Human Stampedes In Malta on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread
 The genus ''Homo'' evolved from ''
The genus ''Homo'' evolved from ''
 Until about 12,000 years ago, all humans lived as
Until about 12,000 years ago, all humans lived as  Following the
Following the
 Estimates of the population at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. Around 50–60 million people lived in the combined eastern and western Roman Empire in the 4th century AD. Bubonic plagues, first recorded in the 6th century AD, reduced the population by 50%, with the Black Death killing 75–200 million people in
Estimates of the population at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. Around 50–60 million people lived in the combined eastern and western Roman Empire in the 4th century AD. Bubonic plagues, first recorded in the 6th century AD, reduced the population by 50%, with the Black Death killing 75–200 million people in
 Most aspects of human physiology are closely Homology (biology), homologous to corresponding aspects of animal physiology. The human body consists of the legs, the torso, the arms, the neck, and the head. An adult human body consists of about 100 trillion (1014) cell (biology), cells. The most commonly defined body systems in humans are the Human nervous system, nervous, the Cardiovascular system, cardiovascular, the Human digestive system, digestive, the Endocrine system, endocrine, the Human immune system, immune, the Integumentary system, integumentary, the Lymphatic system, lymphatic, the Human musculoskeletal system, musculoskeletal, the Human reproductive system, reproductive, the Respiratory system, respiratory, and the urinary system. The dental formula of humans is: . Humans have proportionately shorter palates and much smaller Human tooth, teeth than other primates. They are the only primates to have short, relatively flush canine teeth. Humans have characteristically crowded teeth, with gaps from lost teeth usually closing up quickly in young individuals. Humans are gradually losing their wisdom teeth, third molars, with some individuals having them congenitally absent.
Humans share with chimpanzees a Vestigiality, vestigial tail, Appendix (anatomy), appendix, flexible shoulder joints, grasping fingers and opposable thumbs. Apart from bipedalism and brain size, humans differ from chimpanzees mostly in smelling, hearing and Digestion#Protein digestion, digesting proteins. While humans have a density of hair follicles comparable to other apes, it is predominantly vellus hair, most of which is so short and wispy as to be practically invisible. Humans have about 2 million sweat glands spread over their entire bodies, many more than chimpanzees, whose sweat glands are scarce and are mainly located on the palm of the hand and on the soles of the feet.
It is estimated that the worldwide average Human height, height for an adult human male is about , while the worldwide average height for adult human females is about . Shrinkage of stature may begin in middle age in some individuals but tends to be typical in the extremely Old age, aged. Throughout history, human populations have universally become taller, probably as a consequence of better nutrition, healthcare, and living conditions. The average Body weight, mass of an adult human is for females and for males. Like many other conditions, body weight and body type are influenced by both genetic susceptibility and environment and varies greatly among individuals.
Humans have a far faster and more accurate throw than other animals. Humans are also among the best long-distance runners in the animal kingdom, but slower over short distances. Humans' thinner body hair and more productive sweat glands help avoid heat exhaustion while running for long distances.
Most aspects of human physiology are closely Homology (biology), homologous to corresponding aspects of animal physiology. The human body consists of the legs, the torso, the arms, the neck, and the head. An adult human body consists of about 100 trillion (1014) cell (biology), cells. The most commonly defined body systems in humans are the Human nervous system, nervous, the Cardiovascular system, cardiovascular, the Human digestive system, digestive, the Endocrine system, endocrine, the Human immune system, immune, the Integumentary system, integumentary, the Lymphatic system, lymphatic, the Human musculoskeletal system, musculoskeletal, the Human reproductive system, reproductive, the Respiratory system, respiratory, and the urinary system. The dental formula of humans is: . Humans have proportionately shorter palates and much smaller Human tooth, teeth than other primates. They are the only primates to have short, relatively flush canine teeth. Humans have characteristically crowded teeth, with gaps from lost teeth usually closing up quickly in young individuals. Humans are gradually losing their wisdom teeth, third molars, with some individuals having them congenitally absent.
Humans share with chimpanzees a Vestigiality, vestigial tail, Appendix (anatomy), appendix, flexible shoulder joints, grasping fingers and opposable thumbs. Apart from bipedalism and brain size, humans differ from chimpanzees mostly in smelling, hearing and Digestion#Protein digestion, digesting proteins. While humans have a density of hair follicles comparable to other apes, it is predominantly vellus hair, most of which is so short and wispy as to be practically invisible. Humans have about 2 million sweat glands spread over their entire bodies, many more than chimpanzees, whose sweat glands are scarce and are mainly located on the palm of the hand and on the soles of the feet.
It is estimated that the worldwide average Human height, height for an adult human male is about , while the worldwide average height for adult human females is about . Shrinkage of stature may begin in middle age in some individuals but tends to be typical in the extremely Old age, aged. Throughout history, human populations have universally become taller, probably as a consequence of better nutrition, healthcare, and living conditions. The average Body weight, mass of an adult human is for females and for males. Like many other conditions, body weight and body type are influenced by both genetic susceptibility and environment and varies greatly among individuals.
Humans have a far faster and more accurate throw than other animals. Humans are also among the best long-distance runners in the animal kingdom, but slower over short distances. Humans' thinner body hair and more productive sweat glands help avoid heat exhaustion while running for long distances.
 Like most animals, humans are a ploidy, diploid and eukaryote, eukaryotic species. Each somatic cell has two sets of 23 chromosomes, each set received from one parent; gametes have only one set of chromosomes, which is a mixture of the two parental sets. Among the 23 pairs of chromosomes, there are 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex-determination system, sex chromosomes. Like other mammals, humans have an XY sex-determination system, so that females have the sex chromosomes XX and males have XY.
Like most animals, humans are a ploidy, diploid and eukaryote, eukaryotic species. Each somatic cell has two sets of 23 chromosomes, each set received from one parent; gametes have only one set of chromosomes, which is a mixture of the two parental sets. Among the 23 pairs of chromosomes, there are 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex-determination system, sex chromosomes. Like other mammals, humans have an XY sex-determination system, so that females have the sex chromosomes XX and males have XY.
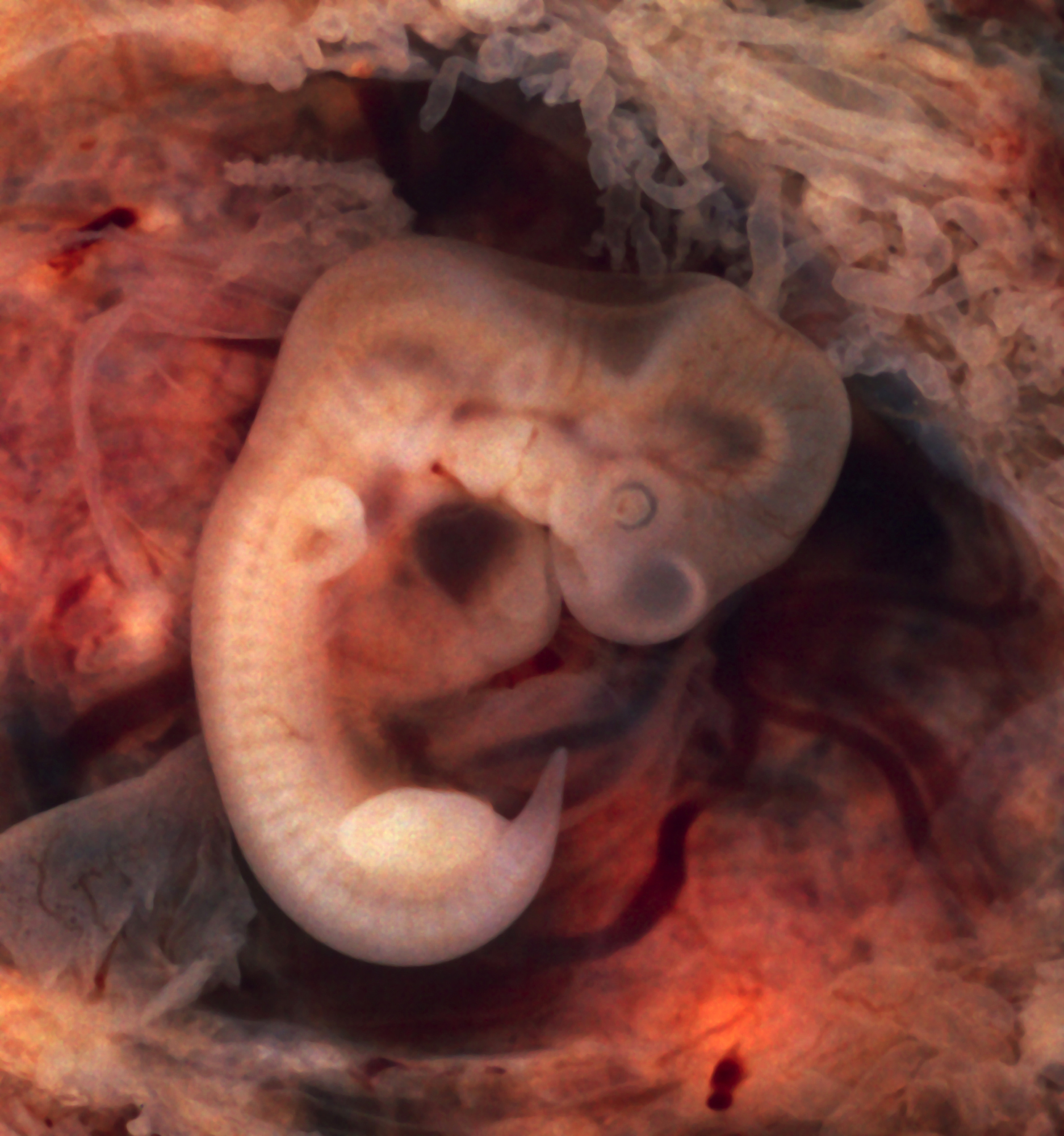 Most human reproduction takes place by internal fertilization via human sexual intercourse, sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. The average gestation period is 38 weeks, but a normal pregnancy can vary by up to 37 days. Embryonic development in the human covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus. Humans are able to Labor induction, induce early labor or perform a caesarean section if the child needs to be born earlier for medical reasons. In developed countries, infants are typically in weight and in height at birth. However, low birth weight is common in developing countries, and contributes to the high levels of infant mortality in these regions.
Compared with other species, human childbirth is dangerous, with a much higher risk of complications and death. The size of the fetus's head is more closely matched to the pelvis than other primates. The reason for this is not completely understood, but it contributes to a painful labor that can last 24 hours or more. The chances of a successful labor increased significantly during the 20th century in wealthier countries with the advent of new medical technologies. In contrast, pregnancy and natural childbirth remain hazardous ordeals in developing regions of the world, with maternal death rates approximately 100 times greater than in developed countries.
Both the mother and the father provide care for human offspring, in contrast to other primates, where parental care is mostly done by the mother. Altricial, Helpless at birth, humans continue to grow for some years, typically reaching sexual maturity at 15 to 17 years of age. The human life span has been split into various stages ranging from three to twelve. Common stages include Infant, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood and old age. The lengths of these stages have varied across cultures and time periods but is typified by an unusually rapid growth spurt during adolescence. Human females undergo
Most human reproduction takes place by internal fertilization via human sexual intercourse, sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. The average gestation period is 38 weeks, but a normal pregnancy can vary by up to 37 days. Embryonic development in the human covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus. Humans are able to Labor induction, induce early labor or perform a caesarean section if the child needs to be born earlier for medical reasons. In developed countries, infants are typically in weight and in height at birth. However, low birth weight is common in developing countries, and contributes to the high levels of infant mortality in these regions.
Compared with other species, human childbirth is dangerous, with a much higher risk of complications and death. The size of the fetus's head is more closely matched to the pelvis than other primates. The reason for this is not completely understood, but it contributes to a painful labor that can last 24 hours or more. The chances of a successful labor increased significantly during the 20th century in wealthier countries with the advent of new medical technologies. In contrast, pregnancy and natural childbirth remain hazardous ordeals in developing regions of the world, with maternal death rates approximately 100 times greater than in developed countries.
Both the mother and the father provide care for human offspring, in contrast to other primates, where parental care is mostly done by the mother. Altricial, Helpless at birth, humans continue to grow for some years, typically reaching sexual maturity at 15 to 17 years of age. The human life span has been split into various stages ranging from three to twelve. Common stages include Infant, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood and old age. The lengths of these stages have varied across cultures and time periods but is typified by an unusually rapid growth spurt during adolescence. Human females undergo
 Humans are
Humans are
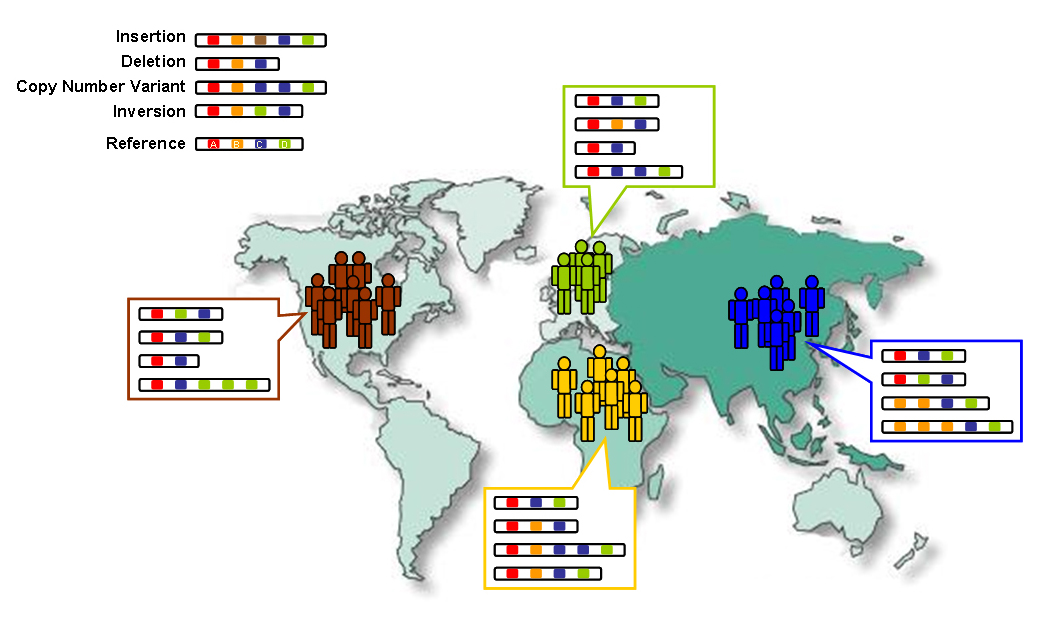 There is biological variation in the human species—with traits such as blood type, genetic diseases, Human skull, cranial features, Human face, facial features, organ systems, eye color, hair color and hair texture, texture, Human height, height and Body shape, build, and Human skin color, skin color varying across the globe. The typical height of an adult human is between , although this varies significantly depending on sex, ethnic origin, and family bloodlines. Body size is partly determined by genes and is also significantly influenced by environmental factors such as diet (nutrition), diet, exercise, and sleep patterns.
