Human Sense on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

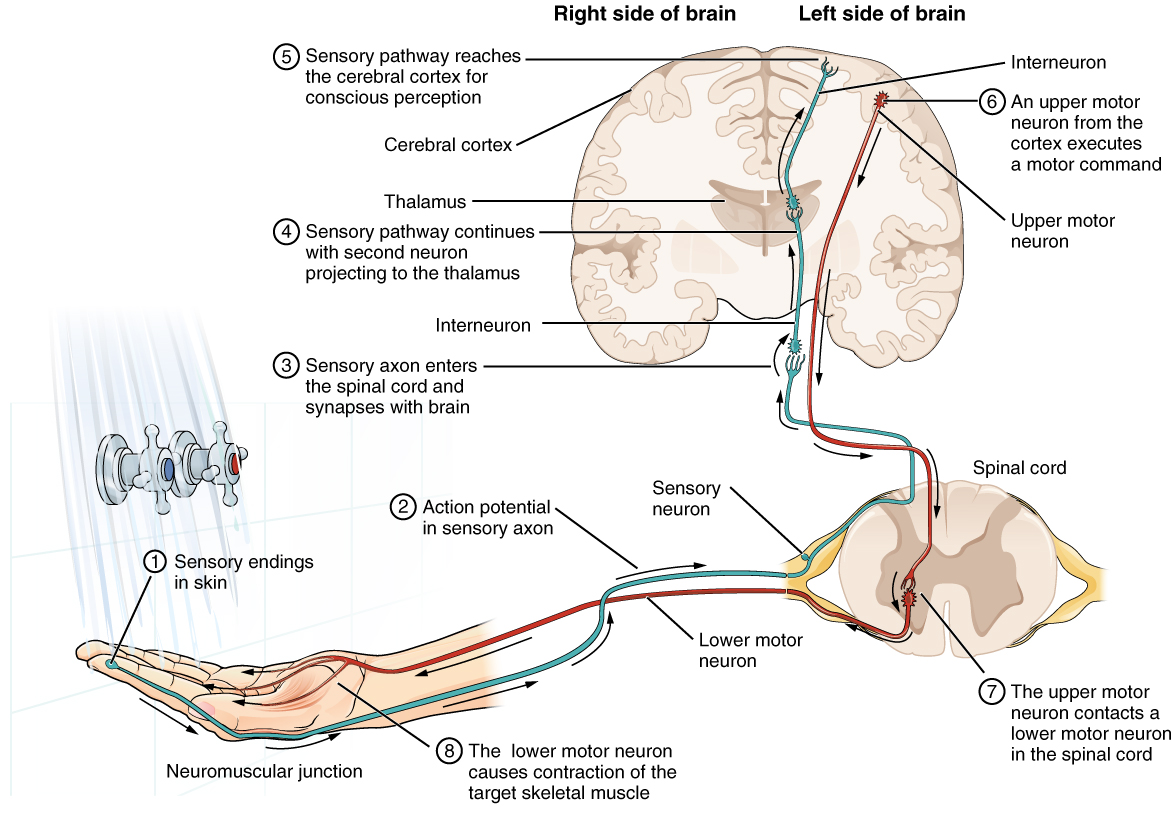 The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing
Experiencing Sensation and Perception
'. Pearson Education, Limited, 2009. p. 12.3 * The end-bulb of Krause, or




 *
*

 The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sensory
Sensory may refer to:
Biology
* Sensory ecology, how organisms obtain information about their environment
* Sensory neuron, nerve cell responsible for transmitting information about external stimuli
* Sensory perception, the process of acquiri ...
information. A sensory system consists of sensory neurons (including the sensory receptor cells), neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved in sensory perception. Commonly recognized sensory systems are those for vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell
Smell may refer to;
* Odor, airborne molecules perceived as a scent or aroma
* Sense of smell, the scent also known scientifically as olfaction
* "Smells" (''Bottom''), an episode of ''Bottom''
* The Smell, a music venue in Los Angeles, Californ ...
, and balance. Senses are transducers from the physical world to the realm of the mind where people interpret the information, creating their perception of the world around them.
The receptive field is the area of the body or environment to which a receptor organ and receptor cells respond. For instance, the part of the world an eye can see, is its receptive field; the light that each rod
Rod, Ror, Ród, Rőd, Rød, Röd, ROD, or R.O.D. may refer to:
Devices
* Birch rod, made out of twigs from birch or other trees for corporal punishment
* Ceremonial rod, used to indicate a position of authority
* Connecting rod, main, coupling, ...
or cone can see, is its receptive field. Receptive fields have been identified for the visual system, auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.
