History Of British Monarchy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of the monarchy of the United Kingdom and its evolution into a constitutional and
The history of the monarchy of the United Kingdom and its evolution into a constitutional and
 The origins of the English monarchy lie in the establishment of
The origins of the English monarchy lie in the establishment of  In 1014, Æthelred the Unready () was invited back from exile if he agreed to address complaints against his earlier rule, including high taxes, extortion and the
In 1014, Æthelred the Unready () was invited back from exile if he agreed to address complaints against his earlier rule, including high taxes, extortion and the

 As a feudal lord, the king gave fiefs to his most important followers, his tenants-in-chief (the barons), who in return owed the king
As a feudal lord, the king gave fiefs to his most important followers, his tenants-in-chief (the barons), who in return owed the king
 William died in 1087 and was succeeded by his son, William II, nicknamed "Rufus" (). Between 1098 and 1099, the Great Hall at Westminster Palace, the king's main residence, was built. It was one of the largest secular buildings in Europe, and a monument to the Anglo-Norman monarchy.
On 2 August 1100, Rufus was killed while hunting in the New Forest. His younger brother, Henry I (), was hastily elected king by the barons at Winchester on August 3 and crowned king at Westminster Abbey on August 5, just three days after his brother's death. At the coronation, Henry not only promised to rule well; he renounced the unpopular policies of his brother and promised to restore the laws of Edward the Confessor. This oath was written down and distributed throughout England as the Coronation Charter, which was reissued by all future 12th-century kings and was incorporated into
William died in 1087 and was succeeded by his son, William II, nicknamed "Rufus" (). Between 1098 and 1099, the Great Hall at Westminster Palace, the king's main residence, was built. It was one of the largest secular buildings in Europe, and a monument to the Anglo-Norman monarchy.
On 2 August 1100, Rufus was killed while hunting in the New Forest. His younger brother, Henry I (), was hastily elected king by the barons at Winchester on August 3 and crowned king at Westminster Abbey on August 5, just three days after his brother's death. At the coronation, Henry not only promised to rule well; he renounced the unpopular policies of his brother and promised to restore the laws of Edward the Confessor. This oath was written down and distributed throughout England as the Coronation Charter, which was reissued by all future 12th-century kings and was incorporated into  The office of
The office of
 On December 19, 1154, Henry II () was for first time crowned ''King of England'' rather than ''King of the English''. It was also the inauguration of a new dynasty, the
On December 19, 1154, Henry II () was for first time crowned ''King of England'' rather than ''King of the English''. It was also the inauguration of a new dynasty, the  Since William the Conqueror's separation of secular and ecclesiastical jurisdiction, church courts claimed exclusive authority to try clergy, including monks and clerics in minor orders. The most contentious issue was "criminous clerks" accused of theft, rape or murder. Church courts could not impose the death penalty or bodily mutilation, and their punishments (
Since William the Conqueror's separation of secular and ecclesiastical jurisdiction, church courts claimed exclusive authority to try clergy, including monks and clerics in minor orders. The most contentious issue was "criminous clerks" accused of theft, rape or murder. Church courts could not impose the death penalty or bodily mutilation, and their punishments (
 Upon Henry's death, his eldest surviving son Richard I (), nicknamed the Lionheart, succeeded to the throne. As king, he spent a total of six months in England. In 1190, the king left England with a large army and fleet to join the Third Crusade to reconquer Jerusalem from Saladin. Richard funded this campaign through taxation (such as the Saladin tithe) as well as selling offices, titles, and land. In his absence, England was governed by William de Longchamp, in whom was consolidated both secular and ecclesiastical power as
Upon Henry's death, his eldest surviving son Richard I (), nicknamed the Lionheart, succeeded to the throne. As king, he spent a total of six months in England. In 1190, the king left England with a large army and fleet to join the Third Crusade to reconquer Jerusalem from Saladin. Richard funded this campaign through taxation (such as the Saladin tithe) as well as selling offices, titles, and land. In his absence, England was governed by William de Longchamp, in whom was consolidated both secular and ecclesiastical power as
 At Westminster Abbey in May 1199, John () was crowned (Latin for King of England) rather than the older form of (King of the English). In 1204, John lost Normandy and his other Continental possessions. The remainder of his reign was shaped by attempts to rehabilitate his military reputation and fund wars of reconquest. Traditionally, the king was expected to fund his government out of his own income derived from the royal
At Westminster Abbey in May 1199, John () was crowned (Latin for King of England) rather than the older form of (King of the English). In 1204, John lost Normandy and his other Continental possessions. The remainder of his reign was shaped by attempts to rehabilitate his military reputation and fund wars of reconquest. Traditionally, the king was expected to fund his government out of his own income derived from the royal  Unlike earlier charters of liberties, Magna Carta included an enforcement mechanism in the form of a council of 25 barons who were permitted to wage "lawful rebellion" against the king if he violated the charter. The king had no intention of adhering to the document and appealed to Pope Innocent who annulled the agreement and excommunicated the rebel barons. This began the First Barons' War, during which the rebels offered the crown to Philip II's son, the future Louis VIII of France. By June 1216, Louis had taken control of half of England, including London. While he had not been crowned, he was proclaimed King Louis I at
Unlike earlier charters of liberties, Magna Carta included an enforcement mechanism in the form of a council of 25 barons who were permitted to wage "lawful rebellion" against the king if he violated the charter. The king had no intention of adhering to the document and appealed to Pope Innocent who annulled the agreement and excommunicated the rebel barons. This began the First Barons' War, during which the rebels offered the crown to Philip II's son, the future Louis VIII of France. By June 1216, Louis had taken control of half of England, including London. While he had not been crowned, he was proclaimed King Louis I at

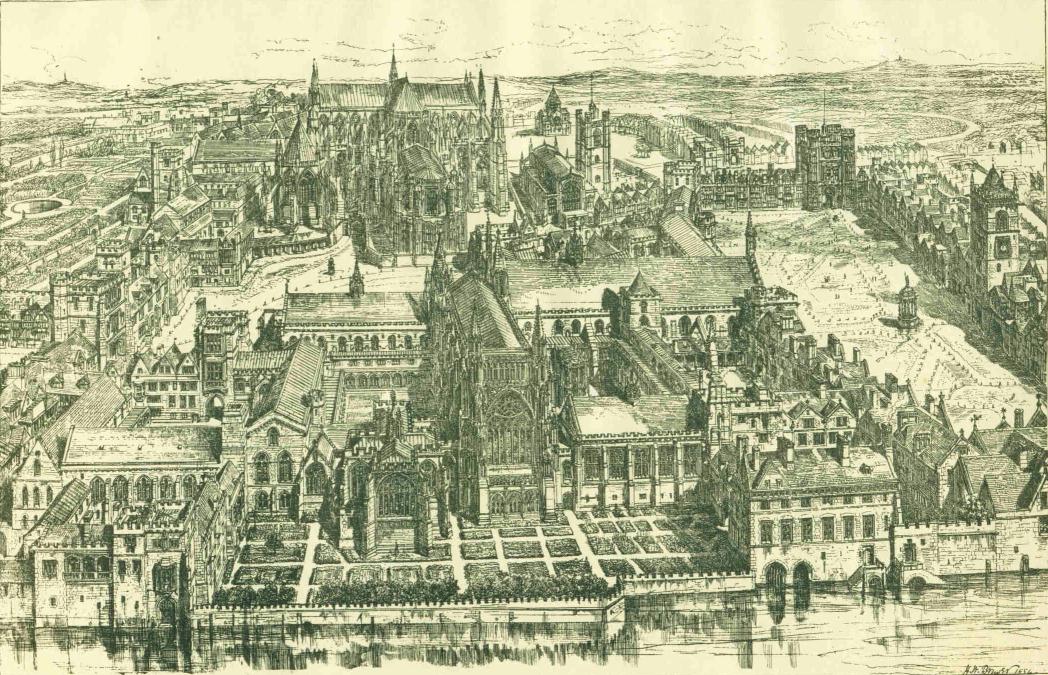 After John's death, loyal barons and bishops took his nine-year-old son to Gloucester Abbey where he was crowned Henry III () in a rushed coronation. This established the precedent that the eldest son became king regardless of age. Henry was the first child king since Æthelred the Unready, and William Marshal, Earl of Pembroke, served as regent until his death in 1219. Marshal led royal forces to victory against the rebel barons and French invaders at the Battles of Lincoln and Sandwich in 1217.
During Henry's reign, the principle that kings were subject to the law gained acceptance. To build support for the new king, his government re-issued Magna Carta in 1216 and 1217 (along with the Charter of the Forest). In January 1225, the Magna Carta was re-issued at a Great Council in return for approval of a tax to fund military campaigns in France. This established a new constitutional precedent in which "military expeditions would be financed at the expense of detailed concessions of political liberties". In 1236, Henry began calling such meetings Parliament. By the 1240s, these early Parliaments had not only assumed power to grant taxes but were also venues where nobles could complain about government policy or corruption.
In 1227, Henry was eighteen years old, and the regency officially ended. Yet, throughout his personal rule the king displayed a tendency to be dominated by foreign favourites. After the fall of the justiciar Hubert de Burgh in 1230, Bishop Peter des Roches became the king's chief minister. While holding no great office himself, the bishop showered his Poitevin relation Peter de Rivaux with a large number of offices. He was placed in charge of the treasury, the
After John's death, loyal barons and bishops took his nine-year-old son to Gloucester Abbey where he was crowned Henry III () in a rushed coronation. This established the precedent that the eldest son became king regardless of age. Henry was the first child king since Æthelred the Unready, and William Marshal, Earl of Pembroke, served as regent until his death in 1219. Marshal led royal forces to victory against the rebel barons and French invaders at the Battles of Lincoln and Sandwich in 1217.
During Henry's reign, the principle that kings were subject to the law gained acceptance. To build support for the new king, his government re-issued Magna Carta in 1216 and 1217 (along with the Charter of the Forest). In January 1225, the Magna Carta was re-issued at a Great Council in return for approval of a tax to fund military campaigns in France. This established a new constitutional precedent in which "military expeditions would be financed at the expense of detailed concessions of political liberties". In 1236, Henry began calling such meetings Parliament. By the 1240s, these early Parliaments had not only assumed power to grant taxes but were also venues where nobles could complain about government policy or corruption.
In 1227, Henry was eighteen years old, and the regency officially ended. Yet, throughout his personal rule the king displayed a tendency to be dominated by foreign favourites. After the fall of the justiciar Hubert de Burgh in 1230, Bishop Peter des Roches became the king's chief minister. While holding no great office himself, the bishop showered his Poitevin relation Peter de Rivaux with a large number of offices. He was placed in charge of the treasury, the

 After Gaveston's death, the most influential men around the king were Hugh Despenser and his son, Hugh Despenser the Younger. The king alienated moderate barons by dispensing royal patronage without parliamentary approval as required by the Ordinances and allowing the Despensers to act with impunity. In 1318, negotiations led to the Treaty of Leake in which the king agreed to abide by the Ordinances of 1311. A permanent royal council was created with eight bishops, four earls, and four barons as members.
Edward's favouritsm toward the Despensers continued to destabilize the kingdom. The Despensers had become the gatekeepers to the king, and their enemies "were liable to be deprived of land or possessions or else thrown into prison". The Welsh Marches were particularly destabilized by Hugh the Younger's accumulation of land. In 1321, a group of marcher lords invaded the Despenser estates, beginning the Despenser War. Edward defeated the baronial opposition in 1322 and overturned the Ordinances. For the next few years, Edward ruled as a tyrant. The author of the ''
After Gaveston's death, the most influential men around the king were Hugh Despenser and his son, Hugh Despenser the Younger. The king alienated moderate barons by dispensing royal patronage without parliamentary approval as required by the Ordinances and allowing the Despensers to act with impunity. In 1318, negotiations led to the Treaty of Leake in which the king agreed to abide by the Ordinances of 1311. A permanent royal council was created with eight bishops, four earls, and four barons as members.
Edward's favouritsm toward the Despensers continued to destabilize the kingdom. The Despensers had become the gatekeepers to the king, and their enemies "were liable to be deprived of land or possessions or else thrown into prison". The Welsh Marches were particularly destabilized by Hugh the Younger's accumulation of land. In 1321, a group of marcher lords invaded the Despenser estates, beginning the Despenser War. Edward defeated the baronial opposition in 1322 and overturned the Ordinances. For the next few years, Edward ruled as a tyrant. The author of the ''
 Five days after his father's abdication, the fourteen-year-old
Five days after his father's abdication, the fourteen-year-old
 As
As
 Bolingbroke was crowned as Henry IV () two weeks after Richard II's deposition. His dynasty was known as the
Bolingbroke was crowned as Henry IV () two weeks after Richard II's deposition. His dynasty was known as the
 As a result of his unifying gestures, Henry V's reign was largely free from domestic strife, leaving the king free to pursue the last phase of the Hundred Years' War with France. The war appealed to English national pride, and Parliament readily granted a double subsidy to finance the campaign, which began in August 1415. In this first campaign, Henry won a legendary victory at the
As a result of his unifying gestures, Henry V's reign was largely free from domestic strife, leaving the king free to pursue the last phase of the Hundred Years' War with France. The war appealed to English national pride, and Parliament readily granted a double subsidy to finance the campaign, which began in August 1415. In this first campaign, Henry won a legendary victory at the
 Alexander III's death in a riding accident in 1286 precipitated a major succession crisis. Scottish leaders appealed to King Edward I of England for help in determining who was the rightful heir. Edward chose Alexander's three-year-old Norwegian granddaughter,
Alexander III's death in a riding accident in 1286 precipitated a major succession crisis. Scottish leaders appealed to King Edward I of England for help in determining who was the rightful heir. Edward chose Alexander's three-year-old Norwegian granddaughter,
 Charles II's reign was marked by the development of the first modern political parties in England. Charles had no legitimate children, and was due to be succeeded by his Roman Catholic brother,
Charles II's reign was marked by the development of the first modern political parties in England. Charles had no legitimate children, and was due to be succeeded by his Roman Catholic brother,
 Victoria's son, Edward VII, became the first monarch of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha in 1901. In 1917, the next monarch, George V, changed "Saxe-Coburg and Gotha" to " Windsor" in response to the anti-German sympathies aroused by the First World War. George V's reign was marked by the separation of Ireland into Northern Ireland, which remained a part of the United Kingdom, and the Irish Free State, an independent nation, in 1922.
Victoria's son, Edward VII, became the first monarch of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha in 1901. In 1917, the next monarch, George V, changed "Saxe-Coburg and Gotha" to " Windsor" in response to the anti-German sympathies aroused by the First World War. George V's reign was marked by the separation of Ireland into Northern Ireland, which remained a part of the United Kingdom, and the Irish Free State, an independent nation, in 1922.
 During the twentieth century, the Commonwealth of Nations evolved from the British Empire. Prior to 1926, the British Crown reigned over the British Empire collectively; the Dominions and Crown Colonies were subordinate to the United Kingdom. The Balfour Declaration of 1926 gave complete self-government to the Dominions, effectively creating a system whereby a single monarch operated independently in each separate Dominion. The concept was solidified by the
During the twentieth century, the Commonwealth of Nations evolved from the British Empire. Prior to 1926, the British Crown reigned over the British Empire collectively; the Dominions and Crown Colonies were subordinate to the United Kingdom. The Balfour Declaration of 1926 gave complete self-government to the Dominions, effectively creating a system whereby a single monarch operated independently in each separate Dominion. The concept was solidified by the
 The history of the monarchy of the United Kingdom and its evolution into a constitutional and
The history of the monarchy of the United Kingdom and its evolution into a constitutional and ceremonial monarchy
A crowned republic, also known as a monarchial republic, is an informal term that has been used to refer to a system of monarchy where the monarch's role may be seen as almost entirely ceremonial and where nearly all of the royal prerogatives are ...
is a major theme in the historical development of the British constitution. The British monarchy traces its origins to the petty kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England
Anglo-Saxon England or Early Medieval England, existing from the 5th to the 11th centuries from the end of Roman Britain until the Norman conquest in 1066, consisted of various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms until 927, when it was united as the Kingdom o ...
and early medieval Scotland, which consolidated into the kingdoms of England and Scotland by the 10th century. Anglo-Saxon England had an elective monarchy
An elective monarchy is a monarchy ruled by an elected monarch, in contrast to a hereditary monarchy in which the office is automatically passed down as a family inheritance. The manner of election, the nature of candidate qualifications, and the ...
, but this was replaced by primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relativ ...
after England was conquered by the Normans in 1066. The Norman and Plantagenet dynasties expanded their authority throughout the British Isles, creating the Lordship of Ireland in 1177 and conquering Wales in 1283. In 1215, King John King John may refer to:
Rulers
* John, King of England (1166–1216)
* John I of Jerusalem (c. 1170–1237)
* John Balliol, King of Scotland (c. 1249–1314)
* John I of France (15–20 November 1316)
* John II of France (1319–1364)
* John I o ...
agreed to limit his own powers over his subjects according to the terms of Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
. To gain the consent of the political community, English kings began summoning Parliaments to approve taxation and to enact statutes. Gradually, Parliament's authority expanded at the expense of royal power.
From 1603, the English and Scottish kingdoms were ruled by a single sovereign in the Union of the Crowns. From 1649 to 1660, the tradition of monarchy was broken by the republican Commonwealth of England, which followed the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Following the installation of William and Mary as co-monarchs in the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
, a constitutional monarchy was established with power shifting to Parliament. The Bill of Rights 1689, and its Scottish counterpart the Claim of Right Act 1689, further curtailed the power of the monarchy and excluded Roman Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
from succession to the throne.
In 1707, the kingdoms of England and Scotland were merged to create the Kingdom of Great Britain, and in 1801, the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland ( ga, label=Classical Irish, an Ríoghacht Éireann; ga, label=Modern Irish, an Ríocht Éireann, ) was a monarchy on the island of Ireland that was a client state of England and then of Great Britain. It existed from ...
joined to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The British monarch was the nominal head of the vast British Empire, which covered a quarter of the world's land area at its greatest extent in 1921.
The Balfour Declaration of 1926 recognised the evolution of the Dominions of the Empire into separate, self-governing countries within a Commonwealth of Nations. In the years after the Second World War, the vast majority of British colonies and territories became independent, effectively bringing the Empire to an end. George VI and his successor, Elizabeth II, adopted the title Head of the Commonwealth as a symbol of the free association of its independent member states. The United Kingdom and fourteen other independent sovereign states that share the same person as their monarch are called Commonwealth realm
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonwealt ...
s. Although the monarch is shared, each country is sovereign and independent of the others, and the monarch has a different, specific, and official national title and style for each realm.
English monarchy
Anglo-Saxon period (800s–1066)
 The origins of the English monarchy lie in the establishment of
The origins of the English monarchy lie in the establishment of Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
kingdoms, which in the 7th century consolidated into seven kingdoms known as the Heptarchy. At certain times, one of the Anglo-Saxon kings was strong enough to claim the title ''bretwalda
''Bretwalda'' (also ''brytenwalda'' and ''bretenanwealda'', sometimes capitalised) is an Old English word. The first record comes from the late 9th-century ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle''. It is given to some of the rulers of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms from ...
'' or overlord of England. In the 9th century, most Anglo-Saxon kingdoms were conquered by Viking invaders. Wessex, however, survived due to the leadership of Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bot ...
() who secured Wessex, absorbed Kent and western Mercia, and assumed the title "king of the Anglo-Saxons". Alfred's son, Edward the Elder (), and grandsons reconquered Anglo-Saxon lands and created a unitary Kingdom of England, though its constituent parts retained strong regional identities. Æthelstan () is often considered the founder of the English monarchy, mainly due to his own propaganda in the form of coins and charters naming him "king of the English".
In theory, all governing authority resided with the king. He alone could make Anglo-Saxon law, raise geld (tax), mint coins, raise the fyrd, or make foreign policy. In reality, kings needed the support of the nobility and the English church
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
to rule. They governed in consultation with the Witan, the council of bishops, ealdormen, and thegns that advised the king. The Witan also elected new kings from among male members of the royal family ( æthelings).The rule of primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relativ ...
was not yet established, so weak candidates could be replaced with stronger ones. A monarch's rule was not legitimate unless consecrated by the church in a coronation. The coronation of Edgar the Peaceful () in 973 served as a model for future British coronation
The coronation of the monarch of the United Kingdom is a ceremony (specifically, initiation rite) in which they are formally invested with regalia and crowned at Westminster Abbey. It corresponds to the coronations that formerly took place in ...
s, including for Elizabeth II's coronation
The coronation of Elizabeth II took place on 2 June 1953 at Westminster Abbey in London. She acceded to the throne at the age of 25 upon the death of her father, George VI, on 6 February 1952, being proclaimed queen by her privy and executive ...
in 1953. Before the king was anointed and crowned, he swore a threefold oath to protect the church, defend his people, and administer justice.
While the capital was at Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs Nation ...
, the king traveled with his itinerant court from one royal vill to another as they collected food rent and heard petitions. At the local level, royal power operated through shire
Shire is a traditional term for an administrative division of land in Great Britain and some other English-speaking countries such as Australia and New Zealand. It is generally synonymous with county. It was first used in Wessex from the beginn ...
s, which were further divided into hundreds. The biannual shire courts tried legal cases, kept the peace, levied taxes, raised troops, and collected information on property rights and inheritance. Shire and hundred courts were presided over by royal officials: the ealdorman for a shire and a reeve
Reeve may refer to:
Titles
*Reeve (Canada), an elected chief executive of some counties, townships, and equivalents
*Reeve (England), an official elected annually by the serfs to supervise lands for a lord
*High-reeve, a title taken by some Englis ...
for a hundred. Royal land grants frequently included the privilege of infangthief and outfangthief, which allowed for seignorial justice, but the most serious offenses (such as murder) could only be tried in the royal courts.
enslavement
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
of free men. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
'' records this agreement, which historian David Starkey called "the first constitutional settlement in English history". In 1016, the Danish prince Cnut () became king of England. During his reign, England was united with the kingdoms of Denmark and Norway in what historians call the North Sea Empire. Because Cnut was not in England for much of his reign, he divided England into four parts ( Wessex, East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
, Mercia, and Northumbria) and appointed trusted earls to rule each region. The creation of large earldoms covering multiple shires necessitated the office of sheriff
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland that is commonly transla ...
or "shire reeve". The sheriff was the earl's deputy as well as the king's direct representative in the shire. Sheriffs oversaw the shire courts as well as the collection of taxes and royal estate dues.
On the death of Cnut's son, Harthacnut
Harthacnut ( da, Hardeknud; "Tough-knot"; – 8 June 1042), traditionally Hardicanute, sometimes referred to as Canute III, was King of Denmark from 1035 to 1042 and King of the English from 1040 to 1042.
Harthacnut was the son of King ...
(), the throne was restored to the House of Wessex with the crowning of Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ; la, Eduardus Confessor , ; ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was one of the last Anglo-Saxon English kings. Usually considered the last king of the House of Wessex, he ruled from 1042 to 1066.
Edward was the son of Æth ...
(), son of Æthelred. By this time, England was a wealthy kingdom well placed for trade and possessing abundant natural resources. It also boasted a sophisticated system of royal administration. Priests attached to the king's chapel acted as royal secretaries—writing letters, charters, and other official documents. Edward appointed the first chancellor
Chancellor ( la, cancellarius) is a title of various official positions in the governments of many nations. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the or lattice work screens of a basilica or law cou ...
, Regenbald, who kept the king's seal and oversaw the writing of charters and writs. The treasury had developed into a permanent institution by this time as well. Supervision of the treasury was one of the responsibilities of the king's or chamberlains
Chamberlain may refer to:
Profession
*Chamberlain (office), the officer in charge of managing the household of a sovereign or other noble figure
People
*Chamberlain (surname)
**Houston Stewart Chamberlain (1855–1927), German-British philosop ...
. London was becoming the political as well as the commercial capital of England. Edward furthered this transition by building Westminster Palace and Westminster Abbey.
In 1066, Edward died childless. Edward the Exile, son of King Edmund Ironside (1016), had the best hereditary claim to the throne, but Harold Godwinson, Earl of Wessex, claimed King Edward promised the throne to him. Harold had greater support among the English people and was made king by the Witan.
House of Normandy (1066–1154)

William the Conqueror
William, Duke of Normandy, disputed Harold's succession. He claimed that Edward the Confessor promised him the throne. He was also the great-nephew of Emma of Normandy, wife of Æthelred and Cnut. In addition, his wife Matilda of Flanders was a direct descendant of Alfred the Great. In 1066, William invaded England, and Harold was killed at the Battle of Hastings. The English then elected (but never crowned) Edgar the Ætheling, the Confessor's fifteen-year-old great-nephew. After English resistance collapsed, Edgar submitted to William, who was crowned king on Christmas Day 1066 at Westminster Abbey. It took nearly five years of fighting before the Norman Conquest of England was secure. Across England, the Normans built castles for defense as well as intimidation of the locals. In London, William ordered construction of the White Tower, the central keep of the Tower of London. Once finished, the White Tower "was the most imposing emblem of monarchy that the country had ever seen, dwarfing all other buildings for miles around." The Conquest was crucial in terms of both political and social change.Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
became the language of the poor, while French (specifically the Anglo-Norman dialect) became the language of government. The native Anglo-Saxon aristocracy was almost entirely replaced by a new Anglo-Norman elite, and most native English lost their land.
The Normans appreciated and preserved the sophisticated English government, which was more centralised than ducal government in Normandy. The Witan's role of consultation and advice was continued in the (Latin for "king's court"). Shire and hundred courts were retained, but the king's court reserved for itself the right to hear pleas of the Crown
In legal terms, a plea is simply an answer to a claim made by someone in a criminal case under common law using the adversarial system. Colloquially, a plea has come to mean the assertion by a defendant at arraignment, or otherwise in response ...
and appeals from lower courts. William also continued the Anglo-Saxon practice of sending out specially appointed justices to local courts to hear cases warranting royal intervention. Likewise, the office of earl was preserved, and William created new earldoms to protect the Welsh border (see Marcher Lord).
English feudalism
Feudalism as practiced in the Kingdoms of England during the medieval period was a state of human society that organized political and military leadership and force around a stratified formal structure based on land tenure. As a military defense a ...
, which first appeared in the Anglo-Saxon period, continued to develop under Norman influence. William I claimed ownership of all land in England. He created royal forests (i.e. royal hunting preserves) and introduced forest law. By the 12th century, royal forests covered nearly a third of England, and forest law was always unpopular with both the rich and the poor for its arbitrary nature.
fealty
An oath of fealty, from the Latin ''fidelitas'' (faithfulness), is a pledge of allegiance of one person to another.
Definition
In medieval Europe, the swearing of fealty took the form of an oath made by a vassal, or subordinate, to his lord. "Fea ...
and military service (or scutage payments). The king was also entitled to be paid feudal reliefs by his barons on certain occasions, such as the knighting of an eldest son, marriage of an eldest daughter, or upon inheriting a fief. Likewise, barons owed feudal aids when the king's eldest son was knighted or eldest daughter married. At times, there was tension between the monarch and his Norman vassals, who were used to French models of government in which royal power was much weaker than in England. The 1075 Revolt of the Earls
The Revolt of the Earls in 1075 was a rebellion of three earls against William I of England (William the Conqueror). It was the last serious act of resistance against William in the Norman Conquest.
Cause
The revolt was caused by the king's refu ...
was defeated by the king, but the monarchy continued to resist forces of feudal fragmentation.
The church was critical to William's conquest of England. In 1066, it owned between 25 and 33 per cent of all land, and appointment to bishoprics and abbacies were important sources of royal patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists su ...
. The Norman invasion received the blessing of Pope Alexander II
Pope Alexander II (1010/1015 – 21 April 1073), born Anselm of Baggio, was the head of the Roman Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1061 to his death in 1073. Born in Milan, Anselm was deeply involved in the Pataria refor ...
, who wanted William to oversee church reform and to remove unfit bishops. William forbade ecclesiastical cases (those involving marriage, wills, and legitimacy) from being heard in secular courts; jurisdiction was handed over to church court
An ecclesiastical court, also called court Christian or court spiritual, is any of certain courts having jurisdiction mainly in spiritual or religious matters. In the Middle Ages, these courts had much wider powers in many areas of Europe than be ...
s. But William also tightened royal control over the church. Bishops were banned from traveling to Rome, and royal permission was needed to enact new canon law or to excommunicate a noble.
Henry I and administrative development
 William died in 1087 and was succeeded by his son, William II, nicknamed "Rufus" (). Between 1098 and 1099, the Great Hall at Westminster Palace, the king's main residence, was built. It was one of the largest secular buildings in Europe, and a monument to the Anglo-Norman monarchy.
On 2 August 1100, Rufus was killed while hunting in the New Forest. His younger brother, Henry I (), was hastily elected king by the barons at Winchester on August 3 and crowned king at Westminster Abbey on August 5, just three days after his brother's death. At the coronation, Henry not only promised to rule well; he renounced the unpopular policies of his brother and promised to restore the laws of Edward the Confessor. This oath was written down and distributed throughout England as the Coronation Charter, which was reissued by all future 12th-century kings and was incorporated into
William died in 1087 and was succeeded by his son, William II, nicknamed "Rufus" (). Between 1098 and 1099, the Great Hall at Westminster Palace, the king's main residence, was built. It was one of the largest secular buildings in Europe, and a monument to the Anglo-Norman monarchy.
On 2 August 1100, Rufus was killed while hunting in the New Forest. His younger brother, Henry I (), was hastily elected king by the barons at Winchester on August 3 and crowned king at Westminster Abbey on August 5, just three days after his brother's death. At the coronation, Henry not only promised to rule well; he renounced the unpopular policies of his brother and promised to restore the laws of Edward the Confessor. This oath was written down and distributed throughout England as the Coronation Charter, which was reissued by all future 12th-century kings and was incorporated into Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
.
During Henry's reign, the royal household was formalised. It was divided into the chapel in charge of royal documents (which evolved into the chancery
Chancery may refer to:
Offices and administration
* Chancery (diplomacy), the principal office that houses a diplomatic mission or an embassy
* Chancery (medieval office), responsible for the production of official documents
* Chancery (Scotlan ...
), the chamber in charge of finances, and the master-marshal in charge of travel. The larger circle of servants and confidantes in the court were part of the . This included the king's mounted household troops, which were several hundred in number. The court remained itinerant during this period, but Henry outlawed the pillaging of local communities by the royal court. Instead, local goods were purchased at fair prices. These reforms were codified in the . The king's closest advisers formed the . During crown-wearings held three times a year, the king met with all his bishops and magnate
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders, or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
s in the ( Latin for "great council"). It is unknown whether these were truly deliberative bodies, but these assemblies were generally dominated by the king.
 The office of
The office of justiciar
Justiciar is the English form of the medieval Latin term ''justiciarius'' or ''justitiarius'' ("man of justice", i.e. judge). During the Middle Ages in England, the Chief Justiciar (later known simply as the Justiciar) was roughly equivalent ...
—effectively the king's chief minister—took shape at this time. The office developed out of the need for a viceroy when the king was in Normandy and was mainly concerned with royal finance and justice. Under the first justiciar, Roger of Salisbury, the Exchequer was established to manage royal finances. The Exchequer produced an annual audit recorded in the pipe rolls. As the royal court was itinerant, it was convenient for people to appeal financial matters directly to the Exchequer, giving rise to the Court of Exchequer.
Under Henry I, the monarchy was financially prosperous. The pipe rolls for 1129–1130 show that the Exchequer collected £23,000 that year. Of this amount, £6,000 came from the county farm—the fixed sum paid annually by sheriffs for the privilege of administering (and profiting from) royal lands in their counties. The geld accounted for £2,374. Other income came from feudal aids and reliefs, court fines and fees, and the royal forests. With annual revenue such as this, the king could meet his ordinary needs, while also having funds for war and other emergencies.
Royal justice became more accessible with the appointment of local justices in each shire and itinerant justices traveling judicial circuits of multiple shires. This gave the monarch a greater role in local government. Historian Tracy Borman
Tracy Joanne Borman (born 1 January 1972) is a historian and author from Scothern, Lincolnshire, England. She is most widely known as the author of ''Elizabeth's Women'', a portrait-gallery of the powerful women who influenced Queen Elizabeth I ...
summarised the impact of Henry I's reforms as "transform ngmedieval government from an itinerant and often poorly organised household into a highly sophisticated administrative kingship based on permanent, static departments."
Succession crisis
Henry married Matilda of Scotland, the niece of Edgar the Ætheling. This marriage was widely seen as uniting the House of Normandy with the House of Wessex and produced two children, Matilda (who marriedHoly Roman Emperor Henry V
Henry V (german: Heinrich V.; probably 11 August 1081 or 1086 – 23 May 1125, in Utrecht) was King of Germany (from 1099 to 1125) and Holy Roman Emperor (from 1111 to 1125), as the fourth and last ruler of the Salian dynasty. He was made co-ru ...
in 1114) and William Adelin (a Norman-French variant of Ætheling). But in 1120, England was thrown into a succession crisis when William Adelin died in the sinking of the '' White Ship''. In 1126, Henry I made a controversial decision to name his daughter Empress Matilda (his only surviving legitimate child) his heir and forced the nobility to swear oaths of allegiance to her. In 1128, the widowed Matilda married Geoffrey of Anjou, and the couple had three sons in the years 1133–1136.
Following Henry's death in 1135, his nephew, Stephen of Blois (), laid claim to the throne and took power with the support of most of the barons. Matilda challenged his reign; as a result, England descended into a period of civil war known as the Anarchy
The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin, the only legiti ...
(1138–1153). Stephen maintained a precarious hold on power but agreed to a compromise under which Matilda's son, Henry FitzEmpress, would succeed him.
Plantagenets (1154–1399)
Henry II and legal reform
 On December 19, 1154, Henry II () was for first time crowned ''King of England'' rather than ''King of the English''. It was also the inauguration of a new dynasty, the
On December 19, 1154, Henry II () was for first time crowned ''King of England'' rather than ''King of the English''. It was also the inauguration of a new dynasty, the House of Plantagenet
The House of Plantagenet () was a royal house which originated from the lands of Anjou in France. The family held the English throne from 1154 (with the accession of Henry II at the end of the Anarchy) to 1485, when Richard III died in b ...
. Henry founded the Angevin Empire, which controlled almost half of France including Normandy, Anjou, Maine, Touraine, and the Duchy of Aquitaine.
Henry's first task was restoring royal authority in a kingdom fractured by years of civil war. In some parts of the country, nobles were virtually independent of the Crown. In 1155, Henry expelled foreign mercenaries and ordered the demolition of illegal castles. He also dealt quickly and effectively with rebellious lords, such as Hugh de Mortimer.
Henry's legal reforms had a profound impact on English government for generations. In earlier times, English law was largely based on custom. Henry's reign saw the first official legislation since the Conquest in the form of Henry's various assizes and the growth of case law
Case law, also used interchangeably with common law, is law that is based on precedents, that is the judicial decisions from previous cases, rather than law based on constitutions, statutes, or regulations. Case law uses the detailed facts of a l ...
. In 1166, the Assize of Clarendon
The Assize of Clarendon was an act of Henry II of England in 1166 that began a transformation of English law and led to trial by jury in common law countries worldwide, and that established assize courts.
Prior systems for deciding the winning ...
established the supremacy of royal courts over manorial and ecclesiastical courts. Henry's legal reforms also transformed the king's personal role in the judicial process into an impersonal legal bureaucracy. The 1176 Assize of Northampton divided the kingdom into six judicial circuits called eyres allowing itinerant royal judges to reach the whole kingdom. In 1178, the king ordered five members of his to remain at Westminster and hear legal cases full time, creating the Court of King's Bench. Writs (standardised royal orders with the great seal attached) were developed to deal with common legal problems. Any freeman could purchase a writ from the chancery and receive royal justice without the king's personal intervention. For example, a writ of novel disseisin commanded a local jury to determine whether someone had been unjustly dispossessed of land.
 Since William the Conqueror's separation of secular and ecclesiastical jurisdiction, church courts claimed exclusive authority to try clergy, including monks and clerics in minor orders. The most contentious issue was "criminous clerks" accused of theft, rape or murder. Church courts could not impose the death penalty or bodily mutilation, and their punishments (
Since William the Conqueror's separation of secular and ecclesiastical jurisdiction, church courts claimed exclusive authority to try clergy, including monks and clerics in minor orders. The most contentious issue was "criminous clerks" accused of theft, rape or murder. Church courts could not impose the death penalty or bodily mutilation, and their punishments (penance
Penance is any act or a set of actions done out of Repentance (theology), repentance for Christian views on sin, sins committed, as well as an alternate name for the Catholic Church, Catholic, Lutheran, Eastern Orthodox, and Oriental Orthodox s ...
and defrocking) were lenient. In 1164, Henry issued the Constitutions of Clarendon, which required criminous clerks who had been defrocked to be handed over to royal courts for punishment as laymen
In religious organizations, the laity () consists of all members who are not part of the clergy, usually including any non-ordained members of religious orders, e.g. a nun or a lay brother.
In both religious and wider secular usage, a layperson ...
. It also forbade appeals to the pope. Archbishop Thomas Becket opposed the Constitutions, and the Becket controversy culminated in his murder in 1170. In 1172, Henry reached a settlement with the church in the Compromise of Avranches. Appeals to Rome were allowed, and secular courts were given jurisdiction over clerics accused of non- felony crimes.
Henry also extended his authority outside of England. In 1157, he invaded Wales and received the submission of Owain Owain () is a name of Welsh origin, variously written in Old Welsh as Ougein, Eugein, Euguen, Iguein, Ou(u)ein, Eug(u)ein, Yuein, and in Middle Welsh as Ewein, Owein, and Ywein. Other variants of the name Owain include Ewein, Iguein, Owein, Ouein, Y ...
of Gywnedd and Rhys ap Gruffydd of Deheubarth. The Scottish king William the Lion was forced to acknowledge the English king as feudal overlord in the Treaty of Falaise. The 1175 Treaty of Windsor confirmed Henry as feudal overlord of most of Ireland.
Richard the Lionheart
Bishop of Ely
The Bishop of Ely is the ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Ely in the Province of Canterbury. The diocese roughly covers the county of Cambridgeshire (with the exception of the Soke of Peterborough), together with a section of nort ...
, papal legate, justiciar and chancellor.
Concerned that John would usurp power while he was on Crusade, Richard made his brother swear to leave England for three years. John broke his oath and was in England by April 1191 leading opposition against Longchamp. From Sicily, Richard sent Archbishop Walter de Coutances to England as his envoy to resolve the situation. In October, a group of barons and bishops led by the Archbishop deposed Longchamp. John was appointed regent, but real power was exercised by Coutances as justiciar.
While returning from Crusade, Richard was imprisoned by Holy Roman Emperor Henry VI for over a year and was not released until England paid an enormous ransom. In 1193, John defected to Philip II of France, and the two plotted to take Richard's lands on the Continent. After a four-year absence, Richard returned to England in March 1194, but he soon left again to wage war against Philip II, who had overrun the Vexin and parts of Normandy. By 1198, Richard had reconquered most of his territory. At the Battle of Gisors
The Battle of Gisors (27 September 1198) was a skirmish fought in Courcelles-lès-Gisors, Oise, Picardy, part of the ongoing fighting between Richard I of England and Philip Augustus of France that lasted from 1194 to Richard's death in April 11 ...
, Richard adopted the motto (French for "God and my Right"), which was later adopted as the royal motto. In 1199, Richard died from wounds received while besieging Châlus-Chabrol. Before his death, the king made peace with John, naming him his successor.
After Richard's return from Crusade, the king created the office of coroner
A coroner is a government or judicial official who is empowered to conduct or order an inquest into Manner of death, the manner or cause of death, and to investigate or confirm the identity of an unknown person who has been found dead within th ...
(from , Latin for "keeper of the pleas of the Crown"). The coroner, alongside the sheriff, was a royal officer responsible for administering justice within a shire.
John and Magna Carta
 At Westminster Abbey in May 1199, John () was crowned (Latin for King of England) rather than the older form of (King of the English). In 1204, John lost Normandy and his other Continental possessions. The remainder of his reign was shaped by attempts to rehabilitate his military reputation and fund wars of reconquest. Traditionally, the king was expected to fund his government out of his own income derived from the royal
At Westminster Abbey in May 1199, John () was crowned (Latin for King of England) rather than the older form of (King of the English). In 1204, John lost Normandy and his other Continental possessions. The remainder of his reign was shaped by attempts to rehabilitate his military reputation and fund wars of reconquest. Traditionally, the king was expected to fund his government out of his own income derived from the royal demesne
A demesne ( ) or domain was all the land retained and managed by a lord of the manor under the feudal system for his own use, occupation, or support. This distinguished it from land sub-enfeoffed by him to others as sub-tenants. The concept or ...
, profits of royal justice, and profits from the feudal system (such as feudal incidents
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
, reliefs, and aids). In reality, this was rarely possible, especially in time of war. To fund his campaigns, John introduced a thirteen percent tax on revenues and movable goods that would become the model for taxation through the Tudor period. The king also raised money by charging high court fees and—in the opinion of his barons—abusing his right to feudal incidents and reliefs. Scutages were levied almost annually, much more often than under earlier kings. In addition, John showed partiality and favouritsm when dispensing justice. This and his paranoia caused his relationship with the barons to break down.
After quarreling with the king over the election of a new Archbishop of Canterbury, Pope Innocent III placed England under papal interdict in 1208. For the next six years, priests refused to say mass, officiate marriages, or bury the dead. John responded by confiscating church property. In 1209, the pope excommunicated John, but he remained unrepentant. It was not until 1213 that John reconciled with the pope, going so far as to convert the Kingdom of England into a papal fief with John as the pope's vassal.
The Anglo-French War of 1213–1214 was fought to restore the Angevin Empire, but John was defeated at the Battle of Bouvines. The military and financial losses of 1214 severely weakened the king, and the barons demanded that he govern according to Henry I's Coronation Charter. On 5 May 1215, a group of barons renounced their fealty to John calling themselves the Army of God and the Holy Church and chose Robert Fitzwalter to be their leader. The rebels numbered about 40 barons together with their sons and vassals. The other barons—around a hundred—worked with Archbishop Langton and the papal legate Guala Bicchieri to effect compromise between the two sides. Over a month of negotiations resulted in the Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
(Latin for "Great Charter"), which was formally agreed to by both sides at Runnymede on 15 June. This document defined and limited the king's powers over his subjects. It would be reconfirmed throughout the 13th century and gain the status of "inalienable custom and fundamental law". Historian Dan Jones notes that:
 Unlike earlier charters of liberties, Magna Carta included an enforcement mechanism in the form of a council of 25 barons who were permitted to wage "lawful rebellion" against the king if he violated the charter. The king had no intention of adhering to the document and appealed to Pope Innocent who annulled the agreement and excommunicated the rebel barons. This began the First Barons' War, during which the rebels offered the crown to Philip II's son, the future Louis VIII of France. By June 1216, Louis had taken control of half of England, including London. While he had not been crowned, he was proclaimed King Louis I at
Unlike earlier charters of liberties, Magna Carta included an enforcement mechanism in the form of a council of 25 barons who were permitted to wage "lawful rebellion" against the king if he violated the charter. The king had no intention of adhering to the document and appealed to Pope Innocent who annulled the agreement and excommunicated the rebel barons. This began the First Barons' War, during which the rebels offered the crown to Philip II's son, the future Louis VIII of France. By June 1216, Louis had taken control of half of England, including London. While he had not been crowned, he was proclaimed King Louis I at St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral is an Anglican cathedral in London and is the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London. It is on Ludgate Hill at the highest point of the City of London and is a Grad ...
, and many English nobles along with King Alexander II of Scotland gave him homage. In the midst of this collapse of royal authority, John died abruptly at Newark Castle on 19 October.
Henry III and origins of Parliament
 After John's death, loyal barons and bishops took his nine-year-old son to Gloucester Abbey where he was crowned Henry III () in a rushed coronation. This established the precedent that the eldest son became king regardless of age. Henry was the first child king since Æthelred the Unready, and William Marshal, Earl of Pembroke, served as regent until his death in 1219. Marshal led royal forces to victory against the rebel barons and French invaders at the Battles of Lincoln and Sandwich in 1217.
During Henry's reign, the principle that kings were subject to the law gained acceptance. To build support for the new king, his government re-issued Magna Carta in 1216 and 1217 (along with the Charter of the Forest). In January 1225, the Magna Carta was re-issued at a Great Council in return for approval of a tax to fund military campaigns in France. This established a new constitutional precedent in which "military expeditions would be financed at the expense of detailed concessions of political liberties". In 1236, Henry began calling such meetings Parliament. By the 1240s, these early Parliaments had not only assumed power to grant taxes but were also venues where nobles could complain about government policy or corruption.
