Hamilton C Shell on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hamilton C shell is a clone of the Unix C shell and
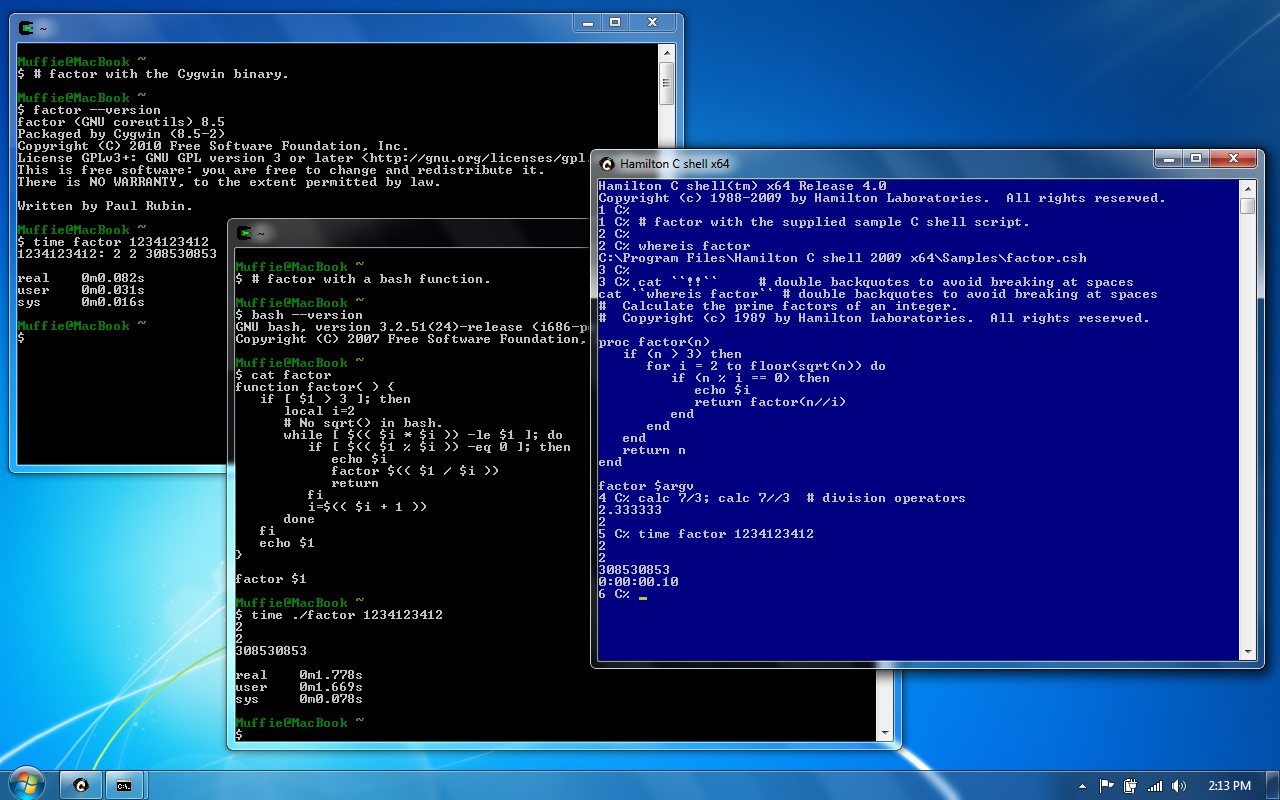 The original C shell uses an ad hoc parser. This has led to complaints about its limitations. It works well enough for the kinds of things users type interactively but not very well for the more complex commands a user might take time to write in a script. It is not possible, for example, to pipe the output of a
The original C shell uses an ad hoc parser. This has led to complaints about its limitations. It works well enough for the kinds of things users type interactively but not very well for the more complex commands a user might take time to write in a script. It is not possible, for example, to pipe the output of a
by Tom Christiansen By contrast, Hamilton uses a top-down
 Lacking
Lacking
Hamilton C shell user guide
{{Unix shells Unix shells OS/2 command shells Windows command shells Scripting languages Unix text processing utilities Unix emulators Programming tools Programming tools for Windows Utilities for Windows 1988 software Programming languages created in 1988
utilities
A public utility company (usually just utility) is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service (often also providing a service using that infrastructure). Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and r ...
