History Of Maharashtra (1947–present) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 From the 6th century CE to the 8th century, the
From the 6th century CE to the 8th century, the
 The
The
Google Book Search
'' The founder of the Suena dynasty was
 In the early 14th century, the Yadava dynasty, which ruled most of present-day Maharashtra, was overthrown by the
In the early 14th century, the Yadava dynasty, which ruled most of present-day Maharashtra, was overthrown by the
 After the collapse of the Tughluqs in 1347, the breakaway
After the collapse of the Tughluqs in 1347, the breakaway

 During much of the 18th century, the
During much of the 18th century, the
Cite: ''"Swarming up from the Himalayas, the Marathas now ruled from the Indus and Himalayas in the north to the south tip of the peninsula. They were either masters directly or they took tribute."'' The Marathas even discussed abolishing the Mughal throne and placing Peshwa

 People from Maharashtra played an important part in the social and religious reform movements as well as the nationalist movement of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Notable
People from Maharashtra played an important part in the social and religious reform movements as well as the nationalist movement of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Notable  In the 1930s, Jedhe merged the non-Brahmin party with the Congress party, changing it from an upper-caste dominated body to a more broadly based but also
In the 1930s, Jedhe merged the non-Brahmin party with the Congress party, changing it from an upper-caste dominated body to a more broadly based but also
 From 1954 to 1955, the people of Marathi speaking areas strongly protested against being included in the bilingual Bombay state. In response, the Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti, Samyukta Maharashtra Movement was formed to fight for a united Maharashtra for the Marathi people. The Mahagujarat Movement also advocated for a separate
From 1954 to 1955, the people of Marathi speaking areas strongly protested against being included in the bilingual Bombay state. In response, the Samyukta Maharashtra Samiti, Samyukta Maharashtra Movement was formed to fight for a united Maharashtra for the Marathi people. The Mahagujarat Movement also advocated for a separate
 The Indian National Congress, Congress party and its allies have ruled the state for the major part during the state's existence. After the brief tenures of Yashwantrao Chavan, who was inducted as defence minister by Prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru, Nehru, and Marotrao Kannamwar, who died after one year in office, Vasantrao Naik was Chief minister from 1963 to 1975. The politics of the state in this period was also dominated by leaders such as Yashwantrao Chavan, Vasantdada Patil, Vasantrao Naik, and Shankarrao Chavan.
Sharad Pawar became a significant personality within the state in 1978 when he broke away from the Congress party to form an alliance government with the Janata party. During his career, Pawar split Congress twice, with significant consequences for state politics. In 1999, after his dispute with the party president Sonia Gandhi over her foreign origins, in 1999, Pawar left the party and formed the Nationalist Congress Party (NCP). The party, however, joined a Indian National Congress, Congress-led coalition to form the state government after the 1999 Assembly elections.
The Congress party enjoyed a nearly unchallenged dominance of the state political landscape, until 1995 when the coalition of Shiv Sena and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) secured an overwhelming majority in the state, beginning a period of coalition governments. Shiv Sena was the larger party in the coalition. From 1999 until 2014, the NCP and INC formed one coalition while Shiv Sena and the BJP formed another for three successive elections, which the INC-NCP alliance won. Prithviraj Chavan of the Congress party was the last Chief Minister of Maharashtra under the Congress-NCP alliance that ruled until 2014.
The Indian National Congress, INC during its rule enjoyed overwhelming support from the state's influential Cooperative sugar factories in Maharashtra, sugar co-operatives, as well as thousands of other cooperatives, such as rural agricultural cooperatives involved in the marketing of dairy and vegetable produce, credit unions, etc.
For the better part of its existence, politics of the state was also dominated by the mainly rural
The Indian National Congress, Congress party and its allies have ruled the state for the major part during the state's existence. After the brief tenures of Yashwantrao Chavan, who was inducted as defence minister by Prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru, Nehru, and Marotrao Kannamwar, who died after one year in office, Vasantrao Naik was Chief minister from 1963 to 1975. The politics of the state in this period was also dominated by leaders such as Yashwantrao Chavan, Vasantdada Patil, Vasantrao Naik, and Shankarrao Chavan.
Sharad Pawar became a significant personality within the state in 1978 when he broke away from the Congress party to form an alliance government with the Janata party. During his career, Pawar split Congress twice, with significant consequences for state politics. In 1999, after his dispute with the party president Sonia Gandhi over her foreign origins, in 1999, Pawar left the party and formed the Nationalist Congress Party (NCP). The party, however, joined a Indian National Congress, Congress-led coalition to form the state government after the 1999 Assembly elections.
The Congress party enjoyed a nearly unchallenged dominance of the state political landscape, until 1995 when the coalition of Shiv Sena and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) secured an overwhelming majority in the state, beginning a period of coalition governments. Shiv Sena was the larger party in the coalition. From 1999 until 2014, the NCP and INC formed one coalition while Shiv Sena and the BJP formed another for three successive elections, which the INC-NCP alliance won. Prithviraj Chavan of the Congress party was the last Chief Minister of Maharashtra under the Congress-NCP alliance that ruled until 2014.
The Indian National Congress, INC during its rule enjoyed overwhelming support from the state's influential Cooperative sugar factories in Maharashtra, sugar co-operatives, as well as thousands of other cooperatives, such as rural agricultural cooperatives involved in the marketing of dairy and vegetable produce, credit unions, etc.
For the better part of its existence, politics of the state was also dominated by the mainly rural
Causes of Farmer Suicides in Maharashtra: An Enquiry. Final Report Submitted to the Mumbai High Court 15 March 2005
The report cited "government's lack of interest, the absence of a safety net for farmers, and lack of access to information related to agriculture as the chief causes for the desperate condition of farmers in the state."
महाराष्ट्राचा गौरवशाली इतिहास / The History of Maharashtra.....
* James Grant Duff, ''History of the Mahrattas,'' 3 vols. London, Longmans, Rees, Orme, Brown, and Green (1826). * Mahadev Govind Ranade, ''Rise of the Maratha Power'' (1900); reprint (1999). * Richard Eaton, The new Cambridge history of India, *
Maharashtra State Past Present & History In Marathi Language
Maharashtra Government's website
{{DEFAULTSORT:Maharashtra (history) History of Maharashtra, Maharashtra
Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
is a state in the western region of India. It is India's second-most populous state and third-largest state by area. The region that comprises the state has a long history dating back to ca. 1300–700 BCE, although the present-day state was not established until 1960 CE.
Prior to Indian independence, notable dynasties and entities that ruled the region include, in chronological order, the Maurya
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
, the Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India ( Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh ...
, the Satavahana dynasty
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late ...
, Rashtrakuta dynasty
Rashtrakuta (IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their ...
, Western Chalukyas
The Western Chalukya Empire ruled most of the Deccan Plateau, western Deccan, South India, between the 10th and 12th centuries. This Kannada people, Kannadiga dynasty is sometimes called the ''Kalyani Chalukya'' after its regal capital at Kalya ...
, the Bahamanis, Deccan sultanates
The Deccan sultanates were five Islamic late-medieval Indian kingdoms—on the Deccan Plateau between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range—that were ruled by Muslim dynasties: namely Ahmadnagar, Berar, Bidar, Bijapur, and Golconda. Th ...
, Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
founded by Shivaji
Shivaji Bhonsale I (; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680), also referred to as Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle Maratha clan. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the declining Adils ...
, and the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
. Ruins
Ruins () are the remains of a civilization's architecture. The term refers to formerly intact structures that have fallen into a state of partial or total disrepair over time due to a variety of factors, such as lack of maintenance, deliberate ...
, monuments
A monument is a type of structure that was explicitly created to commemorate a person or event, or which has become relevant to a social group as a part of their remembrance of historic times or cultural heritage, due to its artistic, hist ...
, tombs
A tomb ( grc-gre, τύμβος ''tumbos'') is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called ''immuremen ...
, forts
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
, and places of worship left by these rulers are dotted around the state. At the time of the Indian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.
The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged ...
in the early 20th century, along with British ruled areas of Bombay presidency
The Bombay Presidency or Bombay Province, also called Bombay and Sind (1843–1936), was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India, with its capital in the city that came up over the seven islands of Bombay. The first mainl ...
, and Central Provinces and Berar
The Central Provinces and Berar was a province of British India and later the Dominion of India which existed from 1903 to 1950. It was formed by the merger of the Central Provinces with the province of Berar, which was territory leased by the B ...
. The region included many British vassal states
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to t ...
. Among these, the erstwhile Hyderabad state
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
was the largest and extended over many modern Indian states. Other states grouped under Deccan States Agency
The Deccan States Agency, also known as the Deccan States Agency and Kolhapur Residency, was a political agency of British India, managing the relations of the British government of the Bombay Presidency with a collection of princely states and ...
included Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarter of the Kolhapur district. In, around 2 C.E. Kolapur's name was 'Kuntal'.
Kolhapur is kn ...
, Miraj
Miraj (Pronunciation: iɾəd͡z ) is a city in Sangli District and also in Maharashtra, India, that was founded in the early 10th century. It was an important jagir of the Adil Shahi court of Bijapur.
Shivaji Maharaj stayed in Miraj for ...
, Sangli
Sangli () is a city and the district headquarters of Sangli District in the state of Maharashtra, in western India. It is known as the Turmeric City of Maharashtra due to its production and trade of the spice. Sangli is situated on the banks o ...
, Aundh, Bhor
Bhor () is a town and a municipal council in Pune district in the state of Maharashtra, India.
Geography
Bhor is located at . It has an average elevation of 588 metres (1929 feet).
Demographics
India census, Bhor had a populati ...
, and Sawantwadi
Sawantwadi an aesthetic land of artists, is an integral part of the Konkan region which is in the mid-western coast of India.
