Heinkel He 112 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Heinkel He 112 is a German fighter aircraft designed by Walter and Siegfried Günter. It was one of four aircraft designed to compete for the 1933 fighter contract of the ''
 In October 1936, the RLM changed the orders for the zero series 112s, instructing Heinkel to complete any A-0s already under construction and then switch the remaining aircraft to an updated design. This gave Heinkel a chance to improve the He 112, which it did by completely redesigning it into an almost entirely new aircraft called the He 112B. It is at this point that it became a modern design that could compete head-to-head with the Bf 109.
The He 112B had a redesigned and cut-down rear fuselage, a new fin and rudder and a completely enclosed cockpit with a bubble-style canopy. The canopy was somewhat more complex than later bubble designs; instead of having two pieces with the majority sliding to the rear, the He 112B canopy was in three pieces, the middle sliding back and over a fixed rear section. Even with the additional framing, the He 112 had excellent visibility for its day. Armament was also standardized on the B model with two 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 17 machine guns in the sides of the cowling with 500 rpg and two 20 mm MG FF cannons in the wings with 60 rpg. For aiming, the cockpit included the new Revi 3B
In October 1936, the RLM changed the orders for the zero series 112s, instructing Heinkel to complete any A-0s already under construction and then switch the remaining aircraft to an updated design. This gave Heinkel a chance to improve the He 112, which it did by completely redesigning it into an almost entirely new aircraft called the He 112B. It is at this point that it became a modern design that could compete head-to-head with the Bf 109.
The He 112B had a redesigned and cut-down rear fuselage, a new fin and rudder and a completely enclosed cockpit with a bubble-style canopy. The canopy was somewhat more complex than later bubble designs; instead of having two pieces with the majority sliding to the rear, the He 112B canopy was in three pieces, the middle sliding back and over a fixed rear section. Even with the additional framing, the He 112 had excellent visibility for its day. Armament was also standardized on the B model with two 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 17 machine guns in the sides of the cowling with 500 rpg and two 20 mm MG FF cannons in the wings with 60 rpg. For aiming, the cockpit included the new Revi 3B
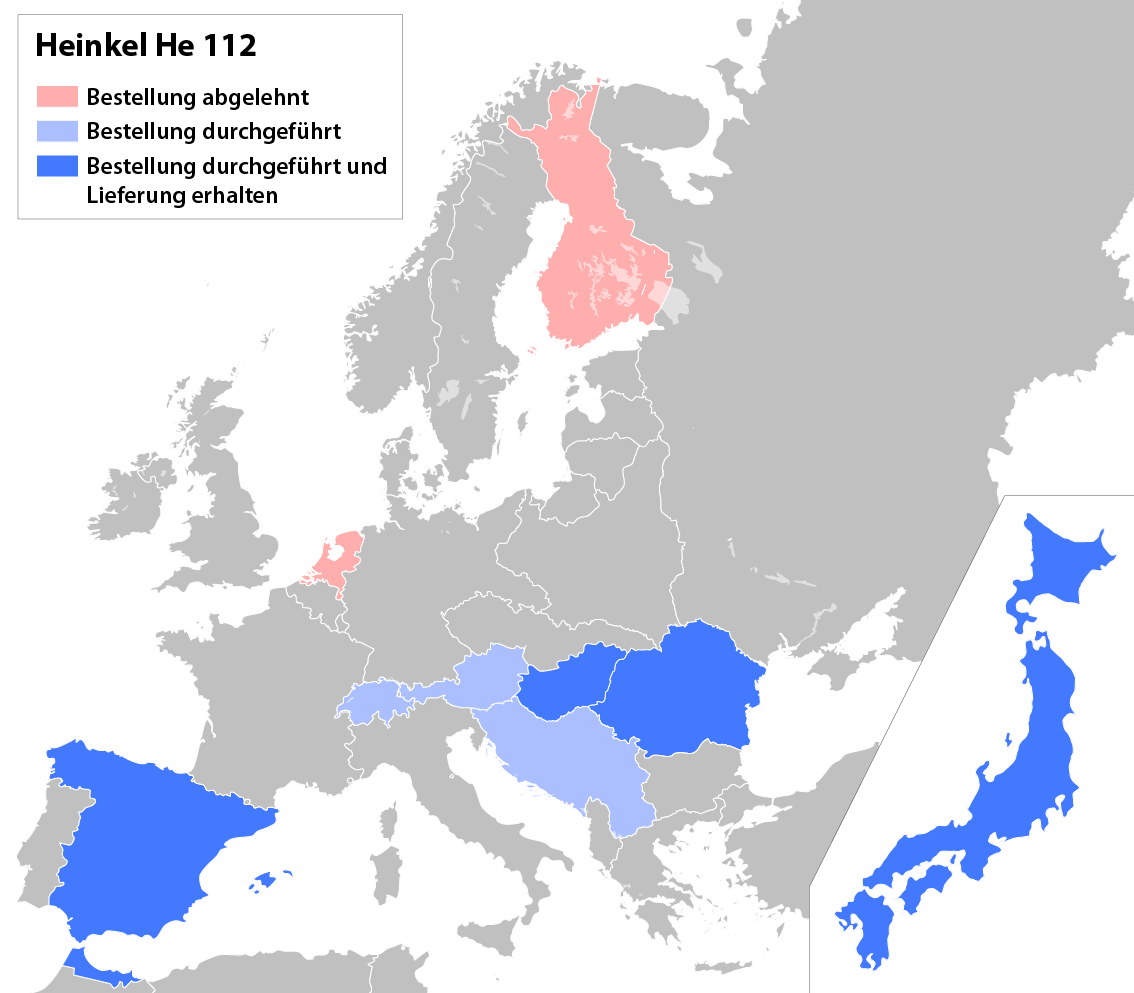
 Like the Germans, Hungary had stiff regulations imposed on its armed forces with the signing of the Treaty of Trianon. In August 1938, the armed forces were re-formed, and with Austria (historically her partner for centuries) being incorporated into Germany, Hungary found herself in the German sphere.
One of the highest priorities for the forces was to re-equip the Hungarian Air Force (Magyar Királyi Honvéd Légierő or MKHL) as soon as possible. Of the various aircraft being considered, the He 112B eventually won out over the competition, and on 7 September, an order was placed for 36 aircraft. The Heinkel production line was just starting, and with Japan and Spain in the queue, it would be some time before the aircraft could be delivered. Repeated pleas to be moved to the top of the queue failed.
Germany had to refuse the first order at the beginning of 1939 because of its claimed neutrality in the Hungarian/Romanian dispute over Transylvania. In addition, the RLM refused to license the 20 mm MG FF cannon to the Hungarians, likely as a form of political pressure. This later insult did not cause a problem, because they planned to replace it with the locally designed 20 mm Danuvia cannon anyway.
