Haida Eddies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Haida Eddies are episodic, clockwise rotating ocean
Haida Eddies are episodic, clockwise rotating ocean
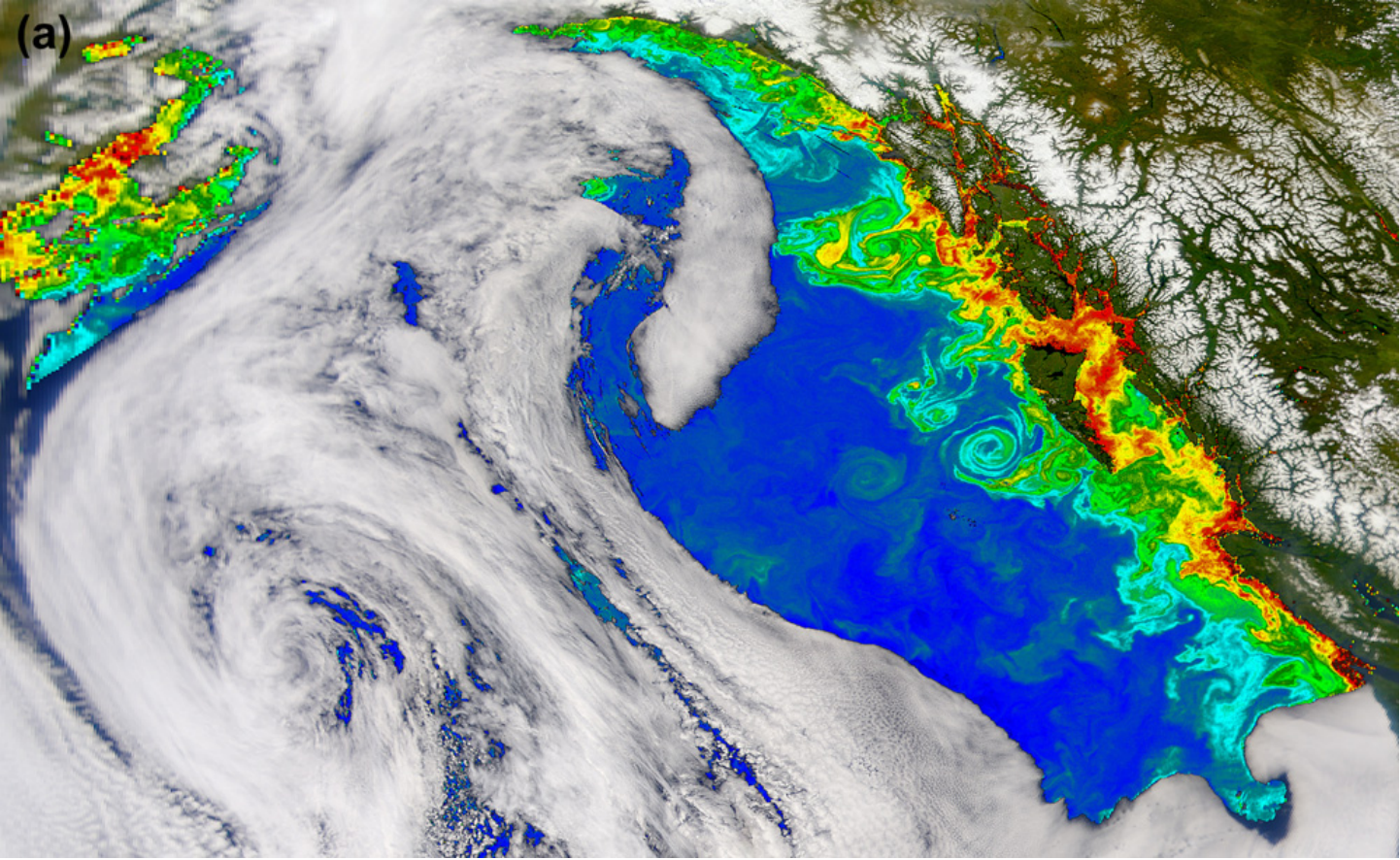 Due to their large size, it was not until the satellite era that scientists were able to observe the full scale and life cycles of Haida eddies. Their extent is such that an ocean liner can move through the eddy without observing its borders, so accurate records did not exist until the late 1980s.
Between 1985-1990, the first US research mission to study changes in
Due to their large size, it was not until the satellite era that scientists were able to observe the full scale and life cycles of Haida eddies. Their extent is such that an ocean liner can move through the eddy without observing its borders, so accurate records did not exist until the late 1980s.
