Herpes Simplex Blepharitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Herpes simplex is a
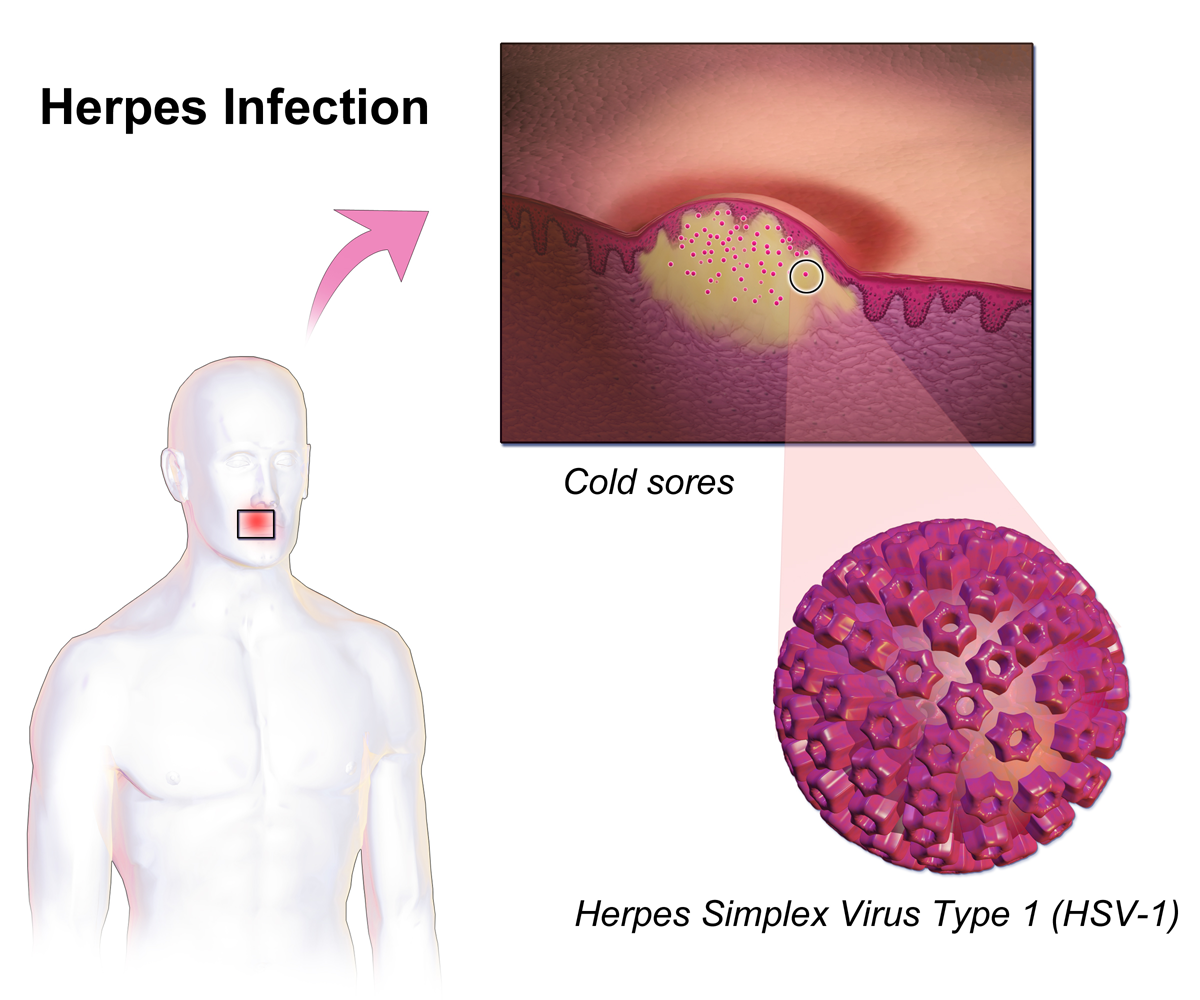 HSV infection causes several distinct medical disorders. Common infection of the skin or mucosa may affect the face and mouth (orofacial herpes), genitalia (genital herpes), or hands (
HSV infection causes several distinct medical disorders. Common infection of the skin or mucosa may affect the face and mouth (orofacial herpes), genitalia (genital herpes), or hands (
 As with almost all sexually transmitted infections, women are more susceptible to acquiring genital HSV-2 than men. On an annual basis, without the use of antivirals or condoms, the transmission risk of HSV-2 from infected male to female is about 8–11%.
This is believed to be due to the increased exposure of mucosal tissue to potential infection sites. Transmission risk from infected female to male is around 4–5% annually. Suppressive antiviral therapy reduces these risks by 50%. Antivirals also help prevent the development of symptomatic HSV in infection scenarios, meaning the infected partner will be seropositive but symptom-free by about 50%. Condom use also reduces the transmission risk significantly. Condom use is much more effective at preventing male-to-female transmission than ''vice versa''. Previous HSV-1 infection may reduce the risk for acquisition of HSV-2 infection among women by a factor of three, although the one study that states this has a small sample size of 14 transmissions out of 214 couples.
However, asymptomatic carriers of the HSV-2 virus are still contagious. In many infections, the first symptom people will have of their own infections is the horizontal transmission to a sexual partner or the vertical transmission of neonatal herpes to a newborn at term. Since most asymptomatic individuals are unaware of their infection, they are considered at high risk for spreading HSV.
