Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also
transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese
Shia Islamist political party and
militant
The English word ''militant'' is both an adjective and a noun, and it is generally used to mean vigorously active, combative and/or aggressive, especially in support of a cause, as in "militant reformers". It comes from the 15th century Latin " ...
group,
led by its
Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's
paramilitary
A paramilitary is an organization whose structure, tactics, training, subculture, and (often) function are similar to those of a professional military, but is not part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. Paramilitary units carr ...
wing is the Jihad Council,
and its political wing is the
Loyalty to the Resistance Bloc party in the
Lebanese Parliament
The Lebanese Parliament ( ar, مجلس النواب, translit=Majlis an-Nuwwab; french: Chambre des députés) is the national parliament of the Republic of Lebanon. There are 128 members elected to a four-year term in multi-member constit ...
.
After the
Israeli invasion of Lebanon in 1982, the idea of Hezbollah arose among Lebanese clerics who had studied in
Najaf, and who adopted the model set out by
Ayatollah Khomeini
Ruhollah Khomeini, Ayatollah Khomeini, Imam Khomeini ( , ; ; 17 May 1900 – 3 June 1989) was an Iranian political and religious leader who served as the first supreme leader of Iran from 1979 until his death in 1989. He was the founder of ...
after the
Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynas ...
in 1979. After failing to agree on a name for the new organisation, the party's founders adopted the name chosen by Ayatollah Khomeini, Hezbollah. The organization was established as part of an Iranian effort, through funding and the dispatch of a core group of
Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (pasdaran) instructors, to aggregate a variety of Lebanese Shia groups into a unified organization to resist the
Israeli occupation
Israeli-occupied territories are the lands that were captured and occupied by Israel during the Six-Day War of 1967. While the term is currently applied to the Palestinian territories and the Golan Heights, it has also been used to refer ...
and improve the standing and status of the long marginalised and underrepresented
Shia community in that country. A contingent of 1,500 pasdaran instructors arrived after the
Syrian government
Government of the Syrian Arab Republic is the union government created by the constitution of Syria where by the president is the head of state and the prime minister is the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Syr ...
, which
occupied Lebanon's eastern highlands, permitted their transit to a base in the Bekaa valley.
During the
Lebanese Civil War, Hezbollah's 1985 manifesto listed its objectives as the expulsion of "the Americans, the French and their allies definitely from Lebanon, putting an end to any colonialist entity on our land", the submission of the Christian
Phalangists to "just power", bringing them to justice "for the crimes they have perpetrated against Muslims and Christians", and permitting "all the sons of our people" to choose the form of government they want, while calling on them to "pick the option of Islamic government".
Hezbollah organised volunteers who fought for the
Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina during the
Bosnian War
The Bosnian War ( sh, Rat u Bosni i Hercegovini / Рат у Босни и Херцеговини) was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1992 and 1995. The war is commonly seen as having started ...
.
From 1985 to 2000, Hezbollah participated in the
South Lebanon conflict against the
South Lebanon Army (SLA) and
Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, צְבָא הַהֲגָנָה לְיִשְׂרָאֵל , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the Israel, State of Israel. It consists of three servic ...
(IDF), which finally led to the rout of the SLA and the retreat of the IDF from South Lebanon in 2000. Hezbollah and the IDF fought each other again in the
2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War, also called the 2006 Israel–Hezbollah War and known in Lebanon as the July War ( ar, حرب تموز, ''Ḥarb Tammūz'') and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War ( he, מלחמת לבנון השנייה, ''Milhemet Leva ...
.
Its military strength has grown so significantly since 2006
that its paramilitary wing is considered more powerful than the
Lebanese Army
)
, founded = 1 August 1945
, current_form = 1991
, disbanded =
, branches = Lebanese Ground ForcesLebanese Air Force Lebanese Navy
, headquarters = Yarze, Lebanon
, flying_hours =
, websit ...
.
Hezbollah has been described as a "
state within a state" and has grown into an organization with seats in the
Lebanese government,
a radio and
a satellite TV station,
social services
Social services are a range of public services intended to provide support and assistance towards particular groups, which commonly include the disadvantaged. They may be provided by individuals, private and independent organisations, or administe ...
and large-scale military deployment of fighters beyond Lebanon's borders.
Hezbollah is part of Lebanon's
March 8 Alliance, in opposition to the
March 14 Alliance. It maintains strong support among
Lebanese Shia Muslims, while
Sunnis
Sunni Islam () is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia ...
have disagreed with its agenda. Hezbollah also has support in some
Christian areas of Lebanon. It receives military training, weapons, and financial support from Iran and political support from Syria.
Since 1990, Hezbollah has participated in Lebanese politics, in a process which is described as the Lebanonisation of Hezbollah, and it later participated in the
government of Lebanon and joined political alliances. After the
2006–08 Lebanese protests and
clashes,
a
national unity government was formed in 2008, with Hezbollah and its opposition allies obtaining 11 of 30 cabinet seats, enough to give them veto power.
In August 2008, Lebanon's new cabinet unanimously approved a draft policy statement that recognizes Hezbollah's existence as an armed organization and guarantees its right to "liberate or recover occupied lands" (such as the
Shebaa Farms).
Since 2012,
Hezbollah involvement in the Syrian civil war has seen it join the Syrian government in its fight against the
Syrian opposition
The Syrian opposition ( ar, المعارضة السورية ', ) is the political structure represented by the Syrian National Coalition and associated Syrian anti-Assad groups with certain territorial control as an alternative Syrian gover ...
, which Hezbollah has described as a
Zionist plot and a "
Wahhabi-Zionist conspiracy" to destroy its alliance with
Bashar al-Assad
Bashar Hafez al-Assad, ', Levantine pronunciation: ; (, born 11 September 1965) is a Syrian politician who is the 19th president of Syria, since 17 July 2000. In addition, he is the commander-in-chief of the Syrian Armed Forces and the ...
against Israel.
Between 2013 and 2015, the organisation deployed its militia in both Syria and Iraq to fight or train local militias to fight against the
Islamic State. The group's legitimacy is considered to have been severely damaged due to the
sectarian nature of the Syrian war.
In the
2018 Lebanese general election
General elections were held in Lebanon on 6 May 2018. Although originally scheduled for 2013, the election was postponed three times in 2013, 2014 and 2017 under various pretexts, including the security situation, the failure of the Parliament ...
, Hezbollah held 12 seats and
its alliance won the election by gaining 70 out of 128 seats in the
Parliament of Lebanon.
Nasrallah declared on 2021 that the group has 100,000 fighters.
Either the entire organization or only its military wing has been designated a
terrorist organization by several countries, including by the
European Union and, since 2017, also by most member states of the
Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, E ...
, with two exceptions –
Lebanon, where Hezbollah is one of the country's most influential political parties, and
Iraq.
[ Russia does not view Hezbollah as a "terrorist organization" but as a "legitimate socio-political force".
]
History
Foundation
In 1982, Hezbollah was conceived by Muslim clerics and funded by Iran primarily to harass the Israeli invasion of Lebanon.Ayatollah Khomeini
Ruhollah Khomeini, Ayatollah Khomeini, Imam Khomeini ( , ; ; 17 May 1900 – 3 June 1989) was an Iranian political and religious leader who served as the first supreme leader of Iran from 1979 until his death in 1989. He was the founder of ...
, and its forces were trained and organized by a contingent of 1,500 Revolutionary Guards that arrived from Iran with permission from the Syrian government
Government of the Syrian Arab Republic is the union government created by the constitution of Syria where by the president is the head of state and the prime minister is the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Syr ...
, which occupied Lebanon's eastern highlands, permitted their transit to a base in the Bekaa valleyRagheb Harb
Ragheb Harb ( ar, راغب حرب; 1952–1984 was a Lebanese leader and Muslim cleric. He was born in Jibchit in 1952, a village in the Jabal Amel region of Southern Lebanon. Harb was an imam and led the regional Shiite resistance against I ...
, a leader of the southern Shia resistance killed by Israel in 1984. Regardless of when the name came into official use, a number of Shi'a groups were slowly assimilated into the organization, such as Islamic Jihad, Organization of the Oppressed on Earth
The Organization of the Oppressed on Earth is a group that claimed responsibility for kidnappings, bombings, and executions in Lebanon in the 1980s. It was considered a precursor to, or another name for, Islamic Jihad and Hezbollah.
Connection ...
and the Revolutionary Justice Organization
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's parami ...
. These designations are considered to be synonymous with Hezbollah by the US, Israel and Canada.
1980s
Hezbollah emerged in South Lebanon during a consolidation of Shia militias as a rival to the older Amal Movement. Hezbollah played a significant role in the Lebanese civil war, opposing American forces in 1982–83 and opposing Amal and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
during the 1985–88 War of the Camps. However, Hezbollah's early primary focus was ending Israel's occupation of southern Lebanonguerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or Irregular military, irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, Raid (military), raids ...
. In 2006, former Israeli prime minister Ehud Barak
Ehud Barak ( he-a, אֵהוּד בָּרָק, Ehud_barak.ogg, link=yes, born Ehud Brog; 12 February 1942) is an Israeli general and politician who served as the tenth prime minister from 1999 to 2001. He was leader of the Labor Party until Jan ...
stated, "When we entered Lebanon … there was no Hezbollah. We were accepted with perfumed rice and flowers by the Shia in the south. It was our presence there that created Hezbollah".asymmetric war
Asymmetric warfare (or asymmetric engagement) is the term given to describe a type of war between belligerents whose relative military power, strategy or tactics differ significantly. This is typically a war between a standing, professional ar ...
using suicide attacks against the Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, צְבָא הַהֲגָנָה לְיִשְׂרָאֵל , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the Israel, State of Israel. It consists of three servic ...
(IDF) and Israeli targets outside of Lebanon.[ Specifically: "Suicide Terrorist Campaigns, 1980–2003", Appendix 1. (p. 253 of Australian paperback edition, published by Scribe Publications)] Hezbollah is reputed to have been among the first Islamic resistance groups in the Middle East to use the tactics of suicide bombing, assassination, and capturing foreign soldiers,Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, which controlled Lebanon at that time, allowed Hezbollah to maintain their arsenal and control Shia areas along the border with Israel.
After 1990
In the 1990s, Hezbollah transformed from a revolutionary group into a political one, in a process which is described as the Lebanonisation of Hezbollah. Unlike its uncompromising revolutionary stance in the 1980s, Hezbollah conveyed a lenient stance towards the Lebanese state.
In 1992 Hezbollah decided to participate in elections, and Ali Khamenei
Sayyid Ali Hosseini Khamenei ( fa, سید علی حسینی خامنهای, ; born 19 April 1939) is a Twelver Shia ''marja and the second and current Supreme Leader of Iran, in office since 1989. He was previously the third president o ...