The western coast of India since 1510 A.D. has assumed great importance in Indian history and history of internationa ...
.
After independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
from the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
in 1947
It was the first year of the Cold War, which would last until 1991, ending with the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Events
January
* January–February – Winter of 1946–47 in the United Kingdom: The worst snowfall in the country in ...
, the state of Maharashtra was formed in 1960 after a campaign to create a Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
-speaking state in the 1950s.
From the 4th century BC until 875, Maharashtri Prakrit
Maharashtri or Maharashtri Prakrit ('), is a Prakrit language of ancient as well as medieval India and the ancestor of Marathi and Konkani.
Maharashtri Prakrit was commonly spoken until 875 CEV.Rajwade, ''Maharashtrache prachin rajyakarte''
and its dialects were the dominant languages of the region. The Marathi language, which evolved from Maharashtri Prakrit, has been the common language since the 9th century. The oldest stone inscriptions in the Marathi language date to around 975 AD, and can be seen in the Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
temple at Shravanabelgola in modern-day Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
at the foot of the Lord Bahubali statue.
Early history


Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular ...
sites belonging to the Jorwe culture
The Jorwe culture was a Chalcolithic archaeological culture which existed in large areas of what is now Maharashtra state in Western India, and also reached north into the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh. It is named after the type site of Jorwe. ...
(ca. 1300–700 BCE) have been discovered throughout the state. The largest settlement discovered of the culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
is at Daimabad
Daimabad is a deserted village and archaeological site on the left bank of the Pravara River, a tributary of the Godavari River in Shrirampur taluka in Ahmednagar district of Maharashtra state in India. This site was discovered by B. P. Bopardi ...
, a Late Harappan
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
site, which had a mud fortification during this period, as well as an elliptical temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
with fire pits. Some settlements show evidence of planning in the layout of rectangular houses and streets or lanes. In the Late Harappan period there was a large migration of people from Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
to northern Maharashtra.
Maharashtra was historically the name of a region which consisted of Aparanta
Aparanta, or Aparantaka (meaning "Western border") was a geographical region of ancient India. It corresponded to the northern part of the Konkan region on the western coast of India. English civil servant-turned-historian J. F. Fleet believed t ...
, Vidarbha
Vidarbha (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, �id̪əɾbʱə is a geographical region in the east of the Indian state of Maharashtra and a Proposed states and union territories of India#Maharashtra, proposed state of central India, comprising th ...
, Mulak, Assaka
Ashmaka (Sanskrit: ) or Assaka (Pali: ) was a Mahajanapada in ancient India which existed between 700 BCE and 425 or 345 BCE according to the Buddhist texts '' Anguttara Nikaya'' and ''Puranas''. It was located around and between the Godavar ...
(Asmaka
Ashmaka (Sanskrit: ) or Assaka (Pali: ) was a Mahajanapada in ancient India which existed between 700 BCE and 425 or 345 BCE according to the Buddhist texts '' Anguttara Nikaya'' and ''Puranas''. It was located around and between the Godavar ...
) and Kuntala. In ancient times tribal communities
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflic ...
of Bhil people
Bhil or Bheel is an ethnic group in western India. They speak the Bhil languages, a subgroup of the Western Zone of the Indo-Aryan languages. As of 2013, Bhils were the largest tribal group in India.
Bhils are listed as tribal people of the s ...
inhabited this area, also known as Dandakaranya
Dandakaranya is a historical region in India, mentioned in the Ramayana. It is identified with a territory roughly equivalent to the Bastar division in the Chhattisgarh state in the central-east part of India. It covers about of land, which inc ...
. There was also an ancient race called "Rattha" ( in Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
), who referred to themselves as "Maharattha" (Maha is Great). The name Maharashtra first appeared in the 7th century in the account of a contemporary Chinese traveler, Huan Tsang.
Linguists and archeologists believe it is likely Maharashtra was inhabited by Dravidian speakers during the middle Rigvedic period, which is determined from Dravidian place names in Maharashtra. Maharashtra region later became part of the Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
with edicts
An edict is a decree or announcement of a law, often associated with monarchism, but it can be under any official authority. Synonyms include "dictum" and "pronouncement".
''Edict'' derives from the Latin edictum.
Notable edicts
* Telepinu Pro ...
of emperor Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
found in the region. Buddhism flourished during this period. Trade, including international trade with Greeks and later with the Roman empire, also flourished, with traders being the main patrons of Buddhist monasteries. Indo-Sythian Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India ( Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh ...
ruled part of the region during the early part of the first millennium.
Middle Kingdoms (200 BCE-13th century CE)
The region that is present-day Maharashtra has formed part of a number of states, including theMaurya empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
, Satavahana dynasty
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late ...
, the Kadamba dynasty, the Vakataka dynasty
The Vakataka dynasty () was an ancient Indian dynasty that originated from the Deccan in the mid-3rd century CE. Their state is believed to have extended from the southern edges of Malwa and Gujarat in the north to the Tungabhadra River in the ...
, the Chalukya dynasty
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynast ...
and the Rashtrakuta dynasty
Rashtrakuta (IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their ...
. Most of these empires extended over large swathes of Indian territory. Some of the greatest monuments in Maharashtra, such as the Ajanta Caves
The Ajanta Caves are approximately thirty rock-cut Buddhist cave monuments dating from the second century BCE to about 480 CE in the Aurangabad district of Maharashtra state in India. The caves include paintings and rock-cut sculptures des ...
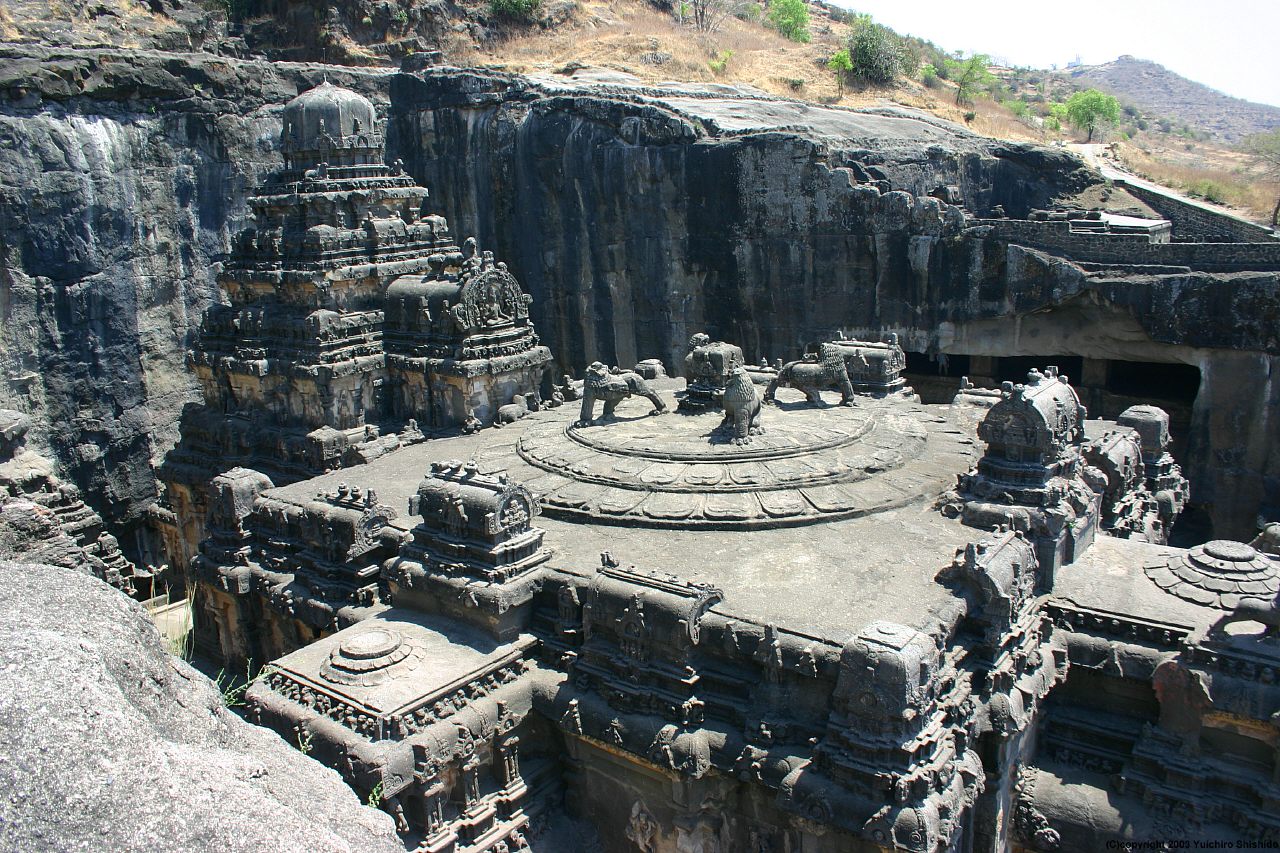
and Ellora Caves
Ellora is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the Aurangabad district of Maharashtra, India. It is one of the largest rock-cut Hindu temple cave complexes in the world, with artwork dating from the period 600–1000 CE., Quote: "These 34 m ...
, were built during the time of these empires.
Classical period (c. 200 BCE – c. 650 CE)
Maharashtra was ruled by theMaurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
in the 4th and 3rd century BCE. Around 230 BCE, it was taken over by the Satavahana dynasty
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late ...
, which ruled the region for the next 400 years. A notable ruler of the Satavahana dynasty was Gautamiputra Satakarni
Gautamiputra Satakarni (Brahmi: 𑀕𑁄𑀢𑀫𑀺𑀧𑀼𑀢 𑀲𑀸𑀢𑀓𑀡𑀺, ''Gotamiputa Sātakaṇi'', IAST: ) was a ruler of the Satavahana Empire in present-day Deccan region of India. He was mentioned as the important and ...
