History of Moravia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of

 Following the defeat of the Magyars by Emperor
Following the defeat of the Magyars by Emperor 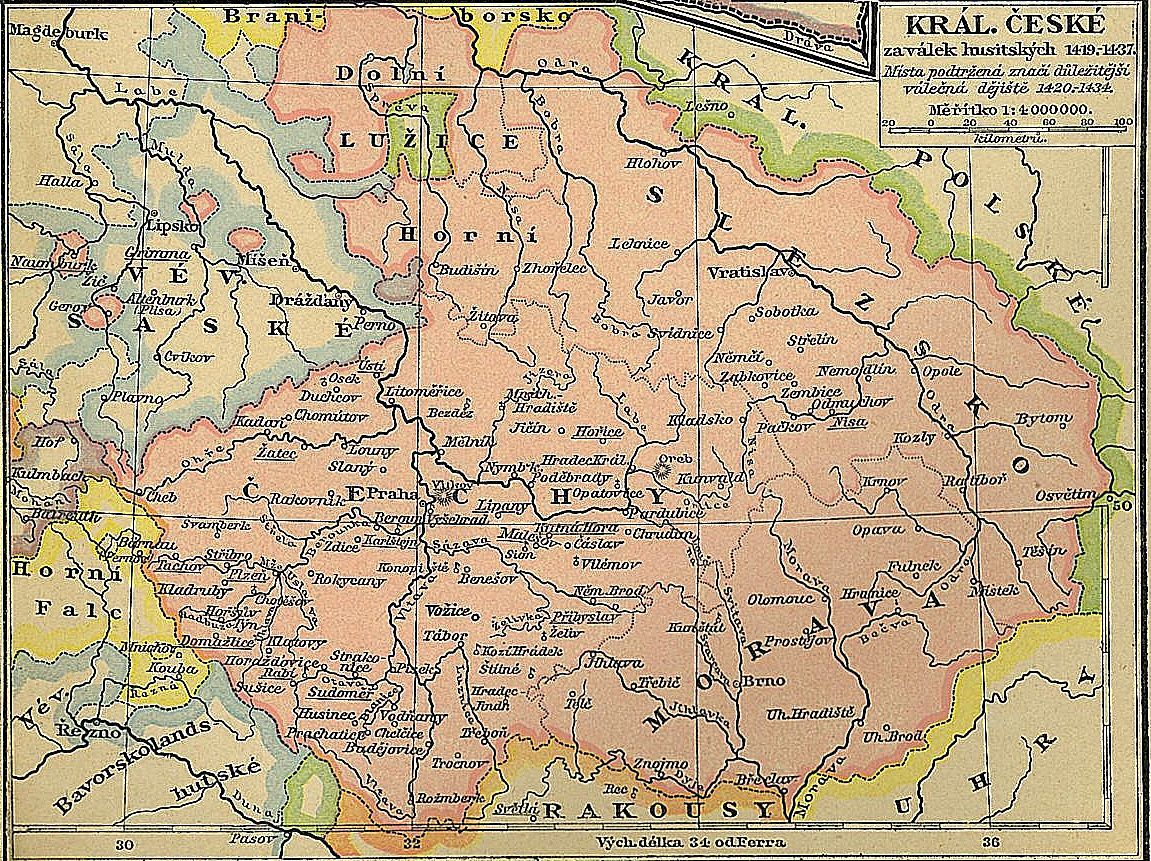 The main line of the
The main line of the
 The epoch 1526–1620 was marked by increasing animosity between Catholic Habsburg kings (emperors) and the Protestant Moravian nobility (and other Crowns') estates. Moravia, like Bohemia, was a Habsburg possession until the end of
The epoch 1526–1620 was marked by increasing animosity between Catholic Habsburg kings (emperors) and the Protestant Moravian nobility (and other Crowns') estates. Moravia, like Bohemia, was a Habsburg possession until the end of
První Československá republika do 1928.jpg, Moravia within Czechoslovakia between 1918–1928
První Československá republika.SVG, Moravia as part of Moravia-Silesia within Czechoslovakia between 1928–1938
Czechoslovakia IV.png, Moravia-Silesia within Czechoslovakia between 1928–1938
CZ-cleneni-Morava-wl.png, Moravia in the Czech Republic
Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The me ...