In October 2011, the anti-HIV drug
As with almost all sexually transmitted infections, women are more susceptible to acquiring genital HSV-2 than men. On an annual basis, without the use of antivirals or condoms, the transmission risk of HSV-2 from infected male to female is about 8–11%.
This is believed to be due to the increased exposure of mucosal tissue to potential infection sites. Transmission risk from infected female to male is around 4–5% annually. Suppressive antiviral therapy reduces these risks by 50%. Antivirals also help prevent the development of symptomatic HSV in infection scenarios, meaning the infected partner will be seropositive but symptom-free by about 50%. Condom use also reduces the transmission risk significantly. Condom use is much more effective at preventing male-to-female transmission than ''vice versa''. Previous HSV-1 infection may reduce the risk for acquisition of HSV-2 infection among women by a factor of three, although the one study that states this has a small sample size of 14 transmissions out of 214 couples.
However, asymptomatic carriers of the HSV-2 virus are still contagious. In many infections, the first symptom people will have of their own infections is the horizontal transmission to a sexual partner or the vertical transmission of neonatal herpes to a newborn at term. Since most asymptomatic individuals are unaware of their infection, they are considered at high risk for spreading HSV.
In October 2011, the anti-HIV drug
 Several
Several
viral infection
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.
Structural Characteristics
Basic structural characteristics, s ...
caused by the herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and '' Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral inf ...
. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected.
Oral herpes
Gingivostomatitis is a combination of gingivitis and stomatitis, or an inflammation of the oral mucosa and gingiva. Herpetic gingivostomatitis is often the initial presentation during the first ("primary") herpes simplex infection. It is of greater ...
involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled wi ...
s in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat.
Genital herpes
Genital herpes is an infection by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) of the genitals. Most people either have no or mild symptoms and thus do not know they are infected. When symptoms do occur, they typically include small blisters that break ope ...
, often simply known as herpes, involves the genitalia. It may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcer
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughing o ...
s. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
s and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in frequency and severity.
Herpetic whitlow
A herpetic whitlow is a lesion ( whitlow), typically on a finger or thumb, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). Occasionally infection occurs on the toes or on the nail cuticle. Herpes whitlow can be caused by infection by HSV-1 or HSV-2. HSV ...
typically involves the fingers or thumb.
Herpes simplex keratitis
Herpetic simplex keratitis is a form of keratitis caused by recurrent herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection in the cornea.
It begins with infection of epithelial cells on the surface of the eye and retrograde infection of nerves serving the cornea ...
involves the eye.
Herpesviral encephalitis
Herpesviral encephalitis, or herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE), is encephalitis due to herpes simplex virus. It is estimated to affect at least 1 in 500,000 individuals per year, and some studies suggest an incidence rate of 5.9 cases per 100,000 ...
involves the brain.
Neonatal herpes involves any part of the body of a newborn, among others.
There are two types of herpes simplex virus, type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2). HSV-1 more commonly causes infections around the mouth while HSV-2 more commonly causes genital infections. They are transmitted by direct contact with body fluids or lesions of an infected individual. Transmission may still occur when symptoms are not present. Genital herpes is classified as a sexually transmitted infection
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, especi ...
. It may be spread to an infant during childbirth. After infection, the viruses are transported along sensory nerves to the nerve cell bodies, where they reside lifelong. Causes of recurrence may include: decreased immune function, stress, and sunlight exposure. Oral and genital herpes is usually diagnosed based on the presenting symptoms. The diagnosis may be confirmed by viral culture
Viral culture is a laboratory technique in which samples of a virus are placed to different cell lines which the virus being tested for its ability to infect. If the cells show changes, known as cytopathic effects, then the culture is positive.
...
or detecting herpes DNA in fluid from blisters. Testing the blood for antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
against the virus can confirm a previous infection but will be negative in new infections.
The most effective method of avoiding genital infections is by avoiding vaginal, oral, and anal sex. Condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of in ...
use decreases the risk. Daily antiviral medication
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do ...
taken by someone who has the infection can also reduce spread. There is no available vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifie ...
and once infected, there is no cure. Paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior ...
(acetaminophen) and topical lidocaine may be used to help with the symptoms. Treatments with antiviral medication such as aciclovir
Aciclovir (ACV), also known as acyclovir, is an antiviral medication. It is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles. Other uses include prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following tra ...
or valaciclovir
Valaciclovir, also spelled valacyclovir, is an antiviral medication used to treat outbreaks of herpes simplex or herpes zoster (shingles). It is also used to prevent cytomegalovirus following a kidney transplant in high risk cases. It is taken ...
can lessen the severity of symptomatic episodes.
Worldwide rates of either HSV-1 or HSV-2 are between 60% and 95% in adults. HSV-1 is usually acquired during childhood. Since there is no cure for either HSV-1 or HSV-2, rates of both inherently increase as people age. Rates of HSV-1 are between 70% and 80% in populations of low socioeconomic status and 40% to 60% in populations of improved socioeconomic status. An estimated 536 million people worldwide (16% of the population) were infected with HSV-2 as of 2003 with greater rates among women and those in the developing world. Most people with HSV-2 do not realize that they are infected.
