Harold Wellman on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Harold William Wellman (25 March 1909 – 28 April 1999) was an English-born New Zealand geologist known for his work on
 Harold Wellman was born in Devonport, England, to Evan Edward Wellman, an engineer in the Royal Navy, and May Kinglake Hoare. In 1927 his father was deployed at Devonport,
Harold Wellman was born in Devonport, England, to Evan Edward Wellman, an engineer in the Royal Navy, and May Kinglake Hoare. In 1927 his father was deployed at Devonport,
1966 encyclopedia entry on Harold WellmanBBC Horizon "The Man Who Moved the Mountains" (13 April 1992)Professor Harold Wellman's theodolite at Tepapa Museum
{{DEFAULTSORT:Wellman, Harold 20th-century New Zealand geologists 1909 births 1999 deaths Fellows of the Royal Society of New Zealand People from Devonport, Plymouth English emigrants to New Zealand University of Canterbury alumni Victoria University of Wellington alumni Victoria University of Wellington faculty People associated with Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (New Zealand) Tectonicists New Zealand miners
plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
. He is notable for his discovery of South Island's Alpine Fault
The Alpine Fault is a geological fault that runs almost the entire length of New Zealand's South Island (c. 480 km) and forms the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate. The Southern Alps have been uplifted on the fa ...
. Wellman became a Fellow of the Royal Society of New Zealand
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a cit ...
in 1954, and was awarded the Hector Memorial Medal
The Hector Medal, formerly known as the Hector Memorial Medal, is a science award given by the Royal Society Te Apārangi in memory of Sir James Hector to researchers working in New Zealand. It is awarded annually in rotation for different science ...
and Prize in 1957 and the McKay Hammer Award in 1959.
Life and career
 Harold Wellman was born in Devonport, England, to Evan Edward Wellman, an engineer in the Royal Navy, and May Kinglake Hoare. In 1927 his father was deployed at Devonport,
Harold Wellman was born in Devonport, England, to Evan Edward Wellman, an engineer in the Royal Navy, and May Kinglake Hoare. In 1927 his father was deployed at Devonport, Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The List of New Zealand urban areas by population, most populous urban area in the country and the List of cities in Oceania by po ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
for three years and the family moved to New Zealand. Harold Wellman first worked as a surveyor, but was soon forced to become a gold prospector on the West Coast West Coast or west coast may refer to:
Geography Australia
* Western Australia
*Regions of South Australia#Weather forecasting, West Coast of South Australia
* West Coast, Tasmania
**West Coast Range, mountain range in the region
Canada
* Britis ...
due to the lack of work available during the depression.
In the mid-1930s Wellman began his geological study while working in mineral exploration for the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, abbreviated DSIR was the name of several British Empire organisations founded after the 1923 Imperial Conference to foster intra-Empire trade and development.
* Department of Scientific and Industria ...
. He initially studied at Canterbury University
The University of Canterbury ( mi, Te Whare Wānanga o Waitaha; postnominal abbreviation ''Cantuar.'' or ''Cant.'' for ''Cantuariensis'', the Latin name for Canterbury) is a public research university based in Christchurch, New Zealand. It was f ...
, later moving to Victoria University where he completed his Bachelor of Science
A Bachelor of Science (BS, BSc, SB, or ScB; from the Latin ') is a bachelor's degree awarded for programs that generally last three to five years.
The first university to admit a student to the degree of Bachelor of Science was the University of ...
(1939) and Master of Science
A Master of Science ( la, Magisterii Scientiae; abbreviated MS, M.S., MSc, M.Sc., SM, S.M., ScM or Sc.M.) is a master's degree in the field of science awarded by universities in many countries or a person holding such a degree. In contrast to ...
(1941). That same year he married Joan Evelyn Butler in Dunedin
Dunedin ( ; mi, Ōtepoti) is the second-largest city in the South Island of New Zealand (after Christchurch), and the principal city of the Otago region. Its name comes from , the Scottish Gaelic name for Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. Th ...
, with whom he had three children.
Between 1952 and 1958 he worked for the New Zealand Geological Survey
GNS Science ( mi, Te Pū Ao), officially registered as the Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences Limited, is a New Zealand Crown Research Institute. It focuses on geology, geophysics (including seismology and volcanology), and nuclear sc ...
based in Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by me ...
. During this time he received major awards for his research, gaining a fellowship from the Royal Society of New Zealand
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a cit ...
in 1954, an honorary Doctor of Sciences
Doctor of Sciences ( rus, доктор наук, p=ˈdoktər nɐˈuk, abbreviated д-р наук or д. н.; uk, доктор наук; bg, доктор на науките; be, доктар навук) is a higher doctoral degree in the Russi ...
from the University of New Zealand
The University of New Zealand was New Zealand's sole degree-granting university from 1874 to 1961. It was a collegiate university embracing several constituent institutions at various locations around New Zealand. After it was dissolved in 196 ...
in 1956 and he was awarded the Royal Society's Hector Memorial Medal and Prize in 1957. He later joined the Department of Geology at Victoria University, becoming chair in 1970 and an emeritus professor in 1975.