System overview
The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, increasin ...
and somatosensory system.
Stimulus
:Organisms need information to solve at least three kinds of problems: (a) to maintain an appropriate environment, i.e., homeostasis; (b) to time activities (e.g., seasonal changes in behavior) or synchronize activities with those ofconspecifics
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species.
Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organis ...
; and (c) to locate and respond to resources or threats (e.g., by moving towards resources or evading or attacking threats). Organisms also need to transmit information in order to influence another's behavior: to identify themselves, warn conspecifics of danger, coordinate activities, or deceive.
Sensory systems code for four aspects of a stimulus; type (modality
Modality may refer to:
Humanities
* Modality (theology), the organization and structure of the church, as distinct from sodality or parachurch organizations
* Modality (music), in music, the subject concerning certain diatonic scales
* Modalitie ...
), intensity, location, and duration. Arrival time of a sound pulse and phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
* Phase space, a mathematic ...
differences of continuous sound are used for sound localization. Certain receptors are sensitive to certain types of stimuli (for example, different mechanoreceptor
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are innervated by sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals that, in animals, ...
s respond best to different kinds of touch stimuli, like sharp or blunt objects). Receptors send impulses in certain patterns to send information about the intensity of a stimulus (for example, how loud a sound is). The location of the receptor that is stimulated gives the brain information about the location of the stimulus (for example, stimulating a mechanoreceptor in a finger will send information to the brain about that finger). The duration of the stimulus (how long it lasts) is conveyed by firing patterns of receptors. These impulses are transmitted to the brain through afferent neurons
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded potentials. This process is called sensory transduction. The cel ...
.
Quiescent state
Most sensory systems have a quiescent state, that is, the state that a sensory system converges to when there is no input. This is well-defined for alinear time-invariant system
In system analysis, among other fields of study, a linear time-invariant (LTI) system is a system that produces an output signal from any input signal subject to the constraints of linearity and time-invariance; these terms are briefly define ...
, whose input space is a vector space, and thus by definition has a point of zero. It is also well-defined for any passive sensory system, that is, a system that operates without needing input power. The quiescent state is the state the system converges to when there is no input power.
It is not always well-defined for nonlinear, nonpassive sensory organs, since they can't function without input energy. For example, a cochlea is not a passive organ, but actively vibrates its own sensory hairs to improve its sensitivity. This manifests as otoacoustic emissions in healthy ears, and tinnitus in pathological ears. There is still a quiescent state for the cochlea, since there is a well-defined mode of power input that it receives (vibratory energy on the eardrum), which provides an unambiguous definition of "zero input power".
Some sensory systems can have multiple quiescent states depending on its history, like flip-flops, and magnetic material with hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of ...
. It can also adapt to different quiescent states. In complete darkness, the retinal cells become extremely sensitive, and there is noticeable " visual snow" caused by the retinal cells firing randomly without any light input. In brighter light, the retinal cells become a lot less sensitive, and consequently visual noise decreases.
Quiescent state is less well-defined when the sensory organ can be controlled by other systems, like a dog's ears that turn towards the front or the sides as the brain commands. Some spiders can use their nets as a large touch-organ, like weaving a skin for themselves. Even in the absence of anything falling on the net, hungry spiders may increase web thread tension, so as to respond promptly even to usually less noticeable, and less profitable prey, such as small fruit flies, creating two different "quiescent states" for the net.
Things become completely ill-defined for a system which connects its output to its own input, thus ever-moving without any external input. The prime example is the brain, with its default mode network
In neuroscience, the default mode network (DMN), also known as the default network, default state network, or anatomically the medial frontoparietal network (M-FPN), is a large-scale brain network primarily composed of the dorsal medial prefro ...
.
Senses and receptors
While debate exists among neurologists as to the specific number of senses due to differing definitions of what constitutes a sense, Gautama Buddha and Aristotle classified five ‘traditional’ human senses which have become universally accepted: touch, taste,smell
Smell may refer to;
* Odor, airborne molecules perceived as a scent or aroma
* Sense of smell, the scent also known scientifically as olfaction
* "Smells" (''Bottom''), an episode of ''Bottom''
* The Smell, a music venue in Los Angeles, Californ ...
