History Of Midway Atoll on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Midway Atoll (
Midway Atoll (
. Star-Advertiser, November 16, 2012 Tours focused on both the unique ecology of Midway, as well as its military history. The economy is derived solely from governmental sources and tourist fees. Nearly all supplies must be brought to the island by ship or plane, although a hydroponic greenhouse and garden supply some fresh fruits and vegetables.
 Midway Atoll is part of a chain of volcanic islands, atolls, and
Midway Atoll is part of a chain of volcanic islands, atolls, and
 In 1903, workers for the Commercial Pacific Cable Company took up residence on the island as part of the effort to lay a trans-Pacific telegraph cable. These workers introduced many non-native species to the island, including the canary, cycad,
In 1903, workers for the Commercial Pacific Cable Company took up residence on the island as part of the effort to lay a trans-Pacific telegraph cable. These workers introduced many non-native species to the island, including the canary, cycad,
Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge and Battle of Midway National Memorial. The channel was widened, and Naval Air Station Midway was completed. Midway was also an important submarine base. On February 14, 1941, President
 During the
During the
 In 1978, the Navy downgraded Midway from a Naval Air Station to a Naval Air Facility and large numbers of personnel and dependents began leaving the island. With the war in Vietnam over, and with the introduction of
In 1978, the Navy downgraded Midway from a Naval Air Station to a Naval Air Facility and large numbers of personnel and dependents began leaving the island. With the war in Vietnam over, and with the introduction of
 Midway Atoll forms part of the Northwest Hawaiian Islands
Midway Atoll forms part of the Northwest Hawaiian Islands
 Midway Atoll, in common with all the Hawaiian Islands, receives substantial amounts of
Midway Atoll, in common with all the Hawaiian Islands, receives substantial amounts of
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge and Battle of Midway National Memorial
(this article incorporated some content from this public domain site)
Diary from the middle of nowhere
BBC's environment correspondent David Shukman reports on the threat of plastic rubbish drifting in the North Pacific Gyre to Midway. Accessed 2008-03-26.
''The Battle of Midway: Turning the Tide in the Pacific,'' a National Park Service Teaching with Historic Places (TwHP) lesson plan
* ttp://www.midwayisland.com/ Past residents of MidwayDiscussion of Midway related topics by former residents and those interested in Midway.
Island Conservation: Midway Atoll Restoration Project
{{authority control
 Midway Atoll (
Midway Atoll (colloquial
Colloquialism (), also called colloquial language, everyday language or general parlance, is the linguistic style used for casual (informal) communication. It is the most common functional style of speech, the idiom normally employed in conver ...
: Midway Islands; haw, Kauihelani, translation=the backbone of heaven; haw, Pihemanu, translation=the loud din of birds, label=none) is a atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
in the North Pacific Ocean. Midway Atoll is an insular area
In the law of the United States, an insular area is a U.S.-associated jurisdiction that is not part of the 50 states or the District of Columbia. This includes fourteen U.S. territories administered under U.S. sovereignty, as well as three sov ...