, supreme leader of Iran, endorsed it. Former Hezbollah secretary general, Subhi al-Tufayli
Subhi al-Tufayli ( ar, صبحي الطفيلي) (born 1948) was the first Secretary-General or leader of Hezbollah for a year. Al-Tufayli is a Shia Islamist, but is a very vocal critic of Iran and the current Hezbollah leadership. He has been an ...
, contested this decision, which led to a schism in Hezbollah. Hezbollah won all twelve seats which were on its electoral list. At the end of that year, Hezbollah began to engage in dialog with Lebanese Christians. Hezbollah regards cultural, political, and religious freedoms in Lebanon as sanctified, although it does not extend these values to groups who have relations with Israel.
In 1997 Hezbollah formed the multi-confessional Lebanese Brigades to Fighting the Israeli Occupation in an attempt to revive national and secular resistance against Israel, thereby marking the "Lebanonisation" of resistance.
Islamic Jihad Organization (IJO)
Whether the Islamic Jihad Organization (IJO) was a ''nom de guerre
A pseudonym (; ) or alias () is a fictitious name that a person or group assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true name (orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individua ...
'' used by Hezbollah or a separate organization, is disputed. According to certain sources, IJO was identified as merely a "telephone organization", and whose name was "used by those involved to disguise their true identity." Hezbollah reportedly also used another name, "Islamic Resistance" (''al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya''), for attacks against Israel.
A 2003 American court decision found IJO was the name used by Hezbollah for its attacks in Lebanon, parts of the Middle East and Europe. The US,
Ideology
The ideology of Hezbollah has been summarized as Shi'i radicalism; Hezbollah follows the Islamic Shi'a
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad designated Ali, ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his S ...
theology developed by Iranian leader Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini
Ruhollah Khomeini, Ayatollah Khomeini, Imam Khomeini ( , ; ; 17 May 1900 – 3 June 1989) was an Iranian political and religious leader who served as the first supreme leader of Iran from 1979 until his death in 1989. He was the founder of ...
.[Adam Shatz, New York Review of Books, 29 April 200]
In Search of Hezbollah
. Retrieved 15 August 2006. Hezbollah was largely formed with the aid of the Ayatollah Khomeini's followers in the early 1980s in order to spread Islamic revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dyna ...
Shi'a
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad designated Ali, ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his S ...
ideology ( ''Wilayat al-faqih'' or Guardianship of the Islamic Jurists) developed by Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini
Ruhollah Khomeini, Ayatollah Khomeini, Imam Khomeini ( , ; ; 17 May 1900 – 3 June 1989) was an Iranian political and religious leader who served as the first supreme leader of Iran from 1979 until his death in 1989. He was the founder of ...
, leader of the "Islamic Revolution" in Iran.Islamic republic
The term Islamic republic has been used in different ways. Some Muslim religious leaders have used it as the name for a theoretical form of Islamic theocratic government enforcing sharia, or laws compatible with sharia. The term has also been u ...
, this goal has been abandoned in favor of a more inclusive approach.
1985 manifesto
On 16 February 1985, Sheik Ibrahim al-Amin issued Hezbollah's manifesto. The ideology presented in it was described as radical. Its first objective was to fight against what Hezbollah described as American and Israeli imperialism, including the Israeli occupation of Southern Lebanon and other territories. The second objective was to gather all Muslims into an " ummah", under which Lebanon would further the aims of the 1979 Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynas ...
of Iran. It also declared it would protect all Lebanese communities, excluding those that collaborated with Israel, and support all national movements—both Muslim and non-Muslim—throughout the world. The ideology has since evolved, and today Hezbollah is a left-wing political entity focused on social injustice.
Translated excerpts from Hezbollah's original 1985 manifesto read:
Attitudes, statements, and actions concerning Israel and Zionism
From the inception of Hezbollah to the present,[United Nations Document A/54/723 S/2000/55, citing Al Hayyat, 30 October 1999 . Retrieved 17 August 2006.] the elimination of the State of Israel has been one of Hezbollah's primary goals. Some translations of Hezbollah's 1985 Arabic-language manifesto state that "our struggle will end only when this entity sraelis obliterated".[Thisreen (Syrian newspaper) 21 June 1999, reprinted by MEMR]
Secretary General of Hizbullah Discusses the New Israeli Government and Hizbullah's Struggle Against Israel
. Retrieved 30 July 2006.
Attitudes and actions concerning Jews and Judaism
Hezbollah officials have said, on rare occasions, that it is only "anti-Zionist" and not anti-Semitic.anti-Judaism
Anti-Judaism is the "total or partial opposition to Judaism as a religion—and the total or partial opposition to Jews as adherents of it—by persons who accept a competing system of beliefs and practices and consider certain genuine Judai ...
, "it is not contingent upon it because Hezbollah's hatred of Jews is more religiously motivated than politically motivated".[ Saad-Ghorayeb, Amal. ''Hizbu'llah: Politics and Religion''. London: Pluto Press, 2002. pp. 168–86.] Robert S. Wistrich
Robert Solomon Wistrich (April 7, 1945 – May 19, 2015) was the Erich Neuberger Professor of European and Jewish history at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and the head of the University's Vidal Sassoon International Center for the Study ...
, a historian specializing in the study of anti-Semitism, described Hezbollah's ideology concerning Jews:
The anti-Semitism of Hezbollah leaders and spokesmen combines the image of seemingly invincible Jewish power ... and cunning with the contempt normally reserved for weak and cowardly enemies. Like the Hamas propaganda for holy war, that of Hezbollah has relied on the endless vilification of Jews as 'enemies of mankind,' 'conspiratorial, obstinate, and conceited' adversaries full of 'satanic plans' to enslave the Arabs. It fuses traditional Islamic anti-Judaism with Western conspiracy myths, Third Worldist anti-Zionism, and Iranian Shiite contempt for Jews as 'ritually impure' and corrupt infidels. Sheikh Fadlallah
Grand Ayatollah Muhammad Husayn Fadlallah (also Sayyed Muhammad Hussein Fadl-Allāh; ar, محمد حسين فضل الله; 16 November 1935 – 4 July 2010) was a prominent twelver Shia cleric from a Lebanese family. Born in Najaf, Iraq, ...
typically insists ... that Jews wish to undermine or obliterate Islam and Arab cultural identity in order to advance their economic and political domination.
Conflicting reports say Al-Manar, the Hezbollah-owned and operated television station, accused either Israel or Jews of deliberately spreading HIV and other diseases to Arabs throughout the Middle East.[Block, Melissa]
"'New Yorker' Writer Warns of Hezbollah's Radicalism."
National Public Radio. 16 August 2006. 16 February 2008. Al-Manar was criticized in the West for airing "anti-Semitic propaganda" in the form of a television drama depicting a Jewish world domination conspiracy theory. The group has been accused by American analysts of engaging in Holocaust denial. In addition, during its 2006 war, it apologized only for killing Israel's Arabs (i.e., non-Jews).The Diary of Anne Frank
''The Diary of a Young Girl'', also known as ''The Diary of Anne Frank'', is a book of the writings from the Dutch-language diary kept by Anne Frank while she was in hiding for two years with her family during the Nazi occupation of the Neth ...
'', a book of the writings from the diary kept by the Jewish child Anne Frank while she was in hiding with her family during the Nazi occupation of the Netherlands. This was after Hezbollah's Al-Manar television channel complained, asking how long Lebanon would "remain an open arena for the Zionist invasion of education?"
Organization

 At the beginning many Hezbollah leaders have maintained that the movement was "not an organization, for its members carry no cards and bear no specific responsibilities," and that the movement does not have "a clearly defined organizational structure." Nowadays, as Hezbollah scholar Magnus Ranstorp reports, Hezbollah does indeed have a formal governing structure, and in keeping with the principle of Guardianship of the Islamic Jurists (''velayat-e faqih''), it "concentrate nbsp;... all authority and powers" in its religious leaders, whose decisions then "flow from the ulama down the entire community."
At the beginning many Hezbollah leaders have maintained that the movement was "not an organization, for its members carry no cards and bear no specific responsibilities," and that the movement does not have "a clearly defined organizational structure." Nowadays, as Hezbollah scholar Magnus Ranstorp reports, Hezbollah does indeed have a formal governing structure, and in keeping with the principle of Guardianship of the Islamic Jurists (''velayat-e faqih''), it "concentrate nbsp;... all authority and powers" in its religious leaders, whose decisions then "flow from the ulama down the entire community."
The supreme decision-making bodies of the Hezbollah were divided between the Majlis al-Shura (Consultative Assembly) which was headed by 12 senior clerical members with responsibility for tactical decisions and supervision of overall Hizballah activity throughout Lebanon, and the Majlis al-Shura al-Karar (the Deciding Assembly), headed by Sheikh Muhammad Hussein Fadlallah and composed of eleven other clerics with responsibility for all strategic matters. Within the Majlis al-Shura, there existed seven specialized committees dealing with ideological, financial, military and political, judicial, informational and social affairs. In turn, the Majlis al-Shura and these seven committees were replicated in each of Hizballah's three main operational areas (the Beqaa, Beirut, and the South).[Ranstorp, ''Hizb'allah in Lebanon,'' (1997), p. 45]
Since the Supreme Leader of Iran is the ultimate clerical authority, Hezbollah's leaders have appealed to him "for guidance and directives in cases when Hezbollah's collective leadership astoo divided over issues and fail dto reach a consensus."
Funding
Funding of Hezbollah comes from Lebanese business groups, private persons, businessmen, the Lebanese diaspora involved in African diamond exploration, other Islamic groups and countries, and the taxes paid by the Shia Lebanese.Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
.Lira
Lira is the name of several currency units. It is the current currency of Turkey and also the local name of the currencies of Lebanon and of Syria. It is also the name of several former currencies, including those of Italy, Malta and Israe ...
, it was estimated that Hezbollah was receiving $3–5 million a month from Iran.
According to reports released in February 2010, Hezbollah received $400 million from Iran.
Social services
Hezbollah organizes and maintains an extensive social development program and runs hospitals, news services, educational facilities, and encouragement of Nikah mut'ah.Hezbollah not only has armed and political wings—it also boasts an extensive social development program. Hezbollah currently operates at least four hospitals, twelve clinics, twelve schools and two agricultural centres that provide farmers with technical assistance and training. It also has an environmental department and an extensive social assistance program. Medical care is also cheaper than in most of the country's private hospitals and free for Hezbollah members.
