Hirat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an
Ahmad Shah Durrani, father of modern Afghanistan
''. Asia Publishing House, Bombay. (PDF versio
66 MB
) In 1716, the Abdali Afghans inhabiting the city revolted and formed their own Sultanate, the Sadozai Sultanate of Herat. They were conquered by the Afsharids in 1732. After
 Herat is first recorded in ancient times, but its precise date of foundation is unknown. Under the Persian
Herat is first recorded in ancient times, but its precise date of foundation is unknown. Under the Persian  However, most sources suggest that Herat was predominantly Zoroastrian. It became part of the Parthian Empire in 167 BC. In the Sasanian period (226-652), 𐭧𐭥𐭩𐭥 ''Harēv'' is listed in an inscription on the Ka'ba-i Zartosht at Naqsh-e Rustam; and ''Hariy'' is mentioned in the
However, most sources suggest that Herat was predominantly Zoroastrian. It became part of the Parthian Empire in 167 BC. In the Sasanian period (226-652), 𐭧𐭥𐭩𐭥 ''Harēv'' is listed in an inscription on the Ka'ba-i Zartosht at Naqsh-e Rustam; and ''Hariy'' is mentioned in the
 At the time of the Arab invasion in the middle of the 7th century, the Sasanian central power seemed already largely nominal in the province in contrast with the role of the Hephthalites tribal lords, who were settled in the Herat region and in the neighboring districts, mainly in pastoral Bādghis and in Qohestān. It must be underlined, however, that Herat remained one of the three Sasanian mint centers in the east, the other two beings
At the time of the Arab invasion in the middle of the 7th century, the Sasanian central power seemed already largely nominal in the province in contrast with the role of the Hephthalites tribal lords, who were settled in the Herat region and in the neighboring districts, mainly in pastoral Bādghis and in Qohestān. It must be underlined, however, that Herat remained one of the three Sasanian mint centers in the east, the other two beings



 Herat was a great trading center strategically located on trade routes from Mediterranean to India or to China. The city was noted for its textiles during the Abbasid Caliphate, according to many references by geographers. Herāt also had many learned sons such as Ansārī. The city is described by Estakhri and Ibn Hawqal in the 10th century as a prosperous town surrounded by strong walls with plenty of water sources, extensive suburbs, an inner citadel, a congregational mosque, and four gates, each gate opening to a thriving market place. The government building was outside the city at a distance of about a mile in a place called Khorāsānābād. A church was still visible in the countryside northeast of the town on the road to
Herat was a great trading center strategically located on trade routes from Mediterranean to India or to China. The city was noted for its textiles during the Abbasid Caliphate, according to many references by geographers. Herāt also had many learned sons such as Ansārī. The city is described by Estakhri and Ibn Hawqal in the 10th century as a prosperous town surrounded by strong walls with plenty of water sources, extensive suburbs, an inner citadel, a congregational mosque, and four gates, each gate opening to a thriving market place. The government building was outside the city at a distance of about a mile in a place called Khorāsānābād. A church was still visible in the countryside northeast of the town on the road to
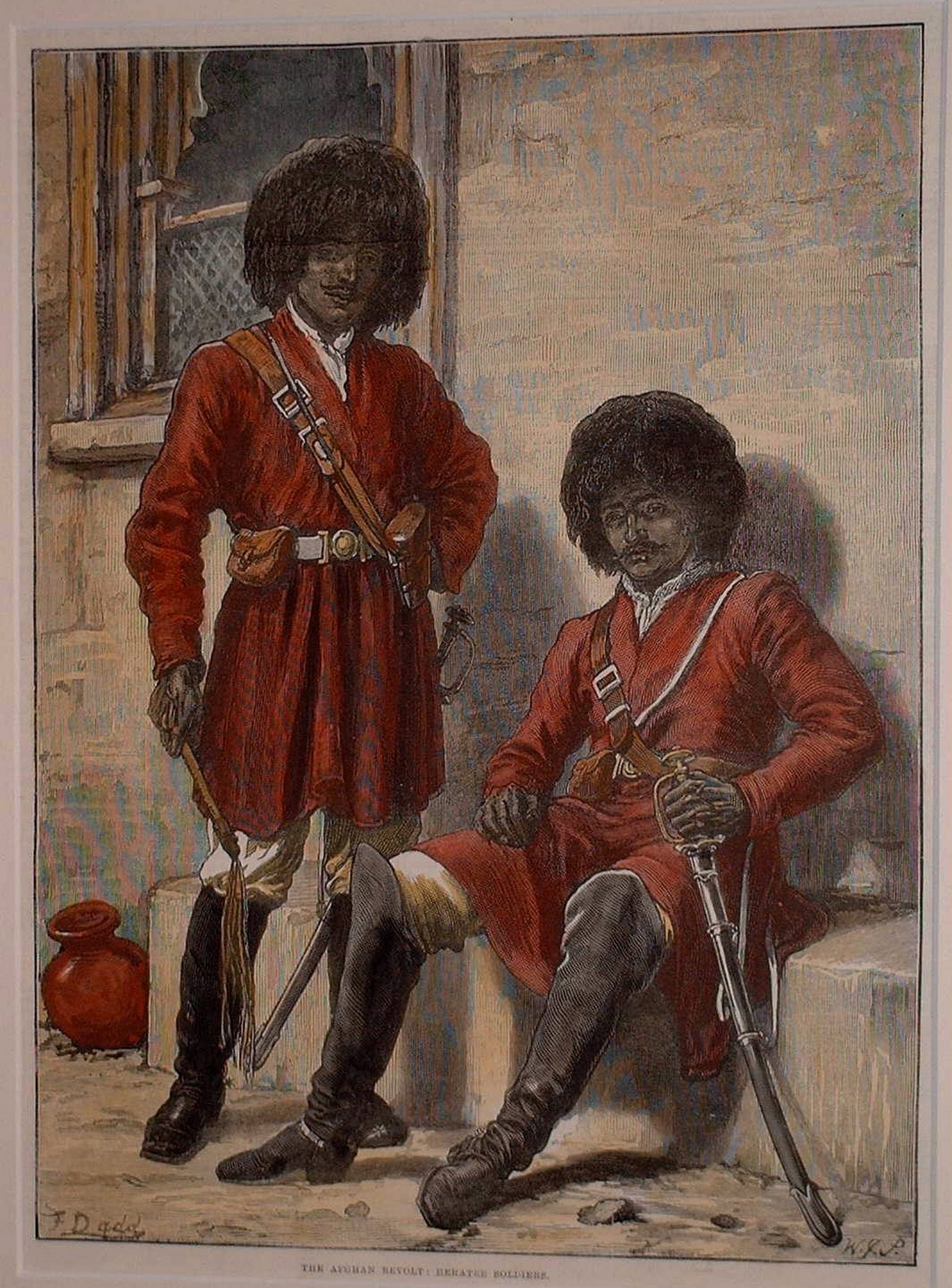

 In 1793, Herat became independent for several years when Afghanistan underwent a civil war between different sons of
In 1793, Herat became independent for several years when Afghanistan underwent a civil war between different sons of
File:Herat Remains of Musallah complex.jpg, Traffic passing on the road near the Herat minarets, 2005.
File:Gawhar shad-1417-2.jpg, The two mausoleums with the minarets, July 2001.