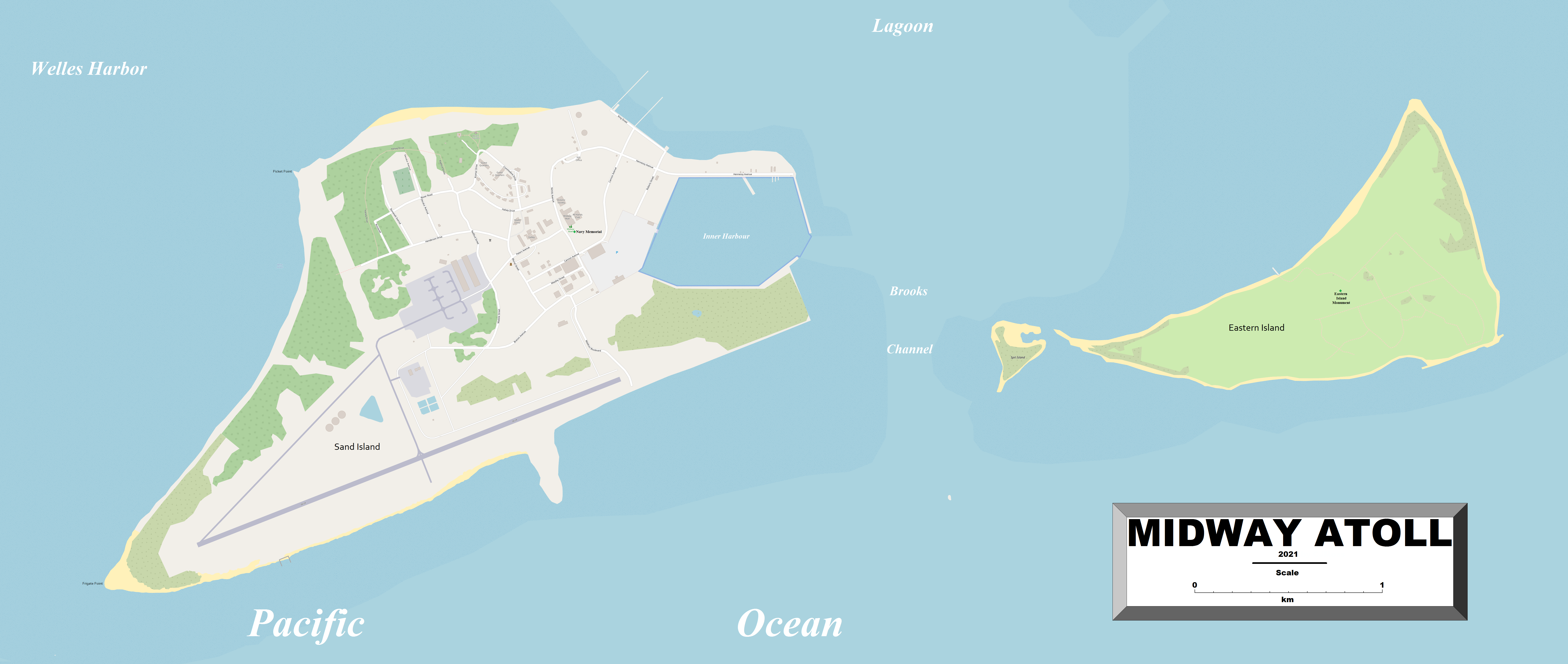
of the United States and is an unorganized and unincorporated territory. The largest island is Sand Island, which has housing and an airstrip. Immediately to the east of Sand Island across the narrow Brooks Channel is Eastern Island, which is uninhabited and no longer has any facilities. Forming a rough, incomplete circle around the two main islands and creating Midway Lagoon is Spit Island, a narrow reef.
Roughly equidistant between North America and Asia, Midway is the only island in the Hawaiian Archipelago
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
that is not part of the state of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
. Unlike the other Hawaiian islands, Midway observes Samoa Time ( UTC−11:00, i.e., eleven hours behind Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently used ...
), which is one hour behind the time in the Hawaii–Aleutian Time Zone
The Hawaii–Aleutian Time Zone observes Hawaii–Aleutian Standard Time (HST) by subtracting ten hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−10:00). The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 150th meridian west of the ...
used in Hawaii. For statistical purposes, Midway is grouped as one of the United States Minor Outlying Islands
The United States Minor Outlying Islands is a statistical designation defined by the International Organization for Standardization's ISO 3166-1 code. The entry code is ISO 3166-2:UM. The minor outlying islands and groups of islands consist ...
. The Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge, encompassing of land and water in the surrounding area, is administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
(FWS). The refuge and most of its surrounding area are part of the larger Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument
The Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument (PMNM) (roughly ) is a World Heritage Site, World Heritage listed National Monument (United States), U.S. National Monument encompassing of ocean waters, including ten islands and atolls of th ...
.
