History of Frisia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Frisians made
Frisians made
Frisia
Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Ger ...
has changed dramatically over time, both through floods and through a change in identity. It is part of the Nordwestblock which is a hypothetical historic region linked by language and culture.
Roman times
The Frisii began settling in Frisia around 500 BC. According toPliny the Younger
Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus, born Gaius Caecilius or Gaius Caecilius Cilo (61 – c. 113), better known as Pliny the Younger (), was a lawyer, author, and magistrate of Ancient Rome. Pliny's uncle, Pliny the Elder, helped raise and educate ...
, in Roman times, the Frisians (or, as it may be, their close neighbours, the Chauci) lived on terps, man-made hills. According to other sources, the Frisians lived along a broader expanse of the North Sea (or "Frisian Sea") coast.
Frisia at this time comprised the present-day provinces of Friesland and North Holland
North Holland ( nl, Noord-Holland, ) is a province of the Netherlands in the northwestern part of the country. It is located on the North Sea, north of South Holland and Utrecht, and west of Friesland and Flevoland. In November 2019, it had a ...
.
Frisians appear to have been among the Germanic groups who invaded Britain during the so-called Migration period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
(''Völkerwanderung''), as Angles and Saxons travelled from their home base through Frisian territory in what is now northern Germany and central Netherlands.Mostert, "Frisians", pp. 194-5.
Kingdom of Frisia
The 8th-century historianBede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom o ...
also used the term 'Frisians' for Franks in the south of Frisia.Bede, ''Historia ecclesiastica'', Book 5, Chapter 10. East Anglian sources called the inhabitants of 'Frisia' Warnii instead of Frisians. In the 7th and 8th centuries, the Frankish chronologies mention this area as the kingdom of the Frisians. However, these were probably not the Frisians of Roman times. This kingdom comprised the coastal provinces of the Netherlands and the German North Sea coast. During this time, the Frisian language was spoken along the entire southern North Sea coast and, today, this region is sometimes referred to as Greater Frisia or ''Frisia Magna''. The 7th-century Frisian realm (650-734) under the kings Aldegisel
Aldegisel, Aldegisl, Aldgillis, Aldgisl, Aldgils or Eadgils (fl. c. 678) was the ruler of Frisia (as king or duke) in the late seventh century contemporarily with Dagobert II and a very obscure figure. All that is known of him is in relation to t ...
and Redbad Radbod, Radbot, Ratbod, Ratpot, Redbod, Redbad, Radboud, Rapoto, or sometimes just Boddo, is a Germanic masculine given name that may refer to:
*Redbad, King of the Frisians (died 719)
*Radbod (prefect) (833–54), Frankish prefect
*Ratbod (archbis ...
, had its centre of power in the city Utrecht. Its end came in 734 at the Battle of the Boarn
The Battle of the Boarn ( fry, Slach oan de Boarn nl, Slag aan de Boorne) was an eighth century battle between the Franks and the Frisians near the mouth of the river Boarn in what is now the Dutch province of Friesland.
Battle
In 734 a Fran ...
, when the Frisians were defeated by the Franks, who then conquered the western part up to the Lauwers. They conquered the area east of the Lauwers in 785, when Charlemagne defeated Widukind. This ''Frisia Magna'' was partly occupied by Vikings in the 840s, until they were expelled between 885 and 920. It has also been suggested that the Vikings did not conquer Frisia, but settled in certain parts (such as the island of Wieringen), where they built simple forts and cooperated and traded with the native Frisians. One of their leaders was Rorik of Dorestad.
Loss of territory
 Frisians made
Frisians made polder
A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as dikes. The three types of polder are:
# Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed
# Flood plains s ...
s in West Friesland, which became more and more separated from Friesland because of floods. The western part of Frisia became the county of Holland in 1101, after a few centuries of a diverging history than the other parts. Frisia began to identify itself as a country with free folk in the Middle Ages. The bishopric of Utrecht
The Bishopric of Utrecht ( nl, Sticht Utrecht) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries, in the present-day Netherlands. From 1024 to 1528, as one of the prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire, it w ...
no longer belonged to Frisia. There were many floods in the 11th and 12th centuries, which led to the deaths of many and eventually formed the Zuider Zee. The largest flood occurred in 1322, in which many hundreds of people drowned.