Between 1985-1990, the first US research mission to study changes in
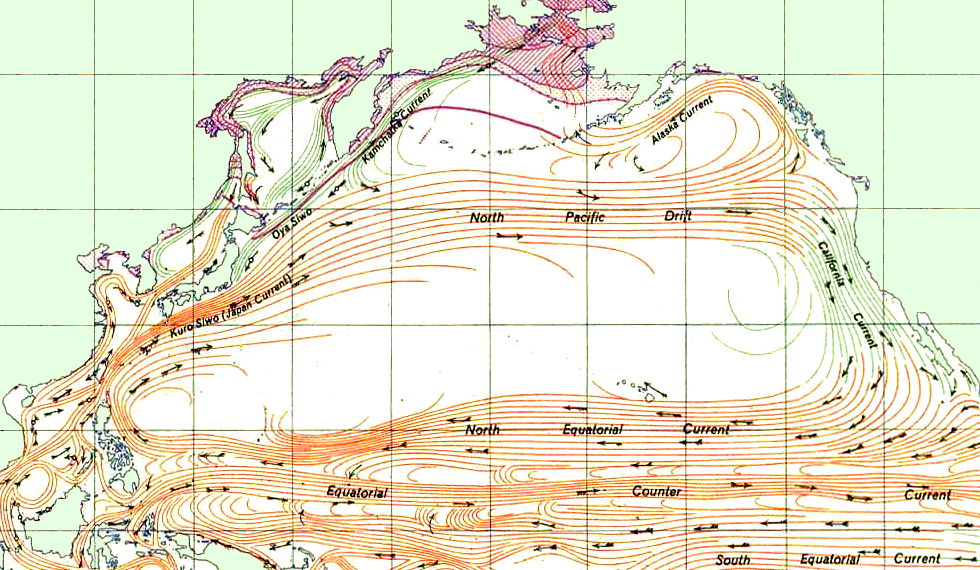 Ocean circulation in the region begins with the transport of waters eastward along the
Ocean circulation in the region begins with the transport of waters eastward along the 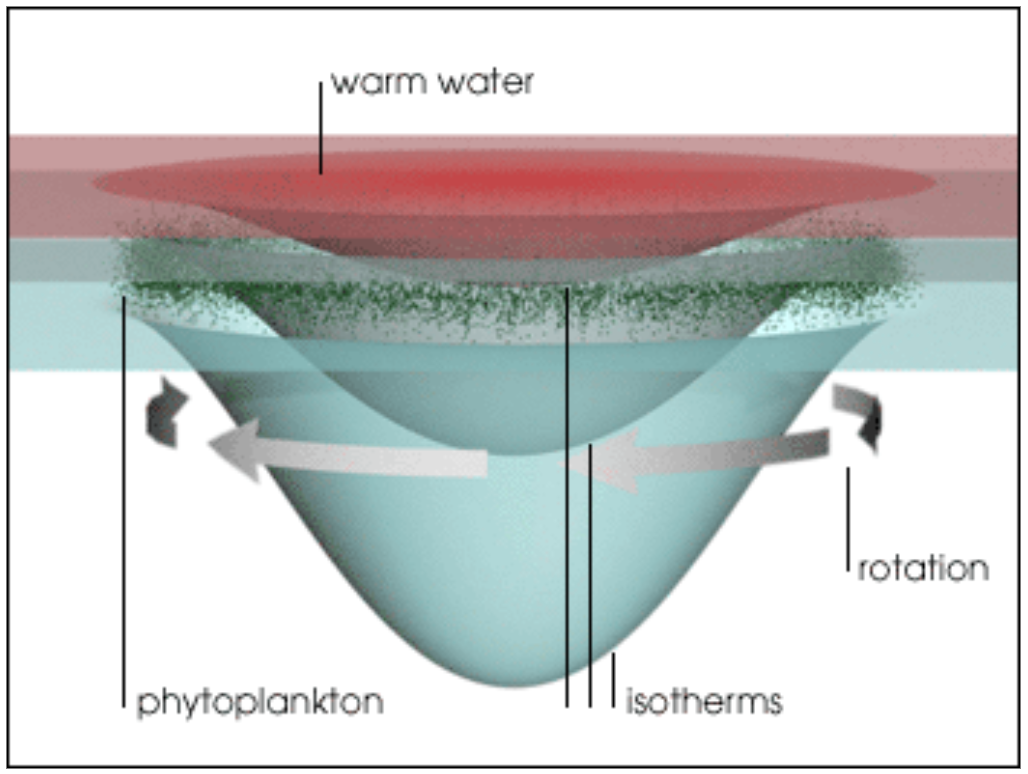
 Haida Eddies are episodic, clockwise rotating ocean
Haida Eddies are episodic, clockwise rotating ocean eddies
In fluid dynamics, an eddy is the swirling of a fluid and the reverse current created when the fluid is in a turbulent flow regime. The moving fluid creates a space devoid of downstream-flowing fluid on the downstream side of the object. Fluid beh ...
that form during the winter off the west coast of British Columbia’s Haida Gwaii
Haida Gwaii (; hai, X̱aaydag̱a Gwaay.yaay / , literally "Islands of the Haida people") is an archipelago located between off the northern Pacific coast of Canada. The islands are separated from the mainland to the east by the shallow Hecat ...
and Alaska’s Alexander Archipelago
The Alexander Archipelago (russian: Архипелаг Александра) is a long archipelago (group of islands) in North America lying off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, the tops of submerged coastal m ...