, one of the Czech lands
The Czech lands or the Bohemian lands ( cs, České země ) are the three historical regions of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia. Together the three have formed the Czech part of Czechoslovakia since 1918, the Czech Socialist Republic since 1 ...
, is diverse and characterized by many periods of foreign governance.
Pre-history
Early modern humans had settled in the region by the Paleolithic. The Předmostíarchaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
site in Moravia is dated to between 24,000 and 27,000 years old.
Ancient Moravia
Around 60 BC theCelt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
ic Volcae
The Volcae () were a Gallic tribal confederation constituted before the raid of combined Gauls that invaded Macedonia c. 270 BC and fought the assembled Greeks at the Battle of Thermopylae in 279 BC. Tribes known by the name Volcae were found si ...
people withdrew from the region and were succeeded in turn by the Germanic Quadi
The Quadi were a Germanic
*
*
*
people who lived approximately in the area of modern Moravia in the time of the Roman Empire. The only surviving contemporary reports about the Germanic tribe are those of the Romans, whose empire had its bord ...
. Several hundred years later, in the 6th century AD the Slavic tribes
This is a list of Slavic peoples and Slavic tribes reported in Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, that is, before the year AD 1500.
Ancestors
*Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers)
** Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of Bal ...
arrived in this territory often crossed during the Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
by successive Germanic and major Slavic tribes. At the end of the 8th century the Moravian Principality came into being in present-day south-eastern Moravia, Záhorie
Záhorie ( hu, Erdőhát) is a region in western Slovakia between by the Little Carpathians to the east and the Morava (river), Morava River to the west. Although not an administrative region, it is one of the List of tourism regions of Slovakia, ...
in south-western Slovakia and parts of Lower Austria. In 833 AD, this became the state of Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavs, Wes ...
with the conquest of the Principality of Nitra
The Principality of Nitra ( sk, Nitrianske kniežatstvo, Nitriansko, Nitrava, lit=Duchy of Nitra, Nitravia, Nitrava; hu, Nyitrai Fejedelemség), also known as the Duchy of Nitra, was a West Slavic polity encompassing a group of settlements th ...
(present-day Slovakia). Their first king was Mojmír I
Mojmir I, Moimir I or Moymir I (Latin: ''Moimarus'', ''Moymarus'', Czech and Slovak: ''Mojmír I.'') was the first known ruler of the Moravian Slavs (820s/830s–846) and eponym of the House of Mojmir. In modern scholarship, the creation of t ...
(ruled 830–846). Louis the German invaded Moravia and replaced Mojmír I with his nephew Rastiz who became St. Rastislav. St. Rastislav (846–870) tried to emancipate his land from the Carolingian influence, so he sent envoys to Rome to get missionaries to come. When Rome refused he turned to Constantinople to the Byzantine emperor Michael. The result was the mission of Saints Cyril and Methodius
Cyril (born Constantine, 826–869) and Methodius (815–885) were two brothers and Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs".
They are credited wit ...
who translated liturgical book
A liturgical book, or service book, is a book published by the authority of a church body that contains the text and directions for the liturgy of its official religious services.
Christianity Roman Rite
In the Roman Rite of the Catholic ...
s into Slavonic, which had lately been elevated by the Pope to the same level as Latin and Greek. Methodius became the first Moravian archbishop, but after his death the German influence again prevailed and the disciples of Methodius were forced to flee. So the unique situation which anticipated the II Vatican Council by several centuries was destroyed. Great Moravia reached its greatest territorial extent in the 890s under Svatopluk I
Svatopluk I or Svätopluk I, also known as Svatopluk the Great (Latin: ''Zuentepulc'', ''Zuentibald'', ''Sventopulch'', ''Zvataplug''; Old Church Slavic: Свѧтопълкъ and transliterated ''Svętopъłkъ''; Polish: ''Świętopełk''; Greek: ...
. At this time, the empire encompassed the territory of the present-day Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
, the western part of present Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
(Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
), as well as Lusatia
Lusatia (german: Lausitz, pl, Łużyce, hsb, Łužica, dsb, Łužyca, cs, Lužice, la, Lusatia, rarely also referred to as Sorbia) is a historical region in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr ...
in present-day Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
and the upper Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
basin in southern Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
. After Svatopluk's death in 895, the Bohemian princes defected to become vassals of the East Frankish ruler Arnulf of Carinthia
Arnulf of Carinthia ( 850 – 8 December 899) was the duke of Carinthia who overthrew his uncle Emperor Charles the Fat to become the Carolingian king of East Francia from 887, the disputed king of Italy from 894 and the disputed emperor from Feb ...