There is evidence that populations have adapted genetically to various external factors. The genes that allow adult humans to Lactose tolerance, digest lactose are present in high frequencies in populations that have long histories of cattle domestication and are more dependent on cow milk. Sickle cell anemia, which may provide increased resistance to malaria, is frequent in populations where malaria is endemic. Populations that have for a very long time inhabited specific climates tend to have developed specific phenotypes that are beneficial for those environments—Allen's rule, short stature and stocky build in cold regions, tall and lanky in hot regions, and with high lung capacities or other High-altitude adaptation in humans, adaptations at high altitudes. Some populations have evolved highly unique adaptations to very specific environmental conditions, such as those advantageous to ocean-dwelling lifestyles and freediving in the Bajau.
Human hair ranges in color from Red hair, red to blond to Brown hair, brown to Black hair, black, which is the most frequent. Hair color depends on the amount of melanin, with concentrations fading with increased age, leading to Grey hair, grey or even white hair. Skin color can range from Dark skin, darkest brown to Light skin, lightest peach, or even nearly white or colorless in cases of albinism. It tends to vary Clinal variation, clinally and generally correlates with the level of ultraviolet radiation in a particular geographic area, with darker skin mostly around the equator. Skin darkening may have evolved as protection against ultraviolet solar radiation. Light skin pigmentation protects against depletion of vitamin D, which requires sunlight to make. Human skin also has a capacity to darken (tan) in response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
There is biological variation in the human species—with traits such as blood type, genetic diseases, Human skull, cranial features, Human face, facial features, organ systems, eye color, hair color and hair texture, texture, Human height, height and Body shape, build, and Human skin color, skin color varying across the globe. The typical height of an adult human is between , although this varies significantly depending on sex, ethnic origin, and family bloodlines. Body size is partly determined by genes and is also significantly influenced by environmental factors such as diet (nutrition), diet, exercise, and sleep patterns.
There is evidence that populations have adapted genetically to various external factors. The genes that allow adult humans to Lactose tolerance, digest lactose are present in high frequencies in populations that have long histories of cattle domestication and are more dependent on cow milk. Sickle cell anemia, which may provide increased resistance to malaria, is frequent in populations where malaria is endemic. Populations that have for a very long time inhabited specific climates tend to have developed specific phenotypes that are beneficial for those environments—Allen's rule, short stature and stocky build in cold regions, tall and lanky in hot regions, and with high lung capacities or other High-altitude adaptation in humans, adaptations at high altitudes. Some populations have evolved highly unique adaptations to very specific environmental conditions, such as those advantageous to ocean-dwelling lifestyles and freediving in the Bajau.
Human hair ranges in color from Red hair, red to blond to Brown hair, brown to Black hair, black, which is the most frequent. Hair color depends on the amount of melanin, with concentrations fading with increased age, leading to Grey hair, grey or even white hair. Skin color can range from Dark skin, darkest brown to Light skin, lightest peach, or even nearly white or colorless in cases of albinism. It tends to vary Clinal variation, clinally and generally correlates with the level of ultraviolet radiation in a particular geographic area, with darker skin mostly around the equator. Skin darkening may have evolved as protection against ultraviolet solar radiation. Light skin pigmentation protects against depletion of vitamin D, which requires sunlight to make. Human skin also has a capacity to darken (tan) in response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. There is relatively little variation between human geographical populations, and most of the variation that occurs is at the individual level. Much of human variation is continuous, often with no clear points of demarcation. Genetic data shows that no matter how population groups are defined, two people from the same population group are almost as different from each other as two people from any two different population groups. Dark-skinned populations that are found in Africa, Australia, and South Asia are not closely related to each other.
Genetic research has demonstrated that human populations native to the African continent are the most genetically diverse and genetic diversity decreases with migratory distance from Africa, possibly the result of Evolutionary bottleneck, bottlenecks during human migration. These non-African populations acquired new genetic inputs from local Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans, admixture with archaic populations and have much greater variation from Neanderthals and Denisovans than is found in Africa, though Neanderthal admixture into African populations may be underestimated. Furthermore, recent studies have found that populations in sub-Saharan Africa, and particularly West Africa, have ancestral genetic variation which predates modern humans and has been lost in most non-African populations. Some of this ancestry is thought to originate from admixture with an Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans#Archaic African hominins, unknown archaic hominin that diverged before the split of Neanderthals and modern humans.
Humans are a Gonochorism, gonochoric species, meaning they are divided into male and female sexes. The greatest degree of genetic Sex differences in humans, variation exists between males and females. While the nucleotide diversity, nucleotide genetic variation of individuals of the same sex across global populations is no greater than 0.1%–0.5%, the genetic difference between Man, males and woman, females is between 1% and 2%. Males on average are 15% heavier and taller than females. On average, men have about 40–50% more upper body strength and 20–30% more lower body strength than women at the same weight, due to higher amounts of muscle and larger muscle fibers. Women generally have a higher
There is relatively little variation between human geographical populations, and most of the variation that occurs is at the individual level. Much of human variation is continuous, often with no clear points of demarcation. Genetic data shows that no matter how population groups are defined, two people from the same population group are almost as different from each other as two people from any two different population groups. Dark-skinned populations that are found in Africa, Australia, and South Asia are not closely related to each other.
Genetic research has demonstrated that human populations native to the African continent are the most genetically diverse and genetic diversity decreases with migratory distance from Africa, possibly the result of Evolutionary bottleneck, bottlenecks during human migration. These non-African populations acquired new genetic inputs from local Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans, admixture with archaic populations and have much greater variation from Neanderthals and Denisovans than is found in Africa, though Neanderthal admixture into African populations may be underestimated. Furthermore, recent studies have found that populations in sub-Saharan Africa, and particularly West Africa, have ancestral genetic variation which predates modern humans and has been lost in most non-African populations. Some of this ancestry is thought to originate from admixture with an Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans#Archaic African hominins, unknown archaic hominin that diverged before the split of Neanderthals and modern humans.
Humans are a Gonochorism, gonochoric species, meaning they are divided into male and female sexes. The greatest degree of genetic Sex differences in humans, variation exists between males and females. While the nucleotide diversity, nucleotide genetic variation of individuals of the same sex across global populations is no greater than 0.1%–0.5%, the genetic difference between Man, males and woman, females is between 1% and 2%. Males on average are 15% heavier and taller than females. On average, men have about 40–50% more upper body strength and 20–30% more lower body strength than women at the same weight, due to higher amounts of muscle and larger muscle fibers. Women generally have a higher
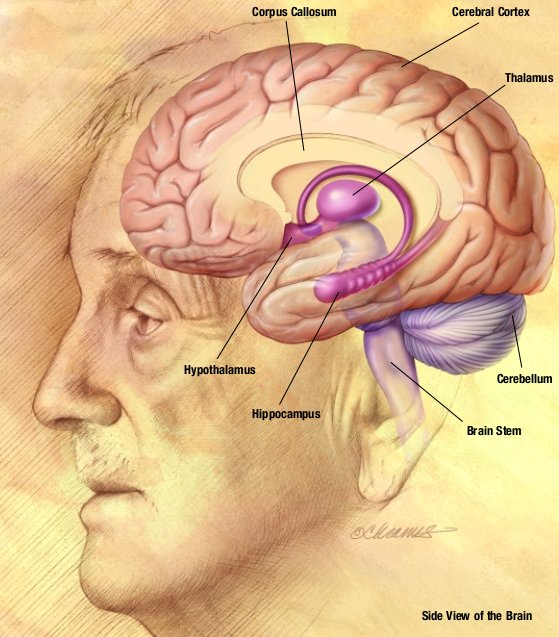 The human brain, the focal point of the central nervous system in humans, controls the peripheral nervous system. In addition to controlling "lower," involuntary, or primarily autonomic nervous system, autonomic activities such as respiration (physiology), respiration and digestion, it is also the locus of "higher" order functioning such as
The human brain, the focal point of the central nervous system in humans, controls the peripheral nervous system. In addition to controlling "lower," involuntary, or primarily autonomic nervous system, autonomic activities such as respiration (physiology), respiration and digestion, it is also the locus of "higher" order functioning such as
 Human motivation is not yet wholly understood. From a psychological perspective, Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a well-established theory that can be defined as the process of satisfying certain needs in ascending order of complexity. From a more general, philosophical perspective, human motivation can be defined as a commitment to, or withdrawal from, various goals requiring the application of human ability. Furthermore, incentive and preference are both factors, as are any perceived links between incentives and preferences. Volition (psychology), Volition may also be involved, in which case willpower is also a factor. Ideally, both motivation and volition ensure the selection, striving for, and Realisation (metrology), realization of goals in an optimal manner, a Function (biology), function beginning in childhood and continuing throughout a lifetime in a process known as socialization.
Emotions are biological states associated with the nervous system brought on by Neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or Suffering, displeasure. They are often Reciprocal influence, intertwined with Mood (psychology), mood, temperament, Personality psychology, personality, disposition, creativity, and motivation. Emotion has a significant influence on human behavior and their ability to learn. Acting on extreme or uncontrolled emotions can lead to social disorder and crime, with studies showing criminals may have a lower emotional intelligence than normal.
Emotional experiences perceived as pleasure, pleasant, such as joy, Interest (emotion), interest or contentment, contrast with those perceived as suffering, unpleasant, like anxiety, sadness, anger, and Depression (mood), despair. Happiness, or the state of being happy, is a human emotional condition. The definition of happiness is a common philosophical topic. Some define it as experiencing the feeling of positive Affect (psychology), emotional affects, while avoiding the negative ones. Others see it as an appraisal of life satisfaction or quality of life. Recent research suggests that being happy might involve experiencing some negative emotions when humans feel they are warranted.
Human motivation is not yet wholly understood. From a psychological perspective, Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a well-established theory that can be defined as the process of satisfying certain needs in ascending order of complexity. From a more general, philosophical perspective, human motivation can be defined as a commitment to, or withdrawal from, various goals requiring the application of human ability. Furthermore, incentive and preference are both factors, as are any perceived links between incentives and preferences. Volition (psychology), Volition may also be involved, in which case willpower is also a factor. Ideally, both motivation and volition ensure the selection, striving for, and Realisation (metrology), realization of goals in an optimal manner, a Function (biology), function beginning in childhood and continuing throughout a lifetime in a process known as socialization.
Emotions are biological states associated with the nervous system brought on by Neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or Suffering, displeasure. They are often Reciprocal influence, intertwined with Mood (psychology), mood, temperament, Personality psychology, personality, disposition, creativity, and motivation. Emotion has a significant influence on human behavior and their ability to learn. Acting on extreme or uncontrolled emotions can lead to social disorder and crime, with studies showing criminals may have a lower emotional intelligence than normal.
Emotional experiences perceived as pleasure, pleasant, such as joy, Interest (emotion), interest or contentment, contrast with those perceived as suffering, unpleasant, like anxiety, sadness, anger, and Depression (mood), despair. Happiness, or the state of being happy, is a human emotional condition. The definition of happiness is a common philosophical topic. Some define it as experiencing the feeling of positive Affect (psychology), emotional affects, while avoiding the negative ones. Others see it as an appraisal of life satisfaction or quality of life. Recent research suggests that being happy might involve experiencing some negative emotions when humans feel they are warranted.
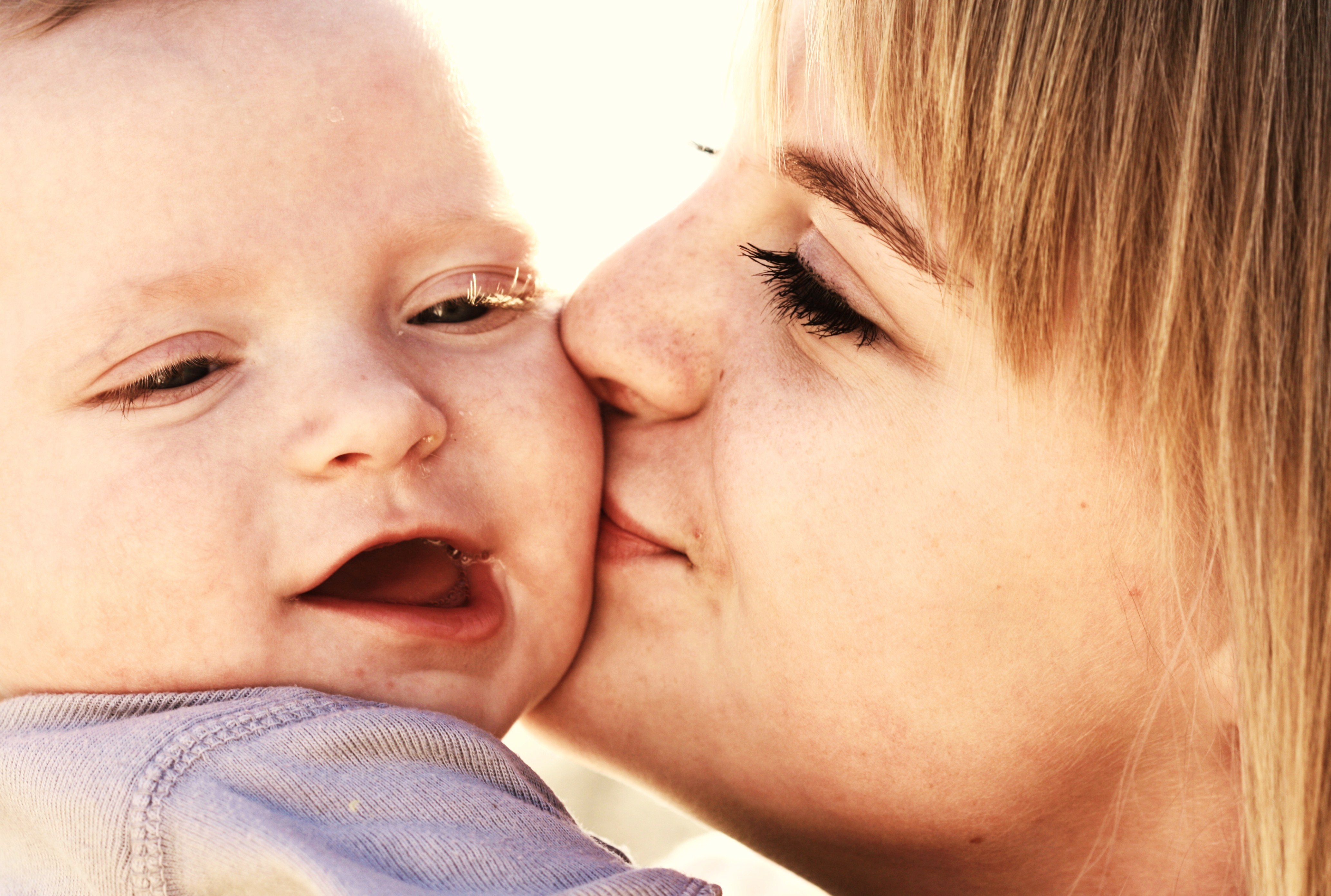 For humans, sexuality involves biological, erotic, Physical intimacy, physical, Emotional intimacy, emotional, social, or Spirituality, spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied with historical contexts over time, it lacks a precise definition. The biological and physical aspects of sexuality largely concern the Human reproduction, human reproductive functions, including the human sexual response cycle. Sexuality also affects and is affected by cultural, political, legal, philosophical, Morality, moral, ethical, and religious aspects of life. Sexual desire, or ''libido'', is a basic mental state present at the beginning of sexual behavior. Studies show that men desire sex more than women and Masturbation, masturbate more often.