V9 was sent to Hungary as a demonstrator after a tour of Romania, and arrived on 5 February 1939. It was test flown by a number of pilots over the next week, and on 14 February, they replaced the propeller with a new three-bladed Junkers design (licensed from Hamilton). While being tested against a CR.32 that day, V9 crashed. On 10 March, a new He 112 B-1/U2 arrived to replace the V9 and was flown by a number of pilots at different fighter units. It was during this time that the Hungarian pilots started to complain about the underpowered engine, as they found that they could reach a top speed of only 430 km/h (270 mph) with the Jumo 210Ea.
With the Japanese and Spanish orders filled, things were looking up for Hungary. However, at that point, Romania placed its order, and was placed at the front of the queue. It appeared that the Hungarian production machines might never arrive, so the MKHL started pressing for a license to build the aircraft locally. In May, the Hungarian Manfred-Weiss company in
Like the Germans, Hungary had stiff regulations imposed on its armed forces with the signing of the Treaty of Trianon. In August 1938, the armed forces were re-formed, and with Austria (historically her partner for centuries) being incorporated into Germany, Hungary found herself in the German sphere.
One of the highest priorities for the forces was to re-equip the Hungarian Air Force (Magyar Királyi Honvéd Légierő or MKHL) as soon as possible. Of the various aircraft being considered, the He 112B eventually won out over the competition, and on 7 September, an order was placed for 36 aircraft. The Heinkel production line was just starting, and with Japan and Spain in the queue, it would be some time before the aircraft could be delivered. Repeated pleas to be moved to the top of the queue failed.
Germany had to refuse the first order at the beginning of 1939 because of its claimed neutrality in the Hungarian/Romanian dispute over Transylvania. In addition, the RLM refused to license the 20 mm MG FF cannon to the Hungarians, likely as a form of political pressure. This later insult did not cause a problem, because they planned to replace it with the locally designed 20 mm Danuvia cannon anyway.
V9 was sent to Hungary as a demonstrator after a tour of Romania, and arrived on 5 February 1939. It was test flown by a number of pilots over the next week, and on 14 February, they replaced the propeller with a new three-bladed Junkers design (licensed from Hamilton). While being tested against a CR.32 that day, V9 crashed. On 10 March, a new He 112 B-1/U2 arrived to replace the V9 and was flown by a number of pilots at different fighter units. It was during this time that the Hungarian pilots started to complain about the underpowered engine, as they found that they could reach a top speed of only 430 km/h (270 mph) with the Jumo 210Ea.
With the Japanese and Spanish orders filled, things were looking up for Hungary. However, at that point, Romania placed its order, and was placed at the front of the queue. It appeared that the Hungarian production machines might never arrive, so the MKHL started pressing for a license to build the aircraft locally. In May, the Hungarian Manfred-Weiss company in
 Germany looked on Romania as an important supplier of war material, notably oil and grain. Looking to secure Romania as an ally, throughout the middle of the 1930s, Germany applied increasing pressure in a variety of forms, best summed up as the "carrot and stick" approach. The carrot came in the form of generous trade agreements for a variety of products and by the late 1930s, Germany formed about ½ of all of Romania's trade. The stick came in the form of Germany siding with Romania's enemies in various disputes.
On 26 June 1940, the
Germany looked on Romania as an important supplier of war material, notably oil and grain. Looking to secure Romania as an ally, throughout the middle of the 1930s, Germany applied increasing pressure in a variety of forms, best summed up as the "carrot and stick" approach. The carrot came in the form of generous trade agreements for a variety of products and by the late 1930s, Germany formed about ½ of all of Romania's trade. The stick came in the form of Germany siding with Romania's enemies in various disputes.
On 26 June 1940, the
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
'', in which it came second behind the Messerschmitt Bf 109. Small numbers were used for a short time by the ''Luftwaffe'' and some were built for other countries, around 100 being completed.
Design and development
In the early 1930s, the German authorities started placing orders for new aircraft, initially training and utility aircraft. Heinkel, as one of the most experienced firms in the country, received contracts for a number of two-seat aircraft, including the He 45, He 46 and He 50. The company also worked on single-seat fighter designs, which culminated in the He 49 and later with the improved He 51. When the He 51 was tested in combat in theSpanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlism, Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebeli ...
, it was shown that speed was far more important than maneuverability. The Luftwaffe took this lesson to heart and started a series of design projects for much more modern aircraft.
In October 1933, Hermann Göring sent out a letter requesting aircraft companies consider the design of a "high speed courier aircraft" – a thinly veiled request for a new fighter. Each company was asked to build three prototypes for run-off testing. By spring 1935, both the Arado and Focke-Wulf aircraft were ready, the BFW arriving in March, and the He 112 in April.
In early May 1934, despite Germany being under a prohibition from the development of new military aircraft, the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM) issued a request for a new single-seat monoplane fighter under the guise that the proposal was for creating a new 'sports plane'. The Technisches Amt outlined specifications, for the supply of a new fighter aircraft, that submissions for the competition had to meet certain characteristics, including; a) have an all-metal construction, b) have a monoplane configuration, c) have retractable landing gear, d) be capable of achieving a top speed of at least at an altitude of , e) endure ninety minutes at full throttle at f) reach an altitude of in seven minutes and have a service ceiling of g) be able to be fitted with a Junkers Jumo 210 engine h) be armed with either two 7.92mm fixed machine guns or one 20mm cannon and i) have a wing loading of less than 100 kg/m2.
In February 1934 three companies, Arado, Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW) and Heinkel, were awarded contracts to develop prototypes for the competition, with a fourth company, Focke-Wulf, being awarded the contract more than six months later in September 1934. The prototypes that were eventually submitted for the competition were the Arado Ar 80, Focke-Wulf Fw 159, Heinkel He 112 and Messerschmitt Bf 109. Heinkel had begun development of its submission in late 1933 in anticipation of the announcement. At the helm of its design project were the Günter brothers, Siegfried and Walter, designers of the He 111, who were then working on the design for the He 112. The first prototype had its first flight in September 1935.
Heinkel's design
Heinkel's design was created primarily by twin brothers Walter and Siegfried Günter, whose designs would dominate most of Heinkel's work. They started work on ''Projekt'' 1015 in late 1933 under the guise of the original courier aircraft, based around the BMW XV inline engine. Work was already under way when the official request went out on 2 May, and on 5 May the design was renamed the He 112. The primary source of inspiration for the He 112 was their earlier He 70 ''Blitz'' ("Lightning") design. The ''Blitz'' was a single-engine, four-passenger aircraft originally designed for use byLufthansa
Deutsche Lufthansa AG (), commonly shortened to Lufthansa, is the flag carrier of Germany. When combined with its subsidiaries, it is the second- largest airline in Europe in terms of passengers carried. Lufthansa is one of the five founding ...
, and it, in turn, was inspired by the famous Lockheed Model 9 Orion mail plane. Like many civilian designs of the time, the aircraft was pressed into military service and was used as a two-seat bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped ...
(although mostly for reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops ( skirmishe ...
) and served in this role in Spain. The ''Blitz'' introduced a number of new construction techniques to the Heinkel company; it was its first low-wing monoplane, its first with retractable landing gear
Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for takeoff or landing. For aircraft it is generally needed for both. It was also formerly called ''alighting gear'' by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Marti ...
, its first all-metal monocoque design, and its elliptical, reverse- gull wing would be seen on a number of later projects. The ''Blitz'' could almost meet the new fighter requirements itself, so it is not surprising that the Günters would choose to work with the existing design as much as possible.
Ernst Heinkel's He 112 submission was a scaled-down version of the He 70, a fast mail-plane, sharing numerous features with it including; an all-metal construction – including its oval cross-section fuselage and two- spar monoplane wings which were covered with flush-head rivets and stressed metal skin-, similar inverted semi-elliptical gullwings and retractable landing gear. The wide-track of the undercarriage, a result of having outward retraction from the low point of the wing's gull-bend, gave the aircraft excellent ground handling for take-off and landing. The open cockpit and fuselage spine behind the headrest mounted into the deep-section fuselage offered the pilot a good view when taxiing and were included to provide excellent vision and make biplane-trained pilots feel more comfortable.
Prototypes
The first prototype, V1, was completed on 1 September 1935. Specifications of the Technisches Amt required that the competing aircraft be fitted with the Junkers Jumo 210, however, as the engine was unavailable, a Rolls-Royce Kestrel V was fitted instead. The V1 prototype of the Heinkel had comparatively large wings and was heavier than its contemporaries, however, due to the wing size, the mass was more evenly spread out resulting in lower wing-loading. The upshot of this was that the aircraft had better turn performance; the downshot was that it generated more drag than expected and had a slowed roll rate. The second prototype, V2, was completed in November. It was powered by a Jumo 210C engine and fitted with a three-blade propeller, but was otherwise identical to the V1. Meanwhile, the data from the V1 factory flights was studied to discover where the unexpected drag was coming from. The Günter brothers identified the large, thick wing as the main culprit, and designed an entirely new smaller and thinner wing with an elliptical planform. As a stop-gap measure, the V2 had its wings clipped by to allow it to compete with the 109. This made the He 112 creep over the wing loading requirements in the specifications, but with the 109 way over the limit, this was not seen as a problem, and the V2 was sent off for testing. The V2, like its predecessor, had problems with spin stability and eventually crashed and was destroyed when test pilot Gerhard Nitschke bailed from the aircraft after losing control during a set of spin tests. The V3 took to the air in January. Largely similar to the V2 and powered with the same engine, the V3 had minor changes including having a larger radiator, fuselage spine and vertical stabilizer, having a single cover over the exhaust ports instead of the more common "stack", and it also included modifications to allow armament to be installed in the cowling. The V3 was the first prototype fitted with armament in the form of two MG17 machine guns. It was later modified once more to include a sliding canopy and a new fully elliptical wing. It was expected to join the V2 in testing but instead was assigned back to Heinkel in early 1937 for tests with rocket propulsion. During a test, the rocket exploded and the aircraft was destroyed, but in an amazing effort the V3 was rebuilt with several changes, including an enclosed cockpit.The contest
At the competing aircraft's demonstration flight for the RLM in October 1935, the thick high-lift aerofoil and open cockpit of the He 112 generated more drag than its contemporary opponent, the Bf 109, causing its performance to suffer despite being equipped with an identical engine. Whereas the Bf 109 prototype was able to clock in a top speed of 467 km/h (290 mph), the He 112 could manage only 440 km/h (273 mph). The other competing aircraft, the Arado Ar 80 and the Focke-Wulf Fw 159, had been plagued with problems from the outset and were outclassed by both the Bf 109 and the He 112 resulting in them being eliminated from any serious consideration. At the end of the demonstrations, Messerschmitt and Heinkel were awarded contracts to produce ten prototypes for further testing and competitive trials. At this point, the He 112 was the favorite over the "unknown" Bf 109, but opinions changed when the Bf 109 V2 arrived on 21 March. All the competitor aircraft had initially been equipped with the Rolls-Royce Kestrel engine, but the Bf 109 V2 had the Jumo. From that point on, it started to outperform the He 112 in almost every way, and even the arrival of the Jumo-engined He 112 V2 on 15 April did little to address this imbalance. The He 112 had better turn performance due to its larger wing, but the Bf 109 was faster at all altitudes and had considerably better agility and aerobatic abilities. During spin tests on 2 March, the Bf 109 V2 showed no problems while the He 112 V2 crashed. Repairs were made to the aircraft and it was returned in April, but it crashed again and was written off. The V1 was then returned to Heinkel on 17 April and fitted with the V2's clipped wings. Meanwhile, news came in that Supermarine had received a contract for full-scale production of the Spitfire. The Spitfire was far more advanced than any existing German aircraft and this caused a wave of concern in the high command of the ''Luftwaffe''. Time now took on as much importance as any quality of the winning aircraft itself, and the RLM was ready to put any reasonable design into production. That design was the Bf 109, which in addition to demonstrating better performance, was considerably easier to build due to fewer compound curves and simpler construction throughout. On 12 March RLM produced a document called ''Bf 109 Priority Procurement'' which indicated which aircraft was now preferred. There were some within the RLM who still favored the Heinkel design, and as a result the RLM then sent out contracts for 10 "zero series" aircraft from both companies. Testing continued until October, at which point some of the additional zero series aircraft had arrived. At the end of September, there were four He 112s being tested, yet none was a match for the Bf 109. From October on, the Bf 109 appears to have been selected as the winner of the contest. Although no clear date is given, in ''Stormy Life'' Ernst Udet himself delivered the news to Heinkel that the Bf 109 had entered series production in 1936. He is quoted as saying, "Pawn your crate off on the Turks or the Japanese or the Romanians. They'll lap it up." With a number of air forces looking to upgrade from biplanes and various designs from the early 1930s, the possibility for foreign sales was promising.He 112A
Prototypes
Heinkel had expected orders for additional aircraft beyond the initial three prototypes, and was able to respond quickly to the new contract for the 10 zero series aircraft. The new aircraft would be given the series designation "He 112 A-0". The first of these new versions, V4, was completed in June 1936. It featured a new elliptical wing, a more powerful 210D engine with a two-speedsupercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.
The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced indu ...
that brought the power to for takeoff and a smaller tailplane. Like the V3, it also sported two fuselage-mounted MG 17 machine guns, unlike the V3, it featured two wing-mounted Oerlikon MG FF cannons that earned it the nickname ''kanonenvogel'' (literally, cannon bird).
A prototype, known as the V5, was designed and built by engineer Wernher von Braun, who would later design the V-2 rocket
The V-2 (german: Vergeltungswaffe 2, lit=Retaliation Weapon 2), with the technical name '' Aggregat 4'' (A-4), was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was develop ...
. This variant of the fighter He 112 was powered by an additional rocket engine. First flown in early 1937, the He 112 V5 demonstrated the feasibility of rocket power for aircraft.
In July, both V5 and V6 were completed. V5 was identical to V4, with the Jumo 210D engine. V6, on the other hand, was completed as the pattern aircraft for the A series production run, and thus included the 210C engine instead of the more powerful, but less available 210D. The only other change was a modification to the radiator, but this would not appear on later A-0 series models. V6 suffered a forced landing on 1 August and was repaired and joined V4 for testing in October.
The last of the prototype A-0 series was V8, which was completed in October. It switched engines entirely and mounted the Daimler-Benz DB 600Aa, along with a three-bladed, fully adjustable, all-metal propeller. The engine was a huge change for the aircraft, producing 716 kW (960 hp) for takeoff and had 33.9 L (2,069 in³) displacement at 686 kg (1,510 lb), compared that to the Jumo 210D's from 19.7 L (1,202 in³) at about the same weight. V8 was seen primarily as a testbed for the new engine, and more importantly, its cooling systems. The DB used a dry liner in the engine that resulted in poor heat flow, so more of the heat was removed by oil as opposed to water, requiring changes to the cooling systems.
In March 1937, the aircraft was assigned to rocket propulsion tests at Peenemünde. It completed these tests later that summer and was returned to the factory, where it was converted back into a normal model. At the end of the year, it was sent to Spain, where it was seriously damaged on 18 July 1938. Once again, it was put back together and was flying four months later. Its fate after this time is not recorded.
Production models
At this point, the prototype stage was ostensibly over, and Heinkel continued building the A-0 as production line models. The naming changed, adding a production number to the end of the name, so the next six examples were known as He 112 A-01 through A-06. All of these included the 210C engine and were essentially identical to V6, with the exception of the radiator. These aircraft were used in just as varied a manner as the earlier V series had been. A-01 flew in October 1936 and was used as the prototype for a future 112 C-0 carrier-based aircraft. It was later destroyed during rocket tests. A-02 flew in November, and then joined the earlier V models at Rechlin-Lärz Airfield for further testing in the contest. A-03 and A-04 were both completed in December, A-03 was a show aircraft and was flown by Heinkel pilots at various air shows and exhibitions, A-04 was kept at Heinkel for various tests. The last two models of the A-0 series, A-05 and A-06, were completed in March 1937. They were both shipped to Japan as the initial machines of the 30 for theImperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
.
He 112B
Prototypes
 In October 1936, the RLM changed the orders for the zero series 112s, instructing Heinkel to complete any A-0s already under construction and then switch the remaining aircraft to an updated design. This gave Heinkel a chance to improve the He 112, which it did by completely redesigning it into an almost entirely new aircraft called the He 112B. It is at this point that it became a modern design that could compete head-to-head with the Bf 109.
The He 112B had a redesigned and cut-down rear fuselage, a new fin and rudder and a completely enclosed cockpit with a bubble-style canopy. The canopy was somewhat more complex than later bubble designs; instead of having two pieces with the majority sliding to the rear, the He 112B canopy was in three pieces, the middle sliding back and over a fixed rear section. Even with the additional framing, the He 112 had excellent visibility for its day. Armament was also standardized on the B model with two 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 17 machine guns in the sides of the cowling with 500 rpg and two 20 mm MG FF cannons in the wings with 60 rpg. For aiming, the cockpit included the new Revi 3B
In October 1936, the RLM changed the orders for the zero series 112s, instructing Heinkel to complete any A-0s already under construction and then switch the remaining aircraft to an updated design. This gave Heinkel a chance to improve the He 112, which it did by completely redesigning it into an almost entirely new aircraft called the He 112B. It is at this point that it became a modern design that could compete head-to-head with the Bf 109.
The He 112B had a redesigned and cut-down rear fuselage, a new fin and rudder and a completely enclosed cockpit with a bubble-style canopy. The canopy was somewhat more complex than later bubble designs; instead of having two pieces with the majority sliding to the rear, the He 112B canopy was in three pieces, the middle sliding back and over a fixed rear section. Even with the additional framing, the He 112 had excellent visibility for its day. Armament was also standardized on the B model with two 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 17 machine guns in the sides of the cowling with 500 rpg and two 20 mm MG FF cannons in the wings with 60 rpg. For aiming, the cockpit included the new Revi 3B reflector gunsight
A reflector sight or reflex sight is an optical sight that allows the user to look through a partially reflecting glass element and see an illuminated projection of an aiming point or some other image superimposed on the field of view. These s ...
.
The first B series airframe to be completed was V7 in October 1936. V7 used the DB 600Aa engine like the A-series V8, and it also used the original V1 style larger wing. This wing was later replaced with a smaller one but instead of the clipped version from the earlier V models, a new single-spar fully elliptical wing was produced. This design became standard for the entire B series. V7 was turned over to von Braun in April 1937 for yet more rocket tests and managed to survive the experience. It was then returned in the summer and sent to Rechlin where it was used as a test aircraft.
The next type was V9 which flew in July 1937, powered by the Jumo 210D engine. V9 can be considered to be the "real" B series prototype, as V7 had received the DB 600Aa originally for experimental reasons. The entire surface was now flush riveted and the aircraft had several other aerodynamic refinements. The radiator was changed again, this time to a semi-retractable design for reduced drag in flight. The aircraft also underwent a weight reduction program which reduced the empty weight to 1,617 kg (3,565 lb).
As a result of all of these changes, the V9 had a maximum speed of 485 km/h (301 mph) at 4,000 m (13,120 ft), and 430 km/h (270 mph) at sea level. This was a full 20 km/h (10 mph) faster than the contemporary Bf 109B. Nevertheless, by this time, the Bf 109 was already being mass-produced and the RLM saw no need for another similar aircraft. It is also worth noting that users of the aircraft generally found it impossible to reach this speed and rarely managed to exceed 418 km/h (260 mph).
The RLM had already contracted for another six He 112s, so production of the prototypes continued. V10 was supposed to receive the 670 kW (960 hp) Junkers Jumo 211A (Junker's new DB 600 competitor) but the engine was not available in time and V10 instead received the new 876 kW (1,175 hp) DB 601Aa. The engine drove V10 to 570 km/h (350 mph) and increased climb rate significantly. V11 was also supposed to get the Jumo 211A but instead received the DB 600Aa.
The last prototype, V12, was actually an airframe taken off the B-1 series production line (which had started by this point). The Jumo 210D was replaced with the new fuel-injected 210Ga, which improved performance of the engine to 522 kW (700 hp) for takeoff, and a sustained output of 503 kW (675 hp) at the reasonably high altitude of 4,700 m (15,420 ft). Better yet, the Ga also decreased fuel consumption, thus increasing the aircraft's endurance. The new engine gave V12 such a boost that it became the pattern aircraft for the planned B-2 series production.
With all of these different versions and experimental engine fits, it might seem like every aircraft differed significantly but with the exception of the engines, the Bs were identical. Due to the shortage of just about any German engine at the time and the possibility that advanced versions could be blocked for export, various models had to be designed with different installations. Thus the B models were different only in their engine, the Jumo 210C in the He 112 B-0, the Jumo 210D in the B-1, and the Jumo 210Ga for the B-2.
Production models
In order to show off the He 112, V9 spent much of the later half of 1937 being flown by pilots from all over the world. It was also sent around Europe for tours and air shows. The effort was a success and orders quickly started coming in. However, a variety of problems meant few of these were ever delivered. The first order was from theImperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
, which had a requirement for a fast climbing interceptor to deal with Tupolev SB bombers over China. After seeing V9 in flight, it quickly placed an order for 24 112Bs, with an option for 48 more. The first four were shipped in December 1937, another eight in the spring, and promises for the rest to arrive in May. Before delivery, the ''Luftwaffe'' unexpectedly took over 12 of the aircraft to bolster its forces during the Sudetenland Crisis. The aircraft were then returned to Heinkel in November, but the Japanese, who were unhappy with the high maintenance workload and lower manoeuvrability compared with fighters like the Mitsubishi A5M
The Mitsubishi A5M, formal Japanese Navy designation , experimental Navy designation Mitsubishi Navy Experimental 9-''Shi'' Carrier Fighter, company designation Mitsubishi ''Ka''-14, was a Japanese carrier-based fighter aircraft. It was the wor ...
, refused to accept them this late and Heinkel was left holding the aircraft.
In November 1937, an Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
n delegation came to see the aircraft, led by ''Generaloberst'' Alexander Löhr, Command-in-Chief of the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' (Austrian Air Force). Test pilot Hans Schalk flew both the Bf 109 and the He 112V9 back to back. Although he felt that both models performed the same, the Heinkel had more balanced steering pressures and better equipment possibilities. They placed an order on 20 December for 42 He 112Bs. Pending the license for the MG FF cannon, these aircraft would remove the cannon and add six THM 10/I bomb shackles which carried small 10 kg (22 lb) anti-personnel bombs. The order was later reduced to 36 examples due to a lack of funds (the He 112B cost ), but the aircraft were never delivered due to the annexation of Austria in the March 1938 Anschluss
The (, or , ), also known as the (, en, Annexation of Austria), was the annexation of the Federal State of Austria into the Nazi Germany, German Reich on 13 March 1938.
The idea of an (a united Austria and Germany that would form a "Ger ...
.
Spain was so impressed with the He 112's performance during evaluation in the civil war that the Spanish Air Force purchased the 12 aircraft in early 1938, and later increased the order by another six (some sources say five). Of the first 12, two were shipped in November, another six in January, and the rest in April.
In April, it looked like Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
would be the next user of the He 112. It placed an order for 30 aircraft, but later cancelled the order and decided to produce other designs under license.
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
appeared to be another potential customer. From January–March 1938, the famous Finnish pilot Gustaf Erik Magnusson travelled to Germany to gain experience in new tactics. He had been on similar tours in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
in the past and was interested to see how the Germans were training their pilots. On a visit to the Heinkel plant in Marienehe, he flew the He 112 and reported it to be the best aircraft he had flown. In May, Heinkel sent the first of the He 112 B-1s to Finland to join an air show. It remained for the next week and was flown by a number of pilots, including Magnusson, who had since returned to Finland. Although all of the pilots liked the aircraft, the cost was so high that the ''Suomen Ilmavoimat'' (Finnish Air Force) decided to stick with the much less expensive Fokker D.XXI
The Fokker D.XXI fighter was designed in 1935 by Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker in response to requirements laid out by the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army Air Force (''Militaire Luchtvaart van het Koninklijk Nederlands-Indisch Leger'', M ...
.
A similar setback would accompany sales efforts targeting the Dutch Air Force, which was looking to purchase 36 fighters to form two new squadrons. A He 112 B-1 arrived for testing on 12 July and quickly proved to be the best aircraft in the competition. Nevertheless, it decided to purchase the locally built (and rather outdated) Koolhoven F.K.58
The Koolhoven F.K.58 was a single engine, interceptor-fighter aircraft designed and mainly manufactured by N V Koolhoven in the Netherlands under contract by France. Intended for ''Armée de l'Air'' use, the F.K.58 saw limited service in the B ...
instead. In the end, the F.K.58s were never delivered because the factory was bombed on 10 May 1940.
Fortunes would be seem to be reversed with Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
. In June 1938, three pilots of the ''Magyar Királyi Honvéd Légierö'' (Royal Hungarian Home Defense Air Force or MKHL) were sent to Heinkel to study V9. They were impressed with what they saw, and on 7 September, an order was placed for 36 aircraft, as well as an offer to license the design for local construction. Through a variety of political mishaps, only three aircraft were ever delivered and licensed production never happened.
The final and perhaps most successful customer for the He 112B was Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
. The ''Forţã Aeronauticã Regalã Românã'' (Royal Romanian Air Force) ordered 24 aircraft in April 1939, and increased the order to 30 on 18 August. Deliveries started in June, with the last being delivered on 30 September.
By this point, war had broken out, and with better models on the market – including Heinkel's own He 100
The Heinkel He 100 was a German pre-World War II fighter aircraft design from Heinkel. Although it proved to be one of the fastest fighter aircraft in the world at the time of its development, the design was not ordered into series production. ...
– no one else was interested in purchasing the design. The production line was closed after a total of only 98 aircraft, 85 of those being the B series models.
He 112R
Early experiments with rocket propulsion
In 1931, the Army Weapons Office testing ground at Kummersdorf had taken over research into liquid-fuelrockets
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entire ...
. In 1932, Wernher von Braun designed a rocket of this kind which used high percentage spirit and liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen—abbreviated LOx, LOX or Lox in the aerospace, submarine and gas industries—is the liquid form of molecular oxygen. It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an a ...
. With this he made the first experiments. In 1934 he fired his second rocket type, the A2, from the North Sea island of Borkum. Having completed the programme of experiments, von Braun was interested in evaluating an aircraft with a rocket motor propulsion system. For this he needed an aircraft and support team. Initially the highest levels at the Army High Command and the Reich Air Ministry (RLM) were opposed to such "fantasies", as they called them. Many people, technicians and academic experts in positions of influence in aeronautics, maintained that an aircraft driven by a tail thrust would experience a change in the centre of gravity and flip over. Very few believed the contrary, but one of them was Ernst Heinkel. Following his offer of unhesitating support, Heinkel placed at the disposal of von Braun an He 112 fuselage shell less wings for the standing tests.
In 1936 von Braun had advanced far enough to begin trials. A great tongue of flame from the rocket motor roared through the fuselage tail to set up the back thrust. Late in 1936 Erich Warsitz was seconded by the RLM to Wernher von Braun and Ernst Heinkel, because he had been recognized as one of the most experienced test pilots of the time, and because he also was technically proficient. Warsitz wrote:
The RLM agreed to lend Neuhardenberg, a large field about 70 kilometres east of Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
, listed as a reserve airfield in the event of war. Since Neuhardenberg had no buildings or facilities, a number of marquees were erected to house the aircraft. In the spring of 1937 the Kummersdorf Club transferred to Neuhardenberg and continued the standing trials with the He 112 fuselage.
In June 1937 Erich Warsitz undertook the initial flight testing of the He 112 fitted with von Braun's rocket engine. Despite the wheels-up landing and having the fuselage on fire, it proved to official circles that an aircraft could be flown satisfactorily with a back-thrust system through the rear.
Also the firm of Hellmuth Walter at Kiel had been commissioned by the RLM to build a rocket engine for the He 112, so there were two different new rocket motor designs at Neuhardenberg; whereas the von Braun's engines were powered by alcohol and liquid oxygen, Walter engines had hydrogen peroxide and calcium permanganate as a catalyst. Von Braun's engine used direct combustion and created fire, the Walter produced hot vapours from a chemical reaction, but both created thrust and provided high speed. The subsequent flights with the He 112 used the Walter-rocket instead of von Braun's; it was more reliable, simpler to operate and the dangers to test pilot Erich Warsitz and machine were less.
After conclusion of the He 112 tests using both rocket motors, the marquees at Neuhardenberg were dismantled at the end of 1937. This coincided with the construction of Peenemünde.
Operational service
Condor Legion
When it was clear the 112 was losing the contest to the Bf 109, Heinkel offered to re-equip V6 with 20 mm cannon armament as an experimental aircraft. She was then broken down and shipped toSpain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
on 9 December and assigned to ''Versuchsjagdgruppe'' 88, a group within the ''Legion Condor'' devoted to testing new aircraft and joined three V-series Bf 109s which were also in testing.
Wilhelm Balthasar, later a Battle of Britain ace pilot used it to attack an armoured train and an armoured car. Other pilots flew it, but the engine seized during landing in July and she was written off.
For the annexation of the Sudetenland, every flight-worthy fighter was pressed into service. The batch of He 112Bs for the Japanese Navy was taken over, but not used before the end of the crisis and shipped to Japan to fulfil orders.
The Japanese rejected the He 112 as a fighter but took 30 for training duties and V11 with its DB 600Aa was used for testing.
The Spanish government purchased 12 He 112Bs. This increased to 19. The He 112s were to operate as top cover for Fiat fighters in the opening stages of the Civil War, the Fiat having considerably worse altitude performance. In the event, only a single kill was made with the He 112 as a fighter and it was moved onto ground-attack work.
During World War II, when Allied forces landed in North Africa, Spanish forces in Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria ...
intercepted stray aircraft of both Allied and German forces. None of these incidents resulted in losses. In 1943, one He 112 of ''Grupo'' nº27 attacked the tail-end aircraft of 11 Lockheed P-38s forcing it down in Algeria after they re-entered French territory having crossed into Spanish Morocco. By 1944, the aircraft were largely grounded due to a lack of fuel and maintenance.
Hungary

 Like the Germans, Hungary had stiff regulations imposed on its armed forces with the signing of the Treaty of Trianon. In August 1938, the armed forces were re-formed, and with Austria (historically her partner for centuries) being incorporated into Germany, Hungary found herself in the German sphere.
One of the highest priorities for the forces was to re-equip the Hungarian Air Force (Magyar Királyi Honvéd Légierő or MKHL) as soon as possible. Of the various aircraft being considered, the He 112B eventually won out over the competition, and on 7 September, an order was placed for 36 aircraft. The Heinkel production line was just starting, and with Japan and Spain in the queue, it would be some time before the aircraft could be delivered. Repeated pleas to be moved to the top of the queue failed.
Germany had to refuse the first order at the beginning of 1939 because of its claimed neutrality in the Hungarian/Romanian dispute over Transylvania. In addition, the RLM refused to license the 20 mm MG FF cannon to the Hungarians, likely as a form of political pressure. This later insult did not cause a problem, because they planned to replace it with the locally designed 20 mm Danuvia cannon anyway.
V9 was sent to Hungary as a demonstrator after a tour of Romania, and arrived on 5 February 1939. It was test flown by a number of pilots over the next week, and on 14 February, they replaced the propeller with a new three-bladed Junkers design (licensed from Hamilton). While being tested against a CR.32 that day, V9 crashed. On 10 March, a new He 112 B-1/U2 arrived to replace the V9 and was flown by a number of pilots at different fighter units. It was during this time that the Hungarian pilots started to complain about the underpowered engine, as they found that they could reach a top speed of only 430 km/h (270 mph) with the Jumo 210Ea.
With the Japanese and Spanish orders filled, things were looking up for Hungary. However, at that point, Romania placed its order, and was placed at the front of the queue. It appeared that the Hungarian production machines might never arrive, so the MKHL started pressing for a license to build the aircraft locally. In May, the Hungarian Manfred-Weiss company in
Like the Germans, Hungary had stiff regulations imposed on its armed forces with the signing of the Treaty of Trianon. In August 1938, the armed forces were re-formed, and with Austria (historically her partner for centuries) being incorporated into Germany, Hungary found herself in the German sphere.
One of the highest priorities for the forces was to re-equip the Hungarian Air Force (Magyar Királyi Honvéd Légierő or MKHL) as soon as possible. Of the various aircraft being considered, the He 112B eventually won out over the competition, and on 7 September, an order was placed for 36 aircraft. The Heinkel production line was just starting, and with Japan and Spain in the queue, it would be some time before the aircraft could be delivered. Repeated pleas to be moved to the top of the queue failed.
Germany had to refuse the first order at the beginning of 1939 because of its claimed neutrality in the Hungarian/Romanian dispute over Transylvania. In addition, the RLM refused to license the 20 mm MG FF cannon to the Hungarians, likely as a form of political pressure. This later insult did not cause a problem, because they planned to replace it with the locally designed 20 mm Danuvia cannon anyway.
V9 was sent to Hungary as a demonstrator after a tour of Romania, and arrived on 5 February 1939. It was test flown by a number of pilots over the next week, and on 14 February, they replaced the propeller with a new three-bladed Junkers design (licensed from Hamilton). While being tested against a CR.32 that day, V9 crashed. On 10 March, a new He 112 B-1/U2 arrived to replace the V9 and was flown by a number of pilots at different fighter units. It was during this time that the Hungarian pilots started to complain about the underpowered engine, as they found that they could reach a top speed of only 430 km/h (270 mph) with the Jumo 210Ea.
With the Japanese and Spanish orders filled, things were looking up for Hungary. However, at that point, Romania placed its order, and was placed at the front of the queue. It appeared that the Hungarian production machines might never arrive, so the MKHL started pressing for a license to build the aircraft locally. In May, the Hungarian Manfred-Weiss company in Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
received the license for the aircraft, and on 1 June, an order was placed for 12 aircraft. Heinkel agreed to deliver a Jumo 210Ga-powered aircraft to serve as a pattern aircraft.