According to CNN, "Hezbollah did everything that a government should do, from collecting the garbage to running hospitals and repairing schools."Lebanese society
Lebanese society is very modern and similar to certain cultures of Southern Europe as the country is "linked ideologically and culturally to Europe through France, and its uniquely diverse religious composition reatea rare environment that sat o ...
.
Political activities
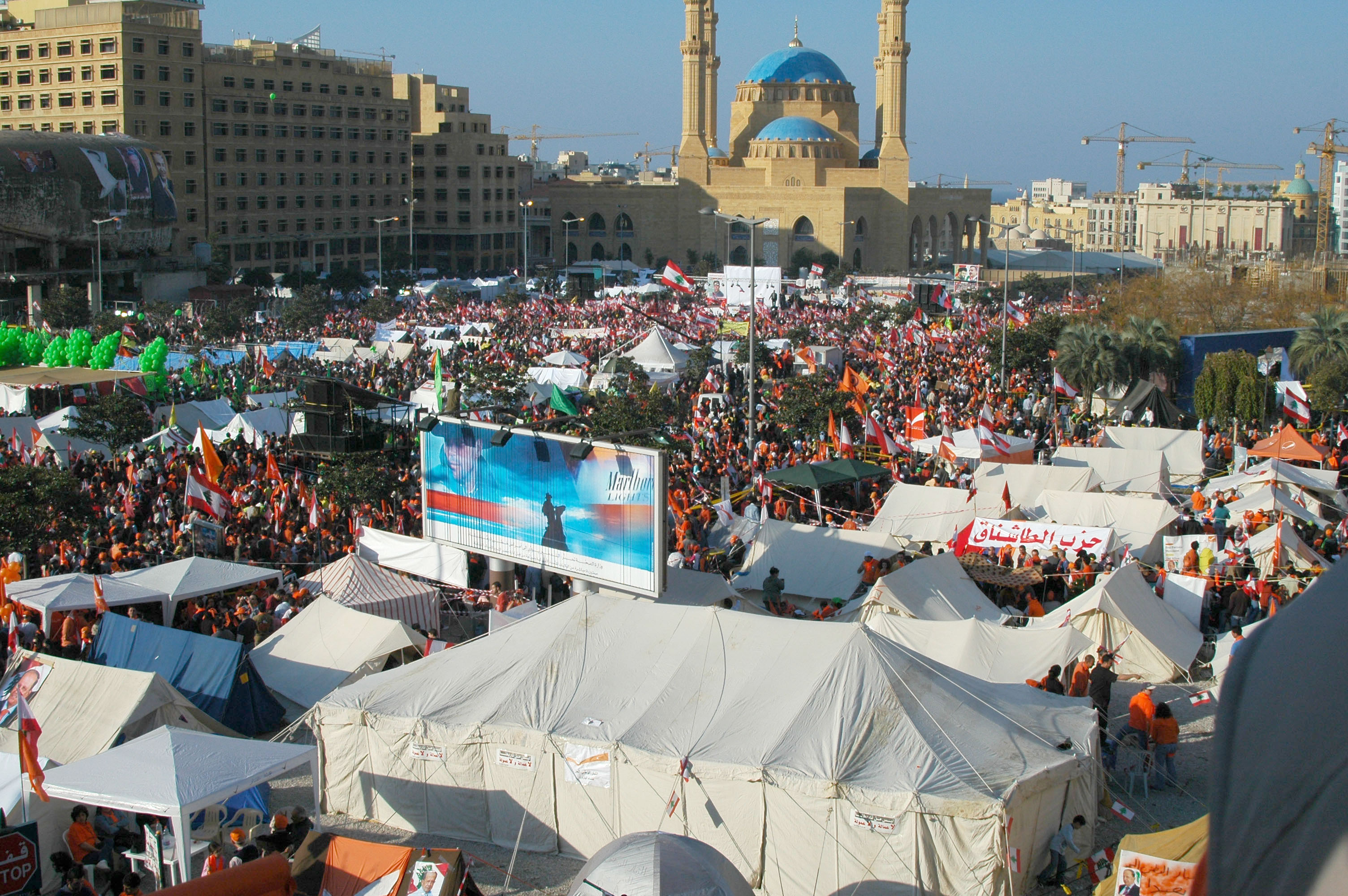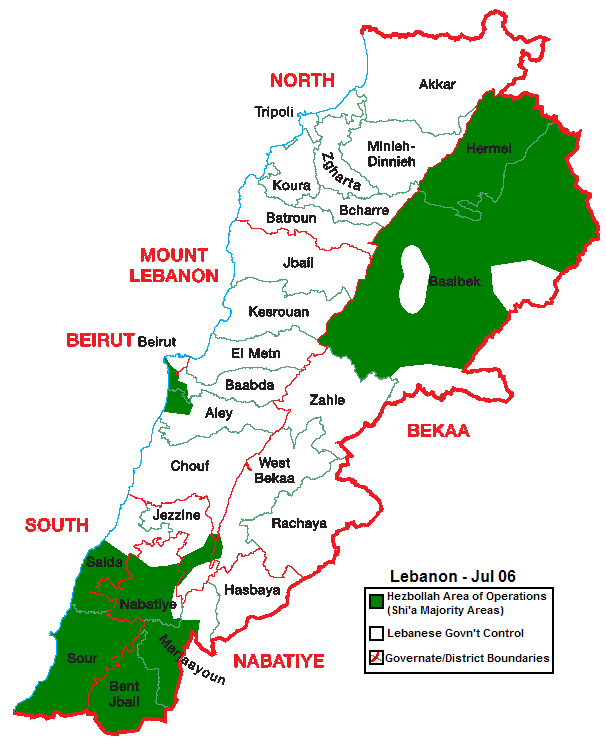
 Hezbollah along with
Hezbollah along with Amal Amal may refer to:
* Amal (given name)
* Åmål, a small town in Sweden
* Amal Movement, a Lebanese political party
** Amal Militia, Amal Movement's defunct militia
* Amal language of Papua New Guinea
* ''Amal'' (film), 2007, directed by Richi ...
is one of two major political parties in Lebanon that represent Shiite Muslims. Unlike Amal, whose support is predominantly in the south of the country, Hezbollah maintains broad-based support in all three areas of Lebanon with a majority Shia Muslim population: in the south, in Beirut and its surrounding area, and in the northern Beqaa valley and Hirmil region.Resistance and Development Bloc
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Comics
* Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm:
** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title
** ''T ...
. According to Daniel L. Byman, it is "the most powerful single political movement in Lebanon." Hezbollah, along with the Amal Movement, represents most of Lebanese Shi'a
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad designated Ali, ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his S ...
. However, unlike Amal, Hezbollah has not disarmed. Hezbollah participates in the Parliament of Lebanon.
Political alliances
Hezbollah has been one of the main parties of the March 8 Alliance since March 2005. Although Hezbollah had joined the new government in 2005, it remained staunchly opposed to the March 14 Alliance. On 1 December 2006, these groups began a series of political protests and sit-in
A sit-in or sit-down is a form of direct action that involves one or more people occupying an area for a protest, often to promote political, social, or economic change. The protestors gather conspicuously in a space or building, refusing to mo ...
s in opposition to the government of Prime Minister Fouad Siniora
Fouad Siniora ( ar, فؤاد السنيورة, translit=Fu'ād as-Sanyūrah; born 19 July 1943) is a Lebanese politician, a former Prime Minister of Lebanon, a position he held from 19 July 2005 to 25 May 2008. He stepped down on 9 November 2009 ...
.Michel Aoun
Michel Naim Aoun ( ar, ميشال نعيم عون ; born 30 September 1933) is a Lebanese politician and former military general who served as the President of Lebanon from 31 October 2016 until 30 October 2022.
Born in Haret Hreik to a Mar ...
and Hassan Nasrallah met in Mar Mikhayel Church, Chiyah, and signed a memorandum of understanding between Free Patriotic Movement and Hezbollah organizing their relation and discussing Hezbollah's disarmament with some conditions. The agreement also discussed the importance of having normal diplomatic relations with Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and the request for information about the Lebanese political prisoners in Syria and the return of all political prisoners and diaspora in Israel.
After this event, Aoun and his party became part of the March 8 Alliance.Lebanese Army
)
, founded = 1 August 1945
, current_form = 1991
, disbanded =
, branches = Lebanese Ground ForcesLebanese Air Force Lebanese Navy
, headquarters = Yarze, Lebanon
, flying_hours =
, websit ...
.Doha Agreement Doha Agreement may refer to:
*Doha Agreement (2008), agreement between rival Lebanese factions
*Fatah–Hamas Doha Agreement, 2012
*Doha Agreement (2020) Doha Agreement may refer to:
*Doha Agreement (2008), agreement between rival Lebanese faction ...
on 21 May 2008, to end the 18-month political feud that exploded into fighting and nearly drove the country to a new civil war.Fouad Siniora
Fouad Siniora ( ar, فؤاد السنيورة, translit=Fu'ād as-Sanyūrah; born 19 July 1943) is a Lebanese politician, a former Prime Minister of Lebanon, a position he held from 19 July 2005 to 25 May 2008. He stepped down on 9 November 2009 ...
on 11 July 2008, with Hezbollah controlling one ministerial and eleven of thirty cabinet places.2018 Lebanese general election
General elections were held in Lebanon on 6 May 2018. Although originally scheduled for 2013, the election was postponed three times in 2013, 2014 and 2017 under various pretexts, including the security situation, the failure of the Parliament ...
, Hezbollah general secretary Hassan Nasrallah presented the names of the 13 Hezbollah candidates.[''Al-Monitor''. ]
Lebanon's new electoral law could spell trouble for traditional parties
' On 22 March 2018, Nasrallah issued a statement outlining the main priorities for the parliamentary bloc of the party, Loyalty to the Resistance, in the next parliament.[Al-Manar. ]
Sayyed Nasrallah Announces Hezbollah Electoral Platform: Combating Corruption Priority
' He stated that rooting out corruption would be the foremost priority of the Loyalty to the Resistance bloc.[ The electoral slogan of the party was 'We will construct and we will protect'.][''L'Orient Le Jour''. ]
Les slogans électoraux de 2018 : un gros flop ?
'' Finally Hezbollah held 12 seats and its alliance won the election by gaining 70 out of 128 seats of Parliament of Lebanon.
Media operations
Hezbollah operates a satellite television station, Al-Manar TV ("the Lighthouse"), and a radio station, al-Nour ("the Light").Gaza
Gaza may refer to:
Places Palestine
* Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea
** Gaza City, a city in the Gaza Strip
** Gaza Governorate, a governorate in the Gaza Strip Lebanon
* Ghazzeh, a village in ...