Etymology
The name is from grc-gre, ἕρπης ''herpēs'', which is related to the meaning "to creep", referring to spreading blisters. The name does not refer to latency.Signs and symptoms
 HSV infection causes several distinct medical disorders. Common infection of the skin or mucosa may affect the face and mouth (orofacial herpes), genitalia (genital herpes), or hands (
HSV infection causes several distinct medical disorders. Common infection of the skin or mucosa may affect the face and mouth (orofacial herpes), genitalia (genital herpes), or hands (herpetic whitlow
A herpetic whitlow is a lesion ( whitlow), typically on a finger or thumb, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). Occasionally infection occurs on the toes or on the nail cuticle. Herpes whitlow can be caused by infection by HSV-1 or HSV-2. HSV ...
). More serious disorders occur when the virus infects and damages the eye ( herpes keratitis), or invades the central nervous system, damaging the brain (herpes encephalitis). People with immature or suppressed immune systems, such as newborns, transplant recipients, or people with AIDS, are prone to severe complications from HSV infections. HSV infection has also been associated with cognitive deficits of bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with ...
, and Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
, although this is often dependent on the genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar wor ...
of the infected person.
In all cases, HSV is never removed from the body by the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
. Following a primary infection, the virus enters the nerves at the site of primary infection, migrates to the cell body of the neuron, and becomes latent in the ganglion
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system there are both sympatheti ...
. As a result of primary infection, the body produces antibodies to the particular type of HSV involved, which can help reduce the odds of subsequent infection of that type at a different site. In HSV-1-infected individuals, seroconversion
In immunology, seroconversion is the development of specific antibodies in the blood serum as a result of infection or immunization, including vaccination. During infection or immunization, antigens enter the blood, and the adaptive immune system ...
after an oral infection helps prevent additional HSV-1 infections such as whitlow, genital herpes, and herpes of the eye. Prior HSV-1 seroconversion seems to reduce the symptoms of a later HSV-2 infection, although HSV-2 can still be contracted.
Many people infected with HSV-2 display no physical symptoms—individuals with no symptoms are described as asymptomatic or as having subclinical
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asym ...
herpes. However, infection with herpes can be fatal.
Other
Neonatal herpes simplex
Neonatal herpes simplex is a rare but serious condition, usually caused by vertical transmission of the herpes simplex virus from mother to newborn. Around 1 in every 3,500 babies in the United States contract the infection.
Signs and Symptoms
Ne ...
is an HSV infection in an infant. It is a rare but serious condition, usually caused by vertical transmission Vertical transmission of symbionts is the transfer of a microbial symbiont from the parent directly to the offspring. Many metazoan species carry symbiotic bacteria which play a mutualistic, commensal, or parasitic role. A symbiont is acquire ...
of HSV-1 or -2 from mother to newborn. During immunodeficiency, herpes simplex can cause unusual lesions in the skin. One of the most striking is the appearance of clean linear erosions in skin creases, with the appearance of a knife cut. Herpetic sycosis
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected.
Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold s ...
is a recurrent or initial herpes simplex infection affecting primarily the hair follicles. Eczema herpeticum
Eczema herpeticum is a rare but severe disseminated infection that generally occurs at sites of skin damage produced by, for example, atopic dermatitis, burns, long-term usage of topical steroids or eczema. It is also known as Kaposi varicellifor ...
is an infection with herpesvirus in patients with chronic atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin (dermatitis). It results in puritis, itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. Clear fluid may come from the affected areas, which often thickens o ...
may result in spread of herpes simplex throughout the eczematous areas.
Herpetic keratoconjunctivitis
Herpetic simplex keratitis is a form of keratitis caused by recurrent herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection in the cornea.
It begins with infection of epithelial cells on the surface of the eye and retrograde infection of nerves serving the corne ...
, a primary infection, typically presents as swelling of the conjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium ...
and eyelids (blepharoconjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is inflammation of the outermost layer of the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness, or itchiness may occur. The ...
), accompanied by small white itchy lesions on the surface of the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power ...
.
Herpetic sycosis is a recurrent or initial herpes simplex infection affecting primarily the hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between h ...
.
Bell's palsy
Although the exact cause ofBell's palsy
Bell's palsy is a type of facial paralysis that results in a temporary inability to control the facial muscles on the affected side of the face. In most cases, the weakness is temporary and significantly improves over weeks. Symptoms can vary fr ...
a type of facial paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 ...
is unknown, it may be related to the reactivation of HSV-1. This theory has been contested, however, since HSV is detected in large numbers of individuals having never experienced facial paralysis, and higher levels of antibodies for HSV are not found in HSV-infected individuals with Bell's palsy compared to those without. Antivirals may improve the condition slightly when used together with corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
in those with severe disease.
Alzheimer's disease
HSV-1 has been proposed as a possible cause ofAlzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
. In the presence of a certain gene variation (APOE
Apolipoprotein E (APOE) is a protein involved in the metabolism of fats in the body of mammals. A subtype is implicated in Alzheimer's disease and cardiovascular disease.
APOE belongs to a family of fat-binding proteins called apolipoproteins. ...
-epsilon4 allele carriers), HSV-1 appears to be particularly damaging to the nervous system and increases one's risk of developing Alzheimer's disease. The virus interacts with the components and receptors of lipoproteins
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, su ...