Opstalboom League
The free Frisians and the city ofGroningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
founded the Opstalboom League to counter feudalism. The league consisted of modern Friesland, Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
, East Frisia
East Frisia or East Friesland (german: Ostfriesland; ; stq, Aastfräislound) is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia ...
and the German North Sea coast, and parts of the Danish North Sea coast ( Schleswig). But the Opstalboom league did not consist only of Frisians, as the area of Zevenwouden and the city of Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
were Saxon. Some Frisians lived under the rule of the counts of Holland in West Friesland. The first known meeting took place in 1156 to settle disagreements between two East Frisian areas. In March 1338 the judges, councilors and communities of all Frisian countries, gathered in Appingedam, concluded a treaty with the king of France, which was also ratified with the seal of the Upstalsboom. That is probably the last formal meeting that took place.
15th century
The 15th century saw the end of the free Frisians. The city ofGroningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
started to dominate Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
. A petty nobleman in East Frisia
East Frisia or East Friesland (german: Ostfriesland; ; stq, Aastfräislound) is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia ...
managed to defeat the other petty noblemen and became count of East Frisia. The Archbishop of Bremen-Hamburg and the king of Denmark
The monarchy of Denmark is a constitutional political system, institution and a historic office of the Kingdom of Denmark. The Kingdom includes Denmark proper and the autonomous administrative division, autonomous territories of the Faroe ...
conquered large areas of Frisia. Only Friesland remained for the Frisian Freedom. Friesland was conquered in the 1490s by Duke Albert of Saxony-Meissen. Later, the giant Pier Gerlofs Donia
Pier Gerlofs Donia ( 1480 – 28 October 1520) was a Frisian rebel leader and pirate. He is best known by his West Frisian nickname ''Grutte Pier'' ("Big Pier"; in the pre-1980 West Frisian spelling written as ''Greate Pier''), or by the Dutch t ...
(Grutte Pier) would fight for his country's freedom. He had many successes, but ultimately failed to secure Frisia's independence. He died a poor farmer in 1520. In 1519 already, his lieutenant Wijard Jelckama took over the command of Donia's armies. He was less successful, yet did have minor victories. When Jelckama eventually got caught in 1523, his armies were not even one third the size they were when he took over four years earlier. He was then tried, found guilty of treason, and decapitated.
Frisian territories
* West Friesland remained a part of Holland and became a part ofNorth Holland
North Holland ( nl, Noord-Holland, ) is a province of the Netherlands in the northwestern part of the country. It is located on the North Sea, north of South Holland and Utrecht, and west of Friesland and Flevoland. In November 2019, it had a ...
around 1800. The current region of West Friesland is smaller than historical West Friesland and there is also an official constitutional region (samenwerkingsregio) of West Friesland for coast protection, the police, and agriculture.
* Friesland got its independence back (with constitutionalized farmer representation) in 1581 and gave it up permanently in 1795. It is now a Dutch province.
*East Frisia
East Frisia or East Friesland (german: Ostfriesland; ; stq, Aastfräislound) is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia ...
was taken over by the Kingdom of Prussia, then annexed by the Kingdom of Holland and after that became a part of the French Empire
French Empire (french: Empire Français, link=no) may refer to:
* First French Empire, ruled by Napoleon I from 1804 to 1814 and in 1815 and by Napoleon II in 1815, the French state from 1804 to 1814 and in 1815
* Second French Empire, led by Nap ...
before being re-annexed by Prussia. Today it is a district of the federal state of Lower Saxony in the Federal Republic of Germany.
*Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
has been a province of the Netherlands since the 16th century.
