Hamitidae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Hamites'' (" hook-like") is a
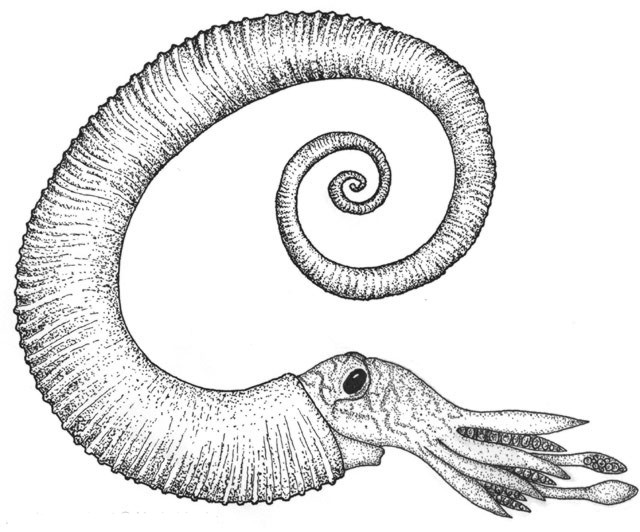 ''Hamites'' species are characterised by a shell that began with an open, sometimes helical, regular spiral that either opened into a single large hook, or else formed three parallel shafts that gave the mature shell the approximate appearance of a paper clip. No ''Hamites'' had spines or other such ornamentation on the shell, but several species appear to have developed apertural modifications when mature; that is, once the ammonite had grown to its final size, the aperture became constricted and was bounded by one or two thickened ribs, known as collars. These have been observed on other ammonites as well, and are assumed to be signs of
''Hamites'' species are characterised by a shell that began with an open, sometimes helical, regular spiral that either opened into a single large hook, or else formed three parallel shafts that gave the mature shell the approximate appearance of a paper clip. No ''Hamites'' had spines or other such ornamentation on the shell, but several species appear to have developed apertural modifications when mature; that is, once the ammonite had grown to its final size, the aperture became constricted and was bounded by one or two thickened ribs, known as collars. These have been observed on other ammonites as well, and are assumed to be signs of
Gault Clay Ammonites, featuring ''Hamites'' and other Hamitidae
{{Taxonbar, from1=Q3729594, from2=Q20894758 Ammonitida genera Turrilitoidea Cretaceous ammonites Ammonites of Australia Aptian genus first appearances Albian genera Cenomanian genus extinctions
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of heteromorph ammonite
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) ...
that evolved late in the Aptian
The Aptian is an age in the geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is a subdivision of the Early or Lower Cretaceous Epoch or Series and encompasses the time from 121.4 ± 1.0 Ma to 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma (million years ago), a ...
stage of the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
and lasted into the Cenomanian
The Cenomanian is, in the ICS' geological timescale, the oldest or earliest age of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or the lowest stage of the Upper Cretaceous Series. An age is a unit of geochronology; it is a unit of time; the stage is a unit in the s ...
stage of the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
. The genus is almost certainly paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
but remains in wide use as a "catch all" for heteromorph ammonites
The Ancyloceratina were a diverse suborder of ammonite most closely related to the ammonites of order Lytoceratina. They evolved during the Late Jurassic but were not very common until the Cretaceous period, when they rapidly diversified and beca ...
of the superfamily Turrilitoidea
Turrilitoidea is a diverse superfamily of Cretaceous ammonites generally considered as heteromorphic and commonly included in the suborder Ancyloceratina. Shells of this diverse group do not coil planospirally, as typical for most ammonitida, am ...
that do not neatly fit into the more derived
Derive may refer to:
* Derive (computer algebra system), a commercial system made by Texas Instruments
* ''Dérive'' (magazine), an Austrian science magazine on urbanism
*Dérive, a psychogeographical concept
See also
*
*Derivation (disambiguatio ...
groupings. In an attempt to identify clades
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, t ...
within the genus, it has been divided up into a series of new genera or subgenera by different palaeontologists
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
, including ''Eohamites'', ''Hamitella'', ''Helicohamites'', ''Lytohamites'', ''Planohamites'', ''Psilohamites'', and ''Sziveshamites''.