Humans can fall anywhere along a continuous scale of sexual orientation, although most humans are heterosexual. While homosexuality, homosexual behavior Homosexual behavior in animals, occurs in some other animals, only humans and Sheep, domestic sheep have so far been found to exhibit exclusive preference for same-sex relationships. Most evidence supports nonsocial, biology and sexual orientation, biological causes of sexual orientation, as cultures that are very tolerant of homosexuality do not have significantly higher rates of it. Research in neuroscience and genetics suggests that other aspects of human sexuality are biologically influenced as well.
Love most commonly refers to a feeling of strong attraction or emotional Attachment (psychology), attachment. It can be impersonal (the love of an object, ideal, or strong political or spiritual connection) or interpersonal (love between humans). When in love dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin and other chemicals stimulate the brain's pleasure center, leading to side effects such as increased heart rate, loss of Anorexia (symptom), appetite and Insomnia, sleep, and an Euphoria, intense feeling of excitement.
For humans, sexuality involves biological, erotic, Physical intimacy, physical, Emotional intimacy, emotional, social, or Spirituality, spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied with historical contexts over time, it lacks a precise definition. The biological and physical aspects of sexuality largely concern the Human reproduction, human reproductive functions, including the human sexual response cycle. Sexuality also affects and is affected by cultural, political, legal, philosophical, Morality, moral, ethical, and religious aspects of life. Sexual desire, or ''libido'', is a basic mental state present at the beginning of sexual behavior. Studies show that men desire sex more than women and Masturbation, masturbate more often.
Humans can fall anywhere along a continuous scale of sexual orientation, although most humans are heterosexual. While homosexuality, homosexual behavior Homosexual behavior in animals, occurs in some other animals, only humans and Sheep, domestic sheep have so far been found to exhibit exclusive preference for same-sex relationships. Most evidence supports nonsocial, biology and sexual orientation, biological causes of sexual orientation, as cultures that are very tolerant of homosexuality do not have significantly higher rates of it. Research in neuroscience and genetics suggests that other aspects of human sexuality are biologically influenced as well.
Love most commonly refers to a feeling of strong attraction or emotional Attachment (psychology), attachment. It can be impersonal (the love of an object, ideal, or strong political or spiritual connection) or interpersonal (love between humans). When in love dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin and other chemicals stimulate the brain's pleasure center, leading to side effects such as increased heart rate, loss of Anorexia (symptom), appetite and Insomnia, sleep, and an Euphoria, intense feeling of excitement.
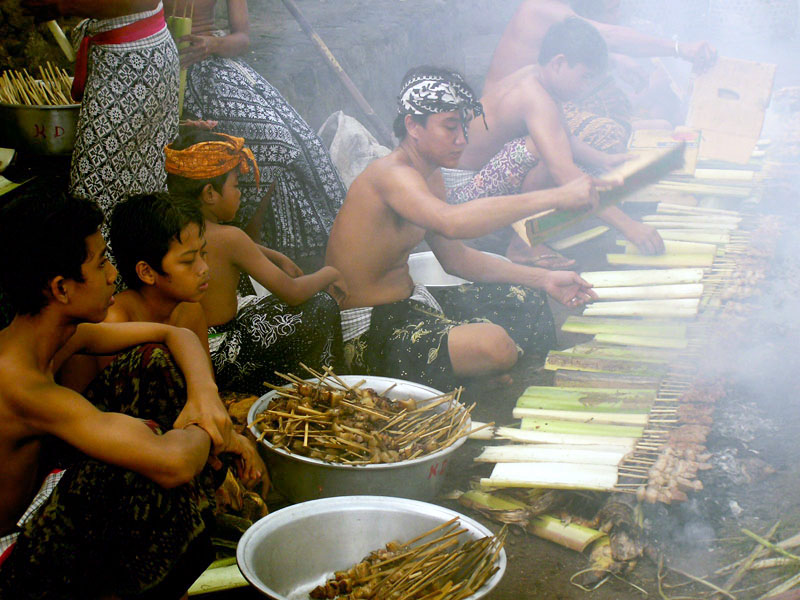
 Art is a defining characteristic of humans and there is evidence for a relationship between creativity and language. The earliest evidence of art was shell engravings made by ''Homo erectus'' 300,000 years before modern humans evolved. Art attributed to ''H. sapiens'' existed at least 75,000 years ago, with jewellery and drawings found in caves in South Africa. There are various hypotheses as to why humans have Adaptation, adapted to the arts. These include allowing them to better problem solve issues, providing a means to control or influence other humans, encouraging cooperation and contribution within a society or increasing the chance of attracting a potential mate. The use of imagination developed through art, combined with logic may have given early humans an evolutionary advantage.
Evidence of humans engaging in musical activities predates cave art and so far music has been Cultural universal, practiced by virtually all known human cultures. There exists a wide variety of music genres and ethnic musics; with humans' musical abilities being related to other abilities, including complex social human behaviours. It has been shown that human brains respond to music by becoming synchronized with the rhythm and beat, a process called Entrainment (biomusicology), entrainment. Dance is also a form of human expression found in all cultures and may have evolved as a way to help early humans communicate. Listening to music and observing dance stimulates the orbitofrontal cortex and other pleasure sensing areas of the brain.
Unlike speaking, reading and writing does not come naturally to humans and must be taught. Still, literature has been present before the invention of words and language, with 30,000-year-old paintings on walls inside some caves portraying a series of dramatic scenes. One of the oldest surviving works of literature is the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', first engraved on ancient
Art is a defining characteristic of humans and there is evidence for a relationship between creativity and language. The earliest evidence of art was shell engravings made by ''Homo erectus'' 300,000 years before modern humans evolved. Art attributed to ''H. sapiens'' existed at least 75,000 years ago, with jewellery and drawings found in caves in South Africa. There are various hypotheses as to why humans have Adaptation, adapted to the arts. These include allowing them to better problem solve issues, providing a means to control or influence other humans, encouraging cooperation and contribution within a society or increasing the chance of attracting a potential mate. The use of imagination developed through art, combined with logic may have given early humans an evolutionary advantage.
Evidence of humans engaging in musical activities predates cave art and so far music has been Cultural universal, practiced by virtually all known human cultures. There exists a wide variety of music genres and ethnic musics; with humans' musical abilities being related to other abilities, including complex social human behaviours. It has been shown that human brains respond to music by becoming synchronized with the rhythm and beat, a process called Entrainment (biomusicology), entrainment. Dance is also a form of human expression found in all cultures and may have evolved as a way to help early humans communicate. Listening to music and observing dance stimulates the orbitofrontal cortex and other pleasure sensing areas of the brain.
Unlike speaking, reading and writing does not come naturally to humans and must be taught. Still, literature has been present before the invention of words and language, with 30,000-year-old paintings on walls inside some caves portraying a series of dramatic scenes. One of the oldest surviving works of literature is the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', first engraved on ancient
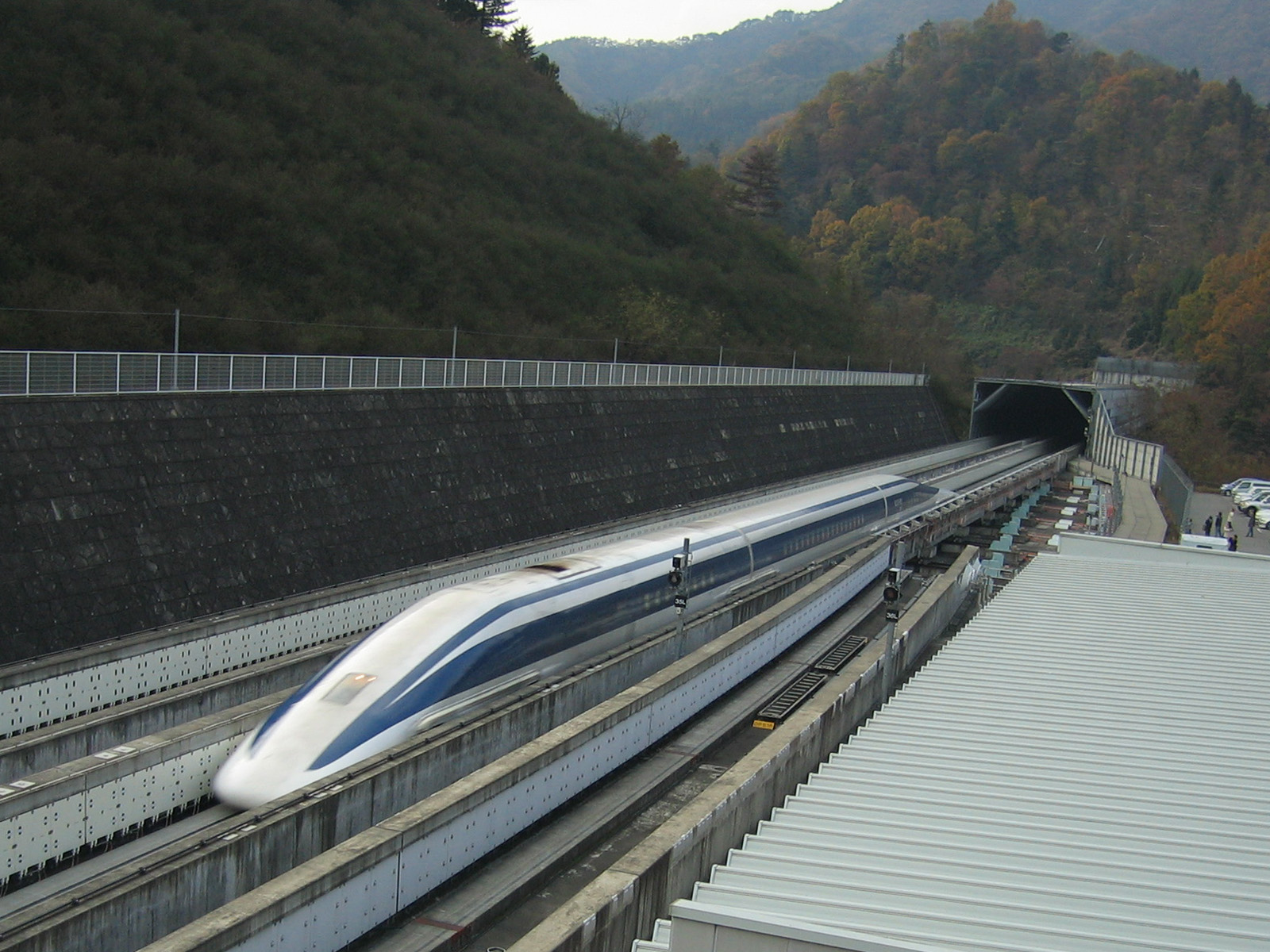 Stone tools were used by proto-humans at least 2.5 million years ago. The use and manufacture of tools has been put forward as the ability that defines humans more than anything else and has historically been seen as an important evolutionary step. The technology became much more sophisticated about 1.8 million years ago, with the Control of fire by early humans, controlled use of fire beginning around 1 million years ago. The wheel and wheeled vehicles appeared simultaneously in several regions some time in the fourth millennium BC. The development of more complex tools and technologies allowed land to be Arable land, cultivated and animals to be Domestication, domesticated, thus proving essential in the development of
Stone tools were used by proto-humans at least 2.5 million years ago. The use and manufacture of tools has been put forward as the ability that defines humans more than anything else and has historically been seen as an important evolutionary step. The technology became much more sophisticated about 1.8 million years ago, with the Control of fire by early humans, controlled use of fire beginning around 1 million years ago. The wheel and wheeled vehicles appeared simultaneously in several regions some time in the fourth millennium BC. The development of more complex tools and technologies allowed land to be Arable land, cultivated and animals to be Domestication, domesticated, thus proving essential in the development of
 Religion is generally defined as a belief system concerning the supernatural, sacred or divinity, divine, and practices, values, institutions and
Religion is generally defined as a belief system concerning the supernatural, sacred or divinity, divine, and practices, values, institutions and
 An aspect unique to humans is their ability to Knowledge transfer, transmit knowledge from one generation to the next and to continually build on this information to develop tools, scientific laws and other advances to pass on further. This accumulated knowledge can be tested to answer questions or make predictions about how the universe functions and has been very successful in advancing human ascendancy. Aristotle has been described as the first scientist, and preceded the rise of scientific thought through the Hellenistic period. Other early advances in science came from the Science and technology of the Han dynasty, Han Dynasty in China and during the
An aspect unique to humans is their ability to Knowledge transfer, transmit knowledge from one generation to the next and to continually build on this information to develop tools, scientific laws and other advances to pass on further. This accumulated knowledge can be tested to answer questions or make predictions about how the universe functions and has been very successful in advancing human ascendancy. Aristotle has been described as the first scientist, and preceded the rise of scientific thought through the Hellenistic period. Other early advances in science came from the Science and technology of the Han dynasty, Han Dynasty in China and during the
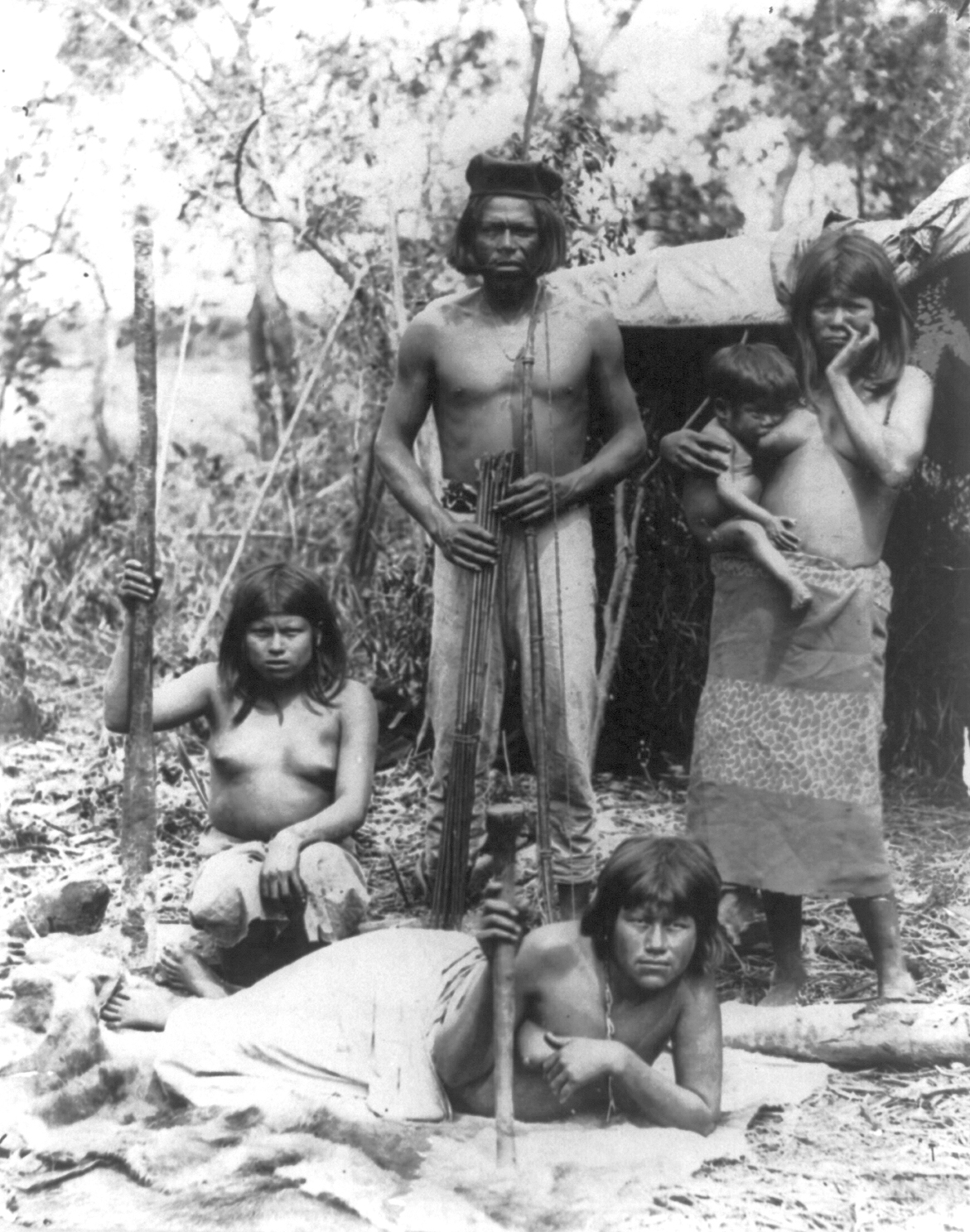 Society is the system of organizations and institutions arising from interaction between humans. Humans are highly social and tend to live in large complex social groups. They can be divided into different groups according to their income, wealth, power (social and political), power, reputation and other factors. The structure of social stratification and the degree of social mobility differs, especially between modern and traditional societies. Human groups range from the size of Family, families to nations. The first form of human social organization is thought to have resembled
Society is the system of organizations and institutions arising from interaction between humans. Humans are highly social and tend to live in large complex social groups. They can be divided into different groups according to their income, wealth, power (social and political), power, reputation and other factors. The structure of social stratification and the degree of social mobility differs, especially between modern and traditional societies. Human groups range from the size of Family, families to nations. The first form of human social organization is thought to have resembled
 Trade, the voluntary exchange of goods and services, is seen as a characteristic that differentiates humans from other animals and has been cited as a practice that gave ''Homo sapiens'' a major advantage over other hominids. Evidence suggests early ''H. sapiens'' made use of long-distance trade routes to exchange goods and ideas, leading to cultural explosions and providing additional food sources when hunting was sparse, while such trade networks did not exist for the now extinct Neanderthals. Early trade likely involved materials for creating tools like obsidian. The first truly international trade routes were around the spice trade through the Roman and medieval periods.