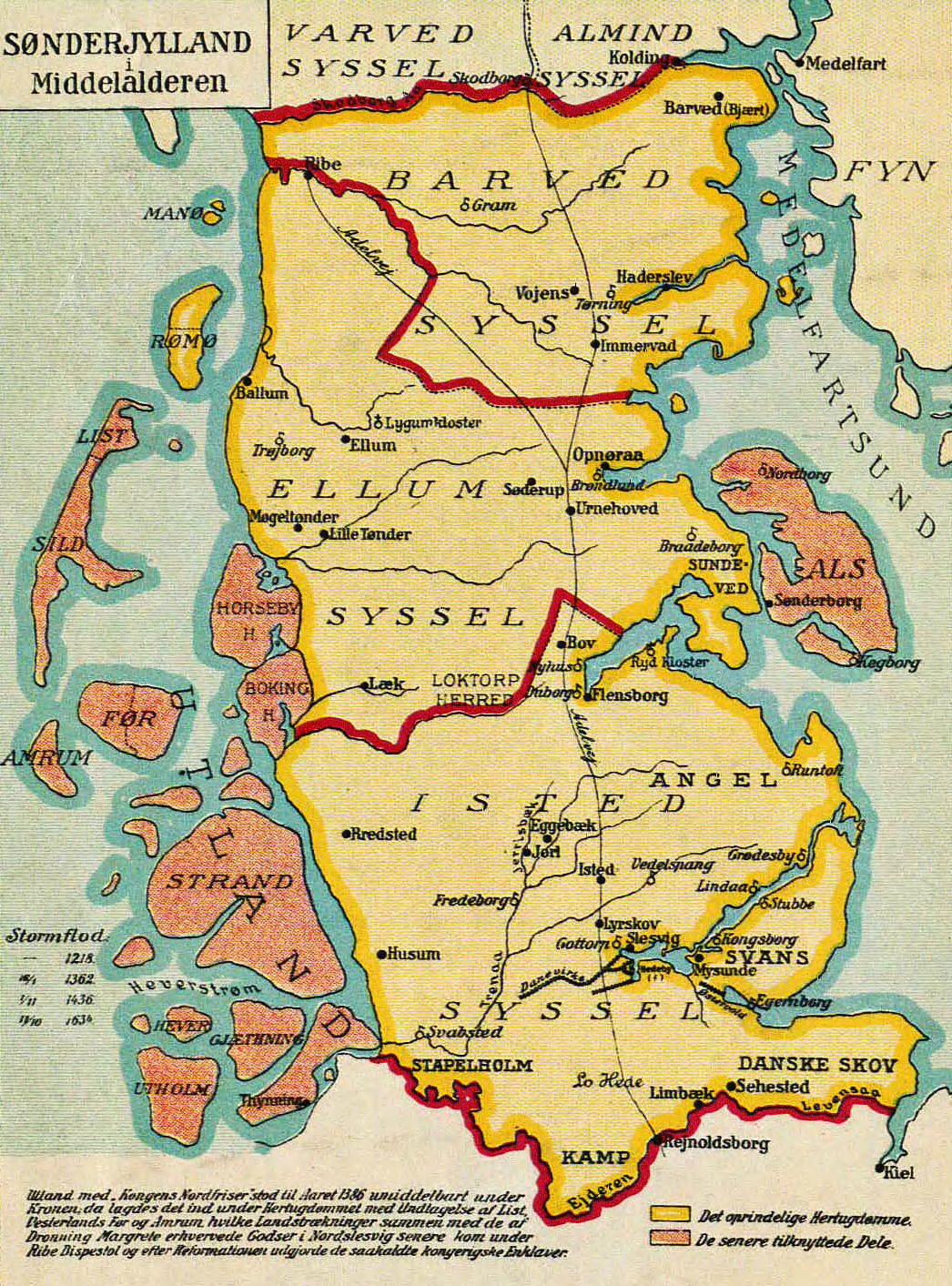
* North Frisia was a part of the Danish duchy of Schleswig (also: '' South Jutland'') and the royal enclaves (Kongerigske enklaver) of the Kingdom of Denmark, and belongs now to the German state of Schleswig-Holstein.
*The Frisian islands off the coast of the Netherlands and Germany are the leftover dunes of flooded lands.
See also
*Canon of Friesland
The Canon of Friesland or Canon of Frisian History ( fy, Kanon fan de Fryske Skiednis) is a list of 41 topics (''11 and 30'', in reference to the Dutch ordinal '' elfendertig'') offering a chronological summary of significant events and individual ...
* List of Frisian battles
Notes
References
Primary sources
*Secondary sources
*Further reading
* * * * * * Originally published in 1967 as a dissertation thesis. * * * * * * * * *{{Cite book , first=Thomas , last=Steensen , title=Geschichte Nordfrieslands von 1918 bis in die Gegenwart , edition=new , publisher=Nordfriisk Instituut , location=Bräist/Bredstedt , year=2006 , series=Geschichte Nordfrieslands, Teil 5; Nordfriisk Instituut, Nr. 190 , isbn=3-88007-336-8 History of Friesland fr:Frise (région historique)