, the West Bank, and Iraq.[Commission of the European Communitie]
Commission document SEC(2006) 160
. Retrieved 31 July 2006.
Materials aimed at instilling principles of nationalism and Islam in children are an aspect of Hezbollah's media operations. The Hezbollah Central Internet Bureau released a video game in 2003 entitled '' Special Force'' and a sequel in 2007 in which players are rewarded with points and weapons for killing Israelis. In 2012, Al-Manar aired a television special praising an 8-year-old boy who raised money for Hezbollah and said: "When I grow up, I will be a communist resistance warrior with Hezbollah, fighting the United States and Israel, I will tear them to pieces and drive them out of Lebanon, the Golan and Palestine, which I love very dearly."
Secret services
Hezbollah's secret services have been described as "one of the best in the world", and have even infiltrated the Israeli army
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; he, צְבָא הַהֲגָנָה לְיִשְׂרָאֵל , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the State of Israel. It consists of three service branc ...
. Hezbollah's secret services collaborate with the Lebanese intelligence agencies
Lebanese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Lebanese Republic
* Lebanese people, people from Lebanon or of Lebanese descent
* Lebanese Arabic, the colloquial form of Arabic spoken in Lebanon
* Lebanese culture
* Lebanese cuisin ...
.Ansariya ambush
The Ansariya ambush took place during the conflict between the Israel Defense Forces occupying South Lebanon and the Islamic Resistance movement of Hizbullah. A unit from the Israeli Navy’s special operation unit, Shayetet 13, on mission in Sou ...
; and the 2000 kidnapping of alleged Mossad agent Elhanan Tannenbaum.
Armed strength
Hezbollah does not reveal its armed strength. The Dubai-based Gulf Research Centre estimated that Hezbollah's armed wing comprises 1,000 full-time Hezbollah members, along with a further 6,000–10,000 volunteers.Fars News Agency
The Fars News Agency is a news agency in Iran managed by the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), an armed wing loyal to Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei. While it describes itself as "Iran's leading independent news agency", it is widely descr ...
, Hezbollah has up to 65,000 fighters. It is often described as more militarily powerful than the Lebanese Army. Israeli commander Gui Zur called Hezbollah "by far the greatest guerrilla group in the world".
In 2010, Hezbollah was believed to have 45,000 rockets. Israeli Defense Forces Chief of Staff Gadi Eisenkot said that Hezbollah possesses "tens of thousands" of long- and short-range rockets, drones, advanced computer encryption capabilities, as well as advanced defense capabilities like the SA-6 anti-aircraft missile system.
Hezbollah possesses the Katyusha-122 rocket, which has a range of 29 km (18 mi) and carries a 15-kg (33-lb) warhead. Hezbollah also possesses about 100 long-range missiles. They include the Iranian-made Fajr-3 and Fajr-5
The Fajr-5 (rarely Fadjr-5, fa, فجر-۵, "Dawn") is an Iranian 333 mm long-range multiple launch rocket system (MLRS). The Fajr-5 was developed during the 1990s and has since been exported to various armed actors in the Middle East.
The F ...
, the latter with a range of , enabling it to strike the Israeli port of Haifa, and the Zelzal-1, with an estimated range, which can reach Tel Aviv. Fajr-3 missiles have a range of and a 45-kg (99-lb) warhead, and Fajr-5 missiles, which extend to , also hold 45-kg (99-lb) warheads.Scud
A Scud missile is one of a series of tactical ballistic missiles developed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It was exported widely to both Second World, Second and Third World, Third World countries. The term comes from the NATO reporti ...
missiles that were provided to them by Syria. Syria denied the reports.
According to various reports, Hezbollah is armed with anti-tank guided missiles, namely, the Russian-made AT-3 Sagger, AT-4 Spigot
The 9K111 ''Fagot'' (russian: Фагот; "bassoon") is a second-generation tube-launched semi-automatic command to line of sight (SACLOS) wire-guided anti-tank missile system of the Soviet Union for use from ground or vehicle mounts. The 9K111 Fa ...
, AT-5 Spandrel, AT-13 Saxhorn-2 'Metis-M', АТ-14 Spriggan 'Kornet'; Iranian-made Ra'ad (version of AT-3 Sagger), Towsan (version of AT-5 Spandrel), Toophan (version of BGM-71 TOW); and European-made MILAN missiles. These weapons have been used against IDF soldiers, causing many of the deaths during the 2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War, also called the 2006 Israel–Hezbollah War and known in Lebanon as the July War ( ar, حرب تموز, ''Ḥarb Tammūz'') and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War ( he, מלחמת לבנון השנייה, ''Milhemet Leva ...
. A small number of Saeghe-2s (Iranian-made version of M47 Dragon) were also used in the war.
For air defense, Hezbollah has anti-aircraft weapons that include the ZU-23 artillery and the man-portable, shoulder-fired SA-7
The 9K32 Strela-2 (russian: Cтрела, "arrow"; NATO reporting name SA-7 Grail) is a light-weight, shoulder-fired, surface-to-air missile (or MANPADS) system. It is designed to target aircraft at low altitudes with passive infrared homing gui ...
and SA-18 surface-to-air missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft syst ...
(SAM). One of the most effective weapons deployed by Hezbollah has been the C-802
The YJ-83 (; NATO reporting name: CSS-N-8 Saccade) is a Chinese subsonic anti-ship cruise missile. It is manufactured by the China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation Third Academy.Gromley et al.: page 101
Description
The YJ-83 uses mi ...
anti-ship missile.
In April 2010, U.S. Secretary of Defense Robert Gates claimed that the Hezbollah has far more missiles and rockets than the majority of countries, and said that Syria and Iran are providing weapons to the organization. Israel also claims that Syria is providing the organization with these weapons. Syria has denied supplying these weapons and views these claims as an Israeli excuse for an attack. Leaked cables from American diplomats suggest that the United States has been trying unsuccessfully to prevent Syria from "supplying arms to Hezbollah in Lebanon", and that Hezbollah has "amassed a huge stockpile (of arms) since its 2006 war with Israel"; the arms were described as "increasingly sophisticated."Eilat
Eilat ( , ; he, אֵילַת ; ar, إِيلَات, Īlāt) is Israel's southernmost city, with a population of , a busy port and popular resort at the northern tip of the Red Sea, on what is known in Israel as the Gulf of Eilat and in Jordan ...
.[Israeli US envoy: Hizbullah has 15,000 rockets on border](_blank)
Jpost.com. Retrieved on 19 October 2010. The IDF has accused Hezbollah of storing these rockets beneath hospitals, schools, and civilian homes.
Military activities
Hezbollah has a military branch known as the Jihad Council,["Hezbollah: Hezbollah and the Recent Conflict."](_blank)
''ADL
Adl ( ar, عدل, ) is an Arabic word meaning 'justice', and is also one of the names of God in Islam. It is equal to the concept of ''Insaf'' انصاف (lit. sense of justice) in the Baháʼí Faith.
Adil ( ar, عادل, ), and Adeel ( ar, � ...
''. 29 September 2006. 26 June 2007. Since then both Israel and Hezbollah have asserted that the organization has gained in military strength.2006 Lebanon war
The 2006 Lebanon War, also called the 2006 Israel–Hezbollah War and known in Lebanon as the July War ( ar, حرب تموز, ''Ḥarb Tammūz'') and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War ( he, מלחמת לבנון השנייה, ''Milhemet Leva ...
, while the majority of Sunni, Druze and Christians believed that they should.Fouad Siniora
Fouad Siniora ( ar, فؤاد السنيورة, translit=Fu'ād as-Sanyūrah; born 19 July 1943) is a Lebanese politician, a former Prime Minister of Lebanon, a position he held from 19 July 2005 to 25 May 2008. He stepped down on 9 November 2009 ...
, guidelines state that Hezbollah enjoys the right to "liberate occupied lands." In 2009, a Hezbollah commander (speaking on condition of anonymity) said, " have far more rockets and missiles owthan we did in 2006."
Lebanese Resistance Brigades
The Lebanese Resistance Brigades ( ar, سرايا المقاومة اللبنانية ''Saraya al-Moukawama al-Lubnaniyya''), also known as the Lebanese Brigades to Resist the Israeli Occupation, were formed by Hezbollah in 1997 as a multifaith (Christian, Druze, Sunni and Shia) volunteer force to combat the Israeli occupation of Southern Lebanon. With the Israeli withdrawal from Lebanon in 2000, the organization was disbanded.
In 2009, the Resistance Brigades were reactivated, mainly comprising Sunni supporters from the southern city of Sidon. Its strength was reduced in late 2013 from 500 to 200–250 due to residents complaints about some fighters of the group exacerbating tensions with the local community.
The beginning of its military activities: the South Lebanon conflict
Hezbollah has been involved in several cases of armed conflict with Israel:
* During the 1982–2000 South Lebanon conflict, Hezbollah waged a guerrilla campaign against Israeli forces occupying Southern Lebanon. In 1982, the Palestine Liberation Organization
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO; ar, منظمة التحرير الفلسطينية, ') is a Palestinian nationalism, Palestinian nationalist political and militant organization founded in 1964 with the initial purpose of establ ...
(PLO) was based in Southern Lebanon and was firing Katyusha rockets into northern Israel from Lebanon. Israel invaded Lebanon to evict the PLO, and Hezbollah became an armed organization to expel the Israelis.
Alleged suicide attacks
 Between 1982 and 1986, there were 36 suicide attacks in Lebanon directed against American, French and Israeli forces by 41 individuals, killing 659.
Between 1982 and 1986, there were 36 suicide attacks in Lebanon directed against American, French and Israeli forces by 41 individuals, killing 659.April 1983 U.S. Embassy bombing
The April 18, 1983 United States embassy bombing was a suicide bombing in Beirut, Lebanon, that killed 32 Lebanese, 17 Americans, and 14 visitors and passers-by. The victims were mostly embassy and CIA staff members, but also included several US ...
(by the Islamic Jihad Organization),["Timeline of Hezbollah Violence."](_blank)
'' CAMERA: Committee for Accuracy in Middle East Reporting in America''. 17 July 2006. 18 November 2006. Later reprinted in ''On Campus'' magazine's Fall 2006 issue and attributed the article to author Gilead Ini.
* The 1983 Beirut barracks bombing
Early on a Sunday morning, October 23, 1983, two truck bombs struck buildings in Beirut, Lebanon, housing American and French service members of the Multinational Force in Lebanon (MNF), a military peacekeeping operation during the Lebanese ...