From 1941 until 1993, the atoll was the home of Naval Air Facility Midway Island
Naval Air Station Midway Island, also known as NAS Midway, Naval Air Facility Midway, and NAF Midway (former ICAO PMDY), was a U.S. Naval Air Station in the Midway Atoll, the northernmost group of the Hawaiian archipelago. It was in operation fr ...
, which played a crucial role in the Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II that took place on 4–7 June 1942, six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor and one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea. The U.S. Navy under Adm ...
, June 4–6, 1942. Aircraft based at the then-named Henderson Field on Eastern Island joined with United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
ships and planes in an attack on a Japanese battle group that sank four carriers, one heavy cruiser and defended the atoll from invasion. The battle was a critical Allied victory and a major turning point of the Pacific campaign of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
About 40 people live on the atoll, mostly staff of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and contract workers. Visitation to the atoll is possible only for business reasons, which includes permanent and temporary staff, contractors, and volunteers, as the tourism program has been suspended due to budget cutbacks. In 2012, the last year that the visitor program was in operation, 332 people made the trip to Midway.Ecotourism ends at Midway Atoll. Star-Advertiser, November 16, 2012 Tours focused on both the unique ecology of Midway, as well as its military history. The economy is derived solely from governmental sources and tourist fees. Nearly all supplies must be brought to the island by ship or plane, although a hydroponic greenhouse and garden supply some fresh fruits and vegetables.
Location
As its name suggests, Midway is roughly equidistant between North America and Asia, and lies almost halfway around the world longitudinally from Greenwich, England. It is near the northwestern end of the Hawaiian archipelago, about one-third of the way from Honolulu, Hawaii, to Tokyo, Japan. Midway is not considered part of the State of Hawaii due to the Hawaiian Organic Act of 1900 that formally annexed Hawaii to the United States as a territory, which defined Hawaii as "the islands acquired by the United States of America under an Act of Congress entitled 'Joint resolution to provide for annexing the Hawaiian Islands to the United States,'" referring to the Newlands Resolution of 1898. While it could be argued that Midway became part of Hawaii when Captain N.C. Brooks of the sealing ship ''Gambia'' sighted it in 1859, it was assumed at the time that Midway was independently acquired by the United States whenCaptain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
William Reynolds of visited in 1867, and thus not part of the Hawaii Territory.
In defining which islands the State of Hawaii would inherit from the Territory, the Hawaii Admission Act of 1959 clarified the question, specifically excluding Midway (along with Palmyra Island, Johnston Island, and Kingman Reef) from the jurisdiction of the state.
Midway Atoll is approximately east of the International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific O ...
, about west of San Francisco, and east of Tokyo.
Geography and geology
 Midway Atoll is part of a chain of volcanic islands, atolls, and
Midway Atoll is part of a chain of volcanic islands, atolls, and seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abru ...
s extending from the Island of Hawaii up to the tip of the Aleutian Islands and known as the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain, between Pearl and Hermes Atoll and Kure Atoll in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands
The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands or Leeward Hawaiian Islands are a series of islands and atolls in the Hawaiian island chain located northwest (in some cases, far to the northwest) of the islands of Kauai and Niihau. Politically, they are all p ...
. It consists of a ring-shaped barrier reef nearly in diameter and several sand islets. The two significant pieces of land, Sand Island and Eastern Island, provide a habitat for millions of seabirds. The island sizes are shown in the table above. The atoll, which has a small population (approximately 60 in 2014, but no indigenous inhabitants), is designated an ''insular area
In the law of the United States, an insular area is a U.S.-associated jurisdiction that is not part of the 50 states or the District of Columbia. This includes fourteen U.S. territories administered under U.S. sovereignty, as well as three sov ...
'' under the authority of the United States Department of the Interior.
Midway was formed roughly 28 million years ago when the seabed underneath it was over the same hotspot
Hotspot, Hot Spot or Hot spot may refer to:
Places
* Hot Spot, Kentucky, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Hot Spot (comics), a name for the DC Comics character Isaiah Crockett
* Hot Spot (Tra ...
from which the Island of Hawaii is now being formed. In fact, Midway was once a shield volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more v ...
