vehicle applications. "Volume transfer" moves pre-compressed air from a stationary tank to the vehicle tank almost instantaneously. Alternatively, a stationary or on-board compressor
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor.
Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can transp ...
can compress air on demand, possibly requiring several hours.
Ships
Large marine diesel engines are started using compressed air, typically stored in large bottles between 20 and 30 bar, acting directly on the pistons via special starting valves to turn the crankshaft prior to beginning fuel injection. This arrangement is more compact and cheaper than an electric starter motor would be at such scales and able to supply the necessary burst of extremely high power without placing a prohibitive load on the ship's electrical generators and distribution system. Compressed air is commonly also used, at lower pressures, to control the engine and act as the spring force acting on the cylinder exhaust valves, and to operate other auxiliary systems and power tools on board, sometimes including pneumatic PID controllers. One advantage of this approach is that in the event of an electrical blackout, ship systems powered by stored compressed air can continue functioning uninterrupted, and generators can be restarted without an electrical supply. Another is that pneumatic tools can be used in commonly wet environments without the risk of electric shock.Hybrid vehicles
While the air storage system offers a relatively low power density and vehicle range, its high efficiency is attractive for hybrid vehicles that use a conventional internal combustion engine as the main power source. The air storage can be used for regenerative braking and to optimize the cycle of the piston engine, which is not equally efficient at all power/RPM levels. Bosch and PSA Peugeot Citroën have developed a hybrid system that uses hydraulics as a way to transfer energy to and from a compressed nitrogen tank. An up to 45% reduction in fuel consumption is claimed, corresponding to 2.9l/100 km (81 mpg, 69 g /km) on the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) for a compact frame likePeugeot 208
The Peugeot 208 is a supermini car (B-segment in Europe) produced by the French automaker Peugeot. Unveiled at the Geneva Motor Show in March 2012 and positioned below bigger 308 and above smaller 108. The 208 replaced the 207 in 2012, and the ca ...
. The system is claimed to be much more affordable than competing electric and flywheel KERS systems and is expected on road cars by 2016.
History of air engines
 Air engines have been used since the 19th century to power mine locomotives, pumps, drills and trams, via centralized, city-level distribution. Racecars use compressed air to start their internal combustion engine (ICE), and large Diesel engines may have starting pneumatic motors.
Air engines have been used since the 19th century to power mine locomotives, pumps, drills and trams, via centralized, city-level distribution. Racecars use compressed air to start their internal combustion engine (ICE), and large Diesel engines may have starting pneumatic motors.
Types of systems
Hybrid systems
Brayton cycle engines compress and heat air with a fuel suitable for an internal combustion engine. For example, natural gas or biogas heat compressed air, and then a conventional gas turbine engine or the rear portion of ajet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term ...
expands it to produce work.
Compressed air engines can recharge an electric battery
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices.
When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negati ...
. The apparently defunct Energine
A compressed-air car is a compressed-air vehicle powered by pressure vessels filled with compressed air. It is propelled by the release and expansion of the air within a motor adapted to compressed air. The car might be powered solely by air, ...
promoted its Pne-PHEV or Pneumatic Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle-system.
Existing hybrid systems
Huntorf, Germany in 1978, and McIntosh, Alabama, U.S. in 1991 commissioned hybrid power plants. Both systems use off-peak energy for air compression and burn natural gas in the compressed air during the power generating phase.Future hybrid systems
The Iowa Stored Energy Park (ISEP) will use aquifer storage rather than cavern storage. The displacement of water in the aquifer results in the regulation of the air pressure by the constant hydrostatic pressure of the water. A spokesperson for ISEP claims, "you can optimize your equipment for better efficiency if you have constant pressure." The power output of the McIntosh and Iowa systems is in the range of 2–300 MW. Additional facilities are under development in Norton, Ohio.FirstEnergy
FirstEnergy Corp is an electric utility headquartered in Akron, Ohio. It was established when Ohio Edison acquired Centerior Energy in 1997. Its subsidiaries and affiliates are involved in the distribution, transmission, and generation of electri ...
, an Akron, Ohio electric utility, obtained development rights to the 2,700 MW Norton project in November 2009.