The famous Musalla of Gawhar Shah of Herat, a large Islamic religious complex consisting of five minarets, several mausoleums along with mosques and madrasas was dynamited during the Panjdeh incident to prevent their usage by the advancing 
 In the 1960s, engineers from the United States built
In the 1960s, engineers from the United States built 
 Herat received damage during the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s, especially its western side. The province as a whole was one of the worst-hit. In April 1983, a series of Soviet bombings damaged half of the city and killed around 3,000 civilians, described as "extremely heavy, brutal and prolonged". Ismail Khan was the leading
Herat received damage during the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s, especially its western side. The province as a whole was one of the worst-hit. In April 1983, a series of Soviet bombings damaged half of the city and killed around 3,000 civilians, described as "extremely heavy, brutal and prolonged". Ismail Khan was the leading



 *Parks
**Park-e Taraki
**Park-e Millat
**Khane-ye Jihad Park
*Monuments
** Herat Citadel (Qala Ikhtyaruddin or Arg)
** Musallah Complex
** Musalla Minarets of Herat
Of the more than dozen minarets that once stood in Herāt, many have been toppled from war and neglect over the past century. Recently, however, everyday traffic threatens many of the remaining unique towers by shaking the very foundations they stand on. Cars and trucks that drive on a road encircling the ancient city rumble the ground every time they pass these historic structures. UNESCO personnel and Afghan authorities have been working to stabilize the Fifth Minaret.
*Museums
**Herat Museum, located inside the Herat Citadel
**
*Parks
**Park-e Taraki
**Park-e Millat
**Khane-ye Jihad Park
*Monuments
** Herat Citadel (Qala Ikhtyaruddin or Arg)
** Musallah Complex
** Musalla Minarets of Herat
Of the more than dozen minarets that once stood in Herāt, many have been toppled from war and neglect over the past century. Recently, however, everyday traffic threatens many of the remaining unique towers by shaking the very foundations they stand on. Cars and trucks that drive on a road encircling the ancient city rumble the ground every time they pass these historic structures. UNESCO personnel and Afghan authorities have been working to stabilize the Fifth Minaret.
*Museums
**Herat Museum, located inside the Herat Citadel
**
 The population of Herat numbered approximately 592,902 in 2021. The city houses a multi-ethnic society and speakers of the Persian language are in the majority. There is no current data on the precise ethnic composition of the city's population, but according to a 2003 map found in the National Geographic Magazine, Persian-speaking
The population of Herat numbered approximately 592,902 in 2021. The city houses a multi-ethnic society and speakers of the Persian language are in the majority. There is no current data on the precise ethnic composition of the city's population, but according to a 2003 map found in the National Geographic Magazine, Persian-speaking
 Herat International Airport was built by engineers from the United States in the 1960s and was used by the Soviet Armed Forces during the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s. It was bombed in late 2001 during
Herat International Airport was built by engineers from the United States in the 1960s and was used by the Soviet Armed Forces during the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s. It was bombed in late 2001 during
File:CH-NB - Afghanistan, Herat- Schrein von Gazar Gah - Annemarie Schwarzenbach - SLA-Schwarzenbach-A-5-19-193.jpg, Outside the Shrine of Gazar Gah, c. 1939
File:US consulate in Herat.jpg, U.S. Consulate in Herat
File:Mausoleum of Mirwais Sadiq Khan in 2009.jpg, Mausoleum of Mirwais Sadiq Khan, son of Ismail Khan, who was killed in 2004 in clashes with the
Detailed map of Herāt cityMap of Herāt and surroundings in 1942
oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment'ksar''with its surrounding feeding source, the palm grove, within a relational and circulatory nomadic system.”
The location of oases has been of critical imp ...
city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safēd Kōh'') in the fertile valley of the Hari River in the western part of the country. An ancient civilization on the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
between the Middle East, Central and South Asia, it serves as a regional hub in the country's west.
Herat dates back to Avestan times and was traditionally known for its wine. The city has a number of historic sites, including the Herat Citadel and the Musalla Complex. During the Middle Ages Herat became one of the important cities of Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
, as it was known as the ''Pearl of Khorasan''. After the conquest of Tamerlane, the city became an important center of intellectual and artistic life in the Islamic world. Under the rule of Shah Rukh the city served as the focal point of the Timurid Renaissance, whose glory matched Florence of the Italian Renaissance as the center of a cultural rebirth. After the fall of the Timurid Empire, Herat has been governed by various Afghan rulers since the early 18th century.Singh, Ganda (1959). Ahmad Shah Durrani, father of modern Afghanistan
''. Asia Publishing House, Bombay. (PDF versio
66 MB
) In 1716, the Abdali Afghans inhabiting the city revolted and formed their own Sultanate, the Sadozai Sultanate of Herat. They were conquered by the Afsharids in 1732. After
Nader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar ( fa, نادر شاه افشار; also known as ''Nader Qoli Beyg'' or ''Tahmāsp Qoli Khan'' ) (August 1688 – 19 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian h ...
's death and Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shāh Durrānī ( ps, احمد شاه دراني; prs, احمد شاه درانی), also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī (), was the founder of the Durrani Empire and is regarded as the founder of the modern Afghanistan. In July 1747, Ahm ...
's rise to power in 1747, Herat became part of Afghanistan. It became an independent city-state in the first half of the 19th century, facing several Iranian invasions until being incorporated into Afghanistan in 1863. The roads from Herat to Iran (through the border town of Islam Qala) and Turkmenistan (through the border town of Torghundi) are still strategically important. As the gateway to Iran, it collects high amount of customs revenue for Afghanistan. It also has an international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries around the world. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports and they must feature longer ...
. Following the 2001 war the city had been relatively safe from Taliban insurgent attacks. In 2021, it was announced that Herat would be listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. On 12 August 2021, the city was seized by Taliban fighters as part of the Taliban's summer offensive.
History
 Herat is first recorded in ancient times, but its precise date of foundation is unknown. Under the Persian
Herat is first recorded in ancient times, but its precise date of foundation is unknown. Under the Persian Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
(550–330 BC), the surrounding district was known by the Old Persian
Old Persian is one of the two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan language, Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native ...
name of ''Haraiva'' (𐏃𐎼𐎡𐎺), and in classical sources, the region was correspondingly known as Areia ( Aria). In the Zoroastrian collection of Avesta, the district is referred as ''Haroiva''. The name of the district and its principal town is a derivative from that of the local river, the Herey River (from Old Iranian ''Harayu'', meaning "with velocity"), which goes through the district and ends south of Herat. Herey is mentioned in Sanskrit as a yellow or golden color equivalent to Persian "Zard" meaning Gold (yellow). The naming of a region and its principal town after the main river is a common feature in this part of the world— compare the adjoining districts/rivers/towns of Arachosia and Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
.
The district ''Aria'' of the Achaemenid Empire is mentioned in the provincial lists that are included in various royal inscriptions, for instance, in the Behistun inscription of Darius I
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his ...
(ca. 520 BC). Representatives from the district are depicted in reliefs, e.g., at the royal Achaemenid tombs of Naqsh-e Rustam and Persepolis. They are wearing Scythian-style dress (with a tunic and trousers tucked into high boot
A boot is a type of footwear. Most boots mainly cover the foot and the ankle, while some also cover some part of the lower calf. Some boots extend up the leg, sometimes as far as the knee or even the hip. Most boots have a heel that is cle ...
s) and a twisted Bashlyk that covers their head, chin and neck.
