Home Row on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Touch typing (also called blind typing, or touch keyboarding) is a style of
 Original layouts for the first few mechanical typewriters were in alphabetical order (ABCDE etc.) Changes were made, mostly responding to suggestions from telegraphists that were among the first users.Koichi Yasuoka∗ and Motoko Yasuoka (2011) On the Prehistory of QWERTY. ZINBUN (2011), 42: 161-17
Original layouts for the first few mechanical typewriters were in alphabetical order (ABCDE etc.) Changes were made, mostly responding to suggestions from telegraphists that were among the first users.Koichi Yasuoka∗ and Motoko Yasuoka (2011) On the Prehistory of QWERTY. ZINBUN (2011), 42: 161-17
/ref> Common letters were moved towards the center and into the upper row. Z and S are close to each other because the American Morse codes of Z and a common digram SE (both ) are near the same, so the telegraphist often needs to wait for more signals before understanding the content. The view that the layout was intentionally redesigned to slow down the operator, to prevent jamming the mechanism, is widespread but not correct. The calculations for keyboard layout were based on the language being typed and this meant different keyboard layouts would be needed for each language. In English-speaking countries, for example, the first row is QWERTY, but in French-speaking countries it is AZERTY. Though mechanical typewriters are now rarely used, moves to change the layout to increase speed have been largely ignored or resisted due to familiarity with the existing layout among touch typists. On July 25, 1888, an American man, Frank Edward McGurrin, who was reportedly the only person using touch typing at the time, won a decisive victory over Louis Traub (operating Caligraph with eight-finger method) in a typing contest held in Cincinnati. The results were displayed on the front pages of many newspapers.Frank Edward McGurrin
''(Very big text, search for "Contest for a Prize of $500")'' McGurrin won US$500 (equivalent to $13,304 in 2019 USD) and popularized the new typing method. Whether McGurrin was actually the first person to touch type or simply the first to be popularly noticed, is disputed. Speeds attained by other typists in other typing competitions at the time suggest that they must have been using similar systems. In 1889, Bates Torrey coined the words "writing by touch" in his article. In 1890, Lovisa Ellen Bullard Barnes defined the words "write by touch" in her book as follows: In 1985, Touch Typist Typing Tutor, developed and released by Sector Software is an early example of typing tutor software. Touch typing is contrasted to ''search and peck'', also known as ''hunt-and-peck'' or ''two-fingered typing''. Instead of relying on the memorized position of keys, the typist finds each key by sight and moves their finger over to press it, usually the index finger of their dominant hand. This method is considered inferior as not only is it slower than touch typing, the typist would have to have their fingers travel a greater distance. Various other styles in between those two exist—for example, using a ''search-and-peck'' method, but with an increased number of fingers; typing without looking at the keyboard, but using fewer than the eight fingers that the home row method uses (commonly, the omission of the little finger as the weakest finger that many will find difficult to hit keys with due to either less strength, less dexterity, or both); moving their entire hand to reach for the desired key; or only moving when a key needs to be pressed instead of always returning to home row after every keystroke.