As it turns out, the He 112 B-2 was never delivered; two more of the B-1/U2s with the Jumo 210Ea were sent instead. On arrival in Hungary, the 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 17 machine guns were removed and replaced with the local 8 mm (.315 in) Gebauer Gebauer is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Christian Gebauer (born 1993), Austrian footballer
* Ernst Gebauer (1782–1865), German painter
* Ferenc Gebauer (1888–1958), Austrian-born Hungarian firearms designer and p ...
1939.M machine guns, and bomb racks were added. The resulting fit was similar to those originally ordered by Austria. Throughout this time, the complaints about the engines were being addressed by continued attempts to license one of the newer 30 L (1,831 in³)-class engines, the Junkers Jumo 211A or the DB 600Aa.
On 30 March 1939, the He 100
The Heinkel He 100 was a German pre-World War II fighter aircraft design from Heinkel. Although it proved to be one of the fastest fighter aircraft in the world at the time of its development, the design was not ordered into series production. ...
V8 took the world absolute speed record, but in stories about the record attempt, the aircraft was referred to as the He 112U. Upon hearing of the record, the Hungarians decided to switch production to this "new version" of the 112, which was based on the newer engines. Then in August, the Commander-in-Chief of the MKHL recommended that the 112 be purchased as the standard fighter for Hungary (although likely referring to the earlier versions, not the "112U").
At this point, the engine issue came to a head. It was clear that no production line aircraft would ever reach Hungary, and now that the war was underway, the RLM was refusing to allow their export anyway. Shipments of the Jumo 211 or DB 601 were not even able to fulfill German needs, so export of the engine for locally built airframes was likewise out of the question.
By September, the ongoing negotiations with the RLM for the license to build the engines locally stalled, and as a result, the MKHL ordered Manfred-Weiss to stop tooling up for the production line aircraft. The license was eventually canceled in December. The MKHL turned to the Italians and purchased the Fiat CR.32 and Reggiane Re.2000
The Reggiane Re.2000 ''Falco'' I was an Italian all metal, low-wing monoplane developed and manufactured by aircraft company Reggiane. The type was used by the ''Regia Aeronautica'' (Italian Air Force) and the Swedish Air Force during the first p ...
. The latter would be the backbone of the MKHL for much of the war.
Nevertheless, the three He 112 B-1/U2 aircraft continued to serve on. In the summer of 1940, tensions with Romania over Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
started to heat up again and the entire MKHL was placed on alert on 27 June. On 21 August, the He 112s were moved forward to the Debrecen
Debrecen ( , is Hungary's second-largest city, after Budapest, the regional centre of the Northern Great Plain region and the seat of Hajdú-Bihar County. A city with county rights, it was the largest Hungarian city in the 18th century and i ...
airfield to protect a vital railway link. The next week, a peaceful resolution was found, and the settlement was signed in Vienna on 30 August. The He 112s returned home the following week.
By 1941, the aircraft were ostensibly assigned to defend the Manfred-Weiss plant, but were actually used for training. When Allied bomber raids started in the spring of 1944, the aircraft were no longer airworthy, and it appears all were destroyed in a massive raid on the Budapest-Ferihegy airport on 9 August 1944.
After the licensed production of the He 112B fell through in 1939, the plan was to switch the production line to build a Manfred-Weiss-designed aircraft called the W.M.23 ''Ezüst Nyíl'' ("Silver Arrow"). The aircraft was basically a He 112B adapted to local construction; the wings were wooden versions of the He 112's planform, the fuselage was made of plywood over a steel frame, and the engine was a licensed version of the 746 kW (1,000 hp)-class Gnome-Rhone Mistral-Major radial.
It would seem that this 'simplified' aircraft would be inferior to the He 112, but in fact the higher-powered engine made all the difference and the W.M.23 proved to be considerably faster than the He 112. Nevertheless, work proceeded slowly and only one prototype was built. The project was eventually canceled outright when the prototype crashed in early 1942.
Japan
TheImperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
purchased 12 Heinkel He 112B-0 fighters, which it designated both as the Heinkel A7He1 and as the Navy Type He Air Defense Fighter. The Japanese flew the A7He1 briefly during the Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Thea ...
, but phased it out of service before the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawa ...
in December 1941 in favor of the Mitsubishi A6M Zero
The Mitsubishi A6M "Zero" is a long-range carrier-based aircraft, carrier-based fighter aircraft formerly manufactured by Mitsubishi Aircraft Company, a part of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and was operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy from 19 ...
. Assuming it still to be in Japanese use, however, the Allies assigned the reporting name "Jerry" to the A7He1 during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
Romania
 Germany looked on Romania as an important supplier of war material, notably oil and grain. Looking to secure Romania as an ally, throughout the middle of the 1930s, Germany applied increasing pressure in a variety of forms, best summed up as the "carrot and stick" approach. The carrot came in the form of generous trade agreements for a variety of products and by the late 1930s, Germany formed about ½ of all of Romania's trade. The stick came in the form of Germany siding with Romania's enemies in various disputes.
On 26 June 1940, the
Germany looked on Romania as an important supplier of war material, notably oil and grain. Looking to secure Romania as an ally, throughout the middle of the 1930s, Germany applied increasing pressure in a variety of forms, best summed up as the "carrot and stick" approach. The carrot came in the form of generous trade agreements for a variety of products and by the late 1930s, Germany formed about ½ of all of Romania's trade. The stick came in the form of Germany siding with Romania's enemies in various disputes.
On 26 June 1940, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
gave Romania a 24-hour ultimatum to return Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of ...
and cede northern Bukovina, even though the latter had never even been a part of Russia. Germany's ambassador to Romania advised the king to submit, and he did. In August, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
reclaimed southern Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; bg, Добруджа, Dobrudzha or ''Dobrudža''; ro, Dobrogea, or ; tr, Dobruca) is a historical region in the Balkans that has been divided since the 19th century between the territories of Bulgaria and Romania. I ...
, with German and Soviet backing. Later that month, German and Italian foreign ministers met with Romanian diplomats in Vienna and presented them with an ultimatum to accept the ceding of northern Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
to Hungary.
Romania was placed in an increasingly bad position as its local allies were gobbled up by Germany, and its larger allies' (Britain and France) assurances of help proved empty, as demonstrated by their lack of action during the invasion of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
. Soon the king was forced from the throne and a pro-German government was formed.
With Romania now firmly in the German sphere of influence, its efforts to re-arm for the coming war were suddenly strongly backed. The primary concern was the air force, the FARR. Its fighter force at the time consisted of just over 100 Polish PZL P.11 aircraft, primarily the P.11b or the locally modified f model, and P.24E. Although these aircraft had been the most advanced fighters in the world in the early 1930s, by the late 1930s, they were hopelessly outclassed by practically everything.
