Health in Poland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 There are high rates of obesity and a rising burden of mental disorders.
According to the National Health Situation Report 2016, the main causes of death in Poland are:
*
There are high rates of obesity and a rising burden of mental disorders.
According to the National Health Situation Report 2016, the main causes of death in Poland are:
*
Health status
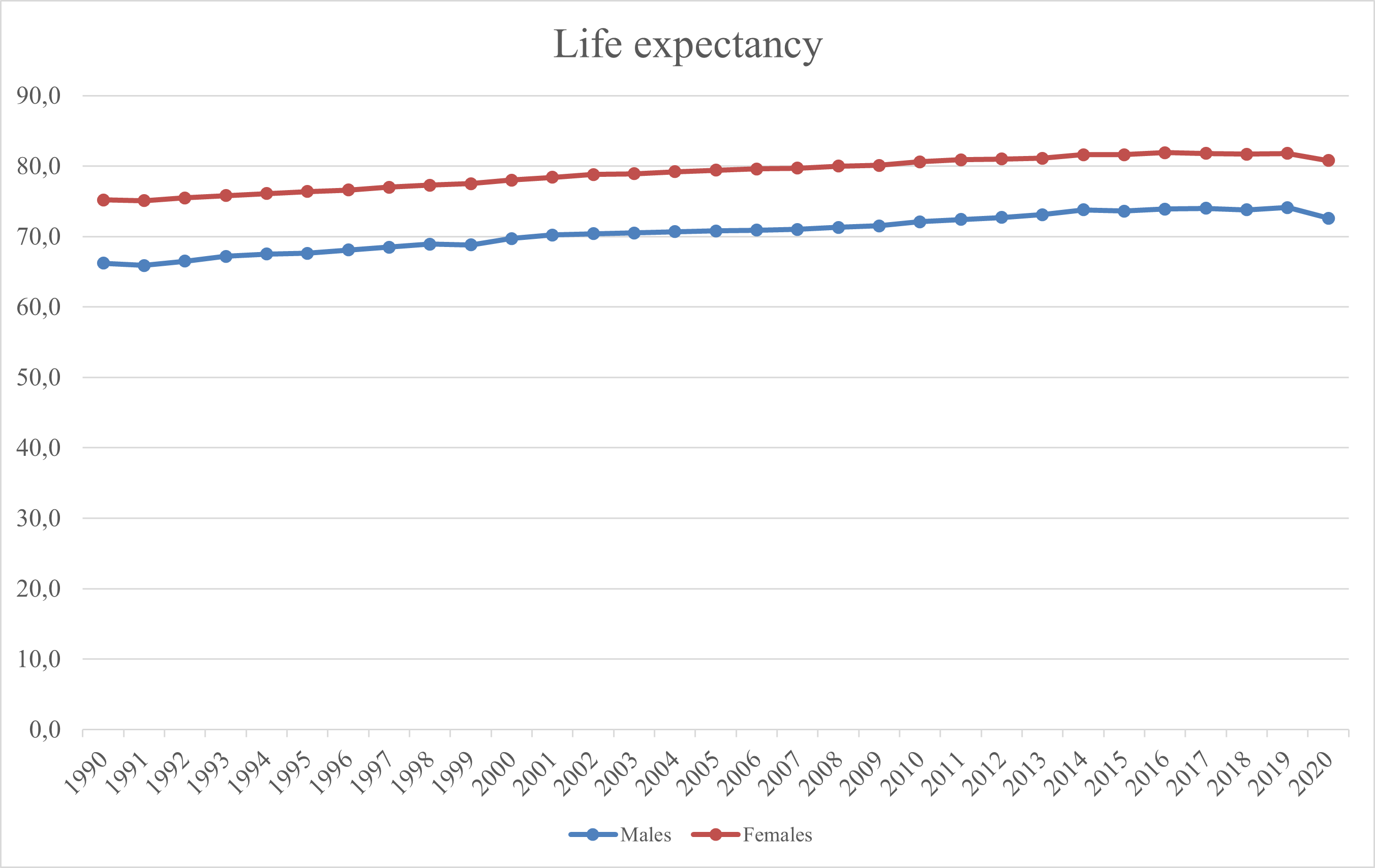
Life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
in Poland at birth was 74.1 years for men in 2019 and 81.8 for women. In 2019 life expectancy for both sexes reached value 77.86 years. Despite that, the life expectancy in Poland was rapidly increasing in the last 30 years, it is still three years below the European Union average, ranking Poland number 29 on the EU life expectancy list by country in 2016. Cardiovascular diseases and lung cancer are the most notable cases of mortality.
 There are high rates of obesity and a rising burden of mental disorders.
According to the National Health Situation Report 2016, the main causes of death in Poland are:
*
There are high rates of obesity and a rising burden of mental disorders.