The type species is ''Hamites attenuatus'' from the early Albian, named by James Sowerby in his ''Mineral Conchology of Great Britain'' of 1814, although the genus itself was created by James Parkinson
James Parkinson (11 April 175521 December 1824) was an English surgeon, apothecary, geologist, palaeontologist and political activist. He is best known for his 1817 work ''An Essay on the Shaking Palsy'', in which he was the first to describe ...
in his 1811 book ''Organic Remains of the Former World''. This James Parkinson is best known as the first scientific description of a disease he called the ''Shaking Palsy'', now referred to as Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
in his honour.
Morphology and ecology
 ''Hamites'' species are characterised by a shell that began with an open, sometimes helical, regular spiral that either opened into a single large hook, or else formed three parallel shafts that gave the mature shell the approximate appearance of a paper clip. No ''Hamites'' had spines or other such ornamentation on the shell, but several species appear to have developed apertural modifications when mature; that is, once the ammonite had grown to its final size, the aperture became constricted and was bounded by one or two thickened ribs, known as collars. These have been observed on other ammonites as well, and are assumed to be signs of
''Hamites'' species are characterised by a shell that began with an open, sometimes helical, regular spiral that either opened into a single large hook, or else formed three parallel shafts that gave the mature shell the approximate appearance of a paper clip. No ''Hamites'' had spines or other such ornamentation on the shell, but several species appear to have developed apertural modifications when mature; that is, once the ammonite had grown to its final size, the aperture became constricted and was bounded by one or two thickened ribs, known as collars. These have been observed on other ammonites as well, and are assumed to be signs of sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
.
The open shell of these ammonites would have made them poor swimmers because of drag, but beyond that fact, very little is certain about their mode of life. It is widely assumed that they were plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankt ...
ic, perhaps catching small prey in the manner of jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella- ...
, but repaired shell damage apparently caused by crabs may indicate that they spent at least some time close to the sea floor.
Phylogeny
The genus ''Hamites'' is of particular interest to palaeontologists because the species included in the genus span a wide range of morphologies including ones apparently similar to several morederived
Derive may refer to:
* Derive (computer algebra system), a commercial system made by Texas Instruments
* ''Dérive'' (magazine), an Austrian science magazine on urbanism
*Dérive, a psychogeographical concept
See also
*
*Derivation (disambiguatio ...
groups of heteromorph ammonites. The genus rapidly diversified during the Albian into a number of morphologically distinct lineages that seem to have given rise to at least three other families of heteromorphs, the Baculitidae
Baculitidae is a family of extinct Ammonoidea, ammonoid cephalopods that lived mostly during the Late Cretaceous, and often included in the suborder Ancyloceratina.
Baculitid genera are characterized by a small to minute initial coil of about tw ...
, Turrilitidae
Turrilitidae is a family of extinct heteromorph ammonite cephalopods. All members had shells that coiled helically that tended to resemble auger shells. The ecological roles turrilitids played is largely unknown, as experts are still speculati ...
, and Scaphitidae. The lineage that gave rise to the helical Turrilitidae, for example, had a shell that initially grew as a helix before straightening out; the Turrilitidae thus appear to have been derived from neotenic
Neoteny (), also called juvenilization,Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young. Bergin & Garvey: CT. is the delaying or slowing of the physiological, or somatic, development of an organism, typically an animal. Neoteny is found in modern humans compared ...
''Hamites'' that retained the helically-coiled juvenile morphology of ''Hamites'' into adulthood.
See also
* '' Baculites'' * '' Scaphites'' * ''Turrilites
''Turrilites'' is a genus of helically coiled ammonoid cephalopods from the lower part of the Upper Cretaceous (Cenomanian and Turonian); generally included in the Ancyloceratina. Previously (Arkell, 1957) it was included in the ammonoid suborder ...
''
References
External links
Gault Clay Ammonites, featuring ''Hamites'' and other Hamitidae
{{Taxonbar, from1=Q3729594, from2=Q20894758 Ammonitida genera Turrilitoidea Cretaceous ammonites Ammonites of Australia Aptian genus first appearances Albian genera Cenomanian genus extinctions