. These eddies are notable for their large size, persistence, and frequent recurrence. Rivers flowing off the North American continent supply the continental shelf in the Hecate Strait
, image = HecateStrait(PittIsland).JPG
, image_size = 260px
, alt =
, caption = Hecate Strait and Pitt Island
, image_bathymetry = Loc-QCS-Hecate-Dixon.png
, alt_bathymetry =
, caption ...
with warmer, fresher, and nutrient-enriched water. Haida eddies are formed every winter when this rapid outflow of water through the strait wraps around Cape St. James at the southern tip of Haida Gwaii, and meets with the cooler waters of the Alaska Current
The Alaska Current is a southwestern shallow warm-water current alongside the west coast of the North American continent beginning at about 48-50°N. The Alaska Current produces large clockwise eddies at two sites: west of the Haida Gwaii ("Haid ...
. This forms a series of plumes which can merge into large eddies that are shed into the northeast Pacific Ocean by late winter, and may persist for up to two years.
Haida eddies can be more than 250 km in diameter, and transport a mass of coastal water approximately the volume of Lake Michigan over 1,000 km offshore into the lower nutrient waters of the northeast Pacific Ocean. These " warm-core rings" transport heat out to sea, supplying nutrients (particularly nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zer ...
and iron) to nutrient depleted areas of lower productivity. Consequently, primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through c ...
in Haida eddies is up to three times higher than in ambient waters, supporting vast phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
-based communities, as well as influencing zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
and icthyoplankton community
A community is a social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place, norms, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, village, tow ...
compositions.
The Haida name is derived from the Haida people
Haida (, hai, X̱aayda, , , ) are an indigenous group who have traditionally occupied , an archipelago just off the coast of British Columbia, Canada, for at least 12,500 years.
The Haida are known for their craftsmanship, trading skills, and ...
native to the region, centered on the islands of Haida Gwaii (formerly known as the Queen Charlotte Islands
Haida Gwaii (; hai, X̱aaydag̱a Gwaay.yaay / , literally "Islands of the Haida people") is an archipelago located between off the northern Pacific coast of Canada. The islands are separated from the mainland to the east by the shallow Heca ...
).
Historical observations
 Due to their large size, it was not until the satellite era that scientists were able to observe the full scale and life cycles of Haida eddies. Their extent is such that an ocean liner can move through the eddy without observing its borders, so accurate records did not exist until the late 1980s.
Between 1985-1990, the first US research mission to study changes in
Due to their large size, it was not until the satellite era that scientists were able to observe the full scale and life cycles of Haida eddies. Their extent is such that an ocean liner can move through the eddy without observing its borders, so accurate records did not exist until the late 1980s.
Between 1985-1990, the first US research mission to study changes in sea surface height
Ocean surface topography or sea surface topography, also called ocean dynamic topography, are highs and lows on the ocean surface, similar to the hills and valleys of Earth's land surface depicted on a topographic map.
These variations are ex ...
using radar altimetry (an instrument used to measure the ocean surface height using a radar pulse in reference to a geoid
The geoid () is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended ...
), was conducted by the US Navy using the Geodetic/Geophysical Satellite (GEOSAT
The GEOSAT (GEOdetic SATellite) was a U.S. Navy Earth observation satellite, launched on March 12, 1985 into an 800 km, 108° inclination orbit, with a nodal period of about 6040 seconds. The satellite carried a radar altimeter capable of m ...
). The primary focus was to study fronts, eddies, winds, waves, and tides; each of these processes produce a change in sea surface height of several meters. In 1986, researchers Gower and Tabata observed clockwise eddies in the Gulf of Alaska using GEOSAT - the first satellite observation of Haida eddies. In 1987, the Ocean Storms program deployed 50 drifters to examine intertidal oscillations and mixing during fall storms and observed eddies propagating westward. Also in 1987, researchers Richard Thomson, Paul LeBlond, and William Emery observed that ocean drifters deployed in the Gulf of Alaska at 100–120 meters below the surface had stopped their eastward motion and actually began to move westward counter to the predominant current. The researchers attributed the unexpected motion to eddies dragging the buoys westward from their path at approximately 1.5 cm/s.
