Hirudin Therapy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Hirudo medicinalis'', the European medicinal leech, is one of several species of leeches used as "medicinal leeches".
Other species of '' Hirudo'' sometimes also used as medicinal leeches include '' H. orientalis'', ''H. troctina'', and '' H. verbana''. The Asian medicinal leech includes '' Hirudinaria manillensis'', and the North American medicinal leech is ''
 Their range extends over almost the whole of Europe and into Asia as far as Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. The preferred habitat for this species is muddy freshwater pools and ditches with plentiful weed growth in temperate climates.
Over-exploitation by leech collectors in the 19th century has left only scattered populations, and reduction in natural habitat through drainage has also contributed to their decline. Another factor has been the replacement of
Their range extends over almost the whole of Europe and into Asia as far as Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. The preferred habitat for this species is muddy freshwater pools and ditches with plentiful weed growth in temperate climates.
Over-exploitation by leech collectors in the 19th century has left only scattered populations, and reduction in natural habitat through drainage has also contributed to their decline. Another factor has been the replacement of

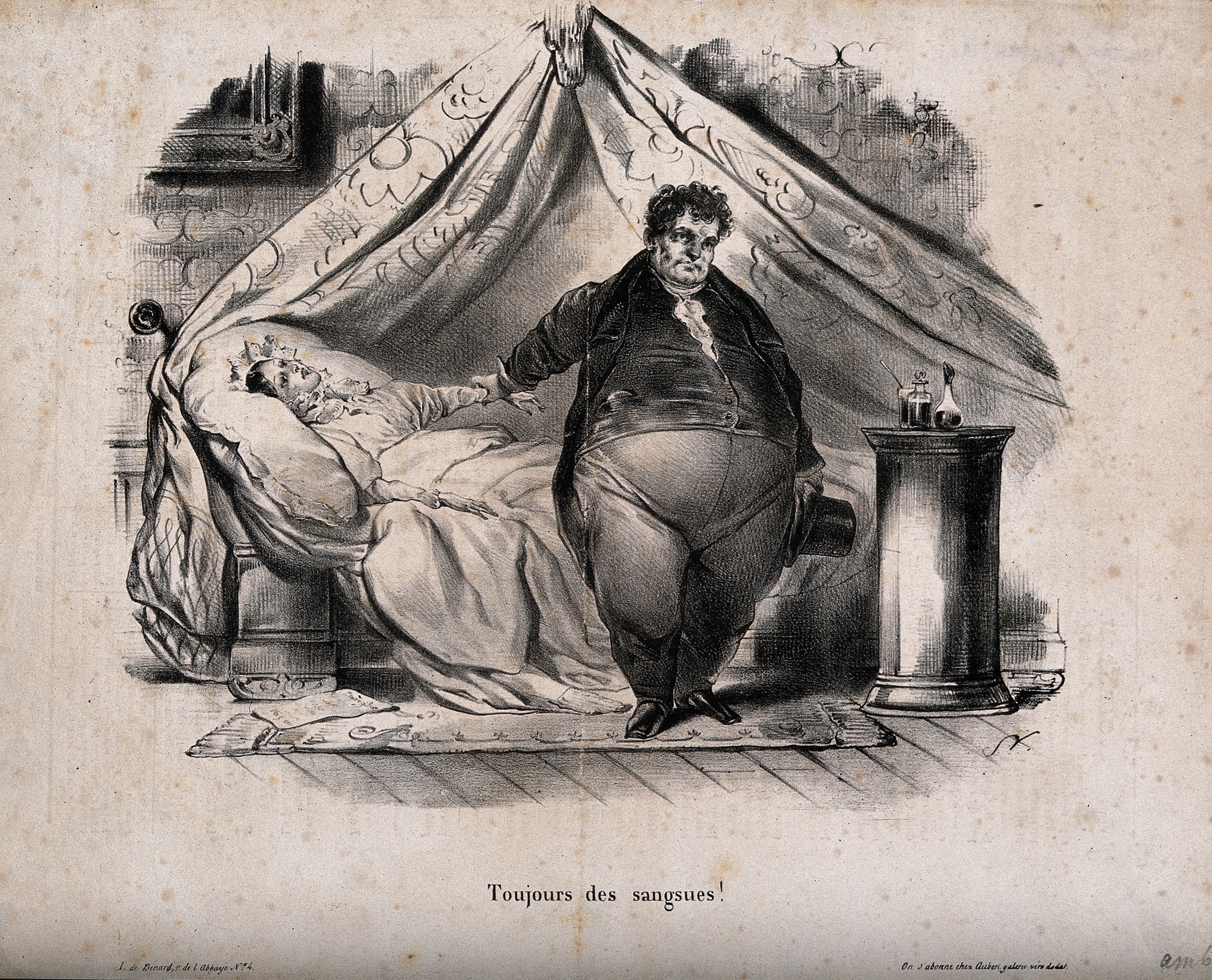 The first description of leech therapy, classified as blood letting, is found in the ''
The first description of leech therapy, classified as blood letting, is found in the '' In medieval and early modern medicine, the medicinal leech (''Hirudo medicinalis'' and its congeners ''H. verbana'', ''H. troctina'', and ''H. orientalis'') was used to remove blood from a patient as part of a process to balance the humors that, according to Galen, must be kept in balance for the human body to function properly. (The four humors of ancient medical philosophy were blood, phlegm, black bile, and yellow bile.) Any sickness that caused the subject's skin to become red (e.g. fever and inflammation), so the theory went, must have arisen from too much blood in the body. Similarly, any person whose behavior was strident and sanguine was thought to be suffering from an excess of blood. Leeches were often gathered by leech collectors and were eventually farmed in large numbers. A unique 19th-century " Leech House" survives in
In medieval and early modern medicine, the medicinal leech (''Hirudo medicinalis'' and its congeners ''H. verbana'', ''H. troctina'', and ''H. orientalis'') was used to remove blood from a patient as part of a process to balance the humors that, according to Galen, must be kept in balance for the human body to function properly. (The four humors of ancient medical philosophy were blood, phlegm, black bile, and yellow bile.) Any sickness that caused the subject's skin to become red (e.g. fever and inflammation), so the theory went, must have arisen from too much blood in the body. Similarly, any person whose behavior was strident and sanguine was thought to be suffering from an excess of blood. Leeches were often gathered by leech collectors and were eventually farmed in large numbers. A unique 19th-century " Leech House" survives in
Taxonomy page
in PubMed with many excellent references
Documentary about alternative medicine with leeches and maggots
* ttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yP_7yDlCMG8 Video footage of the unique Bedale Leech Housebr>Leeches eshop