Early human Economy, economies were more likely to be based around Gift economy, gift giving instead of a bartering system. Early money consisted of Commodity money, commodities; the oldest being in the form of cattle and the most widely used being cowrie shells. Money has since evolved into governmental issued coins, Paper money, paper and electronic money. Human study of economics is a social science that looks at how societies distribute scarce resources among different people. There are massive Economic inequality, inequalities in the division of wealth among humans; the eight richest humans are worth the same monetary value as the poorest half of all the human population.
Trade, the voluntary exchange of goods and services, is seen as a characteristic that differentiates humans from other animals and has been cited as a practice that gave ''Homo sapiens'' a major advantage over other hominids. Evidence suggests early ''H. sapiens'' made use of long-distance trade routes to exchange goods and ideas, leading to cultural explosions and providing additional food sources when hunting was sparse, while such trade networks did not exist for the now extinct Neanderthals. Early trade likely involved materials for creating tools like obsidian. The first truly international trade routes were around the spice trade through the Roman and medieval periods.
Early human Economy, economies were more likely to be based around Gift economy, gift giving instead of a bartering system. Early money consisted of Commodity money, commodities; the oldest being in the form of cattle and the most widely used being cowrie shells. Money has since evolved into governmental issued coins, Paper money, paper and electronic money. Human study of economics is a social science that looks at how societies distribute scarce resources among different people. There are massive Economic inequality, inequalities in the division of wealth among humans; the eight richest humans are worth the same monetary value as the poorest half of all the human population.
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
of primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including huma ...
, characterized by bipedalism
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' a ...
and exceptional cognitive
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
skills due to a large and complex brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
. This has enabled the development of advanced tools
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates ba ...
, culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
, and language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structure
In the social sciences, social structure is the aggregate of patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of individuals. Likewise, society is believed to be grouped into structurally rel ...
s composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideall ...
and kinship
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that ...
networks to political states. Social interaction
A social relation or also described as a social interaction or social experience is the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences, and describes any voluntary or involuntary interpersonal relationship between two or more individuals ...
s between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms
Social norms are shared standards of acceptable behavior by groups. Social norms can both be informal understandings that govern the behavior of members of a society, as well as be codified into rules and laws. Social normative influences or soci ...
, and ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized, b ...
s, which bolster human society
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Socie ...
. Its intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can b ...
and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena
A phenomenon ( : phenomena) is an observable event. The term came into its modern philosophical usage through Immanuel Kant, who contrasted it with the noumenon, which ''cannot'' be directly observed. Kant was heavily influenced by Gottfried W ...
have motivated humanity's development of science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
, philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, mythology
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrat ...
, religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, ...
, and other fields of study
Fields may refer to:
Music
*Fields (band), an indie rock band formed in 2006
*Fields (progressive rock band), a progressive rock band formed in 1971
* ''Fields'' (album), an LP by Swedish-based indie rock band Junip (2010)
* "Fields", a song by ...
.
Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus ''Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely relate ...
'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant
Extant is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Extant taxon, a taxon which is not extinct, ...
member. Anatomically modern human
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
s emerged around 300,000 years ago in Africa, evolving from ''Homo heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of ''H. erectus'' in ...
'' or a similar species and migrating out of Africa
''Out of Africa'' is a memoir by the Danish people, Danish author Karen Blixen. The book, first published in 1937, recounts events of the seventeen years when Blixen made her home in Kenya, then called East Africa Protectorate, British East Afr ...
, gradually replacing or interbreeding
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents (such as in ...
with local populations of archaic humans
A number of varieties of ''Homo'' are grouped into the broad category of archaic humans in the period that precedes and is contemporary to the emergence of the earliest early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') around 300 ka. Omo-Kibish I (Omo I) f ...
. For most of history, humans were nomadic
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
hunter-gatherers. Humans began exhibiting behavioral modernity
Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits that distinguishes current ''Homo sapiens'' from other anatomically modern humans, hominins, and primates. Most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterized by ...
about 160,000–60,000 years ago. The Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
, which began in Southwest Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Anat ...
around 13,000 years ago (and separately in a few other places), saw the emergence of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
and permanent human settlement
In geography, statistics and archaeology, a settlement, locality or populated place is a community in which people live. The complexity of a settlement can range from a minuscule number of dwellings grouped together to the largest of ci ...
. As populations became larger and denser, forms of governance developed within and between communities, and a number of civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
Ci ...
s have risen and fallen. Humans have continued to expand, with a global population of over 8 billion .
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
s and the environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
influence human biological variation in visible characteristics, physiology, disease susceptibility, mental abilities, body size, and life span. Though humans vary in many traits (such as genetic predispositions and physical features), any two humans are at least 99% genetically similar. Humans are sexually dimorphic: generally, males have greater body strength and females have a higher body fat
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular en ...
percentage. At puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. ...
, humans develop secondary sex characteristic
Secondary sex characteristics are features that appear during puberty in humans, and at sexual maturity in other animals. These characteristics are particularly evident in the sexually dimorphic phenotypic traits that distinguish the sexes of a sp ...
s. Females are capable of pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
, usually between puberty, at around 12 years, and menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often d ...
, around the age of 50.
Humans are omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutri ...
, capable of consuming a wide variety of plant and animal material, and have used fire and other forms of heat to prepare and cook
Cook or The Cook may refer to:
Food preparation
* Cooking, the preparation of food
* Cook (domestic worker), a household staff member who prepares food
* Cook (professional), an individual who prepares food for consumption in the food industry
* ...
food since the time of ''H. erectus''. Humans can survive for up to eight weeks without food and three or four days without water. Humans are generally diurnal, sleeping on average seven to nine hours per day. Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globall ...
is dangerous, with a high risk of complications and death. Often, both the mother and the father provide care for their children, who are helpless at birth.
Humans have a large and highly developed prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46, ...
, the region of the brain associated with higher cognition. They are highly intelligent, capable of episodic memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred ...
, have flexible facial expressions, self-awareness
In philosophy of self, self-awareness is the experience of one's own personality or individuality. It is not to be confused with consciousness in the sense of qualia. While consciousness is being aware of one's environment and body and lifesty ...
, and a theory of mind
In psychology, theory of mind refers to the capacity to understand other people by ascribing mental states to them (that is, surmising what is happening in their mind). This includes the knowledge that others' mental states may be different fro ...
. The human mind is capable of introspection
Introspection is the examination of one's own conscious thoughts and feelings. In psychology, the process of introspection relies on the observation of one's mental state, while in a spiritual context it may refer to the examination of one's s ...
, private thought
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to conscious cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, a ...
, imagination
Imagination is the production or simulation of novel objects, sensations, and ideas in the mind without any immediate input of the senses. Stefan Szczelkun characterises it as the forming of experiences in one's mind, which can be re-creations ...
, volition, and forming views on existence
Existence is the ability of an entity to interact with reality. In philosophy, it refers to the ontology, ontological Property (philosophy), property of being.
Etymology
The term ''existence'' comes from Old French ''existence'', from Medieval ...
. This has allowed great technological advancements and complex tool development possible through complex reasoning
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, lang ...
and the transmission of knowledge to subsequent generations. Language, art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
, and trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct excha ...
are defining characteristics of humans. Long-distance trade routes might have led to cultural explosions and resource distribution that gave humans an advantage over other similar species.
Etymology and definition
All modern humans are classified into thespecies
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
''Homo sapiens'', coined by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
in his 1735 work ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomen ...
''. The generic name "''Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus ''Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely relate ...
''" is a learned 18th-century derivation from Latin , which refers to humans of either sex. The word ''human'' can refer to all members of the ''Homo'' genus, although in common usage it generally just refers to ''Homo sapiens,'' the only extant species. The name "''Homo'' ''sapiens''" means 'wise man' or 'knowledgeable man'. There is disagreement if certain extinct members of the genus, namely Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While th ...
s, should be included as a separate species of humans or as a subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
of ''H. sapiens''.
''Human'' is a loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because th ...
of Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English p ...
from Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligib ...
, ultimately from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, the adjectival form of ('man' — in the sense of humankind). The native English term ''man
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromos ...
'' can refer to the species generally (a synonym for ''humanity'') as well as to human males. It may also refer to individuals of either sex, though this form is less common in contemporary English.
Despite the fact that the word ''animal'' is colloquially used as an antonym
In lexical semantics, opposites are words lying in an inherently incompatible binary relationship. For example, something that is ''long'' entails that it is not ''short''. It is referred to as a 'binary' relationship because there are two members ...
for ''human'', and contrary to a common biological misconception, humans are animals. The word ''person
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, ...
'' is often used interchangeably with ''human'', but philosophical debate exists as to whether personhood applies to all humans or all sentient beings, and further if one can lose personhood (such as by going into a persistent vegetative state
A persistent vegetative state (PVS) or post-coma unresponsiveness (PCU) is a disorder of consciousness in which patients with severe brain damage are in a state of partial arousal rather than true awareness. After four weeks in a vegetative stat ...
).
Evolution
Humans are apes ( superfamily Hominoidea). Thelineage
Lineage may refer to:
Science
* Lineage (anthropology), a group that can demonstrate its common descent from an apical ancestor or a direct line of descent from an ancestor
* Lineage (evolution), a temporal sequence of individuals, populati ...
of apes that eventually gave rise to humans first split from gibbons (family Hylobatidae
Gibbons () are apes in the family Hylobatidae (). The family historically contained one genus, but now is split into four extant genera and 20 species. Gibbons live in subtropical and tropical rainforest from eastern Bangladesh to Northeast India ...
) and orangutan
Orangutans are great apes native to the rainforests of Indonesia and Malaysia. They are now found only in parts of Borneo and Sumatra, but during the Pleistocene they ranged throughout Southeast Asia and South China. Classified in the genus ...
s (genus ''Pongo''), then gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or fi ...
s (genus ''Gorilla''), and finally, chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative th ...
s and bonobo
The bonobo (; ''Pan paniscus''), also historically called the pygmy chimpanzee and less often the dwarf chimpanzee or gracile chimpanzee, is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus '' Pan,'' the other being the comm ...
s (genus '' Pan''). The last split, between the human and chimpanzee–bonobo lineages, took place around 8–4 million years ago, in the late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
epoch. During this split, chromosome 2
Chromosome 2 is one of the twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 2 is the second-largest human chromosome, spanning more than 242 million base pairs and representing almost e ...
was formed from the joining of two other chromosomes, leaving humans with only 23 pairs of chromosomes, compared to 24 for the other apes. Following their split with chimpanzees and bonobos, the hominins
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The t ...
diversified into many species and at least two distinct genera. All but one of these lineages—representing the genus ''Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus ''Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely relate ...
'' and its sole extant species ''Homo sapiens''—are now extinct.
 The genus ''Homo'' evolved from ''
The genus ''Homo'' evolved from ''Australopithecus
''Australopithecus'' (, ; ) is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genus ''Homo'' (which includes modern humans) emerged within ''Australopithecus'', as sister to e.g. ''Australopi ...
''. Though fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in ...
from the transition are scarce, the earliest members of ''Homo'' share several key traits with ''Australopithecus''. The earliest record of ''Homo'' is the 2.8 million-year-old specimen LD 350-1
LD 350-1 is the earliest known specimen of the genus ''Homo'', dating to 2.8–2.75 million years ago (mya), found in the Ledi-Geraru site in the Afar Region of Ethiopia. The specimen was discovered in silts above the Gurumaha Tuff section of the ...
from Ethiopia, and the earliest named species are ''Homo habilis
''Homo habilis'' ("handy man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.31 million years ago to 1.65 million years ago (mya). Upon species description in 1964, ''H. habilis'' was highly ...
'' and ''Homo rudolfensis
''Homo rudolfensis'' is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2 million years ago (mya). Because ''H. rudolfensis'' coexisted with several other hominins, it is debated what specimens can be confide ...
'' which evolved by 2.3 million years ago. ''H. erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
'' (the African variant is sometimes called '' H. ergaster'') evolved 2 million years ago and was the first archaic human
A number of varieties of ''Homo'' are grouped into the broad category of archaic humans in the period that precedes and is contemporary to the emergence of the earliest early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') around 300 ka. Omo-Kibish I (Omo I) f ...
species to leave Africa and disperse across Eurasia. ''H. erectus'' also was the first to evolve a characteristically human body plan
A body plan, ( ), or ground plan is a set of morphological features common to many members of a phylum of animals. The vertebrates share one body plan, while invertebrates have many.
This term, usually applied to animals, envisages a "blueprin ...
. ''Homo sapiens'' emerged in Africa around 300,000 years ago from a species commonly designated as either ''H. heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' in ...
'' or ''H. rhodesiensis
''Homo rhodesiensis'' is the species name proposed by Arthur Smith Woodward (1921) to classify Kabwe 1 (the "Kabwe skull" or "Broken Hill skull", also "Rhodesian Man"), a Middle Stone Age fossil recovered from a cave at Broken Hill, or Kabwe, ...