, who defeated Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
invaders. The Vakataka dynasty
The Vakataka dynasty () was an ancient Indian dynasty that originated from the Deccan in the mid-3rd century CE. Their state is believed to have extended from the southern edges of Malwa and Gujarat in the north to the Tungabhadra River in the ...
ruled from approximately 250 to 470 CE.
The Satavahana dynasty mainly used the Prakrit
The Prakrits (; sa, prākṛta; psu, 𑀧𑀸𑀉𑀤, ; pka, ) are a group of vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The term Prakrit is usu ...
language on their coins and for inscriptions on the walls of Buddhist monasteries.
The Chalukya and Rashtrakuta
 From the 6th century CE to the 8th century, the
From the 6th century CE to the 8th century, the Chalukya dynasty
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynast ...
ruled Maharashtra. Two prominent rulers were Pulakeshin II
Pulakeshin II (IAST: Pulakeśin, r. c. 610–642 CE) was the most famous ruler of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi (present-day Badami in Karnataka, India). During his reign, the Chalukya kingdom expanded to cover most of the Deccan region in p ...
, who defeated the north Indian Emperor Harsha
Harshavardhana ( IAST Harṣa-vardhana; c. 590–647 CE) was a Pushyabhuti emperor who ruled northern India from 606 to 647 CE. He was the son of Prabhakaravardhana who had defeated the Alchon Huna invaders, and the younger brother of Rajyav ...
, and Vikramaditya II
Vikramaditya II (reigned 733 – 744 CE) was the son of King Vijayaditya and ascended the Badami Chalukya throne following the death of his father. This information comes from the Lakshmeshwar inscriptions in Kannada dated 13 January 735 A.D. ...
, who defeated Arab invaders in the 8th century. The Rashtrakuta Dynasty
Rashtrakuta (IAST: ') (r. 753-982 CE) was a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the sixth and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their ...
ruled Maharashtra from the 8th to the 10th century. The Arab traveler Sulaiman Sulaiman is an English transliteration of the Arabic name that means "peaceful" and corresponds to the Jewish name Hebrew: שְׁלֹמֹה, Shlomoh) and the English Solomon (/ˈsɒləmən/) . Solomon was the scriptural figure who was king of ...
called the ruler of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty (Amoghavarsha
Amoghavarsha I (also known as Amoghavarsha Nrupathunga I) (r.814–878 CE) was the greatest emperor of the Rashtrakuta dynasty, and one of the most notable rulers of Ancient India. His reign of 64 years is one of the longest precisely dated mo ...
) "one of the 4 great kings of the world". The Chalukya dynasty
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynast ...
and Rashtrakuta dynasty had their capitals in modern-day Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
and used Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native s ...
and Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
as court languages.
From the early 11th century to the 12th century the Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by the ...
, including a large part of Maharashtra, was dominated by the Western Chalukya Empire
The Western Chalukya Empire ruled most of the western Deccan, South India, between the 10th and 12th centuries. This Kannadiga dynasty is sometimes called the ''Kalyani Chalukya'' after its regal capital at Kalyani, today's Basavakalyan in the ...
and the Chola dynasty
The Chola dynasty was a Tamils, Tamil thalassocratic Tamil Dynasties, empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated ...
. Several battles over the Deccan Plateau were fought between these empires during the reigns of Raja Raja Chola I
Rajaraja I (947 CE – 1014 CE), born Arunmozhi Varman or Arulmozhi Varman and often described as Raja Raja the Great or Raja Raja Chozhan was a Chola emperor who reigned from 985 CE to 1014 CE. He was the most powerful Tamil king in South ...
, Rajendra Chola I
Rajendra Chola I (; Middle Tamil: Rājēntira Cōḻaṉ; Classical Sanskrit: Rājēndradēva Cōla; Old Malay: ''Raja Suran''; c. 971 CE – 1044 CE), often referred to as Rajendra the Great, and also known as Gangaikonda Chola (Middle Tami ...
, Jayasimha II, Someshvara I
Someshvara I (; ) was a king of the Western Chalukyas. Also known as "Ahavamalla" or "Trilokamalla", Someshvara succeeded his father Jayasimha II to the throne.
His several military successes in Central India made him a formidable ruler of a ...
and Vikramaditya VI
Vikramaditya VI (r. 1076 – 1126 CE) became the Western Chalukya King after deposing his elder brother Someshvara II, a political move he made by gaining the support of Chalukya vassals during the Chola invasion of Chalukya territory.Sen ( ...
.
Between 800 and 1200 CE, parts of Western Maharashtra, including the Konkan
The Konkan ( kok, कोंकण) or Kokan () is a stretch of land by the western coast of India, running from Damaon in the north to Karwar in the south; with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Deccan plateau in the east. The hinterland ...
region of Maharashtra, were ruled by different Shilahara
The Shilahara Kingdom ( IAST: Śilāhāra; also Sinhara, Shailahara, Shrilara, and Silara) was a royal dynasty that established itself in northern and southern Konkan in 8th century CE, present-day Mumbai and Southern Maharashtra (Kolhapur) d ...
houses based in North Konkan, South Konkan, and Kolhapur respectively. At different periods in their history, the Shilaharas served as the vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. W ...
s of either the Rashtrakutas or the Chalukyas.
Yadav dynasty 12th-14th century
 The
The Yadavas of Devagiri
The Seuna, Sevuna, or Yadavas of Devagiri (IAST: Seuṇa, –1317) was a Medieval Indian dynasty, which at its peak ruled a kingdom stretching from the Narmada river in the north to the Tungabhadra river in the south, in the western part of t ...
dynasty at its peak ruled a kingdom stretching from the Tungabhadra to the Narmada rivers, including present-day Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
, north Karnataka
North Karnataka is a geographical region in Deccan plateau from elevation that constitutes the region of the Karnataka state in India and the region consists of 13 districts. It is drained by the Krishna River and its tributaries the Bhi ...
and parts of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
. Its capital was at Devagiri
Daulatabad Fort, also known as Devagiri Fort or Deogiri Fort, is a historic fortified citadel located in Daulatabad village near Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. It was the capital of the Yadava dynasty (9th century–14th century CE), for a b ...
(present-day Daulatabad in modern Maharashtra). The Yadavas
The Yadava (literally, descended from Yadu) were an ancient Indian people who believed to be descended from Yadu, a legendary king of Chandravamsha lineage. The community was formed of various clans, being the Abhira, Andhaka, Vrishni, and Satv ...
initially ruled as feudatories
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. W ...
of the Western Chalukyas
The Western Chalukya Empire ruled most of the Deccan Plateau, western Deccan, South India, between the 10th and 12th centuries. This Kannada people, Kannadiga dynasty is sometimes called the ''Kalyani Chalukya'' after its regal capital at Kalya ...
. ''The quoted pages can be read aGoogle Book Search
'' The founder of the Suena dynasty was
Dridhaprahara
Dridhaprahara (IAST: Dṛḍhaprahāra, r. c. 860-880) is the earliest historically attested ruler of the Seuna (Yadava) dynasty that ruled the western Deccan region in present-day India.
Early life
According to Jain tradition, Dridhaprahara wa ...
, the son of Subahu. It is unclear where his capital was located; some argue that his capital was Shrinagara, while an early inscription suggests that Chandradityapura (modern Chandwad
Chandwad (IPA:Cāndavaḍa) is a town located in the Nashik district in Maharashtra. It is 250 km from Mumbai. The 11th-century Jain Caves, Renuka devi mandir, Chandreshwar temple and Rangmahal are in Chandwad.
Chandwad is a tehsil of Na ...
in the Nasik
Nashik (, Marathi: aːʃik, also called as Nasik ) is a city in the northern region of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Situated on the banks of river Godavari, Nashik is the third largest city in Maharashtra, after Mumbai and Pune. Nashik ...
district) was the capital. The name Seuna comes from Dridhaprahara's son, Seunachandra, who originally ruled a region called ''Seunadesha'' (present-day Khandesh
Khandesh is a geographic region in Central India, which includes parts of the northwestern portion of Maharashtra as well as Burhanpur District of Madhya Pradesh.
The use of Khandeshi Language (a.k.a. the Ahirani Language) is prevalent in ...
). Bhillama II, a later ruler in the dynasty, assisted Tailapa II
Tailapa II (r. c. 973-997), also known as Taila II and by his title ''Ahavamalla'', was the founder of the Western Chalukya dynasty in southern India. Tailapa claimed descent from the earlier Chalukyas of Vatapi, and initially ruled as a Rashtr ...
in his war with the Paramara
The Paramara dynasty (IAST: Paramāra) was an Indian dynasty that ruled Malwa and surrounding areas in west-central India between 9th and 14th centuries. They belonged to the Parmara clan of the Rajputs.
The dynasty was established in either th ...
king Vakpati Munja
Munja (reigned c. 972-990s CE), also known as Vakpati II, was an Indian ruler from the Paramara dynasty, who ruled in the Malwa region. He is known for consolidating the Paramara kingdom, for patronizing poets and scholars and for achieving the ...
. Seunachandra II helped Vikramaditya VI
Vikramaditya VI (r. 1076 – 1126 CE) became the Western Chalukya King after deposing his elder brother Someshvara II, a political move he made by gaining the support of Chalukya vassals during the Chola invasion of Chalukya territory.Sen ( ...
in gaining his throne.
