Hanifi Rohingya script on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hanifi Rohingya script is a unified script for the Rohingya language. Rohingya was first written in the 19th century with a version of the Perso-Arabic script. In 1975, an orthographic Arabic script was developed, based on the Urdu alphabet.
In the 1980s, Mohammad Hanif and his colleagues created the suitable
GitHub
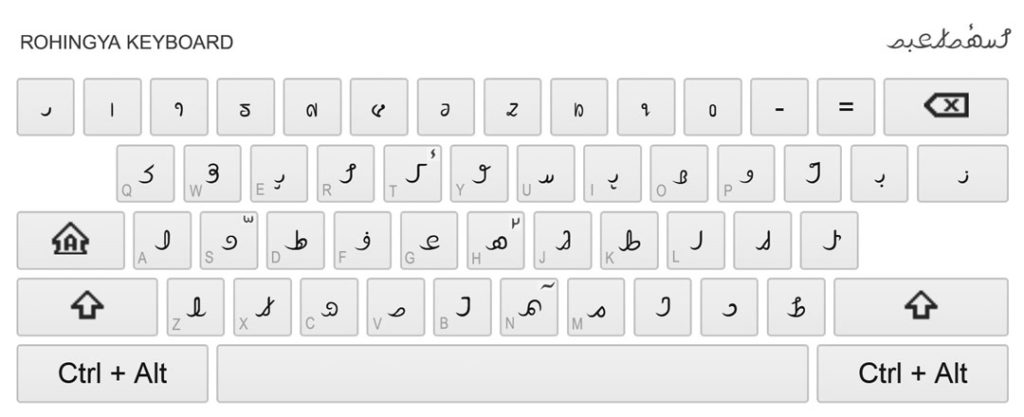 A virtual keyboard was developed by Google for the Rohingya language in 2019 and allows users to type directly in the Rohingya script. The Rohingya Unicode keyboard layout can be foun
A virtual keyboard was developed by Google for the Rohingya language in 2019 and allows users to type directly in the Rohingya script. The Rohingya Unicode keyboard layout can be foun
here
phonetic script
Phonetic transcription (also known as phonetic script or phonetic notation) is the visual representation of speech sounds (or ''phones'') by means of symbols. The most common type of phonetic transcription uses a phonetic alphabet, such as the I ...
based on Arabic letters; it has been compared to the N’ko script. The script also includes a set of decimal numbers.
Characters
Alphabet and pronunciation
Consonants
Vowels
Numerals
Unicode
The Hanifi Rohingya script was added to the Unicode Standard in June 2018 with the release of version 11.0. Proposals to include it in Unicode were written by linguist Anshuman Pandey. The Unicode block for Hanifi Rohingya is U+10D00–U+10D3F and contains 50 characters:Fonts
Google's Noto Sans has developed a Rohingya script font called ''Noto Sans Hanifi Rohingya'', available aGitHub
Rohingya keyboard
 A virtual keyboard was developed by Google for the Rohingya language in 2019 and allows users to type directly in the Rohingya script. The Rohingya Unicode keyboard layout can be foun
A virtual keyboard was developed by Google for the Rohingya language in 2019 and allows users to type directly in the Rohingya script. The Rohingya Unicode keyboard layout can be founhere
References
Rohingya people Alphabets Writing systems of Asia Writing systems introduced in 1980 Arabic script Right-to-left writing systems {{writingsystem-stub