'', the descendants of ''H. erectus'' that remained in Africa. ''H. sapiens'' migrated out of the continent, gradually replacing or interbreeding with local populations of archaic humans. Humans began exhibiting behavioral modernity
Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits that distinguishes current ''Homo sapiens'' from other anatomically modern humans, hominins, and primates. Most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterized by ...
about 160,000-70,000 years ago, and possibly earlier.
The "out of Africa" migration took place in at least two waves, the first around 130,000 to 100,000 years ago, the second (Southern Dispersal
In the context of the recent African origin of modern humans, the Southern Dispersal scenario (also the coastal migration or great coastal migration hypothesis) refers to the early migration along the southern coast of Asia, from the Arabian Pen ...
) around 70,000 to 50,000 years ago. ''H. sapiens'' proceeded to colonize all the continents and larger islands, arriving in Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
60,000 years ago, Australia around 65,000 years ago, the Americas around 15,000 years ago, and remote islands such as Hawaii, Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearl ...
, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
between the years 300 and 1280 CE.
Human evolution was not a simple linear or branched progression but involved interbreeding between related species. Genomic research has shown that hybridization between substantially diverged lineages was common in human evolution. DNA evidence suggests that several genes of Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While th ...
origin are present among all non sub-Saharan African populations, and Neanderthals and other hominins, such as Denisovan
The Denisovans or Denisova hominins ) are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human that ranged across Asia during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic. Denisovans are known from few physical remains and consequently, most of what is known ...
s, may have contributed up to 6% of their genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
to present-day non sub-Saharan African humans.
Human evolution is characterized by a number of morphological, developmental
Development of the human body is the process of growth to maturity. The process begins with fertilization, where an egg released from the ovary of a female is penetrated by a sperm cell from a male. The resulting zygote develops through mitosi ...
, physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
, and behavioral
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well ...
changes that have taken place since the split between the last common ancestor of humans and chimpanzees. The most significant of these adaptations are obligate bipedalism, increased brain size and decreased sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
(neoteny
Neoteny (), also called juvenilization,Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young. Bergin & Garvey: CT. is the delaying or slowing of the physiological, or somatic, development of an organism, typically an animal. Neoteny is found in modern humans compared ...
). The relationship between all these changes is the subject of ongoing debate.
History
hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s. The Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
(the invention of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
) first took place in Southwest Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Anat ...
and spread through large parts of the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by the ...
over the following millennia. It also occurred independently in Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. W ...
(about 6,000 years ago), China, Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
, and the Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
and West Savanna regions of Africa. Access to food surplus led to the formation of permanent human settlement
In geography, statistics and archaeology, a settlement, locality or populated place is a community in which people live. The complexity of a settlement can range from a minuscule number of dwellings grouped together to the largest of ci ...
s, the domestication
Domestication is a sustained multi-generational relationship in which humans assume a significant degree of control over the reproduction and care of another group of organisms to secure a more predictable supply of resources from that group. ...
of animals and the use of metal tools for the first time in history. Agriculture and sedentary lifestyle led to the emergence of early civilizations
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
Civi ...
.
An urban revolution took place in the 4th millennium BC
The 4th millennium BC spanned the years 4000 BC to 3001 BC. Some of the major changes in human culture during this time included the beginning of the Bronze Age and the invention of writing, which played a major role in starting recorded history. ...
E with the development of city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
s, particularly Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ian cities located in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
. It was in these cities that the earliest known form of writing, cuneiform script
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sha ...
, appeared around 3000 BCE. Other major civilizations to develop around this time were Ancient Egypt and the Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
. They eventually traded with each other and invented technology such as wheels, plows and sails. Astronomy and mathematics were also developed and the Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the biggest Egyptian pyramid and the tomb of Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu. Built in the early 26th century BC during a period of around 27 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, ...
was built. There is evidence of a severe drought lasting about a hundred years that may have caused the decline of these civilizations, with new ones appearing in the aftermath. Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
ns came to dominate Mesopotamia while others, such as Poverty Point culture
The Poverty Point culture is the archaeological culture of a prehistoric indigenous peoples who inhabited a portion of North America's lower Mississippi Valley and surrounding Gulf coast from about 1730 – 1350 BC.
Archeologists have identified ...
s, Minoans and the Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and ...
, rose to prominence in new areas. The Bronze Age suddenly collapsed around 1200 BCE, resulting in the disappearance of a number of civilizations and the beginning of the Greek Dark Ages
The term Greek Dark Ages refers to the period of Greek history from the end of the Mycenaean palatial civilization, around 1100 BC, to the beginning of the Archaic age, around 750 BC. Archaeological evidence shows a widespread collaps ...
. During this period iron started replacing bronze, leading to the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
.
In the 5th century BCE, history started being recorded as a discipline, which provided a much clearer picture of life at the time. Between the 8th and 6th century BCE, Europe entered the classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
age, a period when ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
and ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 B ...
flourished. Around this time other civilizations also came to prominence. The Maya civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, archit ...
started to build cities and create complex calendars. In Africa, the Kingdom of Aksum
The Kingdom of Aksum ( gez, መንግሥተ አክሱም, ), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom centered in Northeast Africa and South Arabia from Classical antiquity to the Middle Ages. Based primarily in wh ...
overtook the declining Kingdom of Kush
The Kingdom of Kush (; Egyptian language, Egyptian: 𓎡𓄿𓈙𓈉 ''kꜣš'', Akkadian language, Assyrian: ''Kûsi'', in LXX grc, Κυς and Κυσι ; cop, ''Ecōš''; he, כּוּשׁ ''Kūš'') was an ancient kingdom in Nubia, ce ...
and facilitated trade between India and the Mediterranean. In West Asia, the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
's system of centralized governance became the precursor to many later empires, while the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gol ...
in India and the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
in China have been described as golden ages
A golden age is a period considered the apotheosis in the history of a country or people, a time period when the greatness, greatest achievements were made. The term originated from early ancient Greece, Greek and ancient Rome, Roman poets, who ...
in their respective regions.
 Following the
Following the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rul ...
in 476, Europe entered the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. During this period, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
and the Church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship
* Chris ...
would provide centralized authority and education. In the Middle East, Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
became the prominent religion and expanded into North Africa. It led to an Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
, inspiring achievements in architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
, the revival of old advances in science and technology, and the formation of a distinct way of life. The Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
and Islamic world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
s would eventually clash, with the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On 1 ...
, the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. ...
and the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
declaring a series of holy wars
A religious war or a war of religion, sometimes also known as a holy war ( la, sanctum bellum), is a war which is primarily caused or justified by differences in religion. In the modern period, there are frequent debates over the extent to wh ...
to regain control of the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
from Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s. In the Americas, complex Mississippian societies would arise starting around 800 CE, while further south, the Aztecs
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
and Incas
The Inca Empire (also Quechuan and Aymaran spelling shift, known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, (Quechuan languages, Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) wa ...
would become the dominant powers. The Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
would conquer much of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
in the 13th and 14th centuries. Over this same time period, the Mali Empire
The Mali Empire ( Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or Manden; ar, مالي, Māl ...
in Africa grew to be the largest empire on the continent, stretching from Senegambia
The Senegambia (other names: Senegambia region or Senegambian zone,Barry, Boubacar, ''Senegambia and the Atlantic Slave Trade'', (Editors: David Anderson, Carolyn Brown; trans. Ayi Kwei Armah; contributors: David Anderson, American Council of Le ...
to Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
. Oceania would see the rise of the Tuʻi Tonga Empire
The Tui Tonga Empire, or Tongan Empire, are descriptions sometimes given to Tongan expansionism and projected hegemony in Oceania which began around 950 CE, reaching its peak during the period 1200–1500.
It was centred in Tonga on the island o ...
which expanded across many islands in the South Pacific.
The early modern period in Europe and the Near East (c.1450–1800) began with the final defeat of the Byzantine Empire, and the rise of the Ottoman Empire
The rise of the Ottoman Empire is a period of history that started with the emergence of the Ottoman principality (Osmanlı Beyliği) in , and ended circa 1453. This period witnessed the foundation of a political entity ruled by the Ottoman D ...
. Meanwhile, Japan entered the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characteriz ...
, the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
rose in China and the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
ruled much of India. Europe underwent the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, starting in the 15th century, and the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafarin ...
began with the exploring and colonizing of new regions. This includes the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
expanding to become the world's largest empire and the colonization of the Americas. This expansion led to the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
and the genocide of Native American peoples. This period also marked the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transfo ...
, with great advances in mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to objects r ...
, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
and physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
.
The late modern period
In many periodizations of human history, the late modern period followed the early modern period. It began approximately around the year 1800 and depending on the author either ended with the beginning of contemporary history after World War ...
(1800–present) saw the Technological
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, ...
and Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
bring such discoveries as imaging technology
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
, major innovations in transport and energy development
Energy development is the field of activities focused on obtaining sources of energy from natural resources. These activities include production of renewable, nuclear, and fossil fuel derived sources of energy, and for the recovery and reuse ...
. The United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
underwent great change, going from a small group of colonies to one of the global superpower
A superpower is a state with a dominant position characterized by its extensive ability to exert influence or project power on a global scale. This is done through the combined means of economic, military, technological, political and cultural s ...
s. The Napoleonic Wars raged through Europe in the early 1800s, Spain lost most of its colonies in the New World, while Europeans continued Scramble for Africa, expansion into Africa—where European control went from 10% to almost 90% in less than 50 years—and Oceania. A tenuous Balance of power (international relations), balance of power among European nations collapsed in 1914 with the outbreak of the World War I, First World War, one of the deadliest conflicts in history. In the 1930s, Great Depression, a worldwide economic crisis led to the rise of authoritarian regimes and a World War II, Second World War, involving World War II by country, almost all of the world's countries. Following its conclusion in 1945, the Cold War between the USSR and the United States saw a struggle for global influence, including a nuclear arms race and a Space Race, space race. The current Information Age sees the world becoming increasingly Globalization, globalized and interconnected.
Habitat and population
Early human settlements were dependent on proximity to water resources, water and—depending on the lifestyle—other natural resources used for subsistence, such as populations of animal prey for hunting and arable land for growing crops and grazing livestock. Modern humans, however, have a great capacity for altering their habitat (ecology), habitats by means of technology, irrigation, urban planning, construction, deforestation and desertification. Human settlements continue to be vulnerability, vulnerable to natural disasters, especially those placed in hazardous locations and with low quality of construction. Grouping and deliberate habitat alteration is often done with the goals of providing protection, accumulating comforts or material wealth, expanding the available food, improving aesthetics, increasing knowledge or enhancing the exchange of resources. Humans are one of the most Adaptation, adaptable species, despite having a low or narrow tolerance for many of the earth's extreme environments. Through advanced tools, humans have been able to extend their tolerance to a wide variety of temperatures, humidity, and altitudes. As a result, humans are a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan species found in almost all regions of the world, including tropical rainforest, desert, arid desert, extremely cold arctic regions, and heavily polluted cities; in comparison, most other species are confined to a few geographical areas by their limited adaptability. The human population is not, however, uniformly distributed on the Earth's surface, because the population density varies from one region to another, and large stretches of surface are almost completely uninhabited, like Antarctica and vast swathes of the ocean. Most humans (61%) live in Asia; the remainder live in the Americas (14%), Africa (14%), Europe (11%), and Oceania (0.5%). Within the last century, humans have explored challenging environments such as Antarctica, the deep sea, and outer space. Human habitation within these hostile environments is restrictive and expensive, typically limited in duration, and restricted to Science, scientific, military, or Industry (economics), industrial expeditions. Humans have briefly visited the exploration of the Moon, Moon and made their presence felt on other celestial bodies through human-made robotic spacecraft. Since the early 20th century, there has been continuous human presence in Antarctica through Research stations in Antarctica, research stations and, since 2000, human presence in space, in space through habitation on the International Space Station. Estimates of the population at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. Around 50–60 million people lived in the combined eastern and western Roman Empire in the 4th century AD. Bubonic plagues, first recorded in the 6th century AD, reduced the population by 50%, with the Black Death killing 75–200 million people in
Estimates of the population at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. Around 50–60 million people lived in the combined eastern and western Roman Empire in the 4th century AD. Bubonic plagues, first recorded in the 6th century AD, reduced the population by 50%, with the Black Death killing 75–200 million people in Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
and North Africa alone. Human population was believed to have reached one billion in 1800. It has since then increased exponentially, reaching two billion in 1930 and three billion in 1960, four in 1975, five in 1987 and six billion in 1999. It passed seven billion in 2011 and was expected to pass eight billion in November 2022. It took over two million years of prehistory, human prehistory and human history, history for the human population to reach one billion and only 207 years more to grow to 7 billion. The combined Biomass (ecology), biomass of the carbon of all the humans on Earth in 2018 was estimated at 60 million tons, about 10 times larger than that of all non-domesticated mammals.
In 2018, 4.2 billion humans (55%) lived in urban areas, up from 751 million in 1950. The most urbanized regions are Northern America (82%), Latin America (81%), Europe (74%) and Oceania (68%), with Africa and Asia having nearly 90% of the world's 3.4 billion rural population. Problems for humans living in cities include various forms of pollution and crime, especially in inner city and suburban slums. Humans have had a dramatic Human impact on the environment, effect on the environment. They are apex predators, being rarely preyed upon by other species. Human population growth, industrialization, land development, overconsumption and combustion of fossil fuels have led to Environmental degradation, environmental destruction and pollution that significantly contributes to the ongoing mass extinction of other forms of life. They are the main contributor to global climate change, which may accelerate the Holocene extinction.
Biology
Anatomy and physiology
 Most aspects of human physiology are closely Homology (biology), homologous to corresponding aspects of animal physiology. The human body consists of the legs, the torso, the arms, the neck, and the head. An adult human body consists of about 100 trillion (1014) cell (biology), cells. The most commonly defined body systems in humans are the Human nervous system, nervous, the Cardiovascular system, cardiovascular, the Human digestive system, digestive, the Endocrine system, endocrine, the Human immune system, immune, the Integumentary system, integumentary, the Lymphatic system, lymphatic, the Human musculoskeletal system, musculoskeletal, the Human reproductive system, reproductive, the Respiratory system, respiratory, and the urinary system. The dental formula of humans is: . Humans have proportionately shorter palates and much smaller Human tooth, teeth than other primates. They are the only primates to have short, relatively flush canine teeth. Humans have characteristically crowded teeth, with gaps from lost teeth usually closing up quickly in young individuals. Humans are gradually losing their wisdom teeth, third molars, with some individuals having them congenitally absent.
Humans share with chimpanzees a Vestigiality, vestigial tail, Appendix (anatomy), appendix, flexible shoulder joints, grasping fingers and opposable thumbs. Apart from bipedalism and brain size, humans differ from chimpanzees mostly in smelling, hearing and Digestion#Protein digestion, digesting proteins. While humans have a density of hair follicles comparable to other apes, it is predominantly vellus hair, most of which is so short and wispy as to be practically invisible. Humans have about 2 million sweat glands spread over their entire bodies, many more than chimpanzees, whose sweat glands are scarce and are mainly located on the palm of the hand and on the soles of the feet.