, and the Moravian state ceased to exist after being overrun by invading Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Uralic ...
in 906/7.
Union with Bohemia

 Following the defeat of the Magyars by Emperor
Following the defeat of the Magyars by Emperor Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Francia, East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the olde ...
at the Battle of Lechfeld
The Battle of Lechfeld was a series of military engagements over the course of three days from 10–12 August 955 in which the Kingdom of Germany, led by King Otto I the Great, annihilated the Hungarian army led by '' Harka '' Bulcsú and the ch ...
in 955, Otto's ally Boleslaus I, the Přemyslid ruler of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
, received Moravia. Bolesław I Chrobry of Poland annexed Moravia in 999, and ruled it until 1019, when the Přemyslid prince Bretislaus recaptured it. Since then, Moravia has shared its history with Bohemia. Upon his father's death in 1034, Bretislaus also became the ruler of Bohemia. In 1055, Bretislaus decreed that the Bohemia and Moravia would be inherited together by primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relativ ...
, although he also provided that his younger sons should govern parts (quarters) of Moravia as vassals to his oldest son.
Throughout the Přemyslid era, junior princes often ruled all or part of Moravia from Olomouc
Olomouc (, , ; german: Olmütz; pl, Ołomuniec ; la, Olomucium or ''Iuliomontium'') is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 99,000 inhabitants, and its larger urban zone has a population of about 384,000 inhabitants (2019).
Located on th ...
, Brno
Brno ( , ; german: Brünn ) is a city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava and Svratka rivers, Brno has about 380,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic ...
or Znojmo
Znojmo (; german: Znaim) is a town in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 33,000 inhabitants. Znojmo is the historical and cultural centre of southwestern Moravia and the second most populated town in the South Moravian R ...
, with varying degrees of autonomy from the ruler of Bohemia. (Mainly Dukes of Olomouc usually used to act as "right hand" of Prague dukes and kings. Dukes of Brno and especially those of Znojmo were much more insubordinate.) Moravia reached its height of autonomy in 1182, when Emperor Frederick I Frederick I may refer to:
* Frederick of Utrecht or Frederick I (815/16–834/38), Bishop of Utrecht.
* Frederick I, Duke of Upper Lorraine (942–978)
* Frederick I, Duke of Swabia (1050–1105)
* Frederick I, Count of Zoller ...
elevated Conrad II Otto of Znojmo to the status of a margrave
Margrave was originally the medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or of a kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain feudal families in the Emp ...
,There are no primary testimonies about creating a margraviate (march) as distinct political unit immediately subject to the emperor, independent of Bohemia. This status was short-lived: in 1186, Conrad Otto was forced to obey the supreme rule of Bohemian duke Frederick Frederick may refer to:
People
* Frederick (given name), the name
Nobility
Anhalt-Harzgerode
*Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670)
Austria
* Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198
* Frederick ...
. Three years later, Conrad Otto succeed to Frederick as Duke of Bohemia and subsequently canceled his margrave title. Nevertheless, the margrave title was restored in 1197 when Vladislaus III, Duke of Bohemia
Vladislaus Henry ( cs, Vladislav Jindřich; – 12 August 1222), a member of the Přemyslid dynasty, was elected Duke of Bohemia (as "Vladislaus III") in 1197 and Margrave of Moravia from 1197 until his death. He only served as duke during t ...
resolved the succession dispute between him and his brother Ottokar
Ottokar is the medieval German form of the Germanic name Audovacar.
People with the name Ottokar include:
*Two kings of Bohemia, members of the Přemyslid dynasty
** Ottokar I of Bohemia (–1230)
** Ottokar II of Bohemia (–1278)
*Four Styrian m ...
by abdicating from the Bohemian throne and accepting Moravia as a vassal land of Bohemian (i.e., Prague) rulers. Vladislaus gradually established this land as Margraviate, slightly administratively different from Bohemia.