, which may lead to its development.
Pathophysiology
Herpes is contracted through direct contact with an active lesion or body fluid of an infected person. Herpes transmission occurs between discordant partners; a person with a history of infection (HSV seropositive) can pass the virus to an HSV seronegative person. Herpes simplex virus 2 is typically contracted through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual, but can also be contracted by exposure to infected saliva, semen, vaginal fluid, or the fluid from herpetic blisters. To infect a new individual, HSV travels through tiny breaks in the skin or mucous membranes in the mouth or genital areas. Even microscopic abrasions on mucous membranes are sufficient to allow viral entry. HSV asymptomatic shedding occurs at some time in most individuals infected with herpes. It can occur more than a week before or after a symptomatic recurrence in 50% of cases. Virus enters into susceptible cells by entry receptors such as nectin-1, HVEM and 3-O sulfated heparan sulfate. Infected people who show no visible symptoms may still shed and transmit viruses through their skin; asymptomatic shedding may represent the most common form of HSV-2 transmission. Asymptomatic shedding is more frequent within the first 12 months of acquiring HSV. Concurrent infection with HIV increases the frequency and duration of asymptomatic shedding. Some individuals may have much lower patterns of shedding, but evidence supporting this is not fully verified; no significant differences are seen in the frequency of asymptomatic shedding when comparing persons with one to 12 annual recurrences to those with no recurrences. Antibodies that develop following an initial infection with a type of HSV can reduce the odds of reinfection with the same virus type. In amonogamous
Monogamy ( ) is a form of Dyad (sociology), dyadic Intimate relationship, relationship in which an individual has only one Significant other, partner during their lifetime. Alternately, only one partner at any one time (Monogamy#Serial monogamy, ...
couple, a seronegative female runs a greater than 30% per year risk of contracting an HSV infection from a seropositive male partner. If an oral HSV-1 infection is contracted first, seroconversion will have occurred after 6 weeks to provide protective antibodies against a future genital HSV-1 infection. Herpes simplex is a double-stranded DNA virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and ...
.
Diagnosis
Classification
Herpes simplex virus is divided into two types. However, each may cause infections in all areas. *HSV-1 causes primarily mouth, throat, face, eye, andcentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
infections.
*HSV-2 causes primarily anogenital infections.
Examination
Primary orofacial herpes is readily identified by examination of persons with no previous history of lesions and contact with an individual with known HSV infection. The appearance and distribution of sores is typically presents as multiple, round, superficial oral ulcers, accompanied by acutegingivitis
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms (also called plaque) that is attached ...
. Adults with atypical presentation are more difficult to diagnose. Prodromal symptoms that occur before the appearance of herpetic lesions help differentiate HSV symptoms from the similar symptoms of other disorders, such as allergic
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic der ...
stomatitis
Stomatitis is inflammation of the mouth and lips. It refers to any inflammatory process affecting the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips, with or without oral ulceration.
In its widest meaning, stomatitis can have a multitude of different cau ...
. When lesions do not appear inside the mouth, primary orofacial herpes is sometimes mistaken for impetigo
Impetigo is a bacterial infection that involves the superficial skin. The most common presentation is yellowish crusts on the face, arms, or legs. Less commonly there may be large blisters which affect the groin or armpits. The lesions may be pa ...
, a bacterial infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
. Common mouth ulcers (aphthous ulcer
Aphthous stomatitis, or recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benign and non-contagious mouth ulcers (aphthae) in otherwise healthy individuals. The informal term ''canker sore'' i ...
) also resemble intraoral herpes, but do not present a vesicular stage.
Genital herpes can be more difficult to diagnose than oral herpes, since most people have none of the classical symptoms. Further confusing diagnosis, several other conditions resemble genital herpes, including fungal infection
Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is disease caused by fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected; superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Superficial fungal infections include common ti ...
, lichen planus
Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, and is only named that because it looks like one. It is characterized by polygonal, fla ...
, atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin (dermatitis). It results in puritis, itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. Clear fluid may come from the affected areas, which often thickens o ...
, and urethritis
Urethritis is the inflammation of the urethra. The most common symptoms include painful or difficult urination and urethral discharge. It is a commonly treatable condition usually caused by infection with bacteria. This bacterial infection is oft ...
.
Laboratory testing
Laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicia ...
testing is often used to confirm a diagnosis of genital herpes. Laboratory tests include culture of the virus, direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) studies to detect virus, skin biopsy
Skin biopsy is a biopsy technique in which a skin lesion is removed to be sent to a pathologist to render a microscopic diagnosis. It is usually done under local anesthetic in a physician's office, and results are often available in 4 to 10 days. ...
, and polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) t ...
to test for presence of viral DNA. Although these procedures produce highly sensitive and specific diagnoses, their high costs and time constraints discourage their regular use in clinical practice.
Until the 1980s serological
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given mi ...
tests for antibodies to HSV were rarely useful to diagnosis and not routinely used in clinical practice. The older IgM serologic assay could not differentiate between antibodies generated in response to HSV-1 or HSV-2 infection. However, a glycoprotein G-specific (IgG) HSV test introduced in the 1980s is more than 98% specific at discriminating HSV-1 from HSV-2.
