House Of Swabia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the
 The name Hohenstaufen was first used in the 14th century to distinguish the 'high' (''hohen'')
The name Hohenstaufen was first used in the 14th century to distinguish the 'high' (''hohen'')
 When the last male member of the Salian dynasty, Emperor Henry V, died without heirs in 1125, a controversy arose about the succession. Duke Frederick II and
When the last male member of the Salian dynasty, Emperor Henry V, died without heirs in 1125, a controversy arose about the succession. Duke Frederick II and
 Frederick died in 1190 while on the Third Crusade and was succeeded by his son, Henry VI. Elected king even before his father's death, Henry went to Rome to be crowned emperor. He married Princess Constance of Sicily, and deaths in his wife's family gave him claim of succession and possession of the
Frederick died in 1190 while on the Third Crusade and was succeeded by his son, Henry VI. Elected king even before his father's death, Henry went to Rome to be crowned emperor. He married Princess Constance of Sicily, and deaths in his wife's family gave him claim of succession and possession of the
 By the 1226 Golden Bull of Rimini, Frederick had assigned the military order of the Teutonic Knights to complete the conquest and conversion of the Prussian lands. A reconciliation with the Welfs took place in 1235, whereby Otto the Child, grandson of the late Saxon duke Henry the Lion, was named
By the 1226 Golden Bull of Rimini, Frederick had assigned the military order of the Teutonic Knights to complete the conquest and conversion of the Prussian lands. A reconciliation with the Welfs took place in 1235, whereby Otto the Child, grandson of the late Saxon duke Henry the Lion, was named  By the time of Frederick's death in 1250, little centralized power remained in Germany. The Great
By the time of Frederick's death in 1250, little centralized power remained in Germany. The Great
 The Kyffhäuser Monument was erected to commemorate Frederick I, and was inaugurated in 1896.
On October 29, 1968, the 700th anniversary of the death of Konradin, a society known as "Society for Staufer History" ( de) was founded in Göppingen.
The Castel del Monte, Apulia which was built during the 1240s by the Emperor Frederick II was designated as a World Heritage Site in 1996.
The German artist, Hans Kloss, painted his '' Staufer-Rundbild'' depicting in great detail the history of the House of Hohenstaufen, in Lorch Monastery.
From 2000 to 2018, the Committee of Staufer Friends ( de) has built thirty-eight Staufer steles ( de) in Germany, France, Italy, Austria, Czech Republic and the Netherlands.
The Kyffhäuser Monument was erected to commemorate Frederick I, and was inaugurated in 1896.
On October 29, 1968, the 700th anniversary of the death of Konradin, a society known as "Society for Staufer History" ( de) was founded in Göppingen.
The Castel del Monte, Apulia which was built during the 1240s by the Emperor Frederick II was designated as a World Heritage Site in 1996.
The German artist, Hans Kloss, painted his '' Staufer-Rundbild'' depicting in great detail the history of the House of Hohenstaufen, in Lorch Monastery.
From 2000 to 2018, the Committee of Staufer Friends ( de) has built thirty-eight Staufer steles ( de) in Germany, France, Italy, Austria, Czech Republic and the Netherlands.
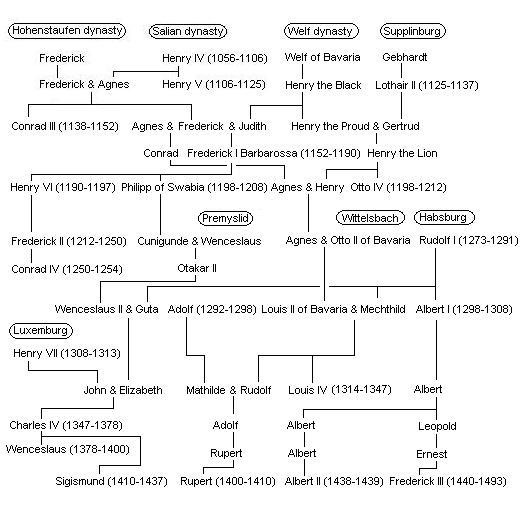

, - , , - , style="text-align:left;", ---- Notes:
''For further detailed dynastic relationships, see also :Family tree of the German monarchs''.