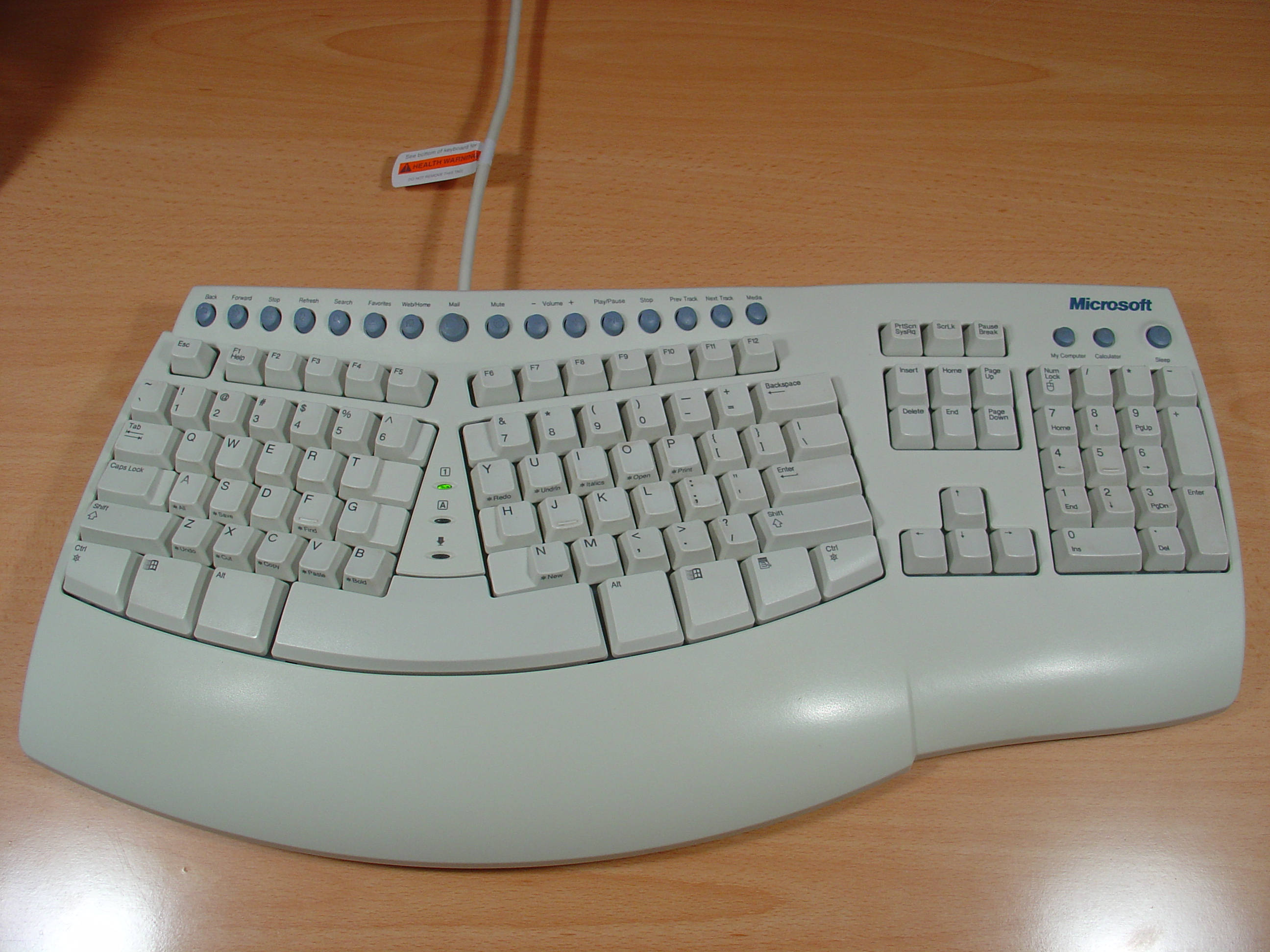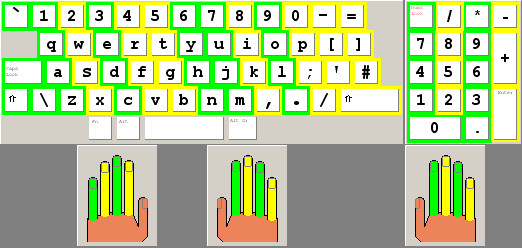
 The "home row" is the center row of keys on a
The "home row" is the center row of keys on a Competition Classifications Lists
Official portal for Intersteno people
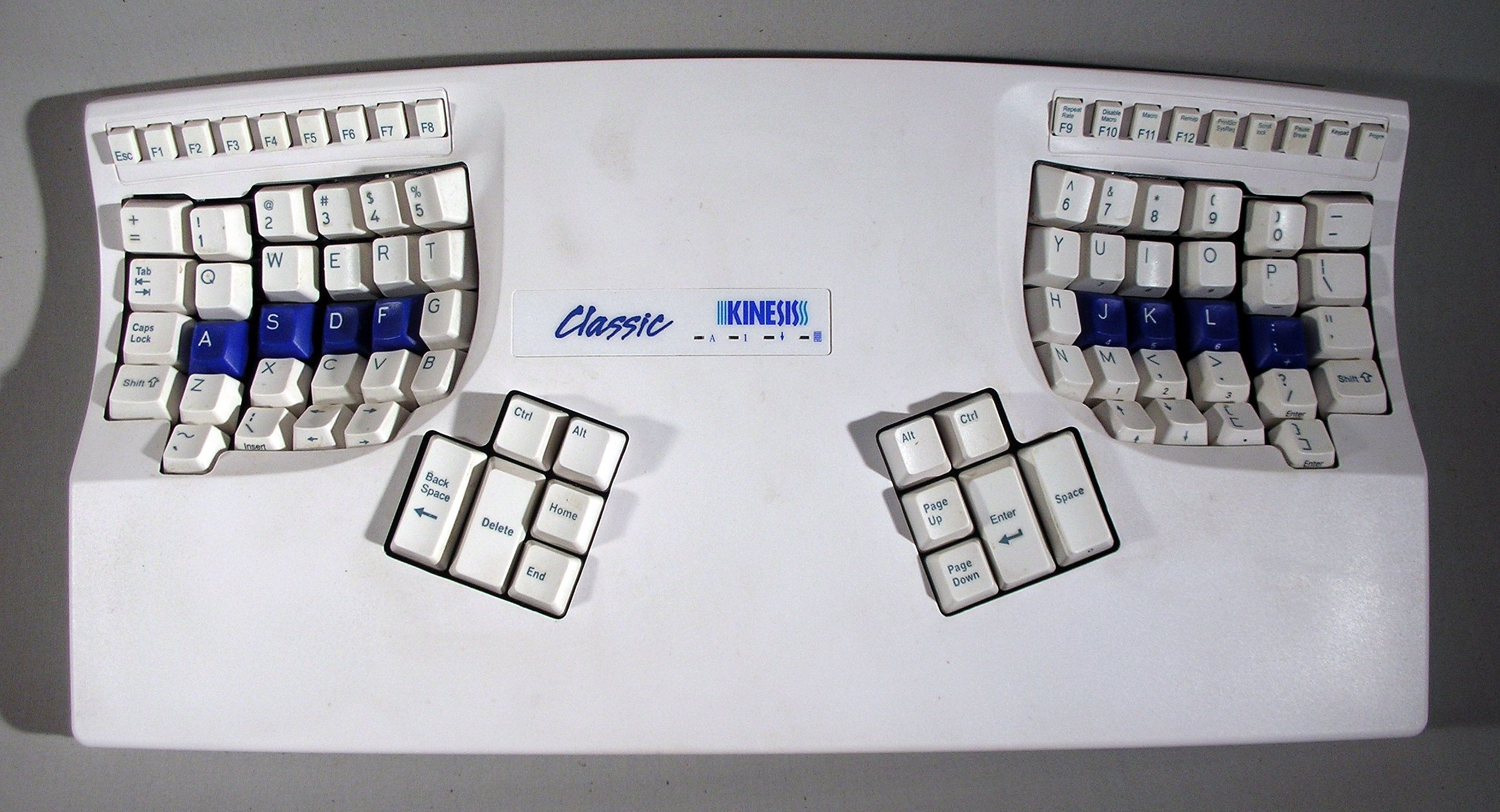 A method taught since the 1960s (and perhaps earlier): The left little finger is used for the keys , the ring finger for , the middle — , the left index finger is responsible for and . On the right side of the keyboard: index — and , middle — , ring — and the little — all other keys on the right side of the upper row. These two methods likely reflect the
A method taught since the 1960s (and perhaps earlier): The left little finger is used for the keys , the ring finger for , the middle — , the left index finger is responsible for and . On the right side of the keyboard: index — and , middle — , ring — and the little — all other keys on the right side of the upper row. These two methods likely reflect the
typing
Typing is the process of writing or inputting text by pressing keys on a typewriter, computer keyboard, mobile phone or calculator. It can be distinguished from other means of text input, such as handwriting and speech recognition. Text can ...