 The main line of the
The main line of the Přemyslid dynasty
The Přemyslid dynasty or House of Přemyslid ( cs, Přemyslovci, german: Premysliden, pl, Przemyślidzi) was a Bohemian royal dynasty that reigned in the Duchy of Bohemia and later Kingdom of Bohemia and Margraviate of Moravia (9th century–130 ...
became extinct in 1306, and in 1310 John of Luxembourg
John the Blind or John of Luxembourg ( lb, Jang de Blannen; german: link=no, Johann der Blinde; cz, Jan Lucemburský; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King of ...
became Margrave of Moravia and King of Bohemia. In 1333, he made his son Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
the next Margrave of Moravia (later in 1346, Charles become also the King of Bohemia). In 1349, Charles gave Moravia to his younger brother John Henry who ruled in the margraviate until his death in 1375, after him Moravia was ruled by his oldest son Jobst of Moravia
Jobst of Moravia ( cs, Jošt Moravský or ''Jošt Lucemburský''; german: Jo(b)st or ''Jodokus von Mähren''; c. 1354 – 18 January 1411), a member of the House of Luxembourg, was Margrave of Moravia from 1375, Duke of Luxembourg and Elector of ...
who was in 1410 elected the Holy Roman King but died in 1411 (at present day, he is buried with his father in the Church of St. Thomas in Brno
Brno ( , ; german: Brünn ) is a city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava and Svratka rivers, Brno has about 380,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic ...
– the Moravian capital which they both ruled from). Moravia and Bohemia remained within the Luxembourg dynasty
The House of Luxembourg ( lb, D'Lëtzebuerger Haus; french: Maison de Luxembourg; german: Haus Luxemburg) or Luxembourg dynasty was a royal family of the Holy Roman Empire in the Late Middle Ages, whose members between 1308 and 1437 ruled as king ...
of Holy Roman kings and emperors (except during the Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, European monarchs loyal to the Cat ...
), until inherited by Albert II of Habsburg
Albert the Magnanimous KG, elected King of the Romans as Albert II (10 August 139727 October 1439) was king of the Holy Roman Empire and a member of the House of Habsburg. By inheritance he became Albert V, Duke of Austria. Through his wife (''j ...
in 1437.
After his death followed the interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
until 1453; land (as the rest of lands of the Bohemian Crown) was administered by the landfriedens (''landfrýdy''). The rule of young Ladislaus the Posthumous
Ladislaus the Posthumous( hu, Utószülött László; hr, Ladislav Posmrtni; cs, Ladislav Pohrobek; german: link=no, Ladislaus Postumus; 22 February 144023 November 1457) was Duke of Austria and King of Hungary, Croatia and Bohemia. He was the ...
subsisted only less than five years and subsequently (1458) the Hussite George of Poděbrady
George of Kunštát and Poděbrady (23 April 1420 – 22 March 1471), also known as Poděbrad or Podiebrad ( cs, Jiří z Poděbrad; german: Georg von Podiebrad), was the sixteenth King of Bohemia, who ruled in 1458–1471. He was a leader of the ...
was elected as the king. He again reunited all Czech lands (then Bohemia, Moravia, Silesia, Upper & Lower Lusatia) into one-man ruled state. In 1466, Pope Paul II
Pope Paul II ( la, Paulus II; it, Paolo II; 23 February 1417 – 26 July 1471), born Pietro Barbo, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States
from 30 August 1464 to his death in July 1471. When his maternal uncle Eugene IV ...
excommunicated George and forbade all Catholics (i.e. c. 15% of population) from continuing to serve him. The Hungarian crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were i ...
followed and in 1469 Matthias Corvinus
Matthias Corvinus, also called Matthias I ( hu, Hunyadi Mátyás, ro, Matia/Matei Corvin, hr, Matija/Matijaš Korvin, sk, Matej Korvín, cz, Matyáš Korvín; ), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1458 to 1490. After conducting several mi ...
conquered Moravia and proclaimed himself (with assistance of rebelling Bohemian nobility Czech nobility consists of the noble families from historical Czech lands, especially in their narrow sense, i.e. nobility of Bohemia proper, Moravia and Austrian Silesia – whether these families originated from those countries or moved into them ...
) as the king of Bohemia.