Around the middle of the 12th century, as Chalukya power waned, the Yadavas declared independence. Their rule reached its peak under Singhana II. The Yadavas of Devagiri used Marathi as their court language. Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
was used as a court language by earlier Yadava rulars. Simhana
Simhana ( IAST: Siṃhaṇa, also transliterated as Singhana; r. c. 1210-1246 was the most powerful ruler of the Seuna (Yadava) dynasty of Deccan region in India. He expanded his kingdom southwards at the expense of the Hoysalas, and fought the C ...
started using Marathi as official court Language. The Yadava capital Devagiri became a magnet for learned scholars in Marathi to showcase and find patronage for their skills. The origin and growth of Marathi literature
Marathi literature is the body of literature of Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language spoken mainly in the Indian state of Maharashtra and written in the Devanagari and Modi script.
History Ancient Era
Maharashtri Prakrit was the southern Prakrit tha ...
is directly linked with the rise of the Yadava dynasty.
According to scholars such as George Moraes, V. K. Rajwade, C. V. Vaidya
Chintaman Vinayak Vaidya (18 October 1861– 20 April 1938) was a Marathi-language historian and writer from Maharashtra, India. He was Chief Justice of Gwalior State for a period. He was born in a Chitpavan Brahmin family.
In 1908, Vaidya chaire ...
, A.S. Altekar
Anant Sadashiv Altekar (24 September 1898 – 25 November 1960; ) was a historian, archaeologist, and numismatist from Maharashtra, India. He was the Manindra Chandra Nandy's Professor and Head of the Department of Ancient Indian History and Cu ...
, D. R. Bhandarkar
Devadatta Ramakrishna Bhandarkar ( mr, देवदत्त रामकृष्ण भांडारकर; 19 November 1875 – 13 May 1950) was an Indian archaeologist and epigraphist who worked with the Archaeological Survey of India (AS ...
, and J. Duncan M. Derrett
John Duncan Martin Derrett (30 August 1922 – 21 October 2012) was Professor of Oriental Laws in the University of London, from 1965 to 1982, and afterwards Emeritus Professor.
Derrett was educated at Emanuel School, London, Jesus College, Oxfor ...
, the Seuna rulers were of Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
descent. Digambar Balkrishna Mokashi noted that the Yadava dynasty "seems to be the first true Maratha empire".
Medieval and Early modern period (1206-1858 CE)
 In the early 14th century, the Yadava dynasty, which ruled most of present-day Maharashtra, was overthrown by the
In the early 14th century, the Yadava dynasty, which ruled most of present-day Maharashtra, was overthrown by the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
ruler Ala-ud-din Khalji
Alaud-Dīn Khaljī, also called Alauddin Khilji or Alauddin Ghilji (), born Ali Gurshasp, was an emperor of the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrativ ...
. Later, Muhammad bin Tughluq
Muhammad bin Tughluq (1290 – 20 March 1351) was the eighteenth Sultan of Delhi. He reigned from February 1325 until his death in 1351. The sultan was the eldest son of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq, founder of the Tughlaq dynasty. In 1321, the youn ...
conquered parts of the Deccan, and temporarily shifted his capital from Delhi to Daulatabad in Maharashtra.
Bahmani and Deccan Sultanates
 After the collapse of the Tughluqs in 1347, the breakaway
After the collapse of the Tughluqs in 1347, the breakaway Bahmani Sultanate
The Bahmani Sultanate, or Deccan, was a Persianate Sunni Muslim Indian Kingdom located in the Deccan region. It was the first independent Muslim kingdom of the Deccan,
governed the region as well as the wider Deccan
The large Deccan Plateau in South India, southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bou ...
region for the next 150 years from Gulbarga
Kalaburagi, formerly known as Gulbarga, is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kalaburagi district and is the largest city in the region of North Karnataka (Kalyana-Karnataka). Kalaburagi is 6 ...
and later from Bidar
Bidar (/ biːd̪ər/) is a city in the north-eastern part of Karnataka state in India. It is the headquarters of Bidar district, which borders Maharashtra and Telangana. It is a rapidly urbanising city in the wider ''Bidar Metropolitan area ...
.
The early period of Islamic rule saw atrocities such as imposition of Jizya
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent Kafir, non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The jizya tax has been unde ...
tax on non-Muslims, temple destruction and forcible conversions. Eventually these incidents largely ceased. For most of this period Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru ...
s were in charge of accounts, whereas revenue collection was in the hands of Marathas who had (hereditary rights) of patilki (revenue collection at village level) and deshmukh
Deshmukh (IAST:Dēśamukh), is a historical title conferred to the rulers of a . It is used as a surname in certain regions of India, specifically in the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh whose family received it as a ...
i (revenue collection over a larger area). A number of families such as Shinde
Shinde (pronunciation: �in̪d̪e is a clan of the Maratha clan system of Kunbi (Kurmi) origin; variations of the name include Scindia and ''Sindhia'', '' Sindia''. The ''Shinde'' last name may be also found in the Dalit community.
The Scindia ...
, Bhosale
The Bhonsle (or Bhonsale, Bhosale, Bhosle) are a prominent group within the Maratha clan system of kunbi origin. They claimed descent from the Sisodia Rajputs but were likely Kunbi tiller-plainsmen.
History Earliest members
The earliest ac ...
, Shirke, Ghorpade, Jadhav
Jadhav is an Indian surname. Notable people with the name include:
* Bharat Jadhav (born 1973), Indian theatre and film producer
* Bhaskar Jadhav, Indian politician
*Dhanaji Jadhav (1650–1708), warrior of the Maratha Empire
*Kedar Jadhav (born 1 ...
, More, Mahadik, Ghatge and Nimbalkar
Nimbalkar is a Maratha clan, which derives its surname from the forest of Nimbalak in Phaltan taluka, Satara district, Maharashtra, India.
Some Nimbalkars served as head of the deshmukhs (''sardeshmukhs'' or ''sardars'') during the period of the ...
loyally served different sultans at different periods in time. Since most of the population was Hindu and spoke Marathi, even sultans such as Ibrahim Adil Shah I
Ibrahim Adil Shah I ( fa, ; 1534–1558) was a Sultan and later Shah of the Indian kingdom of Bijapur. He succeeded his elder brother, Mallu Adil Shah, through the machinations of the Afaqi faction at the court. He was the first Adil Shahi ru ...
adopted Marathi as the court language, for administration and record keeping.
After the break-up of the Bahamani
The Bahmani Sultanate, or Deccan, was a Persianate Sunni Muslim Indian Kingdom located in the Deccan region. It was the first independent Muslim kingdom of the Deccan,
sultanate in 1518, the Maharashtra region was split between five Deccan Sultanates
The Deccan sultanates were five Islamic late-medieval Indian kingdoms—on the Deccan Plateau between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range—that were ruled by Muslim dynasties: namely Ahmadnagar, Berar, Bidar, Bijapur, and Golconda. Th ...
: Nizamshah of Ahmadnagar Sultanate
The Ahmadnagar Sultanate was a late medieval Indian Muslim kingdom located in the northwestern Deccan, between the sultanates of Gujarat and Bijapur. Malik Ahmed, the Bahmani governor of Junnar after defeating the Bahmani army led by general Ja ...
, Adilshah
The Adil Shahi or Adilshahi, was a Shia,Salma Ahmed Farooqui, ''A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: From Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century'', (Dorling Kindersley Pvt Ltd., 2011), 174. and later Sunni Muslim,Muhammad Qasim Firishta's ...
of Bijapur, Qutubshah
The Qutb Shahi dynasty also called as Golconda Sultanate (Persian: ''Qutb Shāhiyān'' or ''Sultanat-e Golkonde'') was a Persianate Shia Islam dynasty of Turkoman origin that ruled the sultanate of Golkonda in southern India. After the coll ...
of Golkonda, Bidarshah of Bidar and Imadshah
Berar Sultanate, also called as Imad Shahi Sultanate was one of the Deccan sultanates, which was founded by an Indian Muslim. It was established in 1490 following the disintegration of the Bahmani Sultanate.
History
Background
The origin of ...
of Elichpur. These kingdoms often fought with each other. United, they decisively defeated the Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hinduism, Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana an ...
of the south in 1565. The present area of Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
was ruled by the Sultanate of Gujarat
The Gujarat Sultanate (or the Sultanate of Guzerat), was a Medieval Indian kingdom established in the early 15th century in Western India, primarily in the present-day state of Gujarat, India. The dynasty was founded by Sultan Zafar Khan Muza ...
before its capture by Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
in 1535.
The Faruqi dynasty
The Farooqi dynasty (also spelt Farooqui, Faruqi) was the ruling dynasty of the Khandesh Sultanate (named after the Khandesh region) from its inception in 1382 till its annexation by the Mughal emperor Akbar in 1601. The founder of the dynasty, M ...
and Rao Shinde family ruled the Khandesh
Khandesh is a geographic region in Central India, which includes parts of the northwestern portion of Maharashtra as well as Burhanpur District of Madhya Pradesh.
The use of Khandeshi Language (a.k.a. the Ahirani Language) is prevalent in ...
region between 1382 and 1601 before finally being annexed by the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. The Mughals under Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
started capturing territories held by the Deccan sultanates towards the end of 16th century. This initiative continued under his successors for almost a century, when most of the present day area of Maharashtra came under Mughal control. However, Mughal control was challenged multiple times during this period. Early in the century the resistance was led by Malik Ambar
Malik Ambar (1548 – 13 May 1626) was a Siddi military leader and prime minister who became a kingmaker and de facto ruler of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate in the Deccan region of India.
Born in the Adal Sultunate, in present-day Ethiopia, Malik ...
, the regent of the Nizamshahi dynasty of Ahmednagar
Ahmednagar (), is a city located in the Ahmednagar district in the state of Maharashtra, India, about 120 km northeast of Pune and 114 km from Aurangabad. Ahmednagar takes its name from Ahmad Nizam Shah I, who founded the town in 1494 ...
from 1607 to 1626. He increased the strength and power of Murtaza Nizam Shah II
Murtaza Nizam Shah II ( 1580–1610) was the Sultan of Ahmadnagar from 1600 to 1610. His rule was dominated by the powerful regent Malik Ambar, under whom he was an effective puppet ruler.