According to the National Health Situation Report 2016, the main causes of death in Poland are:
* Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
(45% of all deaths)
* Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
(25.4% of all deaths)
* Other external reasons: suicide, communication injuries and falls (5.7% of all deaths)
And more specifically, non-communicable diseases which causes most deaths in Poland are:
* Ischemic heart disease
* Stroke
* Lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
* Alzheimer's disease
* Colorectal cancer
Communicable, maternal, neonatal, and nutritional diseases
* Lower respiratory tract infection
Lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) is a term often used as a synonym for pneumonia but can also be applied to other types of infection including lung abscess and acute bronchitis. Symptoms include shortness of breath, weakness, fever, cough ...
Risk factors
Polish population health status and health inequalities combine with many health determinants, including living and working conditions, environmental health, and behavioral risk factors.Behavioral risk factors
The National Health Situation Report 2016 points smoking, alcohol abuse and overweight/obesity as the main factors contributing to years of life lost in thedisability-adjusted life year
The disability-adjusted life year (DALY) is a measure of overall disease burden, expressed as the number of years lost due to ill-health, disability or early death. It was developed in the 1990s as a way of comparing the overall health and life ex ...
scale:
* smoking takes away 18.6 years of life from men and 7.9 years of life from women;
* alcohol abuse is responsible for the loss of 9.5 years of lives for men and 1.7 years of lives for women. Average alcohol consumption is 10.7 liters per person/year, which is slightly higher than the European average of 10.2 liters
* overweight and obesity is responsible for 9.6 years lost in general. The problem of overweight and obesity exists among 62 – 68% of men and 46 – 60% of women
Smoking
The legal age for buying tobacco or alcohol is 18. Smoking itself causes loss of 13.1% of lives, where behavioral factors take away 36% of lives. A blanket ban on smoking in public places was introduced on 15 November 2010, with a penalty fine of up to 500 zlotys. Smoking is effectively banned on public transport, transport stops and stations, schools and universities, workplaces, sports arenas, and other public places. Owners of pubs, restaurants, and other public spots are obliged to place a visible ‘No Smoking’ sign. Smoking rooms, called ‘palarnia’ in Polish, are permitted, but it is not permitted to serve food in them. Municipalities may extend the ban to places such as parks and bus stops.Alcohol consumption
The average consumption of alcohol in 2015 was 19.8 liters per year for men and 5.8 liters per year for women. Beer is consumed much more than wine.Obesity
Overweight andobesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
indicate abnormal or excessive fat growth that presents an upcoming future health risk. A rough measure of obesity among the population is the body mass index (BMI), a person’s weight (in kilograms) divided by the square of height (in meters). A person with a BMI of 30 or more is generally considered obese. A person who has a BMI of 25 or above 25 is deemed to be overweight. Overweight and obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
are major risk factors for many chronic diseases
A chronic condition is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three mon ...
, including diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
, and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
. Once considered a problem only in high-income countries, overweight and obesity are now dramatically rising in low- and middle-income countries, particularly in urban settings.
In 2016, female obesity prevalence in Poland was 22.2%, while male obesity prevalence reached 23.7%.
* From 1997 to 2016, the female 18+ obesity prevalence in Poland increased extensively from 18.1 to 22.2%.
* The male 18+ obesity prevalence in Poland between 1997 and 2016 increased from 14.8% to 23.7%, increasing at an average annual rate of 2.51%.
Health system
Poland offers a free public healthcare system in which all Polish andEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
residents have the right to access public healthcare, supported by the National Health Fund.
The organization's public healthcare funds are allocated from an obligatory contribution of all citizens in Poland. The health insurance contribution currently amounts to 9% of individual income. These deductions are the primary source of funding for public and free health insurance.
However, Poland does offer private health insurance as well. The SARS CoV-2 pandemic has increased interest in private insurance among Poles. After three quarters of 2020, Poles with private health insurance increased by 10.6% year-on-year. The premium value in total exceeded PLN 665 million, the Polish Insurance Association (PIU) has recently announced. More than 3 million Poles already use additional private health insurance. This is more than in the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. During the pandemic, interest in visits to spine specialists and psychological help has increased.
Public spending on healthcare in Poland is among the lowest in the European Union. Polish people pay nearly 10 billion PLN per year on private healthcare, according to a report by INFARMA, an association of pharmaceutical companies.
From 2004 to 2018, Poland's health expenditure as a share of GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
fluctuated substantially, tending to increase, and ending at 6.33% in 2018. Compared to the EU average health spending of 9.85% of GDP in 2018, Poland is still much below standards.
See also
*Health care in Poland
Health care in Poland is insurance based, delivered through a publicly funded health care system called the Narodowy Fundusz Zdrowia, which is free for all the citizens of Poland provided they fall into the "insured" category (usually meaning that ...
References
{{Europe in topic, Health in