, sight, and hearing. Other senses that have been well-accepted in most mammals, including humans, include nociception
Nociception (also nocioception, from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, co ...
, equilibrioception, kinaesthesia, and thermoception. Furthermore, some nonhuman animals have been shown to possess alternate senses, including magnetoreception
Magnetoreception is a sense which allows an organism to detect the Earth's magnetic field. Animals with this sense include some arthropods, molluscs, and vertebrates (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, though not humans). The se ...
and electroreception.
Receptors
The initialization of sensation stems from the response of a specific receptor to a physical stimulus. The receptors which react to the stimulus and initiate the process of sensation are commonly characterized in four distinct categories: chemoreceptors, photoreceptors,mechanoreceptors
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are innervated by sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals that, in animals, a ...
, and thermoreceptors. All receptors receive distinct physical stimuli and transduce the signal into an electrical action potential. This action potential then travels along afferent neurons
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded potentials. This process is called sensory transduction. The cel ...
to specific brain regions where it is processed and interpreted.
Chemoreceptors
Chemoreceptors, or chemosensors, detect certain chemical stimuli and transduce that signal into an electrical action potential. The two primary types of chemoreceptors are: * Distance chemoreceptors are integral to receiving stimuli in gases in the olfactory system through both olfactory receptor neurons and neurons in the vomeronasal organ. * Direct chemoreceptors that detect stimuli in liquids include the taste buds in the gustatory system as well as receptors in theaortic bodies
The aortic bodies are one of several small clusters of peripheral chemoreceptors located along the aortic arch. They are important in measuring partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, and blood pH.
Structure
The aortic bodies ...
which detect changes in oxygen concentration.
Photoreceptors
Photoreceptors are capable ofphototransduction Visual phototransduction is the transduction (physiology), sensory transduction process of the visual system by which light is detected to yield Action potential, nerve impulses in the rod cells and cone cells in the retina of the eye in humans and ...
, a process which converts light ( electromagnetic radiation) into, among other types of energy, a membrane potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges ...
. The three primary types of photoreceptors are:
Cones are photoreceptors which respond significantly to color. In humans the three different types of cones correspond with a primary response to short wavelength (blue), medium wavelength (green), and long wavelength (yellow/red)."eye, human." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2010.
Rods are photoreceptors which are very sensitive to the intensity of light, allowing for vision in dim lighting. The concentrations and ratio of rods to cones is strongly correlated with whether an animal is diurnal or nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sens ...
. In humans rods outnumber cones by approximately 20:1, while in nocturnal animals, such as the tawny owl, the ratio is closer to 1000:1.
Ganglion Cells reside in the adrenal medulla
The adrenal medulla ( la, medulla glandulae suprarenalis) is part of the adrenal gland. It is located at the center of the gland, being surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It is the innermost part of the adrenal gland, consisting of chromaffin cel ...
and retina where they are involved in the sympathetic response. Of the ~1.3 million ganglion cells present in the retina, 1-2% are believed to be photosensitive ganglia. These photosensitive ganglia play a role in conscious vision for some animals, and are believed to do the same in humans.
Mechanoreceptors
Mechanoreceptors are sensory receptors which respond to mechanical forces, such as pressure or distortion. While mechanoreceptors are present in hair cells and play an integral role in the vestibular andauditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.
System overview
The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, increasin ...
s, the majority of mechanoreceptors are cutaneous and are grouped into four categories:
* ''Slowly adapting type 1 receptors'' have small receptive fields and respond to static stimulation. These receptors are primarily used in the sensations of form
Form is the shape, visual appearance, or configuration of an object. In a wider sense, the form is the way something happens.
Form also refers to:
*Form (document), a document (printed or electronic) with spaces in which to write or enter data
...
and roughness.
* ''Slowly adapting type 2 receptors'' have large receptive fields and respond to stretch. Similarly to type 1, they produce sustained responses to a continued stimuli.
* ''Rapidly adapting receptors'' have small receptive fields and underlie the perception of slip.
* ''Pacinian receptors'' have large receptive fields and are the predominant receptors for high-frequency vibration.
Thermoreceptors
Thermoreceptors are sensory receptors which respond to varying temperatures. While the mechanisms through which these receptors operate is unclear, recent discoveries have shown thatmammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s have at least two distinct types of thermoreceptors:Krantz, John. Experiencing Sensation and Perception
'. Pearson Education, Limited, 2009. p. 12.3 * The end-bulb of Krause, or
bulboid corpuscle
The bulboid corpuscles (end-bulbs of Krause) are cutaneous receptors in the human body.