In 1992, Haida eddies were observed by researchers Meyers and Basu as positive sea surface height anomalies using TOPEX-POSEIDON, an altimetry-based satellite platform (like GEOSAT). They specifically noted an increase in the number of Haida eddies during the 1997/1998 El Niño winter. Haida eddy altimetry observations were further supplemented by European Remote Sensing satellites, ERS1 and ERS2. In 1995 Richard Thomson, together with James Gower at the Institute of Ocean Sciences
The Institute of Ocean Sciences is operated by Fisheries and Oceans Canada and is one of the largest marine research centres in Canada. It is located on Patricia Bay and the former British Columbia Highway 17A in Sidney, British Columbia on Vanco ...
in British Columbia, discovered the first clear evidence of eddies along the entire continental margin using temperature maps from infrared observations using National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
(NOAA) satellites. Satellite observations coupled with drifter observations have allowed scientists to resolve physical and biogeochemical structures of Haida eddies.
Formation
General circulation
 Ocean circulation in the region begins with the transport of waters eastward along the
Ocean circulation in the region begins with the transport of waters eastward along the North Pacific Current
The North Pacific Current (sometimes referred to as the North Pacific Drift) is a slow warm water current that flows west-to-east between 30 and 50 degrees north in the Pacific Ocean. The current forms the southern part of the North Pacific Su ...
, also known as the "West Wind Drift", which forms the northern branch of the anticyclonic (clockwise rotation of fluids in Northern Hemisphere) North Pacific subtropical gyre
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determin ...
. The North Pacific current approaches the continental US and bifurcates into the southward flowing California Current
The California Current is a cold water Pacific Ocean current that moves southward along the western coast of North America, beginning off southern British Columbia and ending off southern Baja California Sur. It is considered an Eastern bound ...
and the northward flowing Alaska Current. The latitude of this bifurcation is dependent on changes in the midlatitude (30-60° latitude) westerly atmospheric wind patterns, which is the primary forcing on the ocean's circulation in this region. These westerly winds oscillate around 45°N and can have variable wind speeds. Changes in these winds are based on the large-scale atmospheric circulation which has seasonal (summer/winter), interannual ( ENSO), and decadal (Pacific Decadal Oscillation
The Pacific decadal oscillation (PDO) is a robust, recurring pattern of ocean-atmosphere climate variability centered over the mid-latitude Pacific basin. The PDO is detected as warm or cool surface waters in the Pacific Ocean, north of 20°N. O ...
, or PDO) variability. The northwestward Alaska Current then feeds into the westward Alaskan Coastal Current, and eventually into the Alaskan Stream; together these make up the cyclonic (counterclockwise rotating) subpolar Alaskan gyre, where Haida eddies are found.
In winter, the location of the North Pacific Current bifurcation is approximately 45°N, which is 5° south of where it bifurcates in the summer at approximately 50°N. This has implications as to what water is moved into the Alaskan subpolar gyre. In winter, when the splitting of the current is more south, fresh, warmer waters from river input from the Columbia (47°N) and Fraser Fraser may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Fraser Point, South Orkney Islands
Australia
* Fraser, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb in the Canberra district of Belconnen
* Division of Fraser (Australian Capital Territory), a former federal e ...
(49°N) rivers are transported north. This shift in the North Pacific current location leads to winter currents transporting relatively warmer water poleward from a lower latitude than in the summer. Although the northern branch of the subtropical gyre shifts south in the winter, the subpolar gyre does not shift location, but intensifies in its circulation. This intensification brings a greater volume of water from the south into the subpolar gyre, which again is dependent on the magnitude of atmospheric circulation. For example: the Aleutian Low
The Aleutian Low is a semi-permanent low-pressure system located near the Aleutian Islands in the Bering Sea during the Northern Hemisphere winter. It is a climatic feature centered near the Aleutian Islands measured based on mean sea-level press ...
is a persistent low pressure system over the Gulf of Alaska that can fluctuate on decadal timescales, producing the PDO. If this system is relatively strong during winter, there will be an increase in northward transport of waters along the Alaskan current from southerly winds. Haida eddies have been documented to form predominantly in the winter when bifurcation is south, and favorable atmospheric conditions are met to intensify the subpolar gyre. With these conditions, Haida eddy formation has also been documented to occur from baroclinic
In fluid dynamics, the baroclinity (often called baroclinicity) of a stratified fluid is a measure of how misaligned the gradient of pressure is from the gradient of density in a fluid. In meteorology a baroclinic flow is one in which the densi ...
instabilities from alongshore wind reversals, equatorial Kelvin wave
A Kelvin wave is a wave in the ocean or atmosphere that balances the Earth's Coriolis force against a topographic boundary such as a coastline, or a waveguide such as the equator. A feature of a Kelvin wave is that it is non-dispersive, i.e., the ...