Differential diagnosis
It should not be confused with conditions caused by other viruses in the ''herpesviridae
''Herpesviridae'' is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are also known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ''ἕρπει� ...
'' family such as herpes zoster
Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. ...
, which is caused by varicella zoster virus
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3, HHV3) or ''Human alphaherpesvirus 3'' (taxonomically), is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly affecting chil ...
. The differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that p ...
includes hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common infection caused by a group of enteroviruses. It typically begins with a fever and feeling generally unwell. This is followed a day or two later by flat discolored spots or bumps that may blis ...
due to similar lesions on the skin. Lymphangioma circumscriptum and dermatitis herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic autoimmune blistering skin condition, characterised by intensely itchy blisters filled with a watery fluid. DH is a cutaneous manifestation of coeliac disease, although the exact causal mechanism is not k ...
may also have a similar appearance.
Prevention
 As with almost all sexually transmitted infections, women are more susceptible to acquiring genital HSV-2 than men. On an annual basis, without the use of antivirals or condoms, the transmission risk of HSV-2 from infected male to female is about 8–11%.
This is believed to be due to the increased exposure of mucosal tissue to potential infection sites. Transmission risk from infected female to male is around 4–5% annually. Suppressive antiviral therapy reduces these risks by 50%. Antivirals also help prevent the development of symptomatic HSV in infection scenarios, meaning the infected partner will be seropositive but symptom-free by about 50%. Condom use also reduces the transmission risk significantly. Condom use is much more effective at preventing male-to-female transmission than ''vice versa''. Previous HSV-1 infection may reduce the risk for acquisition of HSV-2 infection among women by a factor of three, although the one study that states this has a small sample size of 14 transmissions out of 214 couples.
However, asymptomatic carriers of the HSV-2 virus are still contagious. In many infections, the first symptom people will have of their own infections is the horizontal transmission to a sexual partner or the vertical transmission of neonatal herpes to a newborn at term. Since most asymptomatic individuals are unaware of their infection, they are considered at high risk for spreading HSV.
In October 2011, the anti-HIV drug
As with almost all sexually transmitted infections, women are more susceptible to acquiring genital HSV-2 than men. On an annual basis, without the use of antivirals or condoms, the transmission risk of HSV-2 from infected male to female is about 8–11%.
This is believed to be due to the increased exposure of mucosal tissue to potential infection sites. Transmission risk from infected female to male is around 4–5% annually. Suppressive antiviral therapy reduces these risks by 50%. Antivirals also help prevent the development of symptomatic HSV in infection scenarios, meaning the infected partner will be seropositive but symptom-free by about 50%. Condom use also reduces the transmission risk significantly. Condom use is much more effective at preventing male-to-female transmission than ''vice versa''. Previous HSV-1 infection may reduce the risk for acquisition of HSV-2 infection among women by a factor of three, although the one study that states this has a small sample size of 14 transmissions out of 214 couples.
However, asymptomatic carriers of the HSV-2 virus are still contagious. In many infections, the first symptom people will have of their own infections is the horizontal transmission to a sexual partner or the vertical transmission of neonatal herpes to a newborn at term. Since most asymptomatic individuals are unaware of their infection, they are considered at high risk for spreading HSV.
In October 2011, the anti-HIV drug tenofovir
Tenofovir disoproxil, sold under the trade name Viread among others, is a medication used to treat chronic hepatitis B and to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretrovirals. It may be used for preven ...
, when used topically in a microbicidal vaginal gel, was reported to reduce herpes virus sexual transmission by 51%.
Barrier methods
Condoms offer moderate protection against HSV-2 in both men and women, with consistent condom users having a 30%-lower risk of HSV-2 acquisition compared with those who never use condoms. Afemale condom
An internal condom (also known as a femidom or female condom) is a barrier device that is used during sexual intercourse as a barrier contraceptive to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Meant as an al ...
can provide greater protection than the male condom, as it covers the labia. The virus cannot pass through a synthetic condom, but a male condom's effectiveness is limited because herpes ulcers may appear on areas not covered by it. Neither type of condom prevents contact with the scrotum, anus, buttocks, or upper thighs, areas that may come in contact with ulcers or genital secretions during sexual activity. Protection against herpes simplex depends on the site of the ulcer; therefore, if ulcers appear on areas not covered by condoms, abstaining from sexual activity until the ulcers are fully healed is one way to limit risk of transmission. The risk is not eliminated, however, as viral shedding capable of transmitting infection may still occur while the infected partner is asymptomatic. The use of condoms or dental dams
A dental dam or rubber dam is a thin, square sheet, usually latex or nitrile, used in dentistry to isolate the operative site (one or more teeth) from the rest of the mouth. Sometimes termed "Kofferdam" (from German), it was designed in the Unit ...
also limits the transmission of herpes from the genitals of one partner to the mouth of the other (or ''vice versa'') during oral sex
Oral sex, sometimes referred to as oral intercourse, is sexual activity involving the stimulation of the genitalia of a person by another person using the mouth (including the lips, tongue, or teeth) and the throat. Cunnilingus is oral sex per ...
. When one partner has a herpes simplex infection and the other does not, the use of antiviral medication, such as valaciclovir
Valaciclovir, also spelled valacyclovir, is an antiviral medication used to treat outbreaks of herpes simplex or herpes zoster (shingles). It is also used to prevent cytomegalovirus following a kidney transplant in high risk cases. It is taken ...