(by the Islamic Jihad Organization), that killed 241 U.S. marines, 58 French paratroopers and 6 civilians at the US and French barracks in Beirut[Hezbollah](_blank)
CFR. org Staff, the US Council on Foreign Relations
The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank
A think tank, or policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, mi ...
, 17 July 2006
* The 1983 Kuwait bombings
The 1983 Kuwait bombings were attacks on six key foreign and Kuwaiti installations on 12 December 1983, two months after the 1983 Beirut barracks bombing. The 90-minute coordinated attack on two embassies, the country's main airport, and petro- ...
in collaboration with the Iraqi Dawa Party.
* The 1984 United States embassy annex bombing
On September 20, 1984, the Shi'a Islamic militant group Hezbollah, with support and direction from the Islamic Republic of Iran, carried out a suicide car bombing targeting the U.S. embassy annex in East Beirut, Lebanon. The attack killed 24 pe ...
, killing 24.
* A spate of attacks on IDF troops and SLA militiamen in southern Lebanon.1992 Israeli Embassy attack in Buenos Aires
The attack on the Israeli embassy in Buenos Aires was a suicide bombing attack on the building of the Israeli embassy of Argentina, located in Buenos Aires, which was carried out on 17 March 1992. 29 civilians were killed in the attack and 242 ...
, killing 29, in Argentina.1994 AMIA bombing
The AMIA bombing occurred on 18 July 1994 in Buenos Aires, Argentina, and targeted the Asociación Mutual Israelita Argentina (AMIA; ), a Jewish Community Centre. Executed as a suicidal attack, a bomb-laden van was driven into the AMIA buildi ...
of a Jewish cultural centre, killing 85, in Argentina.[''Lebanon: Hezbollah and the Jan 15 Bombing''](_blank)
Stratfor, 15 January 2008
* In 2009, a Hezbollah plot in Egypt was uncovered, where Egyptian authorities arrested 49 men for planning attacks against Israeli and Egyptian targets in the Sinai Peninsula.
* The 2012 Burgas bus bombing, killing 6, in Bulgaria. Hezbollah denied responsibility.
During the Bosnian War
Hezbollah provided fighters to fight on the Bosnian Muslim side during the Bosnian War
The Bosnian War ( sh, Rat u Bosni i Hercegovini / Рат у Босни и Херцеговини) was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1992 and 1995. The war is commonly seen as having started ...
, as part of the broader Iranian involvement. "The Bosnian Muslim government is a client of the Iranians," wrote Robert Baer, a CIA agent stationed in Sarajevo during the war. "If it's a choice between the CIA and the Iranians, they'll take the Iranians any day." By war's end, public opinion polls showed some 86 percent Bosnian Muslims had a positive opinion of Iran. In conjunction, Hezbollah initially sent 150 fighters to fight against the Bosnian Serb Army, the Bosnian Muslims' main opponent in the war.[ All Shia foreign advisors and fighters withdrew from Bosnia at the end of conflict.
]
Conflict with Israel
* On 25 July 1993, following Hezbollah's killing of seven Israeli soldiers in southern Lebanon, Israel launched Operation Accountability (known in Lebanon as the Seven Day War), during which the IDF carried out their heaviest artillery and air attacks on targets in southern Lebanon since 1982. The aim of the operation was to eradicate the threat posed by Hezbollah and to force the civilian population north to Beirut so as to put pressure on the Lebanese Government to restrain Hezbollah.[ Cobban, Helena, ] Both sides agreed that civilians should not be targeted, which meant that Hezbollah would be allowed to continue its military activities against IDF forces inside Lebanon.
2000 Hezbollah cross-border raid
On 7 October 2000, three Israeli soldiers—Adi Avitan, Staff Sgt. Benyamin Avraham, and Staff Sgt. Omar Sawaidwere—were abducted by Hezbollah while patrolling the border between the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights and Lebanon. The soldiers were killed either during the attack or in its immediate aftermath. Israel Defense Minister Shaul Mofaz has, however, said that Hezbollah abducted the soldiers and then killed them. The bodies of the slain soldiers were exchanged for Lebanese prisoners in 2004.
2006 Lebanon War
 The 2006 Lebanon War was a 34-day military conflict in Lebanon and northern Israel. The principal parties were Hezbollah paramilitary forces and the Israeli military. The conflict was precipitated by a cross-border raid during which Hezbollah kidnapped and killed Israeli soldiers. The conflict began on 12 July 2006 when Hezbollah militants fired rockets at Israeli border towns as a diversion for an anti-tank missile attack on two armored Humvees patrolling the Israeli side of the border fence, killing three, injuring two, and seizing two Israeli soldiers.
The 2006 Lebanon War was a 34-day military conflict in Lebanon and northern Israel. The principal parties were Hezbollah paramilitary forces and the Israeli military. The conflict was precipitated by a cross-border raid during which Hezbollah kidnapped and killed Israeli soldiers. The conflict began on 12 July 2006 when Hezbollah militants fired rockets at Israeli border towns as a diversion for an anti-tank missile attack on two armored Humvees patrolling the Israeli side of the border fence, killing three, injuring two, and seizing two Israeli soldiers.airstrike
An airstrike, air strike or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighters, heavy bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters and drones. The offic ...
s and artillery fire on targets in Lebanon that damaged Lebanese infrastructure, including Beirut's Rafic Hariri International Airport (which Israel said that Hezbollah used to import weapons and supplies), an air and naval blockade, and a ground invasion of southern Lebanon. Hezbollah then launched more rockets into northern Israel and engaged the Israel Defense Forces in guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or Irregular military, irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, Raid (military), raids ...
from hardened positions. The war continued until 14 August 2006. Hezbollah was responsible for thousands of Katyusha rocket attacks against Israeli civilian towns and cities in northern Israel, which Hezbollah said were in retaliation for Israel's killing of civilians and targeting Lebanese infrastructure. The conflict is believed to have killed 1,191–1,300 Lebanese citizens including combatants[Reuters, 12 September 2006; Al-Hayat (London), 13 September 2006]["Country ReportLebanon," The Economist Intelligence Unit, no. 4 (2006), pp. 3–6.]
2010 gas field claims
In 2010, Hezbollah claimed that the Dalit and Tamar gas field, discovered by Noble Energy roughly west of Haifa in Israeli exclusive economic zone, belong to Lebanon, and warned Israel against extracting gas from them. Senior officials from Hezbollah warned that they would not hesitate to use weapons to defend Lebanon's natural resources. Figures in the March 14 Forces
The March 14 Alliance ( ar, تحالف 14 آذار, taḥāluf 14 adhār}), named after the date of the Cedar Revolution, is a coalition of political parties and independents in Lebanon formed in 2005 that are united by their anti- Syrian stanc ...
stated in response that Hezbullah was presenting
another excuse to hold on to its arms. Lebanese MP Antoine Zahra said that the issue is another item "in the endless list of excuses" meant to justify the continued existence of Hezbullah's arsenal.
2011 attack in Istanbul
In July 2011, Italian newspaper ''Corriere della Sera'' reported, based on American and Turkish sources,[
]Quoting Washington sources, the paper said the attack was meant to avenge the death of Iranian nuclear scientist Masoud Ali Mohammadi who was killed last year. ... Turkish intelligence first attributed the Istanbul attack ... to the Kurdish resistance, but later concluded that Hezbollah, working on behalf of Iran, had organized it. According to the report, three Hezbollah operatives arrived in Istanbul from Beirut to assassinate Kimchi."Report: Hezbollah tried to kill Israeli consul."
''Ynetnews''. 18 July 2011.
2012 planned attack in Cyprus
In July 2012, a Lebanese man was detained by Cyprus police on possible charges relating to terrorism laws for planning attacks against Israeli tourists. According to security officials, the man was planning attacks for Hezbollah in Cyprus and admitted this after questioning. The police were alerted about the man due to an urgent message from Israeli intelligence. The Lebanese man was in possession of photographs of Israeli targets and had information on Israeli airlines flying back and forth from Cyprus, and planned to blow up a plane or tour bus.
2012 Burgas attack
Following an investigation into the 2012 Burgas bus bombing terrorist attack against Israeli citizens in Bulgaria, the Bulgarian government officially accused the Lebanese-militant movement Hezbollah of committing the attack.[Tsvetelia Tsolov]
"Bulgaria blames Hezbollah in bomb attack on Israeli tourists,"
Reuters (5 February 2013). Retrieved 5 May 2013. Five Israeli citizens, the Bulgarian bus driver, and the bomber were killed. The bomb exploded as the Israeli tourists boarded a bus from the airport to their hotel.
Tsvetan Tsvetanov
Tsvetan Genchev Tsvetanov ( bg, Цветан Генчев Цветанов; born 8 April 1965) is a Bulgarian politician and former government official. A former security deputy mayor of Sofia, he was, until 2009, the chairman of the GERB party. ...
, Bulgaria's interior minister, reported that the two suspects responsible were members of the militant wing of Hezbollah; he said the suspected terrorists entered Bulgaria on 28 June and remained until 18 July. Israel had already previously suspected Hezbollah for the attack. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu called the report "further corroboration of what we have already known, that Hezbollah and its Iranian patrons are orchestrating a worldwide campaign of terror that is spanning countries and continents." Netanyahu said that the attack in Bulgaria was just one of many that Hezbollah and Iran have planned and carried out, including attacks in Thailand, Kenya, Turkey, India, Azerbaijan, Cyprus and Georgia.
2015 Shebaa farms incident
In response to an attack against a military convoy comprising Hezbollah and Iranian officers on 18 January 2015 at Quneitra in south of Syria, Hezbollah launched an ambush on 28 January against an Israeli military convoy in the Israeli-occupied Shebaa Farms with anti-tank missiles against two Israeli vehicles patrolling the border, killing 2 and wounding 7 Israeli soldiers and officers, as confirmed by Israeli military.
Assassination of Rafic Hariri
On 14 February 2005, former Lebanese Prime Minister Rafic Hariri was killed, along with 21 others, when his motorcade was struck by a roadside bomb in Beirut. He had been PM during 1992–1998 and 2000–2004. In 2009, the United Nations special tribunal investigating the murder of Hariri reportedly found evidence linking Hezbollah to the murder.
In August 2010, in response to notification that the UN tribunal would indict some Hezbollah members, Hassan Nasrallah said Israel was looking for a way to assassinate Hariri as early as 1993 in order to create political chaos that would force Syria to withdraw from Lebanon, and to perpetuate an anti-Syrian atmosphere n Lebanon
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''.
History
...
in the wake of the assassination. He went on to say that in 1996 Hezbollah apprehended an agent working for Israel by the name of Ahmed Nasrallah—no relation to Hassan Nasrallah—who allegedly contacted Hariri's security detail and told them that he had solid proof that Hezbollah was planning to take his life. Hariri then contacted Hezbollah and advised them of the situation. Saad Hariri responded that the UN should investigate these claims.