. Although the phrase refers to typing without using the sense of sight
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum refl ...
to find the keys—specifically, a touch typist will know their location on the keyboard through muscle memory
Muscle memory is a form of procedural memory that involves consolidating a specific motor task into memory through repetition, which has been used synonymously with motor learning. When a movement is repeated over time, the brain creates a long- ...
—the term is often used to refer to a specific form of touch typing that involves placing the eight fingers in a horizontal row along the middle of the keyboard (the ''home row'') and having them reach for specific other keys. (Under this usage, typists who do not look at the keyboard but do not use home row either are referred to as hybrid typists.) Both two-handed touch typing and one-handed touch typing are possible.
Frank Edward McGurrin, a court stenographer from Salt Lake City, Utah
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the Capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Utah, most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the county seat, seat of Salt Lake County, Utah, Sal ...
who taught typing classes, reportedly invented home row touch typing in 1888.
On a standard QWERTY
QWERTY () is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six keys on the top left letter row of the keyboard ( ). The QWERTY design is based on a layout created for the Sholes and Glidden ty ...
keyboard for English speakers the home row keys are: "ASDF" for the left hand and "JKL;" for the right hand. Most modern computer keyboard
A computer keyboard is a peripheral input device modeled after the typewriter keyboard which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches. Replacing early punched cards and paper tape technology ...
s have a raised dot or bar on the home keys for the index fingers to help touch typists maintain and rediscover the correct positioning of the fingers on the keyboard keys.
History
/ref> Common letters were moved towards the center and into the upper row. Z and S are close to each other because the American Morse codes of Z and a common digram SE (both ) are near the same, so the telegraphist often needs to wait for more signals before understanding the content. The view that the layout was intentionally redesigned to slow down the operator, to prevent jamming the mechanism, is widespread but not correct. The calculations for keyboard layout were based on the language being typed and this meant different keyboard layouts would be needed for each language. In English-speaking countries, for example, the first row is QWERTY, but in French-speaking countries it is AZERTY. Though mechanical typewriters are now rarely used, moves to change the layout to increase speed have been largely ignored or resisted due to familiarity with the existing layout among touch typists. On July 25, 1888, an American man, Frank Edward McGurrin, who was reportedly the only person using touch typing at the time, won a decisive victory over Louis Traub (operating Caligraph with eight-finger method) in a typing contest held in Cincinnati. The results were displayed on the front pages of many newspapers.Frank Edward McGurrin
''(Very big text, search for "Contest for a Prize of $500")'' McGurrin won US$500 (equivalent to $13,304 in 2019 USD) and popularized the new typing method. Whether McGurrin was actually the first person to touch type or simply the first to be popularly noticed, is disputed. Speeds attained by other typists in other typing competitions at the time suggest that they must have been using similar systems. In 1889, Bates Torrey coined the words "writing by touch" in his article. In 1890, Lovisa Ellen Bullard Barnes defined the words "write by touch" in her book as follows: In 1985, Touch Typist Typing Tutor, developed and released by Sector Software is an early example of typing tutor software. Touch typing is contrasted to ''search and peck'', also known as ''hunt-and-peck'' or ''two-fingered typing''. Instead of relying on the memorized position of keys, the typist finds each key by sight and moves their finger over to press it, usually the index finger of their dominant hand. This method is considered inferior as not only is it slower than touch typing, the typist would have to have their fingers travel a greater distance. Various other styles in between those two exist—for example, using a ''search-and-peck'' method, but with an increased number of fingers; typing without looking at the keyboard, but using fewer than the eight fingers that the home row method uses (commonly, the omission of the little finger as the weakest finger that many will find difficult to hit keys with due to either less strength, less dexterity, or both); moving their entire hand to reach for the desired key; or only moving when a key needs to be pressed instead of always returning to home row after every keystroke.