, in conjunction with a condom, further decreases the chances of transmission to the uninfected partner. Topical microbicide
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals ar ...
s that contain chemicals that directly inactivate the virus and block viral entry are being investigated.
Antivirals
Antivirals may reduce asymptomatic shedding; asymptomatic genital HSV-2 viral shedding is believed to occur on 20% of days per year in patients not undergoing antiviral treatment, versus 10% of days while on antiviral therapy.Pregnancy
The risk of transmission from mother to baby is highest if the mother becomes infected around the time of delivery (30% to 60%), since insufficient time will have occurred for the generation and transfer of protective maternal antibodies before the birth of the child. In contrast, the risk falls to 3% if the infection is recurrent, and is 1–3% if the woman is seropositive for both HSV-1 and HSV-2, and is less than 1% if no lesions are visible. Women seropositive for only one type of HSV are only half as likely to transmit HSV as infected seronegative mothers. To prevent neonatal infections, seronegative women are recommended to avoid unprotected oral-genital contact with an HSV-1-seropositive partner and conventional sex with a partner having a genital infection during the last trimester of pregnancy. Mothers infected with HSV are advised to avoid procedures that would cause trauma to the infant during birth (e.g. fetal scalp electrodes, forceps, and vacuum extractors) and, should lesions be present, to electcaesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or mo ...
to reduce exposure of the child to infected secretions in the birth canal. The use of antiviral treatments, such as aciclovir, given from the 36th week of pregnancy, limits HSV recurrence and shedding during childbirth, thereby reducing the need for caesarean section.
Aciclovir is the recommended antiviral for herpes suppressive therapy during the last months of pregnancy. The use of valaciclovir and famciclovir, while potentially improving compliance, have less-well-determined safety in pregnancy.
Management
No method eradicates herpes virus from the body, but antiviral medications can reduce the frequency, duration, and severity of outbreaks.Analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
s such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus arte ...
and paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior ...
(acetaminophen) can reduce pain and fever. Topical anesthetic treatments such as prilocaine
Prilocaine () is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type first prepared by Claes Tegner and Nils Löfgren. In its injectable form (trade name Citanest), it is often used in dentistry. It is also often combined with lidocaine as a topical ...
, lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidoca ...
, benzocaine
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is an ester local anesthetic commonly used as a topical pain reliever or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter anesthetic ointments such as products f ...
, or tetracaine
Tetracaine, also known as amethocaine, is an ester local anesthetic used to numb the eyes, nose, or throat. It may also be applied to the skin before starting an intravenous (injection) to decrease pain from the procedure. Typically it is applied ...
can also relieve itching and pain.
Antiviral
 Several
Several antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do n ...
s are effective for treating herpes, including aciclovir
Aciclovir (ACV), also known as acyclovir, is an antiviral medication. It is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles. Other uses include prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following tra ...
(acyclovir), valaciclovir
Valaciclovir, also spelled valacyclovir, is an antiviral medication used to treat outbreaks of herpes simplex or herpes zoster (shingles). It is also used to prevent cytomegalovirus following a kidney transplant in high risk cases. It is taken ...
, famciclovir
Famciclovir is a guanosine analogue antiviral drug used for the treatment of various herpesvirus infections, most commonly for herpes zoster (shingles). It is a prodrug form of penciclovir with improved oral bioavailability. Famciclovir is mark ...
, and penciclovir
Penciclovir is a guanosine analogue antiviral drug used for the treatment of various herpesvirus infections. It is a nucleoside analogue which exhibits low toxicity and good selectivity. Because penciclovir is absorbed poorly when given orally (b ...
. Aciclovir was the first discovered and is now available in generic
Generic or generics may refer to:
In business
* Generic term, a common name used for a range or class of similar things not protected by trademark
* Generic brand, a brand for a product that does not have an associated brand or trademark, other ...
. Valaciclovir is also available as a generic and is slightly more effective than aciclovir for reducing lesion healing time.
Evidence supports the use of aciclovir and valaciclovir in the treatment of herpes labialis as well as herpes infections in people with cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
. The evidence to support the use of aciclovir in primary herpetic gingivostomatitis is weaker.
Topical
A number oftopical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
antivirals are effective for herpes labialis, including aciclovir, penciclovir, and docosanol
1-Docosanol, also known as behenyl alcohol, is a saturated fatty alcohol containing 22 carbon atoms, used traditionally as an emollient, emulsifier, and thickener in cosmetics.
In July 2000, docosanol was approved for medical use in the Unite ...
.
Alternative medicine
Evidence is insufficient to support use of many of these compounds, includingechinacea
''Echinacea'' is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the daisy family. It has ten species, which are commonly called coneflowers. They are found only in eastern and central North America, where they grow in moist to dry prairies and ope ...
, eleuthero, L-lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated − ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, monolaurin
Monolaurin (abbreviated GML; also called glycerol monolaurate, glyceryl laurate, and 1-lauroyl-glycerol) is a monoglyceride. It is the mono-ester formed from glycerol and lauric acid. Its chemical formula is C15H30O4.
Uses
Monolaurin is most comm ...
bee products, and aloe vera. While a number of small studies show possible benefit from monolaurin, L-lysine, aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat inc ...