, perhaps as large as the island of Lānaʻi
Lanai ( haw, Lānai, , , also ,) is the sixth-largest of the Hawaiian Islands and the smallest publicly accessible inhabited island in the chain. It is colloquially known as the Pineapple Island because of its past as an island-wide pineapple pl ...
. As the volcano piled up lava flows building the island, its weight depressed the crust and the island slowly subsided over a period of millions of years, a process known as isostatic adjustment
Post-glacial rebound (also called isostatic rebound or crustal rebound) is the rise of land masses after the removal of the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, which had caused isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound a ...
.
As the island subsided, a coral reef around the former volcanic island was able to maintain itself near sea level by growing upwards. That reef is now over thick (in the lagoon, , comprised mostly post- Miocene limestones with a layer of upper Miocene (Tertiary ''g'') sediments and lower Miocene (Tertiary ''e'') limestones at the bottom overlying the basalts). What remains today is a shallow water atoll about across. Following Kure Atoll, Midway is the 2nd most northerly atoll in the world.
Infrastructure
The atoll has some of roads, of pipelines, one port on Sand Island ( World Port Index Nr. 56328, MIDWAY ISLAND), and an airfield. , Henderson Field airfield at Midway Atoll, with its one active runway (rwy 06/24, around long) has been designated as an emergency diversion airport for aircraft flying under ETOPS rules. Although the FWS closed all airport operations on November22, 2004, public access to the island was restored from March 2008. Eastern Island Airstrip is a disused airfield that was in use by U.S. forces during the Battle of Midway. It is mostly constructed of Marston Mat and was built by the United States NavySeabees
United States Naval Construction Battalions, better known as the Navy Seabees, form the U.S. Naval Construction Force (NCF). The Seabee nickname is a heterograph of the initial letters "CB" from the words "Construction Battalion". Depending upon ...
.
Climate
Despite being located at 28°12′N, which is north of the Tropic of Cancer, Midway Atoll has a tropical savanna climate ( Köppen ''As'') with very pleasant year-round temperatures. Rainfall is evenly distributed throughout the year, with only two months being able to be classified as dry season months (May and June).History
Midway has no indigenous inhabitants and was uninhabited until the 19th century.19th century
The atoll was sighted on July 5, 1859, by Captain N.C. Brooks, of the sealing ship ''Gambia''. The islands were named the "Middlebrook Islands". Brooks claimed Midway for the United States under the Guano Islands Act of 1856, which authorized Americans to occupy uninhabited islands temporarily to obtainguano
Guano (Spanish from qu, wanu) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. As a manure, guano is a highly effective fertilizer due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. G ...
. There is no record of any attempt to mine guano on the island. On August28, 1867, Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
William Reynolds of formally took possession of the atoll for the United States; the name changed to "Midway" some time after this. The atoll was the first Pacific island annexed by the United States, as the Unincorporated Territory of Midway Island, and was administered by the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
.
The first attempt at settlement was in 1870, when the Pacific Mail Steamship Company started a project of blasting and dredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
a ship channel through the reef to the lagoon using money put up by the United States Congress. The purpose was to establish a mid-ocean coaling station to avoid the high taxes imposed at ports controlled by the Kingdom of Hawai'i. The project was a failure, and the evacuated the channel project's work force in October 1870. The ship ran aground on 21 October at Kure Atoll, stranding 93 men. On 18 November, five men set out in a small boat to seek help. On 19 December, four of the men perished when the boat was upset in the breakers off of Kauai
Kauai, () anglicized as Kauai ( ), is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands (after Niʻihau). With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the 21st largest island ...
. The survivor reached the U.S. Consulate in Honolulu on Christmas Eve
Christmas Eve is the evening or entire day before Christmas Day, the festival commemorating the birth of Jesus. Christmas Day is observed around the world, and Christmas Eve is widely observed as a full or partial holiday in anticipation ...