Life
Born 1580, he was originally given the name Ali ...
and raised a large army. Malik Ambar was a proponent of guerilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tac ...
in the Deccan region and was considered a great foe by Mughal emperor Jehangir
Nur-ud-Din Muhammad Salim (30 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was the fourth Mughal Emperor, who ruled from 1605 until he died in 1627. He was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti.
Ear ...
. He assisted Mughal prince Khurram (later emperor Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mugha ...
) in his struggle against his stepmother, Nur Jahan
Nur Jahan, born Mehr-un-Nissa P ersian: نورجهان (; – 18 December 1645) was the wife and chief consort of the Mughal emperor Jahangir from 1620 until his death in 1627.
Nur Jahan was born Mehr-un-Nissa, as the daughter of a Mirza Ghi ...
, who had ambitions to secure the Delhi throne for her son-in-law. In the second half of the 17th century, the Mughals were constantly challenged by the Marathas under Shivaji, and later his successors.
In fact, the decline of Islamic rule in Deccan started when Shivaji annexed a portion of the Bijapur Sultanate
The Adil Shahi or Adilshahi, was a Shia,Salma Ahmed Farooqui, ''A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: From Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century'', (Dorling Kindersley Pvt Ltd., 2011), 174. and later Sunni Muslim,Muhammad Qasim Firishta's T ...
in the second half of the 17th century. In the process, he became a symbol of Hindu resistance and self-rule.
Maratha Empire (1674–1818 CE)
TheMaratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
dominated the political scene in India from the middle of the 17th century to the early 19th century.
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj

Shivaji
Shivaji Bhonsale I (; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680), also referred to as Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle Maratha clan. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the declining Adils ...
was the founder of the modern Maratha empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
; his policies were instrumental in forging a distinct identity for the Marathi people
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
. He was born in the Bhonsle
The Bhonsle (or Bhonsale, Bhosale, Bhosle) are a prominent group within the Maratha clan system of kunbi origin. They claimed descent from the Sisodia Rajputs but were likely Kunbi tiller-plainsmen.
History Earliest members
The earliest a ...
clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, meaning ...
, sometime in the period 1627 to 1630. Shivaji carved out an enclave from the declining Adilshahi sultanate
The Adil Shahi or Adilshahi, was a Shia,Salma Ahmed Farooqui, ''A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: From Twelfth to the Mid-Eighteenth Century'', (Dorling Kindersley Pvt Ltd., 2011), 174. and later Sunni Muslim,Muhammad Qasim Firishta's ...
of Bijapur
Bijapur, officially known as Vijayapura, is the district headquarters of Bijapur district of the Karnataka state of India. It is also the headquarters for Bijapur Taluk. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural ...
that formed the genesis of the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
. In 1674, he crowned himself as the Chhatrapati (Monarch) of his realm
A realm is a community or territory over which a sovereign rules. The term is commonly used to describe a monarchical or dynastic state. A realm may also be a subdivision within an empire, if it has its own monarch, e.g. the German Empire.
Etym ...
at Raigad Fort
Raigad is a hill fort situated in Mahad, Raigad district of Maharashtra, India. It is one of the strongest fortresses on the Deccan Plateau. It was previously known as Rairee or Rairy fort.
Many constructions and structures on Raigad were b ...
. However, to achieve this he not only had to fight the Mughals and the Adilshahi but also many Maratha Watandars. These Watandars considered their watan a source of economic power and pride and were reluctant to part with it. The Watandars even initially opposed the emergence of Shivaji
Shivaji Bhonsale I (; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680), also referred to as Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle Maratha clan. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the declining Adils ...
, because their economic interests were affected.
Shivaji was an able administrator and established a government that included such modern concepts as a cabinet (''ashtapradhana mandala''), foreign affairs (''dabir'') and internal intelligence. He established an effective civil and military administration, built a powerful navy and erected new forts (e.g. Sindhudurg Fort
Sindhudurg Fort (Marathi pronunciation: in̪d̪ʱud̪uɾɡ is a historical fort that occupies an island in the Arabian Sea, just off the coast of Maharashtra in Western India. The fort was built by Shivaji Maharaj.The fortress lies on the ...
) and strengthened old ones (e.g. Vijaydurg Fort
Vijaydurg (sometimes written as Viziadurg), the oldest fort on the Sindhudurg coast, was constructed during the regime of Raja Bhoja II of the Shilahar dynasty (construction period 1193-1205) and restructured by Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
...
) on the west coast of Maharashtra. He died around April 3, 1680, of dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications ...
.
After Shivaji died, Mughal emperor Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
launched an attack on the Marathas that led to a war lasting 27 years. The death of Aurangzeb in 1707 ended the war and initiated the decline of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
.
Expansion of Maratha Influence in 18th Century under Shahu I and Peshwa rule
 During much of the 18th century, the
During much of the 18th century, the Peshwa
The Peshwa (Pronunciation: e(ː)ʃʋaː was the appointed (later becoming hereditary) prime minister of the Maratha Empire of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, the Peshwas served as subordinates to the Chhatrapati (the Maratha king); later, ...
s, belonging to the (Bhat) Deshmukh
Deshmukh (IAST:Dēśamukh), is a historical title conferred to the rulers of a . It is used as a surname in certain regions of India, specifically in the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh whose family received it as a ...
Marathi Chitpavan Brahmin
The Chitpavan Brahmin or Konkanastha Brahmin is a Hindu Maharashtrian Brahmin community inhabiting Konkan, the coastal region of the state of Maharashtra. Initially working as messengers and spies in the late seventeenth century, the community ...
family, controlled the Maratha army and later became the hereditary heads of the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
from 1749 to 1818. During their reign, the Maratha empire reached its zenith in 1760, dominating most of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. Bajirao I
Baji Rao I (18 August 1700 – 28 April 1740), born as Visaji, also known as Bajirao Ballal (Pronunciation: ad͡ʒiɾaːʋ bəlːaːɭ, was the 7th Peshwa of the Maratha Empire. During his 20-year tenure as a Peshwa, he defeated Nizam-ul-M ...
, a prominent Peshwa
The Peshwa (Pronunciation: e(ː)ʃʋaː was the appointed (later becoming hereditary) prime minister of the Maratha Empire of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, the Peshwas served as subordinates to the Chhatrapati (the Maratha king); later, ...
(general), was only 20 when appointed Peshwa. For his campaigns in North India, he actively promoted young leaders of his own age such as Ranoji Shinde
Ranoji Shinde the founder of the Scindia dynasty from maratha caste that produced outstanding Maratha military commanders during the 18th century. Later the Scindia served as vassals of the British from the northern Princely state of Gwalior.
...
, Malharrao Holkar
Malhar Rao Holkar (16 March 1693 – 20 May 1766) was a noble subedar of the Maratha Empire, in present-day India. He was one of the early officers along with Ranoji Scindia to help spread the Maratha rule to northern states and was given the es ...
, the Puar brothers and Pilaji Gaekwad
Pilajirao Gaekwad (died 14 May 1732) was a Maratha general. He is considered to be the founder of the Gaekwad dynasty of the Maratha Empire, who became Maharaja of Baroda.
Early life
Pilaji was the eldest son of Jhingojirao Kerojirao Gaekwad ...
. These leaders also did not come from the traditional aristocratic families of Maharashtra. All the young leaders chosen by Bajirao I or their descendants later became rulers in their own right during the Maratha Confederacy era. Historian K.K. Datta argues that Bajirao I "may very well be regarded as the second founder of the Maratha Empire".
Another general, Raghoji Bhonsle
Raghoji I (''Raghoji Bhonsle''; ; 1695 – February 1755) or Raghuji the Great of the Bhonsale dynasty, was a Maratha general who took control of the Nagpur Kingdom in east-central India during the reign of Shahu I. His successors ruled the ...
, also expanded the Maratha rule in central and East India and took control of the Nagpur Kingdom
The Kingdom of Nagpur was an Indian kingdom in the 18th and 19th centuries. It came under the rule of the Marathas of the Bhonsle dynasty in the mid-18th century and became part of the Maratha Empire. The city of Nagpur was the capital of the st ...
. In 1737, the Marathas defeated a Mughal army in their capital, in the Battle of Delhi. The Marathas continued their military campaigns against the Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, Nizam
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
, Nawab of Bengal
The Nawab of Bengal ( bn, বাংলার নবাব) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar, ...
and the Durrani Empire to further extend their boundaries.
By 1760, the domain of the Marathas stretched across most of the Indian subcontinent.The Rediscovery of India: A New SubcontinentCite: ''"Swarming up from the Himalayas, the Marathas now ruled from the Indus and Himalayas in the north to the south tip of the peninsula. They were either masters directly or they took tribute."'' The Marathas even discussed abolishing the Mughal throne and placing Peshwa
Vishwasrao
Vishwasrao Bhat (22 July 1742 – 14 January 1761) was the eldest son of Peshwa Balaji Baji Rao of the Maratha Empire and also was the heir to the title of Peshwa.
Vishwasrao had received training in administration and warfare from the age of ...
on the Mughal imperial throne in Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
. At its peak, the empire stretched from Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a States and union territories of India, state in southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India ...
in the south, to Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
(modern-day Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ps, خېبر پښتونخوا; Urdu, Hindko: خیبر پختونخوا) commonly abbreviated as KP or KPK, is one of the Administrative units of Pakistan, four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
) in the north, and Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
in the east. The Northwestern expansion of the Marathas was stopped after the Third Battle of Panipat (1761). However, the Maratha authority in the north was re-established within a decade under Peshwa Madhavrao I
Peshwa Madhavrao Bhat I (February 15, 1745 – November 18, 1772) was the 9th Peshwa of the Maratha Empire. During his tenure, the Maratha empire fully recovered from the losses they suffered during the Third Battle of Panipat, a phenomenon kn ...