Hamdallah Mustawfi, composer of the 14th-century geographical work '' Nuzhat al-Qulub'' writes that:
Herodotus described Herat as ''the bread-basket of Central Asia''. At the time of Alexander the Great in 330 BC, Aria was obviously an important district. It was administered by a satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with consid ...
called Satibarzanes, who was one of the three main Persian officials in the East of the Empire, together with the satrap Bessus
Bessus or Bessos ( peo, *Bayaçā; grc-gre, Βήσσος), also known by his throne name Artaxerxes V ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης; died summer 329 BC), was a Persian satrap of the eastern Achaemenid sa ...
of Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
and Barsaentes Barsaentes ( el, Βαρσαέντης, translit=Barsaéntēs) was a Persians, Persian nobleman, who served as the satrap of Arachosia and Drangiana under the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid King of Kings Darius III ().
Barsaentes took part in the Bat ...
of Arachosia. In late 330 BC, Alexander captured the Arian capital that was called Artacoana Artacoana ( grc, Ἀρτακόανα) or Artacana or Articaudna () or Chortacana or Artacaena, name of the capital of Aria, an eastern satrapy of the Persian empire.
In late 330 B.C. Alexander the Great, according to his biographers, captured Arta ...
. The town was rebuilt and the citadel was constructed. Afghanistan became part of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
.
 However, most sources suggest that Herat was predominantly Zoroastrian. It became part of the Parthian Empire in 167 BC. In the Sasanian period (226-652), 𐭧𐭥𐭩𐭥 ''Harēv'' is listed in an inscription on the Ka'ba-i Zartosht at Naqsh-e Rustam; and ''Hariy'' is mentioned in the
However, most sources suggest that Herat was predominantly Zoroastrian. It became part of the Parthian Empire in 167 BC. In the Sasanian period (226-652), 𐭧𐭥𐭩𐭥 ''Harēv'' is listed in an inscription on the Ka'ba-i Zartosht at Naqsh-e Rustam; and ''Hariy'' is mentioned in the Pahlavi
Pahlavi may refer to:
Iranian royalty
*Seven Parthian clans, ruling Parthian families during the Sasanian Empire
*Pahlavi dynasty, the ruling house of Imperial State of Persia/Iran from 1925 until 1979
**Reza Shah, Reza Shah Pahlavi (1878–1944 ...
catalogue of the provincial capitals of the empire. In around 430, the town is also listed as having a Christian community, with a Nestorian bishop.
In the last two centuries of Sasanian rule, Aria (Herat) had great strategic importance in the endless wars between the Sasanians, the Chionites and the Hephthalites who had been settled in the northern section of Afghanistan since the late 4th century.
Islamization
 At the time of the Arab invasion in the middle of the 7th century, the Sasanian central power seemed already largely nominal in the province in contrast with the role of the Hephthalites tribal lords, who were settled in the Herat region and in the neighboring districts, mainly in pastoral Bādghis and in Qohestān. It must be underlined, however, that Herat remained one of the three Sasanian mint centers in the east, the other two beings
At the time of the Arab invasion in the middle of the 7th century, the Sasanian central power seemed already largely nominal in the province in contrast with the role of the Hephthalites tribal lords, who were settled in the Herat region and in the neighboring districts, mainly in pastoral Bādghis and in Qohestān. It must be underlined, however, that Herat remained one of the three Sasanian mint centers in the east, the other two beings Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan ...
and Marv. The Hephthalites from Herat and some unidentified Turks opposed the Arab forces in a battle of Qohestān in 651-52 AD, trying to block their advance on Nishāpur, but they were defeated
When the Arab armies appeared in Khorāsān in the 650s AD, Herāt was counted among the twelve capital towns of the Sasanian Empire. The Arab army under the general command of Ahnaf ibn Qais in its conquest of Khorāsān in 652 seems to have avoided Herāt, but it can be assumed that the city eventually submitted to the Arabs, since shortly afterward an Arab governor is mentioned there. A treaty was drawn in which the regions of Bādghis and Bushanj were included. As did many other places in Khorāsān, Herāt rebelled and had to be re-conquered several times.
Another power that was active in the area in the 650s was Tang dynasty China which had embarked on a campaign that culminated in the Conquest of the Western Turks. By 659–661, the Tang claimed a tenuous suzerainty over Herat, the westernmost point of Chinese power in its long history. This hold however would be ephemeral with local Turkish tribes rising in rebellion in 665 and driving out the Tang.
In 702 AD Yazid ibn al-Muhallab defeated certain Arab rebels, followers of Ibn al-Ash'ath, and forced them out of Herat. The city was the scene of conflicts between different groups of Muslims and Arab tribes in the disorders leading to the establishment of the Abbasid Caliphate. Herat was also a center of the followers of Ustadh Sis.
In 870 AD, Yaqub ibn Layth Saffari, a local ruler of the Saffarid dynasty conquered Herat and the rest of the nearby regions in the name of Islam.
Pearl of Khorasan
The region of Herāt was under the rule of King Nuh III, the seventh of theSamanid
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan origin. The empire was centred in Kho ...
line—at the time of Sebük Tigin
Abu Mansur Nasir al-Din Sabuktigin ( fa, ابو منصور سبکتگین) ( 942 – August 997), also spelled as Sabuktagin, Sabuktakin, Sebüktegin and Sebük Tigin, was the founder of the Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 367 A.H/977 A.D to 3 ...
and his older son, Mahmud of Ghazni
Yamīn-ud-Dawla Abul-Qāṣim Maḥmūd ibn Sebüktegīn ( fa, ; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ...
. The governor of Herāt was a noble by the name of ''Faik'', who was appointed by Nuh III. It is said that Faik was a powerful, but insubordinate governor of Nuh III, and had been punished by Nuh III. Faik made overtures to Bogra Khan
Bogra Khan Ilak was an ethnic Turkish sovereign who reigned in the latter part of the 10th century over Kashgar, Khotan and other countries intervening between Transoxiana and the Chinese frontier. Of the dynasty to which he belonged and the ext ...
and Ughar Khan of Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
. Bogra Khan answered Faik's call, came to Herāt, and became its ruler. The Samanids fled, betrayed at the hands of Faik to whom the defense of Herāt had been entrusted by Nuh III. In 994, Nuh III invited Alptegin to come to his aid. Alptegin, along with Mahmud of Ghazni, defeated Faik and annexed Herāt, Nishapur
Nishapur or officially Romanized as Neyshabur ( fa, ;Or also "نیشاپور" which is closer to its original and historic meaning though it is less commonly used by modern native Persian speakers. In Persian poetry, the name of this city is wr ...
and Tous.



 Herat was a great trading center strategically located on trade routes from Mediterranean to India or to China. The city was noted for its textiles during the Abbasid Caliphate, according to many references by geographers. Herāt also had many learned sons such as Ansārī. The city is described by Estakhri and Ibn Hawqal in the 10th century as a prosperous town surrounded by strong walls with plenty of water sources, extensive suburbs, an inner citadel, a congregational mosque, and four gates, each gate opening to a thriving market place. The government building was outside the city at a distance of about a mile in a place called Khorāsānābād. A church was still visible in the countryside northeast of the town on the road to
Herat was a great trading center strategically located on trade routes from Mediterranean to India or to China. The city was noted for its textiles during the Abbasid Caliphate, according to many references by geographers. Herāt also had many learned sons such as Ansārī. The city is described by Estakhri and Ibn Hawqal in the 10th century as a prosperous town surrounded by strong walls with plenty of water sources, extensive suburbs, an inner citadel, a congregational mosque, and four gates, each gate opening to a thriving market place. The government building was outside the city at a distance of about a mile in a place called Khorāsānābād. A church was still visible in the countryside northeast of the town on the road to Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan ...