Duchy of Swabia
The Duchy of Swabia (German: ''Herzogtum Schwaben'') was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.
While the ...
from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty's most prominent rulers – Frederick I (1155), Henry VI (1191) and Frederick II (1220) – ascended the imperial throne and also reigned over Italy and Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
. The non-contemporary name of 'Hohenstaufen' is derived from the family's Hohenstaufen Castle on the Hohenstaufen mountain
The Hohenstaufen is a mountain in the Swabian Jura with an elevation of . It and two nearby mountains known as Rechberg and Stuifen together constitute the so-called "Three Kaiser mountains" (Drei Kaiserberge). The Hohenstaufen is easily visible ...
at the northern fringes of the Swabian Jura
The Swabian Jura (german: Schwäbische Alb , more rarely ), sometimes also named Swabian Alps in English, is a mountain range in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, extending from southwest to northeast and in width. It is named after the region of ...
, near the town of Göppingen. Under Hohenstaufen rule, the Holy Roman Empire reached its greatest territorial extent from 1155 to 1268.
Name
 The name Hohenstaufen was first used in the 14th century to distinguish the 'high' (''hohen'')
The name Hohenstaufen was first used in the 14th century to distinguish the 'high' (''hohen'') conical hill
A conical hill (also cone or conical mountain) is a landform with a distinctly conical shape. It is usually isolated or rises above other surrounding foothills, and is often of volcanic origin.
Conical hills or mountains occur in different sha ...
named Staufen Staufen refers to:
*Hohenstaufen, a dynasty of German emperors
*Staufen im Breisgau, a town in Baden-Württemberg, Germany
*Staufen, Aargau, in Switzerland
*Staufen (protein), a protein found in the egg of ''Drosophila''
*Staufen, Austria
The ...
in the Swabian Jura
The Swabian Jura (german: Schwäbische Alb , more rarely ), sometimes also named Swabian Alps in English, is a mountain range in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, extending from southwest to northeast and in width. It is named after the region of ...
(in the district of Göppingen) from the village of the same name in the valley below. The new name was only applied to the hill castle of Staufen Staufen refers to:
*Hohenstaufen, a dynasty of German emperors
*Staufen im Breisgau, a town in Baden-Württemberg, Germany
*Staufen, Aargau, in Switzerland
*Staufen (protein), a protein found in the egg of ''Drosophila''
*Staufen, Austria
The ...
by historians in the 19th century, to distinguish it from other castles of the same name. The name of the dynasty followed suit, but in recent decades, the trend in German historiography has been to prefer the name 'Staufer', which is closer to contemporary usage.
The name 'Staufen' itself derives from ''Stauf'' ( OHG ''stouf'', akin to Early Modern English stoup), meaning ' chalice'. This term was commonly applied to conical hills in Swabia during the Middle Ages. It is a contemporary term for both the hill and the castle, although its spelling in the Latin documents of the time varies considerably: , etc. The castle was built or at least acquired by Duke Frederick I of Swabia
Frederick I (c. 1050 – 1105) before 21 July was Duke of Swabia from 1079 to his death, the first ruler from the House of Hohenstaufen (''Staufer'').
Life
Frederick was the son of Frederick of Büren (c. 1020–1053), Count in the Riesgau and ...
in the latter half of the 11th century.John B. Freed, ''Frederick Barbarossa: The Prince and the Myth'' (Yale University Press, 2016), pp. 5–6.
Members of the family occasionally used the toponymic surname ''de Stauf'' or variants thereof. Only in the 13th century does the name come to be applied to the family as a whole. Around 1215, a chronicler referred to the "emperors of Stauf". In 1247, the Emperor Frederick II himself referred to his family as the ''domus Stoffensis'' (Staufer house), but this was an isolated instance. Otto of Freising (d. 1158) associated the Staufer with the town of Waiblingen, and around 1230, Burchard of Ursberg Burchard of Ursperg, also called Burchard of Biberach (c.1177–1230/1) was a German priest and chronicler. His ''Ursperger Chronicle'' (or ''Chronicon Urspergensis'') is the most important universal history of the late Staufer era.Mathias Herweg, " ...
referred to the Staufer as of the "royal lineage of the Waiblingens" (''regia stirps Waiblingensium''). The exact connection between the family and Waiblingen is not clear, but as a name for the family, it became very popular. The pro-imperial Ghibelline faction of the Italian civic rivalries of the 13th and 14th centuries derived its name from Waiblingen.