The end-bulbs of Krause were named after the German anatomist Wilhelm Krause (1833–1910).
Function
The end-bulbs of Krause were thought to be thermorecept ...
, detects temperatures above body temperature.
* Ruffini's end organ detects temperatures below body temperature.
TRPV1 is a heat-activated channel that acts as a small heat detecting thermometer in the membrane which begins the polarization of the neural fiber when exposed to changes in temperature. Ultimately, this allows us to detect ambient temperature in the warm/hot range. Similarly, the molecular cousin to TRPV1, TRPM8, is a cold-activated ion channel that responds to cold. Both cold and hot receptors are segregated by distinct subpopulations of sensory nerve fibers, which shows us that the information coming into the spinal cord is originally separate. Each sensory receptor has its own “labeled line” to convey a simple sensation experienced by the recipient. Ultimately, TRP channels act as thermosensors, channels that help us to detect changes in ambient temperatures.
Nociceptors
Nociceptors respond to potentially damaging stimuli by sending signals to the spinal cord and brain. This process, callednociception
Nociception (also nocioception, from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, co ...
, usually causes the perception of pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
. They are found in internal organs, as well as on the surface of the body. Nociceptors detect different kinds of damaging stimuli or actual damage. Those that only respond when tissues are damaged are known as "sleeping" or "silent" nociceptors.
* Thermal nociceptors are activated by noxious heat or cold at various temperatures.
* Mechanical nociceptors respond to excess pressure or mechanical deformation.
* Chemical nociceptors respond to a wide variety of chemicals, some of which are signs of tissue damage. They are involved in the detection of some spices in food.
Sensory cortex
All stimuli received by the receptors listed above are transduced to an action potential, which is carried along one or moreafferent neurons
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded potentials. This process is called sensory transduction. The cel ...
towards a specific area of the brain. While the term sensory cortex The sensory cortex can refer informally to the primary somatosensory cortex, or it can be used as a term for the primary and secondary cortices of the different senses (two cortices each, on left and right hemisphere): the visual cortex on the occi ...
is often used informally to refer to the somatosensory cortex, the term more accurately refers to the multiple areas of the brain at which senses are received to be processed. For the five traditional senses in humans, this includes the primary and secondary cortices of the different senses: the somatosensory cortex, the visual cortex, the auditory cortex, the primary olfactory cortex, and the gustatory cortex.Brynie, F.H. (2009). Brain Sense: The Science of the Senses and How We Process the World Around Us. American Management Association. Other modalities have corresponding sensory cortex areas as well, including the vestibular cortex for the sense of balance.
Somatosensory cortex
Located in the parietal lobe, the primary somatosensory cortex is the primary receptive area for the sense of touch and proprioception in the somatosensory system. This cortex is further divided into Brodmann areas 1, 2, and 3.Brodmann area 3
In neuroanatomy, the postcentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus in the lateral parietal lobe of the human brain. It is the location of the primary somatosensory cortex, the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch. Like other sensory areas, ...
is considered the primary processing center of the somatosensory cortex as it receives significantly more input from the thalamus, has neurons highly responsive to somatosensory stimuli, and can evoke somatic sensations through electrical stimulation
Stimulation is the encouragement of development or the cause of activity generally. For example, "The press provides stimulation of political discourse." An interesting or fun activity can be described as "stimulating", regardless of its physica ...
. Areas 1 and 2 receive most of their input from area 3. There are also pathways for proprioception (via the cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ...
), and motor control (via Brodmann area 4). See also: S2 Secondary somatosensory cortex.

Visual cortex
The visual cortex refers to the primary visual cortex, labeled V1 or Brodmann area 17, as well as the extrastriate visual cortical areas V2-V5. Located in the occipital lobe, V1 acts as the primary relay station for visual input, transmitting information to two primary pathways labeled the dorsal and ventral streams. The dorsal stream includes areas V2 and V5, and is used in interpreting visual 'where' and 'how.' The ventral stream includes areas V2 and V4, and is used in interpreting 'what.' Increases in Task-negative activity are observed in the ventral attention network, after abrupt changes in sensory stimuli, at the onset and offset of task blocks, and at the end of a completed trial.Auditory cortex
Located in the temporal lobe, the auditory cortex is the primary receptive area for sound information. The auditory cortex is composed of Brodmann areas 41 and 42, also known as the anterior transverse temporal area 41 and the posterior transverse temporal area 42, respectively. Both areas act similarly and are integral in receiving and processing the signals transmitted from auditory receptors.
