Healthcare In Angola on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]



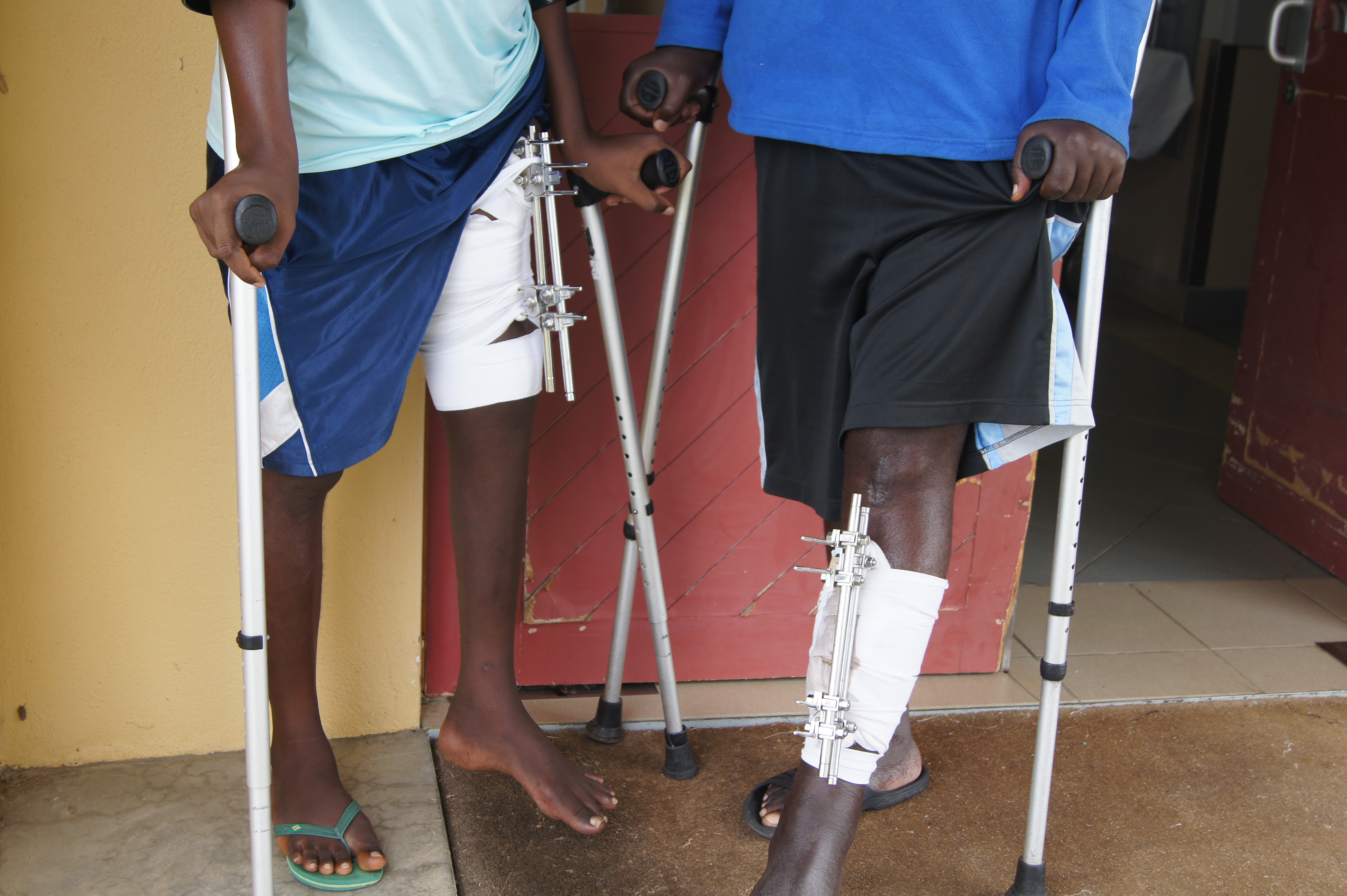
 Healthcare in Angola consists of a network of hospitals, clinics, and dispensaries.
Healthcare in Angola consists of a network of hospitals, clinics, and dispensaries.
April 9, 2012.




 Healthcare in Angola consists of a network of hospitals, clinics, and dispensaries.
Healthcare in Angola consists of a network of hospitals, clinics, and dispensaries.