In Italian historiography, the Staufer are known as the ''Svevi'' (Swabians).
Origins
The origin remains unclear, however, Staufer counts are mentioned in a document of emperorOtto III
Otto III (June/July 980 – 23 January 1002) was Holy Roman Emperor from 996 until his death in 1002. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto III was the only son of the Emperor Otto II and his wife Theophanu.
Otto III was crowned as King of ...
in 987 as descendants of counts of the region of ''Riesgau'' near Nördlingen in the Duchy of Swabia
The Duchy of Swabia (German: ''Herzogtum Schwaben'') was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.
While the ...
, who were related to the Bavarian '' Sieghardinger'' family. A local count Frederick (d. about 1075) is mentioned as progenitor in a pedigree drawn up by Abbot Wibald of Stavelot at the behest of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in 1153. He held the office of a Swabian count palatine; his son Frederick of Buren (c.1020–1053) married Hildegard of Egisheim
Eguisheim (; german: Egisheim; Alsatian dialect, Alsatian: ''Egsa'') is a Communes of France, commune in the Haut-Rhin Departments of France, department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It lies in the historical region of Alsace (german: Els ...
-Dagsburg
Dabo (german: Dagsburg) is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
History
Previous names:Dictionnaire géographique de la Meurthe - Henri Lepage ''Dasburch'' (1188), ''Dasburg'' (1189) ''Dagesburg'' (1227), ...
(d. 1094/95), a niece of Pope Leo IX. Their son Frederick I was appointed Duke of Swabia
The Dukes of Swabia were the rulers of the Duchy of Swabia during the Middle Ages. Swabia was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German kingdom, and its dukes were thus among the most powerful magnates of Germany. The most notable family ...
at Hohenstaufen Castle by the Salian king Henry IV of Germany in 1079.
At the same time, Duke Frederick I was engaged to the king's approximately seventeen-year-old daughter, Agnes. Nothing is known about Frederick's life before this event, but he proved to be an imperial ally throughout Henry's struggles against other Swabian lords, namely Rudolf of Rheinfelden, Frederick's predecessor, and the Zähringen and Welf lords. Frederick's brother Otto was elevated to the Strasbourg bishopric in 1082.
Upon Frederick's death, he was succeeded by his son, Duke Frederick II, in 1105. Frederick II remained a close ally of the Salians, he and his younger brother Conrad
Conrad may refer to:
People
* Conrad (name)
Places
United States
* Conrad, Illinois, an unincorporated community
* Conrad, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Conrad, Iowa, a city
* Conrad, Montana, a city
* Conrad Glacier, Washington ...
were named the king's representatives in Germany when the king was in Italy. Around 1120, Frederick II married Judith of Bavaria from the rival House of Welf
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconia, Franconian family from ...
.
Ruling in Germany
Conrad
Conrad may refer to:
People
* Conrad (name)
Places
United States
* Conrad, Illinois, an unincorporated community
* Conrad, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Conrad, Iowa, a city
* Conrad, Montana, a city
* Conrad Glacier, Washington ...
, the two current male Staufers, by their mother Agnes, were grandsons of late Emperor Henry IV and nephews of Henry V. Frederick attempted to succeed to the throne of the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
(formally known as the King of the Romans
King of the Romans ( la, Rex Romanorum; german: König der Römer) was the title used by the king of Germany following his election by the princes from the reign of Henry II (1002–1024) onward.
The title originally referred to any German k ...
) through a customary election, but lost to the Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
duke Lothair of Supplinburg
Lothair III, sometimes numbered Lothair II and also known as Lothair of Supplinburg (1075 – 4 December 1137), was Holy Roman Emperor from 1133 until his death. He was appointed Duke of Saxony in 1106 and elected King of Germany in 1125 before ...