, and farther away on a hilltop stood a flourishing fire temple
A fire temple, Agiary, Atashkadeh ( fa, آتشکده), Atashgah () or Dar-e Mehr () is the place of worship for the followers of Zoroastrianism, the ancient religion of Iran (Persia).
In the Zoroastrian religion, fire (see ''atar''), together wi ...
, called Sereshk, or Arshak according to Mustawfi.
Herat was a part of the Taherid dominion in Khorāsān until the rise of the Saffarids in Sistān under Ya'qub-i Laith in 861, who, in 862, started launching raids on Herat before besieging and capturing it on 16 August 867, and again in 872. The Saffarids succeeded in expelling the Taherids from Khorasan in 873.
The Sāmānid dynasty was established in Transoxiana by three brothers, Nuh, Yahyā, and Ahmad
Ahmad ( ar, أحمد, ʾAḥmad) is an Arabic male given name common in most parts of the Muslim world. Other spellings of the name include Ahmed and Ahmet.
Etymology
The word derives from the root (ḥ-m-d), from the Arabic (), from the ve ...
. Ahmad Sāmāni opened the way for the Samanid dynasty to the conquest of Khorāsān, including Herāt, which they were to rule for one century. The centralized Samanid administration served as a model for later dynasties. The Samanid power was destroyed in 999 by the Qarakhanids
The Kara-Khanid Khanate (; ), also known as the Karakhanids, Qarakhanids, Ilek Khanids or the Afrasiabids (), was a Turkic khanate that ruled Central Asia in the 9th through the early 13th century. The dynastic names of Karakhanids and Ilek K ...
, who were advancing on Transoxiana from the northeast, and by the Ghaznavids
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest ...
, former Samanid retainers, attacking from the southeast.
Sultan Maḥmud of Ghazni officially took control of Khorāsān in 998. Herat was one of the six Ghaznavid mints in the region. In 1040, Herat was captured by the Seljuk Empire. During this change of power in Herat, there was supposedly a power vacuum which was filled by Abdullah Awn, who established a city-state and made an alliance with Mahmud of Ghazni. Yet, in 1175, it was captured by the Ghurids of Ghor and then came under the Khawarazm Empire in 1214. According to the account of Mustawfi, Herat flourished especially under the Ghurid dynasty in the 12th century. Mustawfi reported that there were "359 colleges in Herat, 12,000 shops all fully occupied, 6,000 bath-houses; besides caravanserais and mills, also a darwish convent and a fire temple". There were about 444,000 houses occupied by a settled population. The men were described as "warlike and carry arms", and they were Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s. The great mosque of Herāt was built by Ghiyasuddin Ghori
Ghiyath al-Din Muhammad, also known as Ghiyath al-Din Ghori born Muhammad (c. 1140-1203 CE), was the Sultan of the Ghurid dynasty from 1163 to 1203. During his reign, aided by his brother, Muhammad Ghori's conquests in Northern India, the Ghuri ...
in 1201. In this period Herāt became an important center for the production of metal goods, especially in bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
, often decorated with elaborate inlays in precious metals.
The Mongols laid siege to Herat twice. The first siege resulted in the surrender of the city, the slaughter of the local sultan's army of 12,000, and the appointment of two governors, one Mongol and one Muslim. The second, prompted by a rebellion against Mongol rule, lasted seven months and ended in June 1222 with, according to one account, the beheading of the entire population of 1,600,000 people by the victorious Mongols, such that "no head was left on a body, nor body with a head."
The city remained in ruins from 1222 to about 1236. In 1244 a local prince Shams al-Din Kart was named ruler of Herāt by the Mongol governor of Khorāsān and in 1255 he was confirmed in his rule by the founder of the Il-Khan dynasty Hulagu. Shamsuddin Kart founded a new dynasty and his successors, especially Fakhruddin Kart and Ghiyasuddin Kart, built many mosques and other buildings. The members of this dynasty were great patrons of literature and the arts. By this time Herāt became known as the ''pearl of Khorasan''.
Timur took Herat in 1380 and he brought the Kartid dynasty to an end a few years later. The city reached its greatest glory under the Timurid princes, especially Sultan Husayn Bayqara
Sultan Husayn Bayqara Mirza ( fa, حسین بایقرا / ''Husayn Bāyqarā''; June/July 1438 – 4 May 1506) was the Timurid ruler of Herat from 1469 until May 4, 1506, with a brief interruption in 1470.
A skilled statesman, Sultan Husayn ...
who ruled Herat from 1469 until May 4, 1506. His chief minister, the poet and author in Persian and Turkish, Mir Ali-Shir Nava'i was a great builder and patron of the arts. Under the Timurids, Herat assumed the role of the main capital of an empire that extended in the West as far as central Persia. As the capital of the Timurid empire, it boasted many fine religious buildings and was famous for its sumptuous court life and musical performance and its tradition of miniature paintings. On the whole, the period was one of relative stability, prosperity, and development of economy and cultural activities. It began with the nomination of Shahrokh, the youngest son of Timur, as governor of Herat in 1397. The reign of Shahrokh in Herat was marked by intense royal patronage, building activities, and the promotion of manufacturing and trade, especially through the restoration and enlargement of the Herat's bāzār. The present Musallah Complex, and many buildings such as the madrasa of Gawhar Shad, Ali Shir mahāl, many gardens, and others, date from this time. The village of Gazar Gah
The Shrine of Khwaja Abd Allah, commonly called the Shrine at Gazur Gah (or just Gazur Gah) and the Abdullah Ansari Shrine Complex, is the funerary compound of the Sufi saint Khwaja Abdullah Ansari. It is located at the village of Gazur Gah, thr ...
, over two km northeast of Herat, contained a shrine that was enlarged and embellished under the Timurids. The tomb of the poet and mystic Khwājah Abdullāh Ansārī (d. 1088), was first rebuilt by Shahrokh about 1425, and other famous men were buried in the shrine area. Herat was shortly captured by Kara Koyunlu between 1458 and 1459.
In 1507 Herat was occupied by the Uzbeks but after much fighting the city was taken by Shah Isma'il, the founder of the Safavid dynasty
The Safavid dynasty (; fa, دودمان صفوی, Dudmâne Safavi, ) was one of Iran's most significant ruling dynasties reigning from 1501 to 1736. Their rule is often considered the beginning of modern Iranian history, as well as one of th ...
, in 1510 and the Shamlu Qizilbash assumed the governorship of the area. Under the Safavids, Herat was again relegated to the position of a provincial capital, albeit one of particular importance. At the death of Shah Isma'il the Uzbeks again took Herat and held it until Shah Tahmasp retook it in 1528. The Persian king, Abbas
Abbas may refer to:
People
* Abbas (name), list of people with the name, including:
**Abbas ibn Ali, Popularly known as Hazrat-e-Abbas (brother of Imam Hussayn)
**Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib, uncle of Muhammad
** Mahmoud Abbas (born 1935), Palest ...
was born in Herat, and in Safavid texts, Herat is referred to as ''a'zam-i bilād-i īrān'', meaning "the greatest of the cities of Iran". In the 16th century, all future Safavid rulers, from Tahmasp I to Abbas I, were governors of Herat in their youth.