, lemon balm, topical zinc, or licorice root cream in treatment, these preliminary studies have not been confirmed by higher-quality randomized controlled studies.
Prognosis
Following active infection, herpes viruses establish alatent
Latency or latent may refer to:
Science and technology
* Latent heat, energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process
* Latent variable, a variable that is not directly observed but inferred ...
infection in sensory and autonomic ganglia
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system there are both sympatheti ...
of the nervous system. The double-stranded DNA of the virus is incorporated into the cell physiology by infection of the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
of a nerve's cell body. HSV latency is static; no virus is produced; and is controlled by a number of viral genes, including latency-associated transcript.
Many HSV-infected people experience recurrence within the first year of infection. Prodrome
In medicine, a prodrome is an early sign or symptom (or set of signs and symptoms) that often indicates the onset of a disease before more diagnostically specific signs and symptoms develop. It is derived from the Greek word ''prodromos'', meaning ...
precedes development of lesions. Prodromal symptoms include tingling (paresthesia
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias ar ...
), itching, and pain where lumbosacral nerves innervate the skin. Prodrome may occur as long as several days or as short as a few hours before lesions develop. Beginning antiviral treatment when prodrome is experienced can reduce the appearance and duration of lesions in some individuals. During recurrence, fewer lesions are likely to develop and are less painful and heal faster (within 5–10 days without antiviral treatment) than those occurring during the primary infection. Subsequent outbreaks tend to be periodic or episodic, occurring on average four or five times a year when not using antiviral therapy.
The causes of reactivation are uncertain, but several potential triggers have been documented. A 2009 study showed the protein VP16 plays a key role in reactivation of the dormant virus. Changes in the immune system during menstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized by the rise and fall of hor ...
may play a role in HSV-1 reactivation. Concurrent infections, such as viral upper respiratory tract infection
An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an illness caused by an acute infection, which involves the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, sinuses, pharynx, larynx or trachea. This commonly includes nasal obstruction, sore throat, t ...
or other febrile diseases, can cause outbreaks. Reactivation due to other infections is the likely source of the historic terms 'cold sore' and 'fever blister'.
Other identified triggers include local injury to the face, lips, eyes, or mouth; trauma; surgery; radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radia ...
; and exposure to wind, ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
, or sunlight.
The frequency and severity of recurrent outbreaks vary greatly between people. Some individuals' outbreaks can be quite debilitating, with large, painful lesions persisting for several weeks, while others experience only minor itching or burning for a few days. Some evidence indicates genetics play a role in the frequency of cold sore outbreaks. An area of human chromosome 21 that includes six genes has been linked to frequent oral herpes outbreaks. An immunity to the virus is built over time. Most infected individuals experience fewer outbreaks and outbreak symptoms often become less severe. After several years, some people become perpetually asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asy ...
and no longer experience outbreaks, though they may still be contagious to others. Immunocompromised individuals may experience longer, more frequent, and more severe episodes. Antiviral medication has been proven to shorten the frequency and duration of outbreaks. Outbreaks may occur at the original site of the infection or in proximity to nerve endings that reach out from the infected ganglia. In the case of a genital infection, sores can appear at the original site of infection or near the base of the spine, the buttocks, or the back of the thighs.
HSV-2-infected individuals are at higher risk for acquiring HIV when practicing unprotected sex with HIV-positive persons, in particular during an outbreak with active lesions.
Epidemiology
Worldwide rates of either HSV-1 and/or HSV-2 are between 60 and 95% in adults. HSV-1 is more common than HSV-2, with rates of both increasing as people age. HSV-1 rates are between 70% and 80% in populations of low socioeconomic status and 40% to 60% in populations of improved socioeconomic status. An estimated 536 million people or 16% of the population worldwide were infected with HSV-2 as of 2003 with greater rates among women and in those in the developing world. Rates of infection are determined by the presence ofantibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
against either viral species
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.
Viruses are classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as morphology, nucleic ...
.
In the US, 58% of the population is infected with HSV-1 and 16% are infected with HSV-2. Among those HSV-2-seropositive, only 19% were aware they were infected. During 2005–2008, the prevalence of HSV-2 was 39% in blacks and 21% in women.
The annual incidence in Canada of genital herpes due to HSV-1 and HSV-2 infection is not known (for a review of HSV-1/HSV-2 prevalence and incidence studies worldwide, see Smith and Robinson 2002). As many as one in seven Canadians aged 14 to 59 may be infected with herpes simplex type 2 virus and more than 90 per cent of them may be unaware of their status, a new study suggests. In the United States, it is estimated that about 1,640,000 HSV-2 seroconversions occur yearly (730,000 men and 910,000 women, or 8.4 per 1,000 persons).
In British Columbia in 1999, the seroprevalence of HSV-2 antibody in leftover serum submitted for antenatal testing revealed a prevalence of 17%, ranging from 7% in women 15–19 years old to 28% in those 40–44 years.
In Norway, a study published in 2000 found that up to 70–90% of genital initial infections were due to HSV-1.
In Nova Scotia, 58% of 1,790 HSV isolates from genital lesion cultures in women were HSV-1; in men, 37% of 468 isolates were HSV-1.