In 1227, Henry was eighteen years old, and the regency officially ended. Yet, throughout his personal rule the king displayed a tendency to be dominated by foreign favourites. After the fall of the justiciar Hubert de Burgh in 1230, Bishop Peter des Roches became the king's chief minister. While holding no great office himself, the bishop showered his Poitevin relation Peter de Rivaux with a large number of offices. He was placed in charge of the treasury, the
After John's death, loyal barons and bishops took his nine-year-old son to Gloucester Abbey where he was crowned Henry III () in a rushed coronation. This established the precedent that the eldest son became king regardless of age. Henry was the first child king since Æthelred the Unready, and William Marshal, Earl of Pembroke, served as regent until his death in 1219. Marshal led royal forces to victory against the rebel barons and French invaders at the Battles of Lincoln and Sandwich in 1217.
During Henry's reign, the principle that kings were subject to the law gained acceptance. To build support for the new king, his government re-issued Magna Carta in 1216 and 1217 (along with the Charter of the Forest). In January 1225, the Magna Carta was re-issued at a Great Council in return for approval of a tax to fund military campaigns in France. This established a new constitutional precedent in which "military expeditions would be financed at the expense of detailed concessions of political liberties". In 1236, Henry began calling such meetings Parliament. By the 1240s, these early Parliaments had not only assumed power to grant taxes but were also venues where nobles could complain about government policy or corruption.
In 1227, Henry was eighteen years old, and the regency officially ended. Yet, throughout his personal rule the king displayed a tendency to be dominated by foreign favourites. After the fall of the justiciar Hubert de Burgh in 1230, Bishop Peter des Roches became the king's chief minister. While holding no great office himself, the bishop showered his Poitevin relation Peter de Rivaux with a large number of offices. He was placed in charge of the treasury, the privy seal
A privy seal refers to the personal seal of a reigning monarch, used for the purpose of authenticating official documents of a much more personal nature. This is in contrast with that of a great seal, which is used for documents of greater impor ...
, and the royal wardrobe
The Royal Wardrobe (also known as the King's Wardrobe) was a building located between Carter Lane and St Andrew's Church, just to the north of what is now Queen Victoria Street in the City of London, near Blackfriars. It was used as a storehou ...
. At the time, the wardrobe was a department that was at the centre of financial and political decisions in the royal household. He was given financial control of the royal household for life, was keeper of the forests and ports, and was, in addition, the sheriff of twenty-one counties. Rivaux used his immense power to enact important administrative reforms. Nevertheless, the accumulation of power by foreigners led Richard Marshal to open rebellion. The bishops as a group threatened Henry with excommunication, which finally made him strip the Poitevin party of power.
Henry then transferred his favouritism to his Lusignan half-brothers, William and Aymer de Valence. By the 1250s, there was widespread resentment against the Lusignans. There was also opposition to Henry's unrealistic plans to conquer the Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
for his second son, Edmund Crouchback. In 1255, the king informed Parliament that as part of the Sicilian campaign he owed the pope the huge sum of £100,000 and that if he defaulted England would be placed under an interdict. By 1257, there was a growing consensus that Henry was unfit to rule.
In 1258, the king was forced to submit to a radical reform programme promulgated at the Oxford Parliament. The Provisions of Oxford transferred royal power to a council of fifteen barons. A parliament would meet three times a year and appoint all royal officers (from justiciar and chancellor to sheriffs and bailiff
A bailiff (from Middle English baillif, Old French ''baillis'', ''bail'' "custody") is a manager, overseer or custodian – a legal officer to whom some degree of authority or jurisdiction is given. Bailiffs are of various kinds and their offi ...
s). The new government's leader was Simon de Montfort, the king's brother-in-law and former friend.
When the king tried to overturn the Provisions of Oxford, Montfort led a rebellion, the Second Barons' War. In 1265, Montfort called a Parliament to consolidate support for the rebellion. For the first time, knights of the shire and burgesses from the important towns were summoned along with barons and bishops. Simon de Montfort's Parliament was an important milestone in the evolution of Parliament. Montfort was killed at the Battle of Evesham
The Battle of Evesham (4 August 1265) was one of the two main battles of 13th century England's Second Barons' War. It marked the defeat of Simon de Montfort, Earl of Leicester, and the rebellious barons by the future King Edward I, who led the ...
in 1265, and royal authority was restored.
Henry traveled less than past kings. As a consequence, he spent large amounts of money on royal palaces. His most expensive projects were the rebuilding of Westminster Palace and Abbey, costing £55,000 (or £40 million in today's currency). He spent a further £9,000 (£6.5 million) on the Tower of London. Westminster Abbey alone nearly bankrupted the king.
Henry III died in 1272, having been king for fifty-six years. His turbulent reign was the third longest of any English monarch.
Edward I

Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal o ...
(), nicknamed Longshanks for his height, was in Italy when he learned that his father had died. He arrived in England in August 1274 determined to restore royal authority. His first act was ordering the Hundred Rolls survey, a detailed investigation into what rights and land the Crown had lost since Henry III's reign. It was also intended to root out corruption by royal officials, and while few people were prosecuted for wrongdoing, it sent a message that Edward was a reformer.
From his father's reign, Edward learned the importance of building national consensus for his policies through Parliament, which he usually summoned twice a year at Easter and Michaelmas. Edward effected his reform program through a series of parliamentary statutes: Statute of Westminster of 1275, Statute of Gloucester of 1278, Statute of Mortmain of 1279, Statute of Acton Burnell Statute merchant and statute staple are two old forms of security, long obsolete in English practice, though references to them still occur in some modern statutes.
The former security was first created by the 1283 Statute of Merchants, or Statute ...
of 1283, and Statute of Westminster of 1285. In 1297, he reissued Magna Carta. In 1295, Edward summoned the Model Parliament, which included knights and burgesses to represent the counties and towns. These "middle earners" were the most important group of taxpayers, and Edward was eager to gain their financial support for an invasion of Scotland.
Through effective management of Parliament, Edward was able to fund his military campaigns in Wales and Scotland. He successfully and permanently conquered Wales, built impressive castles to enforce English domination, and brought the country under English law with the Statute of Wales. In 1301, the king's eldest son, Edward of Caernarfon, was created Prince of Wales and given control of the Principality of Wales. The title continues to be granted to the heirs of British monarchs.
The death of Alexander III of Scotland in 1286 and his granddaughter Margaret of Norway in 1290 left the Scottish throne vacant. The Guardians of Scotland recognised Edward's feudal overlordship and invited him to adjudicate the Scottish succession dispute. In 1292, John Balliol was chosen Scotland's new king, but Edward's brutal treatment of his northern vassal led to the First War of Scottish Independence. In 1307, Edward died on his way to invade Scotland.
Edward II
At his coronation,Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also called Edward of Caernarfon, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir apparent to t ...
() promised not only to uphold the laws of Edward the Confessor as was traditional but also "the laws and rightful customs which the community of the realm shall have chosen". Edward thus abandoned any claim to absolute power and recognised the need to rule in cooperation with Parliament. The new king inherited problems from his father: the Crown was in debt and the war in Scotland was going badly. He compounded these problems by alienating the nobility. The main cause of conflict was the influence wielded by royal favourites, first Piers Gaveston and then Hugh Despenser the Younger.
The king's reliance on favourites proved a convenient scapegoat
In the Bible, a scapegoat is one of a pair of kid goats that is released into the wilderness, taking with it all sins and impurities, while the other is sacrificed. The concept first appears in the Book of Leviticus, in which a goat is designate ...
for the barons, who blamed unpopular policies on them rather than directly oppose the king. When Parliament met in April 1308, Henry de Lacy, Earl of Lincoln, and a delegation of nobles presented the Declaration of 1308, which for the first time explicitly distinguished between the king as a person and the Crown as an institution to which the people owed allegiance (see Doctrine of capacities).
In 1310, Parliament complained that "the state of the king and the kingdom had much deteriorated since the death of the elder King Edward... and the whole kingdom had been not a little injured". Specifically, Edward was accused of being guided by evil counselors, impoverishing the Crown, violating Magna Carta, and losing Scotland. The magnates elected twenty-one ordainers to reform the government. The completed reforms were presented to Edward as the Ordinances in August 1311. Like Magna Carta and the Provisions of Oxford, the Ordinances of 1311 were an attempt to limit the powers of the monarch. It banned the practice of purveyance and going to war without consulting Parliament. Government revenue was to be paid to the exchequer rather than to the royal household, and Parliament was to meet at least once a year. Parliament was to create committees to investigate royal abuses and to appoint royal ministers and officials (such as the chancellor and county sheriffs).
The Ordinances also required the exile of the king's favourite, Gaveston. By January 1312, Edward had publicly repudiated the ordinances, and Gaveston was back in England. Earl Thomas of Lancaster, the king's cousin, led a group of magnates that captured and executed Gaveston. This act nearly plunged England into civil war but negotiations restored an uneasy peace.
 After Gaveston's death, the most influential men around the king were Hugh Despenser and his son, Hugh Despenser the Younger. The king alienated moderate barons by dispensing royal patronage without parliamentary approval as required by the Ordinances and allowing the Despensers to act with impunity. In 1318, negotiations led to the Treaty of Leake in which the king agreed to abide by the Ordinances of 1311. A permanent royal council was created with eight bishops, four earls, and four barons as members.
Edward's favouritsm toward the Despensers continued to destabilize the kingdom. The Despensers had become the gatekeepers to the king, and their enemies "were liable to be deprived of land or possessions or else thrown into prison". The Welsh Marches were particularly destabilized by Hugh the Younger's accumulation of land. In 1321, a group of marcher lords invaded the Despenser estates, beginning the Despenser War. Edward defeated the baronial opposition in 1322 and overturned the Ordinances. For the next few years, Edward ruled as a tyrant. The author of the ''
After Gaveston's death, the most influential men around the king were Hugh Despenser and his son, Hugh Despenser the Younger. The king alienated moderate barons by dispensing royal patronage without parliamentary approval as required by the Ordinances and allowing the Despensers to act with impunity. In 1318, negotiations led to the Treaty of Leake in which the king agreed to abide by the Ordinances of 1311. A permanent royal council was created with eight bishops, four earls, and four barons as members.
Edward's favouritsm toward the Despensers continued to destabilize the kingdom. The Despensers had become the gatekeepers to the king, and their enemies "were liable to be deprived of land or possessions or else thrown into prison". The Welsh Marches were particularly destabilized by Hugh the Younger's accumulation of land. In 1321, a group of marcher lords invaded the Despenser estates, beginning the Despenser War. Edward defeated the baronial opposition in 1322 and overturned the Ordinances. For the next few years, Edward ruled as a tyrant. The author of the ''Vita Edwardi Secundi
The ''Vita Edwardi Secundi'' (''Life of Edward II'') is a Latin chronicle most likely written in 1325 by an unknown English medieval historian contemporary to Edward II. It covers the period from 1307 until its abrupt end in 1325.
Manuscript
T ...
'' wrote of this period,
In 1324, Edward's wife Isabella and their son, Prince Edward, traveled to France on a diplomatic mission. While there, the queen formed an alliance with Roger Mortimer, a marcher lord who had fought against Edward in the Despenser War. Together, they invaded England in 1326 with the intention of deposing Edward. While they faced little resistance, their actions precipitated a constitutional crisis as there was no legal process to remove a crowned and anointed king. At the Parliament of 1327, the Articles of Accusation were drawn up accusing the king of violating his coronation oath and following the advice of evil councilors. On 20 January, Edward II was forced to abdicate. This marked the first time in English history that a monarch was formally deposed from the throne. The former king died on 21 September, probably murdered on the orders of his wife.