On 30 June 2011, the Special Tribunal for Lebanon, established to investigate the death of Hariri, issued arrest warrant
An arrest warrant is a warrant issued by a judge or magistrate on behalf of the state, which authorizes the arrest and detention of an individual, or the search and seizure of an individual's property.
Canada
Arrest warrants are issued by a j ...
s against four senior members of Hezbollah, including Mustafa Badr Al Din.
Involvement in the Syrian Civil War
Hezbollah has long been an ally of the Ba'ath government of Syria, led by the Al-Assad family. Hezbollah has helped the Syrian government
Government of the Syrian Arab Republic is the union government created by the constitution of Syria where by the president is the head of state and the prime minister is the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Syr ...
during the Syrian civil war in its fight against the Syrian opposition
The Syrian opposition ( ar, المعارضة السورية ', ) is the political structure represented by the Syrian National Coalition and associated Syrian anti-Assad groups with certain territorial control as an alternative Syrian gover ...
, which Hezbollah has described as a Zionist plot to destroy its alliance with al-Assad against Israel.n Syria
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''.
History
...
inhabited by Shiites of Lebanese citizenship". Nasrallah said that Hezbollah fighters have died in Syria doing their "jihadist duties".
In 2012, Hezbollah fighters crossed the border from Lebanon and took over eight villages in the Al-Qusayr District of Syria.Free Syrian Army
The Free Syrian Army (FSA) ( ar, الجيش السوري الحر, al-jaysh as-Sūrī al-ḥur) is a loose faction in the Syrian Civil War founded on 29 July 2011 by officers of the Syrian Armed Forces with the goal of bringing down the governm ...
(FSA). An FSA spokesman said, "Hezbollah's invasion is the first of its kind in terms of organisation, planning and coordination with the Syrian regime's air force". Hezbollah said three Lebanese Shiites, "acting in self-defense", were killed in the clashes with the FSA.attack
Attack may refer to:
Warfare and combat
* Offensive (military)
* Charge (warfare)
* Attack (fencing)
* Strike (attack)
* Attack (computing)
* Attack aircraft
Books and publishing
* ''The Attack'' (novel), a book
* '' Attack No. 1'', comic an ...
on weapons destined for Hezbollah occurred in May of the same year.
The leaders of the March 14 alliance and other prominent Lebanese figures called on Hezbollah to end its involvement in Syria and said it is putting Lebanon at risk.["March 14, PSP slam Hezbollah activities in Syria"]
'' The Daily Star'', 19 February 2013. Retrieved 26 February 2013. Subhi al-Tufayli
Subhi al-Tufayli ( ar, صبحي الطفيلي) (born 1948) was the first Secretary-General or leader of Hezbollah for a year. Al-Tufayli is a Shia Islamist, but is a very vocal critic of Iran and the current Hezbollah leadership. He has been an ...
, Hezbollah's former leader, said "Hezbollah should not be defending the criminal regime that kills its own people and that has never fired a shot in defense of the Palestinians." He said "those Hezbollah fighters who are killing children and terrorizing people and destroying houses in Syria will go to hell". The Consultative Gathering, a group of Shia and Sunni leaders in Baalbek
Baalbek (; ar, بَعْلَبَكّ, Baʿlabakk, Syriac-Aramaic: ܒܥܠܒܟ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In Greek and Roman ...
- Hermel, also called on Hezbollah not to "interfere" in Syria. They said, "Opening a front against the Syrian people and dragging Lebanon to war with the Syrian people is very dangerous and will have a negative impact on the relations between the two."Walid Jumblatt
Walid Kamal Jumblatt ( ar, وليد جنبلاط; born 7 August 1949) is a Lebanese Druze politician and former militia commander who has been leading the Progressive Socialist Party since 1977. While leading the Lebanese National Resistance Fr ...
, leader of the Progressive Socialist Party, also called on Hezbollah to end its involvementIslamic extremists
Islamic extremism, Islamist extremism, or radical Islam, is used in reference to extremist beliefs and behaviors which are associated with the Islamic religion. These are controversial terms with varying definitions, ranging from academic und ...
and "pledged that his group will not allow Syrian militants to control areas that border Lebanon".
Involvement in Iranian-led intervention in Iraq
Beginning in July 2014, Hezbollah sent an undisclosed number of technical advisers and intelligence analysts to Baghdad in support of the Iranian intervention in Iraq (2014–present). Shortly thereafter, Hezbollah commander Ibrahim al-Hajj was reported killed in action near Mosul.
Latin America operations
Hezbollah operations in South America began in the late 20th century, centered around the Arab population which had moved there following the 1948 Arab-Israeli War and the 1985 Lebanese Civil War. In 2002, Hezbollah was operating openly in Ciudad del Este. Beginning in 2008 the United States Drug Enforcement Agency began with Project Cassandra to work against Hezbollah activities in regards to Latin American drug trafficking. The investigation by the DEA found that Hezbollah made about a billion dollars a year and trafficked thousands of tons of cocaine into the United States. Another destination for cocaine trafficking done by Hezbollah are nations within the Gulf Cooperation Council. In 2013, Hezbollah was accused of infiltrating South America and having ties with Latin American drug cartels. One area of operations is in the region of the Triple Frontier
The Triple Frontier ( es, Triple Frontera, pt, Tríplice Fronteira) is a tri-border area along the junction of Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay, where the Iguazú and Paraná rivers converge. Near the confluence are the cities of Puerto Igu ...
, where Hezbollah has been alleged to be involved in the trafficking of cocaine; officials with the Lebanese embassy in Paraguay have worked to counter American allegations and extradition attempts. In 2016, it was alleged that money gained from drug sales was used to purchase weapons in Syria. In 2018, ''Infobae'' reported that Hezbollah was operating in Colombia under the name Organization of External Security. That same year, Argentine police made arrest to individuals alleged to be connected to Hezbollah's criminal activities within the nation. It is also alleged that Venezuela aids Hezbollah in its operations in the region. One particular form of involvement is money laundering
Money laundering is the process of concealing the origin of money, obtained from illicit activities such as drug trafficking, corruption, embezzlement or gambling, by converting it into a legitimate source. It is a crime in many jurisdictions ...
.
United States operations
Ali Kourani, the first Hezbollah operative to be convicted and sentenced in the United States, was under investigation since 2013 and worked to provide targeting and terrorist recruiting information to Hezbollah's Islamic Jihad Organization. The organization had recruited a former resident of Minnesota and a military linguist, Mariam Tala Thompson, who disclosed "identities of at least eight clandestine human assets; at least 10 U.S. targets; and multiple tactics, techniques and procedures" before she was discovered and successfully prosecuted in a U.S. court.
Other
In 2010, Ahbash and Hezbollah members were involved in a street battle which was perceived to be over parking issues, both groups later met to form a joint compensation fund for the victims of the conflict.
Financial/economy
During the September 2021 fuel shortage, Hezbollah received a convoy of 80 tankers carrying oil/diesel fuel from Iran.
Attacks on Hezbollah leaders
Hezbollah has also been the target of bomb attacks and kidnappings. These include:
* In the 1985 Beirut car bombing
On 8 March 1985, a car bomb exploded between 9 and 45 metres from the house of Shia cleric Sayyed Mohammad Hussein Fadlallah in Beirut, Lebanon, in a failed assassination attempt by a Lebanese counter-terrorism unit linked to the Central Intelli ...
, Hezbollah leader Mohammad Hussein Fadlallah was targeted, but the assassination attempt failed.
* On 28 July 1989, Israeli commandos kidnapped Sheikh Abdel Karim Obeid, the leader of Hezbollah. This action led to the adoption of UN Security Council resolution 638, which condemned all hostage takings by all sides.
* On 16 February 1992, Israeli helicopters attacked a motorcade in southern Lebanon, killing the Hezbollah leader Abbas al-Musawi, his wife, son, and four others.security zone
Security is protection from, or resilience against, potential harm (or other unwanted coercive change) caused by others, by restraining the freedom of others to act. Beneficiaries (technically referents) of security may be of persons and social ...
10km east of Tyre. Yasin was a senior military commander in southern Lebanon. His companion in the car was also killed. An Israeli civilian was killed and fifteen wounded in the retaliatory rocket fire.
* On 12 February 2008, Imad Mughnieh
Imad Fayez Mughniyeh ( ar, عماد فايز مغنية; 7 December 1962 – 12 February 2008), alias al-Hajj Radwan (), was the founding member of Lebanon's Islamic Jihad Organization and number two in Hezbollah's leadership. Information about ...
was killed by a car bomb in Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, Syria.
* On 3 December 2013, senior military commander Hassan al-Laqis
Hassan Hawlo al-Laqqis ( ar, حسان اللقيس; ?? – 4 December 2013) was Hezbollah’s chief logistics officer and military commander in Lebanon. Laqqis was assassinated when two gunmen shot him four times in the head and neck inside his c ...
was shot outside his home, two miles (three kilometers) southwest of Beirut. He died a few hours later on 4 December.Mohammad Ali Allahdadi
Mohammad-Ali Allahdadi ( fa, محمدعلی اللهدادی; 1963 – January 18, 2015) was a brigadier general in the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps and a military officer in the Quds Force.
A veteran of Iran–Iraq War, he was killed in ...
, were killed.Syrian opposition
The Syrian opposition ( ar, المعارضة السورية ', ) is the political structure represented by the Syrian National Coalition and associated Syrian anti-Assad groups with certain territorial control as an alternative Syrian gover ...
.
Targeting policy
After the September 11, 2001 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial ...
, Hezbollah condemned al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
for targeting civilians in the World Trade Center,massacres in Algeria
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
by Armed Islamic Group, Al-Gama'a al-Islamiyya attacks on tourists in Egypt, the murder of Nick Berg, and ISIL attacks in Paris.
Although Hezbollah has denounced certain attacks on civilians, some people accuse the organization of the bombing of an Argentine synagogue in 1994. Argentine prosecutor Alberto Nisman, Marcelo Martinez Burgos, and their "staff of some 45 people" said that Hezbollah and their contacts in Iran were responsible for the 1994 bombing of a Jewish cultural center in Argentina, in which " ghty-five people were killed and more than 200 others injured."Daniel Benjamin
Daniel Benjamin (born October 16, 1961) is an American diplomat and journalist and was the Coordinator for Counterterrorism at the United States Department of State from 2009 to 2012, appointed by Secretary Hillary Clinton. Benjamin was the dire ...
warned that Hezbollah may attack Europe at any time without any warning. Benjamin said, "Hezbollah maintains a presence in Europe and its recent activities demonstrate that it is not constrained by concerns about collateral damage or political fallout that could result from conducting operations there ... We assess that Hezbollah could attack in Europe or elsewhere at any time with little or no warning" and that Hezbollah has "stepped up terrorist campaigns around the world."