. A civil war between Frederick's dynasty and Lothair's ended with Frederick's submission in 1134. After Lothair's death in 1137, Frederick's brother Conrad was elected King as Conrad III.
Because the Welf duke Henry the Proud, son-in-law and heir of Lothair and the most powerful prince in Germany, who had been passed over in the election, refused to acknowledge the new king, Conrad III deprived him of all his territories, giving the Duchy of Saxony to Albert the Bear and that of Bavaria to Leopold IV, Margrave of Austria. In 1147, Conrad heard Bernard of Clairvaux preach the Second Crusade
The Second Crusade (1145–1149) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusa ...
at Speyer, and he agreed to join King Louis VII of France
Louis VII (1120 – 18 September 1180), called the Younger, or the Young (french: link=no, le Jeune), was King of the Franks from 1137 to 1180. He was the son and successor of King Louis VI (hence the epithet "the Young") and married Duchess ...
in a great expedition to the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
which failed.
Conrad's brother Duke Frederick II died in 1147, and was succeeded in Swabia by his son, Duke Frederick III. When King Conrad III died without adult heir in 1152, Frederick also succeeded him, taking both German royal and Imperial titles.
Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick I (Reign 2 January 1155 – 10 June 1190), known as Frederick Barbarossa because of his red beard, struggled throughout his reign to restore the power and prestige of the German monarchy against the dukes, whose power had grown both before and after the Investiture Controversy under his Salian predecessors. As royal access to the resources of the church in Germany was much reduced, Frederick was forced to go to Italy to find the finances needed to restore the king's power in Germany. He was soon crowned emperor in Italy, but decades of warfare on the peninsula yielded scant results. ThePapacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
and the prosperous city-states of the Lombard League in northern Italy were traditional enemies, but the fear of Imperial domination caused them to join ranks to fight Frederick. Under the skilled leadership of Pope Alexander III
Pope Alexander III (c. 1100/1105 – 30 August 1181), born Roland ( it, Rolando), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 September 1159 until his death in 1181.
A native of Siena, Alexander became pope after a con ...
, the alliance suffered many defeats but ultimately was able to deny the emperor a complete victory in Italy. Frederick returned to Germany. He had vanquished one notable opponent, his Welf cousin, Duke Henry the Lion of Saxony and Bavaria in 1180, but his hopes of restoring the power and prestige of the monarchy seemed unlikely to be met by the end of his life.
During Frederick's long stays in Italy, the German princes became stronger and began a successful colonization of Slavic lands. Offers of reduced taxes and manorial duties enticed many Germans to settle in the east in the course of the ''Ostsiedlung
(, literally "East-settling") is the term for the Early Medieval and High Medieval migration-period when ethnic Germans moved into the territories in the eastern part of Francia, East Francia, and the Holy Roman Empire (that Germans had al ...
''. In 1163 Frederick waged a successful campaign against the Kingdom of Poland in order to re-install the Silesian Silesian as an adjective can mean anything from or related to Silesia. As a noun, it refers to an article, item, or person of or from Silesia.
Silesian may also refer to:
People and languages
* Silesians, inhabitants of Silesia, either a West S ...
dukes of the Piast dynasty. With the German colonization, the Empire increased in size and came to include the Duchy of Pomerania. A quickening economic life in Germany increased the number of towns and Imperial cities, and gave them greater importance. It was also during this period that castles and courts replaced monasteries as centers of culture. Growing out of this courtly culture, Middle High German literature reached its peak in lyrical love poetry, the Minnesang, and in narrative epic poems such as '' Tristan'', '' Parzival'', and the '' Nibelungenlied''.
Henry VI
 Frederick died in 1190 while on the Third Crusade and was succeeded by his son, Henry VI. Elected king even before his father's death, Henry went to Rome to be crowned emperor. He married Princess Constance of Sicily, and deaths in his wife's family gave him claim of succession and possession of the
Frederick died in 1190 while on the Third Crusade and was succeeded by his son, Henry VI. Elected king even before his father's death, Henry went to Rome to be crowned emperor. He married Princess Constance of Sicily, and deaths in his wife's family gave him claim of succession and possession of the Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
in 1189 and 1194 respectively, a source of vast wealth. Henry failed to make royal and Imperial succession hereditary, but in 1196 he succeeded in gaining a pledge that his infant son Frederick would receive the German crown. Faced with difficulties in Italy and confident that he would realize his wishes in Germany at a later date, Henry returned to the south, where it appeared he might unify the peninsula under the Hohenstaufen name. After a series of military victories, however, he fell ill and died of natural causes in Sicily in 1197. His underage son Frederick could only succeed him in Sicily and Malta, while in the Empire the struggle between the House of Staufen and the House of Welf erupted once again.