Edward III
Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
() was crowned king, but it was Mortimer who truly held power. In 1330, the eighteen-year old king began his personal rule after seizing power from Mortimer, who was arrested and executed.
In 1337, King Philip VI of France
Philip VI (french: Philippe; 1293 – 22 August 1350), called the Fortunate (french: le Fortuné, link=no) or the Catholic (french: le Catholique, link=no) and of Valois, was the first king of France from the House of Valois, reigning from 1328 ...
confiscated the Duchy of Aquitaine and the County of Ponthieu from the English king. That same year, Edward made his eldest son, Edward the Black Prince, the Duke of Cornwall
Duke of Cornwall is a title in the Peerage of England, traditionally held by the eldest son of the reigning British monarch, previously the English monarch. The duchy of Cornwall was the first duchy created in England and was established by a ro ...
. This was the first duchy
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a Middle Ages, medieval country, territory, fiefdom, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or Queen regnant, queen in Western European tradition.
There once exis ...
created in England. He also added the fleur-de-lis to the royal arms of England, symbolising his claim to the French throne. Edward's claim was based on his being the only male descendent of his grandfather, King Philip IV of France
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (french: Philippe le Bel), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre as Philip I from 12 ...
. In 1346, Edward invaded France in pursuit of his claim, setting off the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
which would last until 1453. After a successful campaign in France, Edward returned to England and founded the Order of the Garter
The Most Noble Order of the Garter is an order of chivalry founded by Edward III of England in 1348. It is the most senior order of knighthood in the British honours system, outranked in precedence only by the Victoria Cross and the George C ...
at Windsor Castle in 1348.
Edward worked with Parliament to build consensus and support for his wars and, in the process, furthered Parliament's development as an essential institution of government. According to historian David Starkey,
The Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
forced a pause in the war with France. Edward effectively responded to the crisis with legislation to relieve the labour shortage (see Ordinance of Labourers 1349 and Statute of Labourers 1351
The Statute of Labourers was a law created by the English parliament under King Edward III in 1351 in response to a labour shortage, which aimed at regulating the labour force by prohibiting requesting or offering a wage higher than pre-Plague sta ...
) and the creation of justices of the peace to enforce the laws. Fighting resumed in the 1350s. In the 1360 Treaty of Brétigny, Edward renounced his claims to the French throne and was awarded outright sovereignty over Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
, Ponthieu, and Aquitaine.
The year 1376 was challenging for the monarchy. The Good Parliament forced the ill and elderly Edward III to dismiss his ministers and banish the royal mistress, Alice Perrers. The same year, the Black Prince died at the age of forty-five. Edward's new heir was his nine-year-old grandson Richard of Bordeaux. There were concerns that Richard's uncles might usurp power. To strengthen the boy's position, he was recognised in Parliament as heir apparent and given the titles of Prince of Wales, Duke of Cornwall, and Earl of Chester. Having secured the succession, Edward III died in 1377.
Richard II
 As
As Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward the Black Prince, Prince of Wales, and Joan, Countess of Kent. Richard's father died ...
() was ten years old when he became king, his personal rule did not begin until 1381. He surrounded himself with favourites, such as Michael de la Pole and Robert de Vere, and his government was described by one historian as "a high-tax, high-spend, cliquey affair." The backlash began in 1386 when the Wonderful Parliament forced Richard to dismiss de la Pole as chancellor. In 1387, the Lords Appellant defeated the king's army at the Battle of Radcot Bridge, and Richard was reduced to a figurehead. At the Merciless Parliament of 1388, the king's favourites were tried and convicted of treason.
By 1397, Richard had rebuilt his authority and had the Lords Appellant either exiled or executed for treason. Subsequently, the king ruled as a tyrant. When Parliament met at Westminster, the king suppressed dissent with a show of force—two hundred Cheshire archers surrounded the building. In 1399, the king's uncle, John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster
John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster (6 March 1340 – 3 February 1399) was an English royal prince, military leader, and statesman. He was the fourth son (third to survive infancy as William of Hatfield died shortly after birth) of King Edward ...
, died. Lancaster had been the most powerful noblemen in England with thirty castles and a private army of four thousand men. His son, Henry Bolingbroke, was in Paris living in exile but chose to return when Richard confiscated the Lancastrian estates.
In 1399, Richard was campaigning in Ireland when Bolingbroke invaded England and seized power. Richard was captured and imprisoned in the Tower of London on 2 September. A parliamentary committee concluded that Richard should be deposed because of his "perjuries, sacrileges, sodomitical acts, dispossession of his subjects, reduction of his people to servitude, lack of reason, and incapacity to rule". On 30 September, an assembly of the House of Lords and House of Commons met in Westminster Hall. Richard was charged with breaking his coronation oath and violating "the rightful laws and customs of the realm". He was then declared deposed and his subjects freed from all allegiance. Bolingbroke then claimed the vacant throne for himself with Parliament's blessing.
Richard II was not the first English monarch to be deposed; that distinction belongs to Edward II. Edward abdicated in favor of his son and heir. In Richard's case, the line of succession was deliberately broken by Parliament. Historian Tracy Borman
Tracy Joanne Borman (born 1 January 1972) is a historian and author from Scothern, Lincolnshire, England. She is most widely known as the author of ''Elizabeth's Women'', a portrait-gallery of the powerful women who influenced Queen Elizabeth I ...
writes that this "created a dangerous precedent and made the crown fundamentally unstable."House of Lancaster (1399–1461)
Henry IV
 Bolingbroke was crowned as Henry IV () two weeks after Richard II's deposition. His dynasty was known as the
Bolingbroke was crowned as Henry IV () two weeks after Richard II's deposition. His dynasty was known as the House of Lancaster
The House of Lancaster was a cadet branch of the royal House of Plantagenet. The first house was created when King Henry III of England created the Earldom of Lancasterfrom which the house was namedfor his second son Edmund Crouchback in 126 ...
, a reference to his father's title Duke of Lancaster. As part of the coronation, Henry created Knights of the Bath, a tradition that was repeated at all later coronations. He was also the first English monarch to be crowned on the Stone of Scone, which Edward I had taken from Scotland.
In January 1400, the Epiphany Rising failed to free Richard II from Pontefract Castle and restore him to the throne. Henry realized he would have no security as long as Richard lived, so he ordered his death, most likely by starvation. Henry's reign was forever tarnished by the deposition and murder of an anointed king, and he constantly had to fight off plots and rebellions. In 1400, the Welsh Revolt began, and in 1403 the heir to the powerful Percy family, Henry Hotspur
Sir Henry Percy (20 May 1364 – 21 July 1403), nicknamed Hotspur, was an English knight who fought in several campaigns against the Scots in the northern border and against the French during the Hundred Years' War. The nickname "Hotsp ...
, joined the Welsh. Hotspur was defeated at the Battle of Shrewsbury, but this did not quiet challenges to Henry's legitimacy.
When overthrowing Richard, Henry made many promises to win support. One of these was to reduce taxation. Parliament refused to raise taxes even as the king went into debt to fund defensive wars. He did, however, benefit from inheriting the vast Lancastrian estates of his father. He decided to administer these lands separately from the crown lands. The practice of holding the Duchy of Lancaster separate from the crown estate was continued by later monarchs.
Charles VI of France, Richard's father-in-law, refused to recognise Henry. The French revived their claims to Aquitaine, attacked Calais, and aided the Welsh Revolt. But in 1407, the Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War divided France, and the English were keen to take advantage of French disunity. English policy vacillated between the opposing sides as King Henry supported the Armagnac faction
The Armagnac faction was prominent in French politics and warfare during the Hundred Years' War. It was allied with the supporters of Charles, Duke of Orléans against John the Fearless after Charles' father Louis of Orléans was killed on ...
, while his eldest son, Prince Henry, supported the Burgundian faction Burgundian can refer to any of the following:
*Someone or something from Burgundy.
*Burgundians, an East Germanic tribe, who first appear in history in South East Europe. Later Burgundians colonised the area of Gaul that is now known as Burgundy (F ...
. As the king's health declined, Prince Henry assumed a greater role in government, and there were suggestions that the king should abdicate in favor of his son.
Henry V and VI
Abdication became unnecessary when Henry IV died in 1413, and the prince became King Henry V (). He escaped the troubles of his father's reign by making conciliatory gestures toward his father's enemies. He also removed the taint of usurpation by honoring the deceased Richard II and giving him a royal re-burial at Westminster Abbey.Battle of Agincourt
The Battle of Agincourt ( ; french: Azincourt ) was an English victory in the Hundred Years' War. It took place on 25 October 1415 (Saint Crispin's Day) near Azincourt, in northern France. The unexpected English victory against the numerica ...
. The triumphant king returned home to a jubilant nation eager to support further wars of conquest. Parliament gave the king lifetime duties on wine imports and other tax grants. When he was ready to return to France, Parliament granted another double subsidy.
Henry returned to France in 1417 and remained there over three years. In 1420, France agreed to the Treaty of Troyes. Henry was recognised as heir and regent to King Charles VI of France and married his daughter, Catherine of Valois. Charles's son, the Dauphin, was disinherited by the treaty; however, he continued to control over half of France south of the Loire river. There were downsides to the king's frequent absences. While in France, Henry insisted on dealing with petitions from Parliament personally despite the long distances and delays involved. By 1420, the House of Commons was complaining, and funds for further wars in France were more difficult to secure. In 1422, the king fell ill and died while on another campaign in France.
The accession of Henry V's infant son, Henry VI, to the throne gave the French an opportunity to overthrow English rule. The unpopularity of Henry VI's counsellors and his consort, Margaret of Anjou
Margaret of Anjou (french: link=no, Marguerite; 23 March 1430 – 25 August 1482) was Queen of England and nominally Queen of France by marriage to King Henry VI from 1445 to 1461 and again from 1470 to 1471. Born in the Duchy of Lorrain ...
, as well as his own ineffectual leadership, led to the weakening of the House of Lancaster. The Lancastrians faced a challenge from the House of York, so-called because its head, a descendant of Edward III, was Richard, Duke of York, who was at odds with the Queen.
House of York (1461–1485)
Although the Duke of York died in battle in 1460, his eldest son,Edward IV
Edward IV (28 April 1442 – 9 April 1483) was King of England from 4 March 1461 to 3 October 1470, then again from 11 April 1471 until his death in 1483. He was a central figure in the Wars of the Roses, a series of civil wars in England ...
, led the Yorkists to victory in 1461, overthrowing Henry VI and Margaret of Anjou. Edward IV was constantly at odds with the Lancastrians and his own councillors after his marriage to Elizabeth Woodville
Elizabeth Woodville (also spelt Wydville, Wydeville, or Widvile;Although spelling of the family name is usually modernised to "Woodville", it was spelt "Wydeville" in contemporary publications by Caxton, but her tomb at St. George's Chapel, Wind ...
, with a brief return to power for Henry VI. Edward IV prevailed, winning back the throne at Barnet
Barnet may refer to:
People
*Barnet (surname)
* Barnet (given name)
Places United Kingdom
*Chipping Barnet or High Barnet, commonly known as Barnet, one of three focal towns of the borough below.
*East Barnet, a district of the borough below; an ...
and killing the Lancastrian heir, Edward of Westminster, at Tewkesbury. Afterward he captured Margaret of Anjou, eventually sending her into exile, but not before killing Henry VI while he was held prisoner in the Tower. The Wars of the Roses, nevertheless, continued intermittently during his reign and those of his son Edward V
Edward V (2 November 1470 – mid-1483)R. F. Walker, "Princes in the Tower", in S. H. Steinberg et al, ''A New Dictionary of British History'', St. Martin's Press, New York, 1963, p. 286. was ''de jure'' King of England and Lord of Ireland fro ...
and brother Richard III
Richard III (2 October 145222 August 1485) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the House of York and the last of the Plantagenet dynasty. His defeat and death at the Battl ...