Foreign relations
Hezbollah has close relations with Iran. It also has ties with the leadership in Syria, specifically President Hafez al-Assad
Hafez al-Assad ', , (, 6 October 1930 – 10 June 2000) was a Syrian statesman and military officer who served as President of Syria from taking power in 1971 until his death in 2000. He was also Prime Minister of Syria from 1970 to 1 ...
(until his death in 2000) supported it.Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
Palestinian group. Furthermore, Hezbollah was a strong supporter of the second Intifada
The Second Intifada ( ar, الانتفاضة الثانية, ; he, האינתיפאדה השנייה, ), also known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada ( ar, انتفاضة الأقصى, label=none, '), was a major Palestinian uprising against Israel. ...
.Al Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military targets in various countr ...
, although Hezbollah's leaders deny these allegations.Abu Musab al-Zarqawi
Abu Musab al-Zarqawi ( ar, أَبُو مُصْعَبٍ ٱلزَّرْقَاوِيُّ, ', ''Father of Musab, from Zarqa''; ; October 30, 1966 – June 7, 2006), born Ahmad Fadeel al-Nazal al-Khalayleh (, '), was a Jordanian jihadist who ran a t ...
and Wahhabi clerics, consider Hezbollah to be apostate. But United States intelligence officials speculate that there has been contact between Hezbollah and low-level al-Qaeda figures who fled Afghanistan for Lebanon. However, Michel Samaha, Lebanon's former minister of information, has said that Hezbollah has been an important ally of the government in the war against terrorist groups, and described the "American attempt to link Hezbollah to al-Qaeda" to be "astonishing".
Public opinion
According to Michel Samaha, Lebanon's minister of information, Hezbollah is seen as "a legitimate resistance organization that has defended its land against an Israeli occupying force and has consistently stood up to the Israeli army".2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War, also called the 2006 Israel–Hezbollah War and known in Lebanon as the July War ( ar, حرب تموز, ''Ḥarb Tammūz'') and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War ( he, מלחמת לבנון השנייה, ''Milhemet Leva ...
, 87 percent of Lebanese support Hezbollah's "retaliatory attacks on northern Israel", a rise of 29 percentage points from a similar poll conducted in February. More striking, however, was the level of support for Hezbollah's resistance from non-Shiite communities. Eighty percent of Christians polled supported Hezbollah, along with 80 percent of Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
and 89 percent of Sunnis
Sunni Islam () is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia ...
.2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War, also called the 2006 Israel–Hezbollah War and known in Lebanon as the July War ( ar, حرب تموز, ''Ḥarb Tammūz'') and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War ( he, מלחמת לבנון השנייה, ''Milhemet Leva ...
, compared to 66% who blamed Israel to some degree. Additionally, 76% disapproved of the military action Hezbollah took in Israel, compared to 38% who disapproved of Israel's military action in Lebanon.2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War, also called the 2006 Israel–Hezbollah War and known in Lebanon as the July War ( ar, حرب تموز, ''Ḥarb Tammūz'') and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War ( he, מלחמת לבנון השנייה, ''Milhemet Leva ...
, compared to 31% who blamed Israel to some degree.["Israel/Palestinians."](_blank)
PollingReport.com. 10 December 2006. Another August 2006 poll by CNN showed that 69% of the 1,047 Americans polled believed that Hezbollah is unfriendly towards, or an enemy of, the United States.Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
Muslims held an unfavorable opinion of the group.
Some public opinion has started to turn against Hezbollah for their support of Syrian President Assad's attacks on the opposition movement in Syria. Crowds in Cairo shouted out against Iran and Hezbollah, at a public speech by Hamas President Ismail Haniya in February 2012, when Hamas changed its support to the Syrian opposition.
View of Hezbollah
A more recent poll by the pro-Israel, American Washington Institute for Near East Policy declared that support for Hezbollah is declining significantly. Below is a table of the results of their polls from November 2020.
Designation as a terrorist organization or resistance movement
Hezbollah's status as a legitimate political party, a terrorist group, a resistance movement, or some combination thereof is a contentious issue.Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, E ...
, with the exception of Iraq and Lebanon, where Hezbollah is the most powerful political party.Ben Wedeman
Benjamin C. Wedeman (born September 1, 1960) is an American journalist and war correspondent. He is a CNN senior international correspondent based in Rome. He has been with the network since 1994, and has earned multiple Emmy Awards and Edward Mu ...
br>Arab League states condemn Hezbollah as 'terrorist organization'
CNN News 20 November 2017.[ Hezbollah maintains that it is a legitimate resistance movement fighting for the liberation of Lebanese territory.
There is a "wide difference" between American and Arab perception of Hezbollah.][Designation of Foreign Terrorist Organizations](_blank)
Department of State, Federal Register, Vol. 62, No. 195, 8 October 1997 lists the entire group as such. Russia has considered Hezbollah a legitimate sociopolitical organization,[' Russia says Hezbollah, Hamas not terror groups,'](_blank)
The Times of Israel 16 November 2015. and the People's Republic of China remains neutral and maintains contacts with Hezbollah.
In the Western world
The United States Department of State has designated Hezbollah a terrorist organization since 1995. The group remains on Foreign Terrorist Organization and Specially Designated Terrorist lists. According to the Congressional Research Service, "The U.S. government holds Hezbollah responsible for a number of attacks and hostage takings targeting Americans in Lebanon during the 1980s, including the bombing of the U.S. Embassy in Beirut in April 1983 and the bombing of the U.S. Marine barracks in October 1983, which together killed 258 Americans. Hezbollah's operations outside of Lebanon, including its participation in bombings of Israeli and Jewish targets in Argentina during the 1990s and more recent training and liaison activities with Shiite insurgents in Iraq, have cemented the organization's reputation among U.S. policy makers as a capable and deadly adversary with potential global reach."
The United Kingdom was the first government to attempt to make a distinction between Hezbollah's political and military wings, declaring the latter a terrorist group in July 2008 after Hezbollah confirmed its association with Imad Mughniyeh. In 2012, British "Foreign Minister William Hague urged the European Union to place Hezbollah's military wing on its list of terrorist organizations." The United States also urged the EU to classify Hezbollah as a terrorist organization. In light of findings implicating Hezbollah in the bus bombing in Burgas, Bulgaria in 2012, there was renewed discussion within the European Union to label Hezbollah's military wing as a terrorist group. On 22 July 2013, the European Union agreed to blacklist Hezbollah's military wing over concerns about its growing role in the Syrian conflict.
In the midst of the 2006 conflict between Hezbollah and Israel, Russia's government declined to include Hezbollah in a newly released list of terrorist organizations, with Yuri Sapunov, the head of anti-terrorism for the , saying that they list only organizations which represent "the greatest threat to the security of our country". Prior to the release of the list, Russian Defense Minister Sergei Ivanov called "on Hezbollah to stop resorting to any terrorist methods, including attacking neighboring states."
The Quartet's fourth member, the United Nations, does not maintain such a list, however, the United Nations has made repeated calls for Hezbollah to disarm and accused the group of destabilizing the region and causing harm to Lebanese civilians. Human rights organizations Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says it has more than ten million members and sup ...
and Human Rights Watch have accused Hezbollah of committing war crimes against Israeli civilians.
Argentine prosecutors hold Hezbollah and their financial supporters in Iran responsible for the 1994 AMIA Bombing
The AMIA bombing occurred on 18 July 1994 in Buenos Aires, Argentina, and targeted the Asociación Mutual Israelita Argentina (AMIA; ), a Jewish Community Centre. Executed as a suicidal attack, a bomb-laden van was driven into the AMIA buildi ...
of a Jewish cultural center, described by the Associated Press as "the worst terrorist attack on Argentine soil," in which " ghty-five people were killed and more than 200 others injured."[ United Kingdom,][ the Netherlands,]Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
Director of National Intelligence
The director of national intelligence (DNI) is a senior, cabinet-level United States government official, required by the Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004 to serve as executive head of the United States Intelligence Commu ...
removed Hezbollah from the list of "active terrorist threats" against the United States while Hezbollah remained designated as terrorist by the US, and by mid 2015 several Hezbollah officials were sanctioned by the US for their role in facilitating military activity in the ongoing Syrian Civil War. The European Union, France
In the Arab and Muslim world
In 2006, Hezbollah was regarded as a legitimate resistance movement throughout most of the Arab and Muslim world.2009 Hezbollah plot in Egypt The 2009 Hezbollah plot in Egypt involved the arrest of 49 men by Egyptian authorities in the five months preceding April 2009. Egypt accused them of being Hezbollah agents planning attacks against Israeli and Egyptian targets in the Sinai Peninsula ...
, the Egyptian regime of Hosni Mubarak officially classified Hezbollah as a terrorist group.["Egypt: Cairo calls Hezbollah terrorist organization,"](_blank)
LA Times (13 April 2009). Retrieved 5 May 2013. Following the 2012 Presidential elections the new government recognized Hezbollah as a "real political and military force" in Lebanon. The Egyptian ambassador to Lebanon, Ashraf Hamdy, stated that "Resistance in the sense of defending Lebanese territory ... That's their primary role. We ... think that as a resistance movement they have done a good job to keep on defending Lebanese territory and trying to regain land occupied by Israel is legal and legitimate."foreign minister
A foreign affairs minister or minister of foreign affairs (less commonly minister for foreign affairs) is generally a cabinet minister in charge of a state's foreign policy and relations. The formal title of the top official varies between cou ...
Khalid ibn Ahmad Al Khalifah
Khalid bin Ahmed Al Khalifa (born 24 April 1960) is a Bahraini diplomat who served as Bahrain's Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2005 until January 2020. Khalid became only the second foreign minister in Bahrain's history after replacing Moham ...
labeled Hezbollah a terrorist group and accused them of supporting the protesters.Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, E ...
followed the move, with reservation by Iraq and Lebanon. In the summit, Lebanese Foreign Minister Gebran Bassil said that "Hezbollah enjoys wide representation and is an integral faction of the Lebanese community", while Iraqi Foreign Minister Ibrahim al-Jaafari said PMF and Hezbollah "have preserved Arab dignity" and those who accuse them of being terrorists are terrorists themselves. Saudi delegation walked out of the meeting. Israel's Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu called the step "important and even amazing".
A day before the move by the Arab League, Hezbollah leader Nasrallah said that "Saudi Arabia is angry with Hezbollah since it is daring to say what only a few others dare to say against its royal family".