Modern history
By the early 18th century Herat was governed by the Abdali Afghans. AfterNader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar ( fa, نادر شاه افشار; also known as ''Nader Qoli Beyg'' or ''Tahmāsp Qoli Khan'' ) (August 1688 – 19 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian h ...
's death in 1747, Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shāh Durrānī ( ps, احمد شاه دراني; prs, احمد شاه درانی), also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī (), was the founder of the Durrani Empire and is regarded as the founder of the modern Afghanistan. In July 1747, Ahm ...
took possession of the city and became part of the Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire ( ps, د درانيانو ټولواکمني; fa, امپراتوری درانیان) or the Afghan Empire ( ps, د افغانان ټولواکمني, label=none; fa, امپراتوری افغان, label=none), also know ...
.

 In 1793, Herat became independent for several years when Afghanistan underwent a civil war between different sons of
In 1793, Herat became independent for several years when Afghanistan underwent a civil war between different sons of Timur Shah
Timur Shah Durrani (; prs, ;), also known as Timur Shah Abdali or Taimur Shah Abdali (December 1746 – May 20, 1793) was the second ruler of the Afghan Durrani Empire, from November 1772 until his death in 1793. An ethnic Pashtun, he was the se ...
. The Iranians had multiple wars with Herat between 1801 and 1837 (1804, 1807, 1811, 1814, 1817, 1818, 1821, 1822, 1825, 1833). The Iranians besieged the city in 1837, but the British helped the Heratis in repelling them. In 1856, they invaded again, and briefly managed to take the city on October 25; it led directly to the Anglo-Persian War. In 1857 hostilities between the Iranians and the British ended after the Treaty of Paris was signed, and the Persian troops withdrew from Herat in September 1857. Afghanistan conquered Herat on May 26, 1863, under Dost Muhammad Khan, two weeks before his death.
Russian forces
The Armed Forces of the Russian Federation (, ), commonly referred to as the Russian Armed Forces, are the Military, military forces of Russia. In terms of Active duty, active-duty personnel, they are the List of countries by number of milita ...
. Some emergency preservation work was carried out at the site in 2001 which included building protective walls around the Gawhar Shad Mausoleum and Sultan Husain Madrasa, repairing the remaining minaret of Gawhar Shad's Madrasa, and replanting the mausoleum garden.

 In the 1960s, engineers from the United States built
In the 1960s, engineers from the United States built Herat Airport
, image = Plane of Pamir Airways at Herat Airport in 2010.jpg
, image-width = 250px
, caption = A Pamir Airways parked at the airport in 2010
, IATA = HEA
, ICAO = OAHR
, type = Public/Military
, owner ...
, which was used by the Soviet forces during the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan
The Democratic Republic of Afghanistan (DRA),, renamed the Republic of Afghanistan, in 1987, was the Afghan state during the one-party rule of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) from 1978 to 1992.
The PDPA came to power ...
in the 1980s. Even before the Soviet invasion at the end of 1979, there was a substantial presence of Soviet advisors in the city with their families.
Between March 10 and March 20, 1979, the Afghan Army in Herāt under the control of commander Ismail Khan mutinied. Thousands of protesters took to the streets against the Khalq communist regime's oppression led by Nur Mohammad Taraki. The new rebels led by Khan managed to oust the communists and take control of the city for 3 days, with some protesters murdering any Soviet advisers. This shocked the government, who blamed the new administration of Iran following the Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynas ...
for influencing the uprising. Reprisals by the government followed, and between 3,000 and 24,000 people (according to different sources) were killed, in what is called the 1979 Herat uprising
The Herat uprising ( prs, قیام هرات), locally known as the Uprising of 24th Hūt ( prs, قیام بیست و چهار حوت) was an insurrection that took place in and around the city of Herat in western Afghanistan, across several day ...
, or in Persian as the ''Qiam-e Herat''. The city itself was recaptured with tanks and airborne forces
Airborne forces, airborne troops, or airborne infantry are ground combat units carried by aircraft and airdropped into battle zones, typically by parachute drop or air assault. Parachute-qualified infantry and support personnel serving in ai ...
, but at the cost of thousands of civilians killed. This massacre was the first of its kind since the Third Anglo-Afghan War in 1919, and was the bloodiest event preceding the Soviet–Afghan War.

 Herat received damage during the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s, especially its western side. The province as a whole was one of the worst-hit. In April 1983, a series of Soviet bombings damaged half of the city and killed around 3,000 civilians, described as "extremely heavy, brutal and prolonged". Ismail Khan was the leading
Herat received damage during the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s, especially its western side. The province as a whole was one of the worst-hit. In April 1983, a series of Soviet bombings damaged half of the city and killed around 3,000 civilians, described as "extremely heavy, brutal and prolonged". Ismail Khan was the leading mujahideen
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' ( ar, مُجَاهِدِين, mujāhidīn), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' ( ar, مجاهد, mujāhid, strugglers or strivers or justice, right conduct, Godly rule, etc. doers of jihād), an Arabic term th ...
commander in Herāt fighting against the Soviet-backed government.
After the communist government's collapse in 1992, Khan joined the new government and he became governor of Herat Province. The city was relatively safe and it was recovering and rebuilding from the damage caused in the Soviet–Afghan War. However, on September 5, 1995, the city was captured by the Taliban without much resistance, forcing Khan to flee. Herat became the first Persian-speaking city to be captured by the Taliban. The Taliban's strict enforcement of laws confining women at home and closing girls' schools alienated Heratis who are traditionally more liberal and educated, like the Kabulis, than other urban populations in the country. Two days of anti-Taliban protests occurred in December 1996 which was violently dispersed and led to the imposition of a curfew. In May 1999, a rebellion in Herat was crushed by the Taliban, who blamed Iran for causing it.
After the U.S. invasion of Afghanistan
In late 2001, the United States and its close allies invaded Afghanistan and toppled the Taliban government. The invasion's aims were to dismantle al-Qaeda, which had executed the September 11 attacks, and to deny it a safe base of operation ...
, on November 12, 2001, it was captured from the Taliban by forces loyal to the Northern Alliance and Ismail Khan returned to power (see Battle of Herat
The 2001 uprising in Herat was a coordinated insurrection and uprising in the Afghan city of Herat as part of the United States war in Afghanistan. The city was captured on November 12 by Northern Alliance forces as well as Special Forces of ...
). The state of the city was reportedly much better than that of Kabul. In 2004, Mirwais Sadiq, Aviation Minister of Afghanistan and the son of Ismail Khan, was ambushed and killed in Herāt by a local rival group. More than 200 people were arrested under suspicion of involvement.
In 2005, the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) began establishing bases in and around the city. Its main mission was to train the Afghan National Security Forces
The Afghan National Security Forces (ANSF), also known as the Afghan National Defense and Security Forces (ANDSF), were the military and internal security forces of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan.
Structure
The Afghan National Security Forc ...
(ANSF) and help with the rebuilding process of the country. Regional Command West
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
, led by Italy, assisted the Afghan National Army
Afghan may refer to:
*Something of or related to Afghanistan, a country in Southern-Central Asia
* Afghans, people or citizens of Afghanistan, typically of any ethnicity
**Afghan (ethnonym), the historic term applied strictly to people of the Pas ...
(ANA) 207th Corps. Herat was one of the first seven areas that transitioned security responsibility from NATO to Afghanistan. In July 2011, the Afghan security forces assumed security responsibility from NATO.