The subsequent 21-year period of a divided kingdom was decisive for the rising awareness of a specific Moravian identity, distinct from that of Bohemia. Although Moravia was reunited with Bohemia in 1490 when Vladislaus Jagiellon, king of Bohemia, also became king of Hungary, some attachment to Moravian "freedoms" and resistance to government by Prague continued until the end of independence in 1620. In 1526, Vladislaus' son Louis Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
died in battle and the Habsburg Ferdinand I was elected as his successor.
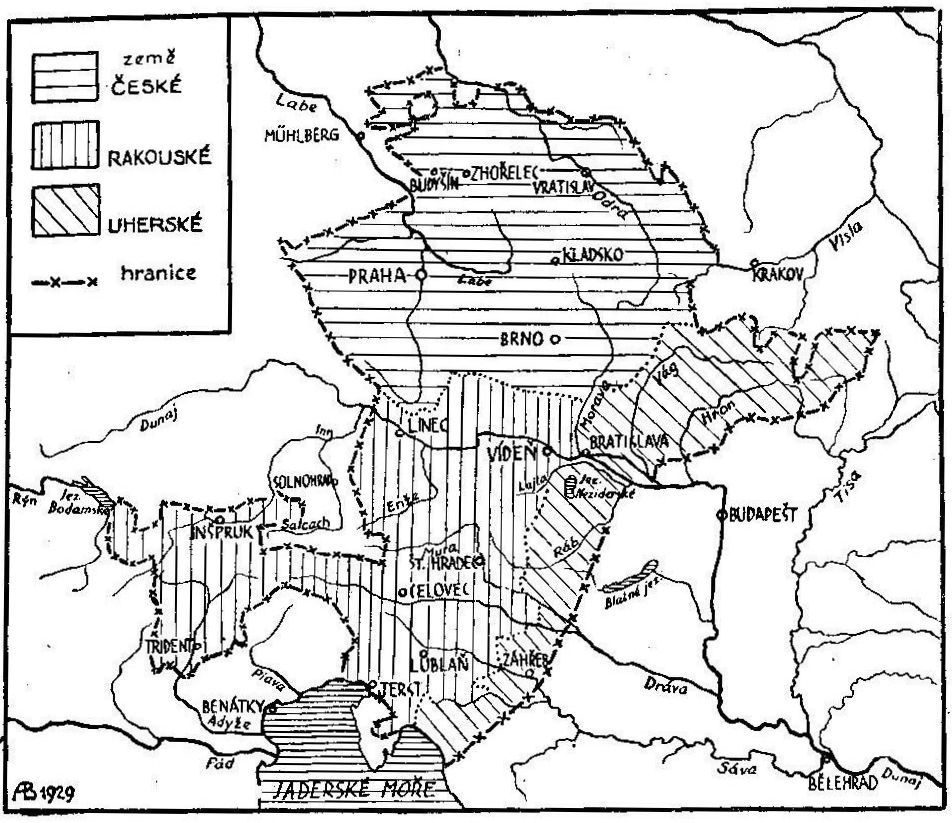
Habsburg rule (1526–1918)
 The epoch 1526–1620 was marked by increasing animosity between Catholic Habsburg kings (emperors) and the Protestant Moravian nobility (and other Crowns') estates. Moravia, like Bohemia, was a Habsburg possession until the end of
The epoch 1526–1620 was marked by increasing animosity between Catholic Habsburg kings (emperors) and the Protestant Moravian nobility (and other Crowns') estates. Moravia, like Bohemia, was a Habsburg possession until the end of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. In 1573 the Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
University of Olomouc
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the ...
was established; this was first university in Moravia. The establishment of a special papal seminary, Collegium Nordicum, made the university a centre of the Catholic Reformation and effort to revive Catholicism in Central and Northern Europe. The second largest group of students were from Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
.
Until 1641 Moravia's capitals were Brno
Brno ( , ; german: Brünn ) is a city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava and Svratka rivers, Brno has about 380,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic ...
and Olomouc
Olomouc (, , ; german: Olmütz; pl, Ołomuniec ; la, Olomucium or ''Iuliomontium'') is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 99,000 inhabitants, and its larger urban zone has a population of about 384,000 inhabitants (2019).
Located on th ...