. Relief ships were despatched and reached Kure Atoll on 4 January 1871. The survivors of the Saginaw wreck reached Honolulu on 14 January 1871.
Early 20th century
 In 1903, workers for the Commercial Pacific Cable Company took up residence on the island as part of the effort to lay a trans-Pacific telegraph cable. These workers introduced many non-native species to the island, including the canary, cycad,
In 1903, workers for the Commercial Pacific Cable Company took up residence on the island as part of the effort to lay a trans-Pacific telegraph cable. These workers introduced many non-native species to the island, including the canary, cycad, Norfolk Island pine
''Araucaria heterophylla'' (synonym ''A. excelsa'') is a species of conifer. As its vernacular name Norfolk Island pine (or Norfolk pine) implies, the tree is endemic to Norfolk Island, an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific ...
, she-oak, coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
, and various deciduous trees; along with ants, cockroaches, termites, centipedes, and countless others.
On January 20, 1903, the United States Navy opened a radio station in response to complaints from cable company workers about Japanese squatters and poachers. Between 1904 and 1908, President Theodore Roosevelt stationed 21 Marines on the island to end wanton destruction of bird life and keep Midway safe as a U.S. possession
Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government of the United States. The various American territories differ from the U.S. states and tribal reservations as they are not so ...
, protecting the cable station.
In 1935, operations began for the Martin M-130 flying boat
A flying boat is a type of fixed-winged seaplane with a hull, allowing it to land on water. It differs from a floatplane in that a flying boat's fuselage is purpose-designed for floatation and contains a hull, while floatplanes rely on fusela ...
s operated by Pan American Airlines. The M-130s island-hopped from San Francisco to the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
, providing the fastest and most luxurious route to the Far East and bringing tourists to Midway until 1941. Only the very wealthy could afford the trip, which in the 1930s cost more than three times the annual salary of an average American. With Midway on the route between Honolulu and Wake Island, the flying boats landed in the atoll and pulled up to a float offshore in the lagoon. Tourists transferred to the Pan Am Hotel or the "Gooneyville Lodge", named after the ubiquitous "Gooney birds" (albatross
Albatrosses, of the biological family Diomedeidae, are large seabirds related to the procellariids, storm petrels, and diving petrels in the order Procellariiformes (the tubenoses). They range widely in the Southern Ocean and the North Pacifi ...
es).
World War II
The location of Midway in the Pacific became important militarily. Midway was a convenient refueling stop on transpacific flights, and was also an important stop for Navy ships. Beginning in 1940, as tensions with the Japanese rose, Midway was deemed second only to Pearl Harbor in importance to the protection of the U.S. West Coast. Airstrips, gun emplacements and a seaplane base quickly materialized on the tiny atoll.Preparing for WarMidway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge and Battle of Midway National Memorial. The channel was widened, and Naval Air Station Midway was completed. Midway was also an important submarine base. On February 14, 1941, President
Franklin Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
issued Executive Order 8682 to create naval defense areas in the central Pacific territories. The proclamation established "Midway Island Naval Defensive Sea Area", which encompassed the territorial waters between the extreme high-water marks and the marine boundaries surrounding Midway. "Midway Island Naval Airspace Reservation" was also established to restrict access to the airspace over the naval defense sea area. Only U.S. government ships and aircraft were permitted to enter the naval defense areas at Midway Atoll unless authorized by the Secretary of the Navy.
Midway's importance to the U.S. was brought into focus on December7, 1941, when the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, ...
. Midway was attacked by two destroyers on the same day, and the Japanese force was successfully repulsed in the first American victory of the war. A Japanese submarine bombarded Midway on February10, 1942.