Due to their close relations, Iran began investing in the development of Herat's power, economy and education sectors. In the meantime, the United States built a consulate in Herat to help further strengthen its relations with Afghanistan. In addition to the usual services, the consulate works with the local officials on development projects and with security issues in the region.
On 12 August 2021, the city was captured by the Taliban during the 2021 Taliban offensive
A military offensive by the Taliban insurgent group and other allied militants led to the fall of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan based in Kabul and marked the end of the nearly 20-year-old War in Afghanistan, that had begun following the ...
.
Geography
Climate
Herat has a cold semi-arid climate ( Köppen climate classification ''BSk''). Precipitation is very low, and mostly falls in winter. Although Herāt is approximately lower than Kandahar, the summer climate is more temperate, and the climate throughout the year is far from disagreeable, although winter temperatures are comparably lower. From May to September, the wind blows from the northwest with great force. The winter is tolerably mild; snow melts as it falls, and even on the mountains does not lie long. Three years out of four it does not freeze hard enough for the people to store ice. The eastern reaches of the Hari River, including the rapids, are frozen hard in the winter, and people travel on it as on a road.Places of interest
*Foreign consulates India, Iran and Pakistan operate their consulate here for trade, military and political links. *Neighborhoods **Shahr-e Naw (Downtown) **Welayat
A wilayah ( ar, وَلاية, wālāya or ''wilāya'', plural ; Urdu and fa, ولایت, ''velâyat''; tr, vilayet) is an administrative division, usually translated as "state", "province" or occasionally as " governorate". The word comes f ...
(Office of the governor)
**Qol-Ordue (Army's HQ)
**Farqa (Army's HQ)
**Darwaze Khosh
**Chaharsu
**Pul-e Rangine
**Sufi-abad
**New-abad
**Pul-e malaan
**Thakhte Safar
**Howz-e-Karbas
**Baramaan
**Darwaze-ye Qandahar
**Darwaze-ye Iraq
**Darwaze Az Kordestan



 *Parks
**Park-e Taraki
**Park-e Millat
**Khane-ye Jihad Park
*Monuments
** Herat Citadel (Qala Ikhtyaruddin or Arg)
** Musallah Complex
** Musalla Minarets of Herat
Of the more than dozen minarets that once stood in Herāt, many have been toppled from war and neglect over the past century. Recently, however, everyday traffic threatens many of the remaining unique towers by shaking the very foundations they stand on. Cars and trucks that drive on a road encircling the ancient city rumble the ground every time they pass these historic structures. UNESCO personnel and Afghan authorities have been working to stabilize the Fifth Minaret.
*Museums
**Herat Museum, located inside the Herat Citadel
**
*Parks
**Park-e Taraki
**Park-e Millat
**Khane-ye Jihad Park
*Monuments
** Herat Citadel (Qala Ikhtyaruddin or Arg)
** Musallah Complex
** Musalla Minarets of Herat
Of the more than dozen minarets that once stood in Herāt, many have been toppled from war and neglect over the past century. Recently, however, everyday traffic threatens many of the remaining unique towers by shaking the very foundations they stand on. Cars and trucks that drive on a road encircling the ancient city rumble the ground every time they pass these historic structures. UNESCO personnel and Afghan authorities have been working to stabilize the Fifth Minaret.
*Museums
**Herat Museum, located inside the Herat Citadel
**Jihad Museum The Jihad Museum is located in the western provincial capital of Herat in Afghanistan. It was built in 2010 as a place for Afghans to understand past conflicts and their history. Since its opening, the museum has welcomed many visitors, includin ...
*Mausoleums and tombs
** Gawhar Shad Mausoleum
** Mausoleum of Khwajah Abdullah Ansari
**Tomb of Jami
**Tomb of khaje Qaltan
**Mausoleum of Mirwais Sadiq
**Jewish cemetery – there once existed an ancient Jewish community in the city. Its remnants are a cemetery and a ruined shrine.
*Mosques
** Jumu'ah Mosque ( Friday Mosque of Herat)
**Gazargah Sharif
**Khalghe Sharif
**Shah Zahdahe
*Hotels
** Serena Hotel (coming soon)
**Diamond Hotel
**Marcopolo Hotel
*Stadiums
**Herat Stadium
*Universities
**Herat University
Herat University (HU; fa, ; ps, ) is a public university located in Herat, the capital of Herat Province, in western Afghanistan. It was inaugurated in 1988, beginning with a faculty of Literature and Humanities. The first President was Abub ...
Demography
 The population of Herat numbered approximately 592,902 in 2021. The city houses a multi-ethnic society and speakers of the Persian language are in the majority. There is no current data on the precise ethnic composition of the city's population, but according to a 2003 map found in the National Geographic Magazine, Persian-speaking
The population of Herat numbered approximately 592,902 in 2021. The city houses a multi-ethnic society and speakers of the Persian language are in the majority. There is no current data on the precise ethnic composition of the city's population, but according to a 2003 map found in the National Geographic Magazine, Persian-speaking Tajik
Tajik, Tadjik, Tadzhik or Tajikistani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Tajikistan
* Tajiks, an ethnic group in Tajikistan, Afghanistan and Uzbekistan
* Tajik language, the official language of Tajikistan
* Tajik (surname)
* Tajik cu ...
and Farsiwan peoples form the majority of the city, comprising around 85% of the population. The remaining population comprises Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
(10%), Hazaras (2%), Uzbeks (2%) and Turkmens (1%).
Persian is the native language of Herat and the local dialect – known by natives as ''Herātī'' – belongs to the ''Khorāsānī'' cluster within Persian. It is akin to the Persian dialects of eastern Iran, notably those of Mashhad
Mashhad ( fa, مشهد, Mašhad ), also spelled Mashad, is the List of Iranian cities by population, second-most-populous city in Iran, located in the relatively remote north-east of the country about from Tehran. It serves as the capital of R ...
and Khorasan Province, which borders Herat. This Persian dialect serves as the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
of the city. The second language that is understood by many is Pashto, which is the native language of the Pashtuns. The local Pashto dialect spoken in Herat is a variant of western Pashto, which is also spoken in Kandahar and southern and western Afghanistan. Religiously, Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
is practiced by the majority, while Shias make up the minority.
The city has high residential density clustered around the core of the city. However, vacant plots account for a higher percentage of the city (21%) than residential land use (18%) and agricultural is the largest percentage of total land use (36%).
The city once had a Jewish community. About 280 families lived in Herat as of 1948, but most of them moved to Israel that year, and the community disappeared by 1992. There are four former synagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of worshi ...
s in the city's old quarter, which were neglected for decades and fell into disrepair. In the late 2000s, the buildings of the synagogues were renovated by the Aga Khan Trust for culture, and at this time, three of them were turned into schools and nurseries, the Jewish community having vanished. The Jewish cemetery is being taken care of by Jalil Ahmed Abdelaziz.