. Edward V disappeared, presumably murdered by Richard. Ultimately, the conflict culminated in success for the Lancastrian branch led by Henry Tudor, in 1485, when Richard III was killed in the Battle of Bosworth Field
The Battle of Bosworth or Bosworth Field was the last significant battle of the Wars of the Roses, the civil war between the houses of Lancaster and York that extended across England in the latter half of the 15th century. Fought on 22 Augu ...
.
Tudors (1485–1603)
King Henry VII then neutralised the remaining Yorkist forces, partly by marrying Elizabeth of York, a Yorkist heir. Through skill and ability, Henry re-established absolute supremacy in the realm, and the conflicts with the nobility that had plagued previous monarchs came to an end. The reign of the second Tudor king,Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
, was one of great political change. Religious upheaval and disputes with the Pope, and the fact that his marriage to Catherine of Aragon
Catherine of Aragon (also spelt as Katherine, ; 16 December 1485 – 7 January 1536) was Queen of England as the first wife of King Henry VIII from their marriage on 11 June 1509 until their annulment on 23 May 1533. She was previously ...
produced only one surviving child, a daughter, led the monarch to break from the Roman Catholic Church and to establish the Church of England (the Anglican Church) and divorce his wife to marry Anne Boleyn.
Wales – which had been conquered centuries earlier, but had remained a separate dominion – was annexed to England under the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. Henry VIII's son and successor, the young Edward VI, continued with further religious reforms, but his early death in 1553 precipitated a succession crisis. He was wary of allowing his Catholic elder half-sister Mary I to succeed, and therefore drew up a will designating Lady Jane Grey
Lady Jane Grey ( 1537 – 12 February 1554), later known as Lady Jane Dudley (after her marriage) and as the "Nine Days' Queen", was an English noblewoman who claimed the throne of England and Ireland from 10 July until 19 July 1553.
Jane was ...
as his heiress. Jane's reign, however, lasted only nine days; with tremendous popular support, Mary deposed her and declared herself the lawful sovereign. Mary I married Philip of Spain, who was declared king and co-ruler. He pursued disastrous wars in France and she attempted to return England to Roman Catholicism (burning Protestants at the stake as heretics in the process). Upon her death in 1558, the pair were succeeded by her Protestant half-sister Elizabeth I. England returned to Protestantism and continued its growth into a major world power by building its navy and exploring the New World.
Scottish monarchy
In Scotland, as in England, monarchies emerged after the withdrawal of the Roman empire from Britain in the early fifth century. The three groups that lived in Scotland at this time were the Picts in the north east, the Britons in the south, including the Kingdom of Strathclyde, and the Gaels or Scotti (who would later give their name to Scotland), of the Irish petty kingdom of Dál Riata in the west. Kenneth MacAlpin is traditionally viewed as the first king of a united Scotland (known as Scotia to writers in Latin, or Alba to the Scots). The expansion of Scottish dominions continued over the next two centuries, as other territories such as Strathclyde were absorbed. Early Scottish monarchs did not inherit the Crown directly; instead, the custom of tanistry was followed, where the monarchy alternated between different branches of the House of Alpin. As a result, however, the rival dynastic lines clashed, often violently. From 942 to 1005, seven consecutive monarchs were either murdered or killed in battle. In 1005, Malcolm II ascended the throne having killed many rivals. He continued to ruthlessly eliminate opposition, and when he died in 1034 he was succeeded by his grandson, Duncan I, instead of a cousin, as had been usual. In 1040, Duncan suffered defeat in battle at the hands ofMacbeth
''Macbeth'' (, full title ''The Tragedie of Macbeth'') is a tragedy by William Shakespeare. It is thought to have been first performed in 1606. It dramatises the damaging physical and psychological effects of political ambition on those w ...
, who was killed himself in 1057 by Duncan's son Malcolm. The following year, after killing Macbeth's stepson Lulach, Malcolm ascended the throne as Malcolm III.
With a further series of battles and deposings, five of Malcolm's sons as well as one of his brothers successively became king. Eventually, the Crown came to his youngest son, David I. David was succeeded by his grandsons Malcolm IV, and then by William the Lion, the longest-reigning King of Scots before the Union of the Crowns. William participated in a rebellion against King Henry II of England but when the rebellion failed, William was captured by the English. In exchange for his release, William was forced to acknowledge Henry as his feudal overlord. The English King Richard I agreed to terminate the arrangement in 1189, in return for a large sum of money needed for the Crusades. William died in 1214, and was succeeded by his son Alexander II. Alexander II, as well as his successor Alexander III, attempted to take over the Western Isles, which were still under the overlordship of Norway. During the reign of Alexander III, Norway launched an unsuccessful invasion of Scotland; the ensuing Treaty of Perth recognised Scottish control of the Western Isles and other disputed areas.
 Alexander III's death in a riding accident in 1286 precipitated a major succession crisis. Scottish leaders appealed to King Edward I of England for help in determining who was the rightful heir. Edward chose Alexander's three-year-old Norwegian granddaughter,
Alexander III's death in a riding accident in 1286 precipitated a major succession crisis. Scottish leaders appealed to King Edward I of England for help in determining who was the rightful heir. Edward chose Alexander's three-year-old Norwegian granddaughter, Margaret
Margaret is a female first name, derived via French () and Latin () from grc, μαργαρίτης () meaning "pearl". The Greek is borrowed from Persian.
Margaret has been an English name since the 11th century, and remained popular througho ...
. On her way to Scotland in 1290, however, Margaret died at sea, and Edward was again asked to adjudicate between 13 rival claimants to the throne. A court was set up and after two years of deliberation, it pronounced John Balliol to be king. Edward proceeded to treat Balliol as a vassal, and tried to exert influence over Scotland. In 1295, when Balliol renounced his allegiance to England, Edward I invaded. During the first ten years of the ensuing Wars of Scottish Independence, Scotland had no monarch, until Robert the Bruce declared himself king in 1306.
Robert's efforts to control Scotland culminated in success, and Scottish independence was acknowledged in 1328. However, only one year later, Robert died and was succeeded by his five-year-old son, David II. On the pretext of restoring John Balliol's rightful heir, Edward Balliol, the English again invaded in 1332. During the next four years, Balliol was crowned, deposed, restored, deposed, restored, and deposed until he eventually settled in England, and David remained king for the next 35 years.
David II died childless in 1371 and was succeeded by his nephew Robert II of the House of Stuart. The reigns of both Robert II and his successor, Robert III, were marked by a general decline in royal power. When Robert III died in 1406, regents had to rule the country; the monarch, Robert III's son James I, had been taken captive by the English. Having paid a large ransom, James returned to Scotland in 1424; to restore his authority, he used ruthless measures, including the execution of several of his enemies. He was assassinated by a group of nobles. James II James II may refer to:
* James II of Avesnes (died c. 1205), knight of the Fourth Crusade
* James II of Majorca (died 1311), Lord of Montpellier
* James II of Aragon (1267–1327), King of Sicily
* James II, Count of La Marche (1370–1438), King C ...
continued his father's policies by subduing influential noblemen but he was killed in an accident at the age of thirty, and a council of regents again assumed power. James III was defeated in a battle against rebellious Scottish earls in 1488, leading to another boy-king: James IV
James IV (17 March 1473 – 9 September 1513) was King of Scotland from 11 June 1488 until his death at the Battle of Flodden in 1513. He inherited the throne at the age of fifteen on the death of his father, James III, at the Battle of Sauchi ...
.
In 1513 James IV launched an invasion of England, attempting to take advantage of the absence of the English King Henry VIII. His forces met with disaster at Flodden Field
The Battle of Flodden, Flodden Field, or occasionally Branxton, (Brainston Moor) was a battle fought on 9 September 1513 during the War of the League of Cambrai between the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland, resulting in an English ...
; the King, many senior noblemen, and hundreds of soldiers were killed. As his son and successor, James V
James V (10 April 1512 – 14 December 1542) was King of Scotland from 9 September 1513 until his death in 1542. He was crowned on 21 September 1513 at the age of seventeen months. James was the son of King James IV and Margaret Tudor, and duri ...
, was an infant, the government was again taken over by regents. James V led another disastrous war with the English in 1542, and his death in the same year left the Crown in the hands of his six-day-old daughter, Mary. Once again, a regency was established.
Mary, a Roman Catholic, reigned during a period of great religious upheaval in Scotland. As a result of the efforts of reformers such as John Knox
John Knox ( gd, Iain Cnocc) (born – 24 November 1572) was a Scottish minister, Reformed theologian, and writer who was a leader of the country's Reformation. He was the founder of the Presbyterian Church of Scotland.
Born in Giffordgat ...
, a Protestant ascendancy was established. Mary caused alarm by marrying her Catholic cousin, Lord Darnley, in 1565. After Lord Darnley's assassination in 1567, Mary contracted an even more unpopular marriage with the Earl of Bothwell
Earl of Bothwell was a title that was created twice in the Peerage of Scotland. It was first created for Patrick Hepburn in 1488, and was forfeited in 1567. Subsequently, the earldom was re-created for the 4th Earl's nephew and heir of line, F ...
, who was widely suspected of Darnley's murder. The nobility rebelled against the Queen, forcing her to abdicate. She fled to England, and the Crown went to her infant son James VI, who was brought up as a Protestant. Mary was imprisoned and later executed by the English queen Elizabeth I.
Irish monarchy
Ireland was historically divided into petty principalities that sometimes acknowledged one of their rulers asHigh King of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ga, Ardrí na hÉireann ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and later sometimes assigned ana ...
. In 1155, the only English pope, Adrian IV, authorised Henry II of England to conquer Ireland and reform the Irish church with the papal bull '' Laudabiliter''. However, Henry took no action until 1171. By that time, a number of English nobles, especially the Welsh Marcher Lords, had invaded Ireland and established control over portions of the island. In 1171, Henry landed in Ireland and the Anglo-Norman lords gave him homage and fealty. He also convinced the native Gaelic nobility to become his vassals. In 1185, Henry gave his youngest son, the future King John of England, the title Lord of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland ( ga, Tiarnas na hÉireann), sometimes referred to retroactively as Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman lords between ...
. John was then sent to Ireland to be crowned as that island's king, but his behavior offended the Irish, who forced John to retreat without being crowned. Thereafter, future English kings used the title Lord of Ireland but mostly ignored the island, preferring to rule through lieutenants for Ireland.
By 1541, King Henry VIII of England had broken with the Church of Rome and declared himself Supreme Head of the Church of England. The Pope's grant of Ireland to the English monarch became invalid, so Henry summoned a meeting of the Irish Parliament to change his title from ''Lord of Ireland'' to ''King of Ireland''. In 1800, as a result of the Irish Rebellion of 1798, the Act of Union merged the kingdom of Great Britain and the kingdom of Ireland into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.