s, and bottom topography. Baroclinic instabilities form when tilting or sloping of isopycnal
Isopycnals are layers within the ocean that are stratified based on their densities and can be shown as a line connecting points of a specific density or potential density on a graph. Isopycnals are often displayed graphically to help visualize " ...
s (horizontal lines of constant density) form. Baroclinic instabilities from alongshore wind reversals occur when a persistent wind along the coast changes direction. For example: in the Gulf of Alaska average winds travel from the south, poleward (termed southerly winds), but during a wind reversal the winds will abruptly shift to a northwesterly wind (coming from the northwest), and the coastal current that was being pushed north will now be pushed south. This change in direction causes rotation in an originally northward flowing current, which results in tilting isopyncals. Kelvin wave
A Kelvin wave is a wave in the ocean or atmosphere that balances the Earth's Coriolis force against a topographic boundary such as a coastline, or a waveguide such as the equator. A feature of a Kelvin wave is that it is non-dispersive, i.e., the ...
s that form along the equator are able to travel along the west coast of North America to the Gulf of Alaska, where their presence can cause disruptions in the poleward current and form baroclinic instabilities. Bottom topography, the third formation process of Haida eddies, can occur because the Alaska current will interact with hills or rock formations below the surface, and this can cause baroclinic instabilities. 
General physical attributes
Haida eddies possess common physical characteristics that are dependent on the attributes of the water that is being transported, and how that influences the overall structure. Haida eddies are characterized as relatively long-lived, transient (departure from the average ocean current along the coast), medium-sized ( mesoscale) ocean eddies that rotate clockwise (anti-cyclonic), and possess a warm, less-saline core, relative to the surrounding waters. These warm waters within the eddy are attributed to thebaroclinic
In fluid dynamics, the baroclinity (often called baroclinicity) of a stratified fluid is a measure of how misaligned the gradient of pressure is from the gradient of density in a fluid. In meteorology a baroclinic flow is one in which the densi ...
downwelling
Downwelling is the process of accumulation and sinking of higher density material beneath lower density material, such as cold or saline water beneath warmer or fresher water or cold air beneath warm air. It is the ''sinking'' limb of a convecti ...
). This phenomenon is referred to as Ekman pumping
Ekman transport is part of Ekman motion theory, first investigated in 1902 by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Winds are the main source of energy for ocean circulation, and Ekman Transport is a component of wind-driven ocean current. Ekman transport occurs w ...
, resulting from a conservation of mass, vertical velocity, and the Coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
. Downwelling of water from convergence produces what is called 'dynamic height anomalies' between the center and the surrounding waters. The anomaly is calculated by taking the difference between the surface of interest, for example the middle of a Haida eddy, and a reference point (in oceanography it is in reference to the geopotential surface, or the geoid
The geoid () is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended ...
). Haida eddies are capable of producing dynamic height Dynamic height is a way of specifying the vertical position of a point above a vertical datum; it is an alternative for orthometric height or normal height.
It can be computed dividing the location's geopotential number by the normal gravity at 4 ...
anomalies between the center and the surrounding waters of 0.12-0.35 m.
Ekman pumping of surface waters, coupled with northward transport of warm waters (from location of bifurcation), dampens the temperature gradient from the surface down to 300 m, so that water temperature within the eddy is warmer below the surface than typical conditions. Stratification
Stratification may refer to:
Mathematics
* Stratification (mathematics), any consistent assignment of numbers to predicate symbols
* Data stratification in statistics
Earth sciences
* Stable and unstable stratification
* Stratification, or st ...
increases between these warmer, less-saline vortices
In fluid dynamics, a vortex ( : vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in th ...
and the surrounding waters by effectively depressing background lines of constant temperature ( isotherms) and salinity (isohalines) (shown in figure). This makes them an ideal vehicle to transport coastal water properties into the Gulf of Alaska because of reduced mixing with surrounding waters.
As Haida eddies break away from the coast into the subpolar gyre, they transport water properties such as temperature, salinity and kinetic energy. A common water mass in the area is the Pacific Subarctic Upper Water (PSUW) mass with conservative (constant through time and space) properties of salinity (32.6-33.6 psu) and temperature (3-15 °C). PSUW moves into the Alaska Current from the North Pacific Current and may be mixed via Haida eddies into the subpolar gyre. Fresh (low salinity) water from rivers are mixed into Haida eddies. They are also able to exchange potential energy and momentum from the coastal mean current, a process that takes energy away from the coastal current and advects it toward the middle of the gyre. On average, the Gulf of Alaska experiences 5.5 Haida eddies per year, with a typical eddy characterized by a dynamical height of approximately 0.179 m, propagation speed of 2 km per day, average core diameter of 97 km, total volume of approximately 3,000 to 6,000 km3, and a duration of 30 weeks.