Philip of Swabia
Because the election of a three-year-old boy to be German king appeared likely to make orderly rule difficult, the boy's uncle, DukePhilip of Swabia
Philip of Swabia (February/March 1177 – 21 June 1208) was a member of the House of Hohenstaufen and King of Germany from 1198 until his assassination.
The death of his older brother Emperor Henry VI in 1197 meant that the Hohenstaufen rule (whi ...
, brother of late Henry VI, was designated to serve in his place. Other factions however favoured a Welf candidate. In 1198, two rival kings were chosen: the Hohenstaufen Philip of Swabia and the son of the deprived Duke Henry the Lion, the Welf Otto IV. A long civil war began; Philip was about to win when he was murdered by the Bavarian count palatine Otto VIII of Wittelsbach in 1208. Pope Innocent III initially had supported the Welfs, but when Otto, now sole elected monarch, moved to appropriate Sicily, Innocent changed sides and accepted young Frederick II and his ally, King Philip II of France, who defeated Otto at the 1214 Battle of Bouvines. Frederick had returned to Germany in 1212 from Sicily, where he had grown up, and was elected king in 1215. When Otto died in 1218, Frederick became the undisputed ruler, and in 1220 was crowned Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
.
Philip changed the coat of arms from a black lion on a gold shield to three leopards, probably derived from the arms of his Welf rival Otto IV.
Ruling in Italy
The conflict between the Staufer dynasty and the Welf had irrevocably weakened the Imperial authority and the Norman kingdom of Sicily became the base for Staufer rule.Frederick II
Emperor Frederick II
Frederick II (German: ''Friedrich''; Italian: ''Federico''; Latin: ''Federicus''; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusa ...
spent little time in Germany as his main concerns lay in Southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half.
The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the peop ...
. He founded the University of Naples in 1224 to train future state officials and reigned over Germany primarily through the allocation of royal prerogatives, leaving the sovereign authority and imperial estates to the ecclesiastical and secular princes. He made significant concessions to the German nobles, such as those put forth in an imperial statute of 1232, which made princes virtually independent rulers within their territories. These measures favoured the further fragmentation of the Empire.
 By the 1226 Golden Bull of Rimini, Frederick had assigned the military order of the Teutonic Knights to complete the conquest and conversion of the Prussian lands. A reconciliation with the Welfs took place in 1235, whereby Otto the Child, grandson of the late Saxon duke Henry the Lion, was named
By the 1226 Golden Bull of Rimini, Frederick had assigned the military order of the Teutonic Knights to complete the conquest and conversion of the Prussian lands. A reconciliation with the Welfs took place in 1235, whereby Otto the Child, grandson of the late Saxon duke Henry the Lion, was named Duke of Brunswick and Lüneburg
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are r ...
. The power struggle with the popes continued and resulted in Frederick's excommunication in 1227. In 1239, Pope Gregory IX excommunicated Frederick again, and in 1245 he was condemned as a heretic by a church council. Although Frederick was one of the most energetic, imaginative, and capable rulers of the time, he was not concerned with drawing the disparate forces in Germany together. His legacy was thus that local rulers had more authority after his reign than before it. The clergy also had become more powerful.
 By the time of Frederick's death in 1250, little centralized power remained in Germany. The Great
By the time of Frederick's death in 1250, little centralized power remained in Germany. The Great Interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
, a period in which there were several elected rival kings, none of whom was able to achieve any position of authority, followed the death of Frederick's son King Conrad IV of Germany in 1254. The German princes vied for individual advantage and managed to strip many powers away from the diminished monarchy. Rather than establish sovereign states however, many nobles tended to look after their families. Their many male heirs created more and smaller estates, and from a largely free class of officials previously formed, many of these assumed or acquired hereditary rights to administrative and legal offices. These trends compounded political fragmentation within Germany. The period was ended in 1273 with the election of Rudolph of Habsburg, a godson of Frederick.
