 Hiawatha ( , also : ), also known as Ayenwathaaa or Aiionwatha, was a precolonial Native American leader and co-founder of the
Hiawatha ( , also : ), also known as Ayenwathaaa or Aiionwatha, was a precolonial Native American leader and co-founder of the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
Confederacy. He was a leader of the Onondaga people, the Mohawk people, or both. According to some accounts, he was born an Onondaga but adopted into the Mohawks.
Legend
Although Hiawatha was actually a real person, he was mostly known through his legend. The events in the legend have been dated to the middle 1100s through the occurrence of an eclipse coincident with the founding of the Iroquois Confederacy.Dates of 1390–1630 have also been proposed. This material and quotations are taken from the Mohawk version of the legend, as related by the prominent chief Seth Newhouse (Dayodekane). For an Onondaga version of the legend, see Parker: "The Hiawatha Tradition". When the founder of the Confederacy, Dekanawidah, known as ''The Great Peacemaker'', first came to Iroquoia, one of the first people he met was Hiawatha, not yet called by that name.His original name seems to be not recorded At that time Hiawatha was a wild man and a cannibal, known as "the man who eats humans." When Dekanawidah came to his cabin he climbed onto the roof, looked down through thesmoke hole Smoke Hole may refer to:
* Smoke hole, a hole in a roof for the smoke from a fire to vent
* Smoke Hole Canyon, or Smoke Hole, a gorge in the Allegheny Mountains of West Virginia, U.S.
** Smoke Hole, West Virginia, a former unincorporated community
...
, where there was a large kettle of water for cooking a meal of human flesh. When Hiawatha came home he looked into the water and saw Dekanawidah's face reflected back to him, which he thought was his own. "In that face he was aware of a beauty, a wisdom and strength, which at first filled him with astonishment and then with shame, for it was not the face of one who killed and ate his fellow men." Dekanawidah came down, sat across the fire from him, and passed on to him the Great Law of Peace. Hiawatha accepted the message, and agreed to stay and work with his own people while Dekanawidah went on to pass the message to other nations.
The principal chief of the Onondaga at that time was a cruel tyrant called Tadodaho, or Atotarho. Tadodaho is described as twisted in both body and mind. "His hair was filled with living snakes. Snakes' eyes looked out from his finger ends." Dekanawidah charged Hiawatha with converting Tadodaho—to "comb the snakes out of adodaho'shair." He gave him the name Hiawatha, which means "he who combs."
After Dekanawidah left, Hiawatha presented his proposals to the Onondaga in councils, but Tadodaho kept frustrating all his efforts and disrupting the councils. He caused the death of Hiawatha's three daughters and his wife by magic. Grief-stricken, Hiawatha left his village and wandered, "stringing wampum and seeking someone who should understand the thirteen-string ceremony of condolence and take away his grief by the spell of the wampum." Finally he came to the territory of the Mohawk, where Dekanawidah had converted the entire nation. Dekanawidah chanted the words that have since been part of the Iroquois ''Requickening Ceremony'': "I wipe away tears from thy face." "using the white fawn-skin of pity…I make it daylight for thee… I beautify the sky. Now shall thou do thy thinking in peace…" Afterwards, Hiawatha joined Dekanawidah in composing the laws of the Great Peace, and the Peace Hymn.
Then Hiawatha and Dekanawidah, together with the Mohawk chiefs, visited each of the other four Nations. They had no trouble with the Oneidas and the Cayugas, but the Senecas were divided against themselves and the Onondagas were afraid of the power of Tadodaho. A solar eclipse helped convince the Senecas, and the Onondagas were brought in by the power of the other four Nations and by the offer to Tadodaho that he become principal chief. "In the end the mind of adodahowas made straight, the crooks were taken out of his body, and Hiawatha combed the snakes out of his hair."