Union of the Crowns and republican phase
Elizabeth I's death in 1603 ended Tudor rule in England. Since she had no children, she was succeeded by the Scottish monarch James VI, who was the great-grandson ofHenry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
's older sister and hence Elizabeth's first cousin twice removed. James VI ruled in England as James I after what was known as the " Union of the Crowns". Although England and Scotland were in personal union under one monarch – James I & VI became the first monarch to style himself "King of Great Britain" in 1604 – they remained two separate kingdoms. James I & VI's successor, Charles I, experienced frequent conflicts with the English Parliament related to the issue of royal and parliamentary powers, especially the power to impose taxes. He provoked opposition by ruling without Parliament from 1629 to 1640, unilaterally levying taxes and adopting controversial religious policies (many of which were offensive to the Scottish Presbyterians
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
and the English Puritans). His attempt to enforce Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
led to organised rebellion in Scotland (the "Bishops' Wars
The 1639 and 1640 Bishops' Wars () were the first of the conflicts known collectively as the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, which took place in Scotland, England and Ireland. Others include the Irish Confederate Wars, the First and ...
") and ignited the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. In 1642, the conflict between the King and English Parliament reached its climax and the English Civil War began.
The Civil War culminated in the execution of the king in 1649, the overthrow of the English monarchy, and the establishment of the Commonwealth of England. Charles I's son, Charles II, was proclaimed King of Great Britain in Scotland, but he was forced to flee abroad after he invaded England and was defeated at the Battle of Worcester. In 1653, Oliver Cromwell, the most prominent military and political leader in the nation, seized power and declared himself Lord Protector
Lord Protector (plural: ''Lords Protector'') was a title that has been used in British constitutional law for the head of state. It was also a particular title for the British heads of state in respect to the established church. It was sometimes ...
(effectively becoming a military dictator, but refusing the title of king). Cromwell ruled until his death in 1658, when he was succeeded by his son Richard. The new Lord Protector had little interest in governing; he soon resigned. The lack of clear leadership led to civil and military unrest, and to a popular desire to restore the monarchy. In 1660, the monarchy was restored and Charles II returned to Britain.
 Charles II's reign was marked by the development of the first modern political parties in England. Charles had no legitimate children, and was due to be succeeded by his Roman Catholic brother,
Charles II's reign was marked by the development of the first modern political parties in England. Charles had no legitimate children, and was due to be succeeded by his Roman Catholic brother, James, Duke of York
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Re ...
. A parliamentary effort to exclude James from the line of succession arose; the "Petitioners", who supported exclusion, became the Whig Party, whereas the "Abhorrers", who opposed exclusion, became the Tory Party. The Exclusion Bill failed; on several occasions, Charles II dissolved Parliament because he feared that the bill might pass. After the dissolution of the Parliament of 1681, Charles ruled without a Parliament until his death in 1685. When James succeeded Charles, he pursued a policy of offering religious tolerance to Roman Catholics, thereby drawing the ire of many of his Protestant subjects. Many opposed James's decisions to maintain a large standing army, to appoint Roman Catholics to high political and military offices, and to imprison Church of England clerics who challenged his policies. As a result, a group of Protestants known as the Immortal Seven invited James II & VII's daughter Mary and her husband William III of Orange to depose the king. William obliged, arriving in England on 5 November 1688 to great public support. Faced with the defection of many of his Protestant officials, James fled the realm and William and Mary (rather than James II & VII's Catholic son) were declared joint Sovereigns of England, Scotland and Ireland.
James's overthrow, known as the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
, was one of the most important events in the long evolution of parliamentary power. The Bill of Rights 1689 affirmed parliamentary supremacy, and declared that the English people held certain rights, including the freedom from taxes imposed without parliamentary consent. The Bill of Rights required future monarchs to be Protestants, and provided that, after any children of William and Mary, Mary's sister Anne would inherit the Crown. Mary II died childless in 1694, leaving William III & II as the sole monarch. By 1700, a political crisis arose, as all of Anne's children had died, leaving her as the only individual left in the line of succession. Parliament was afraid that the former James II or his supporters, known as Jacobites, might attempt to reclaim the throne. Parliament passed the Act of Settlement 1701
The Act of Settlement is an Act of the Parliament of England that settled the succession to the English and Irish crowns to only Protestants, which passed in 1701. More specifically, anyone who became a Roman Catholic, or who married one, bec ...
, which excluded James and his Catholic relations from the succession and made William's nearest Protestant relations, the family of Sophia, Electress of Hanover
Sophia of Hanover (born Princess Sophia of the Palatinate; 14 October 1630 – 8 June 1714) was the Electress of Hanover by marriage to Elector Ernest Augustus and later the heiress presumptive to the thrones of England and Scotland (later Grea ...
, next in line to the throne after his sister-in-law Anne. Soon after the passage of the Act, William III & II died, leaving the Crown to Anne.
After Anne's accession, the problem of the succession re-emerged. The Scottish Parliament, infuriated that the English Parliament did not consult them on the choice of Sophia's family as the next heirs, passed the Act of Security 1704, threatening to end the personal union between England and Scotland. The Parliament of England retaliated with the Alien Act 1705, threatening to devastate the Scottish economy by restricting trade. The Scottish and English parliaments negotiated the Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union ( gd, Achd an Aonaidh) were two Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act 1707 passed by the Parliament of Scotland. They put into effect the te ...
, under which England and Scotland were united into a single Kingdom of Great Britain, with succession under the rules prescribed by the Act of Settlement.
After the 1707 Acts of Union
In 1714, Queen Anne was succeeded by her second cousin, and Sophia's son, George I, Elector of Hanover, who consolidated his position by defeating Jacobite rebellions in 1715 and 1719. The new monarch was less active in government than many of his British predecessors, but retained control over his German kingdoms, with which Britain was now in personal union. Power shifted towards George's ministers, especially to SirRobert Walpole
Robert Walpole, 1st Earl of Orford, (26 August 1676 – 18 March 1745; known between 1725 and 1742 as Sir Robert Walpole) was a British statesman and Whig politician who, as First Lord of the Treasury, Chancellor of the Exchequer, and Leader ...
, who is often considered the first British prime minister, although the title was not then in use. The next monarch, George II, witnessed the final end of the Jacobite threat in 1746, when the Catholic Stuarts were completely defeated. During the long reign of his grandson, George III, Britain's American colonies were lost, the former colonies having formed the United States of America, but British influence elsewhere in the world continued to grow, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was created by the Acts of Union 1800.
From 1811 to 1820, George III suffered a severe bout of what is now believed to be porphyria, an illness rendering him incapable of ruling. His son, the future George IV, ruled in his stead as Prince Regent. During the Regency and his own reign, the power of the monarchy declined, and by the time of his successor, William IV, the monarch was no longer able to effectively interfere with parliamentary power. In 1834, William dismissed the Whig Prime Minister, William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne, and appointed a Tory, Sir Robert Peel
Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet, (5 February 1788 – 2 July 1850) was a British Conservative statesman who served twice as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (1834–1835 and 1841–1846) simultaneously serving as Chancellor of the Exchequer ...
. In the ensuing elections, however, Peel lost. The king had no choice but to recall Lord Melbourne. During William IV's reign, the Reform Act 1832
The Representation of the People Act 1832 (also known as the 1832 Reform Act, Great Reform Act or First Reform Act) was an Act of Parliament, Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom (indexed as 2 & 3 Will. IV c. 45) that introduced major chan ...
, which reformed parliamentary representation, was passed. Together with others passed later in the century, the Act led to an expansion of the electoral franchise and the rise of the House of Commons as the most important branch of Parliament.
The final transition to a constitutional monarchy was made during the long reign of William IV's successor, Victoria. As a woman, Victoria could not rule Hanover, which only permitted succession in the male line, so the personal union of the United Kingdom and Hanover came to an end. The Victorian era was marked by great cultural change, technological progress, and the establishment of the United Kingdom as one of the world's foremost powers. In recognition of British rule over India, Victoria was declared Empress of India in 1876. However, her reign was also marked by increased support for the republican movement, due in part to Victoria's permanent mourning and lengthy period of seclusion following the death of her husband in 1861.
 Victoria's son, Edward VII, became the first monarch of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha in 1901. In 1917, the next monarch, George V, changed "Saxe-Coburg and Gotha" to " Windsor" in response to the anti-German sympathies aroused by the First World War. George V's reign was marked by the separation of Ireland into Northern Ireland, which remained a part of the United Kingdom, and the Irish Free State, an independent nation, in 1922.
Victoria's son, Edward VII, became the first monarch of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha in 1901. In 1917, the next monarch, George V, changed "Saxe-Coburg and Gotha" to " Windsor" in response to the anti-German sympathies aroused by the First World War. George V's reign was marked by the separation of Ireland into Northern Ireland, which remained a part of the United Kingdom, and the Irish Free State, an independent nation, in 1922.
Shared monarchy and modern status
Statute of Westminster 1931
The Statute of Westminster 1931 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that sets the basis for the relationship between the Commonwealth realms and the Crown.
Passed on 11 December 1931, the statute increased the sovereignty of the ...
, which has been likened to "a treaty among the Commonwealth countries".
The monarchy thus ceased to be an exclusively British institution, although it is often still referred to as "British" for legal and historical reasons and for convenience. The monarch became separately monarch of the United Kingdom, monarch of Canada, monarch of Australia, and so forth. The independent states within the Commonwealth would share the same monarch in a relationship likened to a personal union.
George V's death in 1936 was followed by the accession of Edward VIII
Edward VIII (Edward Albert Christian George Andrew Patrick David; 23 June 1894 – 28 May 1972), later known as the Duke of Windsor, was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Empire and Emperor of India from 20 January 19 ...
, who caused a public scandal by announcing his desire to marry the divorced American Wallis Simpson, even though the Church of England opposed the remarriage of divorcees. Accordingly, Edward announced his intention to abdicate; the Parliaments of the United Kingdom and of other Commonwealth countries granted his request. Edward VIII and any children by his new wife were excluded from the line of succession, and the Crown went to his brother, George VI. George served as a rallying figure for the British people during World War II, making morale-boosting visits to the troops as well as to munitions factories and to areas bombed by Nazi Germany. In June 1948 George VI relinquished the title ''Emperor of India'', although remaining head of state of the Dominion of India.
At first, every member of the Commonwealth retained the same monarch as the United Kingdom, but when the Dominion of India became a republic in 1950, it would no longer share in a common monarchy. Instead, the British monarch was acknowledged as " Head of the Commonwealth" in all Commonwealth member states, whether they were realms or republics. The position is purely ceremonial, and is not inherited by the British monarch as of right but is vested in an individual chosen by the Commonwealth heads of government. Member states of the Commonwealth that share the same person as monarch are informally known as Commonwealth realm
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonwealt ...
s.
In the 1990s, republicanism in the United Kingdom grew, partly on account of negative publicity associated with the Royal Family (for instance, immediately following the death of Diana, Princess of Wales
Diana, Princess of Wales (born Diana Frances Spencer; 1 July 1961 – 31 August 1997) was a member of the British royal family. She was the first wife of King Charles III (then Prince of Wales) and mother of Princes William and Harry. Her ac ...
). However, polls from 2002 to 2007 showed that around 70–80% of the British public supported the continuation of the monarchy. This support has remained constant since then—according to a 2018 survey, a majority of the British public across all age groups still support the monarchy's continuation.
See also
* Constitution of the United Kingdom *Family tree of British monarchs
The following is a simplified family tree of the English, Scottish, and British monarchs. For a more detailed chart see: Family tree of English monarchs (from Alfred the Great through Queen Elizabeth I); Family tree of Scottish monarchs (from Ken ...
* List of British royal residences
* List of English ministries
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{British monarchy British monarchy History of the United Kingdom