. Under Madhavrao I, the strongest knights were granted semi-autonomy, creating a confederacy of Maratha states led by the Gaekwad
Gaekwad (also spelt Gaikwar and Gaikwad; mr, Gāyǎkǎvāḍǎ) is a surname native to the Indian state of Maharashtra. The surname is found among the Marathas, Kolis and in Scheduled castes. It is also a common surname among Bharadis, Dhor, an ...
s of Baroda
Vadodara (), also known as Baroda, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Vadodara district and is situated on the banks of the Vishwamitri River, from the state capital ...
, the Holkar
The Holkar (Pronunciation: �o(ː)ɭkəɾ dynasty was a Maratha clan of Dhangar origin in India. The Holkars were generals under Peshwa Baji Rao I, and later became Maharajas of Indore in Central India as an independent member of the Marat ...
s of Indore
Indore () is the largest and most populous Cities in India, city in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It serves as the headquarters of both Indore District and Indore Division. It is also considered as an education hub of the state and is t ...
and Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also syno ...
, the Scindia
The Scindia dynasty (anglicized from Shinde) is a Hindu Maratha dynasty of maratha origin that ruled the erstwhile State of Gwalior. It had the Patil-ship of Kumberkerrab in Wai. It was founded by Ranoji Scindia, who started as a personal servan ...
s of Gwalior
Gwalior() is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located south of Delhi, the capital city of India, from Agra and from Bhopal, the s ...
and Ujjain
Ujjain (, Hindustani language, Hindustani pronunciation: Help:IPA/Hindi and Urdu, �d͡ːʒɛːn is a city in Ujjain district of the States and territories of India, Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Prad ...
, the Bhonsale
The Bhonsle (or Bhonsale, Bhosale, Bhosle) are a prominent group within the Maratha clan system of kunbi origin. They claimed descent from the Sisodia Rajputs but were likely Kunbi tiller-plainsmen.
History Earliest members
The earliest ac ...
s of Nagpur
Nagpur (pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, aːɡpuːɾ is the third largest city and the winter capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the 13th largest city in India by population and according to an Oxford's Economics report, Nag ...
and the Puars
Parmar is a Rajput clan found in Northern and Central India, especially in Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Kutch, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and North Maharashtra.
See also
* Paramara Dynasty
* Panwar Dynasty
* Pawar
* Pan ...
of Dhar
Dhar is a city located in Dhar district of the Malwa region in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India. The city is the administrative headquarters of the Dhar district. Before Indian independence from Great Britain, it was the capital of the Dhar ...
and Dewas
Dewas is a city in the Malwa region of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. The municipality was formerly the seat of two 15-Gun Salute state princely states during the British Raj, Dewas Junior state and Dewas Senior state, ruled by the Pua ...
.
In 1775, the East India Company intervened in a Peshwa family succession struggle in Pune
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, (List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million ...
, leading to the First Anglo-Maratha War
The First Anglo-Maratha War (1775–1782) was the first of three Anglo-Maratha Wars fought between the British East India Company and Maratha Empire in India. The war began with the Treaty of Surat and ended with the Treaty of Salbai. The wa ...
, which resulted in a Maratha victory.
Maratha Navy
Shivaji developed a potentNaval force
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It inc ...
during his rule. In the early part of the 1700s, under the leadership of Kanhoji Angre
Kanhoji Angre (Marathi: कान्होजी आंग्रे, Help:IPA/Marathi, anʱod͡ʒiː aːŋɡɾe, also known as Conajee Angria or Sarkhel Angré (August 1669 – 4 July 1729) was a chief of the Maratha Navy in present-day Ind ...
, this navy dominated the territorial waters of the western coast of India from Bilimora
Bilimora is a city situated on the banks of the river Ambika River, Ambika, in Gandevi taluka & Navsari district of Gujarat state, in India. The city comes under the purview of the Surat Metropolitan Region. The city is roughly south of the c ...
, Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
to Savantwadi
Sawantwadi is a taluka (a unit of administration) in the Sindhudurg district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The taluka headquarters is Sawantwadi which has a municipal council, which is a local civic body. Sawantwadi was formerly the capita ...
. It attacked British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and Siddi
The Siddi (), also known as the Sheedi, Sidi, or Siddhi, or Habshi are an ethnic group inhabiting India and Pakistan. They are primarily descended from the Bantu peoples of the Zanj coast in Southeast Africa and Ethiopia, most whom arrived to ...
Naval ships and kept a check on their naval ambitions. The Maratha Navy
The Maratha Navy was the naval wing of the armed forces of the Maratha Empire, which existed from around mid-17th century to mid-18th century in India.
Formative years
Historian Sir Jadunath Sarkar noted:
In medieval India, the Muslim rul ...
was dominant in the area until around the 1730s, was in a state of decline by the 1770s and ceased to exist by 1818.
Revenue system and Chauth
One of the tools of the empire was collection ofChauth
Chauth (from Sanskrit, meaning ''one fourth'') was a regular tax or tribute imposed from the early 18th century by the Maratha Empire in the Indian subcontinent. It was an annual tax nominally levied at 25% on revenue or produce, hence the name, on ...
or 25% of the revenue from states that submitted to Maratha power. The Marathas also had an elaborate land revenue system which was retained by the British East India Company when they gained control of Maratha territory.
British colonial period (1818–1947 CE)

Company Rule
TheEast India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
controlled Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
beginning in the 17th century and used it as one of their main trading posts. The Company slowly expanded areas under its rule during the 18th century. Their conquest of Maharashtra was completed in 1818 with the defeat of Peshwa
The Peshwa (Pronunciation: e(ː)ʃʋaː was the appointed (later becoming hereditary) prime minister of the Maratha Empire of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, the Peshwas served as subordinates to the Chhatrapati (the Maratha king); later, ...
Bajirao II
Shrimant Peshwa Baji Rao II (10 January 1775 – 28 January 1851) was the 13th and the last Peshwa of the Maratha Empire. He governed from 1795 to 1818. He was installed as a puppet ruler by the Maratha nobles, whose growing power prompted him ...
in the Third Anglo-Maratha War
The Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817–1819) was the final and decisive conflict between the English East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India. The war left the Company in control of most of India. It began with an invasion of Maratha te ...
.
British Raj
The British ruled for more than a century and brought huge changes in every aspect of life for the people of the Maharashtra region. Areas that correspond to present day Maharashtra were under direct or indirect British rule, first under theEast India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
and then, from 1858, under the British crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territorie ...
. During this era, Maharashtra region was divided into the Bombay presidency
The Bombay Presidency or Bombay Province, also called Bombay and Sind (1843–1936), was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India, with its capital in the city that came up over the seven islands of Bombay. The first mainl ...
, Berar Berar may refer to:
*Vidarbha, the eastern region of Maharashtra Province, India, historically known as Berar
*Berar Sultanate (1490–1596), one of the Deccan sultanates
*Berar Subah (1596–1724), a Subah of the Mughal Empire
*Berar Province (1724 ...
, Central provinces
The Central Provinces was a province of British India. It comprised British conquests from the Mughals and Marathas in central India, and covered parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra states. Its capital was Nagpur. ...
, Hyderabad state
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
and various Princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, ...
s such as Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarter of the Kolhapur district. In, around 2 C.E. Kolapur's name was 'Kuntal'.
Kolhapur is kn ...
and Miraj
Miraj (Pronunciation: iɾəd͡z ) is a city in Sangli District and also in Maharashtra, India, that was founded in the early 10th century. It was an important jagir of the Adil Shahi court of Bijapur.
Shivaji Maharaj stayed in Miraj for ...
.
The British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
saw standardization of Marathi grammar
The grammar of the Marathi language shares similarities with other modern Indo-Aryan languages such as Odia language, Odia, Gujarati language, Gujarati or Punjabi language, Punjabi. The first modern book exclusively about the grammar of Marathi la ...
through the efforts of the Christian missionary William Carey. Carey also published the first dictionary of Marathi in devanagari
Devanagari ( ; , , Sanskrit pronunciation: ), also called Nagari (),Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, , page 83 is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental syste ...
script. The most comprehensive Marathi-English dictionary was compiled by Captain James Thomas Molesworth James Thomas Molesworth (1795 – 13 July 1871) was a military officer in the services of the British East India Company, and one of the most prominent lexicographers of the Marathi language.
Early life
James was the youngest son of Richard and ...
and Major Thomas Candy
Thomas Candy (13 December 1804 - 26 February 1877) was an English educator with a lifelong association to India, who made lasting contributions to the lexicography, orthography, and stylistics of the Marathi language.
Article on 'कॅँडी, ...
in 1831. The book is still in print nearly two centuries after its publication. Molesworth Molesworth may refer to:
Places
*Molesworth, Cambridgeshire, a village in Huntingdonshire, Cambridgeshire, England
*Molesworth (crater), a crater on Mars
*Molesworth Station, New Zealand's largest farm
*Molesworth Street, Dublin, Ireland
* Moleswo ...
also worked on standardizing Marathi. He used Brahmins of Pune
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, (List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million ...
for this task and adopted the Sanskrit-dominated dialect spoken by this caste in the city as the standard dialect for Marathi.
 People from Maharashtra played an important part in the social and religious reform movements as well as the nationalist movement of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Notable
People from Maharashtra played an important part in the social and religious reform movements as well as the nationalist movement of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Notable Civil society
Civil society can be understood as the "third sector" of society, distinct from government and business, and including the family and the private sphere.Poona Sarvajanik Sabha
Poona Sarvajanik Sabha, ( mr, पुणे सार्वजनिक सभा) (Also knows as Sarvajanik Sabha ), was a sociopolitical organisation in British India which started with the aim of working as a mediating body between the gover ...