Hiawatha was noted for his speaking skills and message of peace. Dekanawidah, a Huron prophet and spiritual leader, proposed the unification of the Iroquois peoples who shared common ancestry and similar languages, but he suffered from a severe speech impediment which hindered him from spreading his proposal. Hiawatha was a skilled orator, and he was instrumental in persuading the Five Nations to accept the Great Peacemaker's vision and band together to become members of the Iroquois confederacy. The Tuscarora joined the Confederacy in 1722 to become the Sixth Nation. Little else is known of Hiawatha. The reason and time of his death is unknown. However his legacy is still passed on from generation to generation through oral stories, songs, and books.
The 1855 epic poem '' The Song of Hiawatha'' by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow tells the story of a hero of the same name but has no relationship to the historical Hiawatha.
The Iroquois Confederacy
Within theIroquois Confederacy
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
, which originally included five tribes (Mohawk, Onondaga, Oneida, Cayuga, and Seneca), Hiawatha was a leader from the Mohawk tribe. There he was well-known, and highly thought of by all of the tribes. He was a great speaker, and would eventually become the representative for the Great Peacemaker. The Great Peacemaker was a man who hoped to spread peace throughout all of the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) Territory. Due to the fact that he had a severe speech impediment, the Great Peacemaker needed a spokesperson. Hiawatha was willing to speak on behalf of Dekanawidah because violence had been developing throughout the Iroquois Territory. During these times of chaos, a leader named Tadodaho, who had despised the idea of peace, targeted and killed Hiawatha's wife and daughters. Thereafter, Hiawatha became the Peacemaker's speaker, so he could stop the violence. Dewanawidah and Hiawatha eventually obtained peace throughout the Iroquois by promising Tadodaho that Onondaga would become the capital of the Grand Council, the main governing body of the Iroquois. Hiawatha and Dekanawidah created the Great Law of Peace, recorded in wampum belts, to solidify the bond between the original five nations of the Iroquois.
Among the names of the fifty traditional Hoyenah ( sachems) of the Haudenosaunee, Hiawatha (among others) is a representative of the Mohawk, and Tadodaho of the Onondaga.
Hiawatha Belt
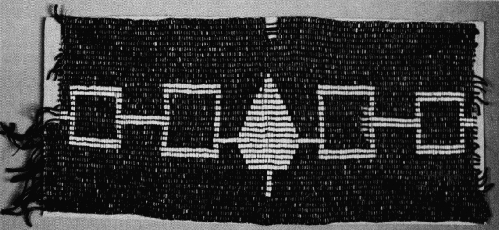 The Hiawatha Belt is a wampum belt that symbolizes peace between the original five nations of the Iroquois. The belt depicts the nations in a specific order from left to right. The Seneca are furthest to the left, representing their position as Keepers of the Western Door. Next is the Cayuga, and in the center of the belt, depicted with a different symbol, is the Onondaga, also known as the Keepers of the Central Fire. Next is the Oneida. Finally, shown farthest to the right is the Mohawk, the Keepers of the Eastern Door. The white line connecting all of the symbols for each tribe together represents the unity of the Iroquois. It also represents the gathering from the Great Law of Peace and the Iroquois Confederacy as a whole.
The wampum belt consists of black or purple-like and white beads that are made up of shells. Found in the Northeast of America, there are quahog clam shells that are often time used for the black and sometimes the white beads of these belts. Most often the Iroquois used various types of whelk spiral shells for the white beads.
Wampum figures in the story of Hiawatha. When Hiawatha was full of grief because his daughters were murdered, the Great Peacemaker gifted Hiawatha with the whelk shells and told him to put them on his eyes and ears and throat. These shells were a sign of healing and purity. Hiawatha used these shells to create unity. The Iroquois Nation believes that the Peacemaker was the one who gifted them the first wampum belt, which later was titled the Hiawatha Belt.
Today the image of the Hiawatha Belt is used on the Flag of the Iroquois Confederacy.