In April 1939, the FARR was offered the Bf 109 as soon as production was meeting German demands. In the meantime, it could take over 24 He 112Bs that were already built. The FARR jumped at the chance and then increased the order to 30 aircraft.
Late in April, a group of Romanian pilots arrived at Heinkel for conversion training, which went slowly because of the advanced nature of the He 112 in comparison to the PZL. When the training was complete, the pilots returned home in the cockpits of their new aircraft. The aircraft, all of them B-1s or B-2s, were "delivered" in this manner starting in July and ending in October. Two of the aircraft were lost, one in a fatal accident during training in Germany on 7 September, and another suffered minor damage on landing while being delivered and was later repaired at SET in Romania.
When the first aircraft started arriving, they were tested competitively against the locally designed IAR.80
The IAR 80 was a Romanian World War II low-wing monoplane, all-metal monocoque fighter and ground-attack aircraft. When it first flew, in 1939, it was comparable to contemporary designs being deployed by the airforces of the most advanced mi ...
prototype. This interesting and little known aircraft proved to be superior to the He 112B in almost every way. At the same time, the test flights revealed a number of disadvantages of the He 112, notably the underpowered engine and poor speed. The result of the fly-off was that the IAR.80 was ordered into immediate production, and orders for any additional He 112s were cancelled.
By 15 September, enough of the aircraft had arrived to re-equip ''Escadrila'' 10 and 11. The two squadrons were formed into the ''Grupul 5 vânãtoare'' (5th Fighter Group), responsible for the defense of Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north ...
. In October, they were renamed as the 51st and 52nd squadrons, still forming the 5th. The pilots had not been a part of the group that had been trained at Heinkel, so they started working their way toward the He 112 using Nardi F.N.305 monoplane trainers. Training lasted until the spring of 1940, when a single additional He 112 B-2 was delivered as a replacement for the one that crashed in Germany the previous September.
During the troubles with Hungary, the 51st was deployed to Transylvania. Hungarian Ju 86s and He 70s started making reconnaissance flights over Romanian territory. Repeated attempts to intercept them failed because of the He 112's low speed. On 27 August, ''Locotenent'' Nicolae Polizu was over Hungarian territory when he encountered a Caproni Ca.135bis bomber flying on a training mission. Several of his 20 mm rounds hit the bomber, which was forced down safely at the Hungarian Debrecen airbase – home of the Hungarian He 112s. Polizu became the first Romanian to shoot down an aircraft in aerial combat.
When Germany prepared to invade the USSR in 1941, Romania joined it in an effort to regain the territories lost the year before. The FARR was made part of ''Luftflotte'' 4, and in preparation for the invasion, ''Grupul 5 vânãtoare'' was sent to Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Centra ...
. At the time, 24 of the He 112s were flyable. Three were left at their home base at Pipera to complete repairs, two others had been lost to accidents, and the fate of the others is unknown. On 15 June, the aircraft were moved again, to Foscani-North in northern Moldavia.
With the opening of the war on 22 June, the He 112s were in the air at 1050 supporting an attack by Potez 63s of ''Grupul 2 bombardment'' on the Soviet airfields at Bolgrad and Bulgãrica. Although some ''flak'' was encountered on the way to and over Bolgrad, the attack was successful and a number of Soviet aircraft were bombed on the ground. By the time they reached Bulgãrica, fighters were in the air waiting for them, and as a result the 12 He 112s were met by about 30 I-16s. The results of this combat were mixed; ''Sublocotenent'' Teodor Moscu shot down one of a pair of I-16s still taking off. When he was pulling out, he hit another in a head-on pass and it crashed into the Danube. He was set upon by several I-16s and received several hits, his fuel tanks were punctured but did not seal. Losing fuel rapidly, he formed up with his wingman and managed to put down at the Romanian airfield at Bârlad. His aircraft was later repaired and returned to duty. Of the bombers, three of the 13 dispatched were shot down.
Over the next few days, the He 112s would be used primarily as ground-attack aircraft, where their heavy armament was considered to be more important than their ability to fight in the air. Typical missions would start before dawn and would have the Heinkels strafe Soviet airbases. Later in the day, they would be sent on search and destroy missions, looking primarily for artillery and trains.
Losses were heavy, most not due to combat, but simply because the aircraft were flying an average of three missions a day and were not receiving adequate maintenance. This problem affected all of the FARR, which did not have the field maintenance logistics worked out at the time. On 29 July, a report on the readiness of the air forces listed only 14 He 112s in flyable condition, and another eight repairable. As a result, the aircraft of the 52nd were folded into the 51st to form a single full strength squadron on 13 August. The men of the 52nd were merged with the 42nd who flew IAR.80s, and were soon sent home to receive IAR.80s of their own. A report from August on the He 112 rated it very poorly, once again noting its lack of power and poor speed.
For a time, the 51st continued in a front-line role, although it saw little combat. When Odessa fell on 16 October, the Romanian war effort ostensibly ended, and the aircraft were considered to be no longer needed at the front. 15 were kept at Odessa and the rest were released to Romania for training duty (although they seem to have seen no use). On 1 November, the 51st moved to Tatarka and then returned to Odessa on the 25th, performing coastal patrol duties all the while. On 1 July 1942, the 51st returned to Pipera and stood down after a year in action.
On 19 July one of the He 112s took to the air to intercept Soviet bombers in what was the first night mission by a Romanian aircraft. As the Soviets were clearly gearing up for a night offensive on Bucharest, the 51st was then re-equipped with Bf 110 night fighter
A night fighter (also known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor for a period of time after the Second World War) is a fighter aircraft adapted for use at night or in other times of bad visibility. Night fighters began to be used ...
s and became the only Romanian night fighter squadron.
By 1943, the IAR.80 was no longer competitive, and the FARR started an overdue move to a newer fighter. The fighter in this case was the Bf 109G. The He 112s found themselves actively being used in the training role at last. The inline engine and general layout of the German designs was considered similar enough to make it useful in this role, and as a result the He 112s came under the control of the ''Corpul 3 Aerian'' (3rd Air Corps). Several more of the He 112s were destroyed in accidents during this time. It soldiered on in this role into late 1944, even after Romania had changed sides and joined the Allies.
Specifications (He 112 A-0 V4)
See also
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * Bernád, Dénes. ''Heinkel He 112 in Action''. Carrollton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, 1996. * * * Fleischer, Seweryn. ''Heinkel 112 (Wydawnictwo Militaria 164)'' (in Polish). Warszawa, Poland: Wydawnictwo Militaria, 2002. . * * * . * * Heinkel, Ernst. ''Stormy Life''. Boston: E.P. Dutton, 1956. * Hirsch, R.S. ''Heinkel 100, 112 (Aero Series 12)''. Fallbrook, California: Aero Publishers, 1967. . * * * * * * * * * . * * . * *External links
{{Authority control 1930s German fighter aircraft He 112 Single-engined tractor aircraft Low-wing aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1935 World War II fighter aircraft of Germany