, the Prarthana Samaj
Prarthana Samaj or "Prayer Society" in Sanskrit, was a movement for religious and social reform in Bombay, India, based on earlier reform movements. Prarthana Samaj was founded by Atmaram Pandurang in 31 March 1867 when Keshub Chandra Sen vi ...
, the Arya Mahila Samaj and the Satya Shodhak Samaj
Satyashodhak Samaj (''Truth-seekers' Society'') was a social reform society founded by Jyotiba Phule in Pune, Maharashtra, on 24 September 1873. It espoused a mission of education and increased social rights and political access for underprivile ...
. The Sarvajanik Sabha took an active part in relief efforts during the famine of 1875–76, and is considered the forerunner of the Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Em ...
established in 1885. The most prominent personalities of Indian Nationalism in the late 19th and early 20th century were Gopal Krishna Gokhale
Gopal Krishna Gokhale ( �ɡoːpaːl ˈkrɪʂɳə ˈɡoːkʰleː9 May 1866 – 19 February 1915) was an Indian 'moderate' political leader and a social reformer during the Indian independence movement. Gokhale was a senior leader of the India ...
and Bal Gangadhar Tilak
Bal Gangadhar Tilak (; born Keshav Gangadhar Tilak (pronunciation: eʃəʋ ɡəŋɡaːd̪ʱəɾ ʈiɭək; 23 July 1856 – 1 August 1920), endeared as Lokmanya (IAST: ''Lokmānya''), was an Indian nationalist, teacher, and an independence a ...
, who were on opposite sides of the political spectrum, were both from Pune. Tilak was instrumental in using Shivaji and Ganesha
Ganesha ( sa, गणेश, ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka, and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped deities in the Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in Ganapatya sect. His image is found throughout India. Hindu d ...
worship to forge a collective Maharashtrian identity for Marathi people. The Marathi social reformers of the colonial era include Mahatma Jyotirao Phule
Jyotirao Govindrao Phule, also known as Mahatma Jyotiba Phule (11 April 1827 – 28 November 1890) was an Indian social activist, thinker, anti-caste social reformer and writer from Maharashtra. His work extended to many fields, including era ...
, his wife Savitribai Phule
Savitribai Phule was an Indian social reformer, educationalist, and poet from Maharashtra. Along with her husband, in Maharashtra, she played an important and vital role in improving women's rights in India. She is considered to be the pioneer ...
, Justice Ranade
Mahadev Govind Ranade (18 January 1842 – 16 January 1901), popularly referred to as Justice Ranade, was an Indian scholar, social reformer, judge and author. He was one of the founding members of the Indian National Congress party and owned ...
, feminist Tarabai Shinde, Dhondo Keshav Karve
''
Dhondo Keshav Karve (18 April 1858 – 9 November 1962), popularly known as Maharshi Karve, was a social reformer in India in the field of women's welfare. He advocated widow remarriage and he himself married a widow. Karve was a pioneer in ...
, Vitthal Ramji Shinde
Vitthal Ramji Shinde (23 April 1873 – 2 January 1944) was one of the most important social and religious reformers in Maharashtra, India. He was prominent among the liberal thinkers and reformists in India, prior to his independence. His grea ...
and Pandita Ramabai
Pandita Ramabai Sarasvati (23 April 1858 – 5 April 1922) was an Indian Social Reformer. She was the first woman to be awarded the titles of '' Pandita'' as a Sanskrit scholar and ''Sarasvati'' after being examined by the faculty of the Unive ...
. Jyotirao Phule was a pioneer in opening schools for girls and Marathi dalits
Dalit (from sa, दलित, dalita meaning "broken/scattered"), also previously known as untouchable, is the lowest stratum of the castes in India. Dalits were excluded from the four-fold varna system of Hinduism and were seen as forming ...
castes.
The non-Brahmin Hindu castes of Maharashtra started organizing at the beginning of the 20th century with the blessing of Shahu of Kolhapur
Shahu (also known as Chhatrapati Rajarshi Shahu, Shahu IV, Rajarshi Shahu Maharaj, Kolhapur's Shahu) (26 June 1874 – 6 May 1922) of the Bhonsle dynasty of Marathas was a Raja (reign. 1894 – 1900) and the first Maharaja (1900–1922) of t ...
. The campaign took off in the early 1920s under the leadership of Keshavrao Jedhe
Keshavrao Marutrao Jedhe (Deshmukh) (25 April 1896 – 12 November 1959) was an Indian independence activist and politician from Pune. He served as a leading figure in the Indian National Congress, and in the Samyukta Maharashtra movement durin ...
and Baburao Javalkar. Both belonged to the Non-Brahmin party. Their early goals included capturing the Ganpati
Ganesha ( sa, गणेश, ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka, and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of En ...
and Shiv Jayanti festivals from Brahmin domination. They combined nationalism with anti-Caste system in India, casteism as the party's aims.
 In the 1930s, Jedhe merged the non-Brahmin party with the Congress party, changing it from an upper-caste dominated body to a more broadly based but also
In the 1930s, Jedhe merged the non-Brahmin party with the Congress party, changing it from an upper-caste dominated body to a more broadly based but also Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
-dominated party. Another notable Marathi figure of the time was B. R. Ambedkar, who led the campaign for the rights of Dalits, a caste that included his own Mahar caste. Ambedkar disagreed with mainstream leaders like Gandhi on issues including untouchability, the government system and the partition of India. He initiated the Dalit Buddhist movement, creating a new school of Buddhism called Navayana, leading to the Dalit movement that still endures. As the nation's first Ministry of Law and Justice (India), Law and Justice Minister, Ambedkar played a pivotal role in writing the constitution of India and is considered the ''Father of the Indian Constitution''.
The ultimatum in 1942 to the British to Quit India Movement, Quit India was given in Mumbai and culminated in the transfer of power and the independence of India in 1947. Raosaheb and Achutrao Patwardhan, Nanasaheb Gore, Shreedhar Mahadev Joshi, Yeshwantrao Chavan, Swami Ramanand Bharti, Nana Patil, Dhulappa Navale, V.S. Page, Vasant Patil, Dhondiram Mali, Aruna Asif Ali, Ashfaqulla Khan and several other leaders from Maharashtra played a prominent role in this struggle. B.G. Kher was the first Chief Minister of the tri-lingual Bombay Presidency in 1937.
By the end of the 19th century a modern manufacturing industry was developing in the city of Mumbai. The main product was cotton and the bulk of work force in these cotton mills was from Western Maharashtra, specifically from the coastal Konkan region. The census recorded for the city in the first half of the 20th century showed that nearly half the population of the city listed Marathi as their mother tongue.
Post-Independence
Bombay State
After India's independence, the Deccan States, including Kolhapur, were integrated into Bombay State, which was created from the former Bombay Presidency in 1950. In 1956, the States Reorganisation Act reorganized the Indian states along linguistic lines, and Bombay State was enlarged by the addition of the predominantlyMarathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
-speaking regions on Marathwada (Aurangabad Division) from erstwhile Hyderabad state
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
and Vidarbha
Vidarbha (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, �id̪əɾbʱə is a geographical region in the east of the Indian state of Maharashtra and a Proposed states and union territories of India#Maharashtra, proposed state of central India, comprising th ...
region from the Central Provinces and Berar
The Central Provinces and Berar was a province of British India and later the Dominion of India which existed from 1903 to 1950. It was formed by the merger of the Central Provinces with the province of Berar, which was territory leased by the B ...
. The southernmost part of Bombay State was ceded to Karnataka, Mysore. Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
state. Annabhau Sathe, Keshavrao Jedhe
Keshavrao Marutrao Jedhe (Deshmukh) (25 April 1896 – 12 November 1959) was an Indian independence activist and politician from Pune. He served as a leading figure in the Indian National Congress, and in the Samyukta Maharashtra movement durin ...
, S.M. Joshi, Shripad Amrit Dange, Pralhad Keshav Atre and Gopalrao Khedkar, Gopalrao Khedkar were prominent activists in the campaign to create a separate state of Maharashtra with Mumbai as its capital. On 1 May 1960, following mass protests and 105 deaths, Bombay State was divided into the new states of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
The state continues to have a dispute with Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnat ...
, to the south, over the regions of Belgaum and Karwar. Some Marathi-majority talukas were also transferred to the Adilabad district, Adilabad, Medak, Nizamabad and Mahaboobnagar districts of new Telugu State (now Telangana), to the east of Maharashtra, in 1956.
Since 1960
The present state of Maharashtra came into being on 1 May 1960 as a Marathi speaking state according to States Reorganisation Act, 1956, Linguistic state reorganization with Congress party's Yashwantrao Chavan being the first chief minister of the state. The state since its inception has seen huge growth in Industry in a number of areas of the state, increased urbanization, and migration of people from other states of India.Government and Politics
 The Indian National Congress, Congress party and its allies have ruled the state for the major part during the state's existence. After the brief tenures of Yashwantrao Chavan, who was inducted as defence minister by Prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru, Nehru, and Marotrao Kannamwar, who died after one year in office, Vasantrao Naik was Chief minister from 1963 to 1975. The politics of the state in this period was also dominated by leaders such as Yashwantrao Chavan, Vasantdada Patil, Vasantrao Naik, and Shankarrao Chavan.
Sharad Pawar became a significant personality within the state in 1978 when he broke away from the Congress party to form an alliance government with the Janata party. During his career, Pawar split Congress twice, with significant consequences for state politics. In 1999, after his dispute with the party president Sonia Gandhi over her foreign origins, in 1999, Pawar left the party and formed the Nationalist Congress Party (NCP). The party, however, joined a Indian National Congress, Congress-led coalition to form the state government after the 1999 Assembly elections.