The Hiawatha Belt is a wampum belt that symbolizes peace between the original five nations of the Iroquois. The belt depicts the nations in a specific order from left to right. The Seneca are furthest to the left, representing their position as Keepers of the Western Door. Next is the Cayuga, and in the center of the belt, depicted with a different symbol, is the Onondaga, also known as the Keepers of the Central Fire. Next is the Oneida. Finally, shown farthest to the right is the Mohawk, the Keepers of the Eastern Door. The white line connecting all of the symbols for each tribe together represents the unity of the Iroquois. It also represents the gathering from the Great Law of Peace and the Iroquois Confederacy as a whole.
The wampum belt consists of black or purple-like and white beads that are made up of shells. Found in the Northeast of America, there are quahog clam shells that are often time used for the black and sometimes the white beads of these belts. Most often the Iroquois used various types of whelk spiral shells for the white beads.
Wampum figures in the story of Hiawatha. When Hiawatha was full of grief because his daughters were murdered, the Great Peacemaker gifted Hiawatha with the whelk shells and told him to put them on his eyes and ears and throat. These shells were a sign of healing and purity. Hiawatha used these shells to create unity. The Iroquois Nation believes that the Peacemaker was the one who gifted them the first wampum belt, which later was titled the Hiawatha Belt.
Today the image of the Hiawatha Belt is used on the Flag of the Iroquois Confederacy.
''The Song of Hiawatha''
Written by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, the 1855 epic poem The Song of Hiawatha tells of the adventures of "Hiawatha" and his heroic deeds. This poem however has little to do with the actual Hiawatha. Longfellow most likely took the name of Hiawatha and applied it to theOjibway
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
demigod ''Manabozho'', and nothing more. This poem tells the story of a legendary heroic Native manHe is nowhere identified as Iroquois. starting from his birth and ending on his ascension to the clouds. It talks of many battles, losses, and moral lessons. Longfellow along with another writer Henry Rowe Schoolcraft, hoped to combine stories of Native Americans and create a sense of pride and remembrance for the Native Americans during the 1820s and later.
Longfellow’s fictional Hiawatha has eclipsed the Hiawatha of legend in popular culture.
See also
* List of peace activistsExplanatory notes
References
Further reading
* Bonvillain, Nancy (2005). ''Hiawatha: founder of the Iroquois Confederacy.'' * Hale, Horatio (1881). ''Hiawatha and the Iroquois confederation: a study in anthropology.'' * Hatzan, A. Leon (1925). ''The true story of Hiawatha, and history of the Six Nations Indians.'' * Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe (1856).The Myth of Hiawatha, and Other Oral Legends, Mythologic and Allegoric, of the North American Indians.
' * Laing, Mary E. (1920). ''The hero of the longhouse.'' * Saraydarian, Torkom and Joann L Alesch (1984). ''Hiawatha and the great peace.'' * Siles, William H. (1986). ''Studies in local history: tall tales, folklore and legend of upstate New York.'' Juvenile audience * Bonvillain, Nancy (1992). ''Hiawatha: founder of the Iroquois Confederacy.'' * Fradin, Dennis B. (1992). ''Hiawatha: messenger of peace.'' * McClard, Megan, George Ypsilantis and Frank Riccio (1989). ''Hiawatha and the Iroquois league.'' * Malkus, Alida (1963). ''There really was a Hiawatha.'' * St. John, Natalie and Mildred Mellor Bateson (1928). ''Romans of the West: untold but true story of Hiawatha.'' * Taylor, C. J. (2004). ''Peace walker: the legend of Hiawatha and Tekanawita.''
External links
Historica's Heritage Minute ''Peacemaker''
a mini-docudrama about the co founders of the Iroquois Confederacy.
Schenectady Digital History Archive
Google Books overview of ''Ancient Society''
''The Great Peacemaker Deganawidah and his follower Hiawatha''
theater play by Living Wisdom School * {{Authority control Iroquois mythology Iroquois people Legendary American people Native American leaders Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown 1525 births 1595 deaths