The RICAS2020 project attempts to use an abandoned mine for adiabatic CAES with heat recovery. The compression heat is stored in a tunnel section filled with loose stones, so the compressed air is nearly cool when entering the main pressure storage chamber. The cool compressed air regains the heat stored in the stones when released back through a surface turbine, leading to higher overall efficiency. A two-stage process has theoretical higher efficiency of around 70%.
Lake or ocean storage
Deep water in lakes and the ocean can provide pressure without requiring high-pressure vessels or drilling into salt caverns or aquifers. The air goes into inexpensive, flexible containers such as plastic bags below in deep lakes or off sea coasts with steep drop-offs. Obstacles include the limited number of suitable locations and the need for high-pressure pipelines between the surface and the containers. Since the containers would be very inexpensive, the need for great pressure (and great depth) may not be as important. A key benefit of systems built on this concept is that charge and discharge pressures are a constant function of depth. Carnot inefficiencies can thereby be reduced in the power plant. Carnot efficiency can be increased by using multiple charge and discharge stages and using inexpensive heat sources and sinks such as cold water from rivers or hot water from solar ponds. Ideally, the system must be very clever — for example, by cooling air before pumping on summer days. A nearly isobaric solution is possible if the compressed gas is used to drive a hydroelectric system. However, this solution requires large pressure tanks located on land (as well as underwater airbags). Also, hydrogen gas is the preferred fluid since other gases suffer from substantial hydrostatic pressures at even relatively modest depths (such as 500 meters). The European electrical utility company E.ON has provided €1.4 million (£1.1 million) in funding to develop undersea air storage bags. Hydrostor in Canada is developing a commercial system of underwater storage "accumulators" for compressed air energy storage, starting at the 1 to 4 MW scale. There is a plan for some type of compressed air energy storage in undersea caves in Northern Ireland.Nearly isothermal compression
 A number of methods of nearly isothermal compression are being developed. Fluid Mechanics has a system with a heat absorbing and releasing structure (HARS) attached to a reciprocating piston. Light Sail injects a water spray into a reciprocating cylinder. SustainX uses an air-water foam mix inside a semi-custom, 120 rpm compressor/expander. All these systems ensure that the air is compressed with high thermal diffusivity compared to the speed of compression. Typically these compressors can run at speeds up to 1000 rpm. To ensure high thermal diffusivity, the average distance a gas molecule is from a heat-absorbing surface is about 0.5 mm. These nearly isothermal compressors can also be used as nearly isothermal expanders and are being developed to improve the round-trip efficiency of CAES.
A number of methods of nearly isothermal compression are being developed. Fluid Mechanics has a system with a heat absorbing and releasing structure (HARS) attached to a reciprocating piston. Light Sail injects a water spray into a reciprocating cylinder. SustainX uses an air-water foam mix inside a semi-custom, 120 rpm compressor/expander. All these systems ensure that the air is compressed with high thermal diffusivity compared to the speed of compression. Typically these compressors can run at speeds up to 1000 rpm. To ensure high thermal diffusivity, the average distance a gas molecule is from a heat-absorbing surface is about 0.5 mm. These nearly isothermal compressors can also be used as nearly isothermal expanders and are being developed to improve the round-trip efficiency of CAES.
See also
* Alternative fuel vehicle * Fireless locomotive *Grid energy storage
Grid energy storage (also called large-scale energy storage) is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Electrical energy is stored during times when electricity is plentiful and inexp ...
* Hydraulic accumulator
* List of energy storage power plants
* Pneumatics
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
Pneumatic systems used in industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located and elec ...
* Zero-emissions vehicle
* Cryogenic energy storage
References
External links
* Compressed Air System of Paris – technical notePart 1
(Special supplement, Scientific American, 1921)
(
Sandia National Labs
Sandia National Laboratories (SNL), also known as Sandia, is one of three research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). Headquartered in Kirtland Air Force Bas ...
, DoE).
* MSNBC articleCities to Store Wind Power for Later Use
January 4, 2006
Power storage: Trapped wind
* ttps://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9D0CEEDE103DF93AA1575AC0A967958260&sec=&spon=&pagewanted=print New York Times Article: Technology; Using Compressed Air To Store Up Electricity
Compressed Air Energy Storage, Entropy and Efficiency
{{DEFAULTSORT:Compressed-Air Energy Storage Energy storage *