HW Virginis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
HW Virginis, abbreviated HW Vir, is an
 Based on variations in the timing of the system's eclipses, in 2008 it was claimed that two giant planets were in orbit around the binary, with masses of 8.47 and 19.2 times the mass of
Based on variations in the timing of the system's eclipses, in 2008 it was claimed that two giant planets were in orbit around the binary, with masses of 8.47 and 19.2 times the mass of
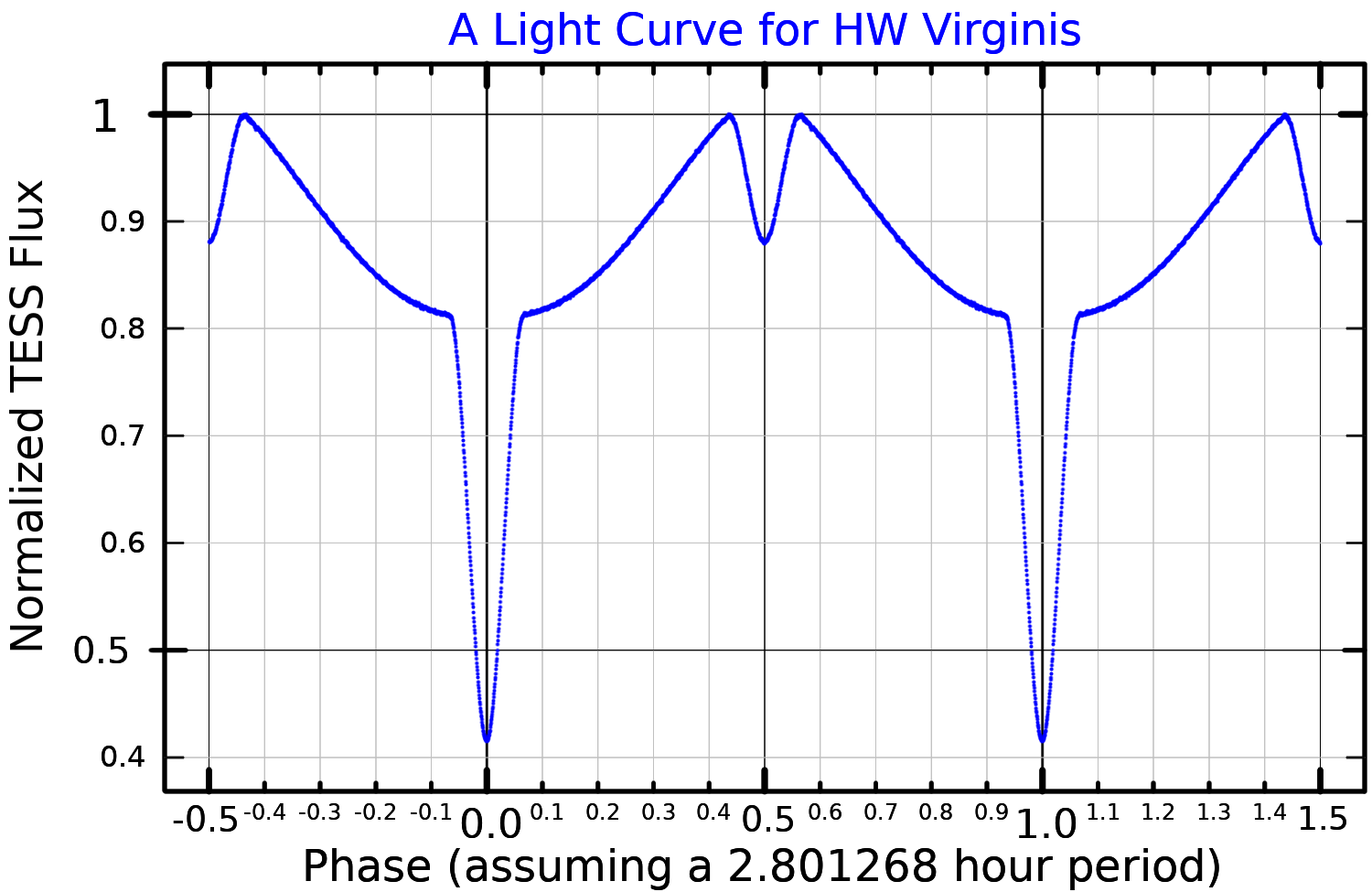
eclipsing binary
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in w ...
system (of the Algol type), approximately 563 light-years away based on the parallax measured by the Gaia spacecraft
''Gaia'' is a space observatory of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 2013 and expected to operate until 2025. The spacecraft is designed for astrometry: measuring the positions, distances and motions of stars with unprecedented preci ...
, in the constellation of Virgo
Virgo may refer to:
*Virgo (astrology), the sixth astrological sign of the zodiac
* Virgo (constellation), a constellation
*Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo
*Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy
* Virgo Su ...
. The system comprises an eclipsing B-type subdwarf
A B-type subdwarf (sdB) is a kind of subdwarf star with spectral type B. They differ from the typical subdwarf by being much hotter and brighter. They are situated at the "extreme horizontal branch" of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. Masse ...
star and red dwarf star. The two stars orbit each other every 0.116795 days.
Eclipse timing variations
 Based on variations in the timing of the system's eclipses, in 2008 it was claimed that two giant planets were in orbit around the binary, with masses of 8.47 and 19.2 times the mass of
Based on variations in the timing of the system's eclipses, in 2008 it was claimed that two giant planets were in orbit around the binary, with masses of 8.47 and 19.2 times the mass of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
orbiting with periods of 9.1 and 15.8 years respectively. The proposed system was later shown to be extremely unstable, with mean lifetimes less than 1000 years in the parameter space allowed by the uncertainties in the data. An alternate, dynamically-stable orbital solution was proposed with a 14.3 Jupiter mass object on a 12-year orbit and an outer companion of 65 Jupiter masses on a 55-year orbit, however it has been noted that the outer companion's orbital parameters are highly unconstrained, again casting doubt on the reality of this model. The problems with modelling this system and the proposed planets orbiting several other post-common envelope binaries has led to the suggestion that the eclipse timing variations used to infer the existence of planets has a non-planetary origin. The eclipse timing variations of HW Virginis were shown to be incompatible with all previous planetary system models as of 2018, and again in 2021. However, eclipse timing variations cannot be explained by known stellar mechanisms either.
See also
* * * * *References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:HW Virginis Algol variables Virgo (constellation) Virginis, HW B-type subdwarfs M-type main-sequence stars 062157 J12442024-0840168 -07 3477 Hypothetical planetary systems