geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
, the truncated triakis tetrahedron, or more precisely an order-6 truncated triakis tetrahedron, is a convex polyhedron
In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices.
A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on ...
with 16 faces
The face is the front of an animal's head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may aff ...
: 4 sets of 3 pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon (from the Greek language, Greek πέντε ''pente'' meaning ''five'' and γωνία ''gonia'' meaning ''angle'') is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple polygon, simple pentagon is ...
s arranged in a tetrahedral
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ...
arrangement, with 4 hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A ''regular hexagon'' h ...
s in the gaps.
Construction
It is constructed from atriakis tetrahedron
In geometry, a triakis tetrahedron (or kistetrahedron) is a Catalan solid with 12 faces. Each Catalan solid is the dual of an Archimedean solid. The dual of the triakis tetrahedron is the truncated tetrahedron.
The triakis tetrahedron can be see ...
by truncating the order-6 vertices. This creates 4 regular hexagon faces, and leaves 12 mirror-symmetric pentagons.
 A topologically similar
A topologically similar equilateral
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each oth ...
polyhedron can be constructed by using 12 regular
The term regular can mean normal or in accordance with rules. It may refer to:
People
* Moses Regular (born 1971), America football player
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* "Regular" (Badfinger song)
* Regular tunings of stringed instrum ...
pentagons with 4 equilateral
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each oth ...
but nonplanar
In graph theory, a planar graph is a graph that can be embedded in the plane, i.e., it can be drawn on the plane in such a way that its edges intersect only at their endpoints. In other words, it can be drawn in such a way that no edges cro ...
hexagons, each vertex with internal angle
In geometry, an angle of a polygon is formed by two sides of the polygon that share an endpoint. For a simple (non-self-intersecting) polygon, regardless of whether it is convex or non-convex, this angle is called an interior angle (or ) if ...
s alternating between 108 and 132 degrees.
Topologically, as a near-miss Johnson solid
In geometry, a near-miss Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron whose faces are close to being regular polygons but some or all of which are not precisely regular. Thus, it fails to meet the definition of a Johnson solid, a polyhedron whose ...
, the four hexagons corresponding to the face planes of a tetrahedron are triambi, with equal edges but alternating angles, while the pentagons only have reflection symmetry.
Full truncation
If all of a triakis tetrahedron's vertices, of both kinds, are truncated, the resulting solid is an irregular icosahedron, whose dual is a ''trihexakis truncated tetrahedron''. Truncation of only the 3-valence vertices yields the order-3 truncated triakis tetrahedron, which looks like atetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ...