Four months later, on June 4, 1942, a major naval battle near Midway resulted in the U.S. Navy inflicting a devastating defeat on the Imperial Japanese Navy. Four Japanese fleet aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a ...
s, , , and , were sunk, along with the loss of hundreds of Japanese aircraft, losses that the Japanese Empire
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
would never be able to replace. The U.S. lost the aircraft carrier , along with a number of its carrier- and land-based aircraft that were either shot down by Japanese forces or bombed on the ground at the airfields. The Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II that took place on 4–7 June 1942, six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor and one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea. The U.S. Navy under Adm ...
was, by most accounts, the beginning of the end of the Imperial Japanese Navy's control of the Pacific Ocean.
Starting in July 1942, a submarine tender was always stationed at the atoll to support submarines patrolling Japanese waters. In 1944, a floating dry dock joined the tender.
After the Battle of Midway, a second airfield was developed, this one on Sand Island. This work necessitated enlarging the size of the island through land fill techniques, that when concluded, more than doubled the size of the island.
Korean and Vietnam Wars
From August 1, 1941, to 1945, it was occupied by U.S. military forces. In 1950, the Navy decommissioned Naval Air Station Midway, only to re-commission it again to support the Korean War. Thousands of troops on ships and aircraft stopped at Midway for refueling and emergency repairs. From 1968 to September10, 1993, Midway Island was a Naval Air Facility. With about 3,500 people living on Sand Island, Midway also supported the U.S. troops during the Vietnam War. In June 1969, President Richard Nixon held a secret meeting withSouth Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam ( vi, Việt Nam Cộng hòa), was a state in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975, the period when the southern portion of Vietnam was a member of the Western Bloc during part of th ...
ese President Nguyen Van Thieu at the Officer-in-Charge house or "Midway House".
Missile Impact Location System
From 1958 through 1960 the United States installed the Missile Impact Location System (MILS) in the Navy managed Pacific Missile Range, later the Air Force managed Western Range, to localize the splash downs of test missile nose cones. MILS was developed and installed by the same entities that had completed the first phase of the Atlantic and U.S. West Coast SOSUS systems. A MILS installation, consisting of both a target array for precision location and a broad ocean area system for good positions outside the target area, was installed at Midway as part of the system supportingIntercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
(ICBM) tests. Other Pacific MILS shore terminals were at the Marine Corps Air Station Kaneohe Bay
Marine Corps Air Station Kaneohe Bay or MCAS Kaneohe Bay is a United States Marine Corps (USMC) airfield located within the Marine Corps Base Hawaii complex, formerly known as Marine Corps Air Facility (MCAF) Kaneohe Bay or Naval Air Station (NAS) ...
supporting Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM) tests with impact areas northeast of Hawaii and the other ICBM test support systems at Wake Island and Eniwetok.
Naval Facility Midway
 During the
During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
the U.S. established a shore terminal, in which output of the array at sea was processed and displayed by means of the Low Frequency Analyzer and Recorder (LOFAR), of the Sound Surveillance System
The Sound Surveillance System (SOSUS) was a submarine detection system based on passive sonar developed by the United States Navy to track Soviet submarines. The system's true nature was classified with the name and acronym SOSUS themselves classi ...
(SOSUS), Naval Facility (NAVFAC) Midway Island, to track Soviet submarines. The facility became operational in 1968 and was commissioned January13, 1969. It remained secret until its decommissioning on September30, 1983, after data from its arrays had been remoted first to Naval Facility Barbers Point, Hawaii, in 1981 and then directly to the Naval Ocean Processing Facility (NOPF) Ford Island, Hawaii. U.S. Navy WV-2 (EC-121K) "Willy Victor" radar aircraft flew night and day as an extension of the Distant Early Warning Line
The Distant Early Warning Line, also known as the DEW Line or Early Warning Line, was a system of radar stations in the northern Arctic region of Canada, with additional stations along the north coast and Aleutian Islands of Alaska (see Proj ...
, and antenna fields covered the islands.
Civilian handover
reconnaissance satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications.
The ...
s and nuclear submarines, Midway's significance to U.S. national security was diminished. The World War II facilities at Sand and Eastern Islands were listed on the National Register of Historic Places on May28, 1987, and were simultaneously added as a National Historic Landmark.