History
Herpes has been known for at least 2,000 years. EmperorTiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
is said to have banned kissing in Rome for a time due to so many people having cold sores. In the 16th century ''Romeo and Juliet
''Romeo and Juliet'' is a Shakespearean tragedy, tragedy written by William Shakespeare early in his career about the romance between two Italian youths from feuding families. It was among Shakespeare's most popular plays during his lifetim ...
'', blisters "o'er ladies' lips" are mentioned. In the 18th century, it was so common among prostitutes that it was called "a vocational disease of women". The term 'herpes simplex' appeared in Richard Boulton's ''A System of Rational and Practical Chirurgery'' in 1713, where the terms 'herpes miliaris' and 'herpes exedens' also appeared. Herpes was not found to be a virus until the 1940s.
Herpes antiviral therapy began in the early 1960s with the experimental use of medications that interfered with viral replication called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) inhibitors. The original use was against normally fatal or debilitating illnesses such as adult encephalitis, keratitis, in immunocompromised (transplant) patients, or disseminated herpes zoster. The original compounds used were 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine, AKA idoxuridine, IUdR, or(IDU) and 1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine or ara-C, later marketed under the name cytosar or cytarabine. The usage expanded to include topical treatment of herpes simplex, zoster, and varicella. Some trials combined different antivirals with differing results. The introduction of 9-β-D-arabinofuranosyladenine, (ara-A or vidarabine), considerably less toxic than ara-C, in the mid-1970s, heralded the way for the beginning of regular neonatal antiviral treatment. Vidarabine was the first systemically administered antiviral medication with activity against HSV for which therapeutic efficacy outweighed toxicity for the management of life-threatening HSV disease. Intravenous vidarabine was licensed for use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
in 1977. Other experimental antivirals of that period included: heparin, trifluorothymidine (TFT), Ribivarin, interferon, Virazole, and 5-methoxymethyl-2'-deoxyuridine (MMUdR). The introduction of 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine, AKA aciclovir, in the late 1970s raised antiviral treatment another notch and led to vidarabine vs. aciclovir trials in the late 1980s. The lower toxicity and ease of administration over vidarabine has led to aciclovir becoming the drug of choice for herpes treatment after it was licensed by the FDA in 1998. Another advantage in the treatment of neonatal herpes included greater reductions in mortality and morbidity with increased dosages, which did not occur when compared with increased dosages of vidarabine. However, aciclovir seems to inhibit antibody response, and newborns on aciclovir antiviral treatment experienced a slower rise in antibody titer than those on vidarabine.
Society and culture
Some people experience negative feelings related to the condition following diagnosis, in particular, if they have acquired the genital form of the disease. Feelings can include depression, fear of rejection, feelings of isolation, fear of being found out, and self-destructive feelings.Herpes support groups
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected.
Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold s ...
have been formed in the United States and the United Kingdom, providing information about herpes and running message forums and dating websites for affected people. People with the herpes virus are often hesitant to divulge to other people, including friends and family, that they are infected. This is especially true of new or potential sexual partners whom they consider casual.
In a 2007 study, 1,900 people (25% of which had herpes) ranked genital herpes second for social stigma, out of all sexually transmitted diseases (HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
took the top spot for STD stigma).
Support groups
United States
An important source of support is the ''National Herpes Resource Center'' which arose from the work of the American Sexual Health Association (ASHA). The ASHA was created in 1914 in response to the increase in sexually transmitted diseases that had spread duringWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. During the 1970s, there was an increase in sexually transmitted diseases. One of the diseases that increased dramatically was genital herpes. In response, ASHA created the National Herpes Resource Center in 1979. The Herpes Resource Center (HRC) was designed to meet the growing need for education and awareness about the virus. One of the projects of the HRC was to create a network of local support (HELP) groups. The goal of these HELP groups was to provide a safe, confidential environment where participants can get accurate information and share experiences, fears, and feelings with others who are concerned about herpes.
UK
In the UK, the Herpes Association (now theHerpes Viruses Association
The Herpes Viruses Association (formerly the Herpes Association) was started in 1982. It is a support group for people with Herpes simplex virus. It conducts information campaigns and attempts to reduce the stigma associated with sexually transm ...
) was started in 1982, becoming a registered charity with a Dept of Health grant in 1985. The charity started as a string of local group meetings before acquiring an office and a national spread.
Research
Research has gone into vaccines for both prevention and treatment of herpes infections. As of October 2022, the U.S.FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
have not approved a vaccine for herpes. However, there are herpes vaccines currently in clinical trials, such as Moderna
Moderna, Inc. ( ) is an American pharmaceutical and biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts that focuses on RNA therapeutics, primarily mRNA vaccines. These vaccines use a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to produ ...
mRNA-1608. Unsuccessful clinical trials have been conducted for some glycoprotein subunit vaccines. As of 2017, the future pipeline includes several promising replication-incompetent vaccine proposals while two replication-competent (live-attenuated) HSV vaccine are undergoing human testing.
A genomic
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dim ...
study of the herpes simplex type 1 virus confirmed the human migration pattern theory known as the out-of-Africa hypothesis.
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Herpes Simplex Biology of bipolar disorder Conditions of the mucous membranes Herpes simplex virus–associated diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Sexually transmitted diseases and infections Virus-related cutaneous conditions Viral diseases Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate