Henry Willis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Henry Willis (27 April 1821 – 11 February 1901), also known as "Father" Willis, was an English organ player and builder, who is regarded as the foremost
Henry Willis (27 April 1821 – 11 February 1901), also known as "Father" Willis, was an English organ player and builder, who is regarded as the foremost

 For the
For the

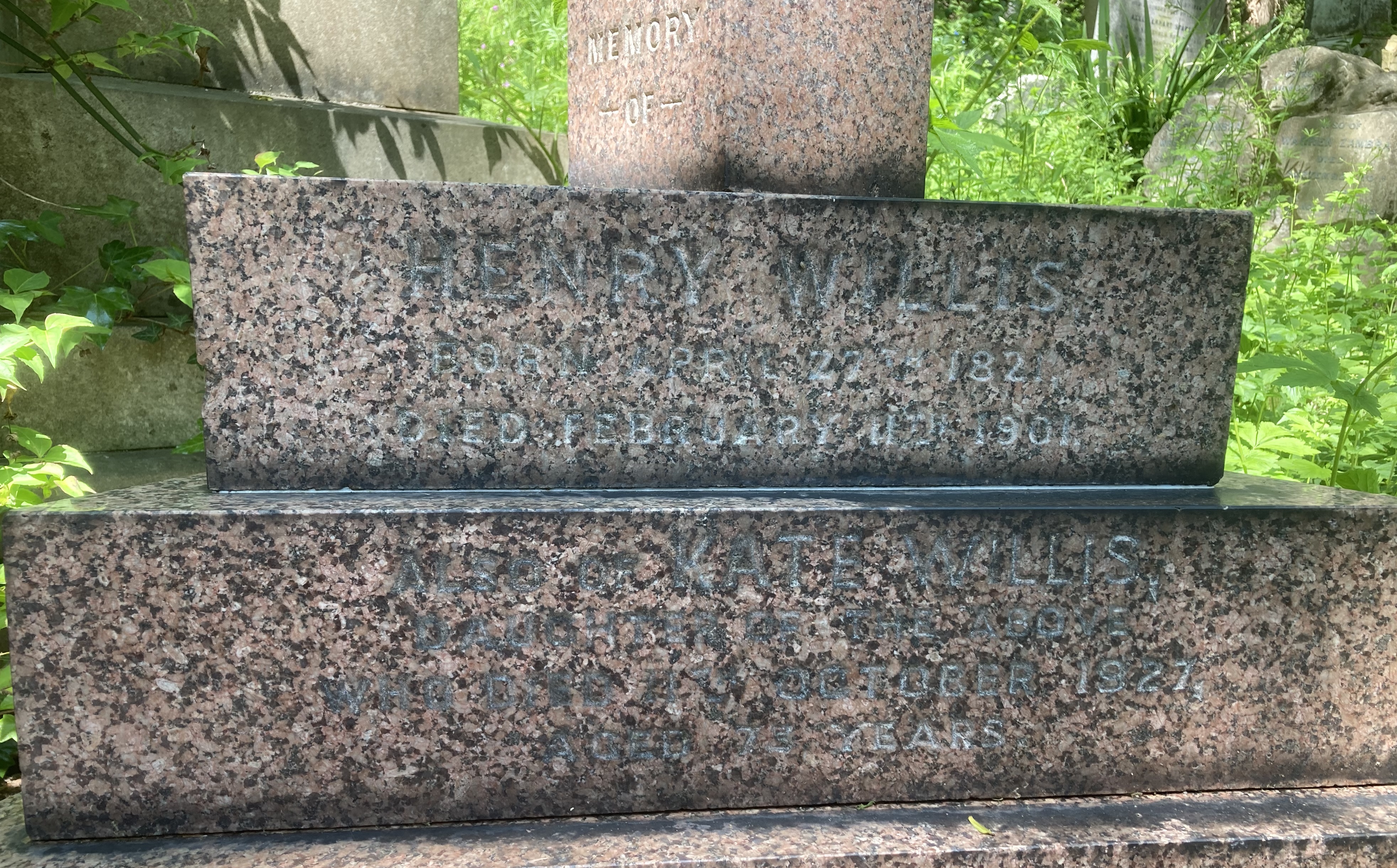 Willis died in London on the 11th February 1901, and is buried on the west side of
Willis died in London on the 11th February 1901, and is buried on the west side of
''The Organ, its evolution, principles of construction and use''
MacDonald and Jane's, London
{{DEFAULTSORT:Willis 1821 births 1901 deaths Burials at Highgate Cemetery British pipe organ builders
 Henry Willis (27 April 1821 – 11 February 1901), also known as "Father" Willis, was an English organ player and builder, who is regarded as the foremost
Henry Willis (27 April 1821 – 11 February 1901), also known as "Father" Willis, was an English organ player and builder, who is regarded as the foremost organ builder
Organ building is the profession of designing, building, restoring and maintaining pipe organs.
The Organ builders , organ builder usually receives a commission to design an organ with a particular disposition of Organ stop, stops, Manual (mu ...
of the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardia ...
. His company Henry Willis & Sons
Henry Willis & Sons is a British firm of pipe organ builders founded in 1845. Although most of their installations have been in the UK, examples can be found in other countries.
Five generations of the Willis family served as principals of th ...
remains in business.
Early life and work
Willis was born inLondon
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, the son of a North London builder, and with George Cooper, later sub-organist of St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral is an Anglican cathedral in London and is the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London. It is on Ludgate Hill at the highest point of the City of London and is a Grad ...
, he learned to play the organ with some help from Thomas Attwood, St Paul's organist. In 1835, Willis was articled to organ builder John Gray (later of Gray and Davison
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed o ...
) for seven years. During this time, he invented the manual and pedal couplers which he used throughout his later career.
Following his apprenticeship he worked for three years in Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral s ...
, assisting an instrument maker, Wardle Evans, who specialised in free reed instruments. Willis later attributed his personal skill in reed voicing to this experience. Willis met Samuel Sebastian Wesley
Samuel Sebastian Wesley (14 August 1810 – 19 April 1876) was an English organist and composer. Wesley married Mary Anne Merewether and had 6 children. He is often referred to as S.S. Wesley to avoid confusion with his father Samuel Wesley.
Bio ...
at Cheltenham, and this led to the re-building of the Gloucester Cathedral
Gloucester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of St Peter and the Holy and Indivisible Trinity, in Gloucester, England, stands in the north of the city near the River Severn. It originated with the establishment of a minster dedicated to S ...
organ in 1847. Willis had become an independent organ builder and commented, "It was my stepping stone to fame... I received £400 for the job, and was presumptuous enough to marry."''The Musical Times'', Vol. 39, No. 663 (May 1898)
Growth of his reputation

 For the
For the Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary The Crystal Palace, structure in which it was held), was an International Exhib ...
of 1851, Willis erected the largest of the organs exhibited with an unprecedented 70 speaking stops. He introduced several novel features, which had a significant effect on organ design. Piston buttons were inserted between the manuals to allow automatic selection of blocks of "stops", and Barker lever servo action was used on the manuals to overcome the constraints of tracker action
Tracker action is a term used in reference to pipe organs and steam calliopes to indicate a mechanical linkage between keys or pedals pressed by the organist and the valve that allows air to flow into pipe(s) of the corresponding note. This is ...
connecting rods for an instrument of such size and complexity. After the exhibition ended, the instrument was erected in reduced form at Winchester Cathedral
The Cathedral Church of the Holy Trinity,Historic England. "Cathedral Church of the Holy Trinity (1095509)". ''National Heritage List for England''. Retrieved 8 September 2014. Saint Peter, Saint Paul and Saint Swithun, commonly known as Winches ...
where in 1854 it now had 49 speaking stops over four manuals and pedals, and the first concave and radiating pedalboard. The pedalboard was the joint idea of Willis and Samuel Sebastian Wesley
Samuel Sebastian Wesley (14 August 1810 – 19 April 1876) was an English organist and composer. Wesley married Mary Anne Merewether and had 6 children. He is often referred to as S.S. Wesley to avoid confusion with his father Samuel Wesley.
Bio ...
with whom Willis collaborated on his next large organ of 100 speaking stops at St George's Hall, Liverpool
St George's Hall is a building on St George's Place, opposite Lime Street railway station in the centre of Liverpool, England. Opened in 1854, it is a Neoclassical building which contains concert halls and law courts, and is recorded in the Na ...
in 1855.
The foremost Victorian organ builder
The Exhibition organ had led to the contract for St George's Hall, Liverpool, where the virtuosic playing of W.T. Best drew large crowds, and also spread the fame of Willis as a builder still further. In a long career stretching to the end of the 19th century, Willis subsequently built the organs at theAlexandra Palace
Alexandra Palace is a Grade II listed entertainment and sports venue in London, situated between Wood Green and Muswell Hill in the London Borough of Haringey. It is built on the site of Tottenham Wood and the later Tottenham Wood Farm. Origi ...
, the Royal Albert Hall
The Royal Albert Hall is a concert hall on the northern edge of South Kensington, London. One of the UK's most treasured and distinctive buildings, it is held in trust for the nation and managed by a registered charity which receives no govern ...
, and St Paul's Cathedral. Among the approximately 1,000 other organs that he built or re-built were the cathedral instruments at Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour, Kent, River Stour.
...
, Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern England, Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Anglo-Scottish border, Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers River Eden, Cumbria, Eden, River C ...
, Coventry
Coventry ( or ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. It is on the River Sherbourne. Coventry has been a large settlement for centuries, although it was not founded and given its ...
, Durham Durham most commonly refers to:
*Durham, England, a cathedral city and the county town of County Durham
*County Durham, an English county
*Durham County, North Carolina, a county in North Carolina, United States
*Durham, North Carolina, a city in No ...
, Edinburgh ( St Mary's Episcopal Cathedral), Exeter
Exeter () is a city in Devon, South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal comm ...
, Glasgow (The High Kirk of Glasgow
Glasgow Cathedral ( gd, Cathair-eaglais Ghlaschu) is a parish church of the Church of Scotland in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest cathedral in mainland Scotland and the oldest building in Glasgow. The cathedral was the seat of the Archbishop ...
), Gloucester, Hereford
Hereford () is a cathedral city, civil parish and the county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, south-west of Worcester and north-west of Gloucester. With a population ...
, Lincoln
Lincoln most commonly refers to:
* Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the sixteenth president of the United States
* Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England
* Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S.
* Lincoln ...
, St David's
St Davids or St David's ( cy, Tyddewi, , "David's house”) is a city and a community (named St Davids and the Cathedral Close) with a cathedral in Pembrokeshire, Wales, lying on the River Alun. It is the resting place of Saint David, Wa ...
, Salisbury
Salisbury ( ) is a cathedral city in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers Avon, Nadder and Bourne. The city is approximately from Southampton and from Bath.
Salisbury is in the southeast of Wil ...
, Truro
Truro (; kw, Truru) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and civil parishes in England, civil parish in Cornwall, England. It is Cornwall's county town, sole city and centre for administration, leisure and retail trading. Its ...
, Wells
Wells most commonly refers to:
* Wells, Somerset, a cathedral city in Somerset, England
* Well, an excavation or structure created in the ground
* Wells (name)
Wells may also refer to:
Places Canada
*Wells, British Columbia
England
* Wells ...
and Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs Nation ...
. In addition there were a large number of concert and parish church organs of note, including the organ at St George's Hall Windsor Castle
Windsor Castle is a royal residence at Windsor in the English county of Berkshire. It is strongly associated with the English and succeeding British royal family, and embodies almost a millennium of architectural history.
The original cast ...
, destroyed by fire in 1992.
The last major instrument which he personally supervised was at St Bees Priory
St Bees Priory is the parish church of St Bees, Cumbria, England. There is evidence for a pre-Norman religious site, and on this a Benedictine priory was founded by the first Norman Lord of Egremont William Meschin, and was dedicated by Archbi ...
in 1899, which he voiced himself, although approaching his 80th year.

Organist
Willis had a series of organist posts. In 1835 he became organist of Christ Church,Hoxton
Hoxton is an area in the London Borough of Hackney, England. As a part of Shoreditch, it is often considered to be part of the East End – the historic core of wider East London. It was historically in the county of Middlesex until 1889. I ...
, and then St John-at-Hampstead
St John-at-Hampstead is a Church of England parish church dedicated to St John the Evangelist (though the original dedication was only refined from St John to this in 1917 by the Bishop of London) in Church Row, Hampstead, London.
History
H ...
from before the middle of 1852, then at Christ Church, Hampstead
Christ Church, Hampstead, is a Church of England church in Hampstead, London. It is a church with particular connections to the old village of Hampstead and the Heath.
Former Prime Minister Clement Attlee was married to his wife, Violet Attlee, ...
from 1852 to 1859, where he had built the organ, and then the Chapel-of-Ease, Islington (now St Mary Magdalene Church) for nearly thirty years until 1895.
Family
He was born to Henry Willis (1792–1872) and Elizabeth. He married Esther Maria Chatterton (1817-1893), the daughter of Randall Chatterton, a silversmith, on 7 April 1847 in St Andrew's Church, Holborn and they had the following children *Vincent Willis (1848–1928) *Edith Willis (1850–1947) *Henry Willis II (1852–1927) *Kate Willis (1853–1927) *Mary Willis (1859–1952) Esther died in 1893 and on 7 August 1894 he married her younger sister, Rosetta Chatterton (1830–1912), at St Thomas' Church,Camden Town
Camden Town (), often shortened to Camden, is a district of northwest London, England, north of Charing Cross. Historically in Middlesex, it is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Camden, and identified in the London Plan as o ...
. As this was before the enactment of the Deceased Wife's Sister's Marriage Act 1907
The Deceased Wife's Sister's Marriage Act 1907 ( 7 Edw.7 c.47) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, allowing a man to marry his dead wife's sister, which had previously been forbidden. This prohibition had derived from a doctrine ...
, it was in breach of the prohibition in the Marriage Act 1835.
Legacy
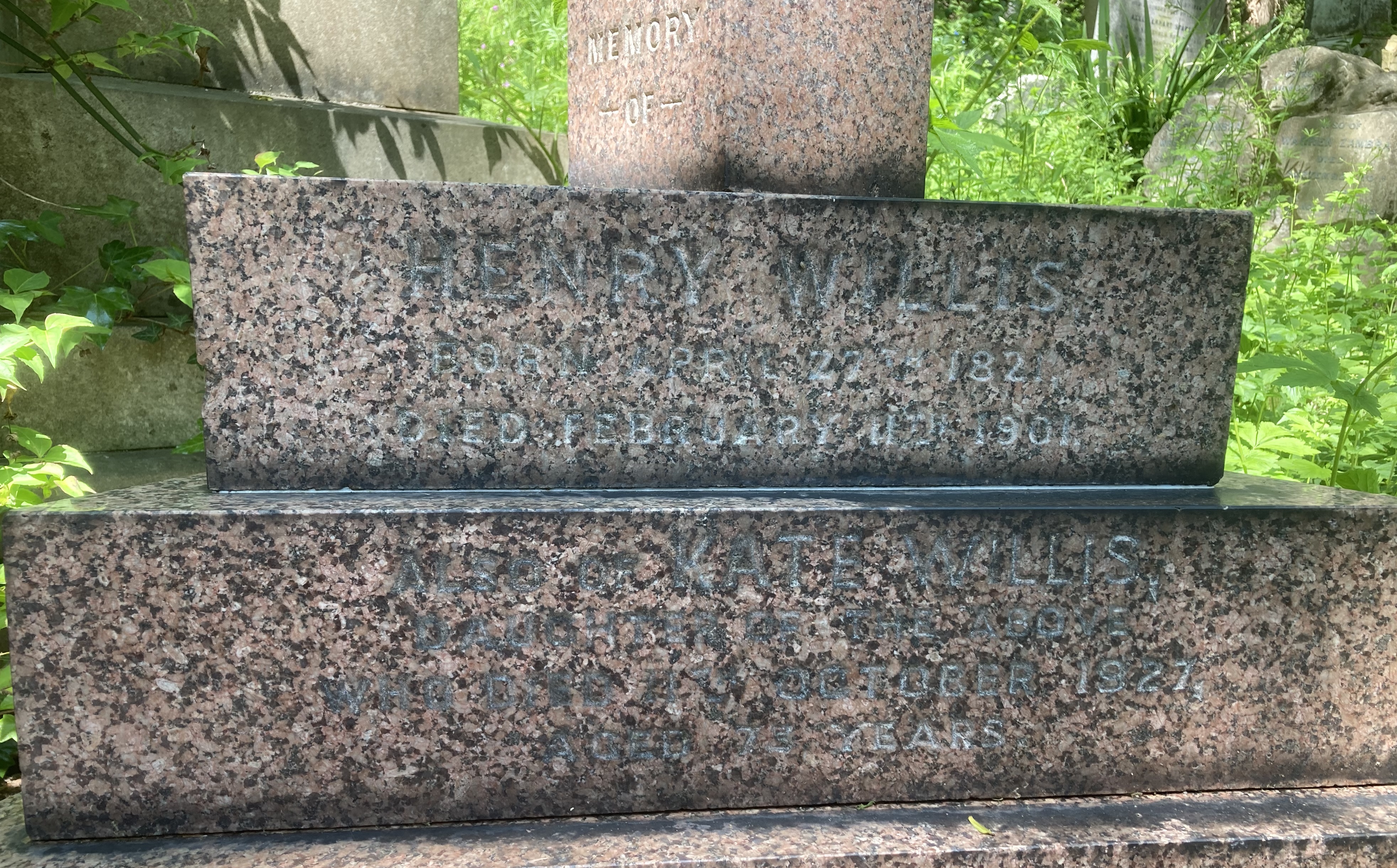 Willis died in London on the 11th February 1901, and is buried on the west side of
Willis died in London on the 11th February 1901, and is buried on the west side of Highgate Cemetery
Highgate Cemetery is a place of burial in north London, England. There are approximately 170,000 people buried in around 53,000 graves across the West and East Cemeteries. Highgate Cemetery is notable both for some of the people buried there as ...
.''Dictionary of National Biography, 1912 Supplement'', p 681.
His instruments can be found across the world, particularly in the former British Empire, and his superb reed voicing and excellent mechanical craftmanship can still be experienced on many instruments today. The last organ built by Willis was at St Nicholas' Chapel, King's Lynn
King's Lynn, known until 1537 as Bishop's Lynn and colloquially as Lynn, is a port and market town in the borough of King's Lynn and West Norfolk in the county of Norfolk, England. It is located north of London, north-east of Peterborough, no ...
which is now under the care of the Churches Conservation Trust
The Churches Conservation Trust is a registered charity whose purpose is to protect historic churches at risk in England. The charity cares for over 350 churches of architectural, cultural and historic significance, which have been transferred in ...
.
Four generations of the Willis family continued the family tradition of organ building until 1997, when Henry Willis IV retired and the first non-family Managing Director was appointed. On 28 November 1998 the total shareholding of the Willis family was acquired. The company, founded in 1845, Henry Willis & Sons
Henry Willis & Sons is a British firm of pipe organ builders founded in 1845. Although most of their installations have been in the UK, examples can be found in other countries.
Five generations of the Willis family served as principals of th ...
, Ltd. still makes organs in Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
.
References
Sources
* William Leslie Sumner (1973''The Organ, its evolution, principles of construction and use''
MacDonald and Jane's, London
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Willis 1821 births 1901 deaths Burials at Highgate Cemetery British pipe organ builders