, but after the capture of Olomouc by the Swedes, the city of Brno become the sole capital (Brno was the only city in Moravia which successfully resisted the invaders). The Margraviate of Moravia had (from 1348 in Olomouc and Brno) its own Diet (parliament) – ''zemský sněm'' (''Landtag'' in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
), whose deputies from 1905 onward were elected separately from the ethnically separate German and Czech constituencies.
In 17th century Moravia, today's oldest theatre building in Central Europe was founded – Reduta Theatre
The Reduta Theatre is a theatre in Brno, Czech Republic. It was built on the city's oldest square, Zelný trh) and began its life in Renaissance times as the Taverna (Tavern) Theatre. In 1767, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart performed with his sister ...
. In 1740, Moravia was invaded by Prussian forces under Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
, and Olomouc was forced to surrender on 27 December 1741. A few months later the Prussians were repelled, mainly because of their unsuccessful siege of Brno in 1742. In 1758, Olomouc was besieged by Prussians again but this time, defenders of Olomouc forced the Prussians to withdraw following the Battle of Domstadtl
The Battle of Domstadtl (also spelled Domstadt, cs, Domašov) was a battle between the Habsburg monarchy and the Kingdom of Prussia in the Moravian village of Domašov nad Bystřicí during the Third Silesian War (part of the Seven Years' Wa ...
. In 1777, a new Moravian bishopric was established in Brno, and the Olomouc bishopric was raised to archbishopric. In 1782, the Margaviate of Moravia was merged with the Austrian Silesia
Austrian Silesia, (historically also ''Oesterreichisch-Schlesien, Oesterreichisch Schlesien, österreichisch Schlesien''); cs, Rakouské Slezsko; pl, Śląsk Austriacki officially the Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia, (historically ''Herzogth ...
into the ''Moravia-Silesia,'' with Brno as its capital city. This lasted until 1850.
20th century
Following the break-up of theAustro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
in 1918, Moravia became part of Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
. As one of the five lands of Czechoslovakia, it had restricted autonomy. In 1928 Moravia ceased to exist as a territorial unity and was merged with Czech Silesia
Czech Silesia (, also , ; cs, České Slezsko; szl, Czeski Ślōnsk; sli, Tschechisch-Schläsing; german: Tschechisch-Schlesien; pl, Śląsk Czeski) is the part of the historical region of Silesia now in the Czech Republic. Czech Silesia is, ...
into the Moravian–Silesian Land. After the German occupation of Czechoslovakia
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
in World War II, Moravia was divided – part was made an administrative unit within the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
The Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia; cs, Protektorát Čechy a Morava; its territory was called by the Nazis ("the rest of Czechia"). was a partially annexed territory of Nazi Germany established on 16 March 1939 following the German oc ...
and the area with more ethnic Germans was absorbed by the German Third Reich
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
.
In 1945 after the end of World War II and Allied defeat of Germany, Czechoslovakia, expelled the ethnic German minority of Moravia to Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. The Moravian–Silesian Land was restored with Moravia as part of it. In 1949 the territorial division of Czechoslovakia was radically changed, as the Moravian-Silesian Land was abolished and Lands were replaced by ''kraje'' (regions), whose borders substantially differ from the historical Bohemian-Moravian border, so Moravia politically ceased to exist after approx. 1116 years (833–1949) of its history.
After the fall of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, the Czechoslovak Federal Assembly condemned the cancellation of Moravian–Silesian land and expressed "firm conviction that this injustice will be corrected" in 1990, however after the breakup
A relationship breakup, breakup, or break-up is the termination of a relationship. The act is commonly termed "dumping omeone in slang when it is initiated by one partner. The term is less likely to be applied to a married couple, where a brea ...
of Czechoslovakia into Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
in 1993, Moravian land remained in the Czech territory, and the latest administrative division of Czech Republic (which was introduced in 2000) is nearly identical with the administrative division of 1949.
Gallery
References
Sources
* Semple, Ellen Churchill. "The Barrier Boundary of the Mediterranean Basin and Its Northern Breaches as Factors in History." ''Annals of the Association of American Geographers'', Vol. 5. (1915), pp 27–59. * Jiří Procházka: Vienna obsessa. Thesaurus Moraviae. Brno 2009. {{ISBN, 80-903476-8-1 Former Slavic countries