In September 2021, U.S' Secretary of State, Antony Blinken commended the combined efforts taken by the United States and the Government of Qatar against Hezbollah financial network which involved the abuse of international financial system by using global networks of financiers and front companies to spread terrorism.
In Lebanon
In an interview during the 2006 Lebanon War, then-President Emile Lahoud stated "Hezbollah enjoys utmost prestige in Lebanon, because it freed our country ... even though it is very small, it stands up to Israel." Following the 2006 War, other Lebanese including members of the government were resentful of the large damage sustained by the country and saw Hezbollah's actions as unjustified "dangerous adventurism" rather than legitimate resistance. They accused Hezbollah of acting on behalf of Iran and Syria.
An official of the Future Movement, part of the March 14 Alliance, warned that Hezbollah "has all the characteristics of a terrorist party", and that Hezbollah is moving Lebanon toward the Iranian Islamic system of government.
In August 2008, Lebanon's cabinet completed a policy statement which recognized "the right of Lebanon's people, army, and resistance to liberate the Israeli-occupied Shebaa Farms, Kafar Shuba Hills, and the Lebanese section of Ghajar village, and defend the country using all legal and possible means."
Scholarly views
Academics specializing in a wide variety of the social sciences believe that Hezbollah is an example of an Islamic terrorist organization. Such scholars and research institutes include the following:
* Walid Phares
Walid Phares ( ar, وليد فارس, ; born December 24, 1957) is a Lebanon, Lebanese-born American scholar and conservative political pundit.
He worked for the Republican presidential campaigns of Mitt Romney presidential campaign, 2012, Mitt R ...
, Lebanese-born terrorism scholar.
* Mark LeVine, American historian
* Avraham Sela, Israeli historian
* Robert S. Wistrich
Robert Solomon Wistrich (April 7, 1945 – May 19, 2015) was the Erich Neuberger Professor of European and Jewish history at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and the head of the University's Vidal Sassoon International Center for the Study ...
, Israeli historian
* Eyal Zisser, Israeli historian
* Siamak Khatami, Iranian scholar
* Rohan Gunaratna, Singaporean scholar[ Gunaratna, Rohan. ''Inside Al Qaeda: Global Network of Terror''. New York: Columbia University Press, 2002. p. 146.]
* Neeru Gaba, Australian scholar
* Tore Bjørgo, Norwegian scholar
* Magnus Norell, of the European Foundation for Democracy
The European Foundation for Democracy (EFD) is a policy centre and a registered EU lobbyist organization based in Brussels, Belgium. Its activities focus on counter-radicalisation, security and the promotion of the European values of democracy ...
* Anthony Cordesman, of the Center for Strategic and International Studies
* Center for American Progress
* United States Institute of Peace
Views of foreign legislators
J. Gresham Barrett brought up legislation in the U.S. House of Representatives which, among other things, referred to Hezbollah as a terrorist organization. Congress members Tom Lantos, Jim Saxton, Thad McCotter, Chris Shays, Charles Boustany, Alcee Hastings, and Robert Wexler referred to Hezbollah as a terrorist organization in their speeches supporting the legislation. Shortly before a speech by Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki, U.S. Congressman Dennis Hastert
John Dennis Hastert (; born January 2, 1942) is an American former politician and convicted felon who represented from 1987 to 2007 and served as the 51st speaker of the United States House of Representatives from 1999 to 2007. The longest-se ...
said, "He aliki Aliki may refer to:
* Aliki (name), a given name, usually Greek
** Aliki, the penname of Aliki Brandenberg, born 1928, children's book author
* Ariki
An ariki (New Zealand, Cook Islands), ꞌariki (Easter Island), aliki (Tokelau, Tuvalu), ali‘ ...
denounces terrorism, and I have to take him at his word. Hezbollah is a terrorist organization."
In 2011, a bipartisan group of members of Congress introduced the Hezbollah Anti-Terrorism Act. The act ensures that no American aid to Lebanon will enter the hands of Hezbollah. On the day of the act's introduction, Congressman Darrell Issa said, "Hezbollah is a terrorist group and a cancer on Lebanon. The Hezbollah Anti-Terrorism Act surgically targets this cancer and will strengthen the position of Lebanese who oppose Hezbollah."
In a Sky News interview during the 2006 Lebanon war, British MP George Galloway
George Galloway (born 16 August 1954) is a British politician, broadcaster, and writer who is currently leader of the Workers Party of Britain, serving since 2019. Between 1987 and 2010, and then between 2012 and 2015, Galloway was a Member o ...
said that Hezbollah is "not a terrorist organization".
Former Swiss member of parliament, Jean Ziegler, said in 2006: "I refuse to describe Hezbollah as a terrorist group. It is a national movement of resistance."
See also
* Military equipment of Hezbollah
This is a list of some of the military equipment used by the paramilitary wing of Hezbollah.
Small arms
Assault and battle rifles
Sniper rifles
Machine guns
Heavy weapons and missiles Anti-tank
Hezbollah has apparently thous ...
* Politics of Lebanon
* Jihad al-Bina
Jihād al-Binā' ( ar, جهاد البناء, meaning "Effort for Reconstruction") is a development foundation run by Hezbollah in Lebanon. The purpose of the organization is to help alleviate the consequences of the Lebanese Civil War and Hezbo ...
* Mleeta museum
* January 2015 Mazraat Amal incident
* Hezbollah Movement in Iraq
** Kata'ib Hezbollah
** Harakah Hezbollah al-Nujaba
** Kata'ib Sayyid al-Shuhada
** Badr Organization
The Badr Organization ( ar, منظمة بدر ''Munaẓẓama Badr''), previously known as the Badr Brigades or Badr Corps, is an Iraqi Shia Islamist political party and military organization headed by Hadi Al-Amiri. The Badr Brigade was the Ir ...
** Kata'ib al-Imam Ali
* Jaysh al-Mahdi (Iraq)
* Al-Ashtar Brigades (Bahrain)
* Liwa Assad Allah (Syria)
* Hezbollah al-Hejaz (Saudi Arabia)
* Harakah al-Sabireen (Palestine)
* Islamic Front for the Liberation of Bahrain
* Islamic Movement (Nigeria)
Notes
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
Books
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Articles
*
External links
UN resolutions regarding Hezbollah
UN Press Release SC/8181
UN, 2 September 2004
Lebanon: Close Security Council vote backs free elections, urges foreign troop pullout
UN, 2 September 2004
Other links
Is Hezbollah Confronting a Crisis of Popular Legitimacy?
Dr. Eric Lob, Crown Center for Middle East Studies, March 2014
Hezbollah
: Financing Terror through Criminal Enterprise, Testimony of Matthew Levitt, Hearing of the Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs, United States Senate
by Mohammed Ben Jelloun, ''Al-Ahram'', 15–21 February 2007
short documentary and extensive information from ''Frontline/World'' on PBS.
– fact file at Ynetnews
{{Authority control
Factions in the Lebanese Civil War
Organizations based in Asia designated as terrorist
Antisemitism in the Arab world
Anti-Zionism in Lebanon
Holocaust denial
Iran–Lebanon relations
Islam and antisemitism
Jihadist groups
Lebanese nationalism
March 8 Alliance
Political parties established in 1982
Political parties in Lebanon
Pro-government factions of the Syrian civil war
Shia Islamist groups
Anti-Western sentiment
Organizations designated as terrorist by Argentina
Organisations designated as terrorist by Australia
Organizations designated as terrorist by Canada
Organizations designated as terrorist by Colombia
Organizations designated as terrorist by Honduras
Organisations designated as terrorist by Japan
Organizations designated as terrorist by Lithuania
Organizations designated as terrorist by Paraguay
Organizations designated as terrorist by Serbia
Islamic terrorism in Lebanon
1985 establishments in Lebanon
Paramilitary organisations based in Lebanon
Anti-ISIL factions in Syria
Anti-ISIL factions in Iraq
Axis of Resistance
 At the beginning many Hezbollah leaders have maintained that the movement was "not an organization, for its members carry no cards and bear no specific responsibilities," and that the movement does not have "a clearly defined organizational structure." Nowadays, as Hezbollah scholar Magnus Ranstorp reports, Hezbollah does indeed have a formal governing structure, and in keeping with the principle of Guardianship of the Islamic Jurists (''velayat-e faqih''), it "concentrate nbsp;... all authority and powers" in its religious leaders, whose decisions then "flow from the ulama down the entire community."
At the beginning many Hezbollah leaders have maintained that the movement was "not an organization, for its members carry no cards and bear no specific responsibilities," and that the movement does not have "a clearly defined organizational structure." Nowadays, as Hezbollah scholar Magnus Ranstorp reports, Hezbollah does indeed have a formal governing structure, and in keeping with the principle of Guardianship of the Islamic Jurists (''velayat-e faqih''), it "concentrate nbsp;... all authority and powers" in its religious leaders, whose decisions then "flow from the ulama down the entire community."

 Hezbollah along with
Hezbollah along with  Between 1982 and 1986, there were 36 suicide attacks in Lebanon directed against American, French and Israeli forces by 41 individuals, killing 659. Hezbollah denies involvement in some of these attacks, though it has been accused of being involved or linked to some or all of these attacks:
* The 1982–1983 Tyre headquarters bombings
* The
Between 1982 and 1986, there were 36 suicide attacks in Lebanon directed against American, French and Israeli forces by 41 individuals, killing 659. Hezbollah denies involvement in some of these attacks, though it has been accused of being involved or linked to some or all of these attacks:
* The 1982–1983 Tyre headquarters bombings
* The  The 2006 Lebanon War was a 34-day military conflict in Lebanon and northern Israel. The principal parties were Hezbollah paramilitary forces and the Israeli military. The conflict was precipitated by a cross-border raid during which Hezbollah kidnapped and killed Israeli soldiers. The conflict began on 12 July 2006 when Hezbollah militants fired rockets at Israeli border towns as a diversion for an anti-tank missile attack on two armored Humvees patrolling the Israeli side of the border fence, killing three, injuring two, and seizing two Israeli soldiers.
Israel responded with
The 2006 Lebanon War was a 34-day military conflict in Lebanon and northern Israel. The principal parties were Hezbollah paramilitary forces and the Israeli military. The conflict was precipitated by a cross-border raid during which Hezbollah kidnapped and killed Israeli soldiers. The conflict began on 12 July 2006 when Hezbollah militants fired rockets at Israeli border towns as a diversion for an anti-tank missile attack on two armored Humvees patrolling the Israeli side of the border fence, killing three, injuring two, and seizing two Israeli soldiers.
Israel responded with