Works and discoveries
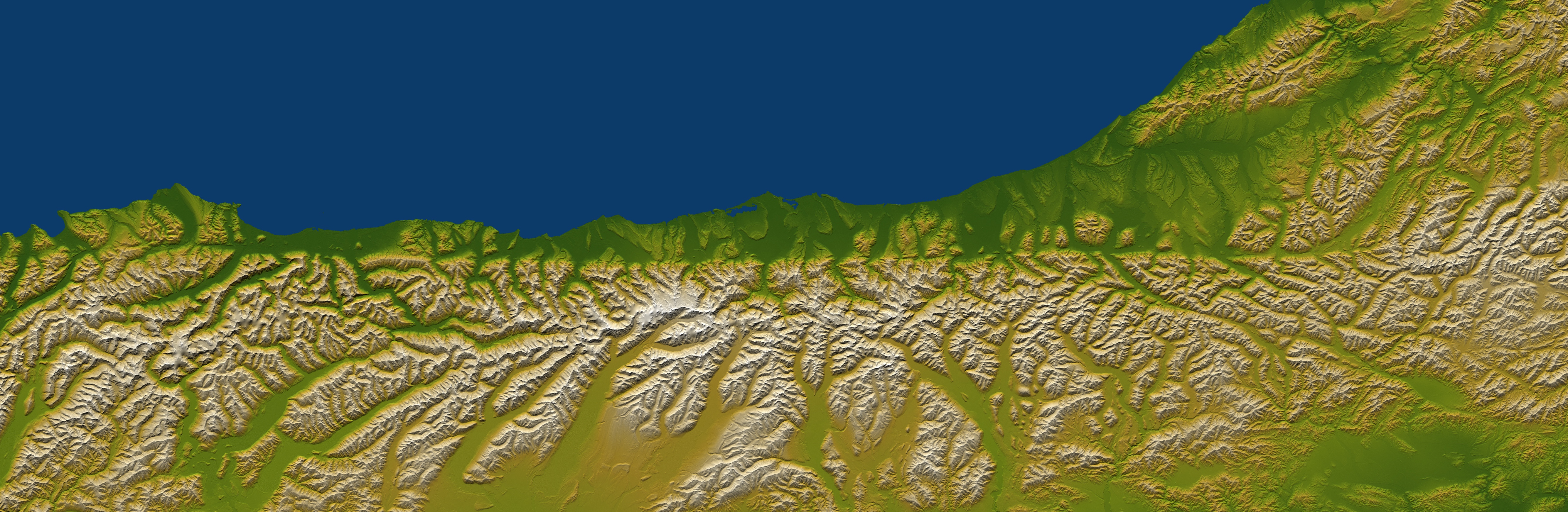
During his career Harold Wellman published on a wide variety of geological topics, however, he was most influential in discovering theAlpine Fault
The Alpine Fault is a geological fault that runs almost the entire length of New Zealand's South Island (c. 480 km) and forms the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate. The Southern Alps have been uplifted on the fa ...
and its importance to New Zealand's geology. In 1940 Harold Wellman first identified that the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Southern ...
was related to a fault line which ran for approximately 650 km (400 miles). The fault was officially named the Alpine Fault in 1942. At the same time, Harold Wellman proposed the 480 km (300 miles) lateral displacement on the Alpine Fault.
This displacement was inferred by Harold Wellman due in part to the similarity of rocks in Southland Southland may refer to:
Places Canada
* Dunbar–Southlands, Vancouver, British Columbia
New Zealand
* Southland Region, a region of New Zealand
* Southland County, a former New Zealand county
* Southland District, part of the wider Southland Reg ...
and Nelson
Nelson may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Nelson'' (1918 film), a historical film directed by Maurice Elvey
* ''Nelson'' (1926 film), a historical film directed by Walter Summers
* ''Nelson'' (opera), an opera by Lennox Berkeley to a lib ...
on either side of the Alpine Fault. Lateral displacements of this magnitude could not be explained by pre-plate tectonics geology and his ideas were not initially widely accepted until 1956. Wellman also proposed in 1964 that the Alpine Fault was a Cenozoic structure, which was in conflict with the older Mesozoic age accepted at the time. This idea coupled with the displacement on the fault proposed that the earth's surface was in relatively rapid constant movement and helped to overthrow the old geosynclinal
A geosyncline (originally called a geosynclinal) is an obsolete geological concept to explain orogens, which was developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, before the theory of plate tectonics was envisaged. Şengör (1982), p. 11 A g ...
hypothesis in favour of plate tectonics.
References
Further reading
* Nathan, S (2005). ''Harold Wellman: a man who moved New Zealand'' Wellington, 2005.External links
1966 encyclopedia entry on Harold Wellman
{{DEFAULTSORT:Wellman, Harold 20th-century New Zealand geologists 1909 births 1999 deaths Fellows of the Royal Society of New Zealand People from Devonport, Plymouth English emigrants to New Zealand University of Canterbury alumni Victoria University of Wellington alumni Victoria University of Wellington faculty People associated with Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (New Zealand) Tectonicists New Zealand miners