The Congress party enjoyed a nearly unchallenged dominance of the state political landscape, until 1995 when the coalition of Shiv Sena and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) secured an overwhelming majority in the state, beginning a period of coalition governments. Shiv Sena was the larger party in the coalition. From 1999 until 2014, the NCP and INC formed one coalition while Shiv Sena and the BJP formed another for three successive elections, which the INC-NCP alliance won. Prithviraj Chavan of the Congress party was the last Chief Minister of Maharashtra under the Congress-NCP alliance that ruled until 2014.
The Indian National Congress, INC during its rule enjoyed overwhelming support from the state's influential Cooperative sugar factories in Maharashtra, sugar co-operatives, as well as thousands of other cooperatives, such as rural agricultural cooperatives involved in the marketing of dairy and vegetable produce, credit unions, etc.
For the better part of its existence, politics of the state was also dominated by the mainly rural
The Indian National Congress, Congress party and its allies have ruled the state for the major part during the state's existence. After the brief tenures of Yashwantrao Chavan, who was inducted as defence minister by Prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru, Nehru, and Marotrao Kannamwar, who died after one year in office, Vasantrao Naik was Chief minister from 1963 to 1975. The politics of the state in this period was also dominated by leaders such as Yashwantrao Chavan, Vasantdada Patil, Vasantrao Naik, and Shankarrao Chavan.
Sharad Pawar became a significant personality within the state in 1978 when he broke away from the Congress party to form an alliance government with the Janata party. During his career, Pawar split Congress twice, with significant consequences for state politics. In 1999, after his dispute with the party president Sonia Gandhi over her foreign origins, in 1999, Pawar left the party and formed the Nationalist Congress Party (NCP). The party, however, joined a Indian National Congress, Congress-led coalition to form the state government after the 1999 Assembly elections.
The Congress party enjoyed a nearly unchallenged dominance of the state political landscape, until 1995 when the coalition of Shiv Sena and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) secured an overwhelming majority in the state, beginning a period of coalition governments. Shiv Sena was the larger party in the coalition. From 1999 until 2014, the NCP and INC formed one coalition while Shiv Sena and the BJP formed another for three successive elections, which the INC-NCP alliance won. Prithviraj Chavan of the Congress party was the last Chief Minister of Maharashtra under the Congress-NCP alliance that ruled until 2014.
The Indian National Congress, INC during its rule enjoyed overwhelming support from the state's influential Cooperative sugar factories in Maharashtra, sugar co-operatives, as well as thousands of other cooperatives, such as rural agricultural cooperatives involved in the marketing of dairy and vegetable produce, credit unions, etc.
For the better part of its existence, politics of the state was also dominated by the mainly rural Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
–Kunbi caste, which accounts for 31% of the population of Maharashtra. They dominated the cooperative institutions; and with the resultant economic power, and controlled politics from the village level up to the Assembly and Lok Sabha. Major past political figures of the Congress party from Maharashtra—such as Keshavrao Jedhe
Keshavrao Marutrao Jedhe (Deshmukh) (25 April 1896 – 12 November 1959) was an Indian independence activist and politician from Pune. He served as a leading figure in the Indian National Congress, and in the Samyukta Maharashtra movement durin ...
, Yashwantrao Chavan, Shankarrao Chavan, Vilasrao Deshmukh, and Sharad Pawar—have been from this group. Of the 18 List of Chief Ministers of Maharashtra, Chief Ministers so far, as many as 10 (55%) have been Maratha. Since the 1980s, this group has also been active in setting up private educational institutions.
In the 1980s, Shiv Sena and the BJP parties began gaining a foothold in the state especially in the urban areas such as Mumbai. The Shiv Sena was formed in the 1960s by Bal Thackeray, Balashaheb Thackerey, a cartoonist and journalist, to advocate and agitate for the interests of Marathi people
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
in Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
. In its early years in the late 1960s, the party specifically targeted immigrants to Mumbai from South India. Over the following decades, the party slowly expanded its base, and took over the then Bombay corporation in the 1980s. The original base of the party was lower middle and working class Marathi people in Mumbai and surrounding urban areas. The leadership of the party came from educated upper caste Maharashtrians. However, since 1990s, strong men have emerged who control their local areas through intimidation and extortion. This has phenomenon has been named "dada-ization" of the party.
In the early 1990s, some of the party leaders incited violence against Muslims which resulted in riots between Hindus and Muslims. The Shiv Sena and the BJP came into the power at the state level in 1995, which was a big blow to the INC. A split emerged within Shiv Sena when Bal Thackeray anointed his son Uddhav Thackeray as his successor over his nephew Raj Thackeray in 2006. Raj Thackeray then left the party and formed a new party called Maharashtra Navnirman Sena (MNS). Raj Thackeray, like his uncle, also tried to win support from the Marathi people, Marathi community by whipping up anti-immigrant sentiment in Maharashtra, for instance against Bihari people, Biharis and other north Indians.
The BJP is closely related to the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), and is part of the Sangh Parivar.In early years, the party originally derived its support from the urban upper castes such as Brahmins and non-Maharashtrians. However, in the 21st century, the party was able to penetrate the Maratha group by fielding Maratha candidates in elections.The RSS was formed in the 1920s in Nagpur by Maharashtrian brahmins, and remains dominated by that community.
Economy
Prior to Indian independence, manufacturing industry in what became Maharashtra was based mainly in the city of Mumbai. After the formation of Maharashtra, the state government established the Maharashtra Industrial Development Corporation (MIDC) in 1962 to spur growth in other areas of the state. In the decades since its formation, MIDC has acted as the primary industrial infrastructure development agency of the government of Maharashtra. Since its inception, MIDC has established at least one industrial area in every district of the state. The areas with biggest industrial growth were the Pune metropolitan region and areas close to Mumbai such as Thane district and Raigad district. After the Economic liberalisation in India, 1991 economic liberalization, Maharashtra began to attract foreign capital, particularly in the information technology and engineering industries. The late 1990s and first decade of the 21st century saw huge development in the Information Technology sector, and IT Parks were set up in Aundh (Pune), Aundh, and Hinjawadi, Hinjewadi areas of Pune. Maharashtra has hundreds of private colleges and universities, including many religious and special-purpose institutions. Most of the private colleges were set up after the State Government of Vasantdada Patil liberalised the Education Sector in 1982. Politicians and leaders involved in the huge cooperative movement in Maharashtra were instrumental in setting up the private institutes Maharashtra was a pioneer in the development of Agricultural Cooperative Societies after independence. In fact, it was an integral part of the then Governing Indian National Congress, Congress party's vision of 'rural development with local initiative'. A 'special' status was accorded to the sugar cooperatives and the government assumed the role of a mentor by acting as a stakeholder, guarantor and regulator, Apart from sugar, Cooperatives played a crucial role in dairy, cotton, and fertiliser industries. Support by the state government led to more than 25,000 cooperatives being set up by 1990s in Maharashtra.Drought of 1972-73
In 1963, the government of Maharashtra asserted that the agricultural situation in the state was constantly being watched and relief measures were taken as soon as any scarcity was detected. On the basis of this, and asserting that the word famine had now become obsolete in this context, the government passed "The Maharashtra Deletion of the Term 'Famine' Act, 1963". They were unable to foresee the drought in 1972 when 25 million people needed help. The relief measures undertaken by the Government of Maharashtra included employment, programmes aimed at creating productive assets such as tree plantation, conservation of soil, excavation of canals, and building Man-made lentic water bodies of Maharashtra, artificial lentic water bodies. The public distribution system distributed food through fair-price shops. No deaths from starvation were reported. Large scale employment to the deprived sections of Maharashtrian society which attracted considerable amounts of food to Maharashtra. The implementation of the Scarcity Manuals in the state prevented the mortality arising from severe food shortages. The relief works initiated by the government helped employ over 5 million people at the height of the drought in Maharashtra leading to effective famine prevention. The effectiveness of the Maharashtra was also attributable to the direct pressure on the government of Maharashtra by the public who perceived that employment via the relief works programme was their right. The public protested by marching, picketing, and even rioting.Nevertheless, the measures taken by the government were praised for being a model program for famine relief.Farmers' suicides
Since 1990s, there has been a huge increase in number of suicides committed by Farmers' suicides in India, Farmers in India with Maharashtra accounting for the largest percentage of cases. The main reason cited was their inability to repay loans mostly taken from banks and NBFC & MFI in India, NBFCs. Other reasons included the difficulty of farming semi-arid regions, poor agricultural income, absence of alternative income opportunities, and the absence of suitable counselling services. In 2004, the Mumbai High Court commissioned a report from the Tata Institute of Social Sciences, Tata Institute on the phenomenon.Staff, InfoChange August 2005. Dandekar A, et al, Tata InstituteCauses of Farmer Suicides in Maharashtra: An Enquiry. Final Report Submitted to the Mumbai High Court 15 March 2005
The report cited "government's lack of interest, the absence of a safety net for farmers, and lack of access to information related to agriculture as the chief causes for the desperate condition of farmers in the state."
References
Citations
Bibliography
महाराष्ट्राचा गौरवशाली इतिहास / The History of Maharashtra.....
* James Grant Duff, ''History of the Mahrattas,'' 3 vols. London, Longmans, Rees, Orme, Brown, and Green (1826). * Mahadev Govind Ranade, ''Rise of the Maratha Power'' (1900); reprint (1999). * Richard Eaton, The new Cambridge history of India, *
External links
Maharashtra State Past Present & History In Marathi Language
Maharashtra Government's website
{{DEFAULTSORT:Maharashtra (history) History of Maharashtra, Maharashtra