Early
for Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
created by Nicole Hamilton at Hamilton Laboratories as a completely original work, not based on any prior code. It was first released on OS/2
OS/2 is a Proprietary software, proprietary computer operating system for x86 and PowerPC based personal computers. It was created and initially developed jointly by IBM and Microsoft, under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci, ...
on December 12, 1988
and on Windows NT
Windows NT is a Proprietary software, proprietary Graphical user interface, graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which, Windows NT 3.1, was released on July 27, 1993. Original ...
in July 1992. The OS/2 version was discontinued in 2003 but the Windows version continues to be actively supported.
Design
Hamilton C shell differs from the Unix C shell in several respects. These include itscompiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primaril ...
architecture, its use of threads, and the decision to follow Windows rather than Unix conventions.
Parser
 The original C shell uses an ad hoc parser. This has led to complaints about its limitations. It works well enough for the kinds of things users type interactively but not very well for the more complex commands a user might take time to write in a script. It is not possible, for example, to pipe the output of a
The original C shell uses an ad hoc parser. This has led to complaints about its limitations. It works well enough for the kinds of things users type interactively but not very well for the more complex commands a user might take time to write in a script. It is not possible, for example, to pipe the output of a foreach
In computer programming, foreach loop (or for-each loop) is a control flow statement for traversing items in a collection. is usually used in place of a standard loop statement. Unlike other loop constructs, however, loops usually maintai ...
statement into grep
grep is a command-line utility for searching plaintext datasets for lines that match a regular expression. Its name comes from the ed command g/re/p (global regular expression search and print), which has the same effect. grep was originally de ...
. There was a limit to how complex a command it could handle.''Csh Programming Considered Harmful''by Tom Christiansen By contrast, Hamilton uses a top-down
recursive descent parser
In computer science, a recursive descent parser is a kind of top-down parser built from a set of mutually recursive procedures (or a non-recursive equivalent) where each such procedure implements one of the nonterminals of the grammar. Thus t ...
that allows it to compile statements to an internal form before running them. As a result, statements can be nested or piped arbitrarily. The language has also been extended with built-in and user-defined procedures, local variables, floating point and additional expression, editing and wildcarding operators, including an "indefinite directory" wildcard construct written as "..." that matches zero or more directory levels as required to make the rest of the pattern match.
Threads
 Lacking
Lacking fork
In cutlery or kitchenware, a fork (from 'pitchfork') is a utensil, now usually made of metal, whose long handle terminates in a head that branches into several narrow and often slightly curved tines with which one can spear foods either to h ...
or a high performance way to recreate that functionality, Hamilton uses the Windows threads facilities instead. When a new thread is created, it runs within the same process space and it shares all of the process state. If one thread changes the current directory or the contents of memory, it's changed for all the threads. It's much cheaper to create a thread than a process but there's no isolation between them. To recreate the missing isolation of separate processes, the threads cooperate to share resources using locks.
Windows conventions
Hamilton differs from other Unix shells in that it also directly supports Windows conventions for drive letters, filename slashes,escape character
In computing and telecommunications, an escape character is a character that invokes an alternative interpretation on the following characters in a character sequence. An escape character is a particular case of metacharacters. Generally, the ...
s, etc.
References
External links
*Hamilton C shell user guide
{{Unix shells Unix shells OS/2 command shells Windows command shells Scripting languages Unix text processing utilities Unix emulators Programming tools Programming tools for Windows Utilities for Windows 1988 software Programming languages created in 1988