in Lodeksa with many excellent references {{Taxonbar, from=Q30041 Animals described in 1758 Biologically-based therapies Leeches Plastic surgery Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Traditional medicine
Macrobdella
''Macrobdella'' is a genus of leeches native to freshwater ecosystems of North America, especially Canada, Mexico, and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or Am ...
decora''.
Morphology
The general morphology of medicinal leeches follows that of most other leeches. Fully mature adults can be up to 20 cm in length, and are green, brown, or greenish-brown with a darker tone on the dorsal side and a lighter ventral side. The dorsal side also has a thin red stripe. These organisms have two suckers, one at each end, called theanterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
and posterior suckers. The posterior is used mainly for leverage, whereas the anterior sucker, consisting of the jaw and teeth, is where the feeding takes place. Medicinal leeches have three jaws (tripartite) that resemble saws, on which are approximately 100 sharp edges used to incise the host. The incision leaves a mark that is an inverted Y inside of a circle. After piercing the skin, they suck out blood while injecting anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where the ...
s ( hirudin). Large adults can consume up to ten times their body weight in a single meal, with 5–15 mL being the average volume taken. These leeches can live for up to a year between feeding.
Medicinal leeches are hermaphrodite
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes.
Many Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrate ...
s that reproduce by sexual mating, laying eggs in clutches of up to 50 near (but not under) water, and in shaded, humid places. A study done in Poland concluded that they have been found inside the nest of large aquatic birds although, their effect on the bird is largely unknown.
Range and ecology
 Their range extends over almost the whole of Europe and into Asia as far as Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. The preferred habitat for this species is muddy freshwater pools and ditches with plentiful weed growth in temperate climates.
Over-exploitation by leech collectors in the 19th century has left only scattered populations, and reduction in natural habitat through drainage has also contributed to their decline. Another factor has been the replacement of
Their range extends over almost the whole of Europe and into Asia as far as Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. The preferred habitat for this species is muddy freshwater pools and ditches with plentiful weed growth in temperate climates.
Over-exploitation by leech collectors in the 19th century has left only scattered populations, and reduction in natural habitat through drainage has also contributed to their decline. Another factor has been the replacement of horses
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
in farming (horses were medicinal leeches' preferred food source) and provision of artificial water supplies for cattle. As a result, this species is now considered near threatened by the IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
, and European medicinal leeches are legally protected through nearly all of their natural range. They are particularly sparsely distributed in France and Belgium, and in the UK there may be as few as 20 remaining isolated populations (all widely scattered). The largest (at Lydd) is estimated to contain several thousand individuals; 12 of these areas have been designated Sites of Special Scientific Interest. There are small, transplanted populations in several countries outside their natural range, including the USA.