It is estimated that the worldwide average Human height, height for an adult human male is about , while the worldwide average height for adult human females is about . Shrinkage of stature may begin in middle age in some individuals but tends to be typical in the extremely Old age, aged. Throughout history, human populations have universally become taller, probably as a consequence of better nutrition, healthcare, and living conditions. The average Body weight, mass of an adult human is for females and for males. Like many other conditions, body weight and body type are influenced by both genetic susceptibility and environment and varies greatly among individuals.
Humans have a far faster and more accurate throw than other animals. Humans are also among the best long-distance runners in the animal kingdom, but slower over short distances. Humans' thinner body hair and more productive sweat glands help avoid heat exhaustion while running for long distances.
Most aspects of human physiology are closely Homology (biology), homologous to corresponding aspects of animal physiology. The human body consists of the legs, the torso, the arms, the neck, and the head. An adult human body consists of about 100 trillion (1014) cell (biology), cells. The most commonly defined body systems in humans are the Human nervous system, nervous, the Cardiovascular system, cardiovascular, the Human digestive system, digestive, the Endocrine system, endocrine, the Human immune system, immune, the Integumentary system, integumentary, the Lymphatic system, lymphatic, the Human musculoskeletal system, musculoskeletal, the Human reproductive system, reproductive, the Respiratory system, respiratory, and the urinary system. The dental formula of humans is: . Humans have proportionately shorter palates and much smaller Human tooth, teeth than other primates. They are the only primates to have short, relatively flush canine teeth. Humans have characteristically crowded teeth, with gaps from lost teeth usually closing up quickly in young individuals. Humans are gradually losing their wisdom teeth, third molars, with some individuals having them congenitally absent.
Humans share with chimpanzees a Vestigiality, vestigial tail, Appendix (anatomy), appendix, flexible shoulder joints, grasping fingers and opposable thumbs. Apart from bipedalism and brain size, humans differ from chimpanzees mostly in smelling, hearing and Digestion#Protein digestion, digesting proteins. While humans have a density of hair follicles comparable to other apes, it is predominantly vellus hair, most of which is so short and wispy as to be practically invisible. Humans have about 2 million sweat glands spread over their entire bodies, many more than chimpanzees, whose sweat glands are scarce and are mainly located on the palm of the hand and on the soles of the feet.
It is estimated that the worldwide average Human height, height for an adult human male is about , while the worldwide average height for adult human females is about . Shrinkage of stature may begin in middle age in some individuals but tends to be typical in the extremely Old age, aged. Throughout history, human populations have universally become taller, probably as a consequence of better nutrition, healthcare, and living conditions. The average Body weight, mass of an adult human is for females and for males. Like many other conditions, body weight and body type are influenced by both genetic susceptibility and environment and varies greatly among individuals.
Humans have a far faster and more accurate throw than other animals. Humans are also among the best long-distance runners in the animal kingdom, but slower over short distances. Humans' thinner body hair and more productive sweat glands help avoid heat exhaustion while running for long distances.
Genetics
 Like most animals, humans are a ploidy, diploid and eukaryote, eukaryotic species. Each somatic cell has two sets of 23 chromosomes, each set received from one parent; gametes have only one set of chromosomes, which is a mixture of the two parental sets. Among the 23 pairs of chromosomes, there are 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex-determination system, sex chromosomes. Like other mammals, humans have an XY sex-determination system, so that females have the sex chromosomes XX and males have XY.
Like most animals, humans are a ploidy, diploid and eukaryote, eukaryotic species. Each somatic cell has two sets of 23 chromosomes, each set received from one parent; gametes have only one set of chromosomes, which is a mixture of the two parental sets. Among the 23 pairs of chromosomes, there are 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex-determination system, sex chromosomes. Like other mammals, humans have an XY sex-determination system, so that females have the sex chromosomes XX and males have XY. Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
s and environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
influence human biological variation in visible characteristics, physiology, disease susceptibility and mental abilities. The exact influence of Environment (biophysical), genes and environment on certain traits is not well understood.
While no humans—not even monozygotic twins—are genetically identical, two humans on average will have a genetic similarity of 99.5%-99.9%. This makes them more Human genetic variation, homogeneous than other great apes, including chimpanzees. This small variation in human DNA compared to many other species suggests a population bottleneck during the Late Pleistocene (around 100,000 years ago), in which the human population was reduced to a small number of breeding pairs. The forces of natural selection have continued to operate on human populations, with evidence that certain regions of the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
display directional selection in the past 15,000 years.
The human genome was first sequenced in 2001 and by 2020 hundreds of thousands of genomes had been sequenced. In 2012 the International HapMap Project had compared the genomes of 1,184 individuals from 11 populations and identified 1.6 million single nucleotide polymorphisms. African populations harbor the highest number of private genetic variants. While many of the common variants found in populations outside of Africa are also found on the African continent, there are still large numbers that are private to these regions, especially Oceania and the Americas. By 2010 estimates, humans have approximately 22,000 genes. By comparing mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA, which is inherited only from the mother, geneticists have concluded that the last female common ancestor whose genetic marker is found in all modern humans, the so-called mitochondrial Eve, must have lived around 90,000 to 200,000 years ago.
Life cycle
 Most human reproduction takes place by internal fertilization via human sexual intercourse, sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. The average gestation period is 38 weeks, but a normal pregnancy can vary by up to 37 days. Embryonic development in the human covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus. Humans are able to Labor induction, induce early labor or perform a caesarean section if the child needs to be born earlier for medical reasons. In developed countries, infants are typically in weight and in height at birth. However, low birth weight is common in developing countries, and contributes to the high levels of infant mortality in these regions.
Compared with other species, human childbirth is dangerous, with a much higher risk of complications and death. The size of the fetus's head is more closely matched to the pelvis than other primates. The reason for this is not completely understood, but it contributes to a painful labor that can last 24 hours or more. The chances of a successful labor increased significantly during the 20th century in wealthier countries with the advent of new medical technologies. In contrast, pregnancy and natural childbirth remain hazardous ordeals in developing regions of the world, with maternal death rates approximately 100 times greater than in developed countries.
Both the mother and the father provide care for human offspring, in contrast to other primates, where parental care is mostly done by the mother. Altricial, Helpless at birth, humans continue to grow for some years, typically reaching sexual maturity at 15 to 17 years of age. The human life span has been split into various stages ranging from three to twelve. Common stages include Infant, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood and old age. The lengths of these stages have varied across cultures and time periods but is typified by an unusually rapid growth spurt during adolescence. Human females undergo
Most human reproduction takes place by internal fertilization via human sexual intercourse, sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. The average gestation period is 38 weeks, but a normal pregnancy can vary by up to 37 days. Embryonic development in the human covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus. Humans are able to Labor induction, induce early labor or perform a caesarean section if the child needs to be born earlier for medical reasons. In developed countries, infants are typically in weight and in height at birth. However, low birth weight is common in developing countries, and contributes to the high levels of infant mortality in these regions.
Compared with other species, human childbirth is dangerous, with a much higher risk of complications and death. The size of the fetus's head is more closely matched to the pelvis than other primates. The reason for this is not completely understood, but it contributes to a painful labor that can last 24 hours or more. The chances of a successful labor increased significantly during the 20th century in wealthier countries with the advent of new medical technologies. In contrast, pregnancy and natural childbirth remain hazardous ordeals in developing regions of the world, with maternal death rates approximately 100 times greater than in developed countries.
Both the mother and the father provide care for human offspring, in contrast to other primates, where parental care is mostly done by the mother. Altricial, Helpless at birth, humans continue to grow for some years, typically reaching sexual maturity at 15 to 17 years of age. The human life span has been split into various stages ranging from three to twelve. Common stages include Infant, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood and old age. The lengths of these stages have varied across cultures and time periods but is typified by an unusually rapid growth spurt during adolescence. Human females undergo menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often d ...
and become Infertility, infertile at around the age of 50. It has been proposed that menopause increases a woman's overall reproductive success by allowing her to invest more time and resources in her existing offspring, and in turn their children (the grandmother hypothesis), rather than by continuing to bear children into old age.
The life span of an individual depends on two major factors, genetics and lifestyle choices. For various reasons, including biological/genetic causes, women live on average about four years longer than men. , the global average life expectancy at birth of a girl is estimated to be 74.9 years compared to 70.4 for a boy. There are significant geographical variations in human life expectancy, mostly correlated with economic development—for example, life expectancy at birth in Hong Kong is 87.6 years for girls and 81.8 for boys, while in the Central African Republic, it is 55.0 years for girls and 50.6 for boys. The developed world is generally aging, with the median age around 40 years. In the third world, developing world, the median age is between 15 and 20 years. While one in five Europeans is 60 years of age or older, only one in twenty Africans is 60 years of age or older. In 2012, the United Nations estimated that there were 316,600 living centenarians (humans of age 100 or older) worldwide.
Diet
 Humans are
Humans are omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutri ...
, capable of consuming a wide variety of plant and animal material. Human groups have adopted a range of diets from purely vegan to primarily carnivorous. In some cases, dietary restrictions in humans can lead to deficiency diseases; however, stable human groups have adapted to many dietary patterns through both genetic specialization and cultural conventions to use nutritionally balanced food sources. The human diet is prominently reflected in human culture and has led to the development of food science.
Until the development of agriculture approximately 10,000 years ago, ''Homo sapiens'' employed a hunter-gatherer method as their sole means of food collection. This involved combining stationary food sources (such as fruits, grains, tubers, and mushrooms, insect larvae and aquatic mollusks) with Game (food), wild game, which must be hunted and captured in order to be consumed. It has been proposed that humans have used fire to prepare and cook
Cook or The Cook may refer to:
Food preparation
* Cooking, the preparation of food
* Cook (domestic worker), a household staff member who prepares food
* Cook (professional), an individual who prepares food for consumption in the food industry
* ...
food since the time of ''Homo erectus''. Around ten thousand years ago, History of agriculture, humans developed agriculture, which substantially altered their diet. This change in diet may also have altered human biology; with the spread of dairy farming providing a new and rich source of food, leading to the evolution of the ability to digest lactose in some adults. The types of food consumed, and how they are prepared, have varied widely by time, location, and culture.
In general, humans can survive for up to eight weeks without food, depending on stored body fat. Survival without water is usually limited to three or four days, with a maximum of one week. In 2020 it is estimated 9 million humans die every year from causes directly or indirectly related to starvation. Childhood malnutrition is also common and contributes to the Disease burden, global burden of disease. However, global food distribution is not even, and obesity among some human populations has increased rapidly, leading to health complications and increased mortality in some developed country, developed and a few developing countries. Worldwide, over one billion people are obese, while in the United States 35% of people are obese, leading to this being described as an "Epidemiology of obesity, obesity epidemic." Obesity is caused by consuming more calories than are expended, so excessive weight gain is usually caused by an energy-dense diet.
Biological variation
 There is biological variation in the human species—with traits such as blood type, genetic diseases, Human skull, cranial features, Human face, facial features, organ systems, eye color, hair color and hair texture, texture, Human height, height and Body shape, build, and Human skin color, skin color varying across the globe. The typical height of an adult human is between , although this varies significantly depending on sex, ethnic origin, and family bloodlines. Body size is partly determined by genes and is also significantly influenced by environmental factors such as diet (nutrition), diet, exercise, and sleep patterns.
There is evidence that populations have adapted genetically to various external factors. The genes that allow adult humans to Lactose tolerance, digest lactose are present in high frequencies in populations that have long histories of cattle domestication and are more dependent on cow milk. Sickle cell anemia, which may provide increased resistance to malaria, is frequent in populations where malaria is endemic. Populations that have for a very long time inhabited specific climates tend to have developed specific phenotypes that are beneficial for those environments—Allen's rule, short stature and stocky build in cold regions, tall and lanky in hot regions, and with high lung capacities or other High-altitude adaptation in humans, adaptations at high altitudes. Some populations have evolved highly unique adaptations to very specific environmental conditions, such as those advantageous to ocean-dwelling lifestyles and freediving in the Bajau.
Human hair ranges in color from Red hair, red to blond to Brown hair, brown to Black hair, black, which is the most frequent. Hair color depends on the amount of melanin, with concentrations fading with increased age, leading to Grey hair, grey or even white hair. Skin color can range from Dark skin, darkest brown to Light skin, lightest peach, or even nearly white or colorless in cases of albinism. It tends to vary Clinal variation, clinally and generally correlates with the level of ultraviolet radiation in a particular geographic area, with darker skin mostly around the equator. Skin darkening may have evolved as protection against ultraviolet solar radiation. Light skin pigmentation protects against depletion of vitamin D, which requires sunlight to make. Human skin also has a capacity to darken (tan) in response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
There is biological variation in the human species—with traits such as blood type, genetic diseases, Human skull, cranial features, Human face, facial features, organ systems, eye color, hair color and hair texture, texture, Human height, height and Body shape, build, and Human skin color, skin color varying across the globe. The typical height of an adult human is between , although this varies significantly depending on sex, ethnic origin, and family bloodlines. Body size is partly determined by genes and is also significantly influenced by environmental factors such as diet (nutrition), diet, exercise, and sleep patterns.
There is evidence that populations have adapted genetically to various external factors. The genes that allow adult humans to Lactose tolerance, digest lactose are present in high frequencies in populations that have long histories of cattle domestication and are more dependent on cow milk. Sickle cell anemia, which may provide increased resistance to malaria, is frequent in populations where malaria is endemic. Populations that have for a very long time inhabited specific climates tend to have developed specific phenotypes that are beneficial for those environments—Allen's rule, short stature and stocky build in cold regions, tall and lanky in hot regions, and with high lung capacities or other High-altitude adaptation in humans, adaptations at high altitudes. Some populations have evolved highly unique adaptations to very specific environmental conditions, such as those advantageous to ocean-dwelling lifestyles and freediving in the Bajau.
Human hair ranges in color from Red hair, red to blond to Brown hair, brown to Black hair, black, which is the most frequent. Hair color depends on the amount of melanin, with concentrations fading with increased age, leading to Grey hair, grey or even white hair. Skin color can range from Dark skin, darkest brown to Light skin, lightest peach, or even nearly white or colorless in cases of albinism. It tends to vary Clinal variation, clinally and generally correlates with the level of ultraviolet radiation in a particular geographic area, with darker skin mostly around the equator. Skin darkening may have evolved as protection against ultraviolet solar radiation. Light skin pigmentation protects against depletion of vitamin D, which requires sunlight to make. Human skin also has a capacity to darken (tan) in response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation. There is relatively little variation between human geographical populations, and most of the variation that occurs is at the individual level. Much of human variation is continuous, often with no clear points of demarcation. Genetic data shows that no matter how population groups are defined, two people from the same population group are almost as different from each other as two people from any two different population groups. Dark-skinned populations that are found in Africa, Australia, and South Asia are not closely related to each other.
Genetic research has demonstrated that human populations native to the African continent are the most genetically diverse and genetic diversity decreases with migratory distance from Africa, possibly the result of Evolutionary bottleneck, bottlenecks during human migration. These non-African populations acquired new genetic inputs from local Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans, admixture with archaic populations and have much greater variation from Neanderthals and Denisovans than is found in Africa, though Neanderthal admixture into African populations may be underestimated. Furthermore, recent studies have found that populations in sub-Saharan Africa, and particularly West Africa, have ancestral genetic variation which predates modern humans and has been lost in most non-African populations. Some of this ancestry is thought to originate from admixture with an Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans#Archaic African hominins, unknown archaic hominin that diverged before the split of Neanderthals and modern humans.