As part of the Base Realignment and Closure process, the Navy facility on Midway has been operationally closed since September10, 1993, although the Navy assumed responsibility for cleaning up environmental contamination.
2011 tsunami
The2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes ...
on March 11 caused many deaths among the bird population on Midway. It was reported that a high wave completely submerged the atoll's reef inlets and Spit Island, killing more than 110,000 nesting seabirds at the National Wildlife Refuge
National Wildlife Refuge System is a designation for certain protected areas of the United States managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. The National Wildlife Refuge System is the system of public lands and waters set aside to c ...
. Scientists on the island, however, do not think it will have long-term negative impacts on the bird populations.
A U.S. Geological Survey study found that the Midway Atoll, Laysan, and Pacific islands like them could become inundated and unfit to live on during the 21st century, due to increased storm waves and rising sea levels.
National Wildlife Refuge and National Monument
Midway was designated an overlayNational Wildlife Refuge
National Wildlife Refuge System is a designation for certain protected areas of the United States managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. The National Wildlife Refuge System is the system of public lands and waters set aside to c ...
on April22, 1988, while still under the primary jurisdiction of the Navy.
From August 1996, the general public could visit the atoll through study ecotours. This program ended in 2002, but another visitor program was approved and began operating in March 2008. This program operated through 2012, but was suspended for 2013 due to budget cuts.
On October 31, 1996, President Bill Clinton signed Executive Order 13022, which transferred the jurisdiction and control of the atoll to the United States Department of the Interior. The FWS assumed management of the Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge. The last contingent of Navy personnel left Midway on June30, 1997, after an ambitious environmental cleanup program was completed.
On September 13, 2000, Secretary of the Interior Bruce Babbitt designated the Wildlife Refuge as the Battle of Midway National Memorial. The refuge is now titled as the "Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge and Battle of Midway National Memorial".
On June 15, 2006, President George W. Bush designated the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands as a national monument. The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands Marine National Monument encompasses , and includes of coral reef habitat. The Monument also includes the Hawaiian Islands National Wildlife Refuge and the Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge.
In 2007, the Monument's name was changed to Papahānaumokuākea () Marine National Monument. The National Monument is managed by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and the State of Hawaii. In 2016 President Obama expanded the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, and added the Office of Hawaiian Affairs as a fourth co-trustee of the monument.
Environment
 Midway Atoll forms part of the Northwest Hawaiian Islands
Midway Atoll forms part of the Northwest Hawaiian Islands Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations.
IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife Int ...
(IBA), designated as such by BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding ...
because of its seabirds and endemic landbirds. The atoll is a critical habitat in the central Pacific Ocean, and includes breeding habitat for 17 seabird species. A number of native species rely on the island, which is now home to 67–70 percent of the world's Laysan albatross population, and 34–39 percent of the global population of black-footed albatross. A very small number of the very rare short-tailed albatross also have been observed. Fewer than 2,200 individuals of this species are believed to exist due to excessive feather hunting in the late nineteenth century. In 2007–08, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service translocated 42 endangered Laysan ducks to the atoll as part of their efforts to conserve the species.
Over 250 different species of marine life are found in the of lagoon and surrounding waters. The critically endangered Hawaiian monk seals raise their pups on the beaches, relying on the atoll's reef fish, squid, octopus and crustaceans. Green sea turtles
The green sea turtle (''Chelonia mydas''), also known as the green turtle, black (sea) turtle or Pacific green turtle, is a species of large sea turtle of the family Cheloniidae. It is the only species in the genus ''Chelonia''. Its range exten ...
, another threatened species, occasionally nest on the island. The first was found in 2006 on Spit Island and another in 2007 on Sand Island. A resident pod of 300 spinner dolphins live in the lagoons and nearshore waters.
The islands of Midway Atoll have been extensively altered as a result of human habitation. Starting in 1869 with the project to blast the reefs and create a port on Sand Island, the environment of Midway atoll has experienced profound changes.