Description
The National Health Service in Angola is run by the Ministry of Health, the Provincial Governments run Provincial Hospitals and the Municipal Administrations run Municipal Hospitals, Health Care Units and Posts. The Municipal Administrations are leading the primary healthcare network. Services are free, since independence in 1975, but very limited in rural areas. Medicine is regulated by the General Health Inspection and the National Directorate of Health which manage the National List of Essential Medicines. Medicinal products are regulated by the National Pricing System. Tendering for medical products is run by the Centralized Medicine Purchase Authority which also distributes medicine.Staffing
Due to the length of the Angolan Civil War, nearly an entire generation of Angolans was not given the opportunity to receive any education. This has led to a dramatic decrease of health workers and added to the poor maternal health problem. In response to the shortage of health workers, Cuban physicians are currently working in the country to improve health overall, as well as to focus on improving maternal health.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mA1SnN4N_zo. Accessed 9, 2012. The health care system has felt the social effects of the War. Due to the large number of people who were unable to receive an education during the War, today, educated medical personnel, administrators, and other needed positions in the governmental system are not able to be filled. The population of Angola has lost nearly an entire generation of educated personnel. It was estimated in 2012 that there were about 0.08 physicians per 1,000 people in Angola.CIA FactbookApril 9, 2012.
Operation
Some improvements were made after the end of the Civil War. According to UNICEF reports in 2005, 2% of the nation's public expenditures were allotted to health care. That number increased after 2005. Larger problems include the shortage of doctors, the destruction of health care facilities throughout the country, and disparities between rural and urban primary care availability. Public spending on health decreased after 2014. The free public health system was still described as severely underfunded and understaffed in 2020. The medical technology and infrastructure is outdated and the system is difficult to access, so both locals and expatriates opt for private healthcare. Private healthcare insurance often has cover for emergency evacuation to better healthcare facilities in South Africa or other neighbouring countries. The Clínica Multiperfil in Luanda, although publicly owned, was granted special status by former President José Eduardo dos Santos, and is allowed to charge for care. Most of its patients are insured politicians and members of the military. Hospitals cannot always provide prescribed medication and patients may have to buy this, and some medical supplies, privately.History
The healthcare system in Angola suffered considerably during the Angolan War of Independence (1961–1975) and the subsequent civil war (1975 – 2002). Healthcare facilities were dilapidated, equipment was not maintained, and medical supplies which are almost all imported were very scarce. Wealthier people could get treatment at private hospitals, but the public system barely functioned. The Government of Japan set up a grant aid project, the "Project for Improvement of Medical Equipment in Primary Health Facilities in Luanda Province", in 2000 with the intention of improving the 27 health centres there. This was followed by finance of almost 3 million yen for the planned reconstruction and repair of Josina Machel Hospital, the main specialist referral centre in the country. Procurement of medical supplies and equipment was, and still is, complicated by the fluctuations in the foreign exchange rate.Hospitals in Angola
The following is a partial list of hospitals in Angola. The best hospitals are located in the capital city, Luanda.Luanda
* Josina Machel Hospital, Luanda, *Americo Boavida Hospital * Lucrécia Paím Maternity Hospital, Luanda *Clínica Multiperfil in Luanda. *CSE - Rádio Nacional de Angola *Clinica Girassol * Hospital Our Lady of Peace (Nossa Senhora da Paz) (Spanish Wikipedia), Cubal *Cajueiros General Hospital,Cazenga Cazenga is an city and the most densely populated of the nine municipalities that make up the province of Luanda, Angola. It has a population of 892,401 (2014 census), with an estimated 1,045,722 in 2019, covering an area of 37 km2.
Administrativ ...
* Centro Evangélico de Medicina do Lubango in Humpata
Humpata is a town and municipality in the province of Huíla, Angola. The municipality had a population of 89,144 in 2014.
Humpata was the primary destination of the Trekboers on the Dorsland Trek in the 1870s. These Afrikaners formed the majo ...
* Bongo Mission Hospital, Huambo, Seventh-day Adventist Hospital
*Chiulo Hospital
See also
*Health in Angola
Health in Angola is rated among the worst in the world.
The Human Rights Measurement Initiative finds that Angola is achieving 55.4% of what it should be fulfilling in terms of the right to health based on what should be possible at its level of ...
References
{{Africa topic, List of hospitals in