Sports
;Professional sports teams from Herat * Stadiums ** Herat Cricket Ground ** Herat StadiumNotable people from Herat
Rulers and emperors
* Tahir ibn Husayn 9th century Abbasid Caliphate army general, and the founder of Tahirid dynasty * Ghiyasuddin Muhammad, was the emperor of the Ghurid dynasty from 1163 to 1202. During his reign, the Ghurid dynasty became a world power, which stretched from Gorgan to Bengal * Mīrzā Shāhrūkh bin Tīmur Barlas, Emperor of the Timurid dynasty of Herāt * Abu Sa'id Mirza, ruler of the Timurid Empire during the mid-fifteenth century * Mīrzā Husseyn Bāyqarāh, Emperor of the Timurid dynasty of Herāt * Shāh Abbās ''The Great'', Emperor ofSafavid Persia
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
* Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shāh Durrānī ( ps, احمد شاه دراني; prs, احمد شاه درانی), also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī (), was the founder of the Durrani Empire and is regarded as the founder of the modern Afghanistan. In July 1747, Ahm ...
, founder of the Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire ( ps, د درانيانو ټولواکمني; fa, امپراتوری درانیان) or the Afghan Empire ( ps, د افغانان ټولواکمني, label=none; fa, امپراتوری افغان, label=none), also know ...
* Emir Dost Mohammad Khan, founder of the Barakzai dynasty, buried in the city
* Sultan Jan Sultan Ahmad Khan bin Sardar 'Azim Mohammadzai (), also known as Sultan Jan () was the ruler of the Principality of Herat from September 1857 to April 1863. He was a nephew of Dost Mohammad Khan. In 1855-56, Sultan Ahmad Khan sent a petition to the ...
, ruler of Herat in the 19th century
Politicians
* Ahmad Maymandi 11th century Persian vizier of the Ghaznavid empire * Ismail Khan, formergovernor of Herat Province
This is a list of the governors of the province of Herat, Afghanistan.
Governors of Herat Province
See also
* List of current governors of Afghanistan
*
Notes
{{AfghanGov
Governors of Herat Province
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an o ...
and Minister of Water and Energy
* Amena Afzali
Amena Safi Afzali (born 1957 ) is a politician in Afghanistan, who became Minister of Work, Social Affairs, Martyred, and Disabled in January 2010 after receiving the confidence vote of the Afghan National Assembly. She had previously served as ...
, politician
* Faramarz Tamanna, politician
Poets
*Asjadi
Abu Nazar ʿAbdul ʿAziz bin Mansur ʿAsjadi ( fa, ابونظر عبدالعزیز بن منصور عسجدی) was a 10th-11th century royal Persian poet of the Ghaznavid empire located in the Ghazni province of today's Afghanistan.
Originating fr ...
, 10th-11th century royal Persian poet at the court of the Ghaznavids
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( fa, غزنویان ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest ...
* Khwājah Abdullāh al-Herawi al-Ansārī, a Persian poet of the 11th century
* Pur-Baha Jami, 13th century Iranian poet, Pun master, satirist, and often scathing social commentator, born in Jam, spent his youth in Herat
* Nūr ud-Dīn Jāmī, a Persian Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
poet of the 15th century
* Nizām ud-Din ʿAlī Shīr Herawi, famous poet and scientist of the Timurid era
* Hatefi
Abd-Allah Hatefi, commonly known as Hatefi (also spelled Hatifi; fa, هاتفی; 1454 – 1521) was a Persian poet and nephew of the distinguished poet Jami (died 1492).
Life
Hatefi was born in 1454 at Khargerd, a village which formed a distric ...
, a Persian poet of the 16th century and nephew of Nūr ud-Dīn Jāmī
* Latif Nazemi, Persian poet
Scientists
* Abu Mansur Muvaffak Harawi, 10th-century Persian physician *Abolfadl Harawi
Abolfadl Harawi ( fa, ابو الفضل هروى) was a 10th-century astronomer who, along with al-Khujandi, studied under the patronage of the Buyid dynasty in Rey Rey may refer to:
*Rey (given name), a given name
*Rey (surname), a surname
* ...
, 10th-century astronomer under the patroange of the Buyids in Rey Rey may refer to:
*Rey (given name), a given name
*Rey (surname), a surname
* Rey (''Star Wars''), a character in the ''Star Wars'' films
* Rey, Iran, a city in Iran
* Ray County, in Tehran Province of Iran
* ''Rey'' (film), a 2015 Indian film
*The ...
, originally from Herat
*Ahmad ibn Farrokh
Ahmad ibn Farrukh, also written Ahmad-i Farrokh, was a 12th-century Persian physician from Herat.
He was one of the teachers of Zayn al-Din al-Jurjani.
He is author of a Persian medicine encyclopaedia titled ''Kifayah'' that is no longer extant ...
, 12th-century Persian physician
* Taftazani, a Muslim polymath of the 14th century
* Muhammad ibn Yusuf al-Harawi
Muhammad ibn Yusuf al-Harawi ( fa, محمد بن یوسف هروی, fl. 1492-1518 and died 1542) was a Persian late 15th century physician from Herat, Safavid Iran, now part of Afghanistan.
In 1518 he composed, in Arabic, an alphabetical medic ...
15th century Persian physician
* Nimat Allah al-Harawi 17th century Persian chronicler at the court of the Mughal Emperor Jahangir
Nur-ud-Din Muhammad Salim (30 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was the fourth Mughal Emperor, who ruled from 1605 until he died in 1627. He was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti.
Ear ...
Religious figures
* Fakhr ad-Din al-Razi, polymath and Islamic scholar of the 12th-century * Hussain Kashefi, a 15th-century Persian prose-stylist and Islamic scholar and scientist * Ali al-Hirawi al-Qari, from 17th century, considered to be one of the masters of hadith and Imams of fiqh * Mujib Rahman Ansari (1982–2022),mullah
Mullah (; ) is an honorific title for Shia and Sunni Muslim clergy or a Muslim mosque leader. The term is also sometimes used for a person who has higher education in Islamic theology and sharia law.
The title has also been used in some Miz ...
and pro- Taliban cleric
Artists
* Ali ibn Abi Bakr al-Harawi 12th and 13th century Persian traveller and first known graffiti artist in theMuslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
world, originally from Herat
* Ustād Kamāl ud-Dīn Behzād, the greatest of the medieval Persian painters
* Mir Ali Heravi
Mir Ali Heravi, also known as Mir Ali Hossein Heravi and Mir Jan, titled as ''Kateb-e Soltani'', was a prominent Persian people, Persian calligrapher and calligraphy teacher of Nastaʿlīq script in the 16th century. He was the second significant P ...
, prominent Persian calligrapher and calligraphy
Calligraphy (from el, link=y, καλλιγραφία) is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instrument. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as "t ...
teacher of Nastaʿlīq script in the 16th century
* Alka Sadat
Alka Sadat ( fa, الکا سادات,(born 1988) is an Afghan documentary and feature film producer, director and cameraman. She became famous with her first 25-minute film ''Half Value Life'', which highlights social injustice and crime; the film ...
, Film producer was born here
* Sonita Alizadeh
Sonita Alizadeh ( prs, سونیتا علیزاده; born 1996) is an Afghan rapper and activist who has been vocal against forced marriages. Alizadeh first gained attention when she released "Brides for Sale," a video in which she raps about d ...
, rapper and activist
Sports
* Nadia Nadim, Afghan-Danishfootball player
A football player or footballer is a sportsperson who plays one of the different types of football. The main types of football are association football, American football, Canadian football, Australian rules football, Gaelic football, rugby le ...