with each face raised by a low triangular frustum
In geometry, a (from the Latin for "morsel"; plural: ''frusta'' or ''frustums'') is the portion of a solid (normally a pyramid or a cone) that lies between two parallel planes cutting this solid. In the case of a pyramid, the base faces are ...
. The dual to that truncation will be the triakis truncated tetrahedron
In geometry, the triakis truncated tetrahedron is a convex polyhedron made from 4 hexagons and 12 isosceles triangles. It can be used to tessellate three-dimensional space, making the triakis truncated tetrahedral honeycomb.
The triakis truncate ...
.

Hexakis truncated tetrahedron
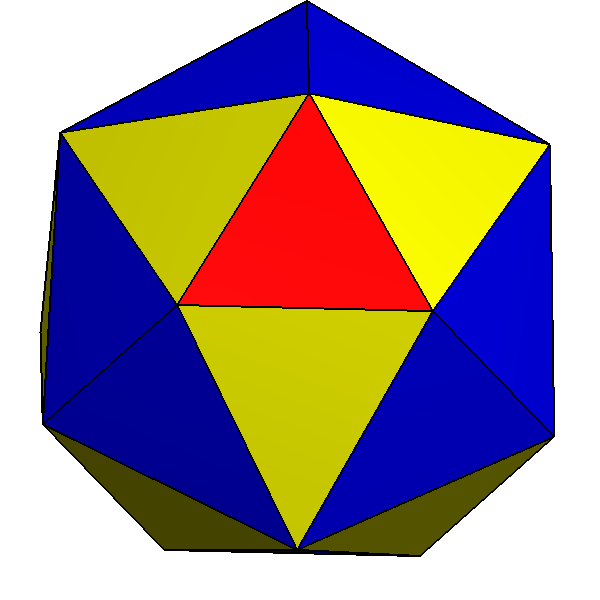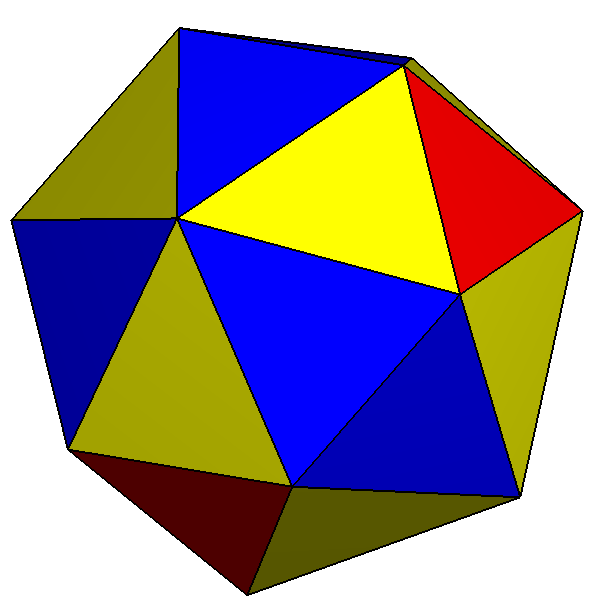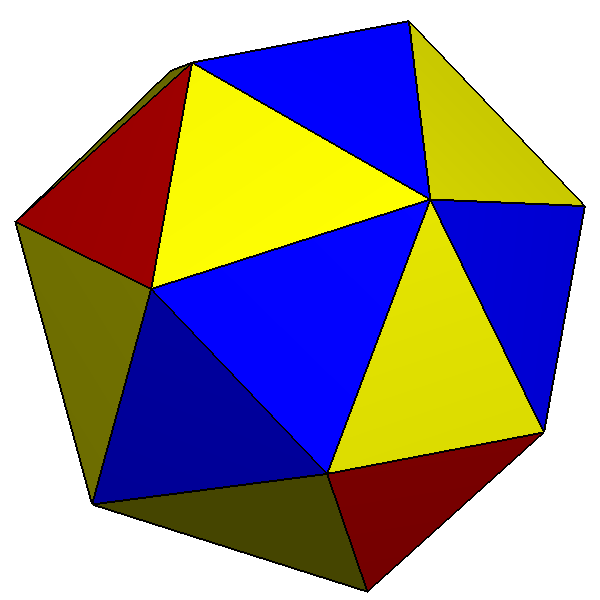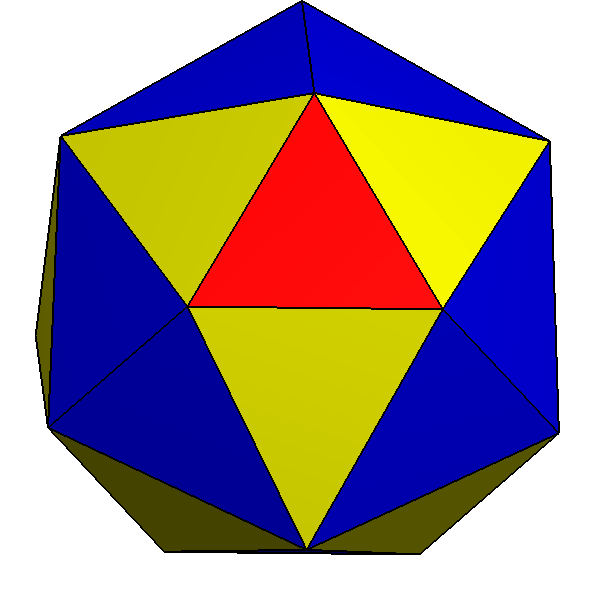 The dual of the ''order-6 Truncated triakis tetrahedron'' is called a hexakis truncated tetrahedron. It is constructed by a
The dual of the ''order-6 Truncated triakis tetrahedron'' is called a hexakis truncated tetrahedron. It is constructed by a truncated tetrahedron
In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 equilateral triangle faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges (of two types). It can be constructed by truncating all 4 vertices of a regular tetrahedr ...
with hexagonal pyramid
In geometry, a hexagonal pyramid is a pyramid with a hexagonal base upon which are erected six isosceles triangular faces that meet at a point (the apex). Like any pyramid, it is self- dual.
A right hexagonal pyramid with a regular hexagon base ...
s augmented. If all of the triangles are made regular, the polyhedron becomes a failed Johnson solid
In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron each face of which is a regular polygon. There is no requirement that each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around each vertex. An example of a Johns ...
, with coplanar triangles in a truncated tetrahedron volume.
See also
*Near-miss Johnson solid
In geometry, a near-miss Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron whose faces are close to being regular polygons but some or all of which are not precisely regular. Thus, it fails to meet the definition of a Johnson solid, a polyhedron whose ...
* Truncated tetrakis cube
The truncated tetrakis cube, or more precisely an order-6 truncated tetrakis cube or hexatruncated tetrakis cube, is a convex polyhedron with 32 faces: 24 sets of 3 bilateral symmetry pentagons arranged in an Octahedral symmetry, octahedral arrange ...
* Truncated triakis octahedron
* Truncated triakis icosahedron
External links
Johnson Solid Near Misses: Number 22
- "t6kT" (
Conway polyhedron notation
In geometry, Conway polyhedron notation, invented by John Horton Conway and promoted by George W. Hart, is used to describe polyhedra based on a seed polyhedron modified by various prefix operations.
Conway and Hart extended the idea of using o ...
)
Polyhedra
Truncated tilings
{{Polyhedron-stub