End of the Staufer dynasty
Conrad IV was succeeded as duke of Swabia by his only son, two-year-old Conradin. By this time, the office of duke of Swabia had been fully subsumed into the office of the king, and without royal authority had become meaningless. In 1261, attempts to elect young Conradin king were unsuccessful. He also had to defend Sicily against an invasion, sponsored by Pope Urban IV (Jacques Pantaléon) and Pope Clement IV (Guy Folques), by Charles of Anjou, a brother of theFrench
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
king. Charles had been promised by the popes the Kingdom of Sicily, where he would replace the relatives of Frederick II. Charles had defeated Conradin's uncle Manfred, King of Sicily, in the Battle of Benevento on 26 February 1266. The king himself, refusing to flee, rushed into the midst of his enemies and was killed. Conradin's campaign to retake control ended with his defeat in 1268 at the Battle of Tagliacozzo, after which he was handed over to Charles, who had him publicly executed at Naples. With Conradin, the direct line of the Dukes of Swabia finally ceased to exist, though most of the later emperors were descended from the Staufer dynasty indirectly.
The last member of the dynasty was Manfred's son, Henry nrico who died in captivity at Castel dell'Ovo on 31 October 1318. Gregorovius, Ferdinand (2010) 897 ''History of the City of Rome in the Middle Ages''. Vol. 5, Part 2, Cambridge University Press.
During the political decentralization of the late Staufer period, the population had grown from an estimated 8 million in 1200 to about 14 million in 1300, and the number of towns increased tenfold. The most heavily urbanized areas of Germany were in the south and the west. Towns often developed a degree of independence, but many were subordinate to local rulers if not immediate to the emperor. Colonization of the east also continued in the thirteenth century, most notably through the efforts of the Teutonic Knights. German merchants also began trading extensively on the Baltic.
Legacy
 The Kyffhäuser Monument was erected to commemorate Frederick I, and was inaugurated in 1896.
On October 29, 1968, the 700th anniversary of the death of Konradin, a society known as "Society for Staufer History" ( de) was founded in Göppingen.
The Castel del Monte, Apulia which was built during the 1240s by the Emperor Frederick II was designated as a World Heritage Site in 1996.
The German artist, Hans Kloss, painted his '' Staufer-Rundbild'' depicting in great detail the history of the House of Hohenstaufen, in Lorch Monastery.
From 2000 to 2018, the Committee of Staufer Friends ( de) has built thirty-eight Staufer steles ( de) in Germany, France, Italy, Austria, Czech Republic and the Netherlands.
The Kyffhäuser Monument was erected to commemorate Frederick I, and was inaugurated in 1896.
On October 29, 1968, the 700th anniversary of the death of Konradin, a society known as "Society for Staufer History" ( de) was founded in Göppingen.
The Castel del Monte, Apulia which was built during the 1240s by the Emperor Frederick II was designated as a World Heritage Site in 1996.
The German artist, Hans Kloss, painted his '' Staufer-Rundbild'' depicting in great detail the history of the House of Hohenstaufen, in Lorch Monastery.
From 2000 to 2018, the Committee of Staufer Friends ( de) has built thirty-eight Staufer steles ( de) in Germany, France, Italy, Austria, Czech Republic and the Netherlands.
Members of the Hohenstaufen family

Holy Roman Emperors and Kings of the Romans
*Conrad III
Conrad III (german: Konrad; it, Corrado; 1093 or 1094 – 15 February 1152) of the Hohenstaufen dynasty was from 1116 to 1120 Duke of Franconia, from 1127 to 1135 anti-king of his predecessor Lothair III and from 1138 until his death in 1152 k ...
, king 1138–1152
*Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on ...
, king 1152–1190, emperor after 1155
* Henry VI, king 1190–1197, emperor after 1191
*Philip of Swabia
Philip of Swabia (February/March 1177 – 21 June 1208) was a member of the House of Hohenstaufen and King of Germany from 1198 until his assassination.