, most influential and greatest Afghan female football player of all time, won the French league title in the 2020-21
The hyphen-minus is the most commonly used type of hyphen, widely used in digital documents. It is the only character that looks like a minus sign or a dash in many character sets such as ASCII or on most keyboards, so it is also used as such. ...
season with Paris Saint-Germain
* Hamidullah Karimi
Hamidullah Karimi (born February 6, 1992) is an Afghan footballer who currently plays as a forward for Indian club Delhi United S.C. He has been capped for the Afghanistan national football team.
Club career
Karimi joined Toofan Harirod F.C. i ...
, Afghan footballer, plays as a forward for Indian club Delhi United FC
*Mohammad Rafi Barekzay
Mohammad Rafi Barekzay (born 6 June 1990) is an Afghan footballer who plays as a midfielder for Toofaan Harirod F.C. in the Afghan Premier League.
Career
Toofaan Harirod F.C.
In 2012, Barekzay joined Afghan team Toofaan Harirod F.C. He did ...
, Afghan footballer, plays as a midfielder for Toofaan Harirod F.C
Others
*Gowhar Shad
Gawhar Shad ( fa, , Gawaršād; meaning "joyful jewel" or "shining jewel"; alternative spelling: Gohar Shād; died 19 July 1457) was the chief consort of Shah Rukh, the emperor of the Timurid Empire.
Life
She was the daughter of Giāth ud-Di ...
, wife of Shāh Rūkh Mīrzā
* Zablon Simintov, last remaining Jew living in Afghanistan
Economy and infrastructure
Transport
Air
 Herat International Airport was built by engineers from the United States in the 1960s and was used by the Soviet Armed Forces during the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s. It was bombed in late 2001 during
Herat International Airport was built by engineers from the United States in the 1960s and was used by the Soviet Armed Forces during the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s. It was bombed in late 2001 during Operation Enduring Freedom
Operation Enduring Freedom (OEF) was the official name used synonymously by the U.S. government for both the War in Afghanistan (2001–2014) and the larger-scale Global War on Terrorism. On 7 October 2001, in response to the September 11 at ...
but had been rebuilt within the next decade. The runway of the airport has been extended and upgraded and as of August 2014 there were regularly scheduled direct flights to Delhi, Dubai, Mashad, and various airports in Afghanistan. At least five airlines operated regularly scheduled direct flights to Kabul.
Rail
Rail connections to and from Herat were proposed many times, during '' The Great Game'' of the 19th century and again in the 1970s and 1980s, but nothing came to life. In February 2002, Iran and the Asian Development Bank announced funding for a railway connecting Torbat-e Heydarieh in Iran to Herat. This was later changed to begin in Khaf in Iran, a railway for both cargo and passengers, with work on the Iranian side of the border starting in 2006. Construction is underway in the Afghan side and it was estimated to be completed by March 2018. There is also the prospect of an extension across Afghanistan toSher Khan Bandar
Sher Khan or Shir Khan ( ps, شیر خان بندر; prs, شیرخان بندر) is a border town in the northern Kunduz Province of Afghanistan, next to the Panj River. The town's main attraction is the Sher Khan Bandar, which is a dry port ...
.
Road
The AH76 highway connects Herat to Maymana and the north. The AH77 connects it east towardsChaghcharan
Chaghcharān (Dari-Persian: ), also called Firozkoh (Dari-Persian: ), is a town and district in central Afghanistan, which serves as the capital of Ghor Province. It is located on the southern side of the Hari River, at an altitude of 2,230 m abov ...
and north towards Mary in Turkmenistan. Highway 1
The following highways are numbered 1.
For roads numbered A1, see list of A1 roads.
For roads numbered B1, see list of B1 roads.
For roads numbered M1, see List of M1 roads.
For roads numbered N1, see list of N1 roads.
For roads numbered ...
(part of Asian highway AH1) links it to Mashhad
Mashhad ( fa, مشهد, Mašhad ), also spelled Mashad, is the List of Iranian cities by population, second-most-populous city in Iran, located in the relatively remote north-east of the country about from Tehran. It serves as the capital of R ...
in Iran to the northwest, and south via the Kandahar–Herat Highway to Delaram.
Gallery
Afghan National Army
Afghan may refer to:
*Something of or related to Afghanistan, a country in Southern-Central Asia
* Afghans, people or citizens of Afghanistan, typically of any ethnicity
**Afghan (ethnonym), the historic term applied strictly to people of the Pas ...
File:Development Bank of Afghanistan.JPG, Shopping center
File:PoleMalanHerat.jpg, Pol-e Mālān
Malan Bridge, also called Pul-i-Malan ( Dari: ), is a two-lane arched bridge over the Hari River, connecting Injil District with Guzara District, both in Afghanistan. It was built around 1110 AD. The bridge is located south of Herat's old c ...
, a historical bridge
File:Herat 6918a.jpg, Pillar of Musallah Complex
File:Herat Ansari tomb.jpg, Khwājah Abdullāh Ansārī shrine, a Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
of the 11th century
File:Gazar Gah cemetery 1.jpg, Gazar Gah
The Shrine of Khwaja Abd Allah, commonly called the Shrine at Gazur Gah (or just Gazur Gah) and the Abdullah Ansari Shrine Complex, is the funerary compound of the Sufi saint Khwaja Abdullah Ansari. It is located at the village of Gazur Gah, thr ...
cemetery
File:Jami Tomb.JPG, Tomb of Jāmi, a poet of the 15th century
File:Herat Jews Cemetery.jpg, The Jewish cemetery
File:View of Herat in 2009.jpg, View of Herat from a hill
Herat in fiction
*The beginning of Khaled Hosseini's 2007 novel ''A Thousand Splendid Suns
''A Thousand Splendid Suns'' is a 2007 novel by Afghan-American author Khaled Hosseini, following the huge success of his bestselling 2003 debut ''The Kite Runner''. Mariam, an illegitimate teenager from Herat, is forced to marry a shoemaker from ...
'' is set in and around Herāt.
* Salman Rushdie's novel ''The Enchantress of Florence
''The Enchantress of Florence'' is the ninth novel by Salman Rushdie, published in 2008. According to Rushdie this is his "most researched book" which required "years and years of reading".
The novel was published on 11 April 2008 by Jonathan ...
'' makes frequent reference to events in Herāt in the Middle Ages.
Sister cities
*Council Bluffs, Iowa
Council Bluffs is a city in and the county seat of Pottawattamie County, Iowa, Pottawattamie County, Iowa, United States. The city is the most populous in Southwest Iowa, and is the third largest and a primary city of the Omaha–Council Bluffs ...
, United States (since 2016)
* Divandarreh, Kurdistan, Iran (since 2021)
See also
* Aria (satrapy) * Geography of Afghanistan * Greater Khorasan * Herāt Province * History of AfghanistanReferences
Sources
* *Attribution
Bibliography
External links
* * * * * *Detailed map of Herāt city
Perry–Castañeda Library Map Collection
The Perry–Castañeda Library Map Collection is an extensive map collection owned by the Perry–Castañeda Library at The University of Texas at Austin.
Many of the maps in the collection have been scanned and are available online, and most ...
, University of Texas at Austin
{{Iranian Architecture
Cities in Afghanistan
Cities in Central Asia
Populated places along the Silk Road
Populated places in Herat Province
Provincial capitals in Afghanistan
Cities founded by Alexander the Great