Health in Gabon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
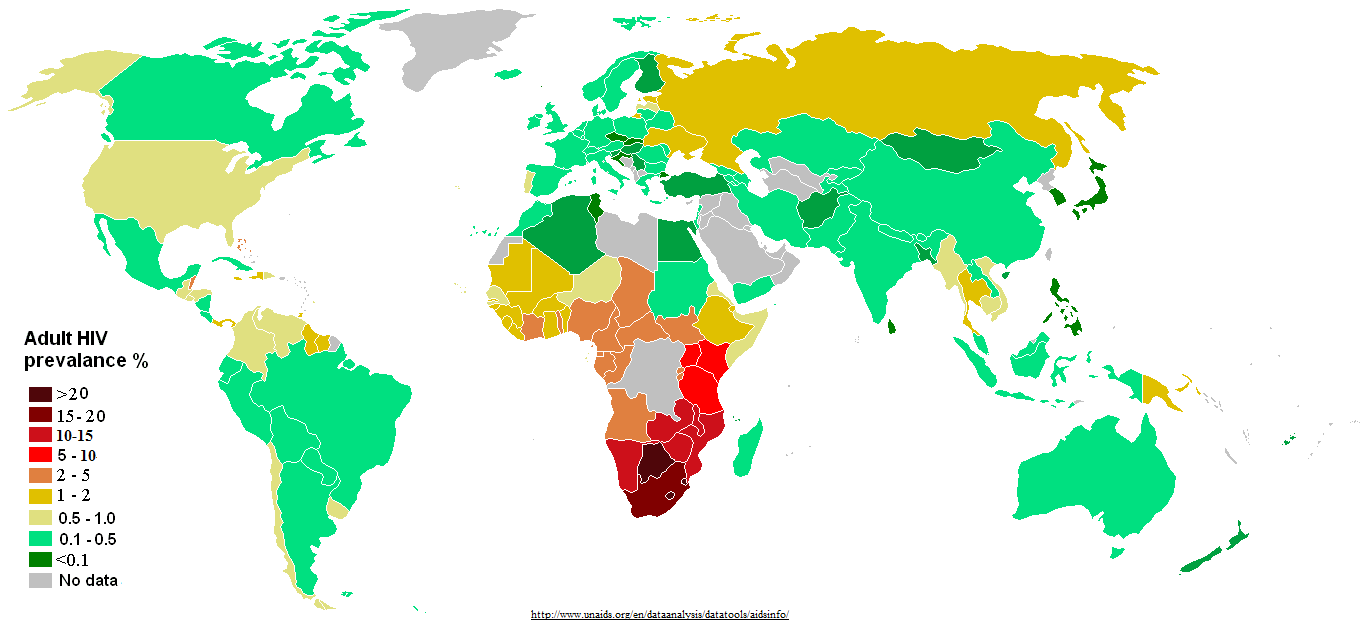 Sub-Saharan Africa has the highest rates of HIV in the world. Lesotho has the highest death rates(33.32%) due to HIV/AIDS followed closely by Eswatini(28.92%), Equatorial guinea(27.77%) and South Africa(27.53%). The burden of disease of HIV/AIDS in Sub-Saharan Africa is the highest in the world as it is the number one cause of death of people in the reproductive age bracket(15-49). Globally, the number of people living with HIV has increased over the span of two decades, however deaths secondary to HIV have reduced significantly.
Sub-Saharan Africa has the highest rates of HIV in the world. Lesotho has the highest death rates(33.32%) due to HIV/AIDS followed closely by Eswatini(28.92%), Equatorial guinea(27.77%) and South Africa(27.53%). The burden of disease of HIV/AIDS in Sub-Saharan Africa is the highest in the world as it is the number one cause of death of people in the reproductive age bracket(15-49). Globally, the number of people living with HIV has increased over the span of two decades, however deaths secondary to HIV have reduced significantly.
The State of the World's Midwifery - Gabon Country Profile
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gabon
Health Trends
Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the nort ...
has one of the highest urbanization rates in Africa with 1 in 5 of its citizens living in the urban areas. 3% of its GDP accounts for its total health expenditure. The life expectancy at birth is 66 years and a half of its population is aged under 20. The most prevalent mortality causing diseases in Gabon in 2019 were mainly cardiovascular disease, neoplasms, respiratory infections and HIV/AIDS, as compared to Malaria, respiratory infections and maternal/neonatal disorders which were the highest causes of mortality in the nineties.
Even though the HIV/AIDS prevalence in Gabon is estimated to be down to 3.0% in 2021 from 5.9% in 2007 in the adult population (ages 15–49), HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
remains a public health challenge in Gabon. HIV/AIDS contributes to 44.21% of total deaths of females in the reproductive age (15-49) and accounts for 15.47% deaths in females of all age groups.
As of 2021, about 47,000 people were living with HIV/AIDS. The UNAIDS 2025 target for HIV/AIDS is for 95% of persons living with HIV to know their HIV status, 95% of those who know their status are to have started with treatments while 95% of those on treatment should have suppressed viral loads. In Gabon 73% of people living with HIV (PLHIV) know their HIV status, 54% are on antiretroviral treatment while there is an absence of data on the percentage of PLHIV with viral load suppression.
 Sub-Saharan Africa has the highest rates of HIV in the world. Lesotho has the highest death rates(33.32%) due to HIV/AIDS followed closely by Eswatini(28.92%), Equatorial guinea(27.77%) and South Africa(27.53%). The burden of disease of HIV/AIDS in Sub-Saharan Africa is the highest in the world as it is the number one cause of death of people in the reproductive age bracket(15-49). Globally, the number of people living with HIV has increased over the span of two decades, however deaths secondary to HIV have reduced significantly.
Sub-Saharan Africa has the highest rates of HIV in the world. Lesotho has the highest death rates(33.32%) due to HIV/AIDS followed closely by Eswatini(28.92%), Equatorial guinea(27.77%) and South Africa(27.53%). The burden of disease of HIV/AIDS in Sub-Saharan Africa is the highest in the world as it is the number one cause of death of people in the reproductive age bracket(15-49). Globally, the number of people living with HIV has increased over the span of two decades, however deaths secondary to HIV have reduced significantly.
Health indicators
*Neonatal Mortality
Perinatal mortality (PNM) refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion o ...
Rate(NMR)
* Under 5 mortality Rate(U5MR)
* Maternal mortality
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pre ...
Rate(MMR)
* stillbirth Rate
Maternal and child healthcare
Gabon has come a long way in improving its maternal and neonatal healthcare services and thus in reducing the number of deaths from maternal and infant related diseases, however maternal mortality ratio and U5MR is still quite high. The maternal mortality ratio per 100,000 births for Gabon is 227. This is comparable with the world average of 223 per 100,000 livebirths. Gabon's U5MR per 1,000 livebirths is 40, also almost at the same level as the global average of 38 deaths per 1000 livebirths. Neonatal mortality rate in Gabon is 19. In Gabon the number of midwives per 1,000 live births is 12 and the lifetime risk of death for pregnant women is 1 in 110.Universal Health Coverage(UHC)
This encompasses the availability of basic health care services to all people of a country with the aim of limiting out of pocket payments for health services thereby protecting people from financial ruin. Universal health coverage explores basic ethical principles that guide what services are provided with consideration to: # Health maximization at the least possible cost. # Giving priority to the 'worse-off' both from a health prospect and a health outcome perspective. # Financial risk protection of the population.UHC in Gabon
A 10% levy on the revenues of mobile phone companies and on mobile phone usage, introduced by Gabon's government in 2008, has helped to more than double the funds for a health insurance program that now covers 99% of the equatorial nation's poor, giving them access to critical health services such as care during pregnancy. This levy is one of a set of measures that increased enrolment in health insurance plans in Gabon to 45% of the population in 2012 from less than 20% in 2007.Right to Health
The Human Rights Measurement Initiative finds that Gabon is fulfilling 62.2% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to health based on its level of income. When looking at the right to health with respect to children, Gabon achieves 84.7% of what is expected based on its current income. In regards to the right to health amongst the adult population, the country achieves only 78.1% of what is expected based on the nation's level of income. Gabon falls into the "very bad" category when evaluating the right to reproductive health because the nation is fulfilling only 23.9% of what the nation is expected to achieve based on the resources (income) it has available.Hospitals
There were 542 medical facilities in Gabon in 2019. Government and other notable hospitals are listed below.References
External links
The State of the World's Midwifery - Gabon Country Profile
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gabon