Hohennagold on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
__NOTOC__
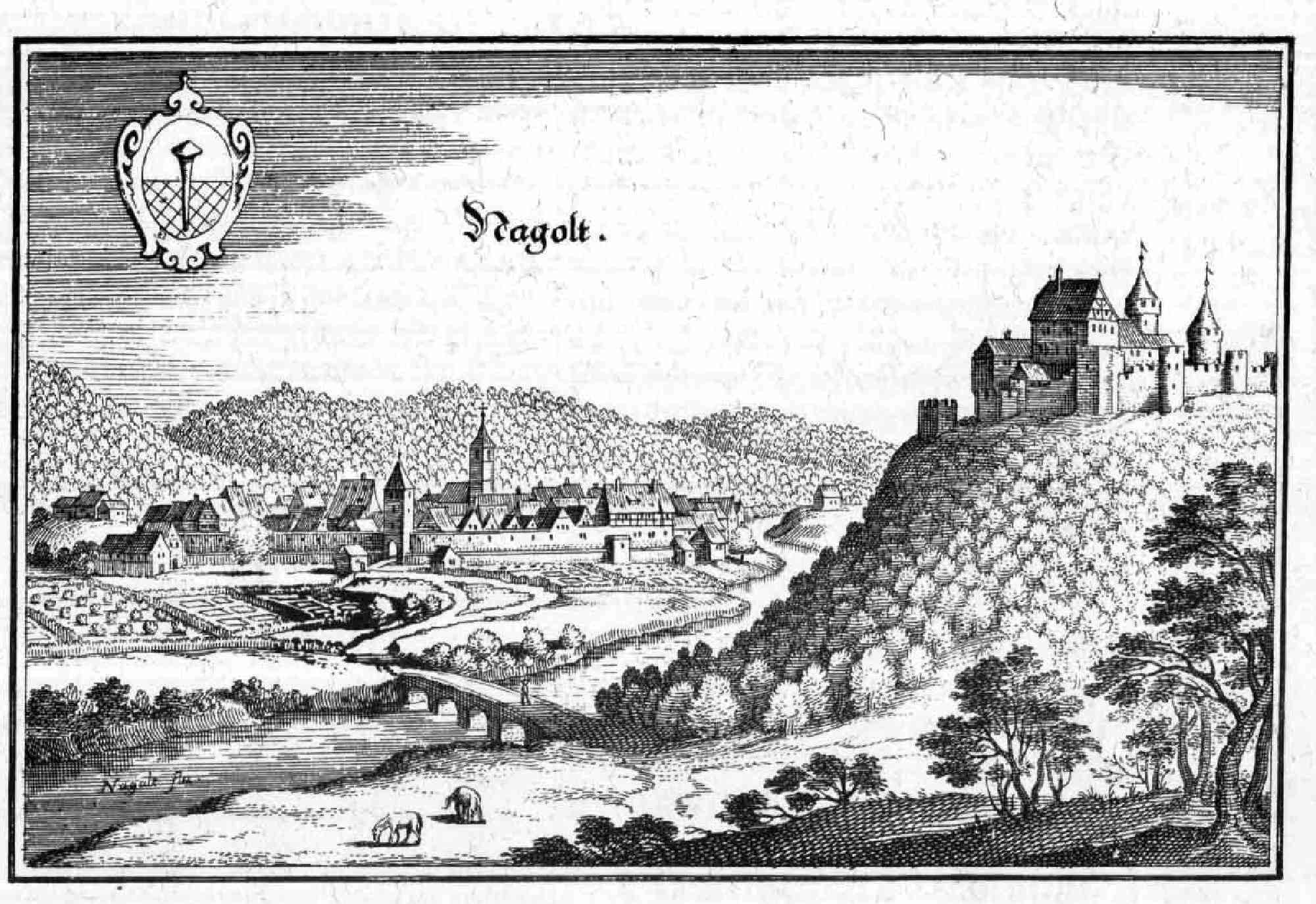
 Hohennagold Castle is a ruined castle situated on a hill, the so-called ''Schlossberg'' (castle mountain), overlooking the
Hohennagold Castle is a ruined castle situated on a hill, the so-called ''Schlossberg'' (castle mountain), overlooking the
Hohennagold Castle
*
Drawing of the castle in its original state
by Wolfgang Braun {{Authority control Ruined castles in Germany

 Hohennagold Castle is a ruined castle situated on a hill, the so-called ''Schlossberg'' (castle mountain), overlooking the
Hohennagold Castle is a ruined castle situated on a hill, the so-called ''Schlossberg'' (castle mountain), overlooking the Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is t ...
town of Nagold. The hill consists predominantly of porphyritic
Porphyritic is an adjective used in geology to describe igneous rocks with a distinct difference in the size of mineral crystals, with the larger crystals known as phenocrysts. Both extrusive and intrusive rocks can be porphyritic, meaning all ...
rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
. The ruins represent a relatively well-preserved 12th-century castle. The keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in c ...
behind the curtain walls, a tower
A tower is a tall Nonbuilding structure, structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from guyed mast, masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting ...
in the north-western corner of the complex as well as the outer ward
An outer bailey or outer ward is the defended outer enclosure of a castle.Friar, Stephen (2003). ''The Sutton Companion to Castles'', Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2003, p. 22. It protects the inner bailey and usually contains those ancillary bui ...
with half-round and angular towers, are still visible. Around the castle there appears to have been a moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
.
History
An early medieval fortification was possibly erected at the location of the future castle around 750 by Count Ruodbrecht, one ofCharlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
's uncles.
The original castle was built around 1100 by the Counts of Nagold, who became the Counts palatine of Tübingen in 1145. The castle complex was extensively expanded between 1153 and 1162.
In the middle of the 13th century the castle passed into the possession of the Counts of Hohenberg
The Counts of Hohenberg (or Margraves of Hohenberg) were an ancient Swabian dynasty in the southwest of the present-day Germany the state of Baden-Württemberg.
In the 13th century, the dynasty of Hohenberg was one of the most prominent lineag ...
. Thereafter, one branch of this family called itself Counts of Nagold and had the castle transformed into their residence in the 13th and 14th century. In 1364 the sold the castle to the Counts of Württemberg
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
. The new owners added bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...
s and towers to the outer ward and had the castle occupied by their '' ministeriales''. Towards the end of the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
, the castle was conquered by Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
n troops in 1645 and severely damaged. In 1646 the remnants of the castle were pulled down.
In 1945 the northwest tower was destroyed by a low-level attack carried out by Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
planes. The castle remains were tentatively restored after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, trying to preserve the castle as a ruin.
See also
* List of castles in Baden-WürttembergReferences
External links
*Hohennagold Castle
*
Drawing of the castle in its original state
by Wolfgang Braun {{Authority control Ruined castles in Germany