Humans are a Gonochorism, gonochoric species, meaning they are divided into male and female sexes. The greatest degree of genetic Sex differences in humans, variation exists between males and females. While the nucleotide diversity, nucleotide genetic variation of individuals of the same sex across global populations is no greater than 0.1%–0.5%, the genetic difference between Man, males and woman, females is between 1% and 2%. Males on average are 15% heavier and taller than females. On average, men have about 40–50% more upper body strength and 20–30% more lower body strength than women at the same weight, due to higher amounts of muscle and larger muscle fibers. Women generally have a higher
There is relatively little variation between human geographical populations, and most of the variation that occurs is at the individual level. Much of human variation is continuous, often with no clear points of demarcation. Genetic data shows that no matter how population groups are defined, two people from the same population group are almost as different from each other as two people from any two different population groups. Dark-skinned populations that are found in Africa, Australia, and South Asia are not closely related to each other.
Genetic research has demonstrated that human populations native to the African continent are the most genetically diverse and genetic diversity decreases with migratory distance from Africa, possibly the result of Evolutionary bottleneck, bottlenecks during human migration. These non-African populations acquired new genetic inputs from local Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans, admixture with archaic populations and have much greater variation from Neanderthals and Denisovans than is found in Africa, though Neanderthal admixture into African populations may be underestimated. Furthermore, recent studies have found that populations in sub-Saharan Africa, and particularly West Africa, have ancestral genetic variation which predates modern humans and has been lost in most non-African populations. Some of this ancestry is thought to originate from admixture with an Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans#Archaic African hominins, unknown archaic hominin that diverged before the split of Neanderthals and modern humans.
Humans are a Gonochorism, gonochoric species, meaning they are divided into male and female sexes. The greatest degree of genetic Sex differences in humans, variation exists between males and females. While the nucleotide diversity, nucleotide genetic variation of individuals of the same sex across global populations is no greater than 0.1%–0.5%, the genetic difference between Man, males and woman, females is between 1% and 2%. Males on average are 15% heavier and taller than females. On average, men have about 40–50% more upper body strength and 20–30% more lower body strength than women at the same weight, due to higher amounts of muscle and larger muscle fibers. Women generally have a higher body fat
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular en ...
percentage than men. Women have Human skin color#Sexual dimorphism, lighter skin than men of the same population; this has been explained by a higher need for vitamin D in females during pregnancy and lactation. As there are chromosomal differences between females and males, some X and Y chromosome-related conditions and Disease, disorders only affect either men or women. After allowing for body weight and volume, the male voice is usually an octave deeper than the female voice. Women have a Sex differences in longevity, longer life span in almost every population around the world.
Psychology
 The human brain, the focal point of the central nervous system in humans, controls the peripheral nervous system. In addition to controlling "lower," involuntary, or primarily autonomic nervous system, autonomic activities such as respiration (physiology), respiration and digestion, it is also the locus of "higher" order functioning such as
The human brain, the focal point of the central nervous system in humans, controls the peripheral nervous system. In addition to controlling "lower," involuntary, or primarily autonomic nervous system, autonomic activities such as respiration (physiology), respiration and digestion, it is also the locus of "higher" order functioning such as thought
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to conscious cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, a ...
, reasoning, and abstraction. These mental function, cognitive processes constitute the mind, and, along with their behavioral consequences, are studied in the field of psychology.
Humans have a larger and more developed prefrontal cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46, ...
than other primates, the region of the brain associated with higher cognition. This has led humans to proclaim themselves to be more intelligence, intelligent than any other known species. Objectively defining intelligence is difficult, with other animals adapting senses and excelling in areas that humans are unable to.
There are some traits that, although not strictly unique, do set humans apart from other animals. Humans may be the only animals who have episodic memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred ...
and who can engage in "mental time travel#Evolution and human uniqueness, mental time travel". Even compared with other social animals, humans have an unusually high degree of flexibility in their facial expressions. Humans are the only animals known to cry emotional tears. Humans are one of the few animals able to self-recognize in mirror tests and there is also debate over to what extent humans are the only animals with a theory of mind
In psychology, theory of mind refers to the capacity to understand other people by ascribing mental states to them (that is, surmising what is happening in their mind). This includes the knowledge that others' mental states may be different fro ...
.
Sleep and dreaming
Humans are generally diurnal. The average sleep requirement is between seven and nine hours per day for an adult and nine to ten hours per day for a child; elderly people usually sleep for six to seven hours. Having less sleep than this is common among humans, even though sleep deprivation can have negative health effects. A sustained restriction of adult sleep to four hours per day has been shown to correlate with changes in physiology and mental state, including reduced memory, fatigue, aggression, and bodily discomfort. During sleep humans dream, where they experience sensory images and sounds. Dreaming is stimulated by the pons and mostly occurs during the REM phase of sleep. The length of a dream can vary, from a few seconds up to 30 minutes. Humans have three to five dreams per night, and some may have up to seven; however most dreams are immediately or quickly forgotten. They are more likely to remember the dream if awakened during the REM phase. The events in dreams are generally outside the control of the dreamer, with the exception of lucid dreaming, where the dreamer is self-aware. Dreams can at times make a Creativity, creative thought occur or give a sense of Artistic inspiration, inspiration.Consciousness and thought
Human consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience or awareness of internal or external existence. Despite centuries of analyses, definitions, explanations and debates by philosophers and scientists, consciousness remains puzzling and controversial, being "at once the most familiar and most mysterious aspect of our lives". The only widely agreed notion about the topic is the intuition that it exists. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied and explained as consciousness. Some philosophers divide consciousness into phenomenal consciousness, which is sensory experience itself, and access consciousness, which can be used for reasoning or directly controlling actions. It is sometimes synonymous with 'the mind', and at other times, an aspect of it. Historically it is associated withintrospection
Introspection is the examination of one's own conscious thoughts and feelings. In psychology, the process of introspection relies on the observation of one's mental state, while in a spiritual context it may refer to the examination of one's s ...
, private thought
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to conscious cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, a ...
, imagination
Imagination is the production or simulation of novel objects, sensations, and ideas in the mind without any immediate input of the senses. Stefan Szczelkun characterises it as the forming of experiences in one's mind, which can be re-creations ...
and volition. It now often includes some kind of experience, cognition, feeling or perception. It may be 'awareness', or 'Meta-cognition, awareness of awareness', or self-awareness
In philosophy of self, self-awareness is the experience of one's own personality or individuality. It is not to be confused with consciousness in the sense of qualia. While consciousness is being aware of one's environment and body and lifesty ...
. There might be different levels or Higher-order theories of consciousness, orders of consciousness, or different kinds of consciousness, or just one kind with different features.
The process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses is known as cognition. The human brain perception, perceives the external world through the senses, and each individual human is influenced greatly by his or her experiences, leading to subjectivity, subjective views of existence
Existence is the ability of an entity to interact with reality. In philosophy, it refers to the ontology, ontological Property (philosophy), property of being.
Etymology
The term ''existence'' comes from Old French ''existence'', from Medieval ...
and the passage of time. The nature of thought is central to psychology and related fields. Cognitive psychology studies cognition, the mental function, mental processes underlying behavior. Largely focusing on the development of the human mind through the life span, developmental psychology seeks to understand how people come to perceive, understand, and act within the world and how these processes change as they age. This may focus on intellectual, cognitive, neural, social, or moral development. Psychologists have developed intelligence tests and the concept of intelligence quotient in order to assess the relative intelligence of human beings and study its Distribution (mathematics), distribution among population.
Motivation and emotion
 Human motivation is not yet wholly understood. From a psychological perspective, Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a well-established theory that can be defined as the process of satisfying certain needs in ascending order of complexity. From a more general, philosophical perspective, human motivation can be defined as a commitment to, or withdrawal from, various goals requiring the application of human ability. Furthermore, incentive and preference are both factors, as are any perceived links between incentives and preferences. Volition (psychology), Volition may also be involved, in which case willpower is also a factor. Ideally, both motivation and volition ensure the selection, striving for, and Realisation (metrology), realization of goals in an optimal manner, a Function (biology), function beginning in childhood and continuing throughout a lifetime in a process known as socialization.
Emotions are biological states associated with the nervous system brought on by Neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or Suffering, displeasure. They are often Reciprocal influence, intertwined with Mood (psychology), mood, temperament, Personality psychology, personality, disposition, creativity, and motivation. Emotion has a significant influence on human behavior and their ability to learn. Acting on extreme or uncontrolled emotions can lead to social disorder and crime, with studies showing criminals may have a lower emotional intelligence than normal.
Emotional experiences perceived as pleasure, pleasant, such as joy, Interest (emotion), interest or contentment, contrast with those perceived as suffering, unpleasant, like anxiety, sadness, anger, and Depression (mood), despair. Happiness, or the state of being happy, is a human emotional condition. The definition of happiness is a common philosophical topic. Some define it as experiencing the feeling of positive Affect (psychology), emotional affects, while avoiding the negative ones. Others see it as an appraisal of life satisfaction or quality of life. Recent research suggests that being happy might involve experiencing some negative emotions when humans feel they are warranted.
Human motivation is not yet wholly understood. From a psychological perspective, Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a well-established theory that can be defined as the process of satisfying certain needs in ascending order of complexity. From a more general, philosophical perspective, human motivation can be defined as a commitment to, or withdrawal from, various goals requiring the application of human ability. Furthermore, incentive and preference are both factors, as are any perceived links between incentives and preferences. Volition (psychology), Volition may also be involved, in which case willpower is also a factor. Ideally, both motivation and volition ensure the selection, striving for, and Realisation (metrology), realization of goals in an optimal manner, a Function (biology), function beginning in childhood and continuing throughout a lifetime in a process known as socialization.
Emotions are biological states associated with the nervous system brought on by Neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or Suffering, displeasure. They are often Reciprocal influence, intertwined with Mood (psychology), mood, temperament, Personality psychology, personality, disposition, creativity, and motivation. Emotion has a significant influence on human behavior and their ability to learn. Acting on extreme or uncontrolled emotions can lead to social disorder and crime, with studies showing criminals may have a lower emotional intelligence than normal.
Emotional experiences perceived as pleasure, pleasant, such as joy, Interest (emotion), interest or contentment, contrast with those perceived as suffering, unpleasant, like anxiety, sadness, anger, and Depression (mood), despair. Happiness, or the state of being happy, is a human emotional condition. The definition of happiness is a common philosophical topic. Some define it as experiencing the feeling of positive Affect (psychology), emotional affects, while avoiding the negative ones. Others see it as an appraisal of life satisfaction or quality of life. Recent research suggests that being happy might involve experiencing some negative emotions when humans feel they are warranted.
Sexuality and love
 For humans, sexuality involves biological, erotic, Physical intimacy, physical, Emotional intimacy, emotional, social, or Spirituality, spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied with historical contexts over time, it lacks a precise definition. The biological and physical aspects of sexuality largely concern the Human reproduction, human reproductive functions, including the human sexual response cycle. Sexuality also affects and is affected by cultural, political, legal, philosophical, Morality, moral, ethical, and religious aspects of life. Sexual desire, or ''libido'', is a basic mental state present at the beginning of sexual behavior. Studies show that men desire sex more than women and Masturbation, masturbate more often.
Humans can fall anywhere along a continuous scale of sexual orientation, although most humans are heterosexual. While homosexuality, homosexual behavior Homosexual behavior in animals, occurs in some other animals, only humans and Sheep, domestic sheep have so far been found to exhibit exclusive preference for same-sex relationships. Most evidence supports nonsocial, biology and sexual orientation, biological causes of sexual orientation, as cultures that are very tolerant of homosexuality do not have significantly higher rates of it. Research in neuroscience and genetics suggests that other aspects of human sexuality are biologically influenced as well.
Love most commonly refers to a feeling of strong attraction or emotional Attachment (psychology), attachment. It can be impersonal (the love of an object, ideal, or strong political or spiritual connection) or interpersonal (love between humans). When in love dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin and other chemicals stimulate the brain's pleasure center, leading to side effects such as increased heart rate, loss of Anorexia (symptom), appetite and Insomnia, sleep, and an Euphoria, intense feeling of excitement.
For humans, sexuality involves biological, erotic, Physical intimacy, physical, Emotional intimacy, emotional, social, or Spirituality, spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied with historical contexts over time, it lacks a precise definition. The biological and physical aspects of sexuality largely concern the Human reproduction, human reproductive functions, including the human sexual response cycle. Sexuality also affects and is affected by cultural, political, legal, philosophical, Morality, moral, ethical, and religious aspects of life. Sexual desire, or ''libido'', is a basic mental state present at the beginning of sexual behavior. Studies show that men desire sex more than women and Masturbation, masturbate more often.
Humans can fall anywhere along a continuous scale of sexual orientation, although most humans are heterosexual. While homosexuality, homosexual behavior Homosexual behavior in animals, occurs in some other animals, only humans and Sheep, domestic sheep have so far been found to exhibit exclusive preference for same-sex relationships. Most evidence supports nonsocial, biology and sexual orientation, biological causes of sexual orientation, as cultures that are very tolerant of homosexuality do not have significantly higher rates of it. Research in neuroscience and genetics suggests that other aspects of human sexuality are biologically influenced as well.
Love most commonly refers to a feeling of strong attraction or emotional Attachment (psychology), attachment. It can be impersonal (the love of an object, ideal, or strong political or spiritual connection) or interpersonal (love between humans). When in love dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin and other chemicals stimulate the brain's pleasure center, leading to side effects such as increased heart rate, loss of Anorexia (symptom), appetite and Insomnia, sleep, and an Euphoria, intense feeling of excitement.
Culture
Humanity's unprecedented set of intellectual skills were a key factor in the species' eventual technological advancement and concomitant domination of the biosphere. Disregarding extinct hominids, humans are the only animals known to teach generalizable information, innately deploy recursive embedding to generate and communicate complex concepts, engage in the "folk physics" required for competent tool design, or cook food in the wild. Teaching and learning preserves the cultural and ethnographic identity of human societies. Other traits and behaviors that are mostly unique to humans include starting fires, phoneme structuring and vocal learning.Language
While many species animal communication, communicate,language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
is unique to humans, a defining feature of humanity, and a cultural universal. Unlike the limited systems of other animals, human language is open—an infinite number of meanings can be produced by combining a limited number of symbols. Human language also has the capacity of Displacement (linguistics), displacement, using words to represent things and happenings that are not presently or locally occurring but reside in the shared imagination of interlocutors.
Language differs from other forms of communication in that it is Origin of speech#Modality-independence, modality independent; the same meanings can be conveyed through different media, audibly in speech, visually by sign language or writing, and through tactile media such as braille. Language is central to the communication between humans, and to the sense of identity that unites nations, cultures and ethnic groups. There are approximately six thousand different languages currently in use, including sign languages, and many thousands more that are extinct language, extinct.