Advantages
Speed
Touch type training can improve an individual's typing speed and accuracy dramatically. Speeds average around 30–40 WPM ( words per minute), while a speed of 60–80 WPM is the approximate speed to keep up with one's thoughts. A Microsoft survey suggested that many managers expect employees to be able to type at a minimum of 50 WPM. Professional career typists can exceed 100 WPM repeatedly and continuously (secretarial, data entry, etc.). Routine practice is required to maintain a high typing speed and accuracy.Reduced switching of attention
A touch typist does not need to move the sight between the keyboard (that is obscured with fingers and may be poorly lit) and other areas that require attention. This increases productivity and reduces the number of errors.Reduced neck strain
Touch typing helps improve posture and reduce neck pain by keeping one's eyes focused on the display and avoiding a constant need to glance at the keyboard.Disputes over advantages
There are many other typing styles in between novice-style " hunt and peck" and touch typing. For example, many hunt-and-peck typists have the keyboard layout memorized and are able to type while focusing their gaze on the screen. One study examining 30 subjects, of varying different styles and expertise, has found minimal difference in typing speed between touch typists and self-taught hybrid typists. According to the study, "The number of fingers does not determine typing speed... People using self-taught typing strategies were found to be as fast as trained typists... instead of the number of fingers, there are other factors that predict typing speed... fast typists... keep their hands fixed on one position, instead of moving them over the keyboard, and more consistently use the same finger to type a certain letter." To quote doctoral candidate Anna Feit: "We were surprised to observe that people who took a typing course performed at similar average speed and accuracy as those that taught typing to themselves and only used 6 fingers on average". However, the study has been criticised for only selecting subjects with average typing speeds up to 75 words per minute, thus lacking generalizability for faster typist.Training
A touch typist starts by placing their fingers on the "start position" in the middle row and knows which finger to move and how much to move it for reaching any required key. Learning typically includes first printing exercises containing only letters on or near the standard position and then gradually mastering other rows. It is important to learn placing fingers into the start position blindly as the hands are frequently raised from the keyboard to operate the line feed lever (in the past) or (more recently) the computer mouse. The keys F and J frequently contain some surface features that allow the typist to recognize them by touch alone, thus removing the need to look down at the keys to reset the fingers at the home row. The typing speed can be increased gradually and speeds of 60 WPM or higher can be achieved. The increase in speed varies between individuals. Many websites and software products are available to learn touch typing and many of these are free. Learning touch typing can be stressful both to the fingers as well as the mind in the beginning, but once it is learned to a decent level, it exerts minimal stress on the fingers. For individuals with past typing experience, learning to touch type is particularly difficult due to motivational reasons: the initial performance level in touch typing is far lower than in visually guided typing; therefore it does not initially seem worthwhile to study touch typing. Typing speed generally improves with practice. While practicing, it is important to ensure that there are no weak keys. Typing speed is typically determined by how slow these weak keys are typed rather than how fast the remaining keys are typed. If a stage is reached where irrespective of the amount of practice, typing speed is not increasing, it is advisable to let some time pass and continue serious practice thereafter as typing speeds typically tend to increase with time even when no serious practice is done.Home row
typewriter
A typewriter is a mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an inked ribbon selective ...
or computer keyboard
A computer keyboard is a peripheral input device modeled after the typewriter keyboard which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches. Replacing early punched cards and paper tape technology ...