A number of invasive exotics have been introduced; for example, ironwood trees from Australia were planted to act as windbreaks. Of the 200 species of plants on Midway, 75 percent are non-native. Recent efforts have focused on removing non-native plant species and re-planting native species.
Lead paint on the buildings posed an environmental hazard (avian lead poisoning Animal lead poisoning (also known as avian plumbism, or avian saturnism for birds) is a veterinary condition and pathology caused by increased levels of the heavy metal lead in animal's body.
Lead interferes with a variety of body and natural proc ...
) to the albatross population of the island. In 2018, a project to strip the paint was completed.
Pollution
 Midway Atoll, in common with all the Hawaiian Islands, receives substantial amounts of
Midway Atoll, in common with all the Hawaiian Islands, receives substantial amounts of marine debris
Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a sea or ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing ...
from the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. Consisting of 90 percent plastic, this debris accumulates on the beaches of Midway. This garbage represents a hazard to the bird population of the island. Every year 20 tons of plastic debris washes up on Midway, with 5 tons of that debris being fed to Albatross chicks. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service estimates at least of plastic washes up every week.
Of the 1.5 million Laysan Albatrosses that inhabit Midway, nearly all are found to have plastic in their digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
. Approximately one-third of the chicks die. These deaths are attributed to the albatrosses confusing brightly colored plastic with marine animals (such as squid and fish) for food. Recent results suggest that oceanic plastic develops a chemical signature that is normally used by seabirds to locate food items.
Because albatross chicks do not develop the reflex to regurgitate until they are four months old, they cannot expel the plastic pieces. Albatrosses are not the only species to suffer from the plastic pollution; sea turtles
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, ...
and monk seals also consume the debris. A variety of plastic items wash upon the shores, from cigarette lighters to toothbrushes and toys. An albatross on Midway can have up to 50 percent of its intestinal tract filled with plastic.
Transportation
The usual method of reaching Sand Island, Midway Atoll's only populated island, is on chartered aircraft landing at Sand Island's Henderson Field, which also functions as an emergency diversion point runway for transpacific flights.See also
* Desert island * List of islandsReferences
Further reading
Natural history
*Hubert, Mabel, Carl Frings, and H. Franklin – ''Sounds of Midway: Calls of Albatrosses of Midway.'' *Mearns, Edgar Alexander – ''A List of the Birds Collected by Dr. Paul Bartsch in the Philippine Islands, Borneo, Guam, and Midway Island, with Descriptions of Three New Forms.'' * *Military history
* * * * * * * * *External links
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge and Battle of Midway National Memorial
(this article incorporated some content from this public domain site)
Diary from the middle of nowhere
BBC's environment correspondent David Shukman reports on the threat of plastic rubbish drifting in the North Pacific Gyre to Midway. Accessed 2008-03-26.
''The Battle of Midway: Turning the Tide in the Pacific,'' a National Park Service Teaching with Historic Places (TwHP) lesson plan
* ttp://www.midwayisland.com/ Past residents of MidwayDiscussion of Midway related topics by former residents and those interested in Midway.
{{authority control
Midway Atoll
Midway Atoll (colloquial: Midway Islands; haw, Kauihelani, translation=the backbone of heaven; haw, Pihemanu, translation=the loud din of birds, label=none) is a atoll in the North Pacific Ocean. Midway Atoll is an insular area of the Unit ...
Articles containing video clips
Atolls of Hawaii
Cenozoic Hawaii
Coral reefs of the United States
Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain
Pacific islands claimed under the Guano Islands Act
IUCN Category IV
National Wildlife Refuges in the United States insular areas
Northwestern Hawaiian Islands
Oligocene volcanoes
Paleogene Oceania
Protected areas established in 1988
Reefs of the Pacific Ocean
Seabird colonies
United States Minor Outlying Islands
World War II sites
National Memorials of the United States
Island restoration
Important Bird Areas of United States Minor Outlying Islands
Important Bird Areas of Oceania