The arts
Human arts can take many forms including Visual arts, visual, Literary arts, literary and Performing arts, performing. Visual art can range from paintings and sculptures to film, interaction design andarchitecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
. Literary arts can include prose, poetry and dramas; while the performing arts generally involve theatre, music and dance. Humans often combine the different forms (for example, music videos). Other entities that have been described as having artistic qualities include Culinary arts, food preparation, Video games as an art form, video games and medicine. As well as providing entertainment and transferring knowledge, the arts are also used for The arts and politics, political purposes.  Art is a defining characteristic of humans and there is evidence for a relationship between creativity and language. The earliest evidence of art was shell engravings made by ''Homo erectus'' 300,000 years before modern humans evolved. Art attributed to ''H. sapiens'' existed at least 75,000 years ago, with jewellery and drawings found in caves in South Africa. There are various hypotheses as to why humans have Adaptation, adapted to the arts. These include allowing them to better problem solve issues, providing a means to control or influence other humans, encouraging cooperation and contribution within a society or increasing the chance of attracting a potential mate. The use of imagination developed through art, combined with logic may have given early humans an evolutionary advantage.
Evidence of humans engaging in musical activities predates cave art and so far music has been Cultural universal, practiced by virtually all known human cultures. There exists a wide variety of music genres and ethnic musics; with humans' musical abilities being related to other abilities, including complex social human behaviours. It has been shown that human brains respond to music by becoming synchronized with the rhythm and beat, a process called Entrainment (biomusicology), entrainment. Dance is also a form of human expression found in all cultures and may have evolved as a way to help early humans communicate. Listening to music and observing dance stimulates the orbitofrontal cortex and other pleasure sensing areas of the brain.
Unlike speaking, reading and writing does not come naturally to humans and must be taught. Still, literature has been present before the invention of words and language, with 30,000-year-old paintings on walls inside some caves portraying a series of dramatic scenes. One of the oldest surviving works of literature is the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', first engraved on ancient
Art is a defining characteristic of humans and there is evidence for a relationship between creativity and language. The earliest evidence of art was shell engravings made by ''Homo erectus'' 300,000 years before modern humans evolved. Art attributed to ''H. sapiens'' existed at least 75,000 years ago, with jewellery and drawings found in caves in South Africa. There are various hypotheses as to why humans have Adaptation, adapted to the arts. These include allowing them to better problem solve issues, providing a means to control or influence other humans, encouraging cooperation and contribution within a society or increasing the chance of attracting a potential mate. The use of imagination developed through art, combined with logic may have given early humans an evolutionary advantage.
Evidence of humans engaging in musical activities predates cave art and so far music has been Cultural universal, practiced by virtually all known human cultures. There exists a wide variety of music genres and ethnic musics; with humans' musical abilities being related to other abilities, including complex social human behaviours. It has been shown that human brains respond to music by becoming synchronized with the rhythm and beat, a process called Entrainment (biomusicology), entrainment. Dance is also a form of human expression found in all cultures and may have evolved as a way to help early humans communicate. Listening to music and observing dance stimulates the orbitofrontal cortex and other pleasure sensing areas of the brain.
Unlike speaking, reading and writing does not come naturally to humans and must be taught. Still, literature has been present before the invention of words and language, with 30,000-year-old paintings on walls inside some caves portraying a series of dramatic scenes. One of the oldest surviving works of literature is the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', first engraved on ancient Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
n tablets about 4,000 years ago. Beyond simply passing down knowledge, the use and sharing of imaginative fiction through stories might have helped develop humans' capabilities for communication and increased the likelihood of securing a mate. Storytelling may also be used as a way to provide the audience with moral lessons and encourage cooperation.
Tools and technologies
 Stone tools were used by proto-humans at least 2.5 million years ago. The use and manufacture of tools has been put forward as the ability that defines humans more than anything else and has historically been seen as an important evolutionary step. The technology became much more sophisticated about 1.8 million years ago, with the Control of fire by early humans, controlled use of fire beginning around 1 million years ago. The wheel and wheeled vehicles appeared simultaneously in several regions some time in the fourth millennium BC. The development of more complex tools and technologies allowed land to be Arable land, cultivated and animals to be Domestication, domesticated, thus proving essential in the development of
Stone tools were used by proto-humans at least 2.5 million years ago. The use and manufacture of tools has been put forward as the ability that defines humans more than anything else and has historically been seen as an important evolutionary step. The technology became much more sophisticated about 1.8 million years ago, with the Control of fire by early humans, controlled use of fire beginning around 1 million years ago. The wheel and wheeled vehicles appeared simultaneously in several regions some time in the fourth millennium BC. The development of more complex tools and technologies allowed land to be Arable land, cultivated and animals to be Domestication, domesticated, thus proving essential in the development of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
—what is known as the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
.
China developed paper, the printing press, gunpowder, the compass and List of Chinese inventions, other important inventions. The continued improvements in smelting allowed forging of copper, bronze, iron and eventually steel, which is used in railways, skyscrapers and many other products. This coincided with the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, where the invention of automated machines brought major changes to humans' lifestyles. Modern technology is observed as Accelerating change, progressing exponentially, with major innovations in the 20th century including: Electricity generation, electricity, penicillin, semiconductors, internal combustion engines, the Internet, Fertilizer, nitrogen fixing fertilisers, airplanes, computers, Car, automobiles, Combined oral contraceptive pill, contraceptive pills, nuclear fission, the Green Revolution, green revolution, radio, scientific plant breeding, rockets, air conditioning, television and the assembly line.
Religion and spirituality
 Religion is generally defined as a belief system concerning the supernatural, sacred or divinity, divine, and practices, values, institutions and
Religion is generally defined as a belief system concerning the supernatural, sacred or divinity, divine, and practices, values, institutions and ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized, b ...
s associated with such belief. Some religions also have a moral code. The Evolutionary psychology of religion, evolution and the history of the Evolutionary origin of religions, first religions have recently become areas of active scientific investigation. While the exact time when humans first became religious remains unknown, research shows credible evidence of religious behaviour from around the Middle Paleolithic era (45-200 Tya (unit), thousand years ago). It may have evolved to play a role in helping enforce and encourage cooperation between humans.
There is no accepted academic definition of what constitutes religion. Religion has taken on many forms that vary by culture and individual perspective in alignment with the geographic, social, and linguistic diversity of the planet. Religion can include a belief in life after death (commonly involving belief in an afterlife), the origin of life, the nature of the universe (religious cosmology) and its ultimate fate (eschatology), and what is morality, moral or immoral. A common source for answers to these questions are beliefs in transcendence (religion), transcendent divine beings such as deities or a singular God, although not all religions are theistic.
Although the exact level of religiosity can be hard to measure, a majority of humans profess some variety of religious or spiritual belief. In 2015 the plurality were Christians, Christian followed by Muslims, Hindus and Buddhism, Buddhists. As of 2015, about 16%, or slightly under 1.2 billion humans, were irreligious, including those with no religious beliefs or no identity with any religion.
Science and philosophy
 An aspect unique to humans is their ability to Knowledge transfer, transmit knowledge from one generation to the next and to continually build on this information to develop tools, scientific laws and other advances to pass on further. This accumulated knowledge can be tested to answer questions or make predictions about how the universe functions and has been very successful in advancing human ascendancy. Aristotle has been described as the first scientist, and preceded the rise of scientific thought through the Hellenistic period. Other early advances in science came from the Science and technology of the Han dynasty, Han Dynasty in China and during the
An aspect unique to humans is their ability to Knowledge transfer, transmit knowledge from one generation to the next and to continually build on this information to develop tools, scientific laws and other advances to pass on further. This accumulated knowledge can be tested to answer questions or make predictions about how the universe functions and has been very successful in advancing human ascendancy. Aristotle has been described as the first scientist, and preceded the rise of scientific thought through the Hellenistic period. Other early advances in science came from the Science and technology of the Han dynasty, Han Dynasty in China and during the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
. The Scientific Revolution, scientific revolution, near the end of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, led to the emergence of modern science.
A chain of events and influences led to the development of the scientific method, a process of observation and experimentation that is used to differentiate science from pseudoscience. An understanding of mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
is unique to humans, although other species of animals have some numerical cognition. All of science can be divided into three major branches, the formal sciences (e.g., logic and mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
), which are concerned with formal systems, the applied sciences (e.g., engineering, medicine), which are focused on practical applications, and the empirical sciences, which are based on empirical observation and are in turn divided into natural sciences (e.g., physics, chemistry, biology) and social sciences (e.g., psychology, economics, sociology).
Philosophy is a field of study where humans seek to understand fundamental truths about themselves and the world in which they live. Philosophical inquiry has been a major feature in the development of humans' intellectual history. It has been described as the "no man's land" between definitive scientific knowledge and dogmatic religious teachings. Philosophy relies on reason and evidence, unlike religion, but does not require the empirical observations and experiments provided by science. Major fields of philosophy include metaphysics, epistemology, Logic (philosophy), logic, and axiology (which includes ethics and aesthetics).
Society
 Society is the system of organizations and institutions arising from interaction between humans. Humans are highly social and tend to live in large complex social groups. They can be divided into different groups according to their income, wealth, power (social and political), power, reputation and other factors. The structure of social stratification and the degree of social mobility differs, especially between modern and traditional societies. Human groups range from the size of Family, families to nations. The first form of human social organization is thought to have resembled
Society is the system of organizations and institutions arising from interaction between humans. Humans are highly social and tend to live in large complex social groups. They can be divided into different groups according to their income, wealth, power (social and political), power, reputation and other factors. The structure of social stratification and the degree of social mobility differs, especially between modern and traditional societies. Human groups range from the size of Family, families to nations. The first form of human social organization is thought to have resembled hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
Band society, band societies.
Gender
Human societies typically exhibit Gender identity, gender identities and gender roles that distinguish between Masculinity, masculine and Femininity, feminine characteristics and prescribe the range of acceptable behaviours and attitudes for their members based on their sex. The most common categorisation is a gender binary of men and women. Many societies recognise a third gender, or less commonly a fourth or fifth. In some other societies, Non-binary gender, non-binary is used as an umbrella term for a range of gender identities that are not solely male or female. Gender roles are often associated with a division of social norm, norms, practice (social theory), practices, clothing, dress, social behavior, behavior, rights, duty, duties, Privilege (social inequality), privileges, social status, status, and power (social and political), power, with men enjoying more rights and privileges than women in most societies, both today and in the past. As a Social constructionism, social construct, gender roles are not fixed and vary historically within a society. Challenges to predominant gender norms have recurred in many societies. Little is known about gender roles in the earliest human societies. Early modern humans probably had a range of gender roles similar to that of modern cultures from at least the Upper Paleolithic, while theNeanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While th ...
s were less sexually dimorphic and there is evidence that the behavioural difference between males and females was minimal.
Kinship
All human societies organize, recognize and classify types of social relationships based on relations between parents, children and other descendants (consanguinity), and relations through marriage (Affinity (law), affinity). There is also a third type applied to godparents or Adoption, adoptive children (Fictive kinship, fictive). These culturally defined relationships are referred to as kinship. In many societies, it is one of the most important social organizing principles and plays a role in transmitting status and inheritance. All societies have rules of incest taboo, according to which marriage between certain kinds of kin relations are prohibited, and some also have rules of preferential marriage with certain kin relations.Ethnicity
Human ethnic groups are a social category that Identity (social science), identifies together as a group based on shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. These can be a common set of traditions, ancestry,language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
, history, society
A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Socie ...
, culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
, nation, religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, ...
, or social treatment within their residing area. Ethnicity is separate from the concept of Race (human categorization), race, which is based on physical characteristics, although both are socially constructed. Assigning ethnicity to a certain population is complicated, as even within common ethnic designations there can be a diverse range of subgroups, and the makeup of these ethnic groups can change over time at both the collective and individual level. Also, there is no generally accepted definition of what constitutes an ethnic group. Ethnic groupings can play a powerful role in the social identity and solidarity of ethnopolitical units. This has been closely tied to the rise of the nation state as the predominant form of political organization in the 19th and 20th centuries.
Government and politics
As farming populations gathered in larger and denser communities, interactions between these different groups increased. This led to the development of governance within and between the communities. Humans have evolved the ability to change affiliation with various social groups relatively easily, including previously strong political alliances, if doing so is seen as providing personal advantages. This cognitive flexibility allows individual humans to change their political ideologies, with those with higher flexibility less likely to support authoritarian and nationalistic stances. Governments create laws and policies that affect the citizens that they govern. There have been List of forms of government, many forms of government throughout human history, each having various means of obtaining power and the ability to exert diverse controls on the population. As of 2017, more than half of all national governments are democracy, democracies, with 13% being autocracy, autocracies and 28% containing elements of both. Many countries have formed Intergovernmental organization, international political organizations and alliances, the largest being the United Nations with 193 member states.Trade and economics
 Trade, the voluntary exchange of goods and services, is seen as a characteristic that differentiates humans from other animals and has been cited as a practice that gave ''Homo sapiens'' a major advantage over other hominids. Evidence suggests early ''H. sapiens'' made use of long-distance trade routes to exchange goods and ideas, leading to cultural explosions and providing additional food sources when hunting was sparse, while such trade networks did not exist for the now extinct Neanderthals. Early trade likely involved materials for creating tools like obsidian. The first truly international trade routes were around the spice trade through the Roman and medieval periods.
Early human Economy, economies were more likely to be based around Gift economy, gift giving instead of a bartering system. Early money consisted of Commodity money, commodities; the oldest being in the form of cattle and the most widely used being cowrie shells. Money has since evolved into governmental issued coins, Paper money, paper and electronic money. Human study of economics is a social science that looks at how societies distribute scarce resources among different people. There are massive Economic inequality, inequalities in the division of wealth among humans; the eight richest humans are worth the same monetary value as the poorest half of all the human population.
Trade, the voluntary exchange of goods and services, is seen as a characteristic that differentiates humans from other animals and has been cited as a practice that gave ''Homo sapiens'' a major advantage over other hominids. Evidence suggests early ''H. sapiens'' made use of long-distance trade routes to exchange goods and ideas, leading to cultural explosions and providing additional food sources when hunting was sparse, while such trade networks did not exist for the now extinct Neanderthals. Early trade likely involved materials for creating tools like obsidian. The first truly international trade routes were around the spice trade through the Roman and medieval periods.
Early human Economy, economies were more likely to be based around Gift economy, gift giving instead of a bartering system. Early money consisted of Commodity money, commodities; the oldest being in the form of cattle and the most widely used being cowrie shells. Money has since evolved into governmental issued coins, Paper money, paper and electronic money. Human study of economics is a social science that looks at how societies distribute scarce resources among different people. There are massive Economic inequality, inequalities in the division of wealth among humans; the eight richest humans are worth the same monetary value as the poorest half of all the human population.
Conflict
Humans commit violence on other humans at a rate comparable to other primates, but have an increased preference for killing adults, Infanticide (zoology), infanticide being more common among other primates. It is predicted that 2% of early ''H. sapiens'' would be murdered, rising to 12% during the medieval period, before dropping to below 2% in modern times. There is great variation in violence between human populations with rates of homicide in societies that have legal systems and strong cultural attitudes against violence at about 0.01%. The willingness of humans to kill other members of their species en masse through organized conflict (i.e., war) has long been the subject of debate. One school of thought holds that war evolved as a means to eliminate competitors, and has always been an innate human characteristic. Another suggests that war is a relatively recent phenomenon and has appeared due to changing social conditions. While not settled, current evidence indicates warlike predispositions only became common about 10,000 years ago, and in many places much more recently than that. War has had a high cost on human life; it is estimated that during the 20th century, between 167 million and 188 million people died as a result of war.See also
* * * List of human evolution fossilsNotes
References
External links
{{Authority control, state=expanded Humans, Apex predators Articles containing video clips Mammals described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Tool-using mammals