Biogeochemical and nutrient dynamics
Biogeochemical dynamics in Haida eddies are typically characterized by highly productive, yet relatively nutrient depleted surface waters, that may be replenished by diffusion and mixing from nutrient abundant sub-surface core waters. This nutrient exchange is also often facilitated by seasonal fluctuations in the surfacemixed layer
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, surface heat fluxes, or processes such as evaporat ...
depth (~20 m in winter, up to 100 m in summer), bringing the low-nutrient surface waters in contact with the nutrient-rich core waters as the mixed layer deepens. Upon eddy formation in winter, surface water concentrations are high in nutrients including nitrate, carbon, iron, and others that are important for biological production. However, they are quickly consumed by phytoplankton through spring and summer, until fall when the now reduced nutrient concentrations can be slowly replenished by mixing with the sub-surface core waters. The net effect of Haida eddies on macronutrients
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
and trace metal micronutrient
Micronutrients are nutrient, essential dietary elements required by organisms in varying quantities throughout life to orchestrate a range of physiological functions to maintain health. Micronutrient requirements differ between organisms; for exam ...
s is that of offshore transport of materials from coastal waters to open ocean, increasing offshore primary productivity inside the eddy formation site.
Dissolved iron
The southeast and central Gulf of Alaska tends to be iron-limited, and Haida eddies deliver large quantities of iron-rich coastal waters into these regions. In High-Nutrient, Low-Chlorophyll (HNLC) areas, iron tends to limit phytoplankton growth more than macronutrients, so the delivery of iron plays an important role in stimulating biological activity. While surface waters within the eddy are similar to that of ambient HNLC waters, waters in the eddy core are highly iron-enriched. Iron is delivered upward to the surface from the eddy core as a result of physical transport properties as the eddy decays or interacts with other eddies. This iron flux into the photic zone (where light is abundant to support growth), is associated with an increase in spring and summer primary production, and drawdown of macronutrients as they are consumed by phytoplankton. Increased iron concentrations have been observed to persist in the core of the eddy up to 16 months after eddy formation. Physical transport properties retain a supply of iron to the surface from the still iron-rich eddy core for the lifetime of the eddy. Because of the large vertical iron transport, Haida eddies contribute a significant portion of the total iron available for biological use. Total dissolved iron concentrations in Haida eddies are approximately 28 times higher than open ocean waters of the Alaska gyre. The daily average supply of iron upwelled from the eddy core is 39 times higher than the iron introduced by average daily dust deposition in the northeast Pacific. Despite the fact that seasonal shallowing and strengthening of thethermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with ...
may inhibit mixing between the surface layer and enriched waters below (reducing iron exchange between the two by as much as 73%), concentrations are still an order of magnitude higher than ambient waters, delivering an estimated 4.6 x 106 moles Moles can refer to:
* Moles de Xert, a mountain range in the Baix Maestrat comarca, Valencian Community, Spain
* The Moles (Australian band)
*The Moles, alter ego of Scottish band Simon Dupree and the Big Sound
People
*Abraham Moles, French engin ...
of iron annually to the Gulf of Alaska. This loading is comparable to the total iron delivery from atmospheric dust or major volcanic eruptions. Thus, the arrival of Haida eddies may introduce anywhere from 5–50% of the annual dissolved iron supply in the upper 1,000 m of the Gulf of Alaska.
In the summer of 2012, an iron fertilization
Iron fertilization is the intentional introduction of iron to iron-poor areas of the ocean surface to stimulate phytoplankton production. This is intended to enhance biological productivity and/or accelerate carbon dioxide () sequestration fr ...
experiment deposited 100 tons of finely-ground iron oxides into a Haida eddy in an effort to increase salmon returns through an attempt to increase primary production. This resulted in the highest chlorophyll concentrations measured within an eddy, and the most intense phytoplankton bloom in the last ten years in the northeast Pacific. However, the impact of this bloom on higher trophic
Trophic, from Ancient Greek τροφικός (''trophikos'') "pertaining to food or nourishment", may refer to:
* Trophic cascade
* Trophic coherence
* Trophic egg
* Trophic function
* Trophic hormone
* Trophic level index
* Trophic level
* Trop ...
organisms such as zooplankton and fish is not known.
Carbon
Concentrations ofdissolved inorganic carbon
Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) is the sum of the aqueous species of inorganic carbon in a solution. Carbon compounds can be distinguished as either organic or inorganic, and as dissolved or particulate, depending on their composition. Organic ...
(DIC) and nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zer ...