The death of his older brother Emperor Henry VI in 1197 meant that the Hohenstaufen rule (whi ...
, king 1198–1208
* Frederick II, king 1208–1250, emperor after 1220
* Henry (VII), king 1220–1235 (under his father Emperor Frederick II)
* Conrad IV, king 1237–1254 (until 1250 under his father Emperor Frederick II)
The first ruling Hohenstaufen, Conrad III, like the last one, Conrad IV, was never crowned emperor. After a 20-year period (Great interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
1254–1273), the first Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
was elected king.
Kings of Italy
''Note: The following kings are already listed above as German Kings'' *Conrad III
Conrad III (german: Konrad; it, Corrado; 1093 or 1094 – 15 February 1152) of the Hohenstaufen dynasty was from 1116 to 1120 Duke of Franconia, from 1127 to 1135 anti-king of his predecessor Lothair III and from 1138 until his death in 1152 k ...
1128–1135
* Frederick I 1154–1190
* Henry VI 1191–1197
Kings of Sicily
''Note: Some of the following kings are already listed above as German Kings'' * Henry VI 1194–1197 * Frederick 1198–1250 ** Henry (VII) 1212–1217 (nominal king under his father) *Conrad
Conrad may refer to:
People
* Conrad (name)
Places
United States
* Conrad, Illinois, an unincorporated community
* Conrad, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Conrad, Iowa, a city
* Conrad, Montana, a city
* Conrad Glacier, Washington ...
1250–1254
* Conradin 1254–1258/1268
* Manfred 1258–1266
Dukes of Swabia
''Note: Some of the following dukes are already listed above as German Kings'' * Frederick I, Duke of Swabia (''Friedrich'') (r. 1079–1105) * Frederick II, Duke of Swabia (r. 1105–1147) *Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on ...
(Frederick III of Swabia)(r. 1147–1152) ''King in 1152 and Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
in 1155''
* Frederick IV, Duke of Swabia (r. 1152–1167)
* Frederick V, Duke of Swabia (r. 1167–1170)
* Frederick VI, Duke of Swabia (r. 1170–1191)
* Conrad II, Duke of Swabia
Conrad II (February/March 1172 – 15 August 1196), was Duke of Rothenburg (1188–1191) and Swabia from 1191 until his death. He was the fifth son of Frederick I Barbarossa and Beatrice I, Countess of Burgundy.
Life
After the third-born son o ...
(r. 1191–1196)
* Philip of Swabia
Philip of Swabia (February/March 1177 – 21 June 1208) was a member of the House of Hohenstaufen and King of Germany from 1198 until his assassination.
The death of his older brother Emperor Henry VI in 1197 meant that the Hohenstaufen rule (whi ...
(r. 1196–1208) ''King in 1198''
* Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II (German language, German: ''Friedrich''; Italian language, Italian: ''Federico''; Latin: ''Federicus''; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Em ...
(r. 1212–1216) ''King in 1212 and Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
in 1220''
* Henry (VII) of Germany (r. 1216–1235), ''King 1220–1235''
* Conrad IV (r. 1235–1254) ''King in 1237''
* Conrad V (Conradin) (r. 1254–1268)
Family tree of the House of Hohenstaufen
, - , , - , style="text-align:left;", ---- Notes:
''For further detailed dynastic relationships, see also :Family tree of the German monarchs''.
See also
*Dukes of Swabia family tree
The Dukes of Swabia were the rulers of the Duchy of Swabia during the Middle Ages. Swabia was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German kingdom, and its dukes were thus among the most powerful magnates of Germany. The most notable family ...
* Guelphs and Ghibellines
The Guelphs and Ghibellines (, , ; it, guelfi e ghibellini ) were factions supporting the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor, respectively, in the Italian city-states of Central Italy and Northern Italy.
During the 12th and 13th centuries, ri ...
Notes
References
*External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Hohenstaufen, House Of 1070s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1079 establishments in Europe 1260s disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1268 disestablishments in Europe German kings Holy Roman Emperors Italian noble families Noble families of the Holy Roman Empire Salian dynasty Sicilian royal houses