Primary olfactory cortex
Located in the temporal lobe, the primary olfactory cortex is the primary receptive area forolfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, it ...
, or smell. Unique to the olfactory and gustatory systems, at least in mammals, is the implementation of both peripheral
A peripheral or peripheral device is an auxiliary device used to put information into and get information out of a computer. The term ''peripheral device'' refers to all hardware components that are attached to a computer and are controlled by the ...
and central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
mechanisms of action. The peripheral mechanisms involve olfactory receptor neurons which transduce a chemical signal along the olfactory nerve
The olfactory nerve, also known as the first cranial nerve, cranial nerve I, or simply CN I, is a cranial nerve that contains sensory nerve fibers relating to the sense of smell.
The afferent nerve fibers of the olfactory receptor neurons tr ...
, which terminates in the olfactory bulb. The chemoreceptors in the receptor neurons that start the signal cascade are G protein-coupled receptors. The central mechanisms include the convergence of olfactory nerve axons into glomeruli in the olfactory bulb, where the signal is then transmitted to the anterior olfactory nucleus, the piriform cortex, the medial amygdala, and the entorhinal cortex, all of which make up the primary olfactory cortex.
In contrast to vision and hearing, the olfactory bulbs are not cross-hemispheric; the right bulb connects to the right hemisphere and the left bulb connects to the left hemisphere.

Gustatory cortex
The gustatory cortex is the primary receptive area for taste. The word ''taste'' is used in a technical sense to refer specifically to sensations coming from taste buds on the tongue. The five qualities of taste detected by the tongue include sourness, bitterness, sweetness, saltiness, and the protein taste quality, called umami. In contrast, the term ''flavor'' refers to the experience generated through integration of taste with smell and tactile information. The gustatory cortex consists of two primary structures: the anterior insula, located on theinsular lobe
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe, parietal and frontal lobes) within each brain hemisphere, ...
, and the frontal operculum, located on the frontal lobe. Similarly to the olfactory cortex, the gustatory pathway operates through both peripheral and central mechanisms. Peripheral taste receptors, located on the tongue, soft palate, pharynx, and esophagus, transmit the received signal to primary sensory axons, where the signal is projected to the nucleus of the solitary tract in the medulla, or the gustatory nucleus of the solitary tract complex. The signal is then transmitted to the thalamus, which in turn projects the signal to several regions of the neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, sp ...
, including the gustatory cortex.
The neural processing of taste is affected at nearly every stage of processing by concurrent somatosensory information from the tongue, that is, mouthfeel. Scent, in contrast, is not combined with taste to create flavor until higher cortical processing regions, such as the insula and orbitofrontal cortex.
Human sensory system
The human sensory system consists of the following subsystems: * Visual system *Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.
System overview
The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, increasin ...
* Somatosensory system consists of the receptors, transmitters (pathways) leading to S1, and S1 that experiences the sensations labelled as touch, pressure, vibration, temperature (warm or cold), pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
(including itch and tickle), and the sensations of muscle movement and joint position including posture, movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
, and facial expression (collectively also called proprioception)
* Gustatory system
* Olfactory system
* Vestibular system
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes ...
* Interoceptive system
Diseases
Amblyopia
Amblyopia, also called lazy eye, is a disorder of sight in which the brain fails to fully process input from one eye and over time favors the other eye. It results in decreased vision in an eye that typically appears normal in other aspects. Amb ...
* Anacusis
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken la ...
* Color blindness
* Deafness
See also
* Multisensory integration * Neural adaptation * Neural coding *Sensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
* Sensory augmentation
* Sensory neuroscience
Sensory neuroscience is a subfield of neuroscience which explores the anatomy and physiology of neurons that are part of sensory systems such as vision, hearing, and olfaction. Neurons in sensory regions of the brain respond to stimuli by firing o ...
* Sensory systems in fish
Most fish possess highly developed sense organs. Nearly all daylight fish have color vision that is at least as good as a human's (see vision in fishes). Many fish also have chemoreceptors that are responsible for extraordinary senses of taste an ...
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sensory System Nervous system Sensory systems Sensory organs