(NO3−), which are important macronutrients for photosynthesis, are quickly depleted in Haida eddy surface waters through most of their first year due to uptake by biological primary production. This uptake of nutrients, which is largely carried out by phytoplankton, leads to observable increases in chlorophyll-a (Chl-''a'') concentrations.Crawford, W.R., Brickley, P.J., Peterson, T.D., Thomas, A.C., Impact of Haida Eddies on chlorophyll distribution in the Eastern Gulf of Alaska, In Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, Volume 52, Issues 7â€"8, 2005, Pages 975-989, ISSN 0967-0645, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2005.02.011. In summer, a large portion of the DIC pool is consumed due to increased production of coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdo ...
s, which are phytoplankton that use bicarbonate ion to build their calcium carbonate (CaCO3) shells, releasing carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
(CO2) in the process. This process also leads to a summertime reduction in total alkalinity, which is a measure of the capacity of seawater to neutralize acids, and is largely determined by bicarbonate and carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate g ...
ion concentrations. Surrounding surface waters show similar, or even slightly higher concentrations of DIC, total alkalinity, and nitrates, and may at times exchange surface waters with Haida eddies, as witnessed when Haida-2000 merged with Haida-2001. Although some nutrient exchange takes place at the surface, export of organic carbon out of the eddy is not enhanced, and there is little change in organic carbon concentrations at depth, suggesting that the organic carbon formed through primary production is largely being recycled within the eddies.
In February, surface concentrations of CO2 (as quantified by ƒCO2), in the eddy center and edges start out relatively oversaturated relative to atmospheric CO2 concentrations, but quickly drop, partially due to biological production. By June, ƒCO2 becomes undersaturated relative to atmospheric concentrations, but increases slightly again through summer, aided by warming temperatures. In the eddy center, ƒCO2 usually reaches near equilibrium with the atmosphere by fall (depending on timing of the mixed layer deepening), when vertical entrainment
Entrainment may refer to:
* Air entrainment, the intentional creation of tiny air bubbles in concrete
* Brainwave entrainment, the practice of entraining one's brainwaves to a desired frequency
* Entrainment (biomusicology), the synchronization o ...
and mixing from below can replenish ƒCO2, as well as the now-depleted DIC and nitrate concentrations. Lower ƒCO2 tends to persist through summer in edge waters however, most likely due to the presence of enhanced biological production, as suggested by the presence of higher Chl-''a'' concentrations. Ambient waters typically reach parity with atmospheric CO2 by spring, after a smaller initial decrease early in the year. Net atmospheric CO2 removal by Haida eddies is estimated to be 0.8-1.2 x 106 tons per year, underscoring the important role they play in the Gulf of Alaska.
Other trace metals
Transport and delivery of othertrace metal
Trace metals are the metals subset of trace elements; that is, metals normally present in small but measurable amounts in animal and plant cells and tissues and that are a necessary part of nutrition and physiology. Many biometals are trace me ...
s in the Gulf of Alaska are also enhanced by Haida eddies and may result in increased burial of trace metals in marine sediments where they can no longer be used to support biological growth. Evidence suggests Haida eddies may be an important source of dissolved silver ions, with eddy surface water concentrations three to four times higher compared to ambient waters. Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is al ...
uptake rates by marine diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising sev ...
s in Haida eddies are three times that observed in ambient waters, suggesting strong diatom population growth. Haida eddies are important sources of silver for diatom production, as silver is incorporated into the silicate shells of diatoms and the transport of silver associated with Haida eddies promotes diatom growth. Silver is sequestered by this production and eventually transported to depth by sinking particles of organic matter, linking silver to the marine silicate cycle.
Large quantities of dissolved aluminum and manganese ions are also supplied to the Gulf of Alaska via eddy transport of coastal waters enriched from riverine inputs. The quantity transported is also comparable to that deposited by atmospheric dust. This supply of trace metals impacts the rate of dissolved iron removal because the particles tend to aggregate together and sink to the seafloor, a process which may account for 50-60% of dissolved aluminum and manganese removal. Additionally, there is evidence for enhanced delivery of cadmium and copper to the Gulf of Alaska by Haida eddies.
Macronutrients
Haida eddies can produce low silicate and high nitrate, chlorophyll, and sedimentation events offshore. Eddies that form nearshore in the Gulf of Alaska carry shelf nutrients west into the High-Nutrient, Low-Chlorophyll (HNLC) andoligotrophic
An oligotroph is an organism that can live in an environment that offers very low levels of nutrients. They may be contrasted with copiotrophs, which prefer nutritionally rich environments. Oligotrophs are characterized by slow growth, low rates of ...
(low-nutrient) waters of the northeast Pacific, or south into seasonally nitrate-depleted waters. If eddies head southward from the Gulf of Alaska toward British Columbia, waters in the eddy become enriched in nutrients at the expense of the seawater they are capturing nutrients from, leaving coastal waters relatively nutrient poor. If eddies head west into the HNLC waters of the central Gulf of Alaska basin, they transport particulate matter and supply the photic zone with nitrate that is up to three times greater than typical seasonal transport, increasing spring productivity.