. On the most common type of English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to t ...
keyboard, the QWERTY
QWERTY () is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six keys on the top left letter row of the keyboard ( ). The QWERTY design is based on a layout created for the Sholes and Glidden ty ...
layout, " " and " " are the home keys on the home row.
The middle row of the keyboard is termed "home row" because typists are trained to keep their fingers on these keys and return to them after pressing any other key that is not on the home row.
Some keyboards have a small bump on certain keys of the home row. This helps returning the fingers to the home row for touch typing.
For instance, to type the word ''poll'' on a QWERTY keyboard, one would place all of one's finger
A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers (Pentadactyly). Chambers 1 ...
s on the home row. (The right hand
In human biology, handedness is an individual's preferential use of one hand, known as the dominant hand, due to it being stronger, faster or more dextrous. The other hand, comparatively often the weaker, less dextrous or simply less subjec ...
should be covering " " with the right thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thu ...
on the while the left hand covers " " with the left thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thu ...
on the .) The typist will then use their little finger
The little finger, or pinkie, also known as the baby finger, fifth digit, or pinky finger, is the most ulnar and smallest digit of the human hand, and next to the ring finger.
Etymology
The word "pinkie" is derived from the Dutch word ''pi ...
to reach for the "" key located just above the semicolon
The semicolon or semi-colon is a symbol commonly used as orthographic punctuation. In the English language, a semicolon is most commonly used to link (in a single sentence) two independent clauses that are closely related in thought. When a ...
and then return the little finger
The little finger, or pinkie, also known as the baby finger, fifth digit, or pinky finger, is the most ulnar and smallest digit of the human hand, and next to the ring finger.
Etymology
The word "pinkie" is derived from the Dutch word ''pi ...
back to the semicolon
The semicolon or semi-colon is a symbol commonly used as orthographic punctuation. In the English language, a semicolon is most commonly used to link (in a single sentence) two independent clauses that are closely related in thought. When a ...
key from which it originated. The ring finger
The ring finger, third finger, fourth finger, leech finger, or annulary is the fourth digit of the human hand, located between the middle finger and the little finger.
Sometimes the term ring finger only refers to the fourth digit of a left-h ...
, located on the "" key will be moved directly upwards to press the "" key and then back. Finally, the same ring finger
The ring finger, third finger, fourth finger, leech finger, or annulary is the fourth digit of the human hand, located between the middle finger and the little finger.
Sometimes the term ring finger only refers to the fourth digit of a left-h ...
will remain on the "" key and press it twice. Experienced typists can do this at speeds of over 100 words per minute.Official portal for Intersteno people
Other methods
 A method taught since the 1960s (and perhaps earlier): The left little finger is used for the keys , the ring finger for , the middle — , the left index finger is responsible for and . On the right side of the keyboard: index — and , middle — , ring — and the little — all other keys on the right side of the upper row. These two methods likely reflect the
A method taught since the 1960s (and perhaps earlier): The left little finger is used for the keys , the ring finger for , the middle — , the left index finger is responsible for and . On the right side of the keyboard: index — and , middle — , ring — and the little — all other keys on the right side of the upper row. These two methods likely reflect the layout
Layout may refer to:
* Page layout, the arrangement of visual elements on a page
** Comprehensive layout (comp), a proposed page layout presented by a designer to their client
* Layout (computing), the process of calculating the position of ob ...
of the typewriters from early days when some of them had no and/or keys.
There exist special ergonomic keyboards designed for both typing methods. The keyboard is split between the keys and or and .
Some specialized high-end computer keyboards are designed for touch typists. For example, many manufacturers provide blank mechanical keyboards. A trained touch typist should not mind using a blank keyboard. This kind of keyboard may force hunt and peck users to type without looking, similar to Braille keyboards used by the visually impaired.
See also
* Dvorak keyboard layout, an alternative English keyboard layout, advertised as optimised for comfort and speed * :Typing software, software that is designed for teaching users to touch typeReferences
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Touch Typing Typing Input/output Computer keyboards