The species is protected under Appendix II of CITES meaning international trade (including in parts and derivatives) is regulated by the CITES permitting system.
Medical usage
Beneficial secretions
Medicinal leeches have been found to secretesaliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
containing about 60 different proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
. These achieve a wide variety of goals useful to the leech as it feeds, helping to keep the blood in liquid form and increasing blood flow in the affected area. Several of these secreted proteins serve as anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where the ...
s (such as hirudin), platelet aggregation inhibitors (most notably apyrase, collagenase, and calin), vasodilators, and proteinase inhibitors. It is also thought that the saliva contains an anesthetic, as leech bites are generally not painful.

Historically
 The first description of leech therapy, classified as blood letting, is found in the ''
The first description of leech therapy, classified as blood letting, is found in the ''Sushruta Samhita
The ''Sushruta Samhita'' (सुश्रुतसंहिता, IAST: ''Suśrutasaṃhitā'', literally "Suśruta's Compendium") is an ancient Sanskrit text on medicine and surgery, and one of the most important such treatises on this subj ...
'', an ancient Sanskrit medical text. It describes 12 types of leeches (6 venomous and 6 non-venomous).
Diseases where leech therapy was indicated include skin diseases, sciatica, and musculoskeletal pains.
Bedale
Bedale ( ) is a market town and civil parish in the district of Hambleton, North Yorkshire, England. Historically part of the North Riding of Yorkshire, it is north of Leeds, south-west of Middlesbrough and south-west of the county town of ...
, North Yorkshire on the bank of the Bedale Beck, used to store medicinal leeches until the early 20th century.
A recorded use of leeches in medicine was also found during 200 BC by the Greek physician Nicander
Nicander of Colophon ( grc-gre, Νίκανδρος ὁ Κολοφώνιος, Níkandros ho Kolophṓnios; fl. 2nd century BC), Greek poet, physician and grammarian, was born at Claros (Ahmetbeyli in modern Turkey), near Colophon, where his famil ...
in Colophon. Medical use of leeches was discussed by Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
in '' The Canon of Medicine'' (1020s), and by Abd al-Latif al-Baghdadi in the 12th century. The use of leeches began to become less widespread towards the end of the 19th century.
Manchester Royal Infirmary used 50,000 leeches a year in 1831. The price of leeches varied between one penny and threepence halfpenny each. In 1832 leeches accounted for 4.4% of the total hospital expenditure. The hospital maintained an aquarium for leeches until the 1930s.
Today
Medicinal leech therapy (also referred to as ''Hirudotherapy'' or ''Hirudin therapy'') made an international comeback in the 1970s in microsurgery, used to stimulate circulation to salvage skin grafts and other tissue threatened by postoperative venous congestion, particularly in finger reattachment and reconstructive surgery of the ear, nose, lip, and eyelid. Other clinical applications of medicinal leech therapy include varicose veins, muscle cramps, thrombophlebitis, and osteoarthritis, among many varied conditions. The therapeutic effect is not from the small amount of blood taken in the meal, but from the continued and steady bleeding from the wound left after the leech has detached, as well as the anesthetizing, anti-inflammatory, and vasodilating properties of the secreted leech saliva. The most common complication from leech treatment is prolonged bleeding, which can easily be treated, but more serious allergic reactions and bacterial infections may also occur. Leech therapy was classified by the US Food and Drug Administration as a medical device in 2004. Because of the minuscule amounts of hirudin present in leeches, it is impractical to harvest the substance for widespread medical use. Hirudin (and related substances) are synthesized using recombinant techniques. Devices called "mechanical leeches" that dispenseheparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatm ...
and perform the same function as medicinal leeches have been developed, but they are not yet commercially available.
See also
* Helminthic therapy – other medical use of parasites * Ichthyotherapy – medical use of fishReferences
External links
Taxonomy page
in PubMed with many excellent references
Documentary about alternative medicine with leeches and maggots
* ttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yP_7yDlCMG8 Video footage of the unique Bedale Leech Housebr>Leeches eshop
in Lodeksa with many excellent references {{Taxonbar, from=Q30041 Animals described in 1758 Biologically-based therapies Leeches Plastic surgery Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Traditional medicine