The timing of advection from the eddy has important seasonal implications on the delivery of nutrients. The high-nutrient and high-iron coastal water is carried into the Gulf of Alaska from either the core of the eddy or the outer ring. The core of the eddy contains warm, fresh, nutrient-rich waters formed in winter, and with the addition of sunlight, produces strong spring bloom
The spring bloom is a strong increase in phytoplankton abundance (i.e. stock) that typically occurs in the early spring and lasts until late spring or early summer. This seasonal event is characteristic of temperate North Atlantic, sub-polar, and ...
s of primary productivity offshore. As the eddy drifts westward in late spring and summer, the outer ring mixes coastal and deep ocean waters in large arcs around the eddy edge. This process has an effect hundreds of kilometers offshore, and facilitates the exchange of nutrients between shelf to deep ocean from late winter to the following autumn.
Biology
Nutrients trapped and transported by Haida eddies support more biological growth compared to surrounding, low-nutrient ocean water. Elevated measurements of chlorophyll in eddy centers, as compared to surrounding water, indicate that eddies increase primary production, and can support multiple phytoplankton blooms within a single year. These blooms are not only caused by increased nutrients, but also the eddy's ability to transport biota from the coast into the eddy. Spring blooms are caused by sufficient light reaching the warm, nutrient-rich water contained in the middle of the eddy, due to anticyclonic rotation. A second bloom can occur once the eddy has moved closer to the deep ocean, when the outer reaches of the eddy can gather nutrient-rich water from either the coast or from an adjacent eddy. Coastal water transported by this outer ring advection can move from the coast into the eddy in six days which also allows for the rapid transport of coastal algae into the nutrient-rich eddy waters. A late summer bloom can occur if storms produce vertical convection of the mixed layer, causing it to deepen and trap nutrients from below into the region of primary production. High eddy kinetic energy (EKE) may also increase chlorophyll concentration in eddies. Northern Gulf of Alaska and Haida eddy regions have more chlorophyll when EKE was higher, which can be caused by storms, producing higher mixing of the mixed layer and introducing nutrients from below. Because of the correlation, research suggests that EKE could be used to predict chlorophyll blooms. Haida eddies affect zooplankton distribution by transporting nearshore species into the deep ocean. During the first summer that an eddy moves offshore, nearshore species often dominate zooplankton communities, but decline after one or two years as the eddy dissipates. Species that performdiel vertical migration
Diel vertical migration (DVM), also known as diurnal vertical migration, is a pattern of movement used by some organisms, such as copepods, living in the ocean and in lakes. The word ''diel'' comes from the Latin ''dies'' day, and means a 24-h ...
can remain in the eddy core for longer periods of time.
The influence of Haida eddies on larger organisms remains poorly understood. They are thought to influence winter feeding habits of northern fur seals by providing food at a low energy expense. Ichthyoplankton
Ichthyoplankton (from Greek: ἰχθύς, , "fish"; and πλαγκτός, , "drifter") are the eggs and larvae of fish. They are mostly found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 metres deep, which is sometimes called the epip ...
composition within eddies is significantly different than that of surrounding ocean water. The species composition is based on where an eddy forms, and thus what coastal species it acquired. Fish larval species richness
Species richness is the number of different species represented in an ecological community, landscape or region. Species richness is simply a count of species, and it does not take into account the abundances of the species or their relative a ...
correlates with distance from an eddy center, with higher richness closer to the core. The icthyoplankton communities also change depending on the age of the eddy.
See also
*Mesoscale ocean eddies
In fluid dynamics, an eddy is the swirling of a fluid and the reverse current (water), current created when the fluid is in a Turbulence, turbulent flow regime. The moving fluid creates a space devoid of downstream-flowing fluid on the downstream ...
*Baroclinity
In fluid dynamics, the baroclinity (often called baroclinicity) of a stratified fluid is a measure of how misaligned the gradient of pressure is from the gradient of density in a fluid. In meteorology a baroclinic flow is one in which the densi ...
*Ekman transport
Ekman transport is part of Ekman motion theory, first investigated in 1902 by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Winds are the main source of energy for ocean circulation, and Ekman Transport is a component of wind-driven ocean current. Ekman transport occurs w ...
*Aleutian Low
The Aleutian Low is a semi-permanent low-pressure system located near the Aleutian Islands in the Bering Sea during the Northern Hemisphere winter. It is a climatic feature centered near the Aleutian Islands measured based on mean sea-level press ...
References
{{Cyclones Bodies of water of Alaska Bodies of water of British Columbia